Neuroscience weeks 1-5
1/225
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
226 Terms
Nervous system divided into
CNS and PNS
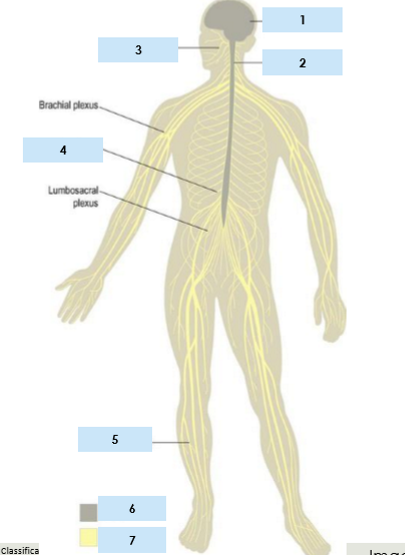
Central nervous system components
Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system
consists of sensory and motor fibres to and from CNS
12 pairs of cranial nerves - emerge from base of brain
31 pairs of spinal nerves - emerge between vertebrae
PNS divisions
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Somatic nervous system
innervates skeletal musculature
controls voluntary actions
Autonomic nervous system
= visceromotor system
innervates internal organs and other visceral structures
controls automatic actions
Autonomic nervous system divisions
Sympathetic system
Parasympathetic system
Sympathetic nervous system
in sympathy with emotions
fight or flight response
e.g. dilated pupils, dry mouth, fast heart rate
Parasympathetic system
Restoration of body’s energy
digest
causing pupils to constrict
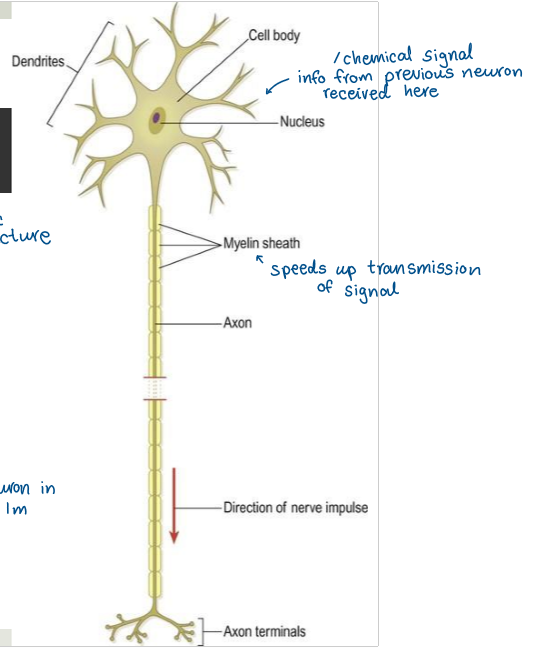
Neurons
= nerve cells
basic structural and functional unit of NS
use electrochemical impulses
receive, integrate and transmit info
Neuron communicates with postsynaptic cell
Other neuron - via synapse
smooth muscle fibre or grand - via neuroeffector junction
skeletal muscle fibres - via neuromuscular junction
Functions of neurons
Afferent
Efferent
Association
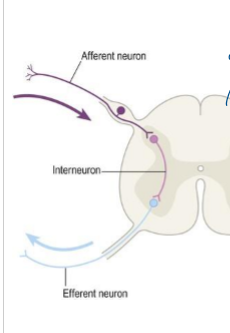
Afferent neurons
bring impulses toward the CNS
adding to CNS
Efferent neurons
Carry impulses away from CNS to periphery
exiting CNS
Association neurons
Interconnections in brain and spinal cord
e.g. interneuron
Neuroglia
= glia cells
Support cells of NS
Types of neuroglia
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes (CNS) and Schwann cells (PNS)
Microglia
Astrocytes
main type of glia, most numerous
structural support, metabolic fxns and regulate passage of molecules between bloodstream and CNS
Oligodendrocytes (CNS) and Schwann cells (PNS)
Wrap axons in myelin sheath to increase speed of conduction/transmission of electrochemical signal
Microglia
Help to regulate brain development, maintenance of neuronal networks, injury repair and waste clearance
Grey matter
mainly cell bodies, dendrites and synapses
White matter
nerve fibres with lipid-rich myelin sheaths - myelinated axons
Nucleus
collection of neuronal cell bodies in CNS
Tract
Bundle of axons with common point of origin and termination, in CNS
Fasciculus
2 or more tracts running in company, in CNS
Ganglion
Collection of neuronal cell bodies, in PNS
Nerve
Bundle of axons in PNS
What are the two main parts of the human nervous system?
Central nervous system (CNS) and Peripheral nervous system (PNS).
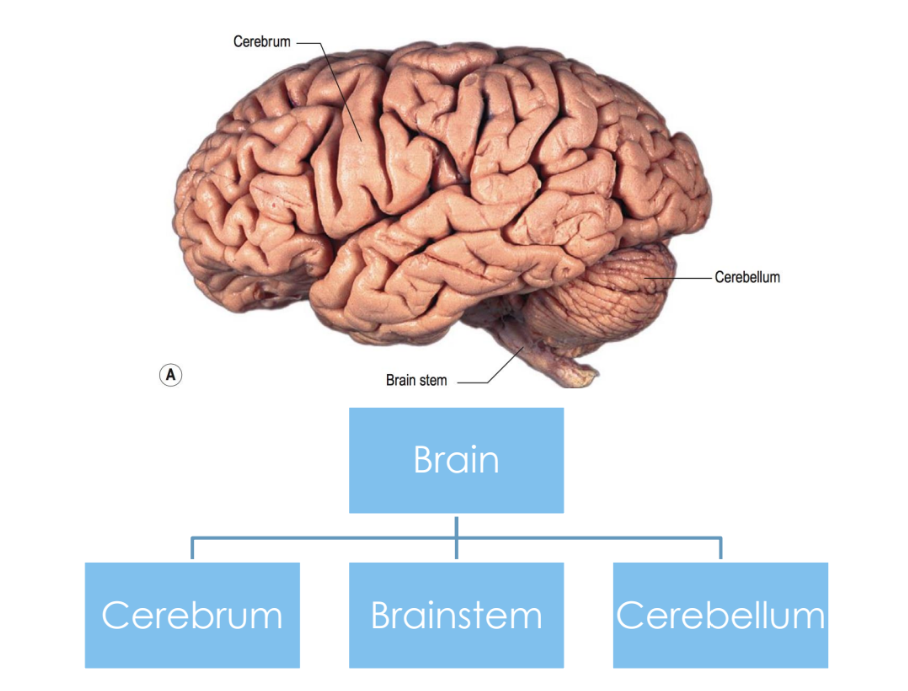
Brain broken up into 3 sections
Cerebrum
Brainstem
Cerebellum
Cerebrum hemispheres
2, L and R
separated by longitudinal fissure
connected by corpus callosum
some functions of hemispheres lateralised, e.g. left hemisphere dominant for language in most people
What separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum?
The transverse fissure
Cerebrum - grey matter
Cerebral cortex - 2-4mm grey matter, gyri and sulci (convolutions - maximize SA)
What separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe?
Central sulcus.
What separates temporal lobe from rest of brain?
Sylvian (lateral) fissure
What separates the parietal and occipital lobes?
Parieto-occipital sulcus
Frontal lobe
largest lobe
houses Broca’s area
prefrontal cortex houses primary motor area
Primary motor area
region of the frontal lobe responsible for voluntary movement controls
located on precentral sulcus
Primary somatosensory area
located in parietal lobe
responsible for processing sensory information from the body, such as touch, temperature, and pain.
Angular and supramarginal gyrus
located in parietal lobe
important for connections from Broca’s to Wernicke’s area
Temporal lobe houses
Wernicke’s area - important for language comprehension: spoken, written and gestures
primary auditory area
Primary auditory area
Responsible for initial detection and processing of auditory info, where first auditory info gets passed to
Occipital lobe
smallest lobe
houses primary visual area
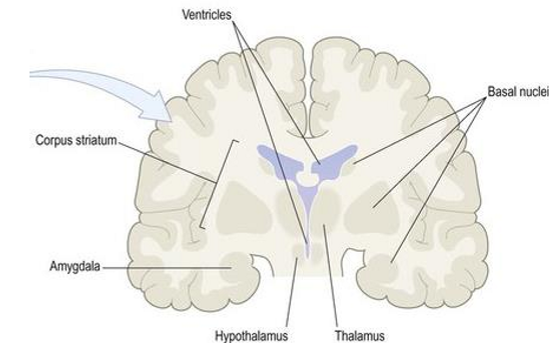
Grey matter structures within cerebrum
Basal ganglia - striatum (corpus striatum)
Caudate nucleus
Lentiform nucleus - putamen, globus pallidus
Amygdala
Diencephalon - thalamus, hypothalamus
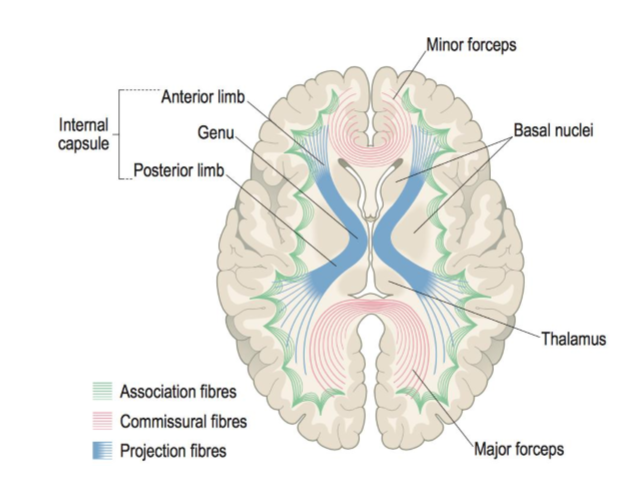
Types of white matter fibres in the cerebrum
association
projection
commissural
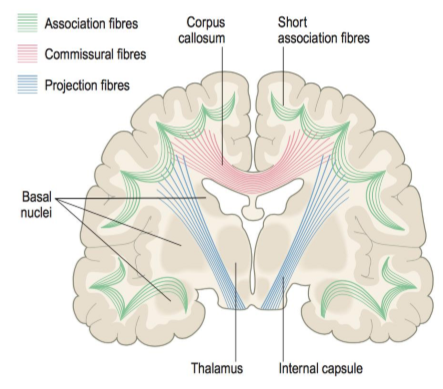
Association fibres
small u-shaped = short distance connections
fascicles = long distance connections within hemisphere
Projection fibres
afferent = carry sensory info from body to brain
efferent = carry motor impulses from brain & spinal cord
most travel through corona radiata
axons from corona radiate gathered into internal capsule
What type of fibers connect corresponding cortical areas in both hemispheres?
Commissural fibers.
e.g. corpus callosum
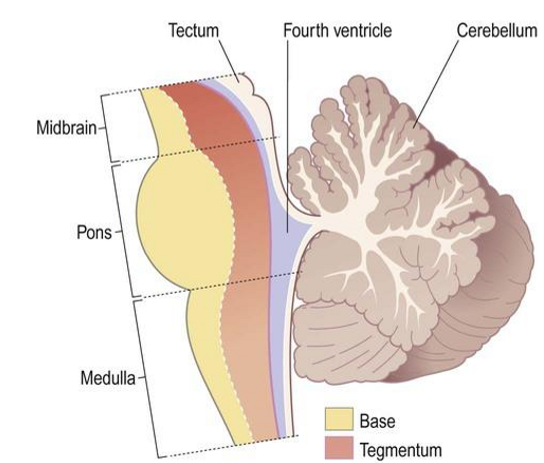
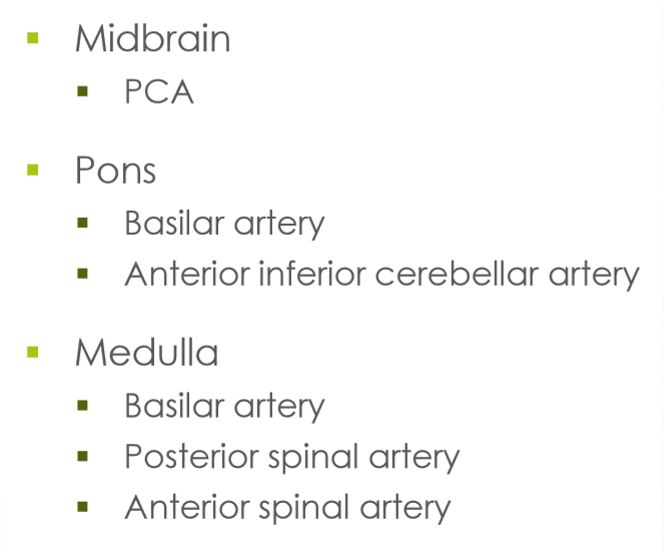
Brain stem divisions
midbrain
pons
medulla oblongata
Base - mainly descending axons
Tegmentum - nuclei of CN 3-12, reticular formation (brain stem reflexes e.g. cough, gag), ascending sensory tracts
What are the three layers of protective membranes covering the CNS?
Dura mater, Arachnoid mater, and Pia mater.
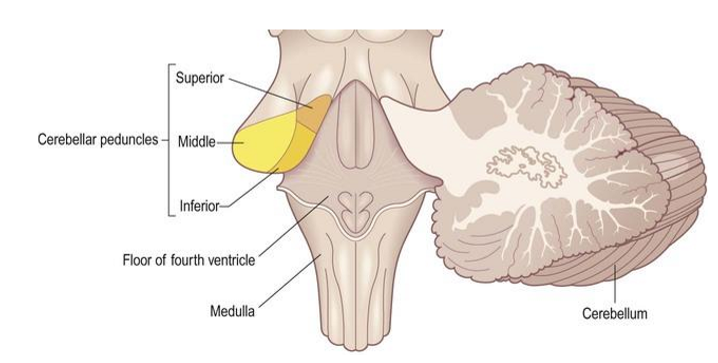
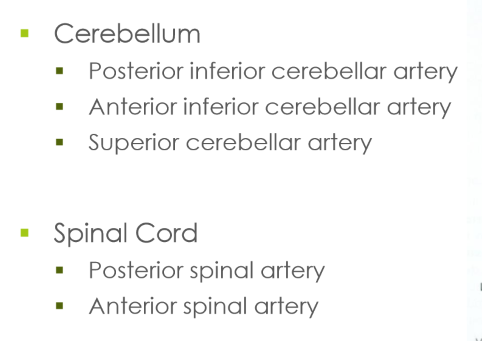
Cerebellum
2 cerebellar hemispheres, vermis connects them
outside = grey matter
inside = white matter
connected to brainstem by cerebellar peduncles
What part of the brain controls posture, muscle tone, and coordination?
Cerebellum.
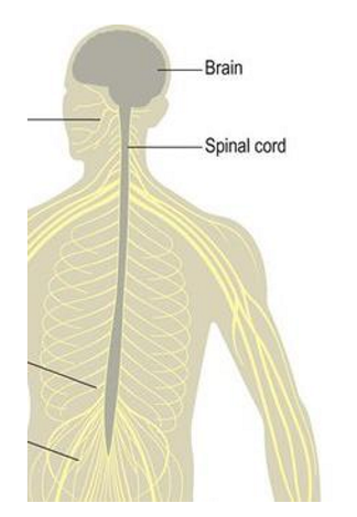
Spinal cord
continuation of brainstem
protected by vertebral column
What is the function of the spinal cord?
Transmission link between brain and body
motor info: brain to muscles, visceral organs, glands
somatosensory info: from periphery to brain
pain touch, temp
controls many body reflexes
Spinal cord structure
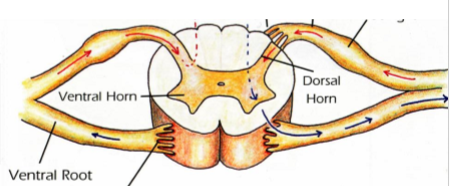
H-shaped core of grey matter
Outside = white matter
Ventral horn with ventral roots - motor axons to periphery
dorsal horn with dorsal roots - sensory axons bringing info to spinal cord
What is decussation in the context of the cerebrum?
The crossing of sensory and motor fibers at some point, resulting in contralateral processing.
Protective coverings of CNS
skull and vertebral column
cranial and spinal meninges
Cranial & spinal meninges
3 layers of protective membranes:
dura mater - tough, attached to inside of skull
arachnoid mater - resembles cobweb, doesn’t follow gyri and sulci
pia mater - delicate, follows surface of brain
What space lies between the arachnoid mater and pia mater?
Subarachnoid space, filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
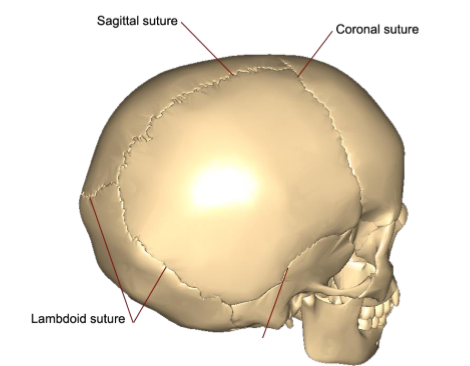
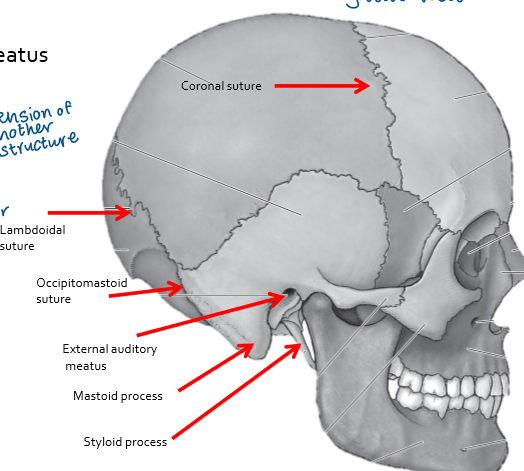
Sutures
Joints of the cranial bones, where different parts of the skull connect, appear as jagged lines
coronal
sagittal
lamdoidal
occipitomastoid
Foramen
Hollow passage way, opening
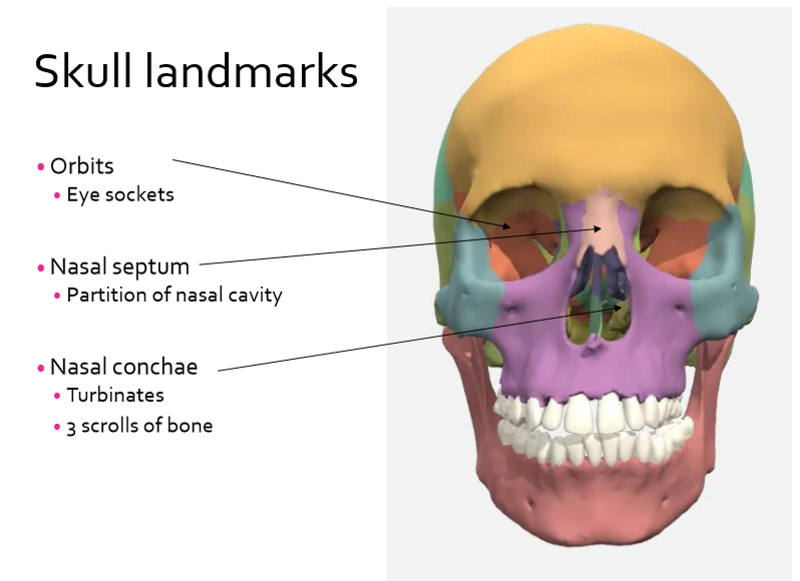
Skull landmarks
orbits
nasal septum
nasal conchae
frons - forehead
occiput - posterior (back of head)
vertex - superior (highest point)
Temporae - temple
Skull landmarks continued
calvaria - skullcap
cranial fossa - anterior, medial, posterior
foramen magnum - spinal cord, vertebral arteries, spinal arteries
external auditory meatus - ear canal
mastoid process
styloid process
sutures: coronal, sagittal, lamdoidal, occipitomastoid
Cranial bones
8 in total:
frontal
temporal x2
parietal x2
occipital
ethmoid
sphenoid
protects the brain
attachment for membranes and muscles
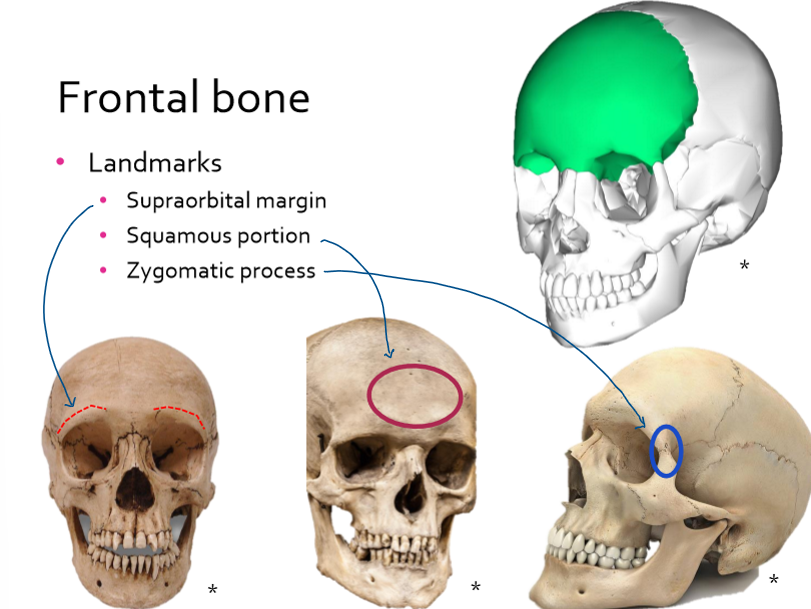
Frontal bone landmarks
supraorbital margin
squamous portion
zygomatic process
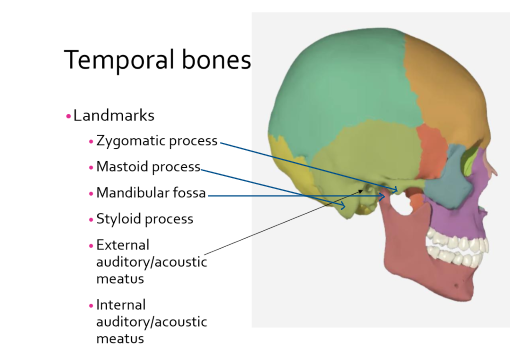
Temporal bones landmarks
zygomatic process
mastoid process
mandibular fossa
styloid process
external auditory/acoustic meatus
internal auditory/acoustic meatus
Parietal bones
forms the sides and roof of the cranium/skull
sagittal suture
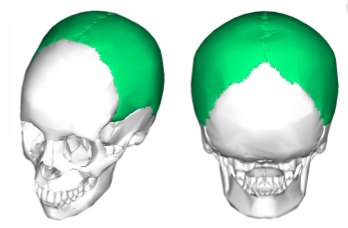
Occipital bone landmarks
foramen magnum - hole that allows brain stem and vessels through
occipital condyles - rounded areas which allow connection to the vertebrae, allow head to move in different ways, forms joint with vertebrae
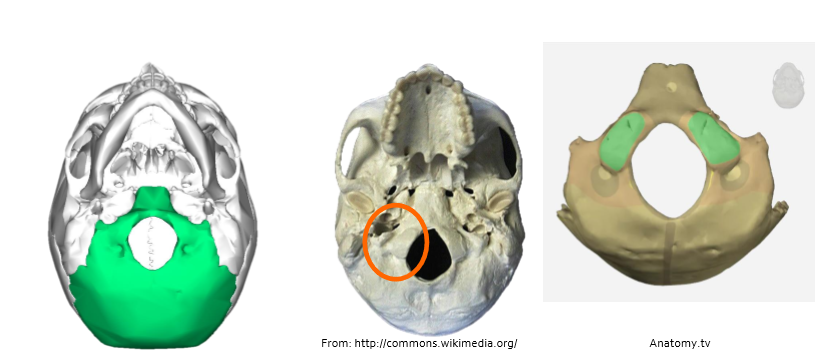
Sphenoid bone
forms bottom bits of orbits
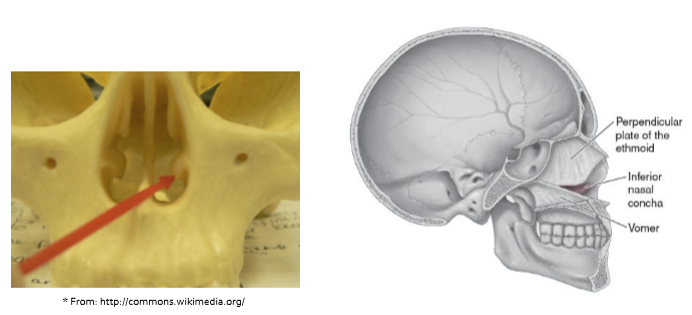
Ethmoid bone
rests on top of sphenoid bone
perpendicular plate which helps form nasal septum
Facial bones
14 in total, majority have left and right
maxillae x2
mandible
zygomatic x2
nasal x2
palatine x2
lacrimal x2
vomer
inferior nasal concha x2
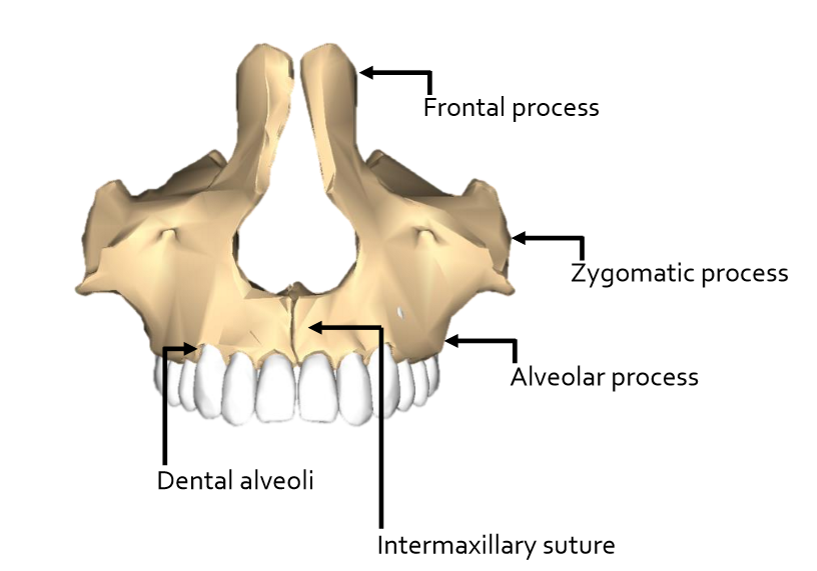
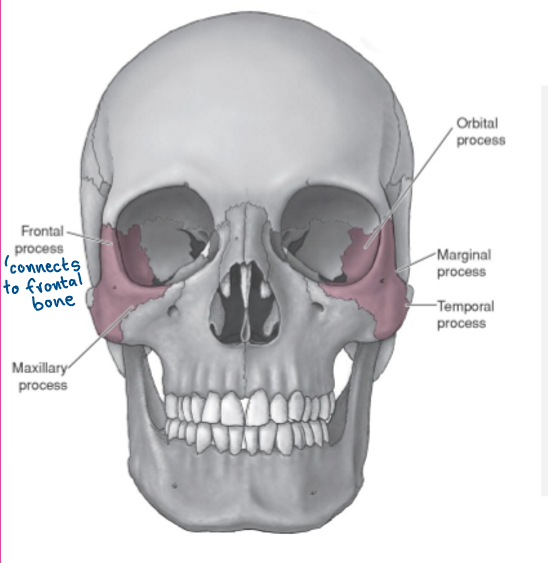
Maxillae landmarks
upper jaw - forms anterior 2/3 of hard palate
zygomatic process
frontal process
alveolar process - houses upper teeth
intermaxillary suture- where the L & R sections meet
palatine process
incisive foramen
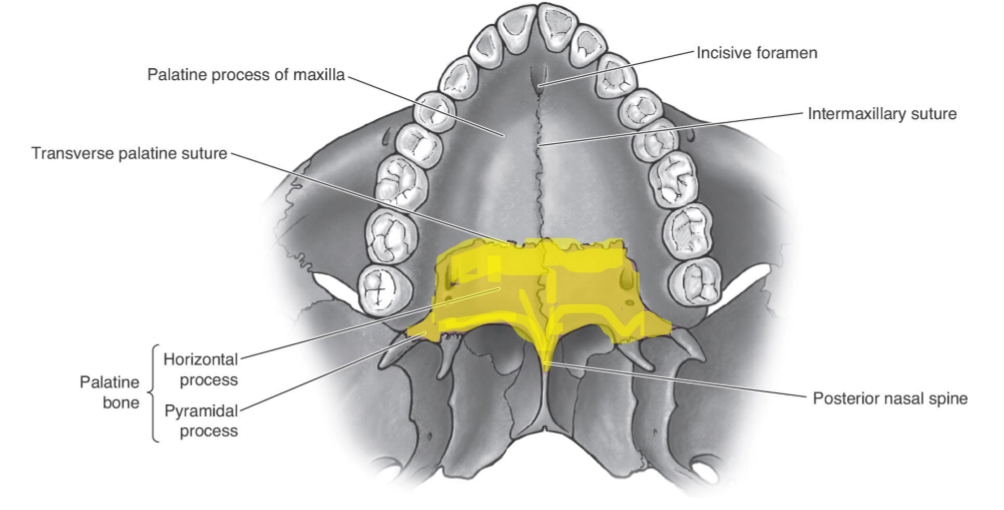
Palatine bones
form posterior 1/3 of hard palate
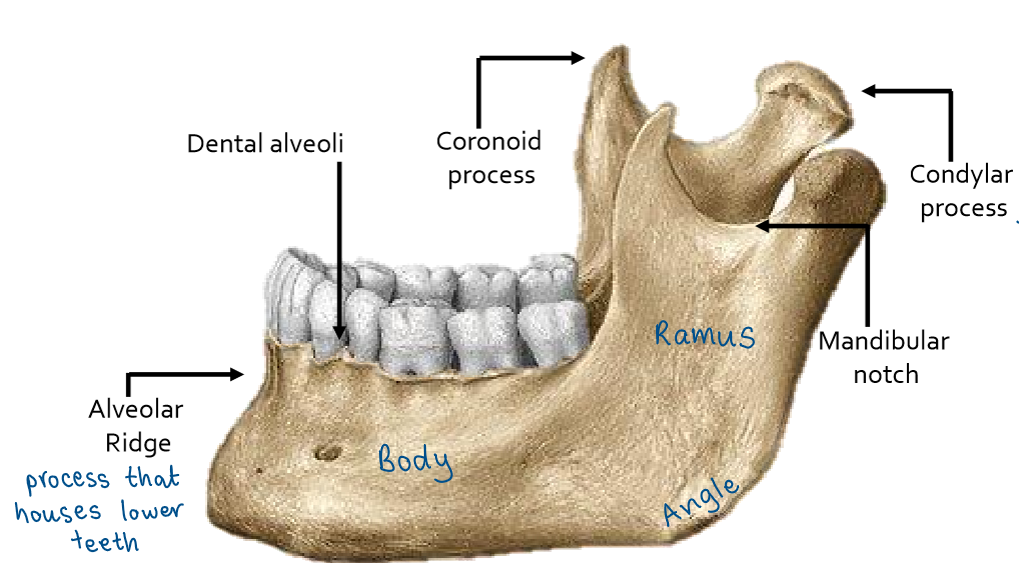
Mandible landmarks
lower jaw bone
body
angle
ramus - coronoid process, condylar process, mandibular notch
Mandible landmarks cont.
mental symphysis
mental protuberance
mental tubercles
alveolar ridge - dental alveoli
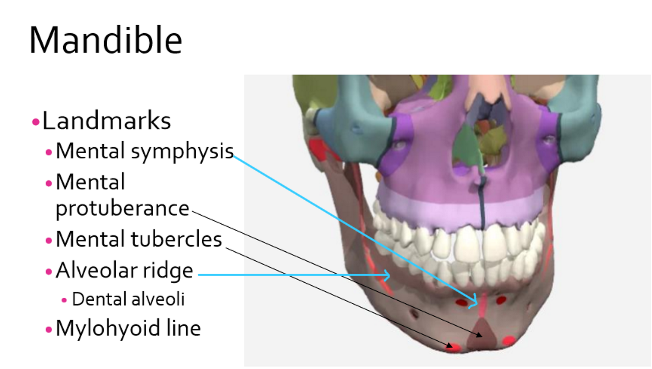
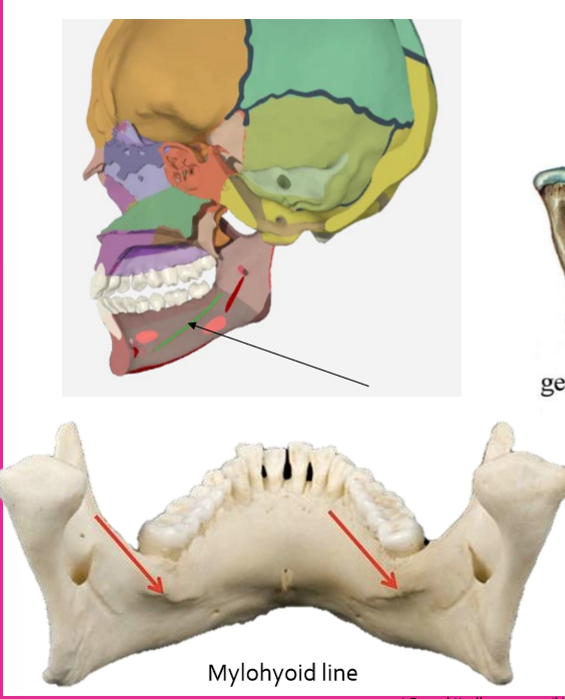
Mandible - mylohyoid line
important for speech and swallowing
connects all the way inside the mandible
Zygomatic bones
cheekbones
helps form orbits and cheeks, allow for attachment of muscles
Nasal bones
form bridge of nose
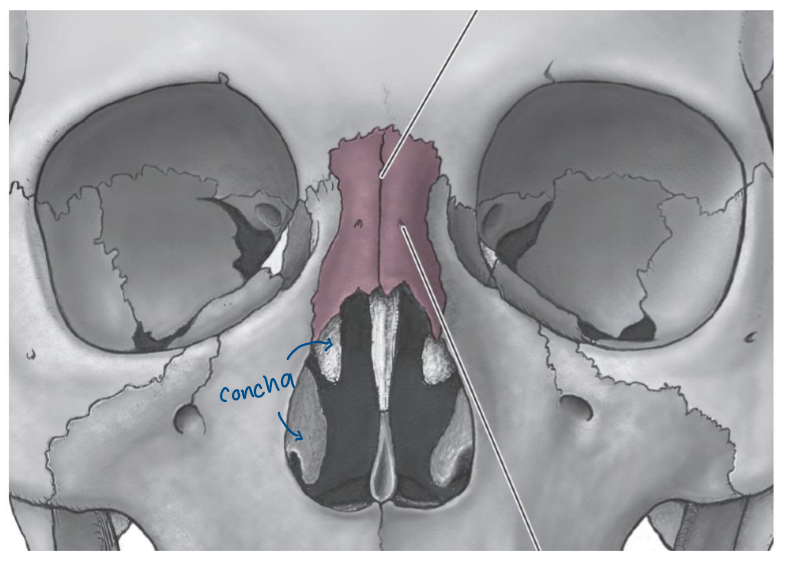
Inferior nasal concha
Lacrimal bones
help form orbits
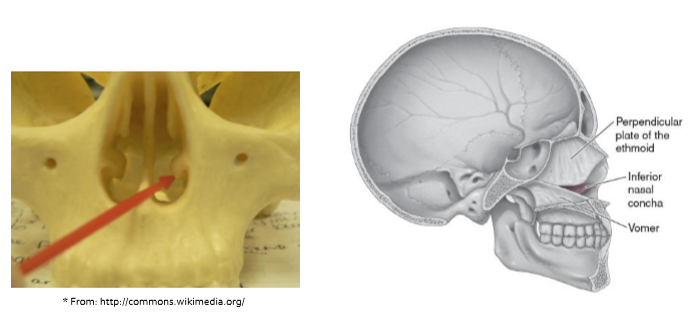
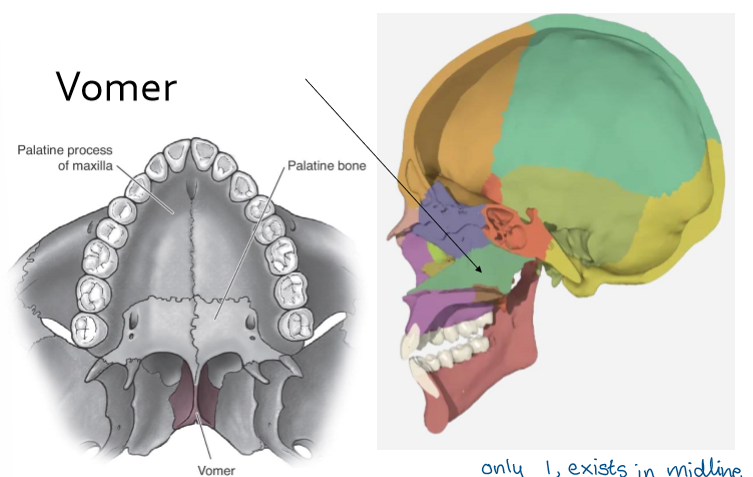
Vomer
helps form nasal septum
exists in midline
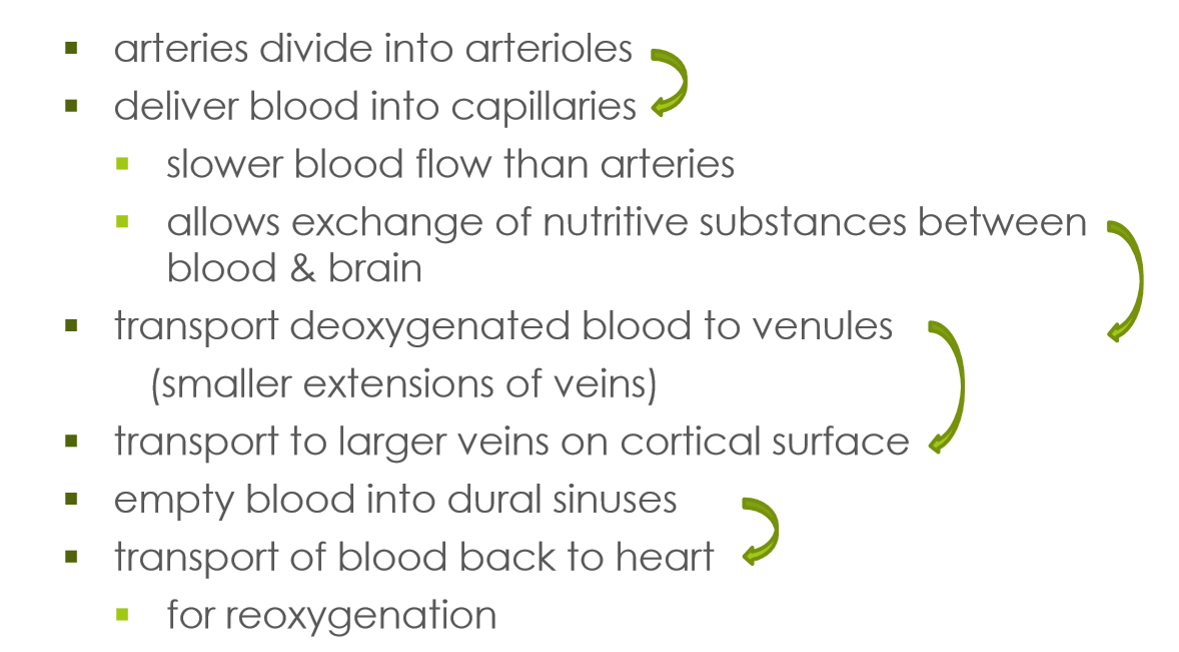
Arteries
carry oxygenated blood to brain or tissue
Veins
return deoxygenated blood back to heart
Capillaries
very small blood vessels between arteries and veins that distribute oxygen-rich blood to the body
join arterial system to venous system, allowing exchange of oxygen and nutrients
Vascular network - aorta
main artery
carries blood from left ventricle to all parts of body (except lungs)
Aortic arch divides into 4 branches
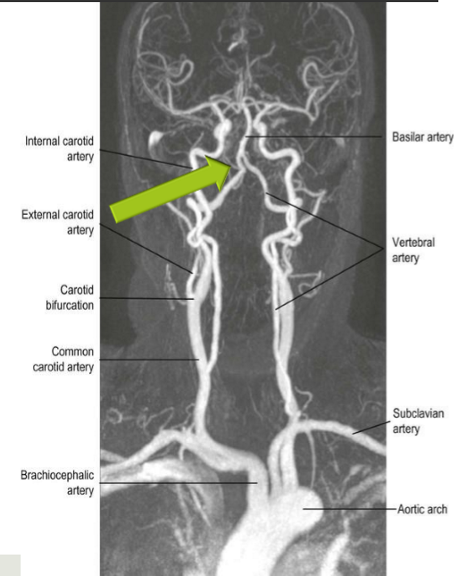
2 carotid arteries: internal and external carotid
2 subclavian arteries: left and right vertebral arteries
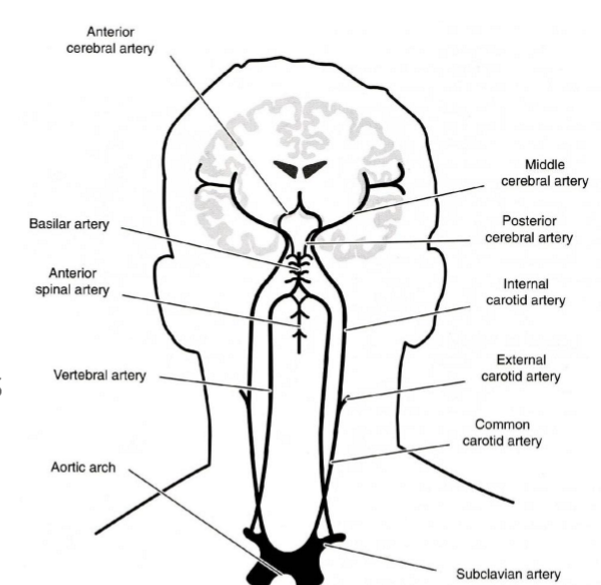
What two arterial systems supply blood to the brain?
Internal carotid arteries (anterior - towards the front)
vertebral arteries (posterior - towards the back)
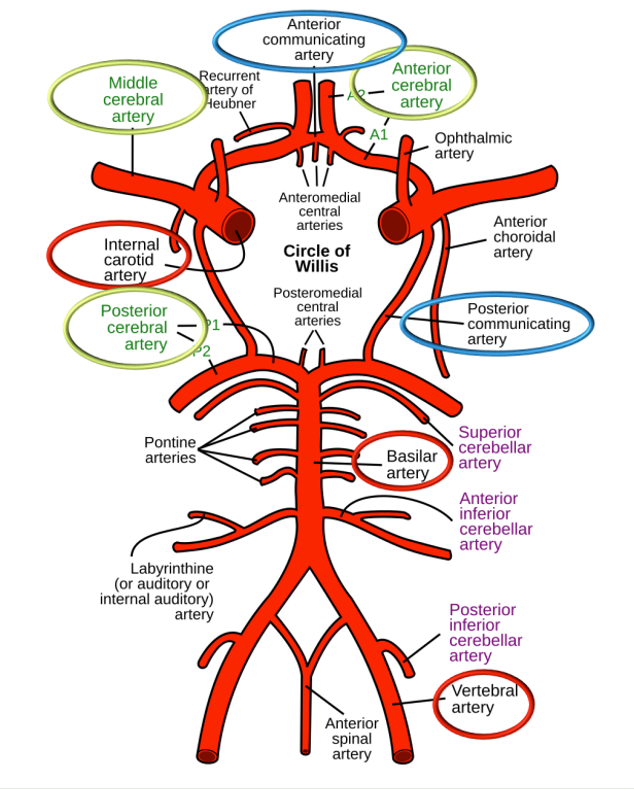
Internal carotid arteries
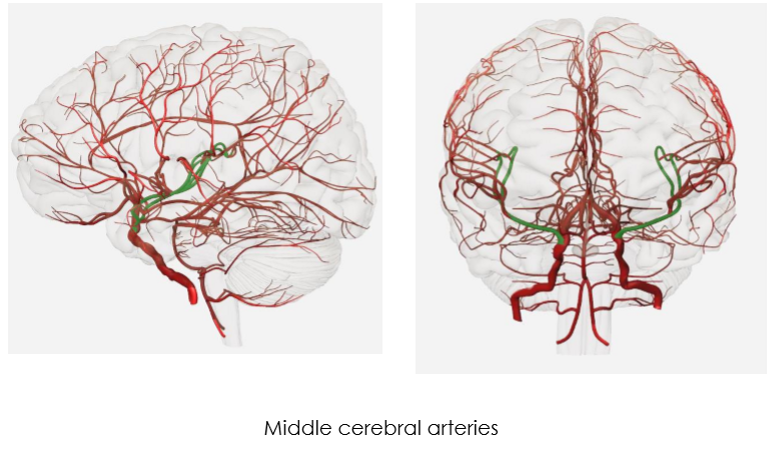
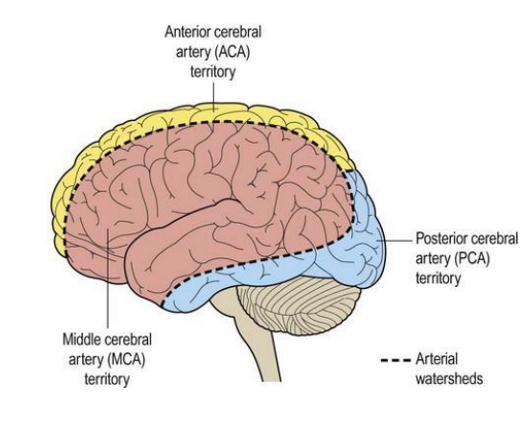
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)
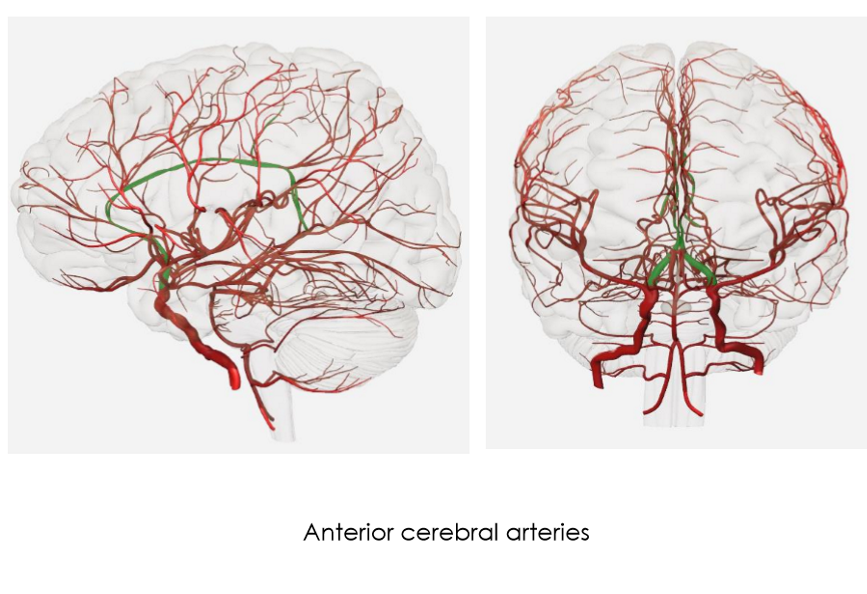
Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA)
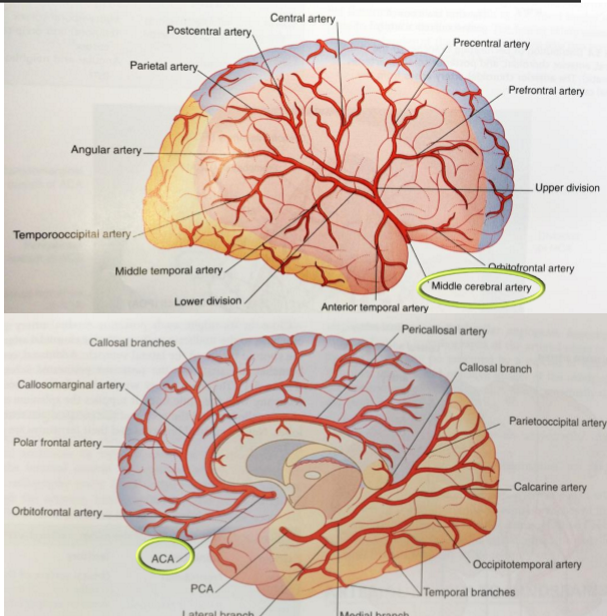
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)
supplies lateral surface of frontal, parietal & temporal lobes
comes up sylvian fissure
supplies 80% of carotid blood
major areas for: motor and sensory functions, speech
Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA)
supplies medial surface of frontal & parietal lobes, corpus callosum, basal ganglia
much smaller than MCA
supplies 20% of carotid blood
Vertebral arteries
give off numerous branches that supply: spinal cord, medulla, pons, midbrain & cerebellum
at lower border of pons: merge to form 1 basilar artery (in front of brain stem), then divide into 2 posterior cerebral arteries (PCA)
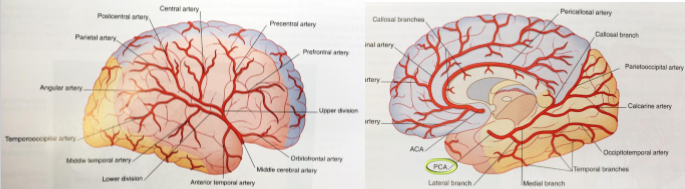
Posterior cerebral arteries (PCA)
supplies lateral & inferior temporal lobes
supplies lateral & medial occipital lobes
Watershed areas
Vascular border zones
where small-end branches of cerebral arteries approach each other
Circle of Willis (CoW)
at base of brain, arteries linked by communicating vessels
connects posterior supply of brain to anterior supply
Provides some redundancy, if blockage in one vessel another vessel can supply blood, allows blood to move from right side to left side and front and back of brain
Brainstem’s blood supply
Cerebellar & Spinal Cord blood supply
Vascular network
Function of blood
supplies nutrition: glucose and oxygen
remvoes metabolic waste
Why do neurons need an uninterrupted supply of oxygenated blood to function?
can’t store glucose and oxygen sources
Cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
stroke
brain damage caused by sudden vascular disruptions
2 main types: ischemia and hemorrhage
Ischemia
blocked artery resulting in part of brain losing blood supply
most common type of CVA’s, > 80%
2 types: thrombosis and embolism