AP Euro Unit 1 | CH 2 Renaissance & Age of Discovery
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Renaissance, Northern Renaissance, New Monarchs, Age of Exploration
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
3 Key Shifts from Middle Ages → Renaissance
Feudalism → Centralized State / National Identity.
Manorialism/Agriculture → Urban Capitalism / Trade.
Religious → Secular / Individualism.
Italian City-States (Political Structure)
Independent Oligarchies (ruled by wealthy merchant families, e.g., Medici).
Weakness: Fragmented and competitive; prone to foreign invasion.
Italy's Advantage: Geography (Gateway between East/West) → immense wealth.
Florence Social Classes
Grandi: Old rich nobles.
Popolo Grosso: "Fat people" (new rich capitalists/bankers).
Popolo Minuto: "Little people" (poor).
Conflict: Ciompi Revolt (1378)—uprising of the poor due to plague/social unrest; led to brief chaotic rule by lower classes.
Renaissance Diplomacy
Innovation: Created to maintain Balance of Power among city-states (Treaty of Lodi).
Tools: Resident embassies, modern espionage, and alliances to monitor enemies.
Fall of Constantinople (1453)
Event: Ottoman Turks conquered the Byzantine capital.
Impact: Closed trade routes to East (spurring exploration); Greek scholars fled to Italy (fueling Humanism).
Humanism (Definition & Goal)
Study: Studia Humanitatis (Classics: Grammar, Rhetoric, History).
Goal: Virtú (reach full human potential) & Public Service, secularism, individualism.
Petrarch
"Father of Humanism."
Revived classical texts (Cicero) and wrote vernacular sonnets.
Argued for studying both religious and secular works.
Castiglione’s Book of the Courtier
Guidebook: How to be the ideal "Renaissance Man."
Traits: Multifaceted (skilled in arts + war), well-mannered, possesses grace.
Women was same as Courtier but emphasized grace/beauty & self-awarness.
Christine de Pisan
Educated noblewomen; wrote The City of Ladies.
Defended women's intellect and ability against misogyny.
Platonism (Florentine Academy)
Revival of Plato's philosophy (reason to connect to perfect world), sponsored by Medicis.
Pico della Mirandola’s Oration on the Dignity of Man: Humans have free will to shape their own destiny.
Lorenzo Valla
Humanist who used textual criticism to prove the Donation of Constantine was a forgery.
Undermined Church auth.
Leonardo da Vinci
The ultimate "Renaissance Man" (artist, engineer, scientist).
Mona Lisa (psychological depth); The Last Supper (perspective, geometry, emotion).
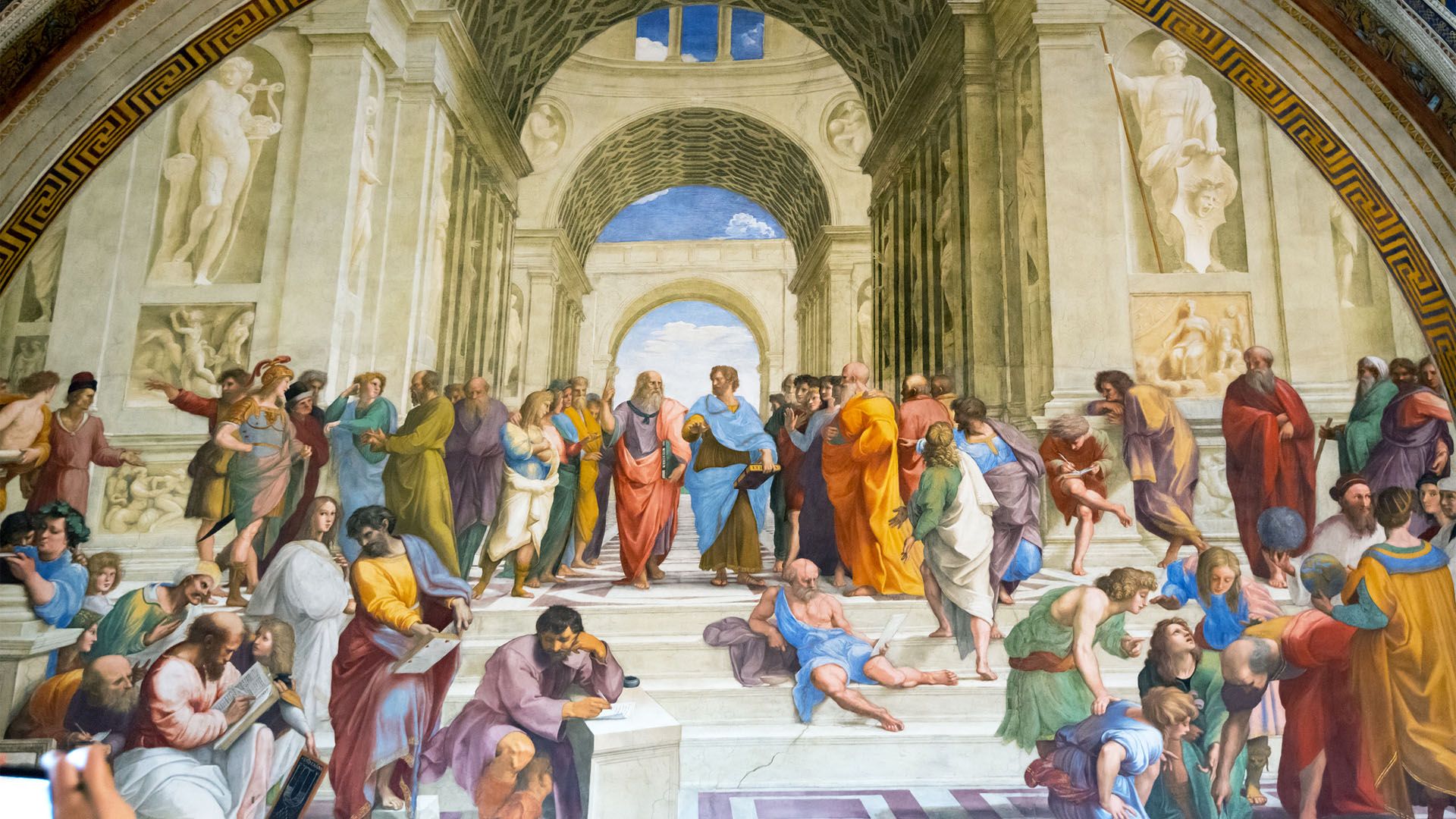
School of Athens (Raphael)
Significance: Perfect example of High Renaissance.
Themes: Balance, harmony, and Secularism (glorifies Greek philosophers like Plato/Aristotle in the Vatican), patronized by Pope.

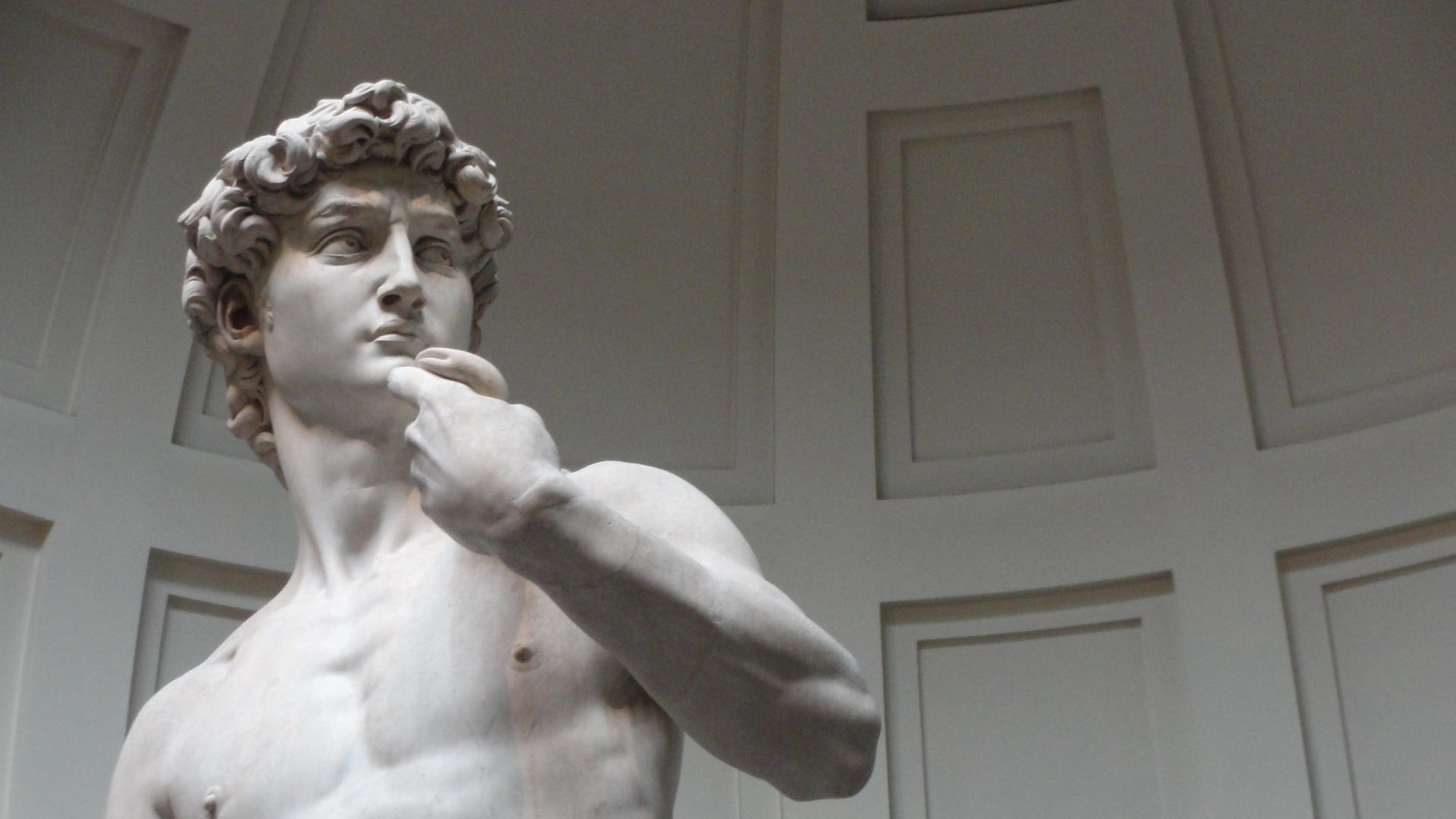
Michelangelo
"Melancholy Genius" sculptor and painter.
David (glorifies human form); Sistine Chapel (Neoplatonic mixing of biblical/classical figures).

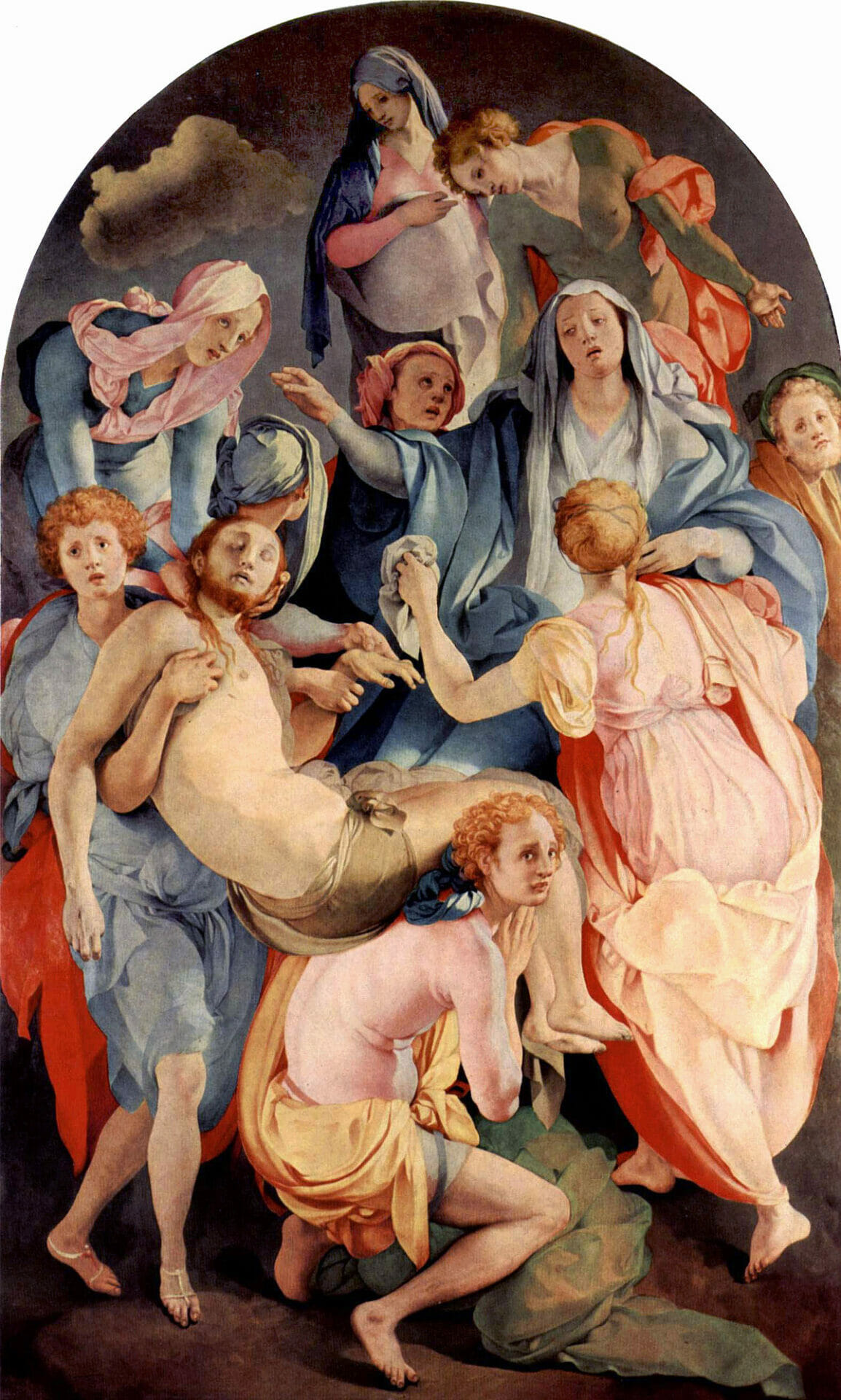
Mannerism
Context: Late Renaissance (turmoil/Reformation).
Style: Rejected balance/symmetry. Used distortion, elongation, and clashing colors to show emotion/anxiety.
Pontormo’s Entombment of Christ: Unnatural features like man w/ pink skin & women floating

The Prince (Machiavelli)
Goal: A unified Italy (free from "barbarians").
Thesis: "The ends justify the means." Better to be feared than loved.
Politics: Secular and pragmatic; removed morality from ruling.
France (New Monarchs)
Rulers: Charles VII (created permanent army); Louis XI ("Spider King"—conquered Burgundy, efficient tax), Francis I (Concordat of Bologna)
Printing Press (Impact)
Inventor: Gutenberg (~1450).
Effects: Book cost ↓, Literacy ↑.
Crucial for: Spreading Humanist/Reformation ideas (Luther), challenging Church authority, standardizing language.
Erasmus
"Prince of the Humanists." Christian Humanist.
Wrote In Praise of Folly (satirized Church corruption).
Goal: Reform the Church from within through education (simple faith).
Reuchlin Affair (Germany)
Humanists defended Johann Reuchlin (academic freedom) after a Pfefferkorn suppressed Jew writings & attacked him
Spanish Humanism
Goal of strengthening Church
Complutensian Polygot Bible: Multi-lang (Hebrew, Greek, Latin) bible by Cisneros for reforms
Portuguese Exploration Model
Direction: East (around Africa).
Empire Style: Trading Post Empire (factories) on coasts of Africa/India.
Key Tech: Caravel, Astrolabe, Magnetic Compass.
Dias (Rounded Cape of Good Hope) & Da Gama (reached Indian spice trade)
Spanish Exploration
Focus: Westward route across Atlantic.
Columbus (1492): "Discovered" Americas while seeking Asia.
Magellan: Crew circumnavigated the globe.
Bartolomé de Las Cases
Priest who criticized Spanish brutality (Black Legend)
Inadvertently encouraged African slavery as "humane" alternative.
Spanish Labor Systems
Encomienda: Royal grant giving colonists right to forced native labor/tribute in exchange for "protection."
Repartimiento/Mita: Rotating forced labor tax.
Charles V
Became Holy Roman Emperor w/ financial support by Fuggers
Controlled Habsburg & Spanish Empire
Sacked Rome → decline of Italian Ren.
Virtú
Humanistic: Untapped human potential/success (individualism)
Roman: Civic heroism (led to Machiavelli)
Machiavelli: Criminal virtu, cruel but good leaders
Civic Humanism
Idea: Education should prepare men for active public service / politics (“Renaissance Man”)
Model: Cicero (Roman Republic).
Key Figure: Leonardo Bruni.
Christian Humanism
Northern movement to reform/simplify the Church and society through education and early Christian writings
Treaty of Lodi (1454)
Peace agreement establishing a balance of power among Italian city-states.
Provided 40 years of peace until the French invasions.
Girolamo Savonarola
Preacher told Florentines that Charles VIII’s (France) invasion of Italy was divine punishment
Charles enter w/o resistance → further invasions, decline of autonomy
His theocracy ended w/ his execution
Julius II
“Warrior pope” due to political focus (secular)
Suppressed Borgias & drove Venetians from Romagna
Holy League to oust France from Italy
Patronized arts (Michelangelo, Raphael)
Secured Papal States
Sack of Rome (1527)
Charles V’s troops looted Rome.
Symbolizes the end of the Italian Renaissance and Italian independence.
Patronage
New wealth from trade/banking
Financial support from wealthy ppl/institutions for status, reviving classics & leading to new secular ideas
Mercantilism
Economic Theory: Wealth = Bullion (Gold/Silver).
Zero-Sum: One nation's gain is another's loss.
Policy: Export > Import. Colonies exist only to enrich the mother country.
Jacob Burckhardt
Historian who saw Ren. as prototype of modern secular world away from medieval era
Full release of man
Criticized for exaggeration (Burke) due to continuation from medieval era & earlier Renaissances
Concordat of Bologna (1516)
Agreement: Between Francis I (France) & Pope.
Terms: King gets to appoint bishops (control church); Pope gets revenue.
Effect: Kept France Catholic during Reform & increased king auth
England (New Monarchs)
Ruler: Henry VII (Tudor).
Tactics: Ended War of the Roses; used Star Chamber (royal court w/o jury) to check noble power; avoided wars to gain financial independence from Parliament.
Spain (New Monarchs)
Rulers: Ferdinand (Aragon) & Isabella (Castile) united.
Actions: Completed Reconquista (1492); enforced religious unity via Inquisition (persecuting heretics); sponsored Columbus.
Spanish Inquisition
Church under control of monarchy
Tortured Jews & Moors who didn’t convert
Anti-Semitism in Euro. (Jews persecuted)
Unified Spain’s religion but lost taxes
Holy Roman Empire Political Structure
Structure: Decentralized collection of ~300 states; Emperor elected by 7 Electors (Golden Bull).
Habsburgs: Charles V ruled HRE + Spain; vast empire but weak central authority due to Reformation and local princes.
Commercial Revolution
Economic shift: Rise of capitalism, banking, and joint-stock companies, money economy
Caused by influx of New World bullion (Price Revolution/inflation) and population growth
Hanseatic League
Merchant guild of German trading cities.
Dominated Northern European trade before the rise of nation-states.
Joint-Stock Company
Business entity where investors pool money for a common purpose (exploration).
Precursor to modern corporations; reduced individual risk (e.g., British East India Co.).
Northern Renaissance Art
Focus: Daily life, peasants, detail-oriented realism, religious piety.
Pieter Bruegel: Return of the Hunters (landscapes/peasant life).
Albrecht Dürer: Woodcuts and self-portraits (blended Northern detail w/ Italian perspective).
Spanish vs. Portuguese Exploration
Portuguese: India, trade, slave plantations
Spanish: Americas, gold/expansion, forced labor (Encomienda, debt peonage)
Both: God, cheaper/shorter Asian routes, using natives
Spanish Agriculture Systems
Hacienda: Estates owned by peninsulares (Spanish-born) or creoles (Spanish born in Amer)
Plantations: Labored by African slaves for sugar
Urban Service: Gov’t offices, law; peninsulares/creoles
"New Monarchs" (3 Main Strategies)
Goal: Centralize power, reduce noble influence, enforce law & order.
Tactics: Professional standing armies (instead of feudal levies), alliance with towns/middle class (for taxes), control over clergy, mercantilism.
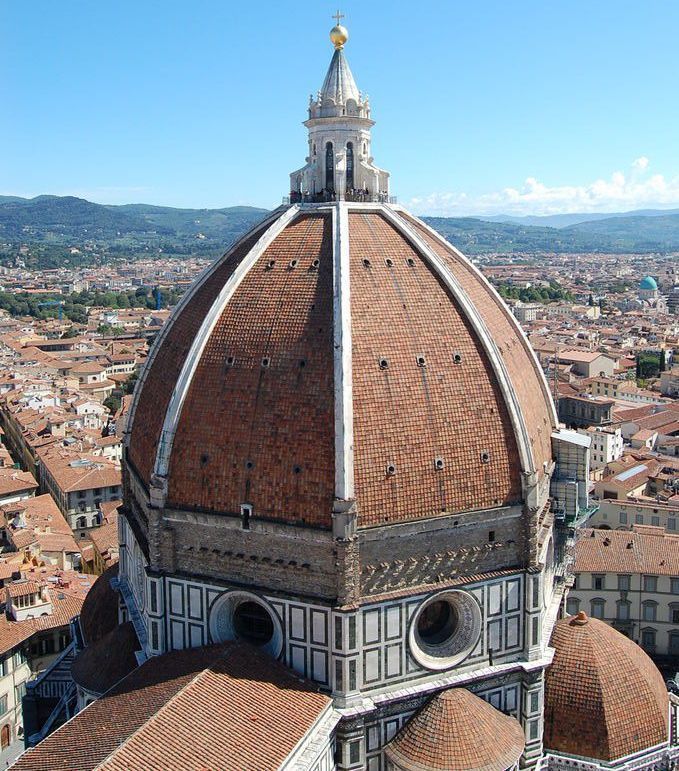
Brunelleschi
Created Cathedral of Florence’s dome
Rediscovered the science of perspective & studied Roman architecture

Thomas More
English Christian Humanist; advisor to Henry VIII.
Wrote Utopia: A critique of society by imagining a perfect socialist island based on reason (Plato’s Republic)
Reconquista
Centuries-long campaign by Spanish Christians to retake Spain from the Moors (Muslims).
Ended in 1492 with the fall of Granada.
Prince Henry "The Navigator"
Portuguese prince who sponsored exploration schools.
Motives: Gold, spices, spreading Christianity, bypassing Italian monopolies.
Treaty of Tordesillas
Pope divided the New World between Spain (West) and Portugal (East/Brazil).
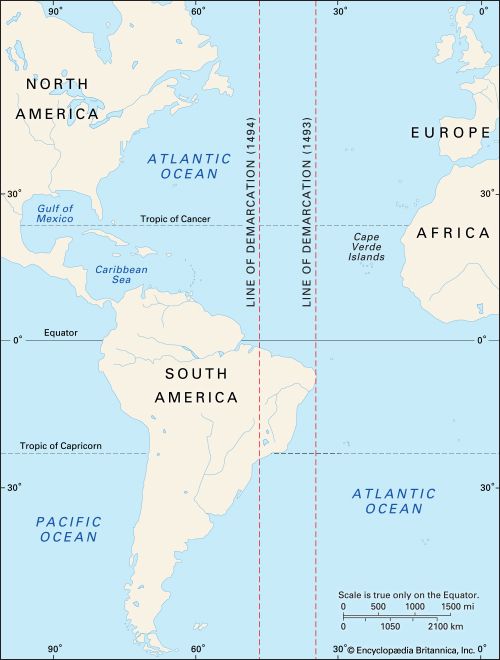
Columbian Exchange
To Europe: Potatoes/Maize (Pop. Explosion), Syphilis, Tobacco, Bullion.
To Americas: Smallpox/Measles (90% death rate), Horses, Cattle, Guns.
Price Revolution
Slow, steady inflation across Europe in 16th c.
Causes: Population growth (demand) + New World gold/silver.
Fuggers / Medicis
Wealthy banking families (German/Italian) who financed monarchs (like Charles V) and wars, replacing feudal lords as power brokers.
Star Chamber (England)
Monarch: Henry VII (Tudor).
Purpose: Secret court to try powerful nobles without a jury.
Result: Reduced aristocratic power.
Secularism vs. Individualism
Secularism: Focus on the material world (here & now) rather than the afterlife.
Individualism: Celebration of unique personal genius/achievement (virtú) over community.
Motives for Exploration
God: Spread Christianity (Jesuits/Missionaries).
Gold: Spices (Asia) and bullion (Americas).
Glory: Renaissance individualism/fame.
Spanish Conquistadors
Hernán Cortés: Conquered Aztecs (Mexico) using tech, disease, and native allies.
Francisco Pizarro: Conquered Incas (Peru) by capturing Atahualpa (ruler).
Amerigo Vespucci: Proved distinct "New World" continent.
The Italian Wars (1494–1559)
Cause: Ludovico (Milan) invited Charles VIII (France) to intervene (breakdown of Treaty of Lodi).
Key Figures: Julius II ("Warrior Pope" fought France); Charles V vs. Francis I (Habsburg-Valois War).
Result: Sack of Rome (1527) by Charles V's troops. Italy loses independence; Spain dominates.
Renaissance Art Characteristics
Techniques: Linear perspective (3D depth), Chiaroscuro (light/shadow), geometric balance, naturalism, secularism/idealism (Italy).
Themes: Classical mythology, secular portraits, human-centric religious scenes.
Women’s Role During Ren.
Recieved limited edu due to being confined to domestic spheres (wives/mothers), emphasizing honor & chastity
Held influence as patrons of arts
Increased literacy w/ printing press