Neuro 17 | Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia Disorders
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is Ataxia?
A neurological condition characterized by a lack of muscle coordination, affecting a person’s ability to perform voluntary movements smoothly and accurately.

What is the finger-nose-finger test?
in the finger-nose-finger test, the person touches their finger to their nose, then extends it to touch the examiner’s finger checking for coordination and ataxia.
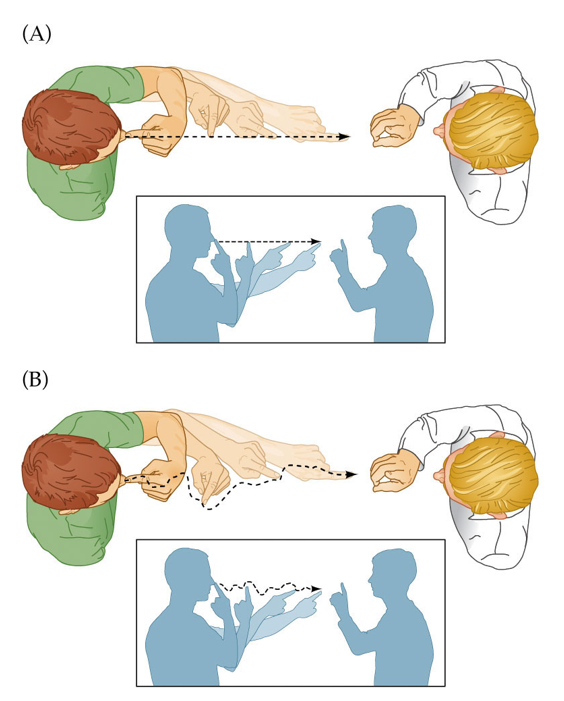
If the finger-nose-finger test is not performed correctly, what does it indicate?
Appendicular ataxia, which affects limb coordination.

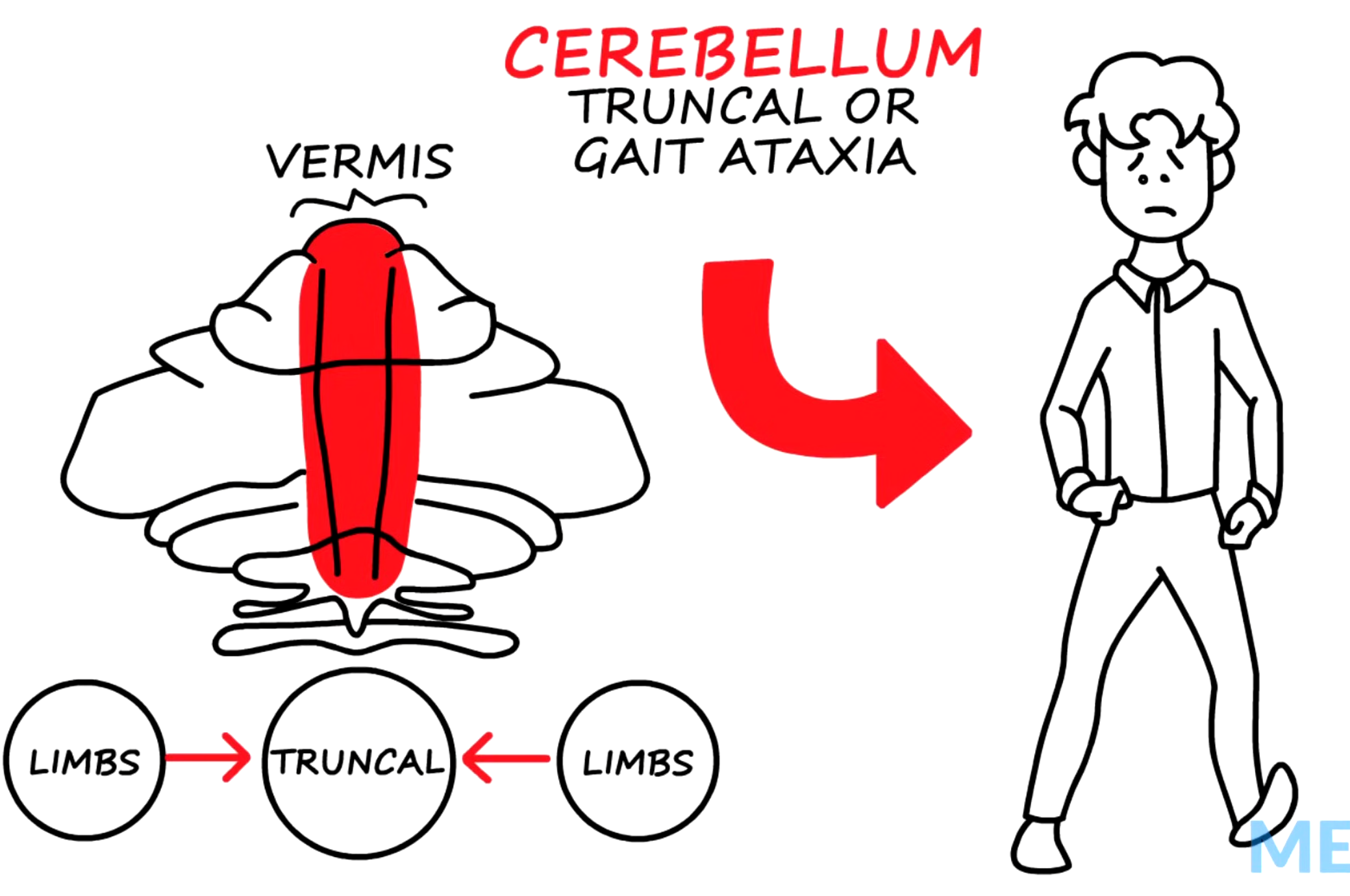
What causes truncal ataxia?
Lesions in the cerebellar vermis (midline) cause a wide-based, unsteady gait, resembling a "drunklike" walk.
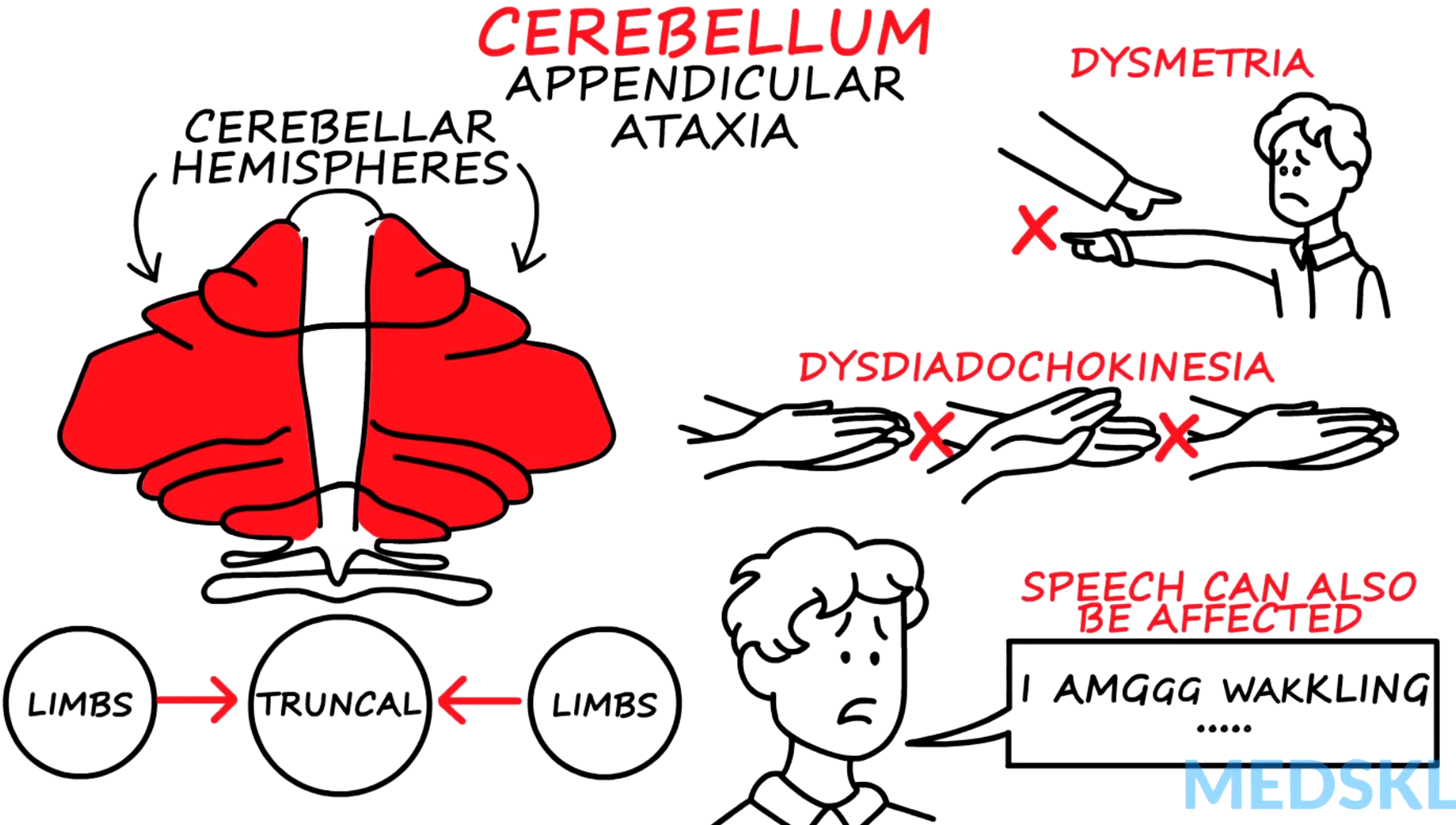
What causes appendicular ataxia?
Lesions in the intermediate and lateral cerebellar hemispheres affect limb movement, leading to uncoordinated motions in the arms and legs.
What is the major reason for cerebellar degeneration/ataxia?
Alcohol abuse
What is Parkinson’s Disease?
A progressive neurological disorder that affects movement. It is characterized by an asymmetrical ‘pill-rolling’ resting tremor (a rhythmic movement resembling rolling a pill between fingers), bradykinesia, rigidity and gait instability
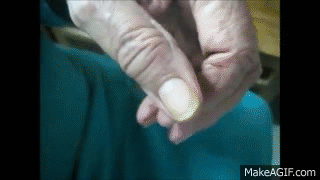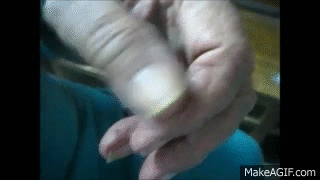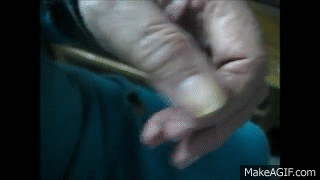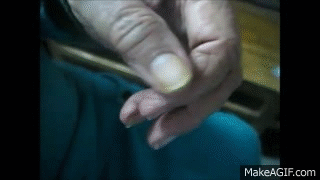
What causes Parkinson’s Disease?
The loss of dopamine production in a part of the brain called the substantia nigra, leading to movement and coordination issues.
Patient’s with Parkinson’s usually respond to which therapy?
Levodopa (precursor to dopamine)
Has dopa in the name—easy to remember

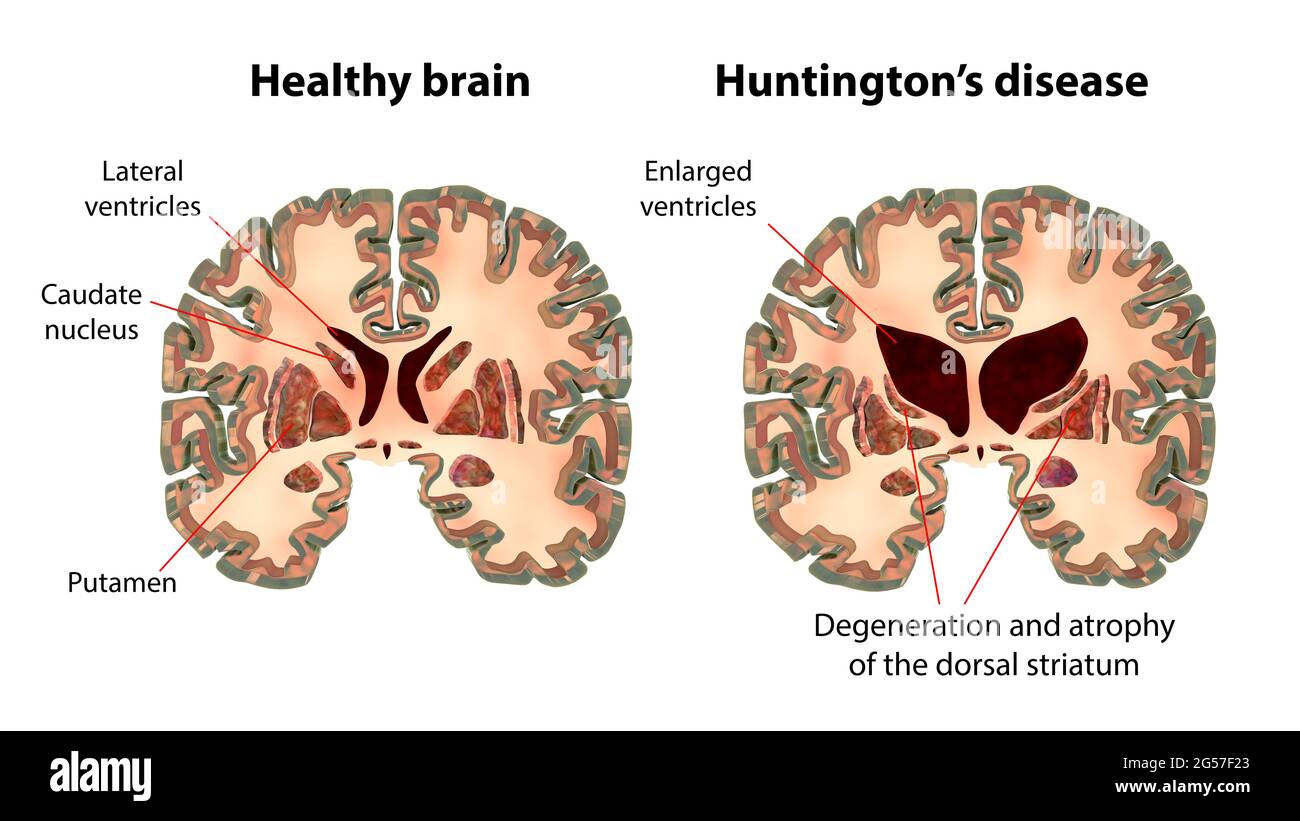
What is Huntington’s Disease
Huntington's disease is an inherited, autosomal dominant disorder that causes progressive brain degeneration.
What are symptoms of Huntington’s Disease
involuntary, jerky movements (chorea), cognitive decline (dementia), and psychiatric issues, ultimately resulting in death.

Hallmark sign of Huntington’s Disease?
Gradual shrinkage of the striatum, with a particular focus on the caudate nucleus.
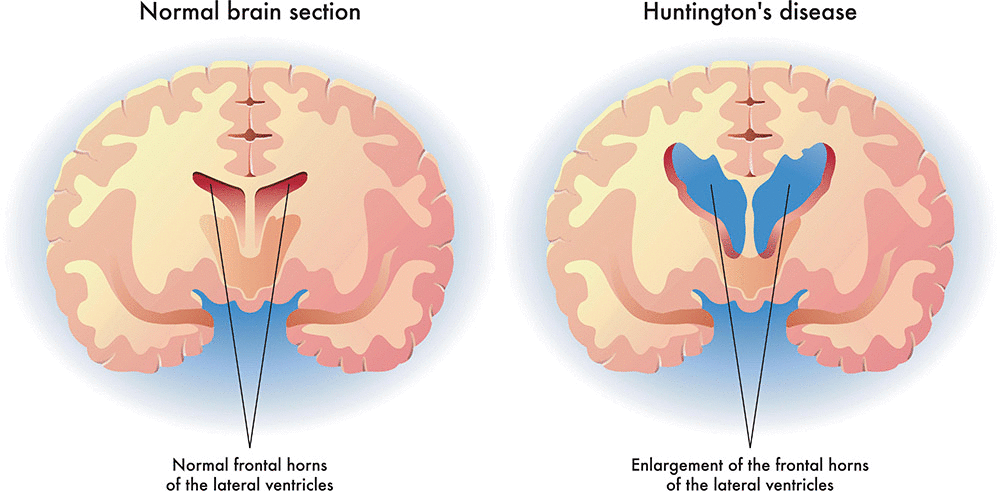
What type of genetic inheritance pattern does Huntington's Disease follow?
Autosomal Dominant
How does rigidity present in basal ganglia disorders like Parkinson's disease?
When someone tries to move a limb, there is a constant resistance or stiffness throughout the entire motion, making the movement feel uniformly stiff or difficult to bend.
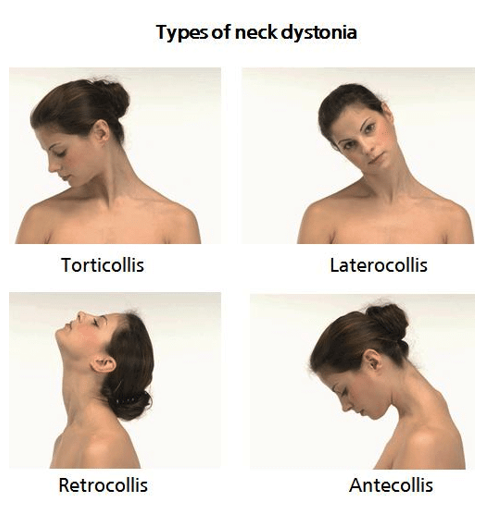
What is dystonia?
Dystonia is a movement disorder where muscles contract uncontrollably, causing twisting, repetitive movements or abnormal postures.
Focal dystonias affect specific body parts, like torticollis, which causes involuntary contractions in the neck muscles, making the head twist or tilt.

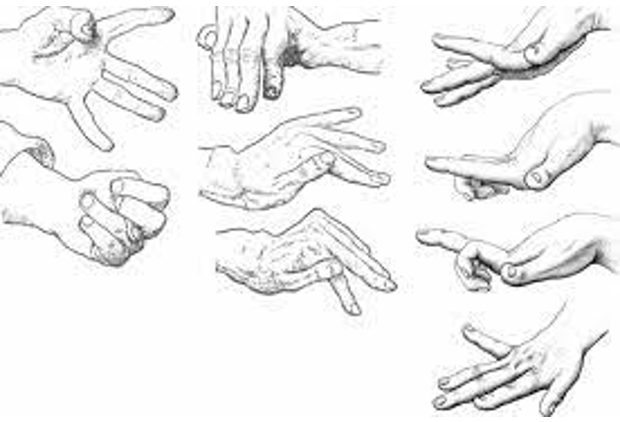
What is athetosis?
A movement disorder characterized by slow, involuntary, writhing movements, typically affecting the hands, fingers, feet, and toes

What is ballismus?
A movement disorder that causes large, flinging or rotating movements of the arms and legs, often affecting muscles closer to the body (proximal muscles).
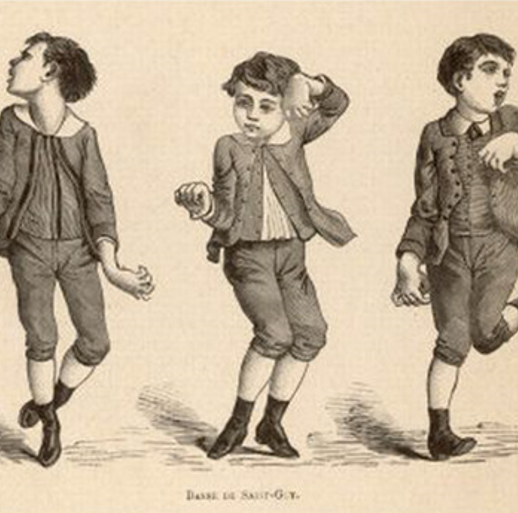


What is chorea?
A movement disorder with rapid, irregular, and involuntary movements that can affect the face, hands, and other body parts, making motions appear dance-like or jerky.

What is the major cause of chorea?
Major cause of chorea is Huntington’s disease
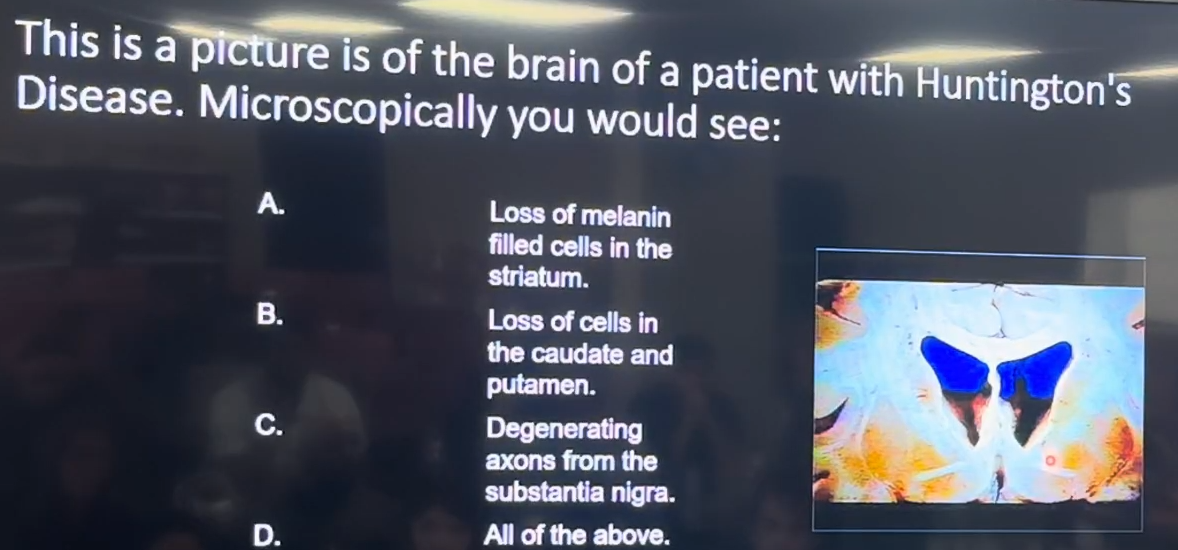
This is a picture of a patient with Huntington’s Disease. Microscopically you would see:
A. Loss of melanin filled cells in the striatum
B. Loss of cells in the caudate and putamen
C. Degenerating axons from the substantia nigra
D. All of the above
B (loss of cells in the caudate and putamen) (striatum) is the correct answer because it describes changes typically associated with Huntington's disease, not Parkinson's.
The basal ganglia exert their effects on motor behavior through the:
A. Rubrospinal tract
B. Vestibulospinal tract
C. Reticulospinal tract
D. Corticospinal tract
E. All of the above
D. Corticospinal tract
The basal ganglia influence motor behavior primarily through the corticospinal tract, which is central to voluntary movement control.
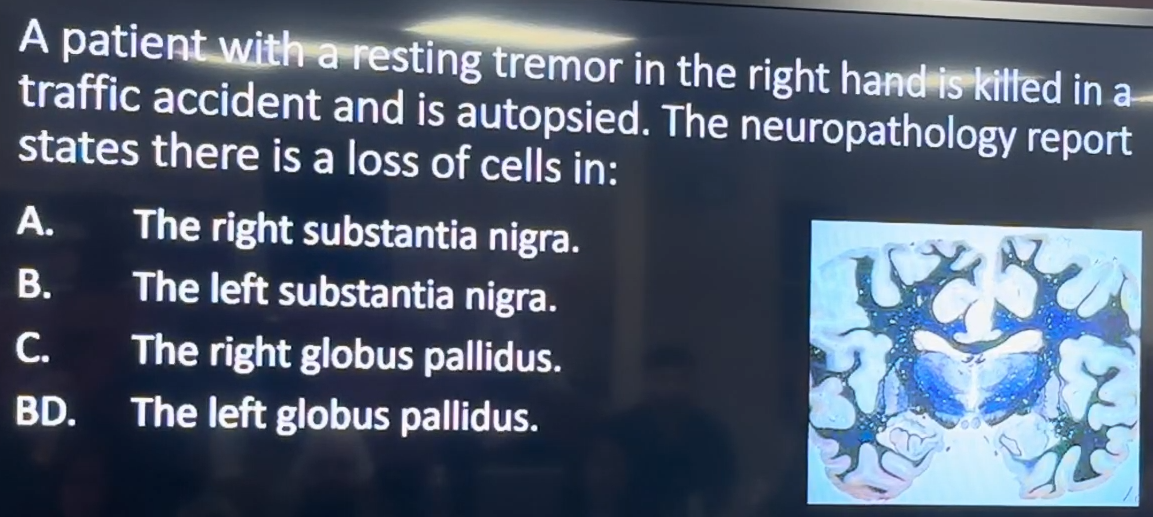
A patient with a resting tremor in the right hand is killed in a traffic accident and is autopsied. The neuropathology report states there is a loss of cells in:
A. The right substantia nigra.
B. The left substantia nigra.
C. The right globus pallidus.
D. The left globus pallidus.
B. The left substantia nigra
In Parkinson's disease, a resting tremor typically indicates damage to the substantia nigra, the brain area responsible for dopamine production, which affects movement. This condition shows contralateral effects on the body due to the way neural pathways cross.
A patient exhibiting an uncoordinated gait has presented at the clinic. Which of the following is the most plausible cause of this patient's health problem?
A. Cerebellar dysfunction
B. A lesion in the pons
C. Dysfunction of the medulla
A. Cerebellar dysfunction
The cerebellum is primarily responsible for coordinating movements and maintaining balance. Cerebellar dysfunction often leads to an uncoordinated gait, known as ataxia, which is a common symptom of cerebellar damage. Lesions in the pons or medulla are less directly associated with coordination issues.

A patient in the ER goes into malignant hyperthermia due to an abnormal reaction to the anesthetic. The nurse knows that the area of the brain that regulates body temperature is which of the following?
A. Cerebellum
B. Thalamus
C. Hypothalamus
D. Midbrain
C. Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is the area of the brain responsible for regulating body temperature, among other vital functions. It plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis, including responses to changes in temperature. In cases like malignant hyperthermia, where body temperature rises uncontrollably, the hypothalamus is directly involved in temperature regulation.

The nurse is planning the care of a patient with Parkinson’s disease. The nurse should be aware that treatment will focus on what pathophysiological phenomenon?
A) Premature degradation of acetylcholine
B) Decreased availability of dopamine
C) Insufficient synthesis of epinephrine
D) Delayed reuptake of serotonin
Decreased availability of dopamine
Parkinson's disease is primarily caused by a decrease in dopamine levels due to the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra of the brain. Treatment for Parkinson's often focuses on increasing dopamine availability or mimicking its effects to help manage symptoms.
The nurse caring for an 80-year-old patient knows that she has a pre-existing history of dulled tactile sensation. The nurse should first consider what possible cause for this patient’s diminished tactile sensation?
A) Damage to cranial nerve VIII
B) Adverse medication effects
C) Age-related neurologic changes
D) An undiagnosed cerebrovascular accident in early adulthood
C) Age-related neurologic changes
Dulled tactile sensation is common in elderly patients due to age-related neurological changes. These changes can lead to decreased sensitivity in touch and other senses, making this the most likely cause in an 80-year-old patient. The other options are less common explanations for age-related loss of tactile sensation.