Histo Lab- Urinary System (Aughey)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
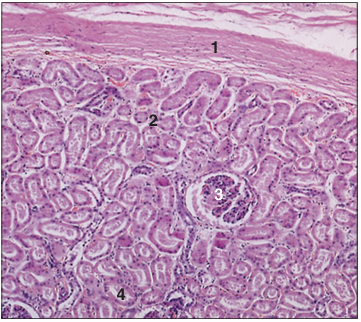
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Kidney (horse). (1) Capsule. (2) Outer area of the cortex. (3) Renal corpuscle. (4) Uriniferous tubules. H & E. ×62.5.
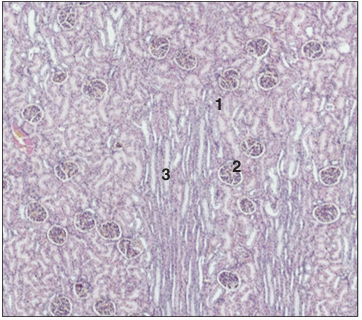
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Kidney cortex (dog). (1) Renal corpuscle. (2) Uriniferous tubules. (3) Medullary ray. H & E. ×12.
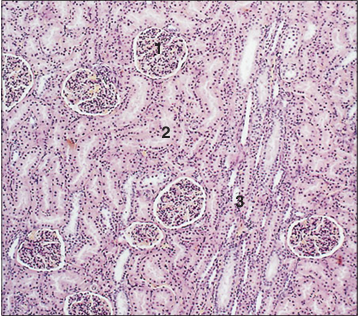
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Kidney cortex (dog). (1) Renal corpuscle. (2) Uriniferous tubules. (3) Medullary ray. H & E. ×125.
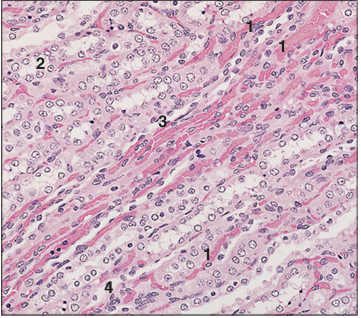
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Kidney medulla (dog). (1) Blood vessels. (2) Collecting tubules. (3) Ascending thin limb. (4) Descending thin limb. H & E. ×125.
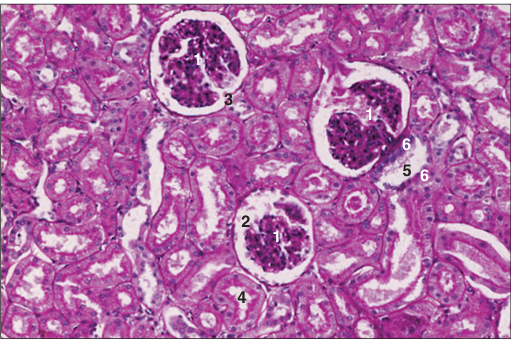
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__ 6.__
Stain used:
Kidney (horse). (1) Renal corpuscle with (2) capsular space (3) the urinary pole. (4) Proximal convoluted tubule. (5) Distal convoluted tubule with (6) the macula densa. H/PAS. ×250.
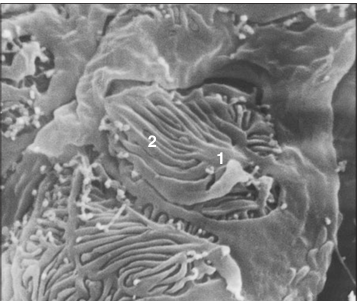
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__
Stain used:
Kidney (dog). (1) Part of the podocyte. (2) Secondary foot processes, the pedicles – the filtration slit pores are the spaces between the solid pedicles. Scanning electron micrograph.×1500.
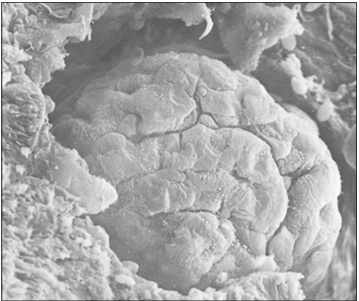
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Kidney (dog). The renal corpuscle projects from the surrounding tissue. Scanning electron micrograph. ×500.
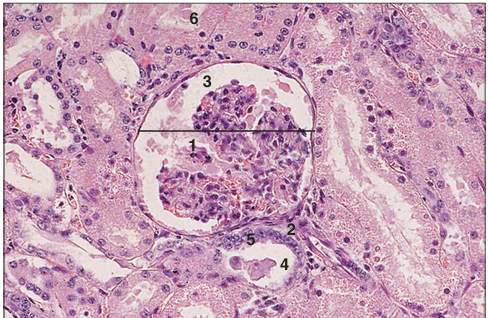
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__ 5.__ 6.__
Stain used:
Kidney (horse). The width of the glomerular capsule is shown by the line. (1) Renal corpuscle with epithelial cells and mesangium. (2) Vascular pole. (3) Capsular space. (4) Distal convoluted tubule. (5) The macula densa. (6) Proximal convoluted tubule. H & E. ×250.
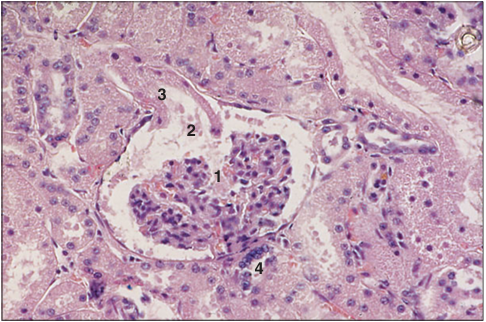
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Kidney (horse). (1) Renal corpuscle with epithelial cells and mesangium. (2) Urinary pole opening into (3) the proximal convoluted tubule. (4) Distal convoluted tubule and macula densa. H & E. ×250.
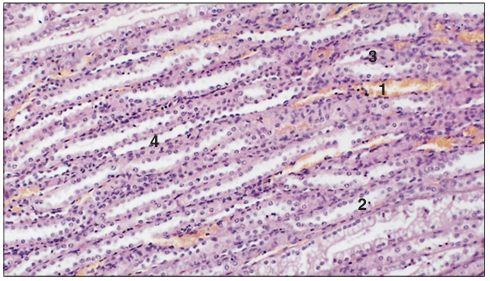
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
Kidney medulla (dog). (1) Capillaries lined by endothelium. (2) Collecting tubules lined by cuboidal cells. (3) Ascending limb lined by cuboidal epithelium. (4) Descending limb lined by squamous epithelium. H & E. ×125.
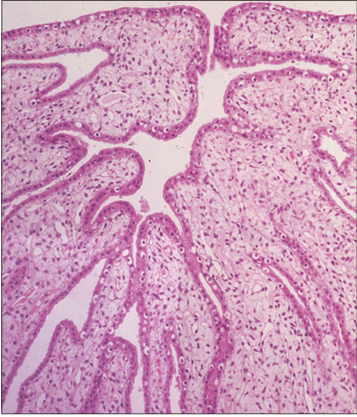
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Kidney. Renal pelvis (sheep). The renal pelvis is lined by urethelium resting on a vascular lamina propria. H & E. ×62.5.
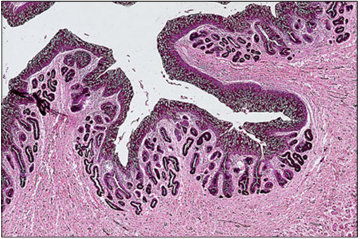
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Kidney. Renal pelvis (horse). The renal pelvis is lined by urethelium; simple mucus-secreting glands are present in the lamina propria. H/PAS. ×62.5.
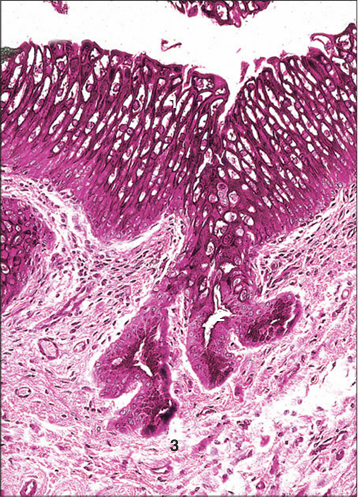
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Ureter (horse). (1) Urethelium. (2) Simple mucus secreting tubular glands. (3) Vascular lamina propria. H/PAS. ×250.
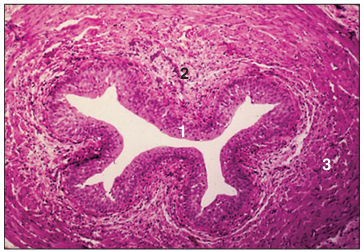
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
Ureter (dog). (1) Urethelium lines the lumen of the ureter. (2) Vascular lamina propria. (3) Muscularis externa. H & E. ×62.5.
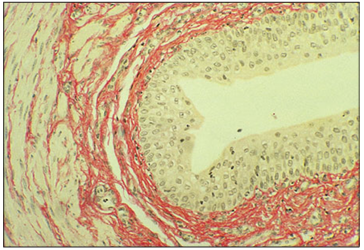
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Ureter (dog). The elastic fibres are stained reddish orange. Van Giesen. ×62.5.
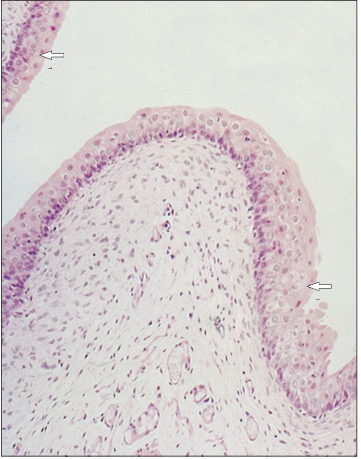
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
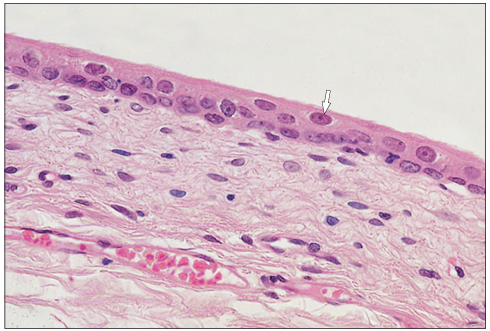
Urinary bladder (dog). The bladder is relaxed and the surface cells are rounded adjacent to the lumen (arrowed). H & E. ×125.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Urinary bladder (dog). The bladder is stretched and the surface cells are flattened (arrowed). H & E. ×250.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
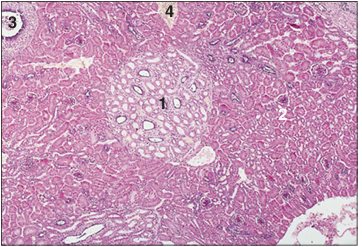
Kidney (bird). (1) The central, pale staining medullary area is surrounded by (2) the much denser staining cortical area. (3) Lobar duct. (4) Renal vein. H & E. ×25.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__ 4.__
Stain used:
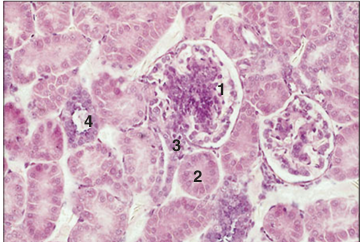
Kidney cortex (bird). (1) The renal corpuscule has a central mass of epithelial cells and mesangial cells. (2) Proximal convoluted tubule. (3) Distal convoluted tubule. (4) Small collecting tubule with low columnar mucus-secreting epithelium. H & E. ×125.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Parts:
1.__ 2.__ 3.__
Stain used:
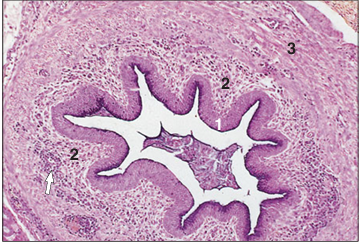
Ureter (bird). (1) Pseudostratified mucus-secreting epithelium lines the lumen. (2) Cellular lamina propria with groups of lymphocytes (arrowed). (3) Muscularis externa. H/PAS. ×125.
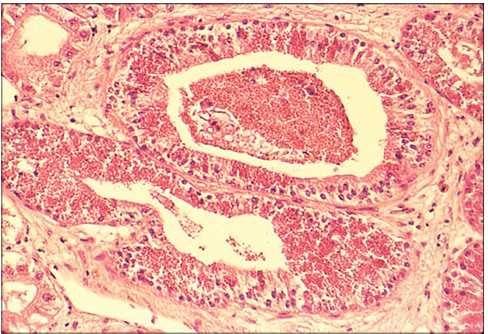
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
The kidneys of some species of sexually mature male snakes and lizards possess a characteristic ‘sexual segment granulation’ which is discerned by a marked hypertrophy and eosinophilic granularity of the distal convoluted tubules. This makes the kidneys of sexually mature males readily distinguishable from the kidneys of sexually mature females of the same species. Illustrated is a section of kidney from a mature male timber rattlesnake (Crotalus horridus). H & E. ×125.