APHUG Unit 1: Maps, Distance, Place
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Toponym
a place name
Global Grid System
a pattern formed on a map or globe by latitude and longitude
International Date Line (180th Meridian)
the line of longitude that marks where each new day begins
Reference map
show locations of places as well as human and natural geographic features
Examples of reference maps
Political map, Physical map, Road Map
Political map
maps that are designed to show governmental boundaries of countries and states
physical map
highlights naturally ocurring features
Thematic maps
a map that displays not only locations but maps a topic or theme of information with the location
types of thematic maps
Isoline, Chloropleth, Dot Distribution, cartogram, graduated symbol
Chloropleth Map
A thematic map that uses shading or colors to represent spatial data
Isoline Map
A thematic map with lines that connect points of equal value.
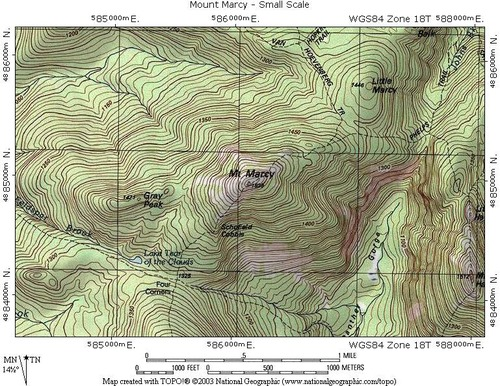
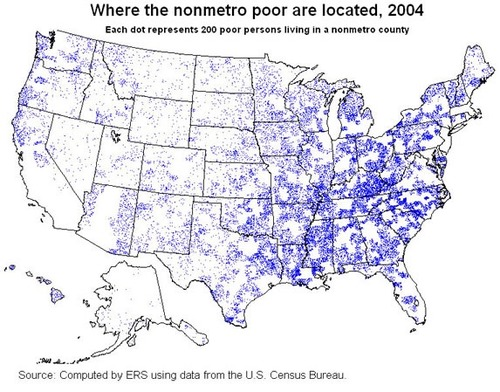
Dot Distribution Map
A map where dots are used to demonstrate the frequency or intensity of a particular phenomena
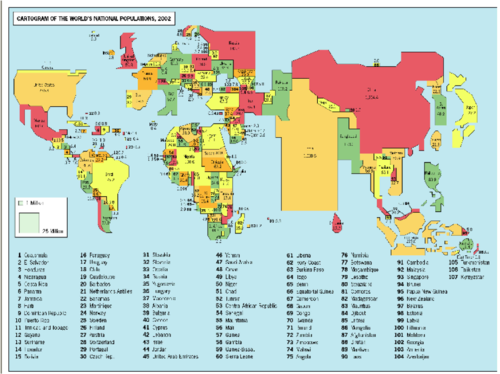
Cartogram Map
A map in which the shape or size is distorted in order to demonstrate a variable such as population or economic production
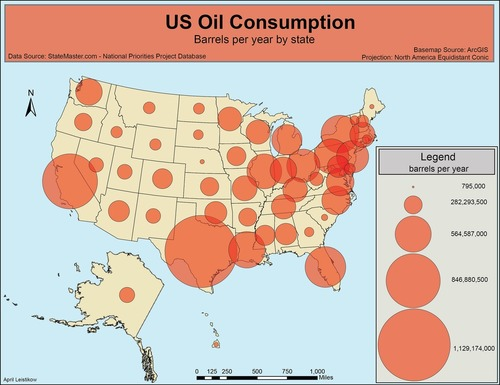
graduated symbol map
A map with symbols that change in size according to the value of the attribute they represent.
Projection
a method of taking a 3D object and putting in on a 2D plane
Mercator Projection
a map projection of the earth onto a cylinder. Distorts the land area at the poles
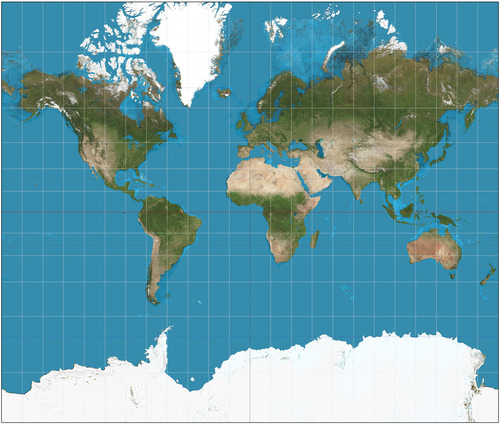
Gall-Peters Projection
equal area projection that distorts the shape of land masses (looks stretched out)
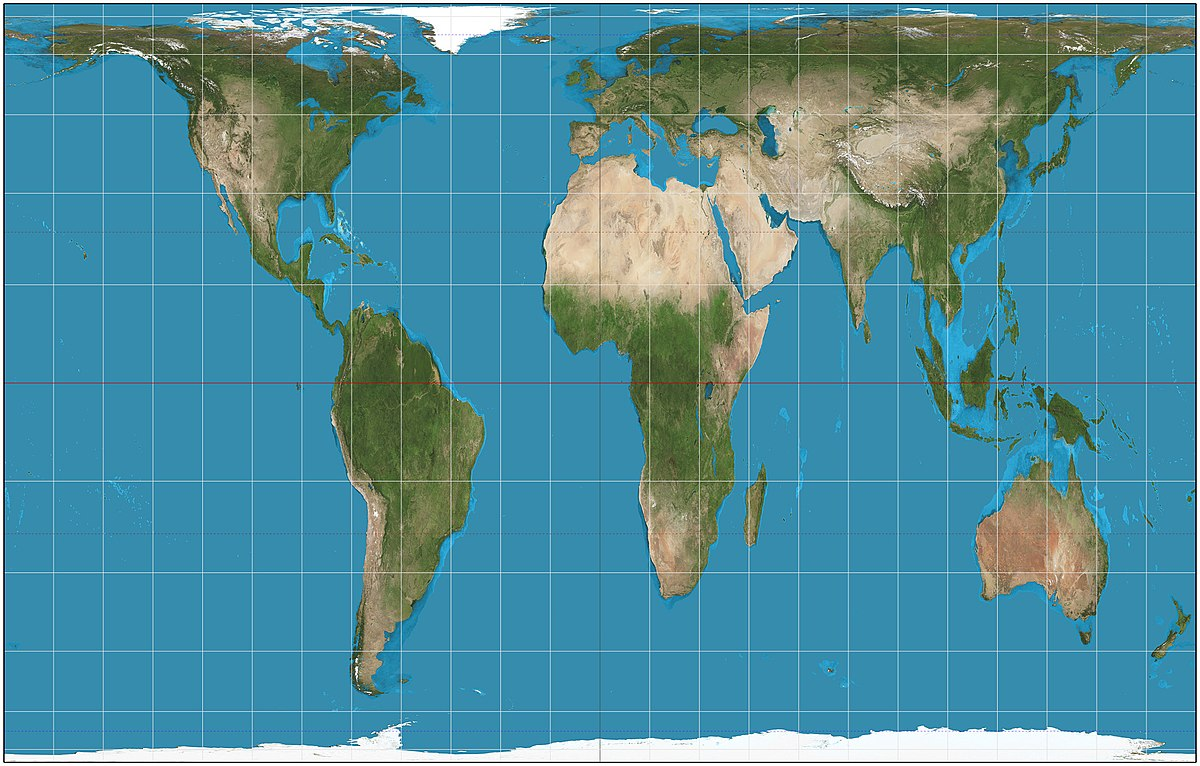
Robinson Projection
A projection that shows shapes and size without extreme distortion. Most classrooms use this projection.
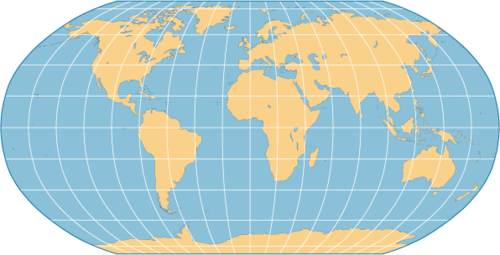
Map Scale
distance on a map relative to the distance on Earth
Absolute location
describing where something is using the exact site on an objective coordinate system
Relative location
describing the position of a place compared to another landmark (the deli is across the street from)
Absolute distance
describing how far a distance is using an objective measurement (miles, kilometers, etc.)
Relative distance
describing the distance between locations using non-traditional measurements of distance (it is north from)
Sense of Place
Emotional connection to a place familiar to one due to recognizable features, sounds, smells etc
the three different aspects of a place
location, site, situation
site
The physical character of a place, including its geographic characteristics.
For example the site of Istanbul includes the fact that it is on a land bridge connecting Asia and Europe, and also a water bridge (strait) connecting the Black Sea and the Mediterranean
situation
the location of a place relative to the places that are around it
example: the situation of New Jersey is that it is part of a highly populated and connected area on the East Coast of the US
GIS (Geographic Information Systems)
software that captures, manages, analyzes, and displays data that is collected geographically
GPS (Global Positioning System)
a system that measures distance from a series of satellites to determine location on the planet
Remote sensing
the science of making measurements of the earth using sensors on airplanes or satellites
Geospatial
relating to data that is specific to one location
Quantitative data
objective data that is fact based, usually measurable and usually expressed in numbers
Census
an official count of individuals in a population (in the USA, it happens every 10 years)
Qualitative data
subjective information that is opinion based, is usually descriptive, and often expressed as text
properties of Distribution
density, concentration, and pattern
Density
the number of objects divided by the measurement of area
Concentration
how closely packed together objects are
pattern
refers to the geometric distribution of objects in an area
Cultural Landscape
the visible changes that humans make to the environment (buldings, crops, paths, etc)
Distance decay
the idea that the interaction between two places declines as the distance between them increases
Formal region
region where people share common attributes or traits like language, climate, or political system
Functional region
a region based around a node or focal point - terrestrial radio broadcasts are an example of this
Vernacular/perceptual region
a region based on people’s ascribed sense of place
Spatial distribution
arrangement of a phenomenon across the Earth's surface
Spatial Interaction
the flow of information, products, and human beings from one location to another (migration, shopping, commuting, trips)
Sustainability
meeting the needs of the present while also leaving resources for future generations
Time-space compression
the idea that the world feels smaller than it used to because of increased technology in transportation and communication
Environmental determinism
the belief that a physical environment is THE reason that some societies are strong while others are weaker
Environmental possibilism
the belief that a physical environment plays a role in the development of a society, but is NOT the ONLY factor at work