Dynamic Equilibrium: Reactivity 2.3
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Define dynamic equilibrium
A state in reversible reactions where:
the continuous forward and reverse reaction rates are equal. (Ratef=Rater)
the concentration of reactants and products remains constant. ([R]=[R] & [P]=[P])
in a closed system.
Define equilibrium
A state in which reactant and product concentrations remain constant.
equation for rate
(Change in concentration)/ (change in time)
difference between equal and constant
equal is used when comparing two things
constant is used when comparing something to itself
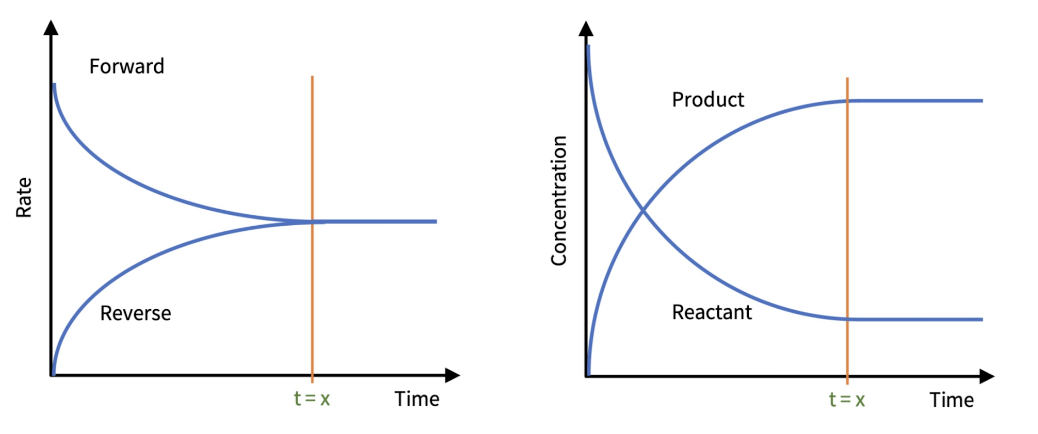
Explain why the forward curve is above the reverse curve at the start.
because its at maximum rate due to the reactants having maximum concentration and therefore more frequent collisions happening.
Define irreversible reaction
reactants can form products, but products cannot form reactants
State three situations with irreversible reactions.
Reactions that produce gaseous products in an open system
Reactions that produce solid precipitates
Reactions between a strong acid and strong base
Explain why reactions that produce gaseous products in an open system are irreversible reactions.
Once released into the surrounding, gaseous particles are too far apart to collide with each other and react back into its reactant.
State an example of an irreversible reaction where the reaction produces a gaseous product in an open system.
2Na(s)+2HCl(aq)→2NaCl(aq)+H2(g)
State an example of an irreversible reaction where the reaction produces a solid precipitate
Pb(NO3)2(aq)+2Kl(aq)→Pbl2(s)+2KNO3(aq)
State an example of an irreversible reaction where the reaction is between a strong acid and strong base.
HCl(aq)+NaOH(aq)→NaCl(aq)H2O(l)
Define acids.
Substance that produces H+ when dissolved in water.
Define bases.
Substance that produces OH- when dissolved in water.
Define strong acids and bases.
Acids and bases that undergo 100% dissociation.
Define weak acids and bases.
Acids and bases that do not undergo 100% dissociation.
Explain 100% dissociation.
Breaking up of 100% of a compound into simpler constituents
State an example of a strong acid.
HCl → H++Cl-
State an example of a strong base.
NaOH→Na+ + OH-
Define reversible reactions.
Reactions that have both forward and reverse reactions simultaneously.
Define physical reactions.
Reactions that result in ONLY a change in the reactant’s state
Define chemical reactions.
Reaction in which valence electrons are transferred to break bonds of the reactant and form new bonds for the products.
State an example of a physical reaction/ system.
Br2(l)⇌Br2(g)
State an example of a chemical reaction/ system.
2NO2(g)⇌2NO(g)+O2(g)
State the two types of reversible reactions.
physical reaction
chemical reaction
Explain saturated solutions using equilibrium.
dissolution rate = precipitation rate (at dynamic equilibrium) due to maximum amount of dissolved solute
Explain unsaturated solutions using equilibrium
Can dissolve more solute until saturation is reached.
Not in equilibrium state.
State the observations of a reaction at equilibrium state at a macroscopic level:
No observable changes in the system’s properties
State the observations of a reaction at equilibrium state at a microscopic level:
continuous interconversion of reactants and products
Define heterogenous equilibrium
Reaction at an equilibrium state with reactants of different phases.
Define homogenous equilibrium.
Reaction at an equilibrium state with reactants of same phases.
Define equilibrium position
Proportion of reactant and product in an equilibrium mixture (percentage)
Explain the phrase “lie to the right” in terms of equilibrium position.
Products>reactants
Explain the phrase “lie to the left” in terms of equilibrium position.
Reactants> products