Materials - Part C - Metal Processing techniques Processing Routes
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
In metal manufacturing, what is the main method behind liquid processing?
Casting
What are the 4 mains steps in casting?
Melt metal
Introduction into mould cavity
Solidification
Finishing process (post processing)
What are the 2 mains ways to optimise a casted practice?
Porosity is kept to a minimum
Defects and inclusions are reduced in number and size
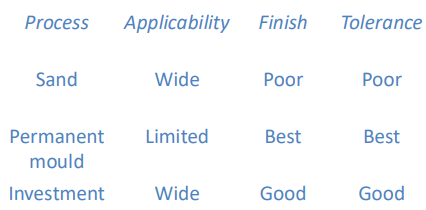
What are the 3 types of casting techniques?
Sand casting
Investment Casting
Permanent mould
How do the techniques compare to each other in terms of applicability, finish and tolerance?
How do they vary economically?
Sand casting is the cheapest but offers the lowest production rate.
Investment casting has medium mould and equipment costs with medium production rate of around 100 units per hour.
Permanent mould casting is medium on all 3 categories but offers highest production rate.
When would use each technique?
Sand casting would be used for 1 off prototype components when part quality or dimensions are not critical.
Investment casting would be used for one off or small batch production for bespoke parts where quality is more of a concern.
Permanent mould casting is used when producing large quantities if high quality parts.
What are the different types of solid state processing techniques?
Primary
Rolling
Extrusion
Forging
Secondary
Wire drawing
Machining
When rolling metal what factors increase rolling force?
Increasing flow stress
Increasing rolling reduction
Increasing roll radius
Increasing width
What are the main steps in extrusion?
Round billet is placed in chamber
Billet is forced through die by ram
The die shape dictates the final cross section
What are the two main types of extrusion?
Direct extrusion - Billet slides relative to the container wall.
Indirect extrusion - Die moves towards the billet.
What key parameter can be adjusted to change the force required for a given extrusion ratio (ratio of the billet cross section over the die cross section)?
Changing the die angle changes the force required and there exists an optimal die angle for a given configuration.
What are defects that can occur in the previous 2 solid state processing techniques?
Rolling - Surface cracking
Temp is too high
Temp is too low
Rolling speed is too high.
Extrusion - Piping: when impurities move to the centre like a funnel
changing flow pattern
Machining billet prior to extrusion.
What it the main process behind forging?
Deformation of metal components at elevated temperature to achieve desired shape.
What is meant by a materials forgeability?
It is the materials ability to withstand deformation at low temperatures without cracking.
What is the main parameter to calculate when forging a part?
The upsetting force calculated using this equation.
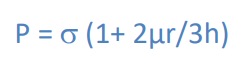
What is the specialised form of forging?
Isothermal forging: Involves heating dies to the same temperature as the workpiece.
What advantages does this technique pose?
Cooling / flow stress of the material is eliminated
Forging can be carried out over a very narrow temperature range
Much greater control of the microstructural and therefore mechanical properties
Very good dimensional accuracy
What is the main type of defect that can occur with forging?
Surface cracking.
What is a problem that can occur in parts produced by all three solid state processing techniques?
Anisotropy - Non consistent material properties throughout the materials.