11. LO11: Selective Coronal Polishing
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
What is the primary reason clients seek dental solutions related to their teeth's appearance?
Dissatisfaction with the appearance of their teeth.
Do tooth stains directly contribute to periodontal disease or caries?
No, stains are considered a cosmetic concern, not a pathologic condition.
What are the three categories of dental deposits reviewed in LO 8?
Soft deposits, Hard deposits, and Stain.
What are the two classification methods used for tooth stain?
Depending on their source and depending on their location.
What are the two types of stains based on their source?
Exogenous Stains and Endogenous Stains.
Define Exogenous Stains.
Stains that originate from the outside of the tooth (e.g., food, beverages, tobacco, chromogenic bacteria).
Define Endogenous Stains.
Stains that originate from within the tooth (e.g., tetracycline, pulpal trauma, developmental conditions).
What are the two types of stains based on their location?
Extrinsic Stains and Intrinsic Stains.
Define Extrinsic Stains.
Stains that occur on the tooth surface.
What is the source classification for Extrinsic Stains?
Always exogenous.
How are Extrinsic Stains managed (removed)?
By scaling and/or polishing.
Define Intrinsic Stains.
Stains that are incorporated within the tooth structure.
Can Intrinsic Stains be removed by scaling or polishing?
No, they cannot be removed by scaling or polishing.
Intrinsic stains can be categorized as which source types?
Exogenous or endogenous.
Name three factors associated with alterations during tooth development that can cause intrinsic stains.
Antibiotic use (tetracycline), fever, infection, and ingestion of high amounts of systemic fluoride.

What condition in a tooth can result in grey intrinsic staining?
Nonvital teeth (pulpal trauma)
silver amalgams
RCT tooth

What are two treatment options for managing the appearance of intrinsic stains?
Tooth Whitening (= Tooth Bleaching) and Cosmetic Restorative Procedures.
What determines whether whitening/bleaching/ restorative procedures is used?
Determined by stain severity and client’s level of concern
Can whitening toothpastes be used to remove intrinsic stains?
Only some as few contain bleaching agents. most use an abrasive. results are not great for intrinsic stains
What substance is commonly used in tooth whitening procedures?
A peroxide gel.
Which stain colors respond better to tooth whitening? and is it permanent?
Stains in the yellow to brown range than blue to gray range
not a permanent solution, will need touch ups
Which form of professional tooth whitening has the most scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness?
Custom professionally dispensed home-use products.
What type of intrinsic stain may necessitate cosmetic restorative procedures like veneers or full crowns?
Deep stains, pitted teeth, and grayish-blue stains.
Who performs most restorative procedures?
The dentist but hygienist should be able to explain the procedures to the patients
What is a veneer?
Very thin shells (made of composite resin or porcelain) that attach to the front part of the teeth.
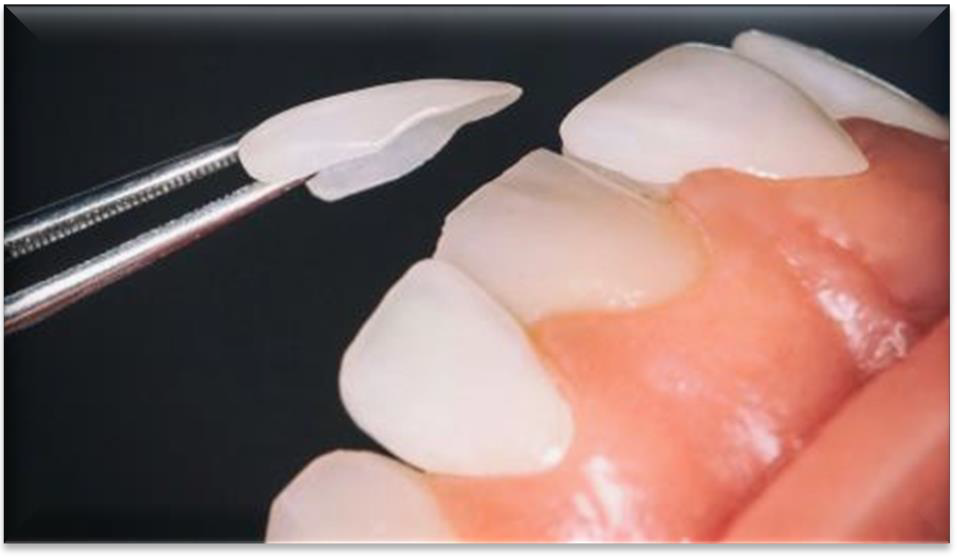
What is a full crown ("cap")?
A hollow artificial tooth (made of composite, porcelain, metal, or PFM) that covers discoloured, misshapen, decayed, or damaged teeth.

Name three common external sources that lead to Extrinsic Staining.
Chromogenic bacteria, tobacco, red wine, tea/coffee/soda, blueberries, certain drugs, or exposure to metallic compounds.
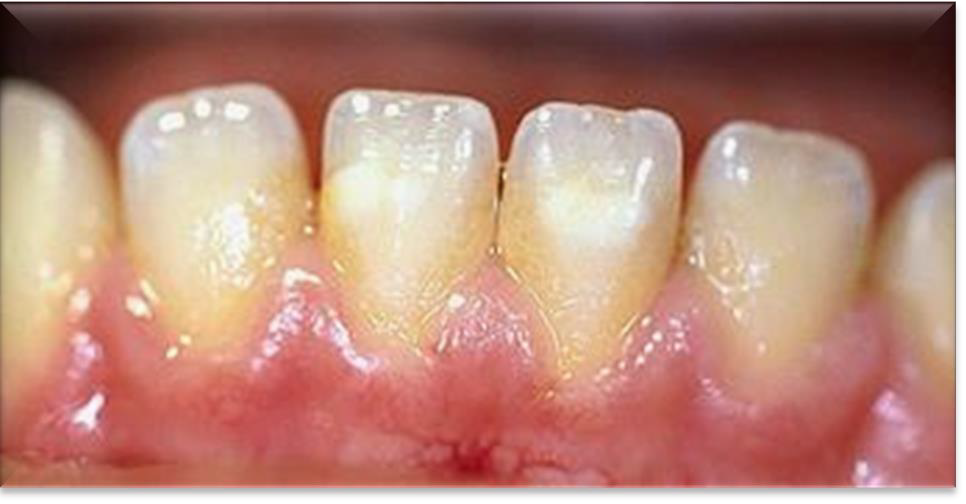
What causes Yellow extrinsic stain?
Oral biofilm.
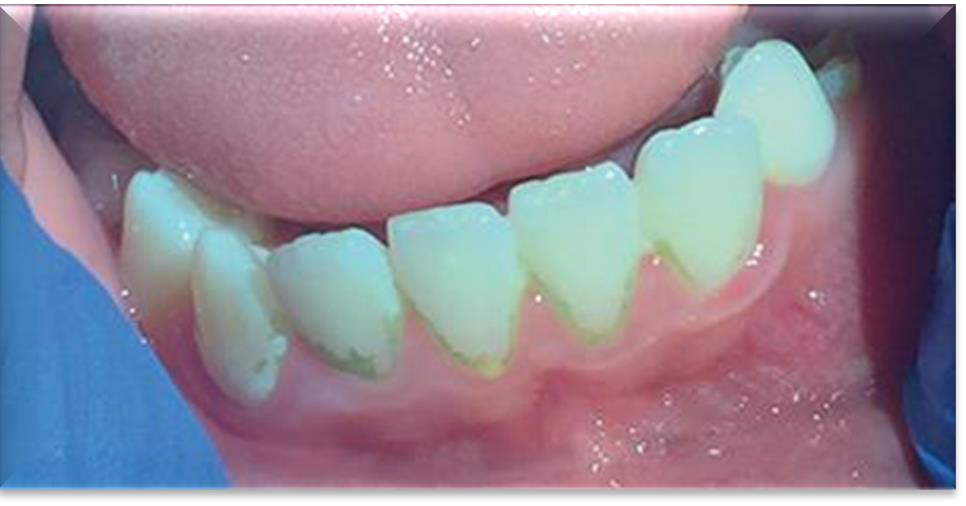
What causes Green or Orange extrinsic stain?
Chromogenic bacteria (poor oral hygiene).
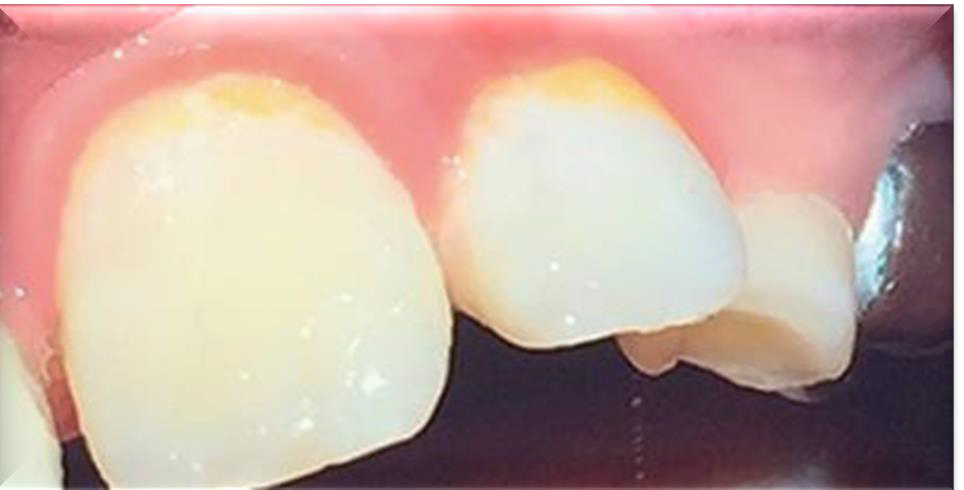
What causes gray/brown staining?
Marijuana

What causes Black Line Stain?
Bacteria and iron in the saliva.
What is the physical appearance of Black Line Stain?
A thin band, about 1 mm wide, located slightly coronal to the gingival margin.
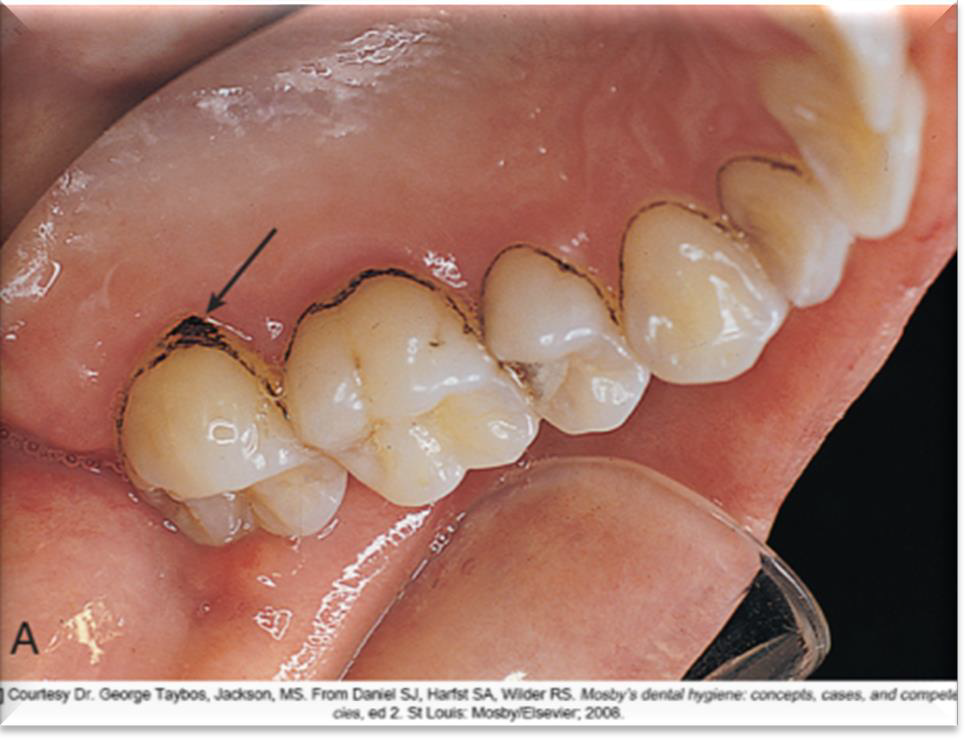

Name three chemical products that can cause Brown Stain.
Tobacco, food and beverage pigments, Stannous Fluoride (SnF2), Chlorhexidine (Chx), or CPC (Cetylpyridinium Chloride).
some mouth rinses and toothpaste
What three entities can extrinsic stain adhere to?
Directly to the tooth, to oral biofilm, or to calculus.
What management recommendation regarding whitening toothpaste requires caution?
Caution concerning abrasion and erosion.
What assessment step in the CNIH procedures involves checking for stain?
Deposit Detection.
In the Deposit Detection form, what 3 things are listed?
Determine if stain is intrinsic or extrinsic
Determine if stain is localized or generalized:
Localized = <1/3rd the dentition
Generalized = > 1/3rd the dentition
Determine if stain is light, moderate, or heavy
No specific criteria
On the Deposit Detection Clinical Form, how is Localized Stain defined?
Affecting less than 1/3rd (< 1/3rd) of the dentition.
Is there a specific criteria to determine if stain is light, mod, or severe?
No specific criteria
On the Deposit Detection Clinical Form, how is Generalized Stain defined?
Affecting more than 1/3rd (1/3rd) of the dentition.
What method is the safest choice for removing stain on exposed roots?
Ultrasonic on low power with slimline inserts.
What is the purpose of Rubber Cup Polishing?
A cosmetic procedure to remove extrinsic stains from the enamel surfaces of teeth after scaling.
What are two other terms for Rubber Cup Polishing?
Coronal polishing or "a prophy."
Does rubber cup polishing have therapeutic value for periodontal health?
No. It is a non-essential procedure to improve the appearance of anterior teeth
What does Rubber cup polishing use to abrade stains from tooth surfaces?
Uses an abrasive polishing agent and a slowly revolving polishing cup
What three items are necessary for rubber cup polishing?
A slow-speed handpiece
prophylaxis angle with a rubber cup (and bristle brush)
and prophylaxis paste.
Why is full mouth polishing not done anymore?
possible adverse effects on:
tooth surfaces
restorations
soft tissues
What current practice does evidence support instead of polishing all clients' teeth? and how is each client assessed?
Selective polishing, focused on crowns of teeth
each client is assessed individually to make note of # of restorations and condition of teeth
In selective polishing, what criteria determine which tooth surfaces are polished?
Tooth surfaces with visible extrinsic stains after scaling is completed.
Name three dental structures or conditions that should be avoided during selective polishing due to potential damage.
Newly erupted teeth, cementum, dentin, demineralized areas, and restored tooth surfaces.
What is one adverse effect of polishing on enamel?
It removes the microscopic fluoride-rich outer layer of enamel.
What type of enamel area loses significantly more surface structure during polishing?
Demineralized areas, also known as "white spot lesions."
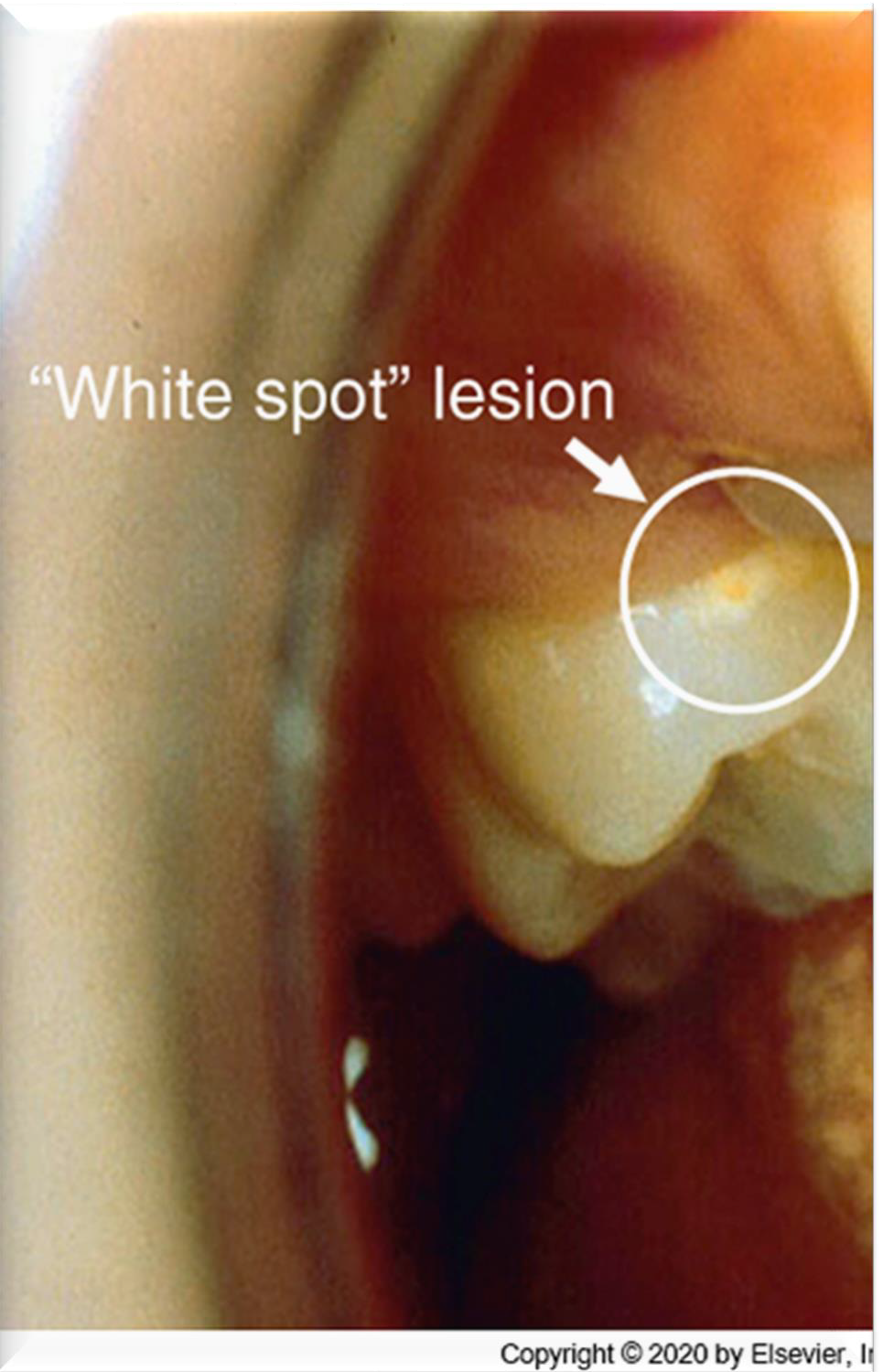
Why do root surfaces (cementum and dentin) risk tooth wear during polishing?
Because they are softer than enamel.
What is the safest choice for removing stain on root surfaces?
Ultrasonic
What can polishing cause due to thinner enamel/exposed dentin or cementum?
Polishing may cause tooth sensitivity
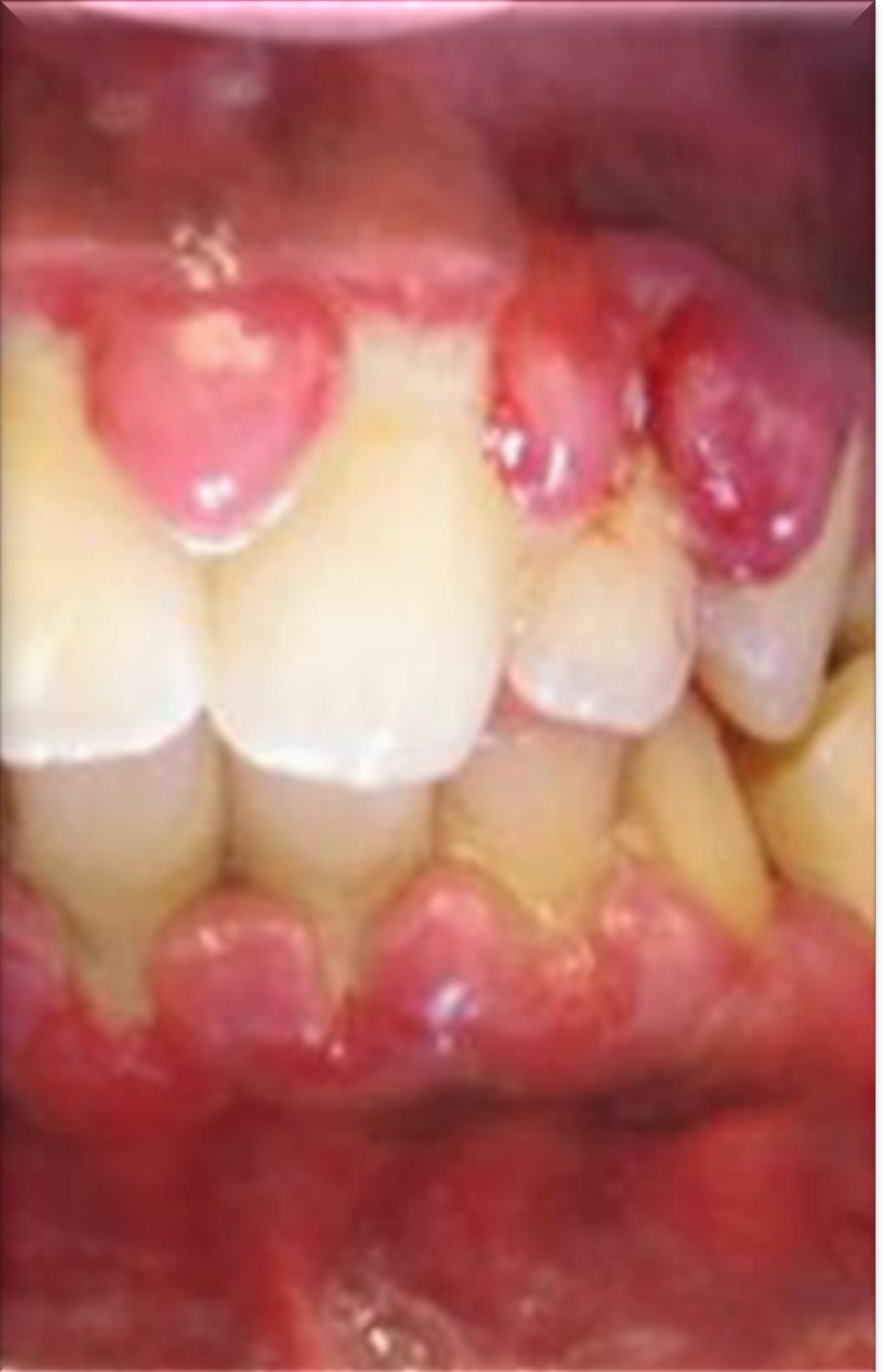
What adverse effect can improper technique cause in inflamed gingiva?
Trauma, and abrasive particles from the paste can embed in the gingiva and delay healing.
What can cause trauma to the gingiva in regards to polishing?
Improper technique
Why do we have to use low abrasive techniques to polish restorations?
Polishing can damage restorations by making the surfaces rough
What is the solution for polishing restored teeth without damage?
Use a low abrasive prophy paste designed for restorations.
Why are newly erupted primary teeth at higher risk of pulpal discomfort from polishing heat?
The pulp chamber is larger, and the pulp is closer to the outer surface of the tooth compared to a permanent tooth.

What generates heat causing pulpal discomfort, especially in newly erupted teeth?
If the pressure, speed, and/or abrasiveness of the prophy paste is not ideal.
What adverse effect of polishing requires the dental hygienist to follow AGDP Protocol (N95 mask, HVE, LVE)?
The creation of aerosols which can transmit infectious disease.
Name three contraindications for rubber cup polishing related to the tooth structure.
Absence of extrinsic stain
newly erupted teeth (especially primary)
demineralization/active caries
areas of recession (NOT FOR ROOTH SURFACES)
hypersensitive teeth
or dental implant abutments.
acute gingival inflammation
allergies to ingredients in prophy paste
Clients with a known communicable disease (that can be spread by aerosols)
Clients with a high susceptibility to infections (clients with respiratory or pulmonary disease; debilitated individuals)
What is one contraindication related to client health or risk of spread?
Clients with a known communicable disease (that can be spread by aerosols) or clients with a high susceptibility to infections (e.g., respiratory/pulmonary disease).
What should a clinician do if a client's gingiva is enlarged, soft, spongy, or bleeds easily before polishing?
Schedule polishing for a separate appointment if needed.
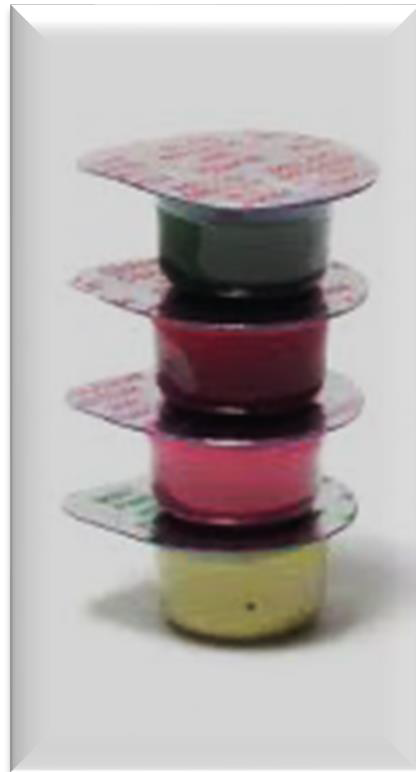

List the 5 equipment/materials needed to polish
slow speed hand piece motor
Contra-angle attachment
Prophy Head (including shank)
latch, snap on, screw-type
Compatible prophy cup/ bristle brush
Prophy paste
The prophylactic angle typically consists of what three main parts?
The prophy head, the contra-angle, and the slow-speed motor.
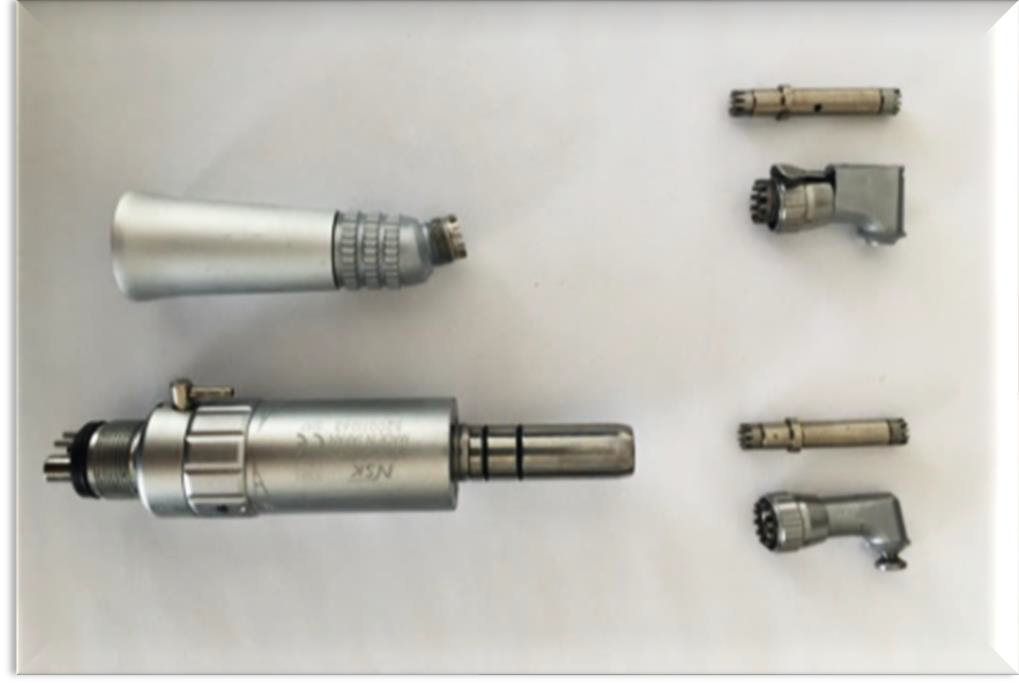

Which two types of prophy head attachments are used at CNIH?
Latch-type and Snap-on.

What type of attachment is used for occlusal surfaces only?
Bristle brushes.


In terms of equipment set up, how are the prophy head, contra angle, rubber cups set up?
The prophy head is attached to the contra-angle (the cogs must line up)
The contra-angle attaches to the slow-speed motor, which attaches to one ofthe air-driven lines in the dental unit
A bristle brush or rubber polishing cup is inserted on the prophy head

How is the slow speed activated?
by pressing on the rheostat with the toe of your foot
What do you need to make sure of before activating handpiece?
Make sure rheostat switch is turned towards the metal button (to ensure the water to the handpiece line is off)
What do we need to make sure of before polishing the teeth (rheostat)
Make sure you regulate the speed before adapting the rubber cup or bristle brush to the tooth
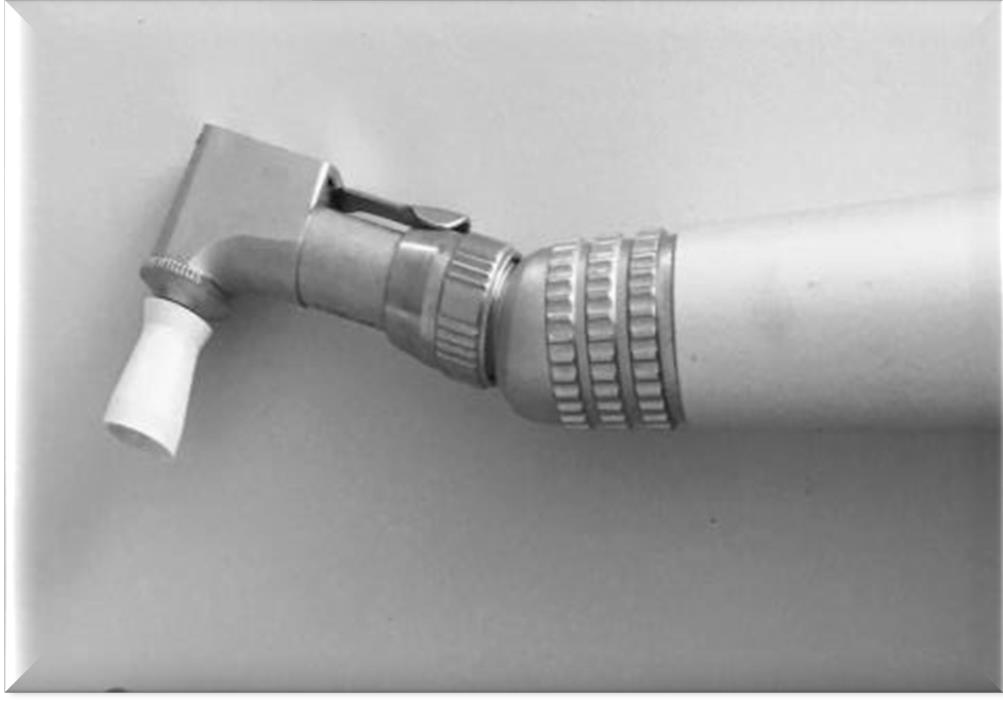
What materials are prophy heads most commonly made of?
stainless steel and are reusable after reprocessing
use MIFU for lubrication and reprocessing
disposable ones are available as well

What angles are prophy heads available in?
Contra angle (more ergonomic) or right angle
what surfaces are rubber cups and bristles used for?
rubber cups are all for all surfaces and bristles are only for occlusals

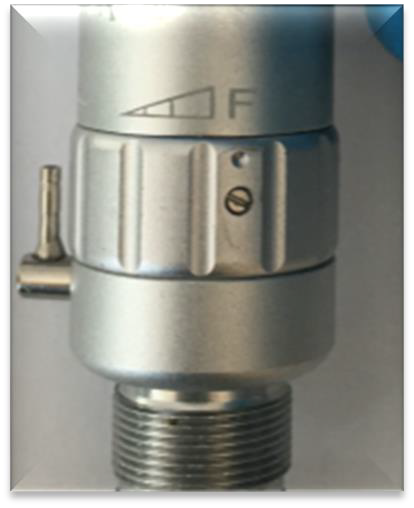
What must the clinician ensure is set correctly to prevent snap-on or screw-on attachments from falling off?
The slow-speed handpiece must be set to Forward (F) and not Reverse (R).

Why is special care must be taken to ensure the rubber cup or bristle brush is securely attached to the prophy angle
If the cups falls off, the client could swallow or inhale it
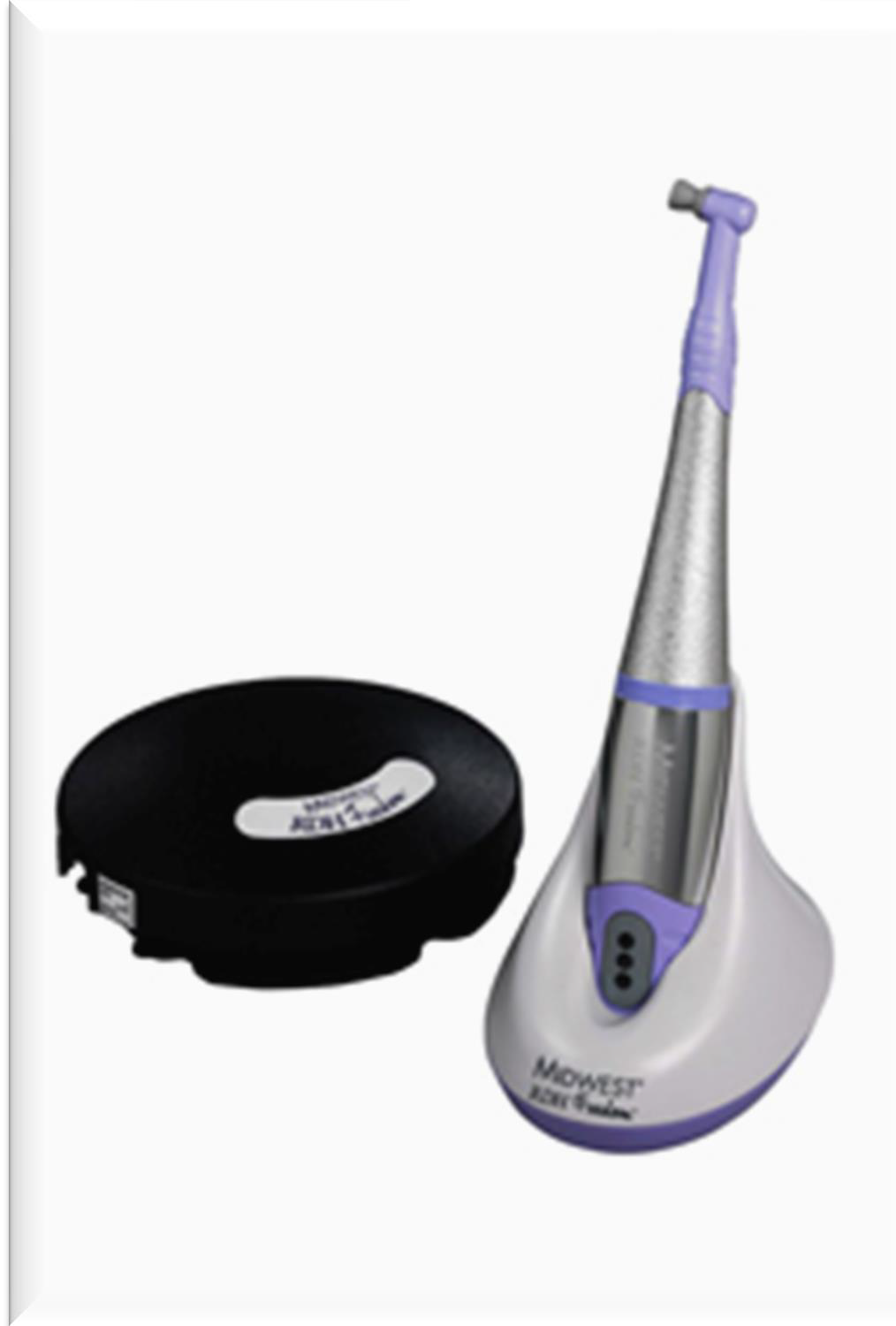
Describe cordless polishers
Battery-driven cordless polishing systems with wireless rheostats are becoming more common
More ergonomic (lightweight and there is not cord to restrict the clinician’s movement)
What does the "grit" of prophy paste refer to?
Particle size.
What two characteristics are affected by the grit of the polishing paste?
The cleaning rate and the scratch pattern produced on the tooth surface.
One of the key factors to safe and effective tooth polishing is choosing the appropriate _____?
Prophy paste
Available in different grits (superfine, fine, medium, coarse, extra-coarse)
Are all brands of polishing paste the same grit?
no, there is no industry standard for defining grit
What is the recommended evidence-based method for selecting prophy paste grit?
Use the finest polishing paste grit that will achieve the desired result.
Name three additive ingredients that can be added to commercial prophy pastes.
Are they effective?
Fluoride, remineralizing agents, whitening ingredients, or desensitizing agents.
More evidence is needed to support the efficacy of these products

What grit prophy paste is used in most cases and why?
Super fine/fine grit
Least amount of surface abrasion
Will increase tooth surface cleanliness, lustre and smoothness

Why is it not recommended/unethical to use course grit?
Can scratch & roughen tooth surfaces, potentially making them more likely to accumulate oral biofilm & stain
Can cause dentinal hypersensitivity & damage to restorations
Its use is unethical unless necessary for removing heavy tenacious stain
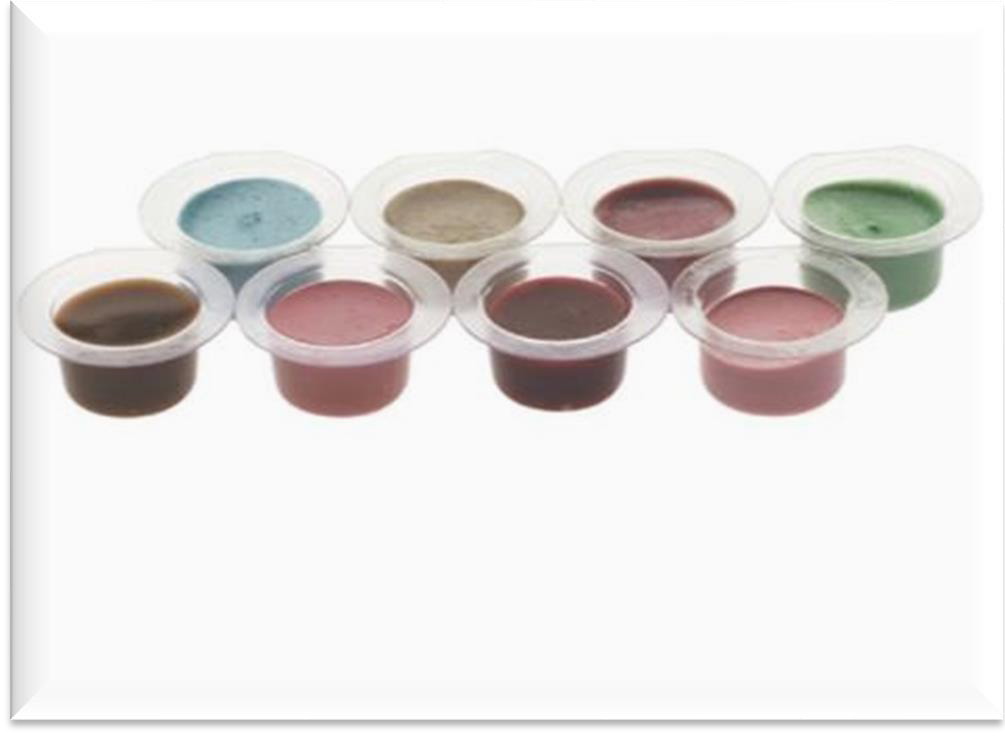

In what forms can prophy pastes be found (container wise)
Available as individual cups (one-time use)
Available in small tubs (use with spatula and dappen dish)
Finger rings (to hold the prophy paste) often come with the products

List the 5 variables influencing tooth structure loss in terms of polishing
Abrasiveness of prophy paste
Quantity of prophy paste
Contact time of the rubber cup or bristle brush on the tooth surface
Speed (rpms) of the rubber cup or bristle brush
Pressure of the rubber cup or bristle brush on the tooth surface
What is the maximum recommended speed for polishing?
Low speed (< 3000 rpms).
How long should the rubber cup/bristle brush be in contact with the tooth surface?
Short, intermittent contact of 1 to 2 seconds.
Is a secure fulcrum required to polish? should you use a light or heavy touch?
yes, secure fulcrum is required and always use a light intermittent touch
What must never be used on enamel?
A dry abrasive paste or an empty rubber cup/brush. (will overheat)
When documenting a selective polish, what specific details about the paste must be included?
The brand of paste used (e.g., Nupro paste), flavor (e.g., mint), and grit (e.g., fine grit).
What three components make up the mixture used in the air polishing method?
Warm water, a polishing powder, and air.
Air polishing is a method of extrinsic stain removal. Describe the 2 ways it can be delivered.
Prophy Jet: A specially designed device; activated by a foot pedal (CNIH)
A device that connects to the dental unit handpiece tubing
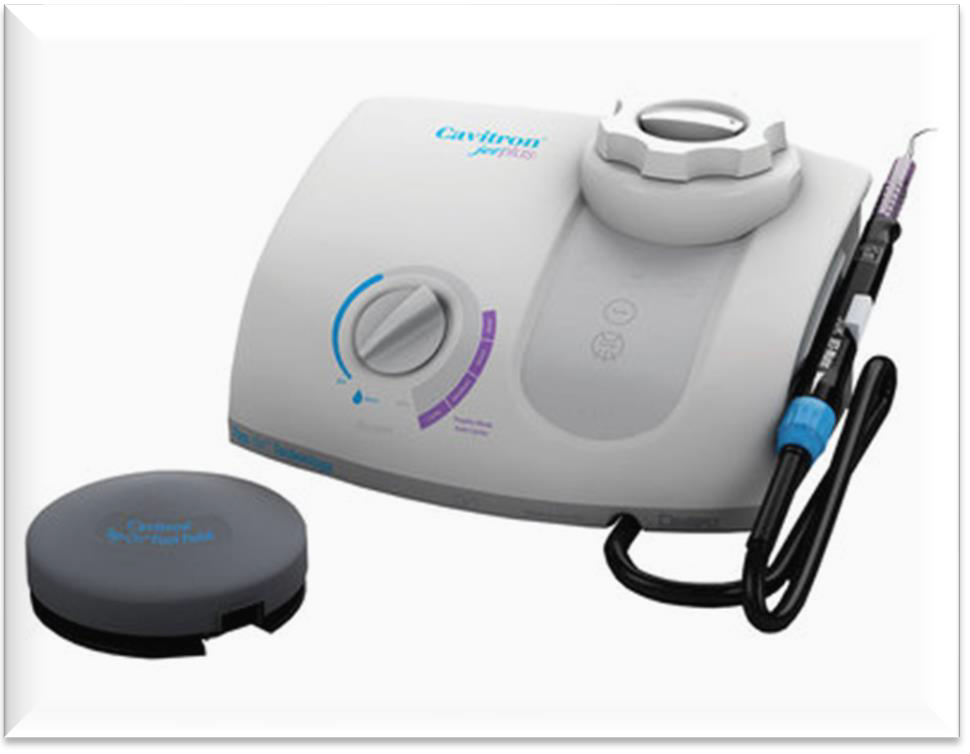
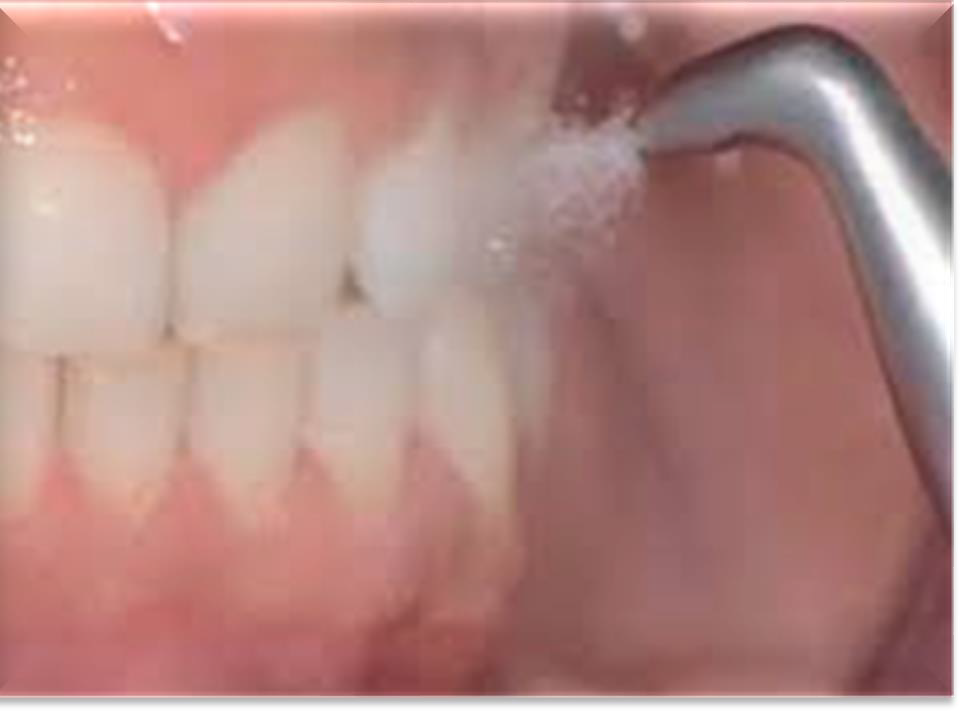
What is the purpose of supragingival air polishing?
To remove stain.
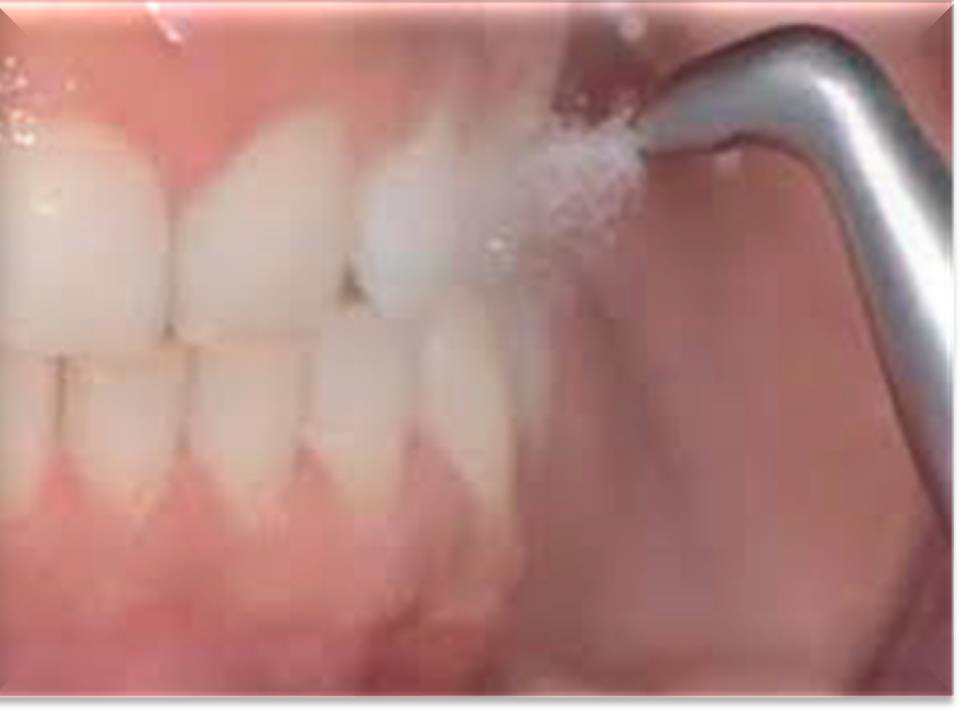
What common abrasive powder is used for supragingival air polishing?
Sodium bicarbonate.

What potential damage can abrasive prophy powders cause?
Significant defects in restorations and in root surfaces.
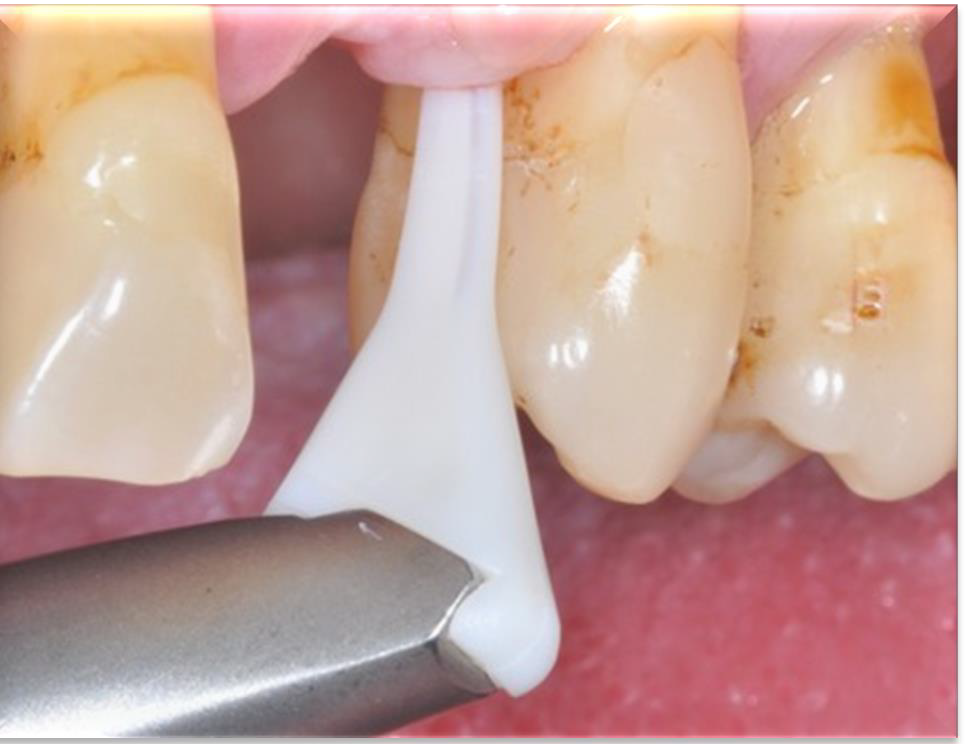
What is the purpose of subgingival air polishing?
To remove oral biofilm
Must use a low abrasive powder!
Pockets >5 mm require a special nozzle