NS 1150 Prelim 4
1/141
Earn XP
Description and Tags
L21-L28, A4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
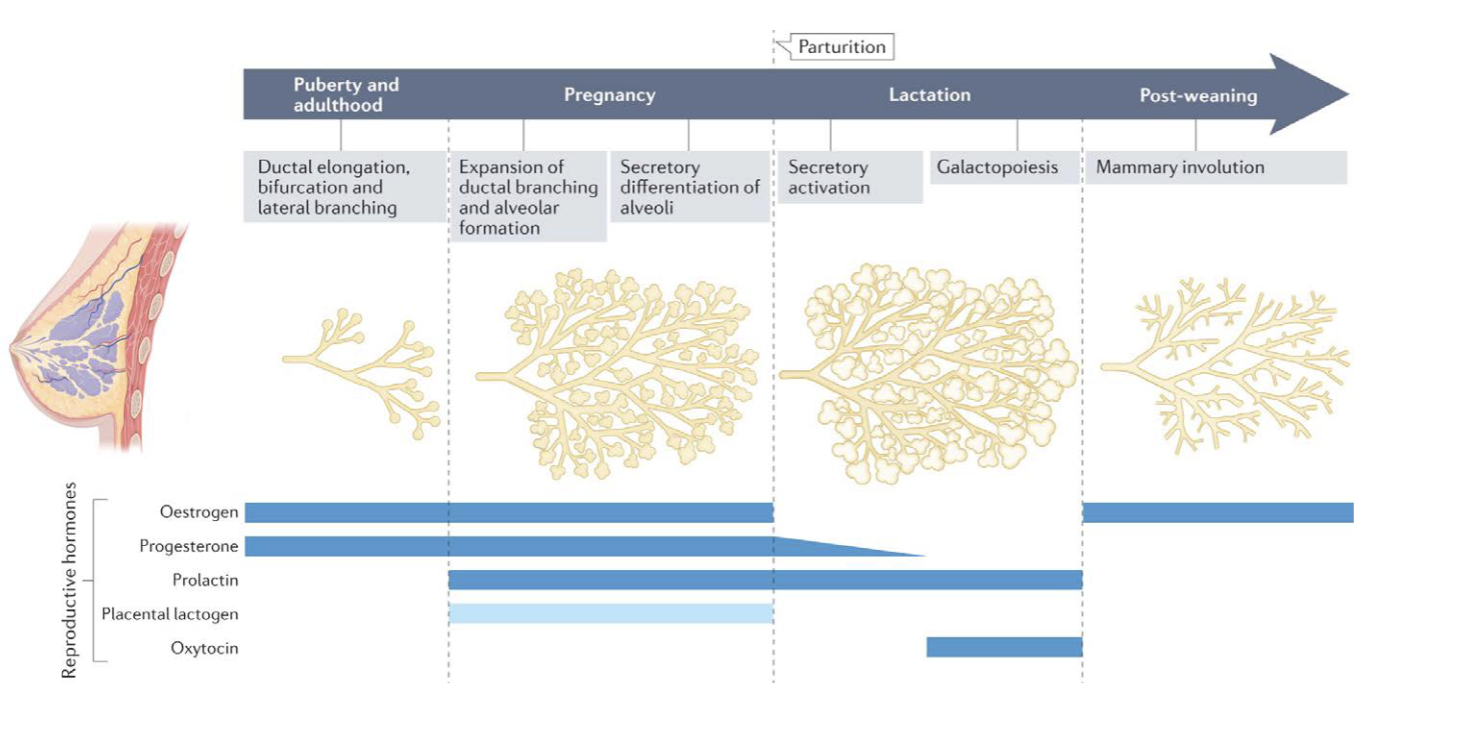
How is Human Milk Produced
Produced in mammary glands through hormones through a process called lactation which begins during pregnancy and contiunes
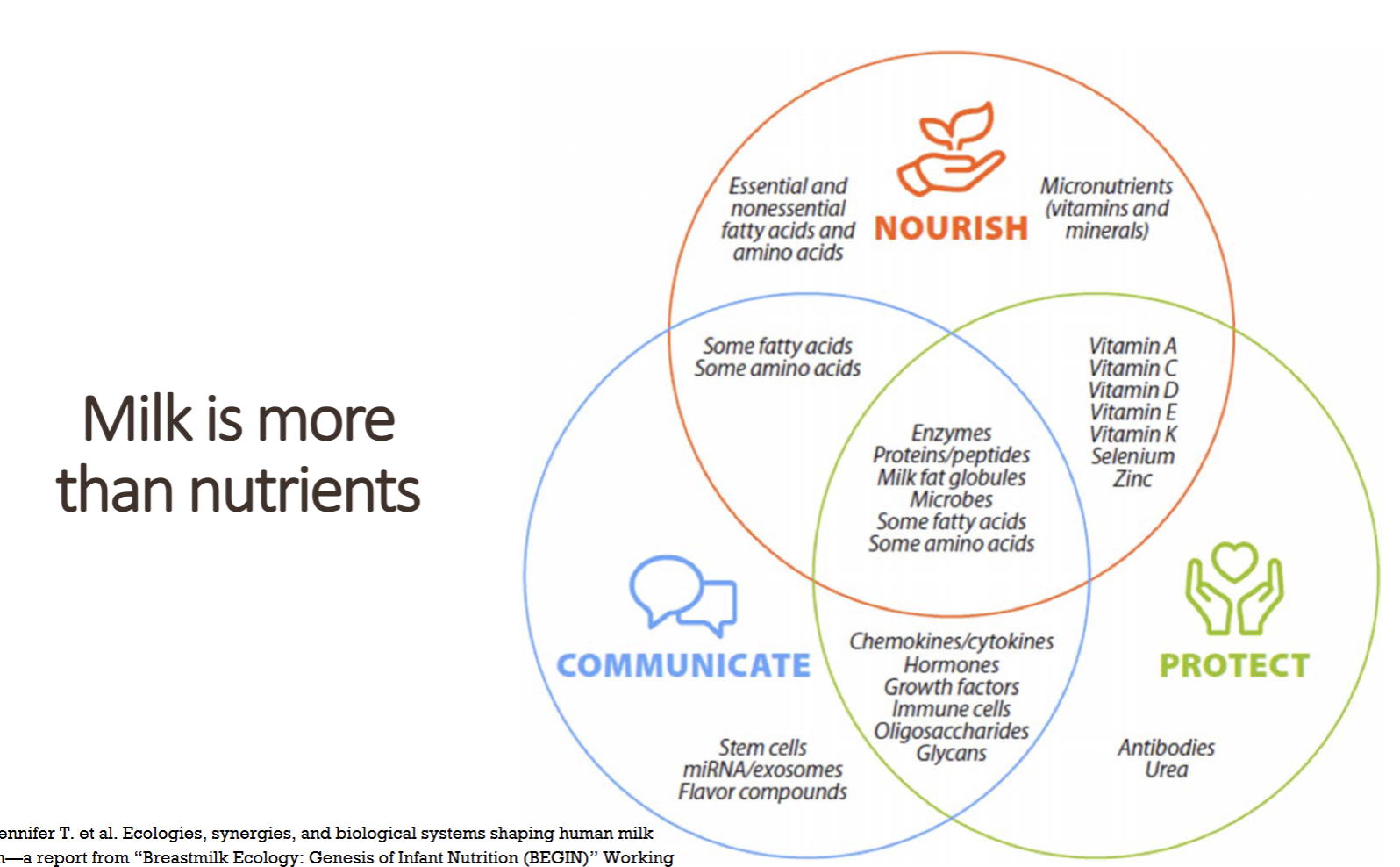
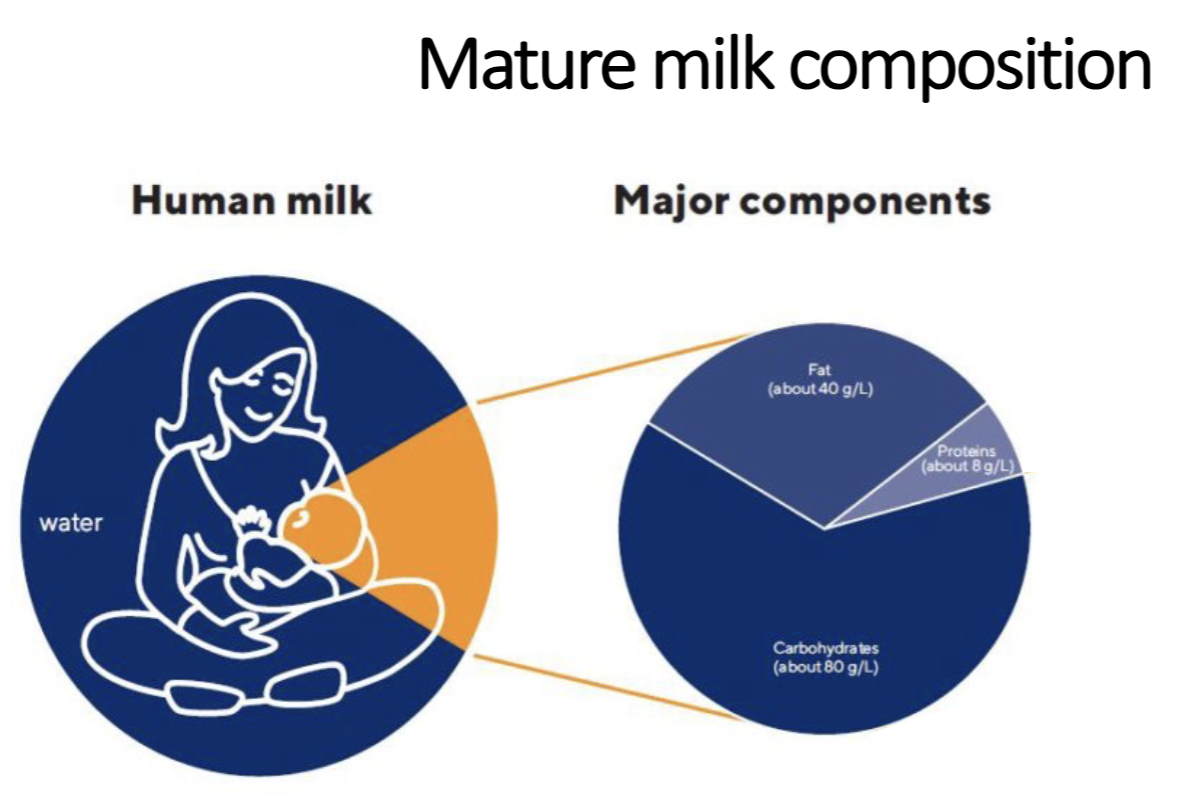
Composition of Human Milk
Nourish, Communicate, and Protect
Carbohydrates(oligosaccharides & Lactose), Fat, Protein,
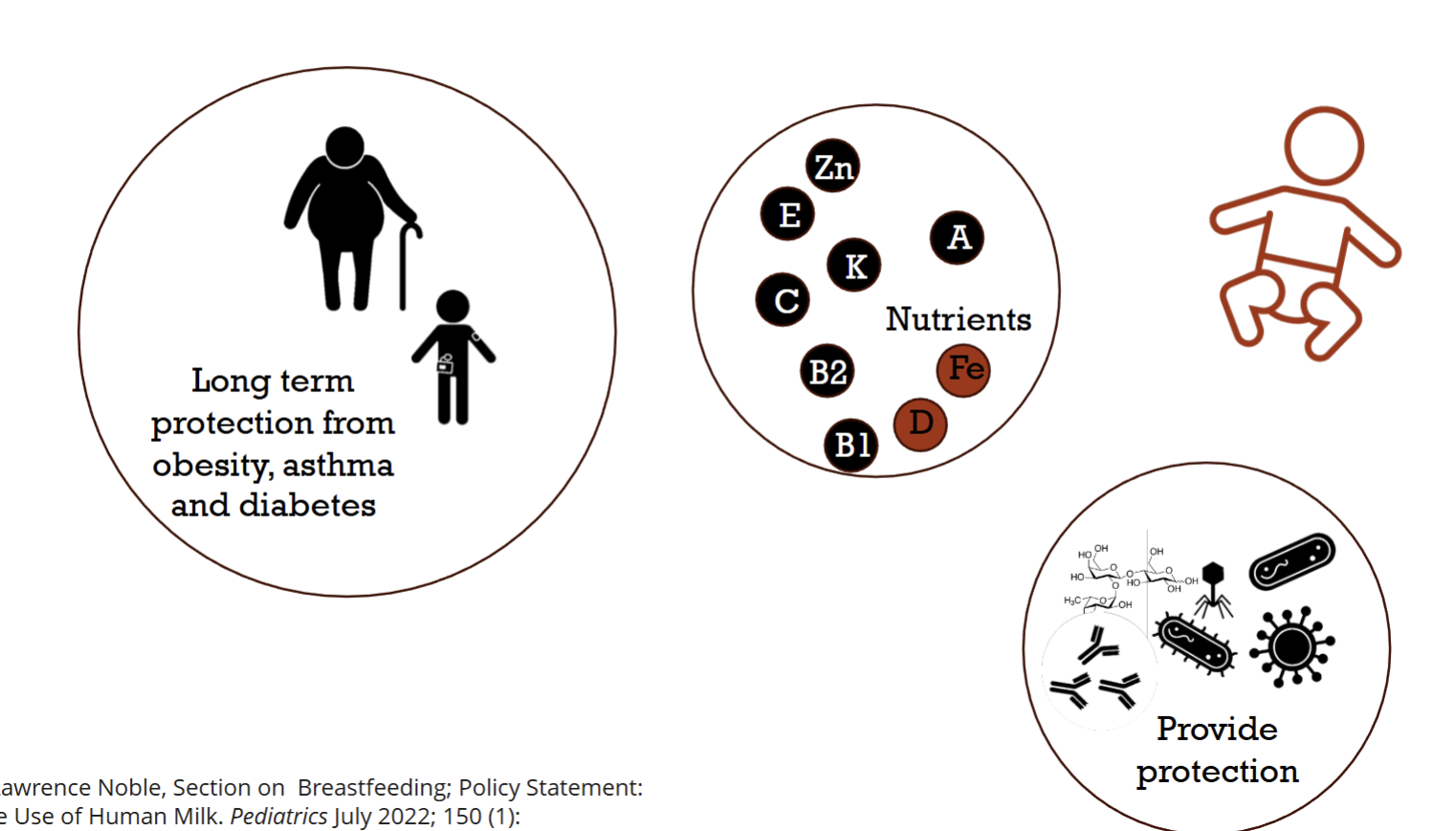
Benefits of Breastfeeding
Baby Benefits:
Long-term protection from obesity, asthma, & diabetes
Nutrient
Provide protection
Mother Benefits:
Reduce risk for breast & ovarian cancer
Reduce risk of postpartum depression
Reduce risk for type 2 diabetes
Recommended Breastfeeding Time legnth by AAP and WHO
6 months and then to 2 years (with complmentary food)
Contra-Indications of Breastfeeding
Untreated HIV
Human T Cell Leukemia-Lymphoma Virus Infection
Ongoing Drugs Use
Temporary stop breastfeeding while chemotherapy
Breastfeeding Pathology that affect breastmilk
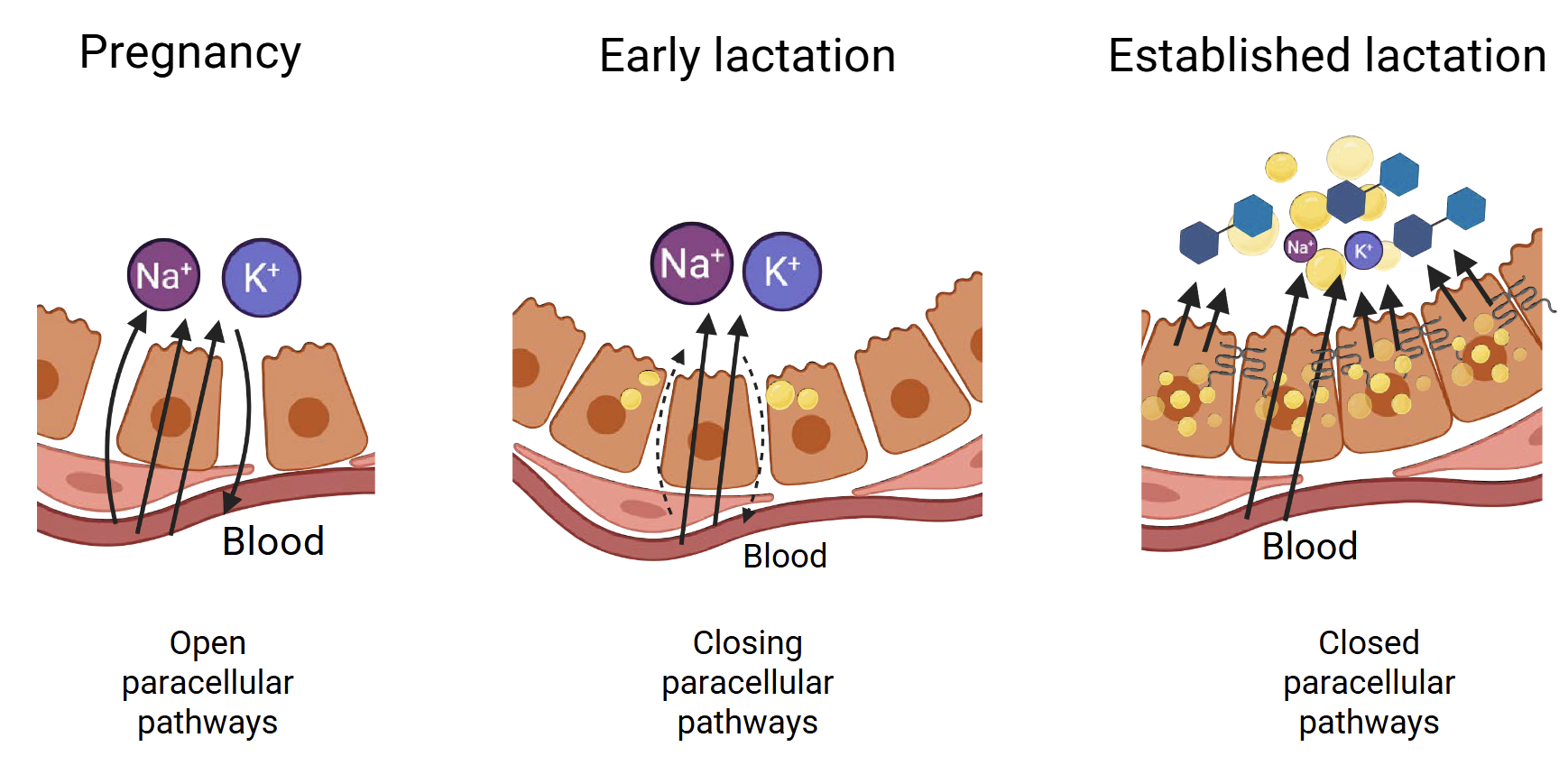
First 14 days postpartum are important for lactation development
Pregnancy - Open paracellular pathway
Early Lactation - Closing paracellular pathyway
Established Lactation - Closed paracellular pathway
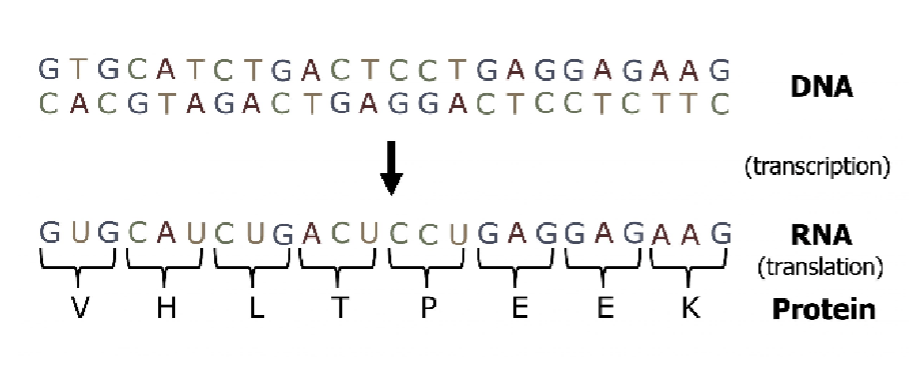
DNA is a made from
Polymers of Nucleotides
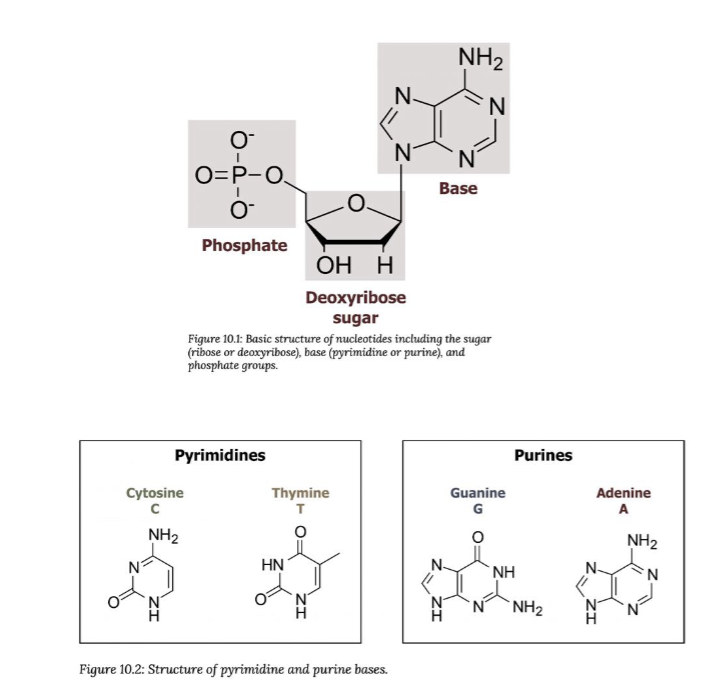
Nitrogenous bases consist of
Purine
Adenine(A)
Guanine(G)
Pyrimidine
Cytosine(C)
Thymine(T)
Uracil(U)
Structure of DNA
Double Helix Structure
Sugar and phosphate of the nucleotides form backbone
Nitrogenous bases are stacked inside
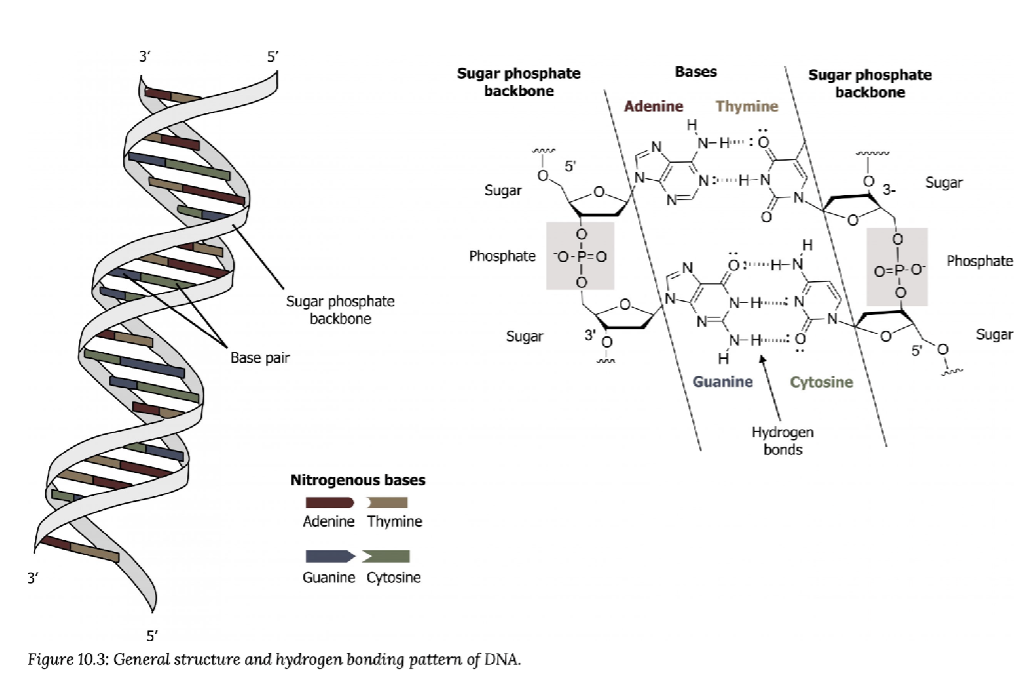
Chargaff’s Rule
A%=T%
C%=G%

What is a Gene
A sequence of DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA and/or Protein
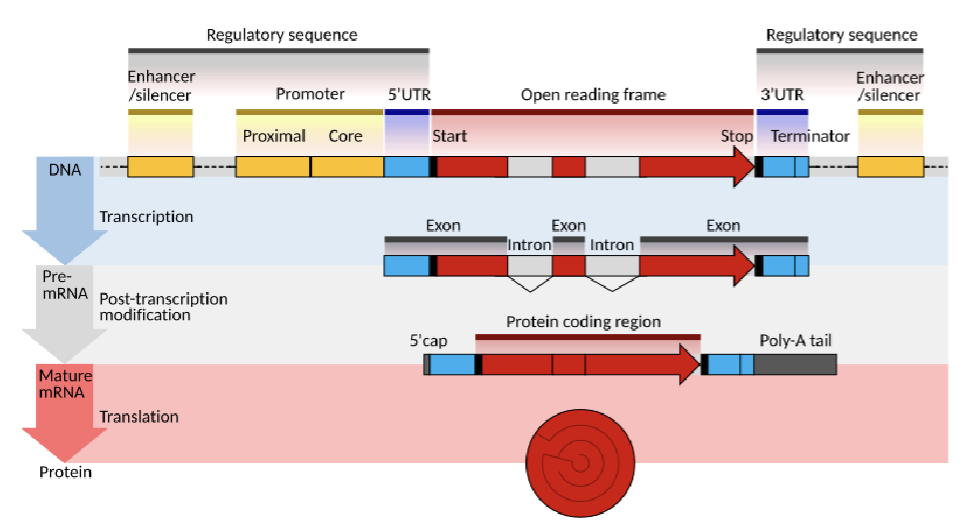
Components of a Gene
Promotor Sequence - Binding sites for RNA transcription machinery
Exons - protein coding sequences
Introns - non-protein coding sequences
5’UTR/3’UTR - Untranslated region that contain non protein coding that transcribed into RNA and regulate protein translation
Enhancer/Silencer - regulate efficiency of gene transcription
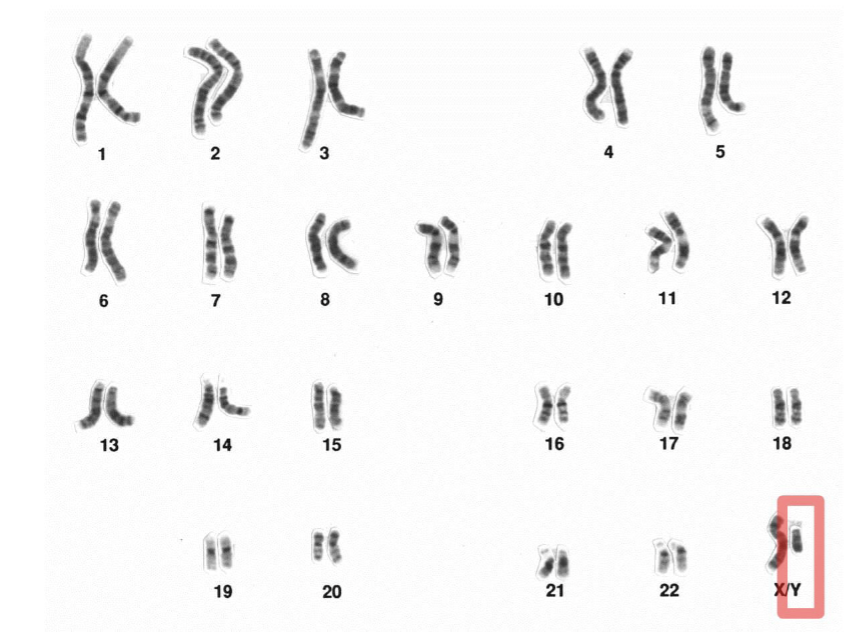
Organization of Human Genome
46 Chromosomes:
22 pairs of autosomes
1 pair of sex chromosomes: XX(Female) & XY(Male)
Where does genetic diversity come from (3)
1) Genetic Mutations
2) Meiosis Cell Division
3) Sexual Reproduction by combining the genetic material from 2 individuals

Mechanism of Genetic Mutations
Exogenous Cause
UV
Irradiation
Tabacoo
Industrial pollutatns
Endogenous Cause
Reactive Oxygen Species
Errors in DNA replication
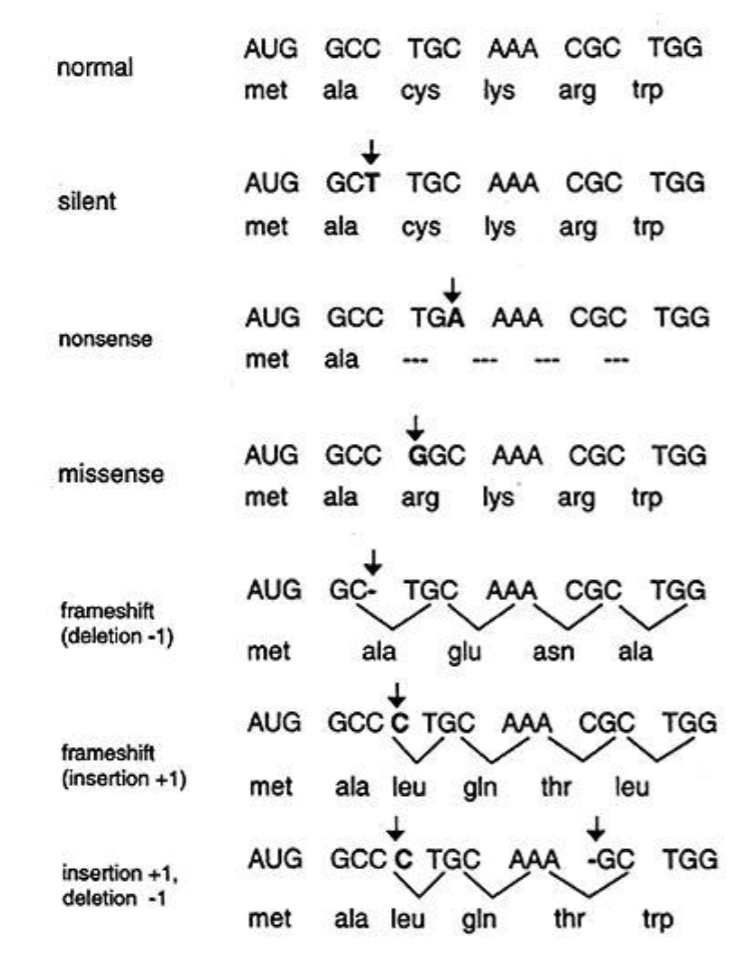
Consequences of DNA Mutation(4 types)
Silent Mutation - Doesn’t impact the encoded protein sequence
Missense Mutation - Changes the encoded amino acid(may or may not impact)
Nonsense Mutation - Changes amino acid to stop
Frameshift - insertion or deletion of a nucleotide will change the codon reading frame(significantly change amino acid)
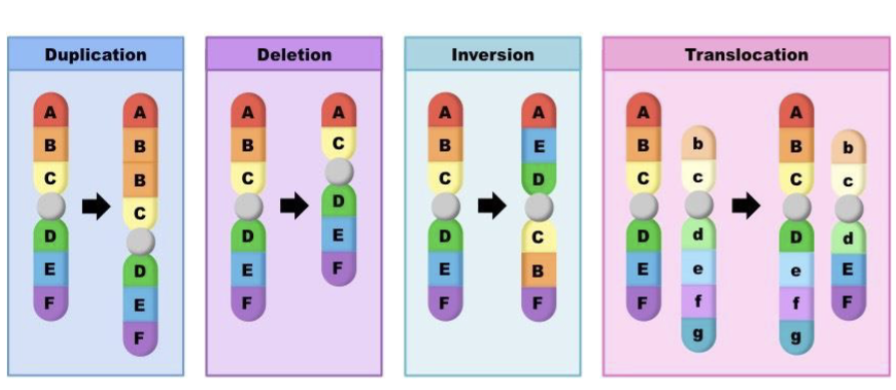
Consequences of Chromosomal Mutation(4 types)
Duplication - increase the copy number of gene leading to increased expression
Deletion - loss of gene
Inversion - disrupt gene at border of the inversion
Translocation - fuse 2 different gene to create a fusion protein or bring a gene under control of a different promotor
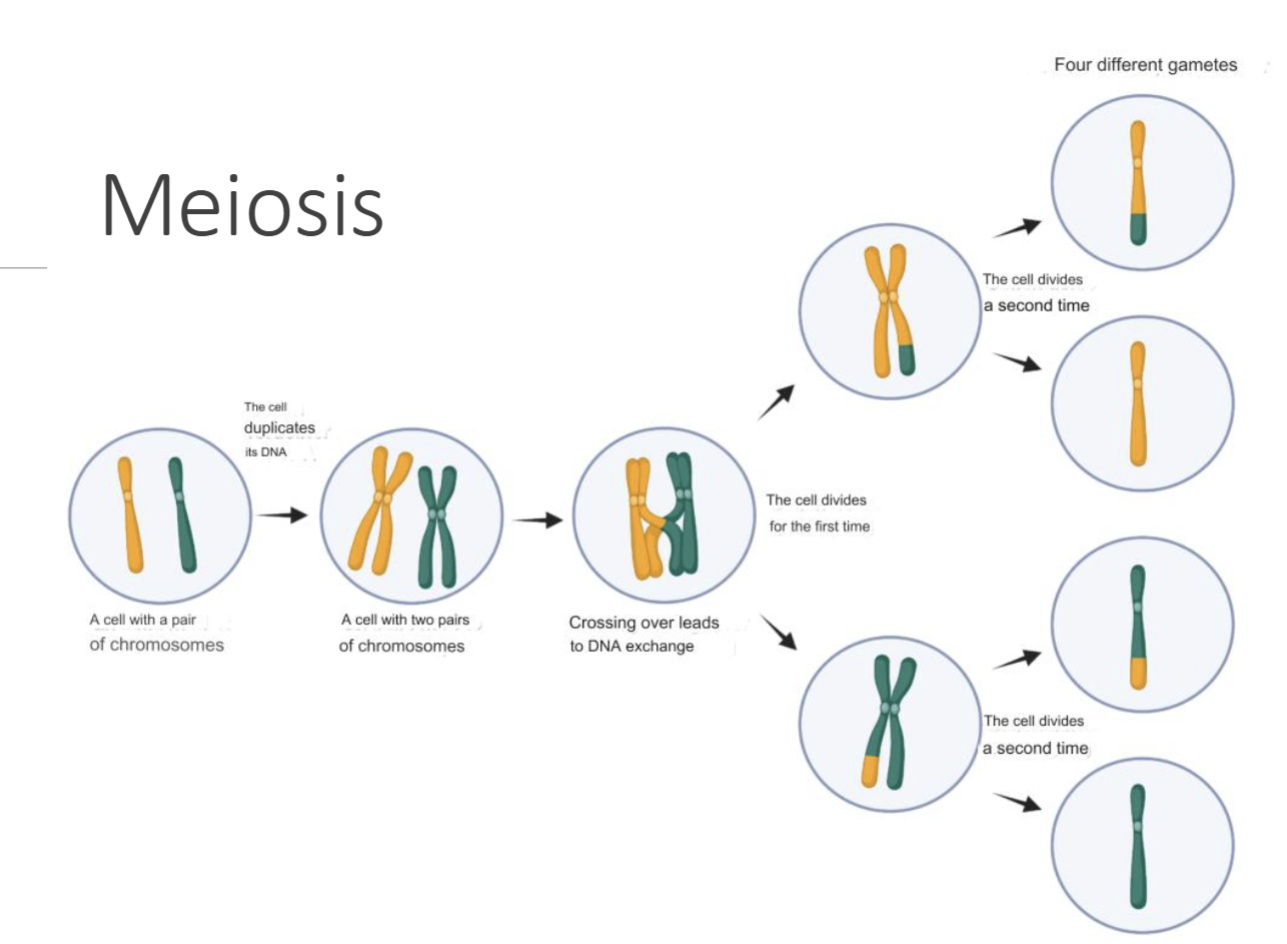
What mechanism of Meiosis (Gametes) Cell Division gives genetic diversity
1) Crossing Overs
2) Independent Assortment
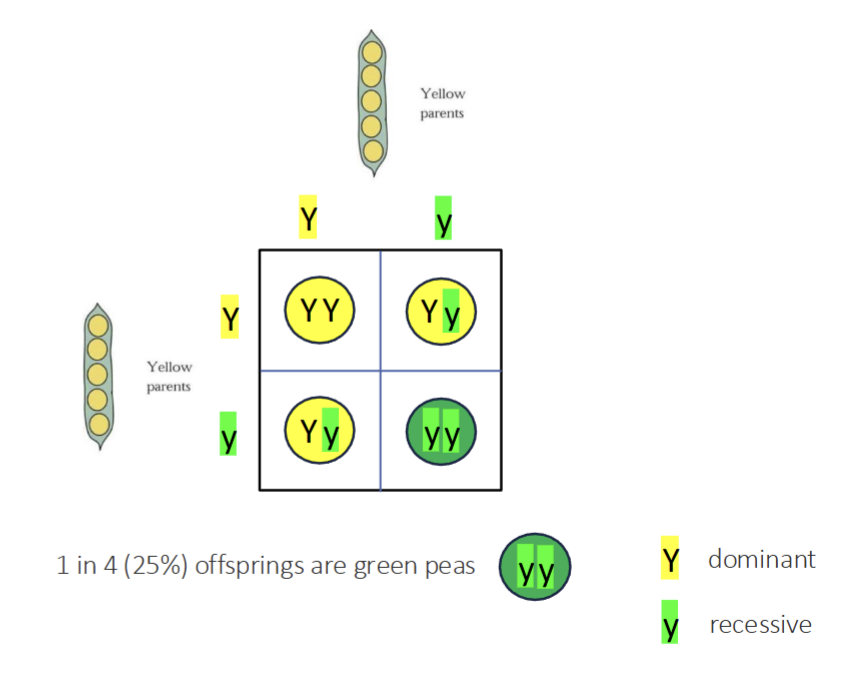
Sexual Reproduction:Mendelian Inheritance
Allele (y or Y)
Dominant Allele: determines phenotype w/1 copy
Recessive Allele: determines phenotype w/2 copies
Homozygous (yy or YY)
Heterozygous (Yy)
Monogenic Disorder(Mutation in single gene: autosomal recessive) in Human Nutrition (3 types)
Absorption Disorder: Cystic fibrosis, Hereditary hemochromatosis
Metabolic Synthesis/Processing Disorder: Phenylketonuria
Energy Generation Disorder: Mitochondrial Defects
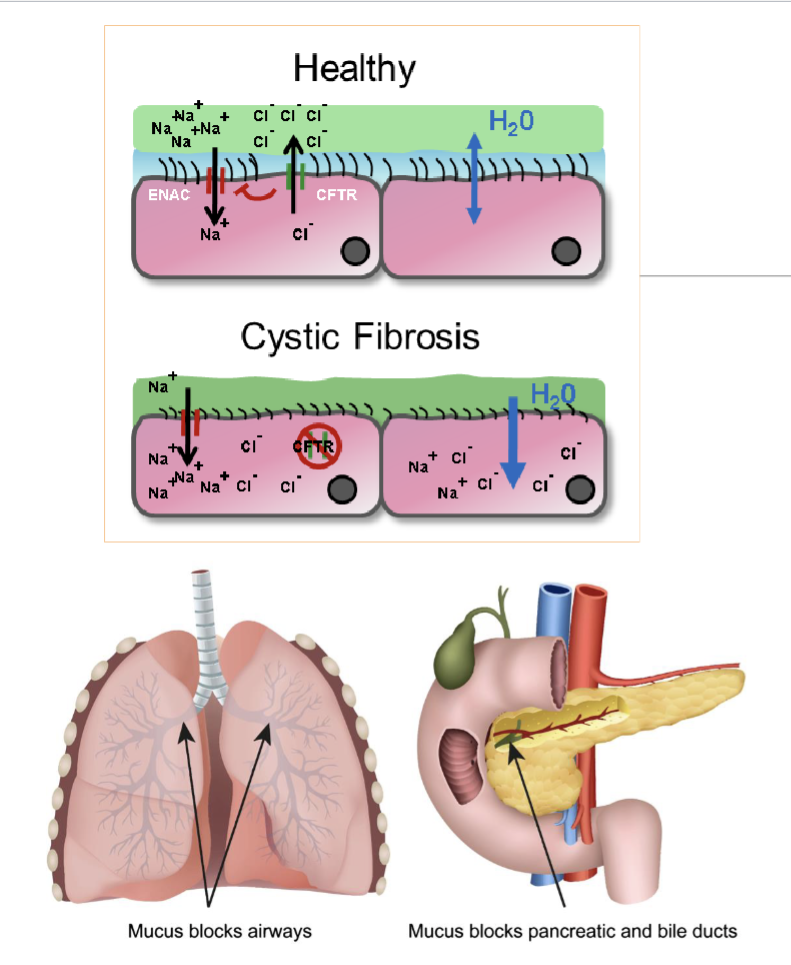
Cystic fibrosis
Autosomal recessive genetic disorder by co-inheriting 2 mutatn allels of the CFTR gene on chromosome 7
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator(CFTR) is an ion channel that transport Chloride ions into surface lumens in airways within lungs, pancreas, and GI
Movement of Chloride into extracellular space creates an osmotic gradient to ensure mucus in lumen has adequate water content to reduce viscosity and improve mobility of mucus
In Cystic fibrosis loss of CFTR ion channel lead to thickened mucus, leading to poor lung function due to mucus buildup, pancreatitis, and decreased absorption of fats, carbs, and protein
patients need extra pancreatic enzyme oral supplements(pancreases) with meals to aid digestion
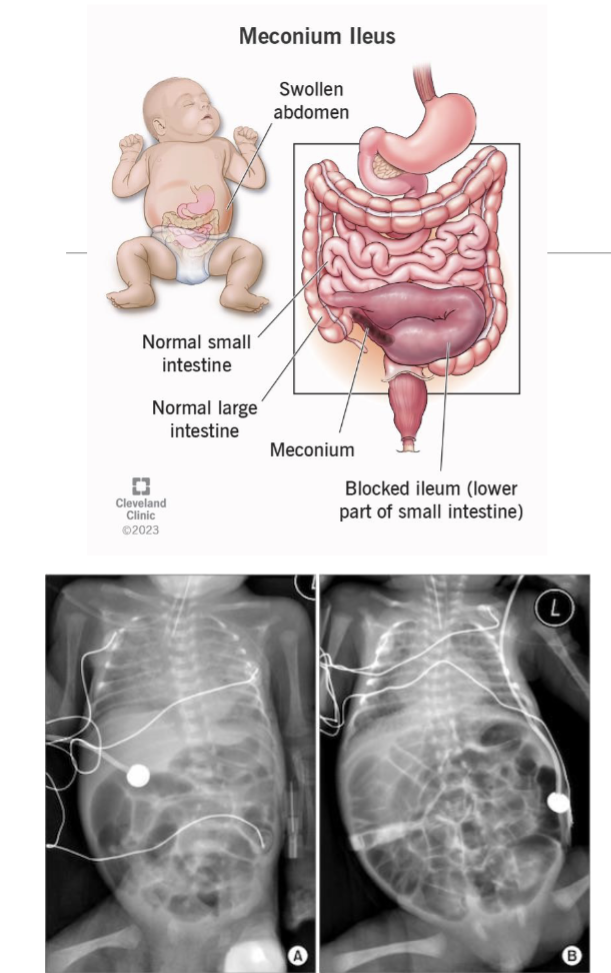
Cystic Fibrosis in newborns/infants
Meconium ileus where thickened mucus accumulates in the ileum casuing abdominal distention and obstruction of GI tract
treated with an enema(lubricant) applied via rectum(then surgery if not sucessful)
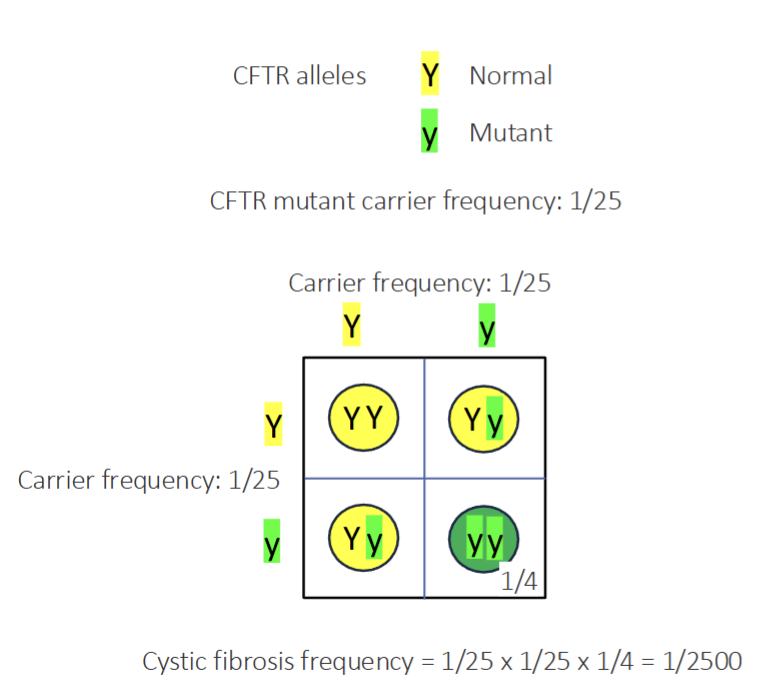
What is one of the most common monogenic disorders in population of European descent
Cystic Fibrosis
Carrier is 1/25
Newborn 1/2500
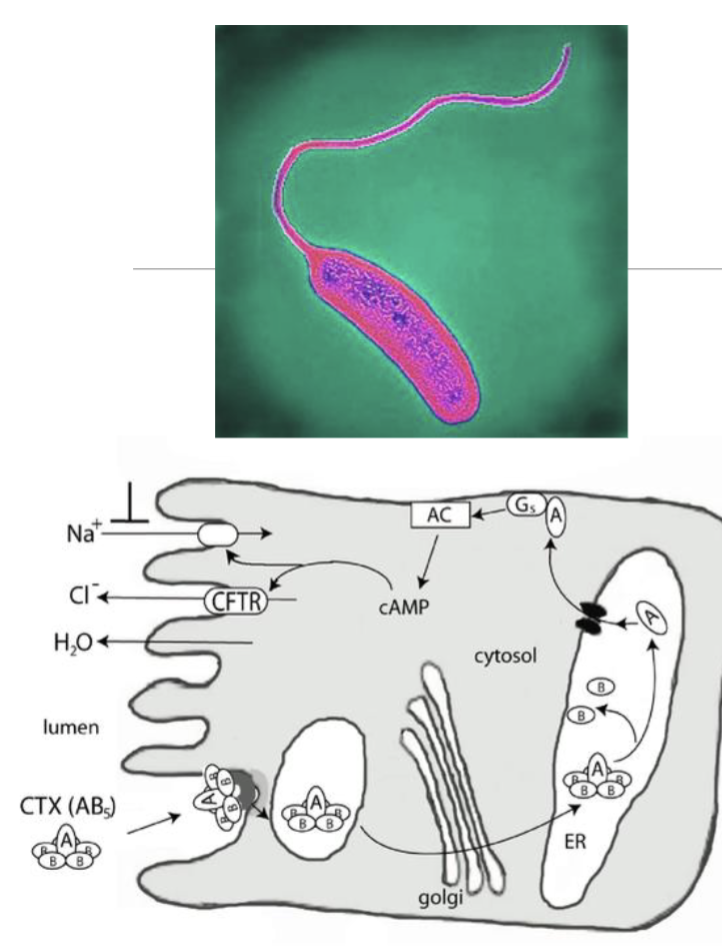
Cystic fibrosis: Protection against cholera
Cholera is caused by the bacteria: Vibro cholerae which secretes toxin that causes overactivity in the CFTR ion channel, resulting in excessive water loss into the bowel lumen and diarrhoea
CFTR mutation carriers do not suffer cystic fibrosis, but express reduced CFTR ion channels so are less susceptible to chlorea toxin
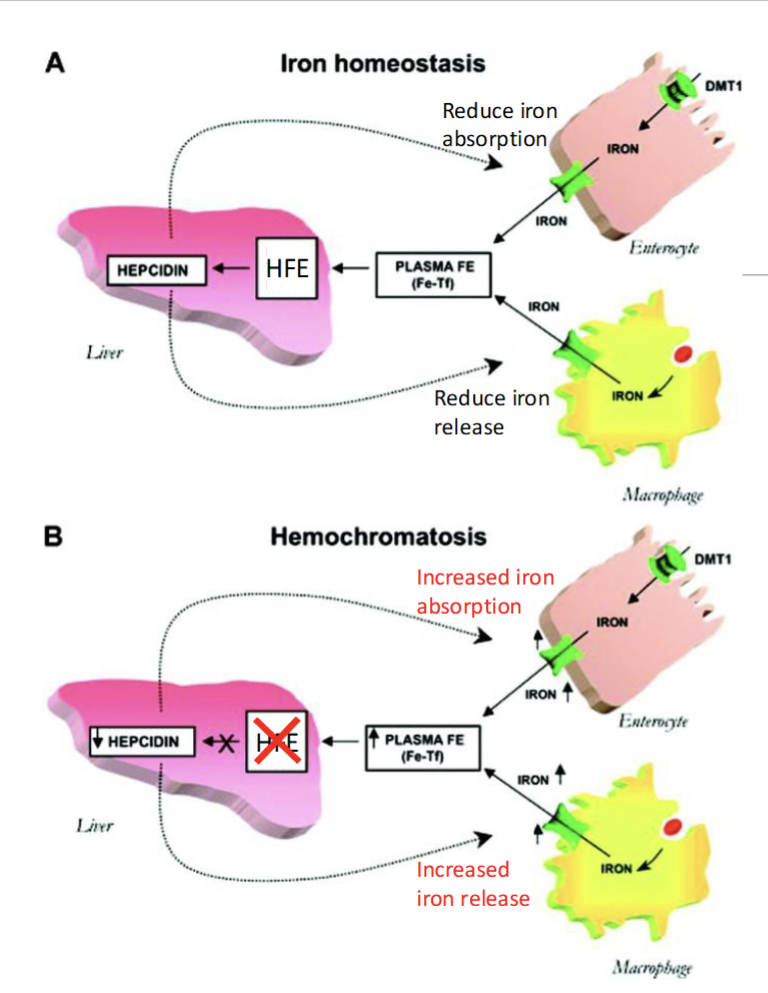
Absorption Disorder: Hereditary Hemochromatosis
Iron is absorbed in SI, stored in liver & macrophages, & utilized for hemoglobin synthesis and as a metal co-factor for enzyme and redox reaction
No physiological route to excrete iron from body, so iron is stored carefully maintained
increased circulating iron level in the blood, liver protein HFE stimulate protein hepcidin which reduces iron absorption in bowel & reduce release of iron stored in macrophage
inherit 2 mutant alleles of HFE, the stimulation to release hepcidin is lost leading to increased absorption and release of iron into the body
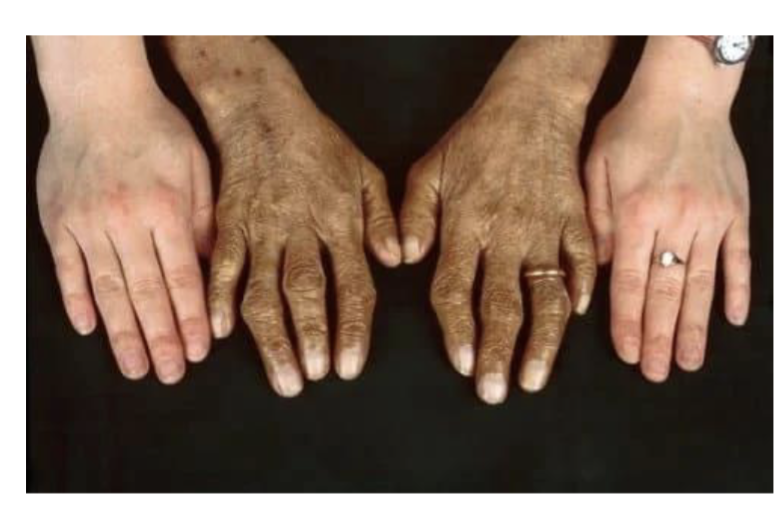
Prominent feature of Hereditary Hemochromatosis
iron accumulation in the skin leading to the darker “bronze” apperance, permanent damage to the heart, liver, pancreas, and brain
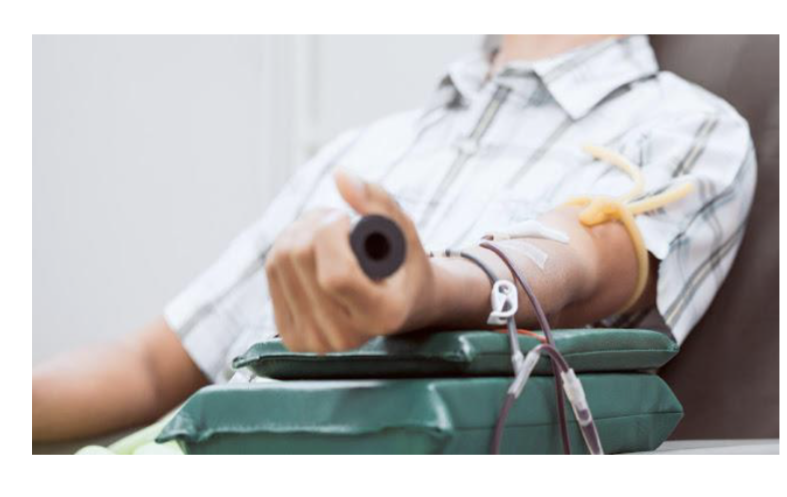
Treatment of Hereditary Hemochromatosis
Regular phlebotomy(removal of blood) as a method of removing excess iron: reliable blood donors
Drugs that bind to iron(iron chelators), which the kidney can then excrete in the urine
hypothesized that the HFE mutation evolved to minimize the impact of menstruation which cause iron deficiency
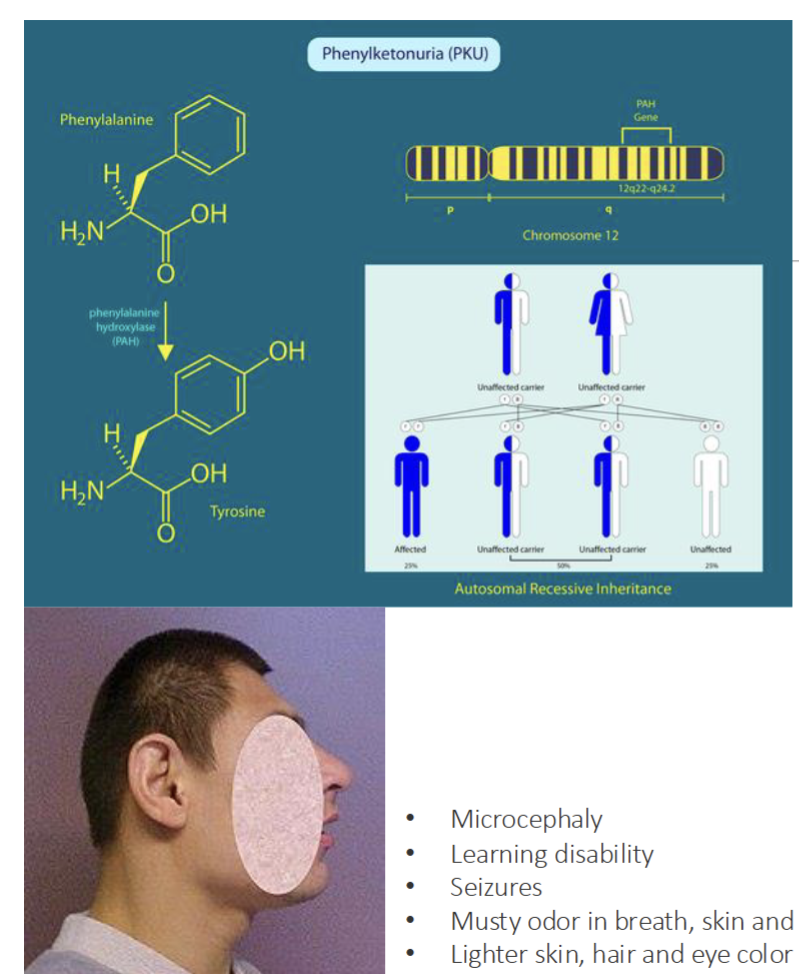
Metabolic synthesis/Processing Disorder: Phenylketonuria
Rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder caused by co-inheriting 2 mutatn allels of the PAH gene on chromosome 12
PAH gene encodes the phenylalanine hydroxylase enzyme that convert amino acid phenylalanine to tyrosine
In phenylketonuria, the loss of PAH enzyme activity results in toxic accmulation of phenylalanine that interfere with newborn development of brain and nervous system
Phenylketonuria during pregnancy
Mother’s PAH enzyme activity can protect the developing fetus from phenylalanine accumulation
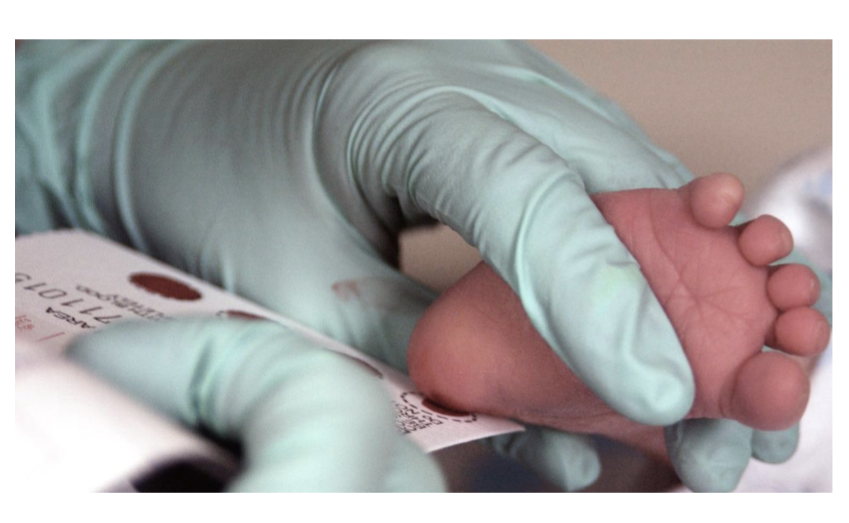
All newborns are screened for phenylketonuria using a blood test to test for high levels of phenylalanine in the blood
Treatments for Phenylketonuria
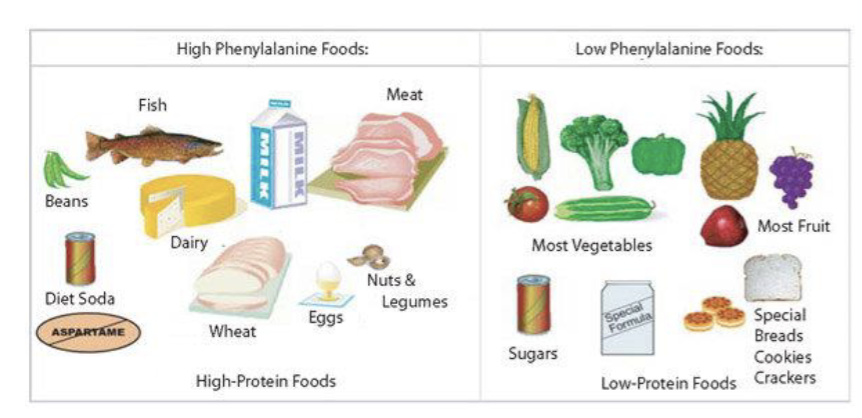
Avoiding high protein diet including:
meat and fish
eggs and cheese
nuts and seeds
flour based food: bread, pasta, cakes, and biscuits
soya, quorn, and tofu
Regular blood test are taken to check blood levels of phenylalanine
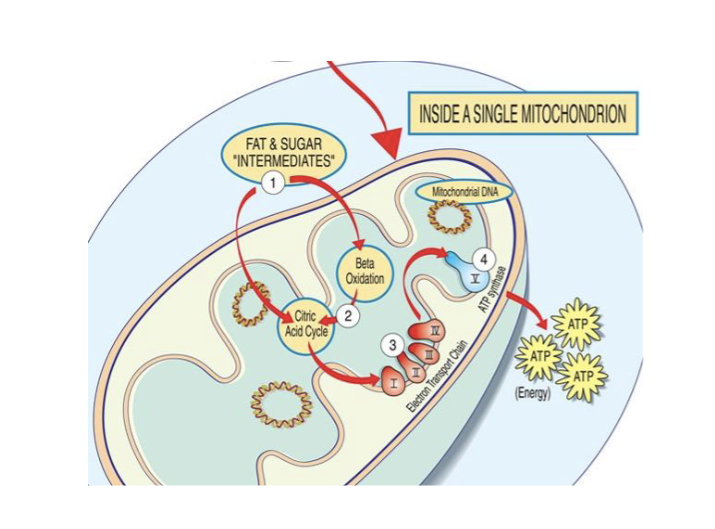
Energy Generation Disorder: Mitochondrial Defects
Mitchondria role in converting nutrients into ATP
Symptoms reflect insufficiency of ATP in muscles, nerves, and brain
muscle weakness
exercise intolerance
seizures, headaches
Ataxia
Vision Defects
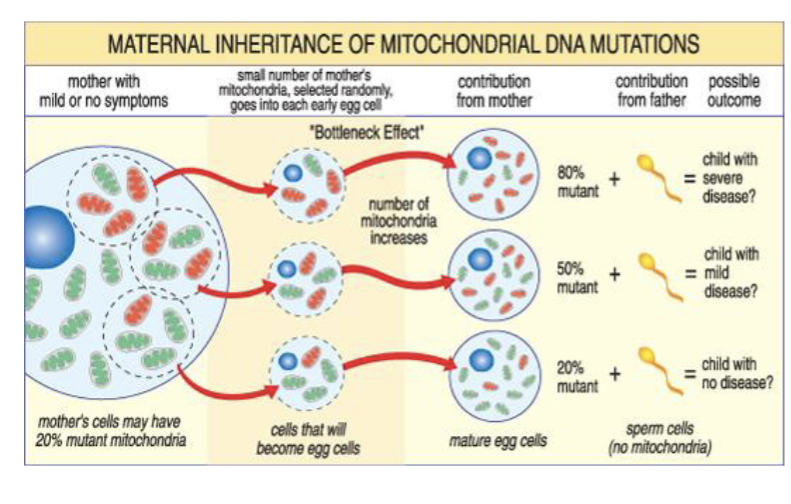
Inheritance of mitochondrial diorder
2 types of genes essential lfor mitchondria function
Gene encoded in the nuclear genome lead to autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, & X-linked pattern
Mitochondrial genome inherited in a maternal pattern that is always from mother
During conception, when sperm fuses with egg, the sperms mitochondria do not contirbute to the fertilized egg, so all mitochondria come from mother
Egg will have hundreds of individul mitchondria, so severity of mitochondria disease reflects the number of mutated mitochondria in egg
Non-Mendelian Inheritance
Physical characteristics and human diseaes are polygenic
phenotype is determined by combination of multiple genes
phenotype can also be influenced by environment and genetic factors
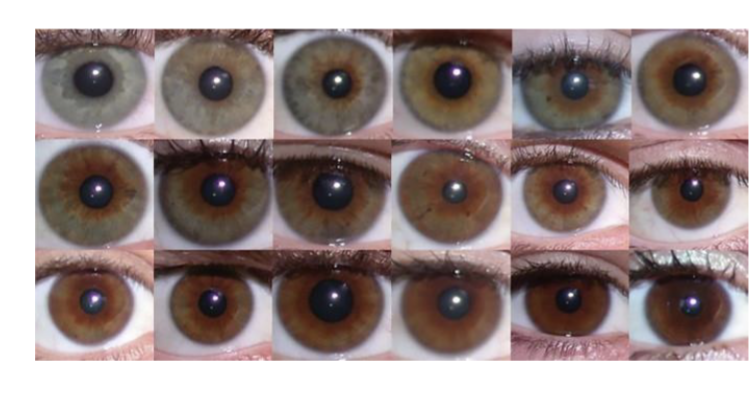
Polygenic Traits
At least 8 genes determine the color of the human eye
a greater number of genes = increased complexity in inheritance pattern
How do we identify if specific genes play a role in the pathology of a trait or disease(4)
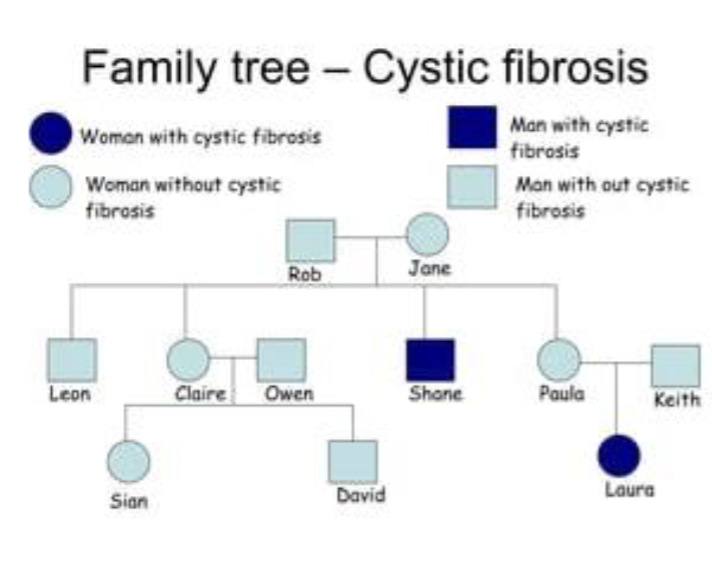
Family History
Twin Studies
Adoption studies
Genome wide association studies
Family History
Collecting info on family members with and without the disease
In Mendelian inheritance, this should lead to predictable pattern of inheritance
Polygenic diseases do not exhibit Mendelian inheritance
Typically 1 or more first degree relative with the same disease will indicate heritable genetic factors that influence disease
Interaction between specific genes and environment influence disease onset
Incomplete info on family members beyond immediate family circle
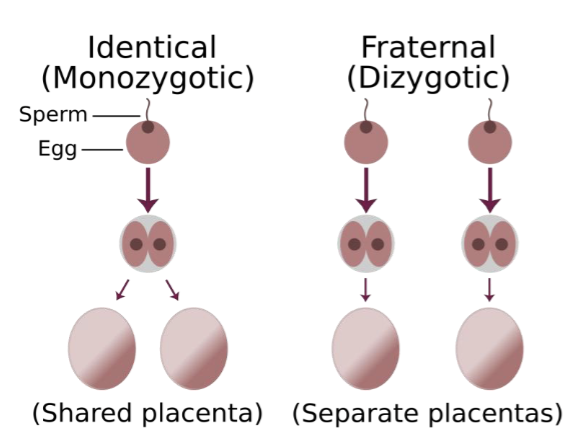
Twin Studies
Identical twins(monozygotic) form as a result of a single embryo dividing into two embryos and share 100% genetic identity
Fraternal twins(dizygotic) form from fertilization of two separate eggs by 2 separate sperms, respectively, and share 50% genetic identity
If disease in monozygotic twin»dizygotic twin suggest a genetic factor play a role in disease development
Adoption Studies
Studies compare groups of adoptees with their adopted families as well as their natural families
Adoptees typically share no genetic identity with their adopted family, & 50% genetic identity with their biological parents
If disease/trait in adoptees is strongly correlated w/the biologial parents, this indicates a genetic component that impacts the development of the disease

Genome Wide Association Studies(GWAS)
Powerful method to identify a statistically significant association between a genetic mutation and a polygenic disease
An observational case-control study: collect info from cohorts of individuals with and without the disease: disease that are more frequently present in the disease population compared to control population
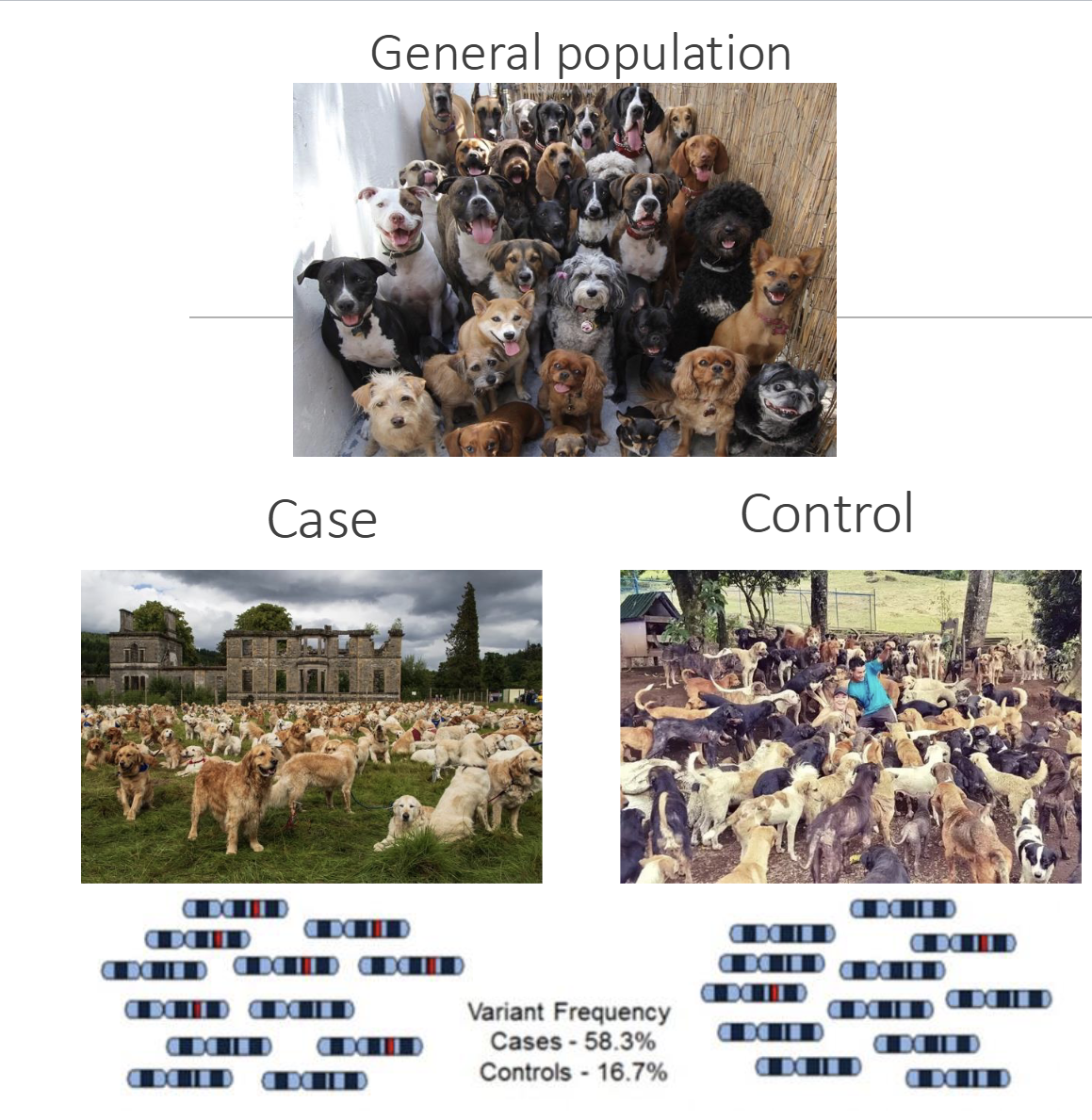
How do we find mutations in GWAS studies
Whole genome sequencing to find mutations: expensive and not yet feasible to perform for every subject in large studies
Single nucleotide polymorphism database use existing data with known locations of mutations present in the general population: cheaper and only part of gene
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism(SNP) are point mutations
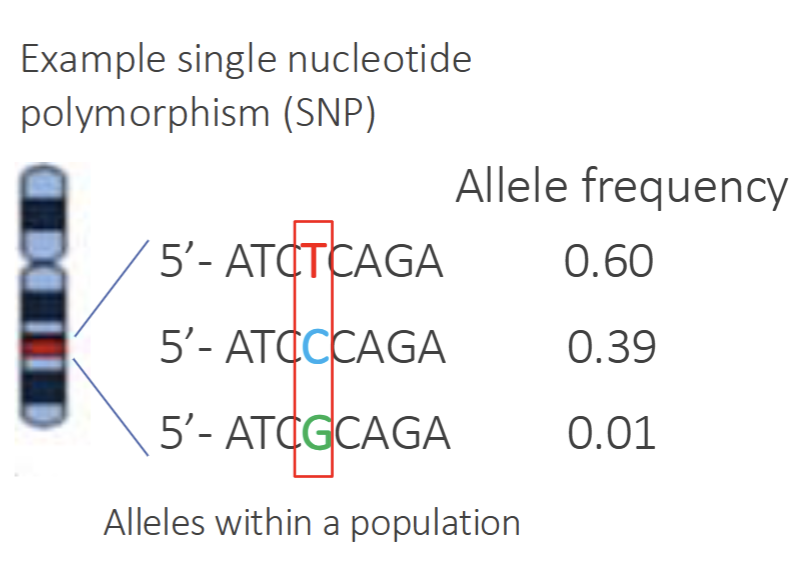

What happens if a SNP is associated with a disease
SNP is the mutation in a gene that causes the disease but very rare as majority of SNP are non-gene coding regions
SNP are more like genetic “bookmarks” highlighting a region of the chromosome that could contain the real disease or mutation that impacts disease development
More SNPs = more likely that we find a SNP that associates with the disease
SNP databases will have SNPs that cover length of each chromosome: Human Genome Project
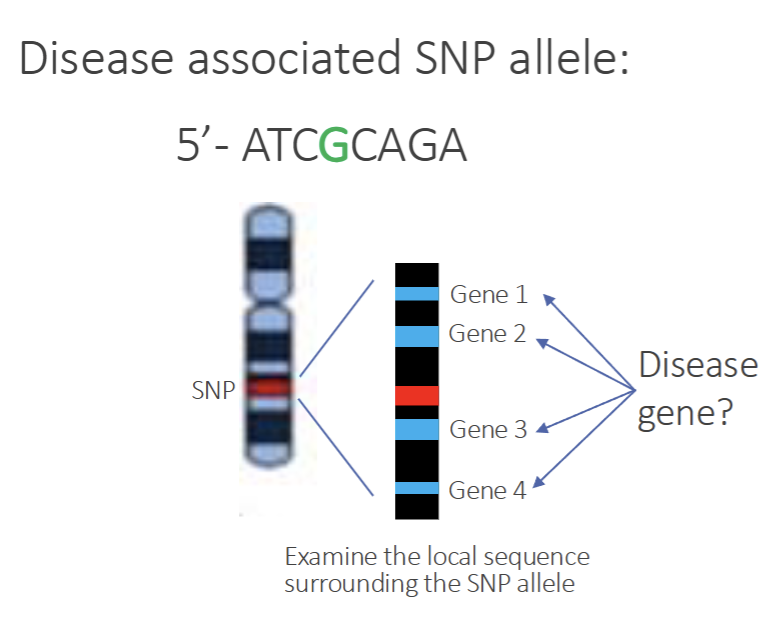
Advantages of GWAS(Genome Wide Association Studies)
Ability to use very large sample size to identify diverse number of genetic variation that contribute to the phenotype
Rare genetic variants that only affect specific populations can be identified
Genetics of Obesity
Enviornmental factor play a major role
Twin Studies(meta analysis on 88 independent twin study)
existence of genetic factors that determine BMI and Obesity
Family Study
Also agree twin studies showwing importance of genetic factor determining BMI
Heritability Index Range: 0-1
0 = trait is not determined by genetics
1 = trait is completely determined by genetics
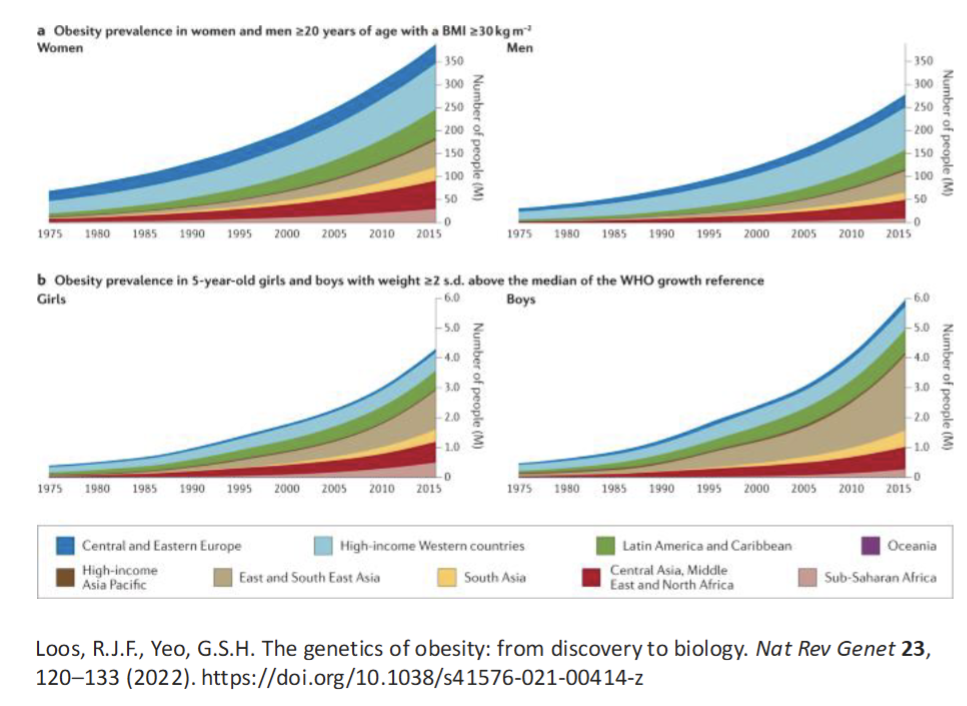
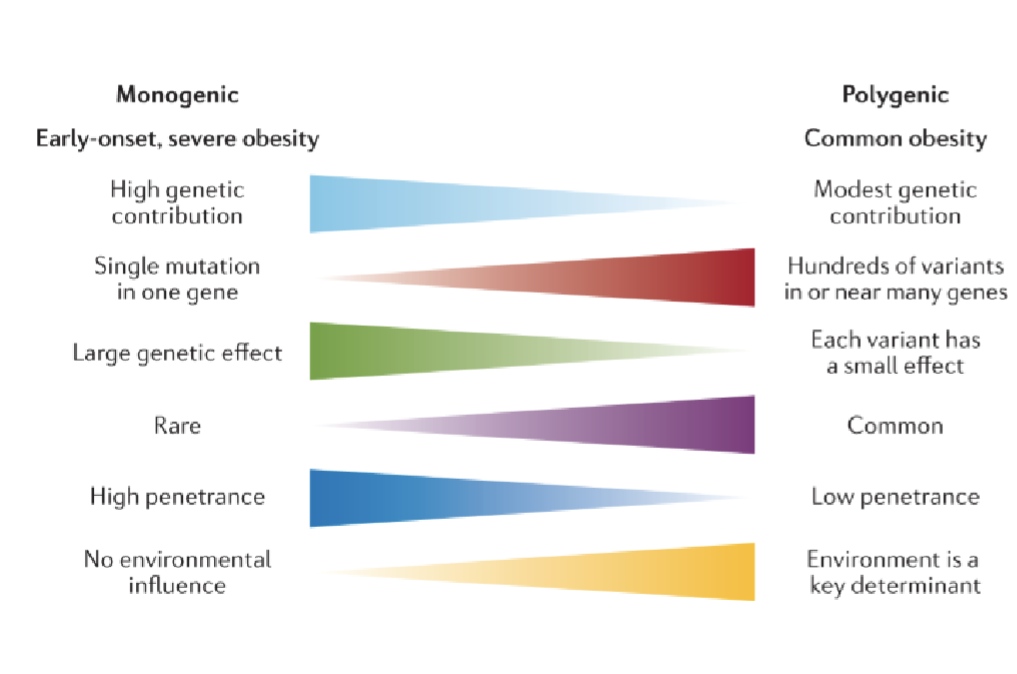
2 Forms of Genetic Obesity
Monogenic(early onset, severe obesity)
High Genetic contribution
Single mutation in one gene
Large genetic effect
Rare
High penetrance
No environmental influence
Polygenic(Common obesity)
Modest genetic contribution
Hundreds of variants in or near many genes
Each variant has a small effect
Common
Low penetrance
Enviroment is a key determinant
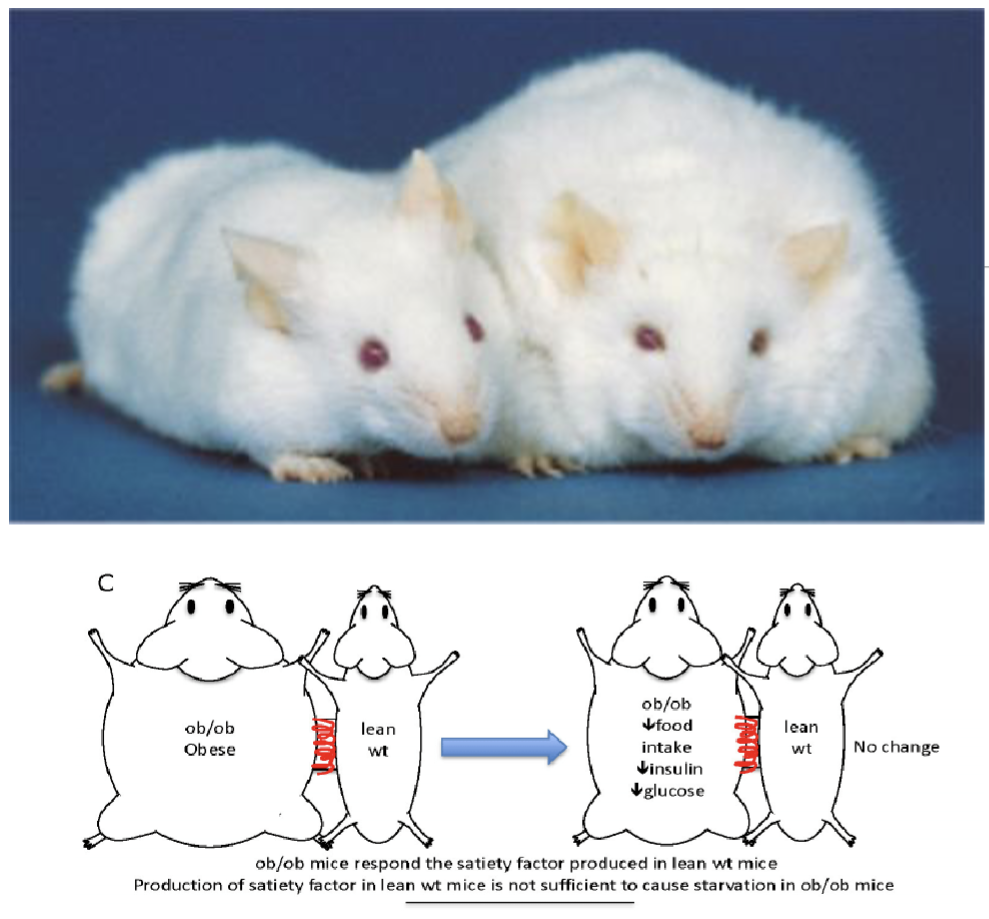
Monogenetic Obesity: Leptin
Identified in mice or the (ob) mouse model
ob mouse exhibit hyperphagia(excessive eating) leading to obesity
Performed a parabiosis experiemnt where blood vessel from a normal mouse was connected to the ob mouse
Surgically connected ob mouse showed decrease food intake leading to weight loss
By sharing a blood supply, normal mouse must be sharing its satiety factor with the ob
Protein hormone called leptin
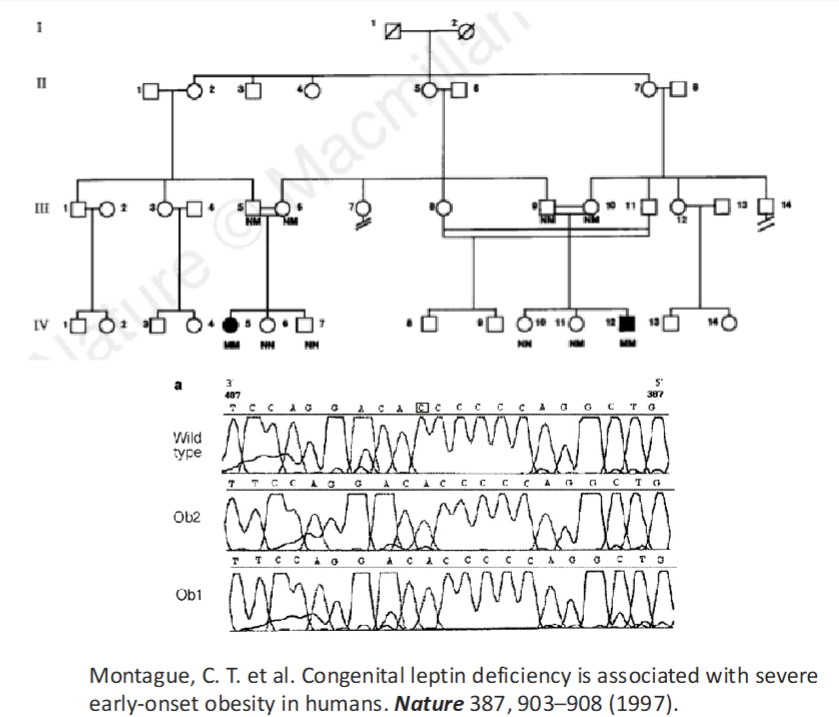
Congenital Leptin Deficiency
A family with congenital leptin deficiency was reported in 1997
Affected individuals were homozygous for a single nucleotide deletion in their leptin gene causing a frameshift mutation
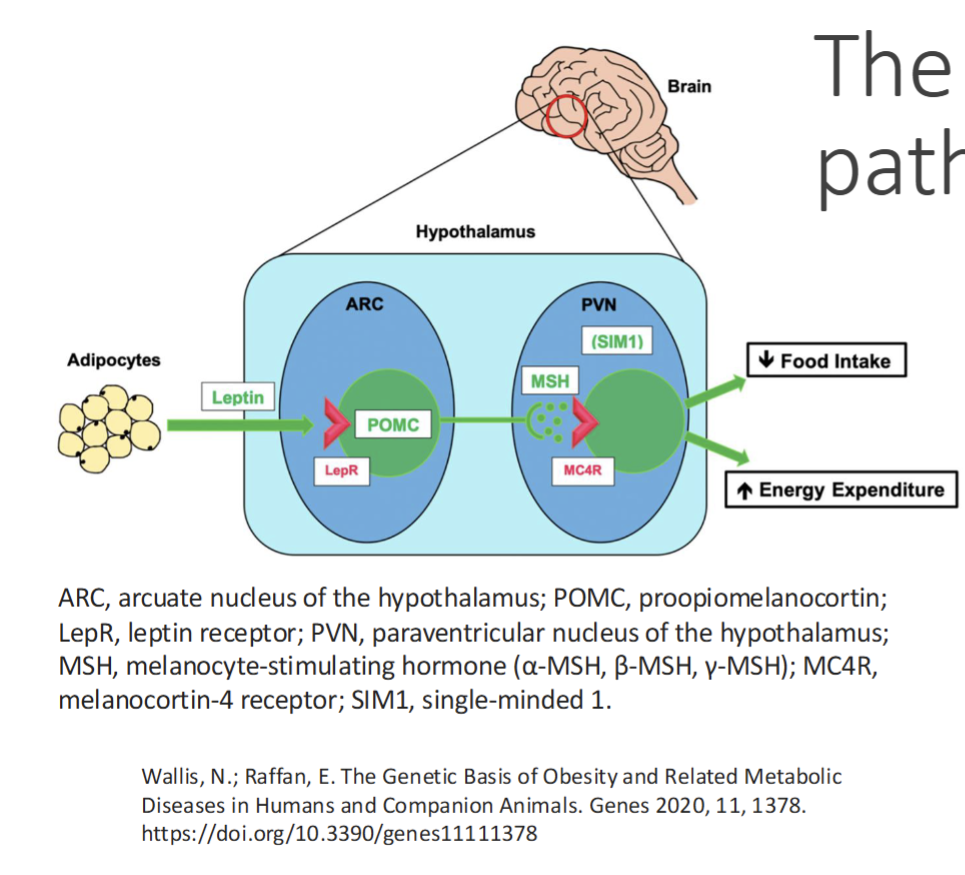
Leptin-Melanocortin pathway
Leptins action is in the CNS, where it activates the hypothalamic leptin-melanocortin pathway
In the hypothalamus, leptin acts on leptin receptors on neurons that produce the protein proopiomelanocortin(POMC)
POMC undergoes proteolytic cleavage to produce a number of neuroactive pepide like MSH
MSH peptides act on melanocortin receptor 4(MC4R) expressed on neurons in the paraventricular nucleus(PVN) within the hypothalamus resulting in reduction of food intake and modified energy metabolism
Polygenic Obesity(Common Obesity)
Caused by additive effect of hundreds/thousands of common genetic variants
GWAS have identified more than 1100 independent loci associated with a range of obesity traits(3-5%)
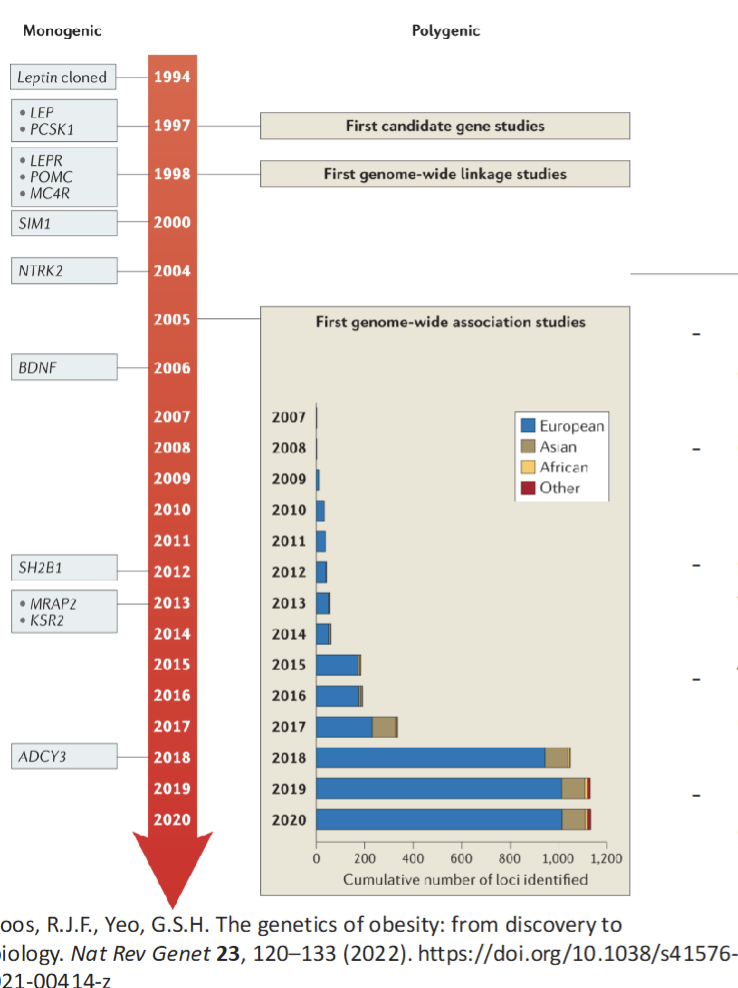
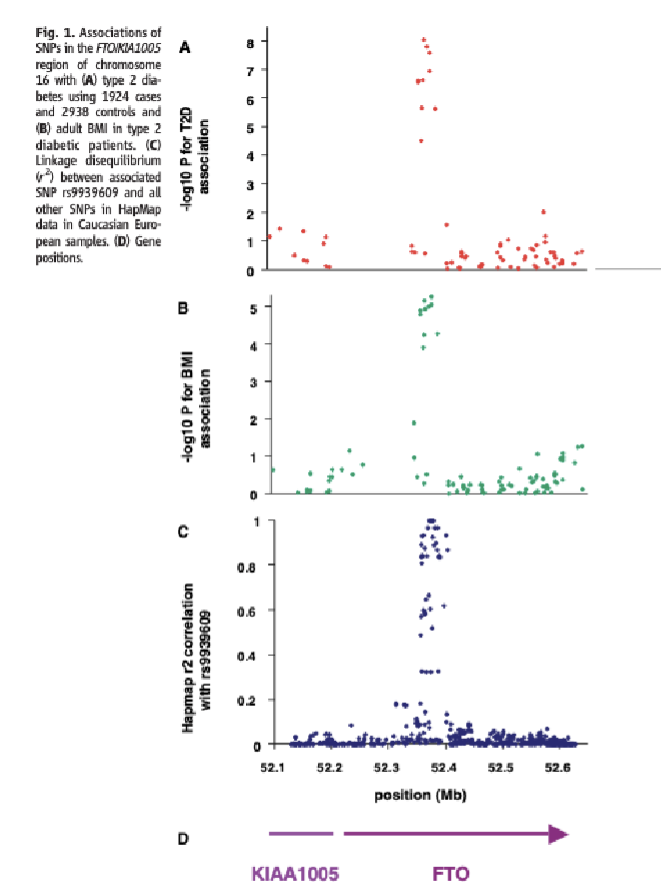
Polygenic Obesity: Fat mass - and obesity- associated (FTO) gene
GWAS identified several SNPs in the intron of FTO that was associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes
FTO encodes for alpha-ketogultarate-dependent dioxygenase enzyme that removes methyl groups from RNA
FTO in obesity remains unclear, but later transpired that obesity association for this locus is at least in large part due to altered regulation of a neighboring gene, iroquois homeobox 3(IRX3) which has an impact on peripheral adipocyte metabolism
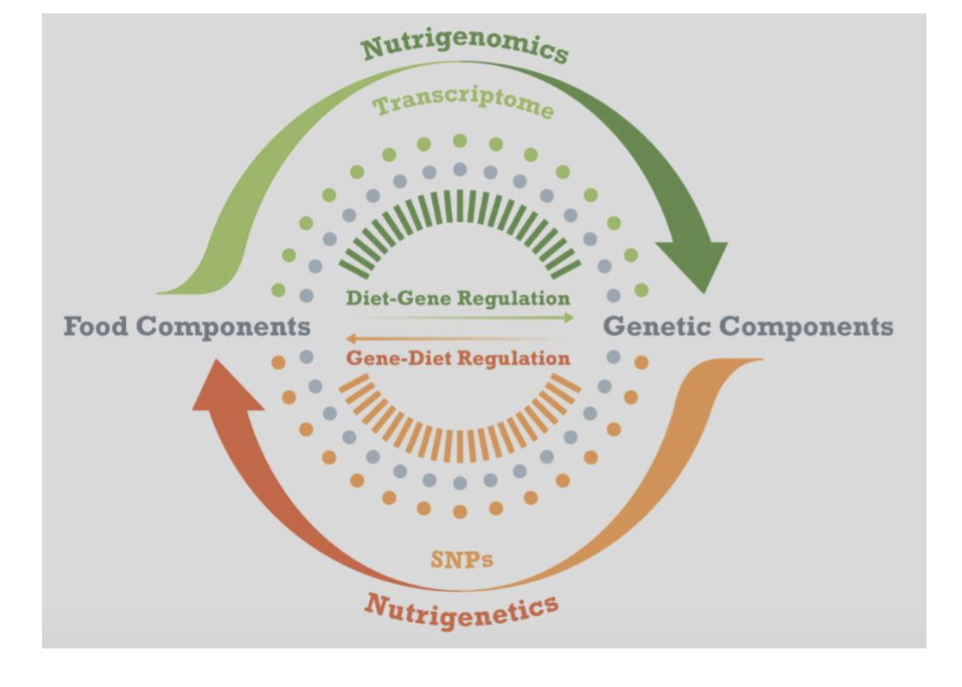
Nutritional Genomics & Nutrigenetics
Nutrigenomics - the study of the effects of nutrients on the expression of an individuals genetic makeup
Nutrigenetics - the study of how genotype determines metabolism of food components, nutrient requirements, and dietary tolerance
Examples of Nutrigenetic
Hereditary hemochromatosis
Phenylketonuria
Lactose intolerance - genetic deficiency of lactase enzyme
Alchol flushing syndrome - genetic mutation in acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 enzyme
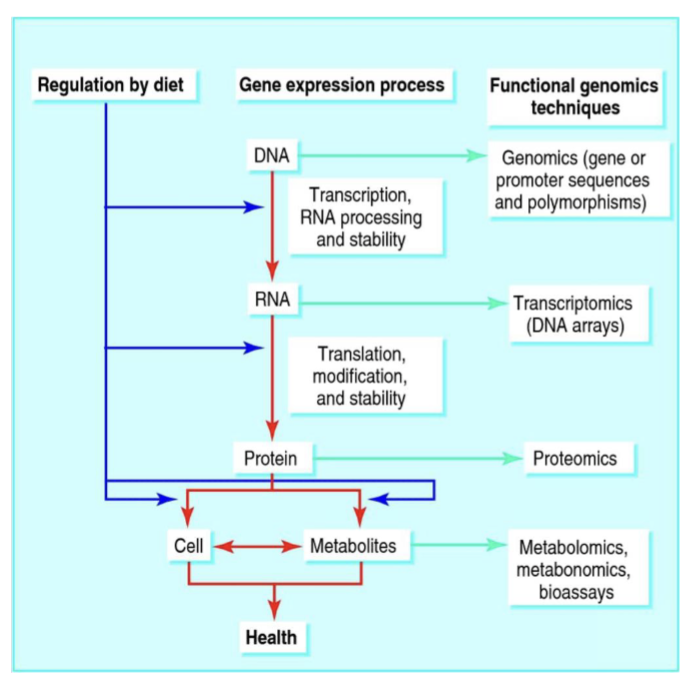
Examples of Nutrigenomics
Influence of bioactive components in food on gene expression and phenotype
Impact gene expression at any point in the process(Transcription, translocation, post translational modification)
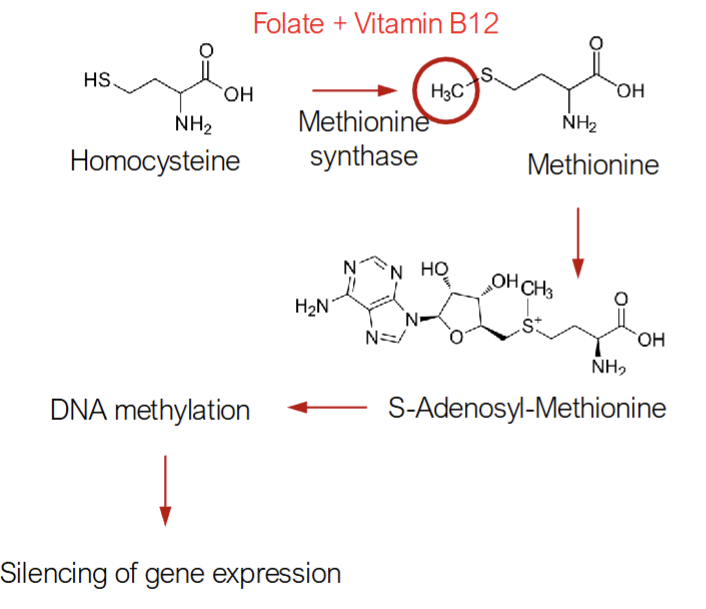
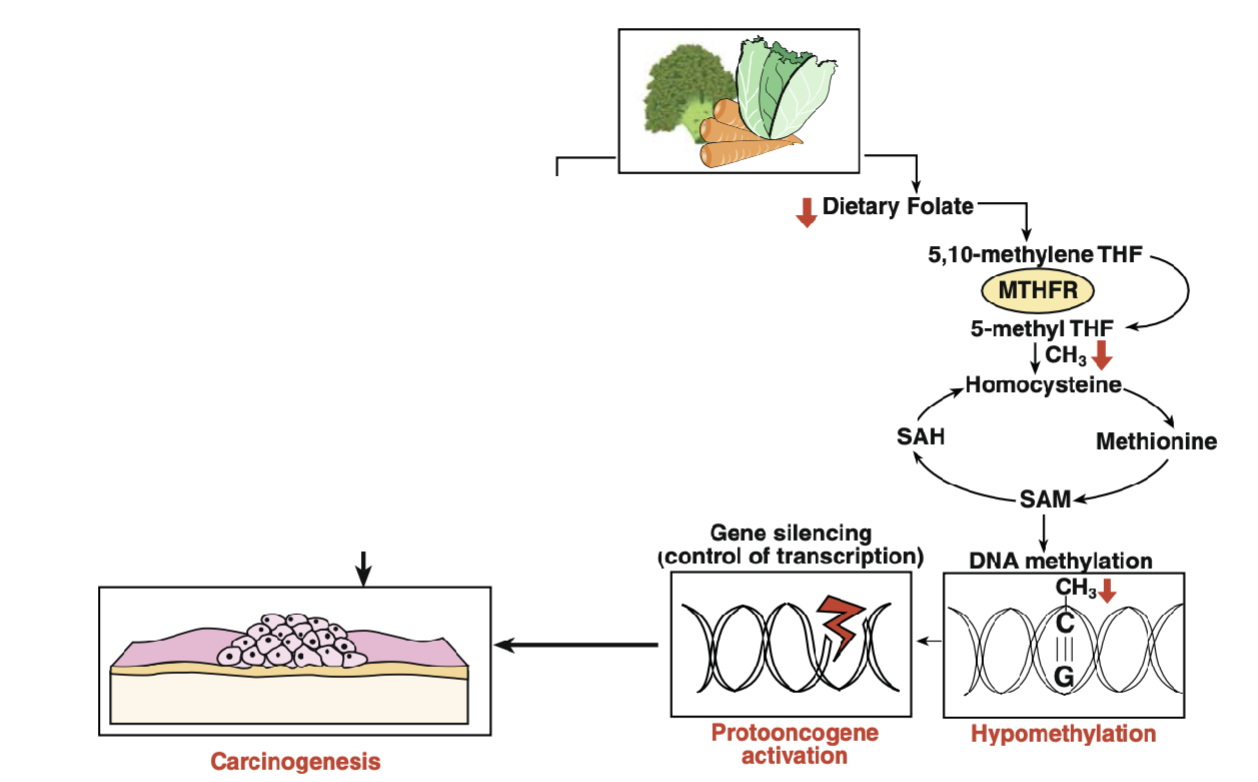
S-Adenosyl-Methionine Deficiency
Folate provides the methyl group that is added onto homocysteine to make methionine & vitamin B12 is the cofactor for the enzyme methionine synthase
Methionine is subsequently converted to S-Adenosyl-Methionine(SAM) which is utilized by DNA methyltransferase enzyme to methylate DNA
DNA methylation is an important mechanism of silencing gene expression by shutting down transcription of genes
Folate Deficiency limits SAM synthesis leading to hypomethylation of DNA which lead to inappropriate expression of gene
What is Cancer
Abnormal growth and spread of cells that arise from failure to control cell growth and migration
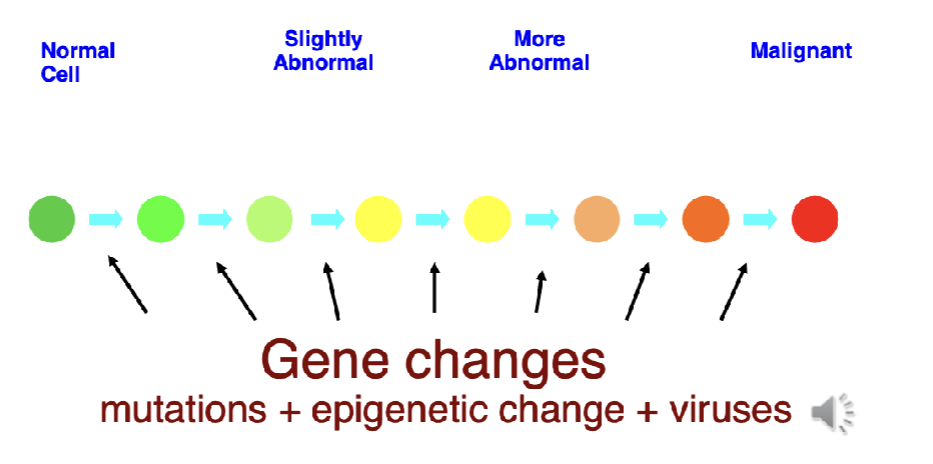
Cancer is a genetic disease
Genetic info encoded in our genome provides the instruction for growth and development
Changes in this genetic codde can lead to aberrant instructions that causes cancer
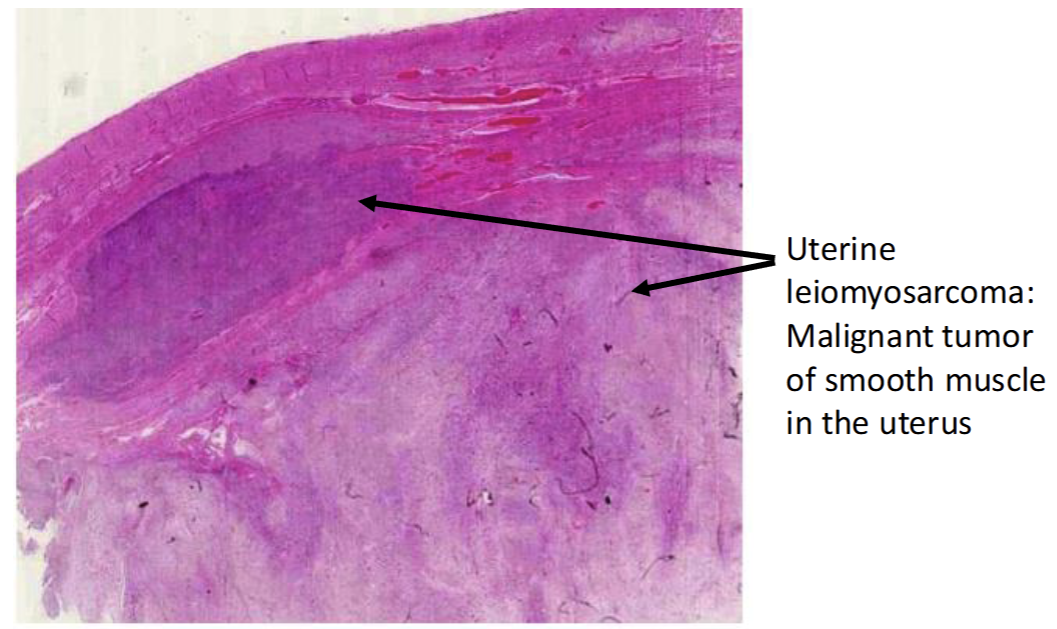
Terminology: Tumor, Benign, Malignant, & Metastasis
Tumor = Describes an abnormal growth of cells which can be benign or malignant (cancerous)
Benign = A tumor that is not capable of spreading to other tissues, locally or to distant organs(metastasis)
A benign tumor is not a cancer, but a benign tumor can acquire further genetic mutations to become a malignant tumor
Malignant = A tumor with the ability and potential to spread and form metastasis.
A malignant tumor = cancer(interchangeably).
Describes a functional property of the tumor, and tumor doesn’t have to form any metastases to be classified as malignant.
Histological appearance of the primary malignant tumor often correlated with its potential to metastasize
Metastasis = process of forming new colonies of tumor in distant organs/tissues
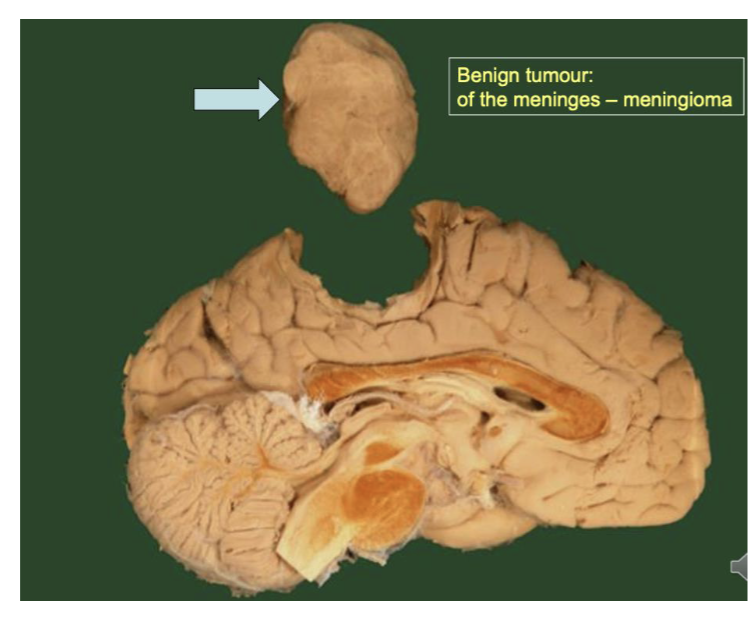
Histological apperance under the microscope of Benign Tumor
Benign tumor
Confined to original site of the body
Clearly defined and intact boundaries
Often physically separated from surrounding tissue by a capsule of connective tissue
Cells often resemble the apperance of normal cells
Histological apperance under the microscope of Malignant Tumor
Malignant Tumor
Poorly defined boundaries that can exhibit disruption with infiltration of cells into surrounding tissue
exhibit more abnormal apperances including large nucleus, loss of normal cellular structures, and loss of normal organization with neighboring cells
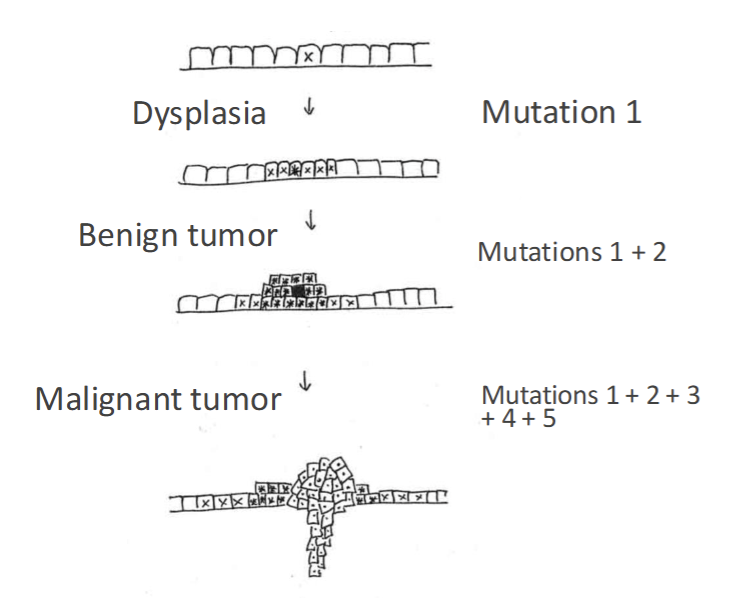
Causes of Cancer
Mutations in genes cause cancer
Understand origins of DNA mutations
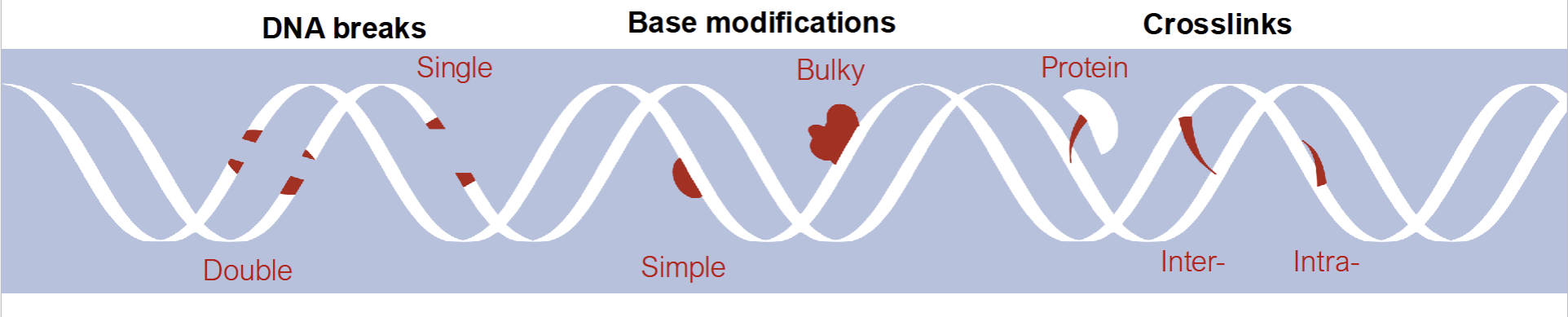
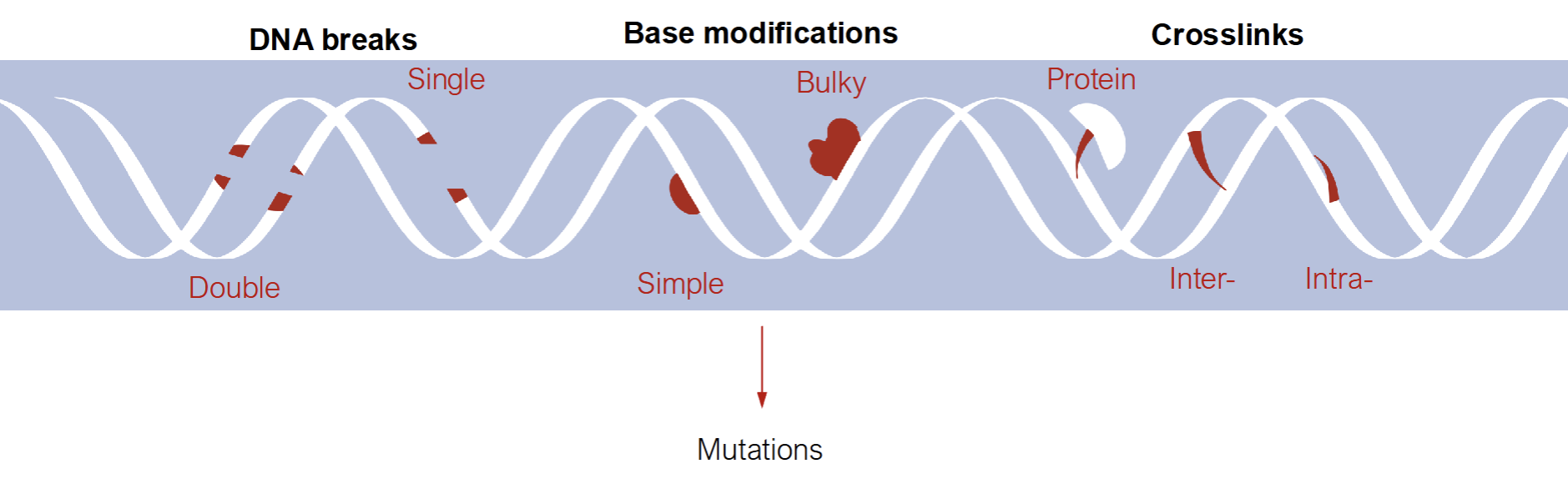
Different Types of DNA Damage
DNA breaks
Base modification
Crosslinks
Challenges in discovering the cause of cancer (3)
1) Heterogeneous disease: cause of one type of cancer does not necessarily cause other type of cancer
2) Cancer usually takes several years/decades to develop, so challenging to track down the initiating cause of cancer
3) Cancer develops from a multi-step process; therefore a normal may require multiple insults from different causes to turn into a cancer
Methods used to discover casues of Cancer
Epidemiology Method
Observational studies that identify an association between enviromental factor and specific cancer
lung cancer and tobacco smoking
DOESN’T ESTABLISH CAUSATION
Experimental Method
Bacterial & Cell line model to test if specific chemicals cause DNA mutation
Animal models to test if specific chemicals lead to cancer formation
DOESNT NOT ALWAYS MODEL HUMAN CANCER
How Does Nutrition Contribute to Causes of Cancer (5)
1) Direct voluntary consumption of carcinogen: alcohol
2) Contamination of cosumed food: aflatoxin
3) Food Borne infectious pathogen can cause cancer
4) Deficiency in specific nutrient can increase DNA damage
5) Clear epidemiology association between obesity and cancer but mechanism currently not well understand
Alcohol & Cancer
All alcoholic drinks are associated with increased risk of cancer
Cancer related to alcohol reflects epithelial cells of the GI tract
Mechanism of Alcohol carcinogenicity
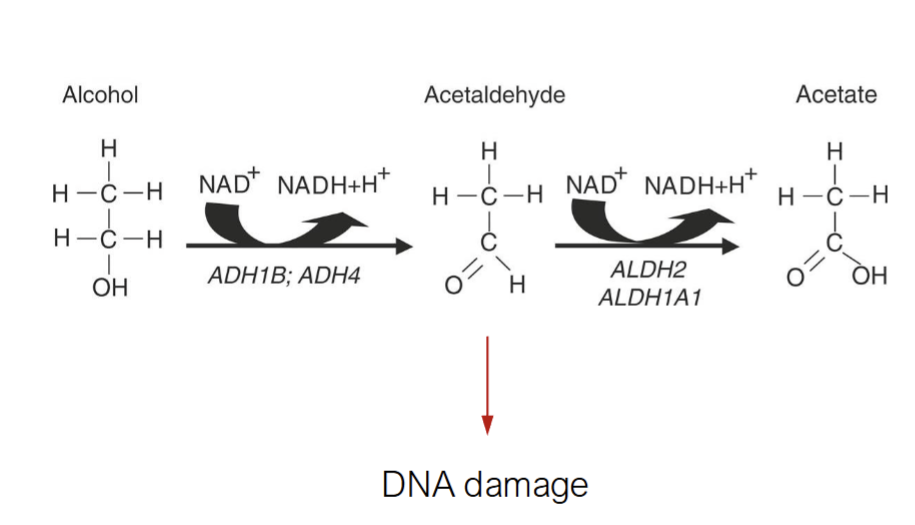
Ethanol is metabolized to acetaldehyde which damages DNA to cause mutations
Mammals have evolved acetaldehyde detoxification enzyme ALDH1A1 & ALDH2 to prevent toxic accumulation of acetaldehyde
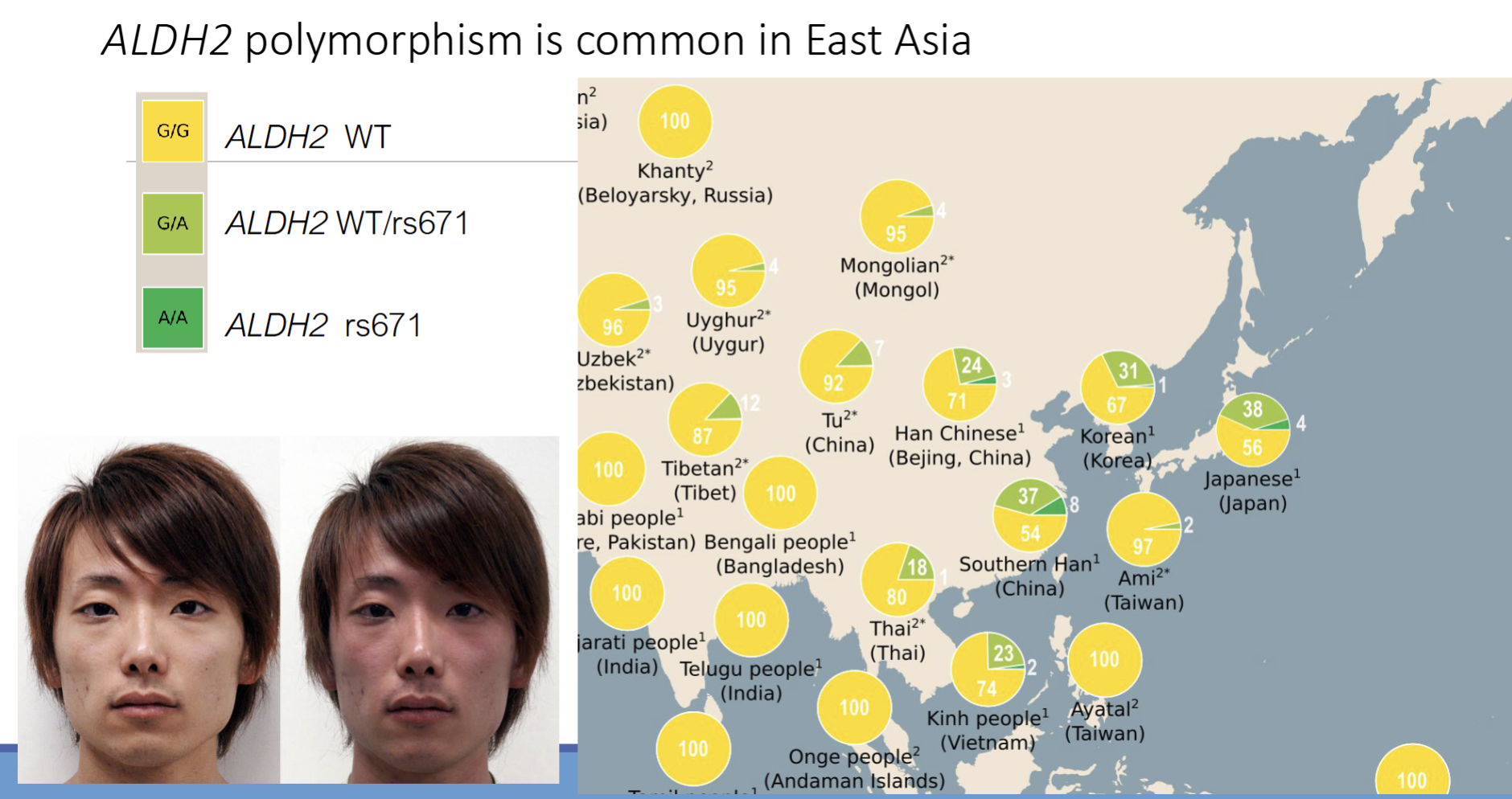
What region is ALDH2 polymorphism common
EAST Asia
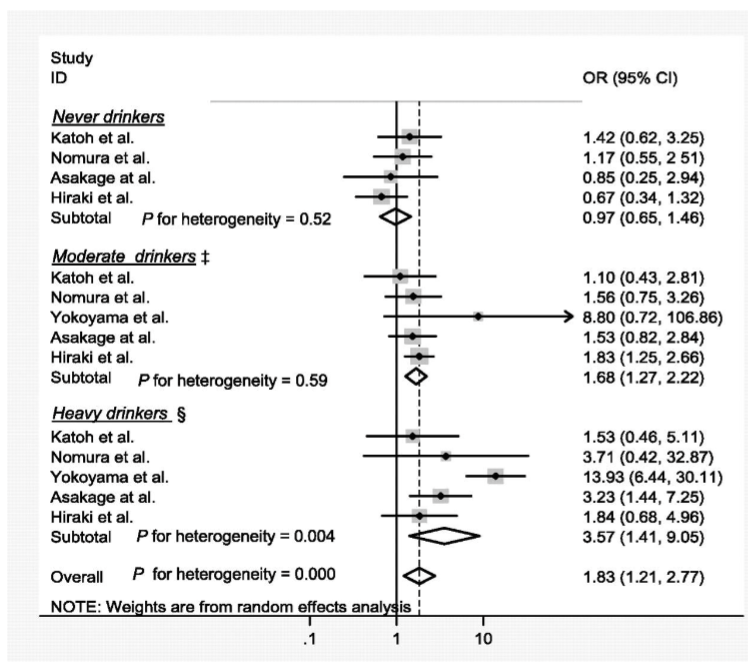
Cancer risk between ALDH2 polymorphism and alcohol intake
Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 and Head and Neck Cancer
Meta-analysis of multiple observational studies shows the odds ratio(OR) of developing head and neck cancer in individuals with ALDH2 polymorphism vs general
OR = 1 means equal likelihood of developing cancer compared to general population
OR = 2, twice as likely to develop cancer compared to general population
People with Alcohol flushing syndrome shouldn’t drink alcohol
Aflatoxin & Cancer
Aflatoxin B1 is a potent toxin produced by the fungus Aspergillus flavus
can contminate many agricultural crops like peanuts, corn, cereal grains
aflatoxin B1 remain stable during drying, storage, and processing of crops
ingestion of food with aflatoxin B1 is associated with increased DNA dmage & hepatocellular carcinoma
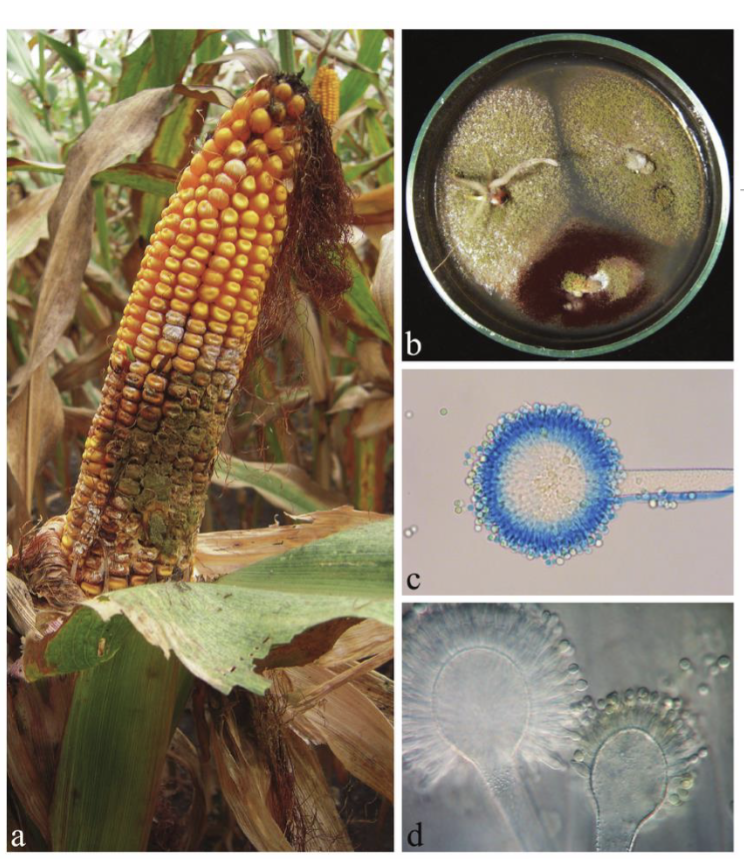

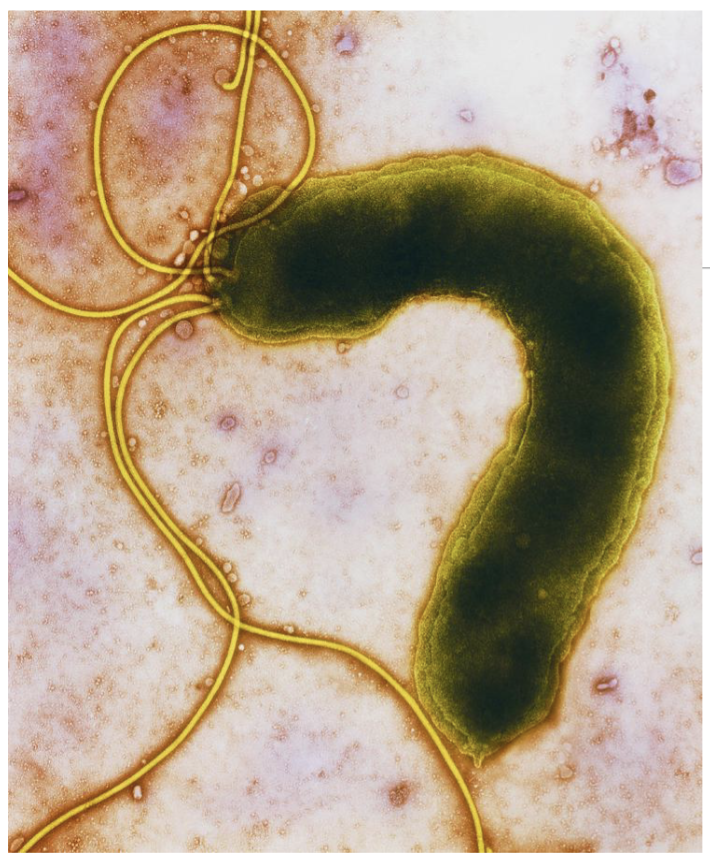
Heliobacter Pylori & Cancer
H-Pylori is a sprial shaped bacterium that infects the stomach lining
transmitted via contaminated food and water
In stomach, H-pylori survive the acid environment in stomach by neutralizing the surrounding acid, and burrowing into the mucus layer of the stomach
H-Pylori infection causes injury to the gastric epithelium, leading gastritis, & gastric ulcers
Untreated leads to ROS = DNA damage & cell proliferation = high chance of mutation
Folate Deficiency & Cancer
Folate Deficiency has been implicated in development of cancers of colon, breast, ovary, pancreas, brain, lung, and cervix
Individuals with high dietary folate intake exhibit reduced risk of colon cancer compared to low intake
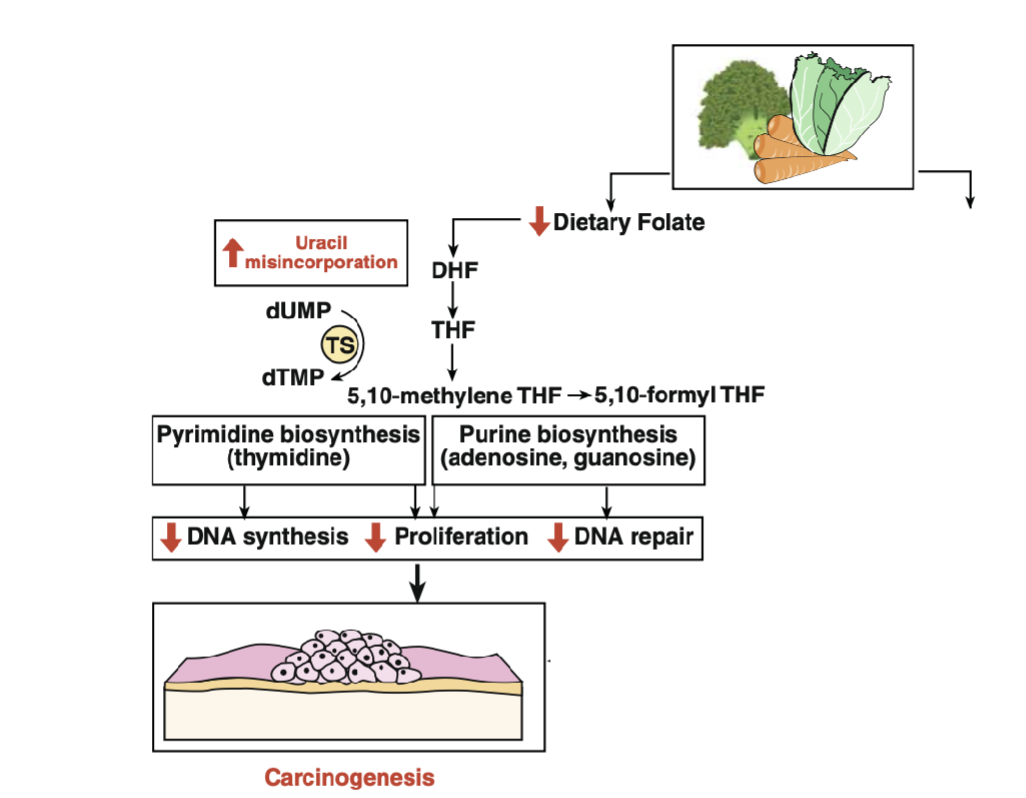
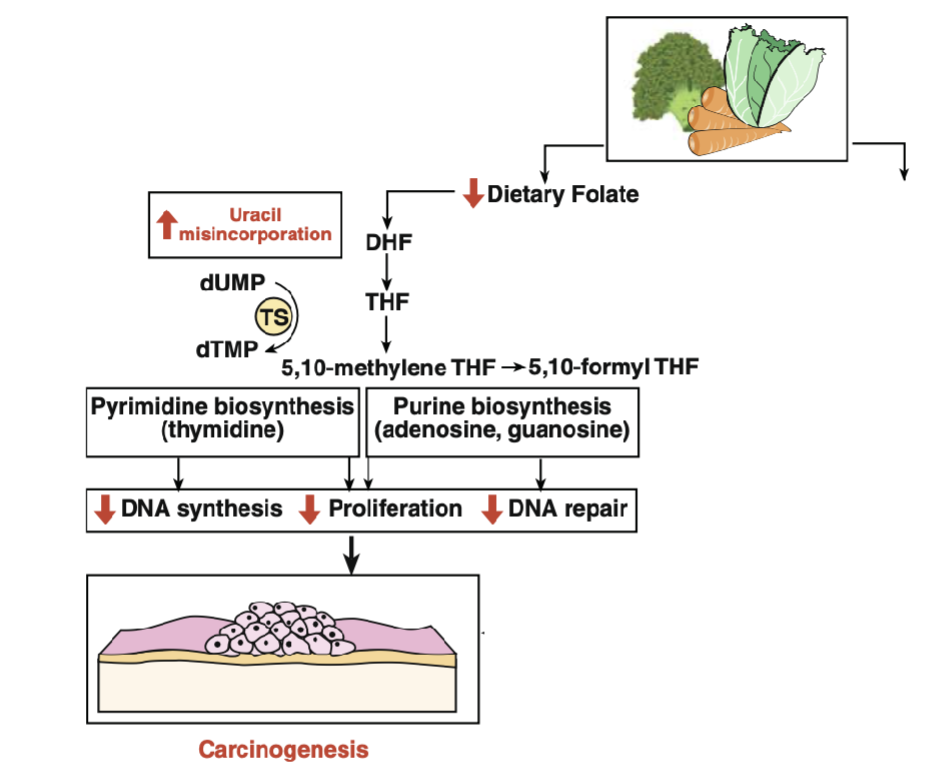
Mechanism of Carcinogenesis from Folate Deficiency: Uracil Misincorporation
Uracil Misincorporation
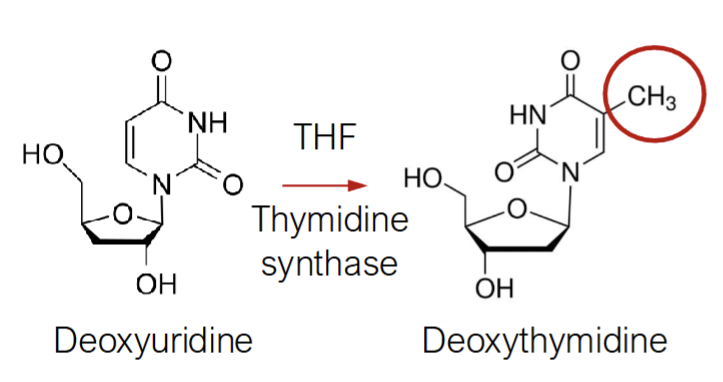
Folate is required for the conversion of deoxyuridine(dU) to deoxythymidine(dT), an essential nucleotide required for DNA replication and DNA repair
Folate deficiency limits dT synthesis & elevates dU
As dT and dU are structurally similar, dU is incorporated into DNA
dU in DNA is unstable(break DNAstrand) and excised by DNA repair enzyme
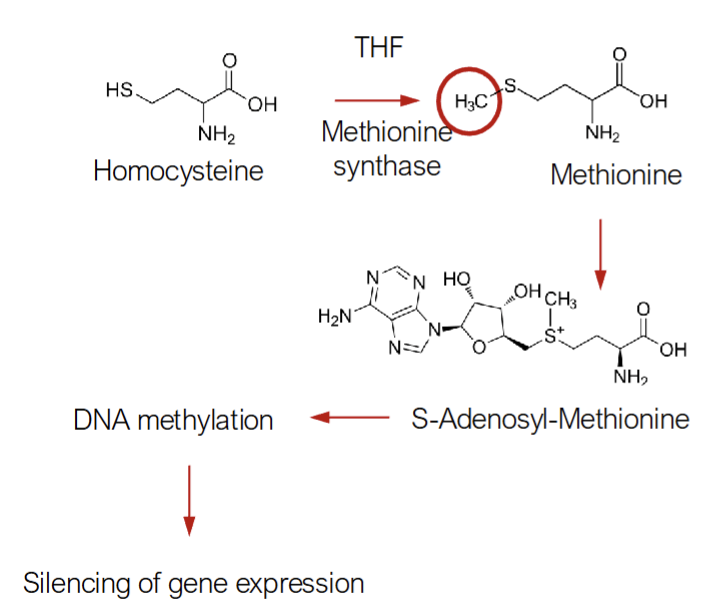
Mechanism of Carcinogenesis from Folate Deficiency: S-Adenosyl-Methionine Deficiency
S-Adenosyl-Methionine Deficiency
Folate provides the methyl group that is added onto homocysteine to make methionine & vitamin B12 is the cofactor for the enzyme methionine synthase
Methionine is subsequently converted to S-Adenosyl-Methionine(SAM), which is utilized by DNA methyltransferase enzyme to methylate DNA
DNA methylation is an important mechanism of silencing gene expression by shutting down transcription of genes
Folate Deficiency limits SAM synthesis leading to hypomethylation of DNA which lead to inappropriate expression of gene
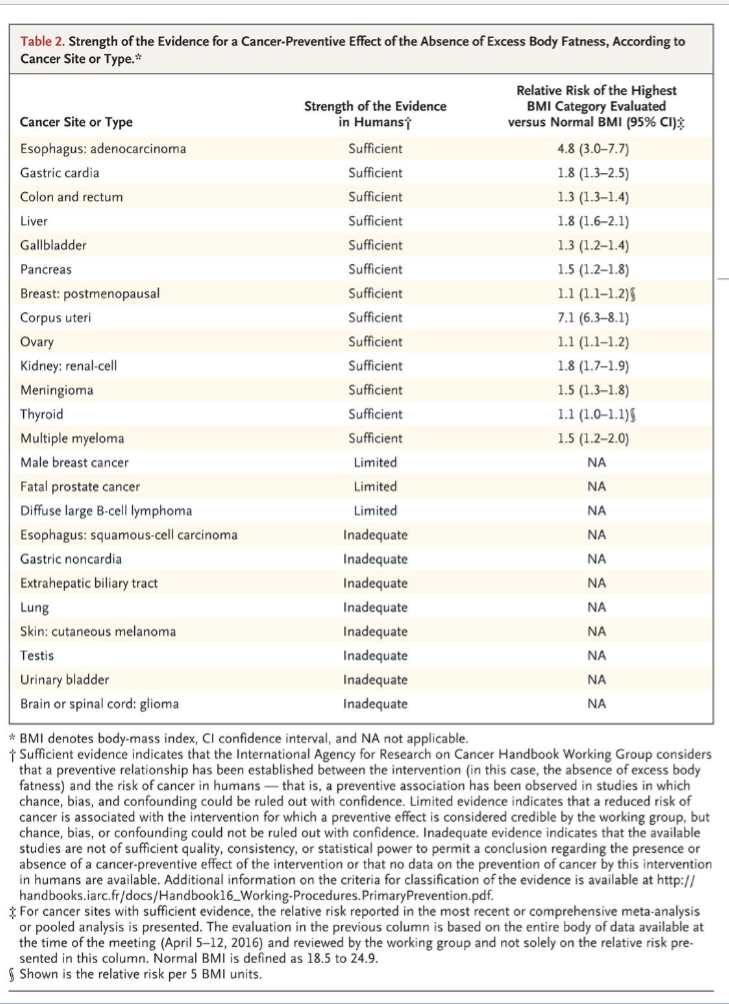
Obesity & Cancer
Nearly all of the evidence linking obesity to cancer risk comes from large cohort observational studies
More than 1000 observational studies on cancer risk and excess body fatness have been conducted
Significant associations between BMI and Cancer risk were reported
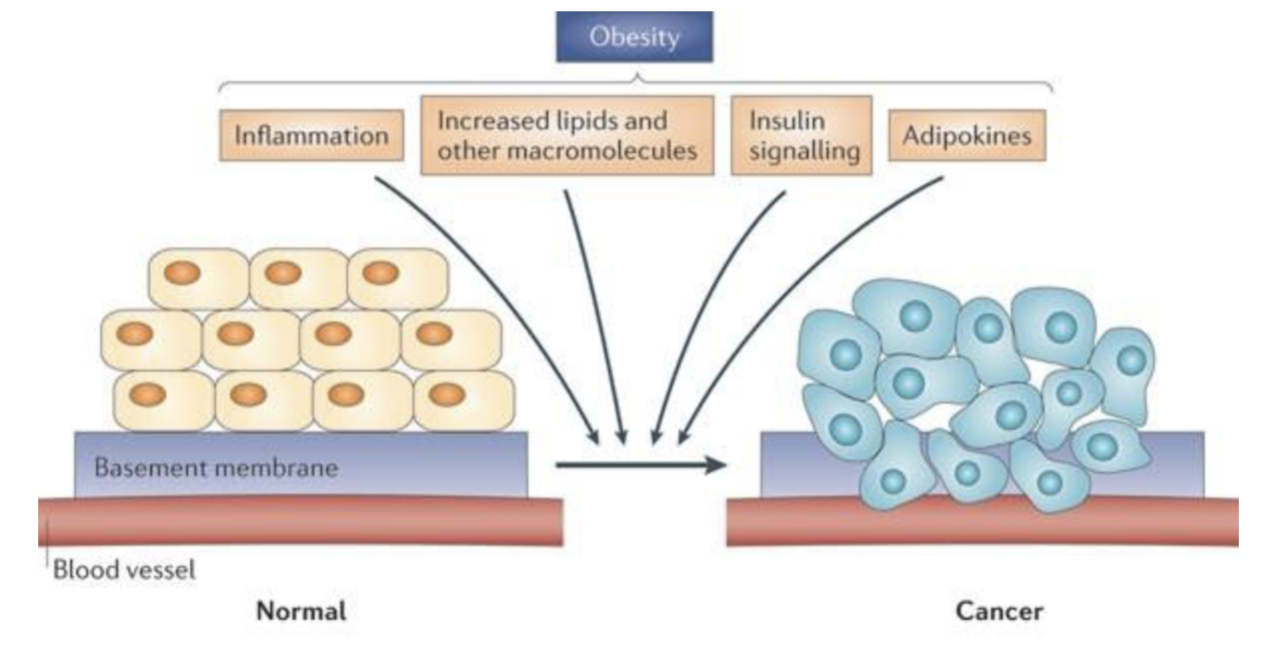
Mechanisms of Obesity and Cancer(not fully understood yet)
Obesity leads to mechanisms like
Chronic inflammation
Increased circulating a lipids as nutrient for cancer cells
increased insulin and insulin growth factor 1 (IGF-1) are utilized by cancer cells as growth factors
Fat cells(Adipocytes) secrete adipokines, hormones that play roles in cancer development
leptin is an adipokine that regulate appetite but can also stimulate growth of cancer cells
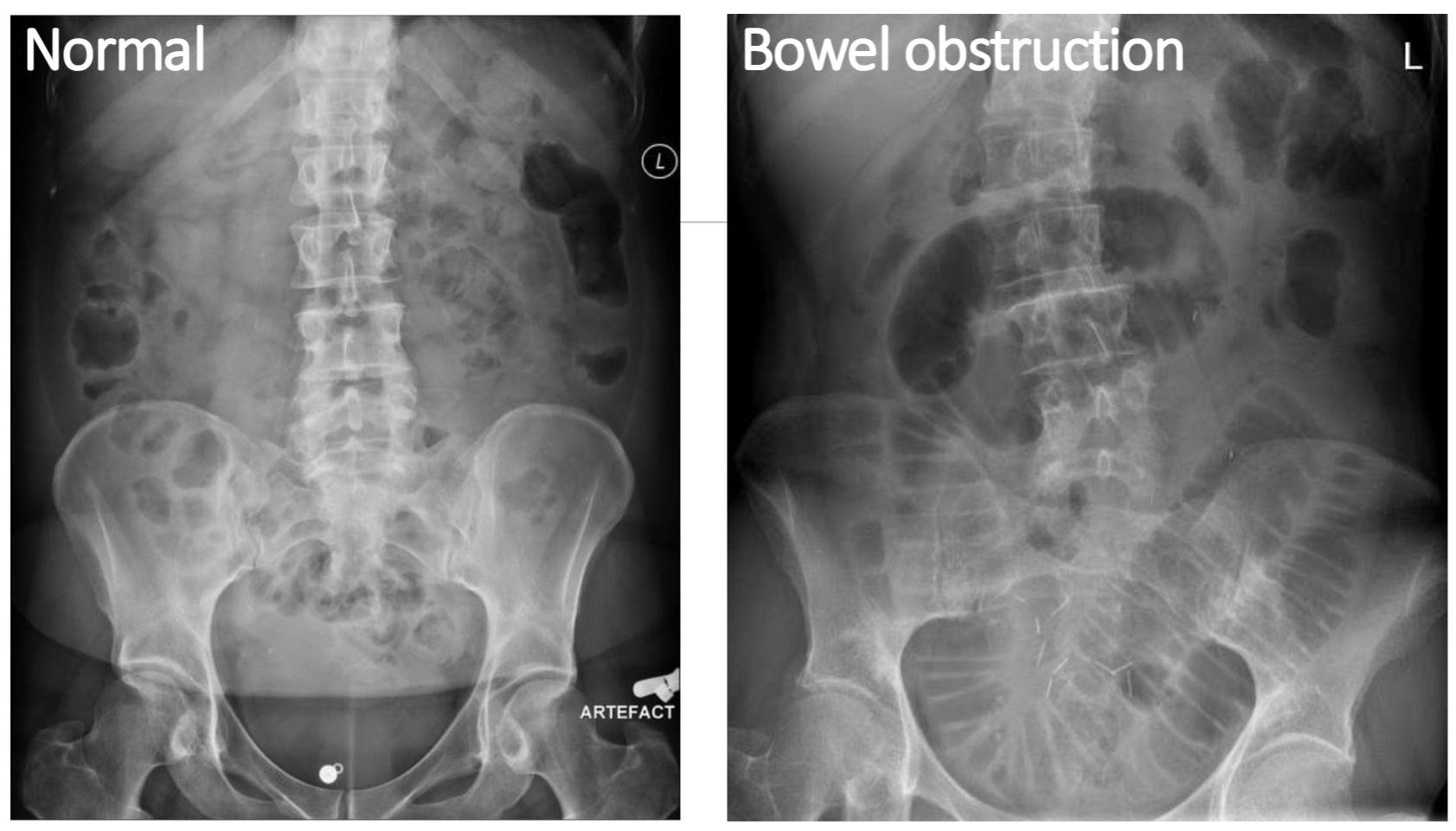
Cancer impact diet and Nutrition: Obstruction
Airway causing hypoxia - reduced energy for eating, discomfort can reduce appetite
Oral-pharynx/esophagus - dysphagia(difficult swallowing)
Lower GI obstruction - nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain reduces appetite and reduce GI absorption
Urinary Tract - discomfort can reduce appetite, acute kidney failure lead to vomitting
Cancer impact diet and Nutrition: Compression
Compression of GI tract can lead to obstruction
Compression of brain and nerves can impact muscles involved in eating and swallowing
Cancer impact diet and Nutrition: Pain
Compression/infilration of nerves
Ulceration
Bone fracture
Pain Reduces appetite
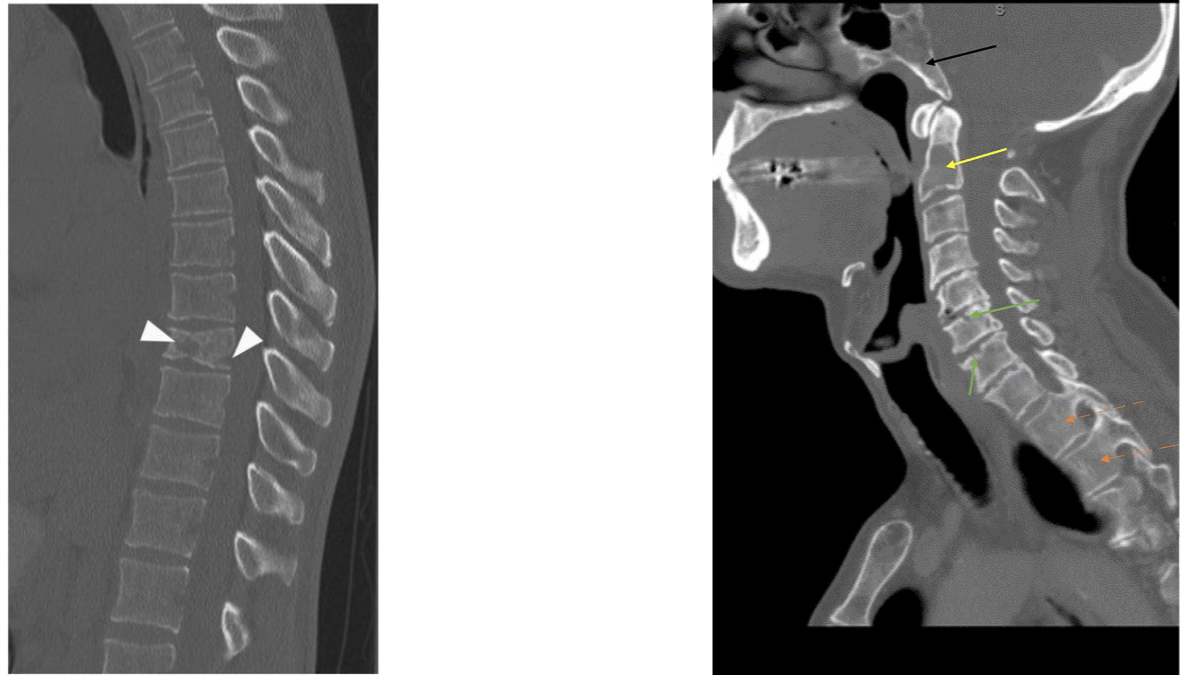
Cancer impact diet and Nutrition: Bleeding
Chronic Gastrointestinal Bleeding can lead to iron deficiency
Cancer impact diet and Nutrition: Inappropriate Secretion of Hormone
Insulin secreted by pancreatic beta cell tumor - cause persisent hypoglycemia
PTHrp secreted by lung cancer - cause hypercalcemia
ADH secreted by lung cancer - cause hyponatremia from excess water reabsorption in kidney (Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH secretion SIADH)
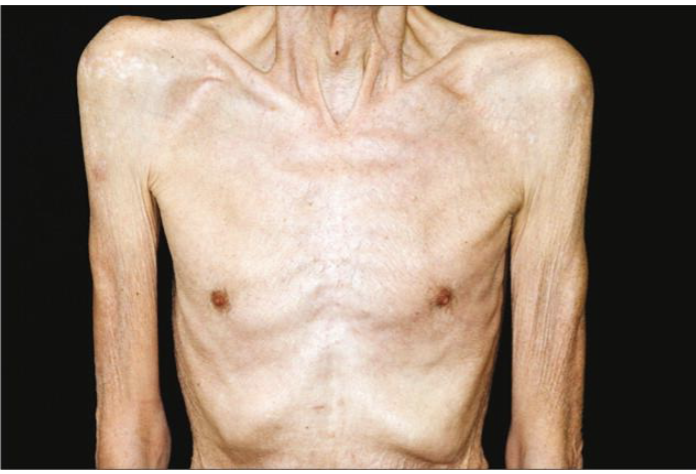
Cancer impact diet and Nutrition: Cachexia
Cachexia - metabolic wasting syndrome commonly in people with advanced cancer
involuntary weight loss, including loss of fat and muscle, loss of appetite, weakness and fatigue
Not reversed by increase dietary intake
complex metablic state that involves increased breakdown of protein
Cancer impact diet and Nutrition: Cancer Treatment
Nausea and Votmiting caused by systemic chemotherapy - Reduce oral intake
Mucositis - inflammation of GI lining from chemotherapy and radiotherapy
Causing SIADH
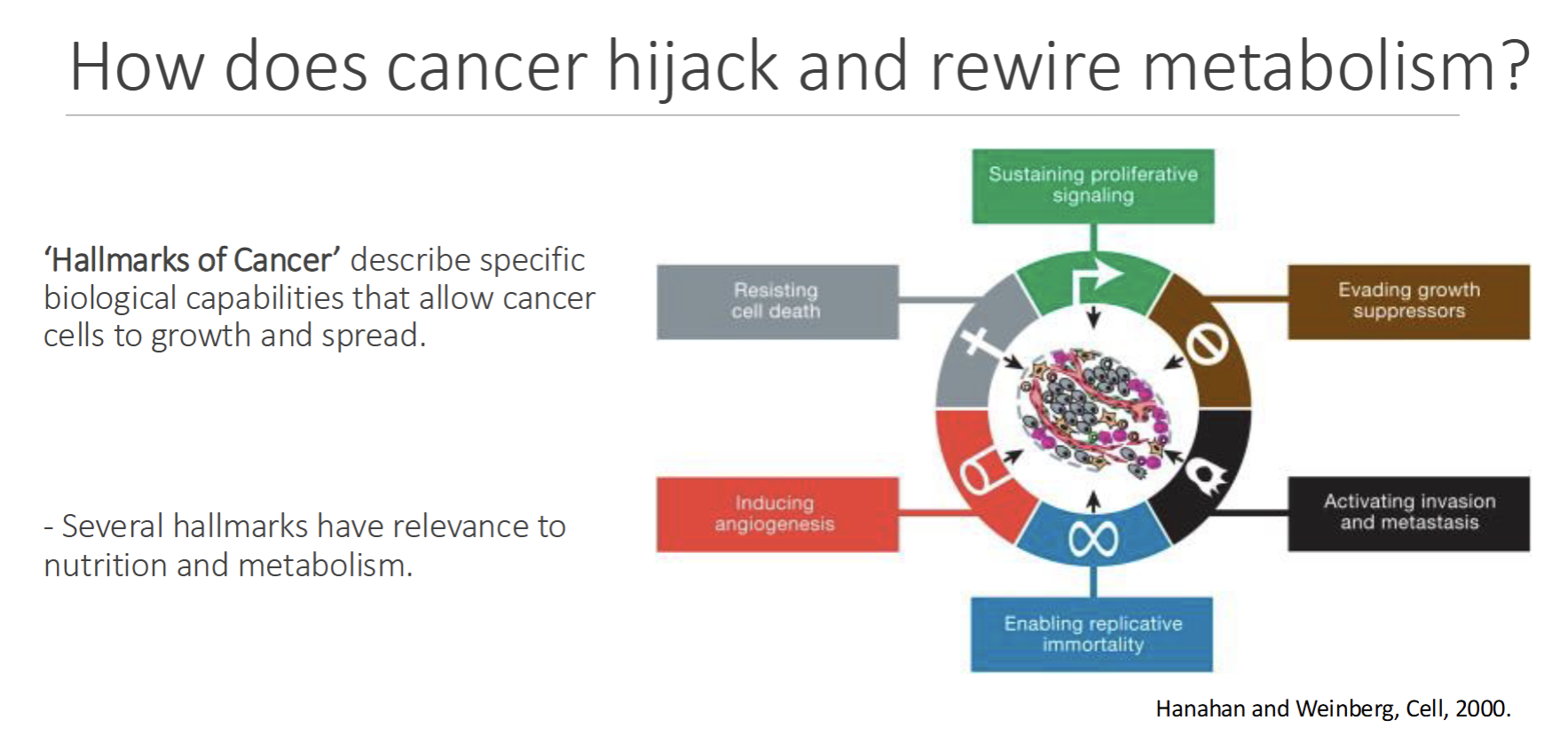
6 Hallmark of Cancer
Specific biological capabilites of cancer
Sustain proliferative signaling
Evade growth suppressor
Metastasis
Imortatlity
Induce Angiogensis
Resist Cell Death
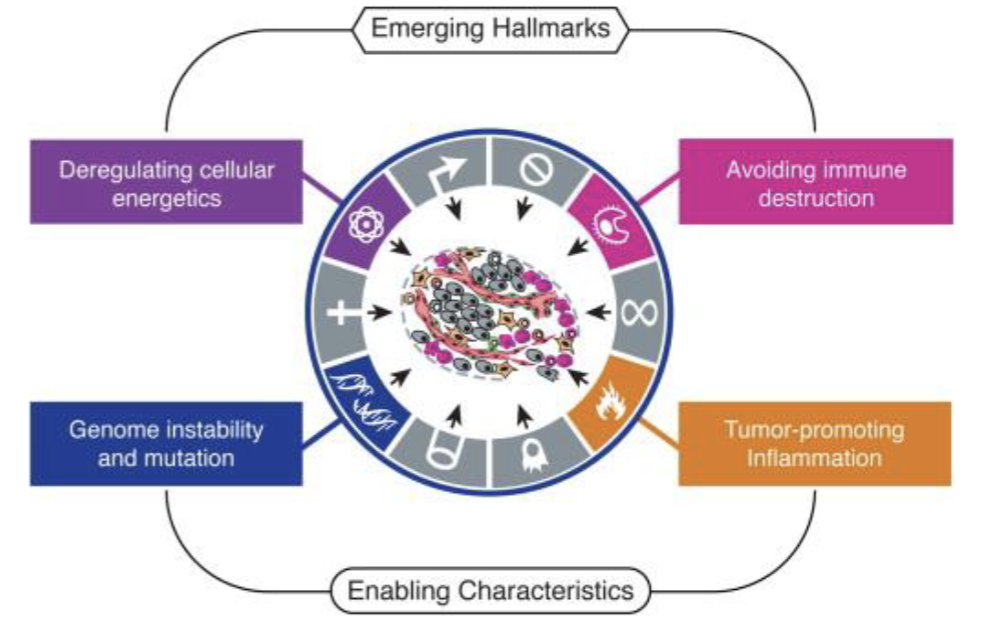
Emerging Hallmarks of Cacner
Avoid Immume Destruction
Tumor Promoing inflammation
Genome instability/mutation
Deregulating cellular energetics
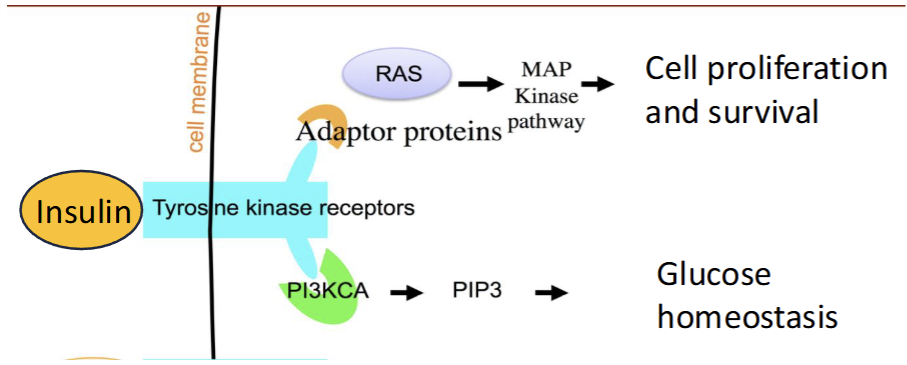
How does Cancer Hijack and Rewire Metabolism: Growth Factors
Hijack growth promoting signaling pathways to sustain growth
Cancer mutate gene in growth factor signaling pathways to grow in absence of signals
i.e insulin signaling pathway where receptor is overexpressed in cancer leading to more proliferation
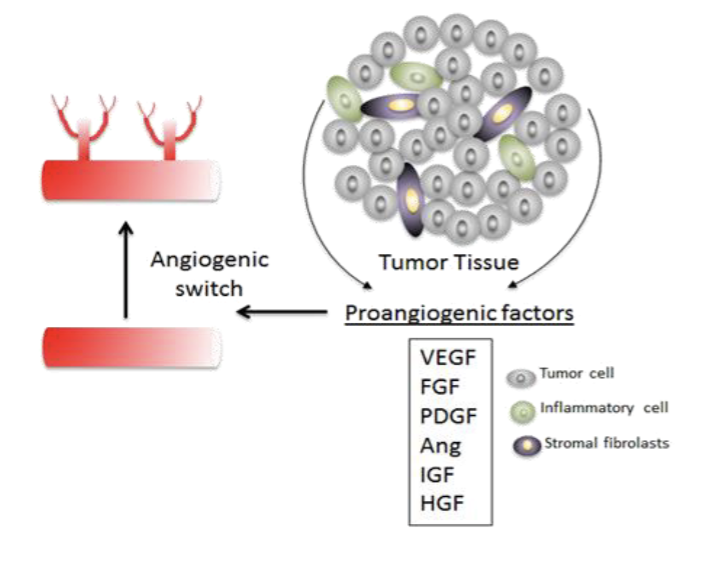
How does Cancer Hijack and Rewire Metabolism: Induce Angiogensis
Induce angiogenesis to increase blood supply to cancer
Angiogenesis = process of sprouting new blood vessel from existing vessel
Cancer turn on proaniogenic factor to secure blood supply, but new vessel are fragile and prone to bleeding which can help cancer spread
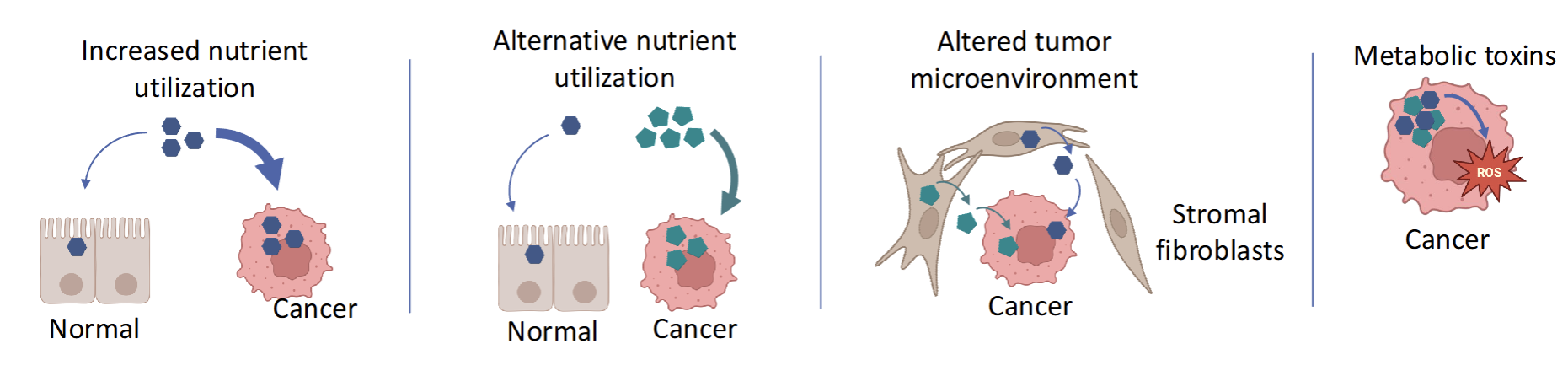
How does Cancer Hijack and Rewire Metabolism: Dysregulating cellular energetics(4 types)
increased nutrient utilization
alternative nutrient utilization
altered tumor microenvironment
metabolic toxin
Increased Nutrient Utilization
Ccancer cells exhibit increased glucose uptake and utilization: Warburg effect
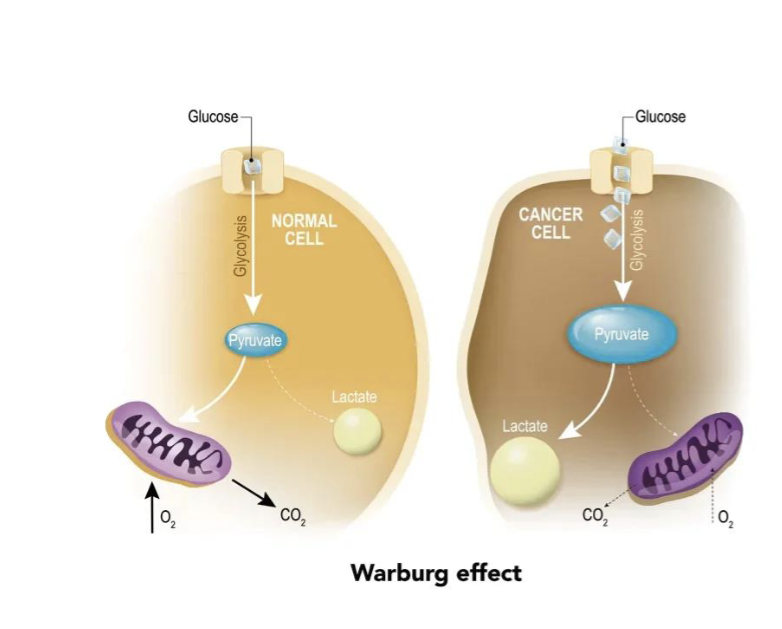
Increased Nutrient Utilization: Altered Bioenergetics
Altered Bioenergetics: increased glucose use is for synthesis of other essential macromolecules
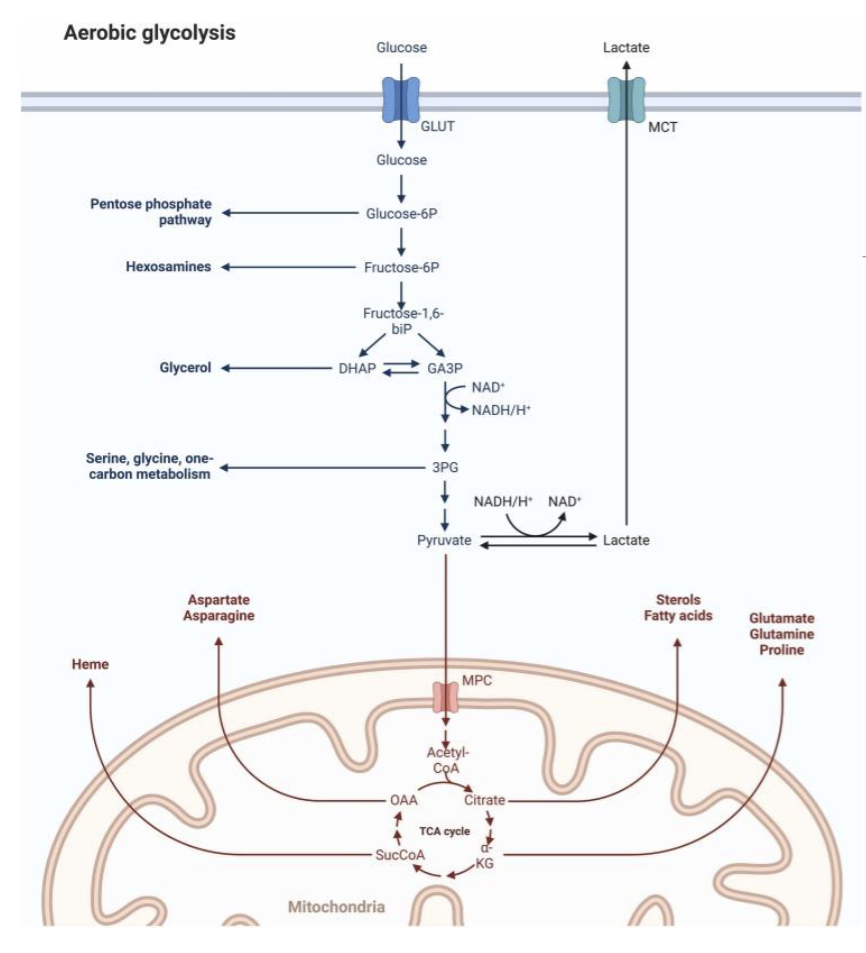
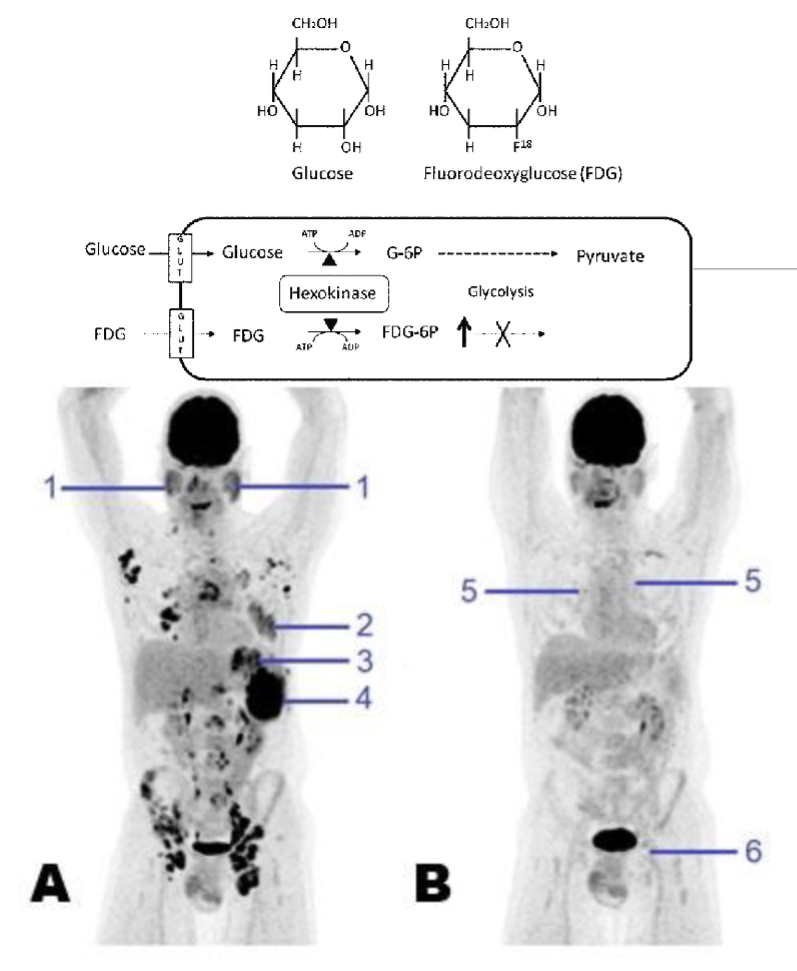
Increased Nutrient Utilization: FDG-PET Imaging
18F Fluorodeoxyglucose is an analogue taken up by cells and can be detected by positron emission tomography
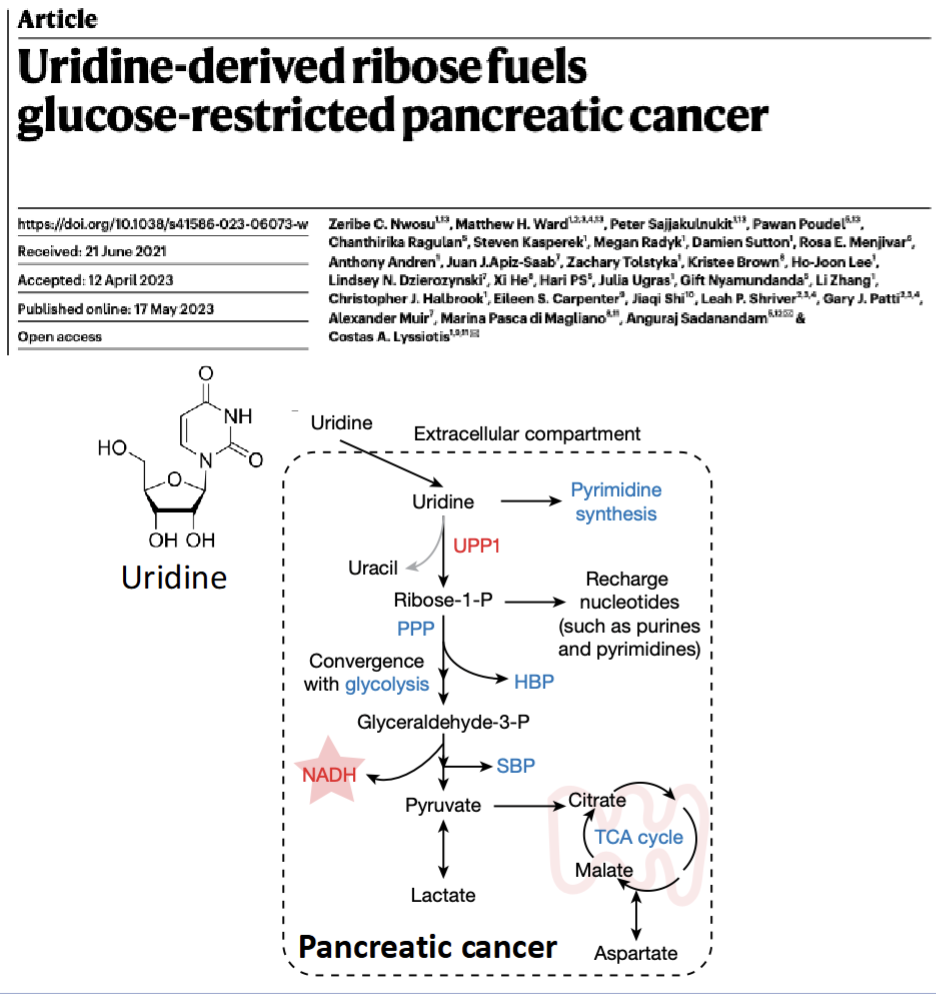
Alternative nutrient utilization
Cancer can use other nutrients
Pancreatic cancer uses uridine(ribionucleotide where sugar feed into glycolysis
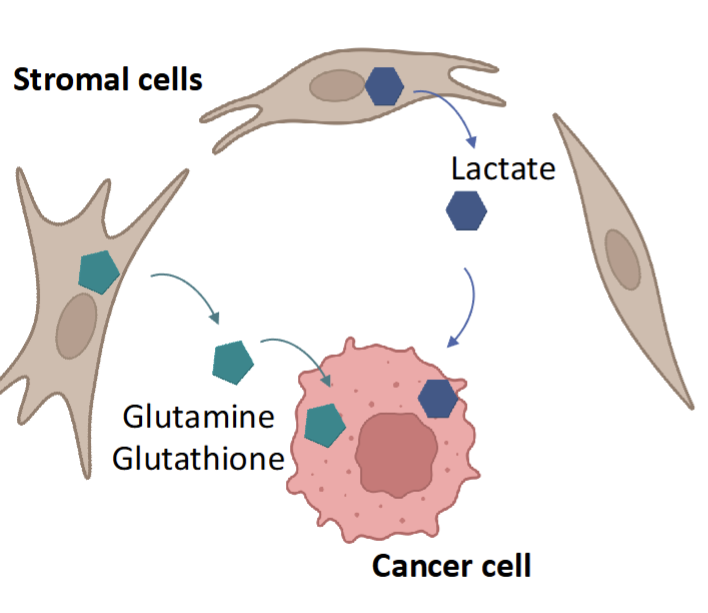
Altered tumor microenvironment
Cancer can modulate neighboring stromal cells like fibroblast and adipoicyte
secretion of lactate,glutamine, and glutathione to help growth of cancer
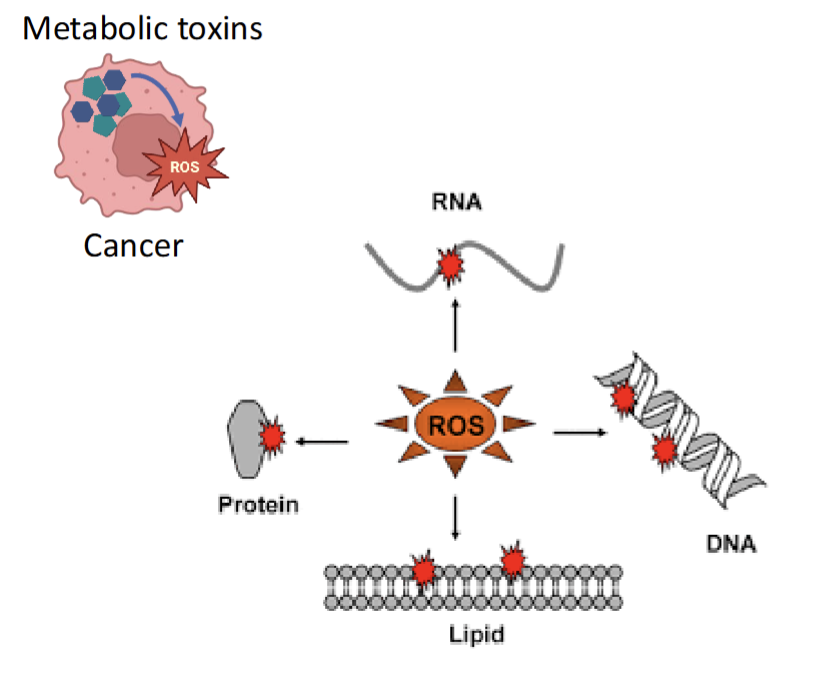
Metabolic Toxin
Increased production of ROS, but cancer protect themselves by increasing expressing of ROS detoxification gene like superoxide dismutase and catalse
Cancer Therapy Terminiology: Cure, Remission, Relapse
Cure = complete eradication of cancer cell from body
rarely acheived
Remission = no longer detect the cancer after treatment
Relapse = subsequently growth of cancer after remission
Surgery Treatment & Side Effects
Best method to achieve cure if tumor is localized
Side Effects
Lymphoedema: after breast surgery where excision of lymphatic vessel in axilla lead to accumlation of lymph in arm
Stoma: after bowel surgery where end of resected bowel is externalized at abdomen to allow drainage of fecal content into a stoma bag

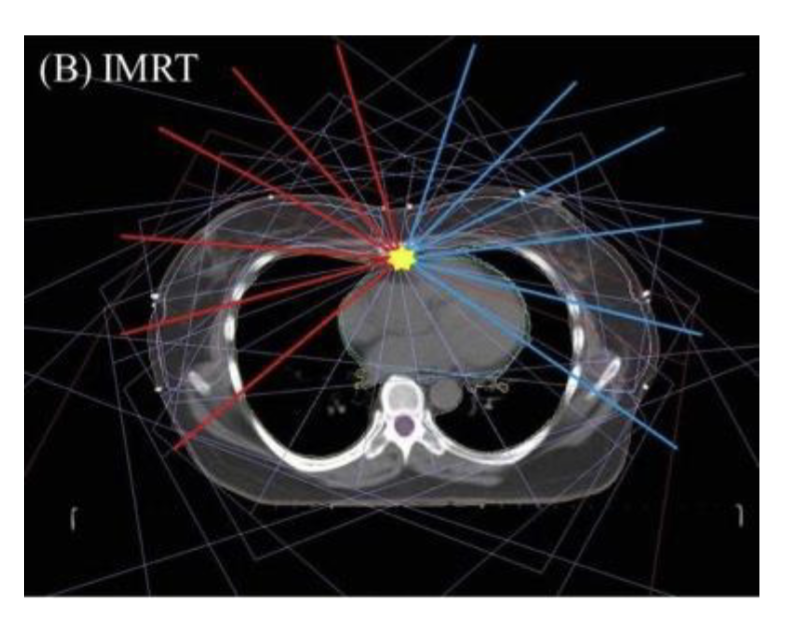
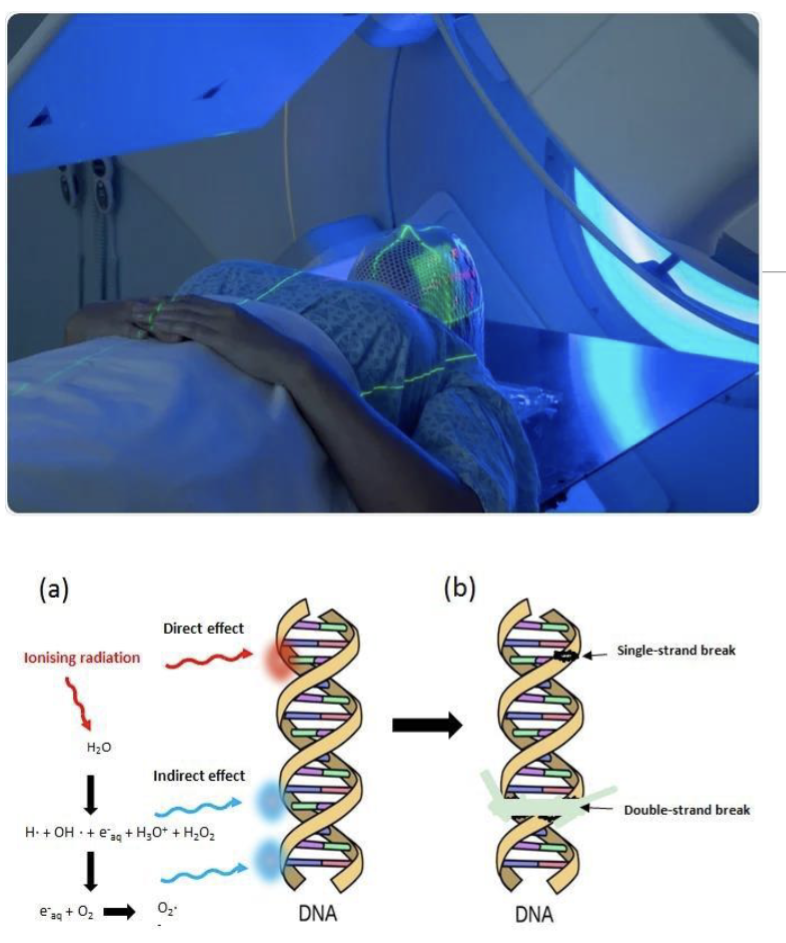
Radiotherapy & Side effects
Targeted Delivery of ionizing radiation to Cancer leading to DNA damage
Side Effect:
Bone marrow suppression
Nausea vomit
Hair loss
Fatigue
Secondary Cancer
To minimize damage try to use smaller dose
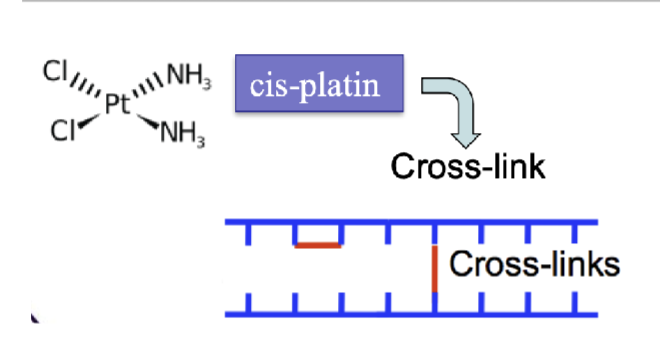
Chemotherapy & Side effects
Delivery of cytotoxic agent systemically into body to target cancer(multiple routes)
Side effect:
DNA damage (cisplatin)
inhibit synthesis of DNA nucleotide (methotrextate)
Disrupt mitosis (taxol)
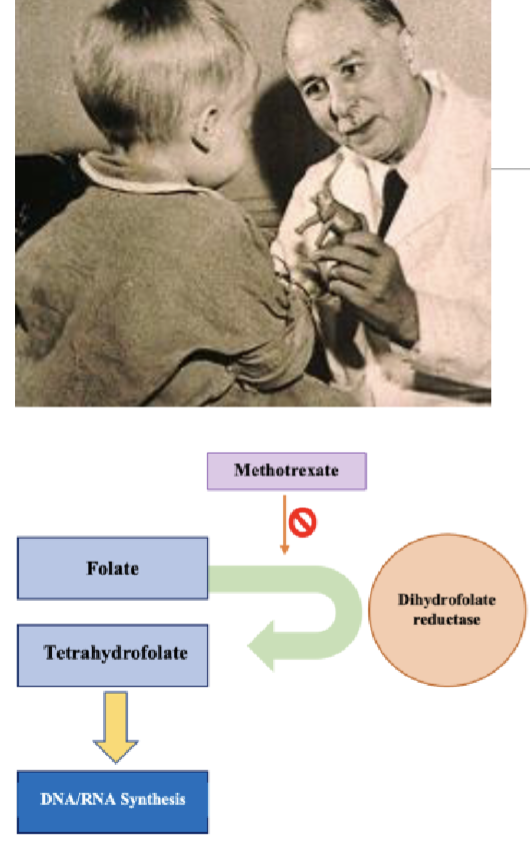
Targeting cancer metabolism: Anti-folates
Aminopterin and methotrexate are drugs that inhibit enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (role in folate cycle) thus reducing synthesis of nucleotides since no THF
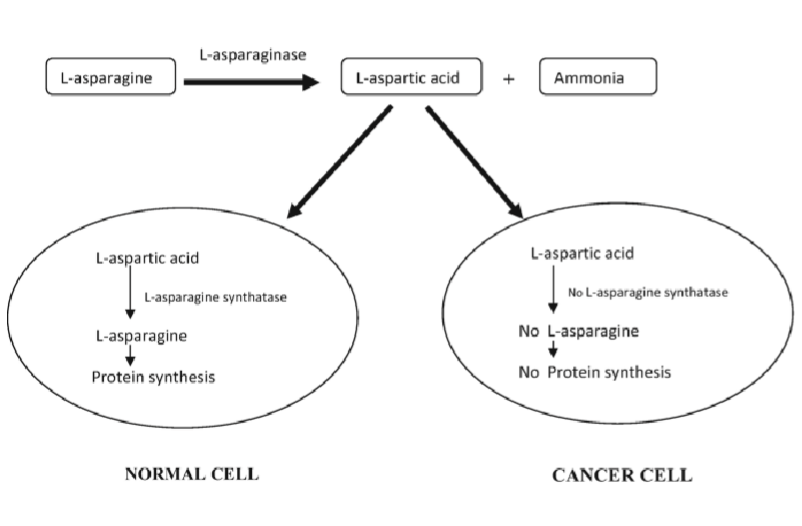
Targeting cancer metabolism: Asparaginase
Asparagine is non essential amino acid synthesized by asparagine synthetase enzyme
acute lymphoid leukemia cell do not express asaragine synthetase therefore they rely on external asparagine
Asaparaginase depletes asparagines from blood starving ALL cells: normal cell can produce their own but not cancer
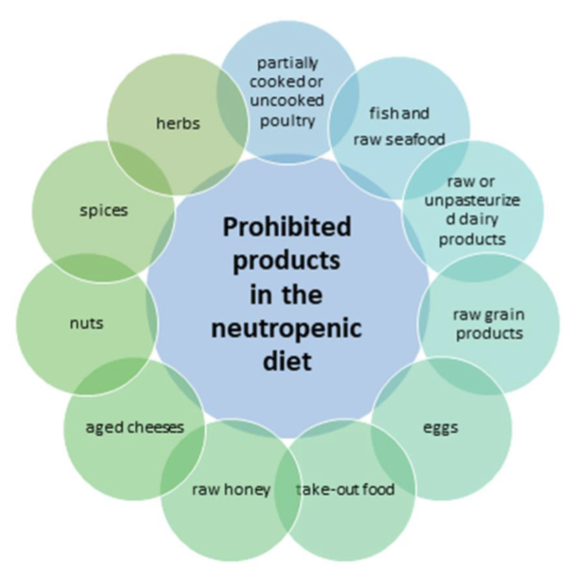
Nutrition During Cancer Treatment
1) Maintain General Health to protect agaisnt treatment related side effect
2) Avoid certain food/drink that could interact with bioactivity of cancer drug
3) Avoid food that increase risk of food borne infection
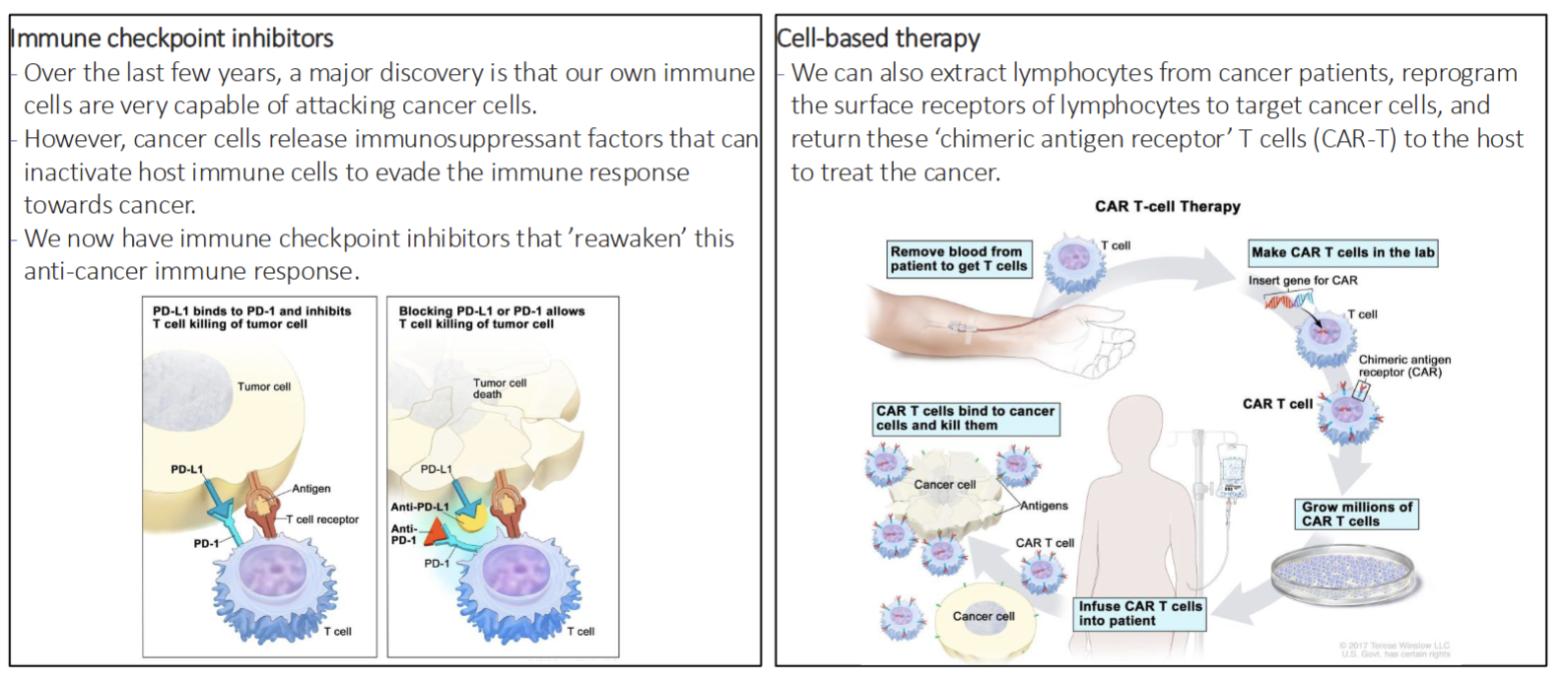
Immunotherapy
Immume checkpoint inhibitors - reawaken anti cancer immume response countering cancer cells immunosuppressent factors
Cell Based Thearpy - extract lymphocytes from cancer patient, reprogram their surface receptor to target cancer cells “chimeric antigen receptor T cells(CAR-T)
Mediterranean Diet vs Ketogenic Diet
Mediterranean - Healthy Fats (fish and meat)
Ketogenic - Low Carb, Medium Protein, High Fat