Anatomy midterm JOINTS AND MUSCLES
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
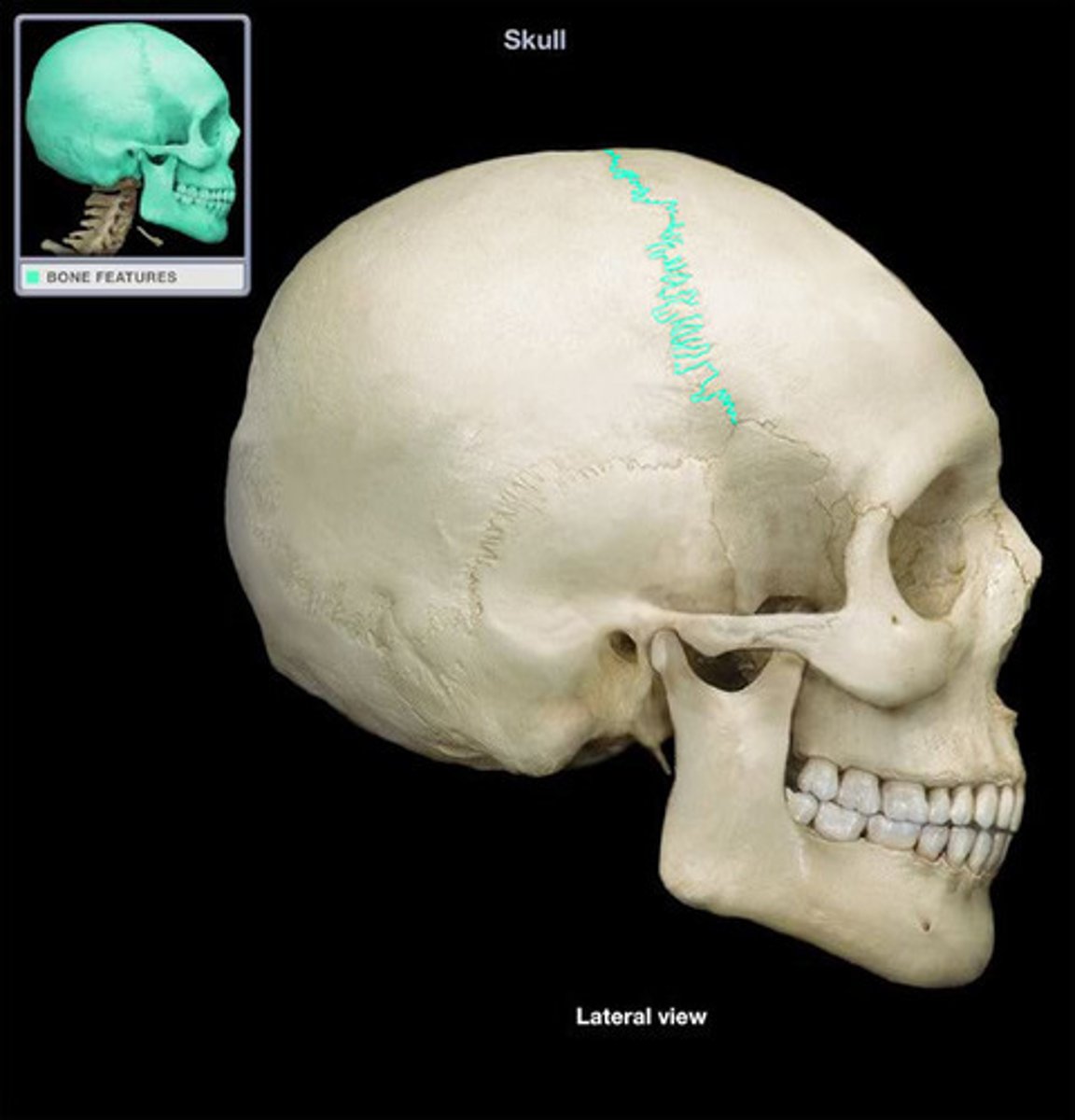
Synarthrosis
An immovable joint.
Example: Cranial Bones
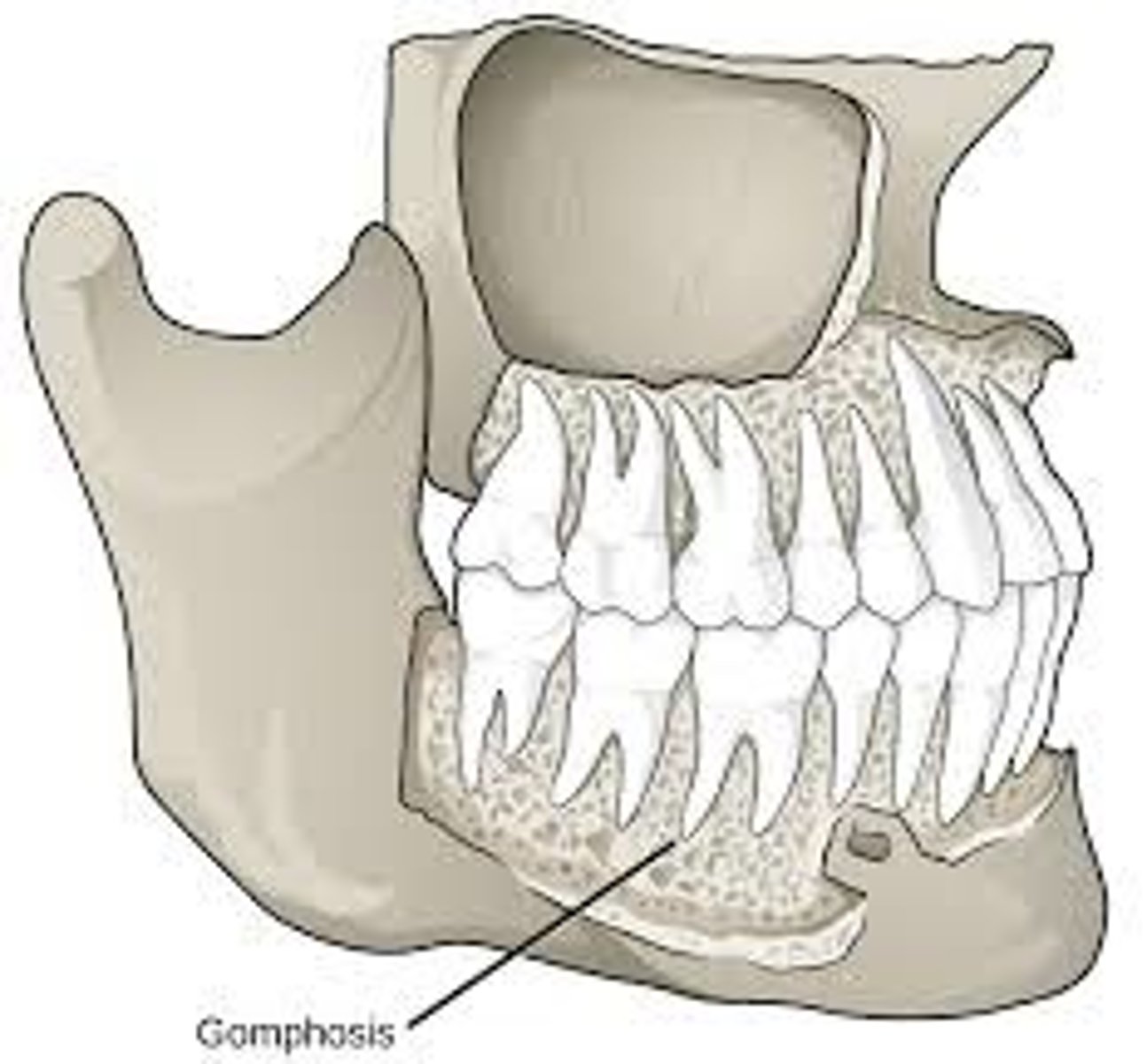
Gomphoses (fibrous)
Peg-in-socket joints of teeth in alveolar sockets
Fibrous connection is the periodontal ligament
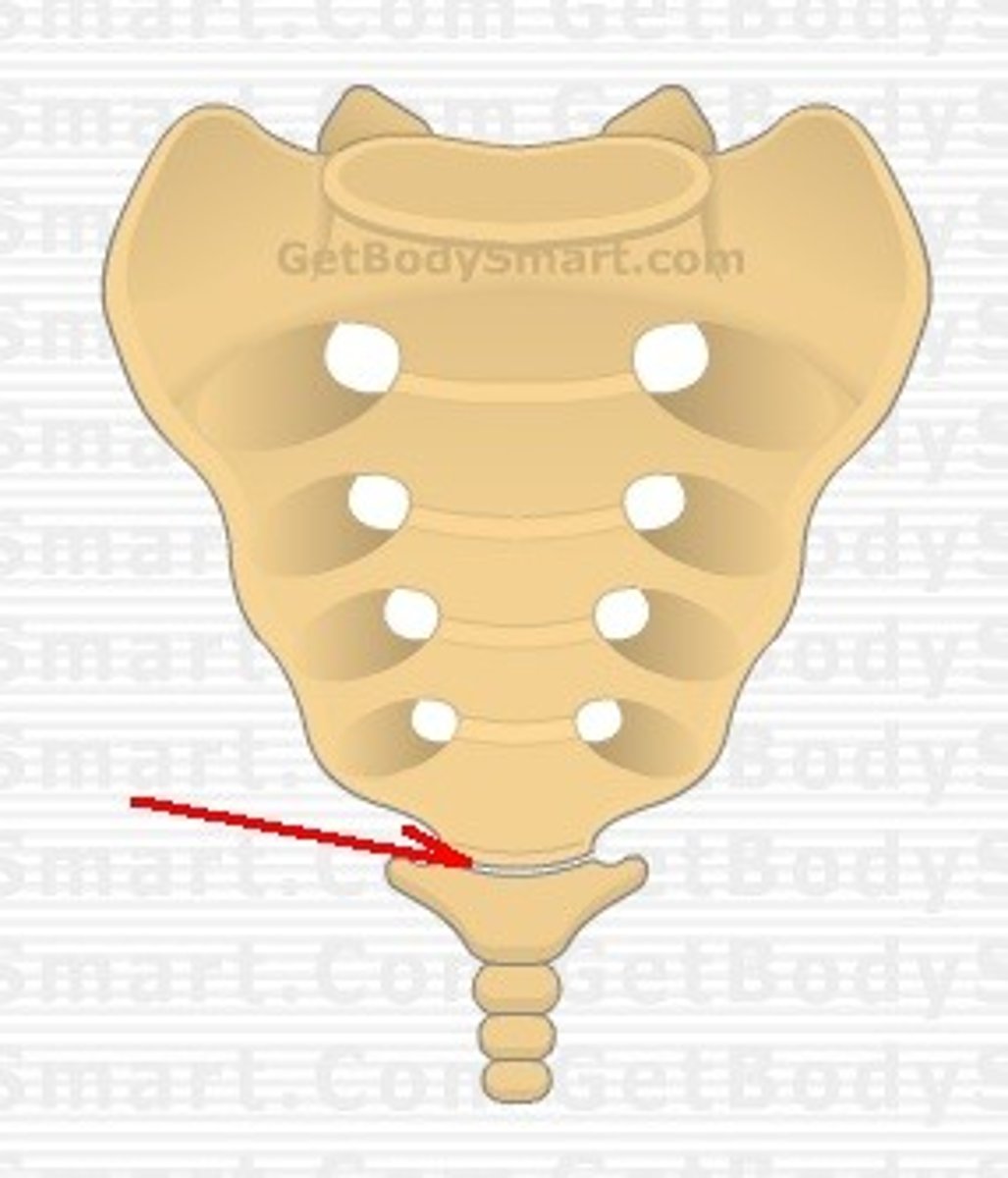
synchondrosis (cartilaginous joint)
an almost immovable joint between bones bound by a layer of cartilage, as in the vertebrae.
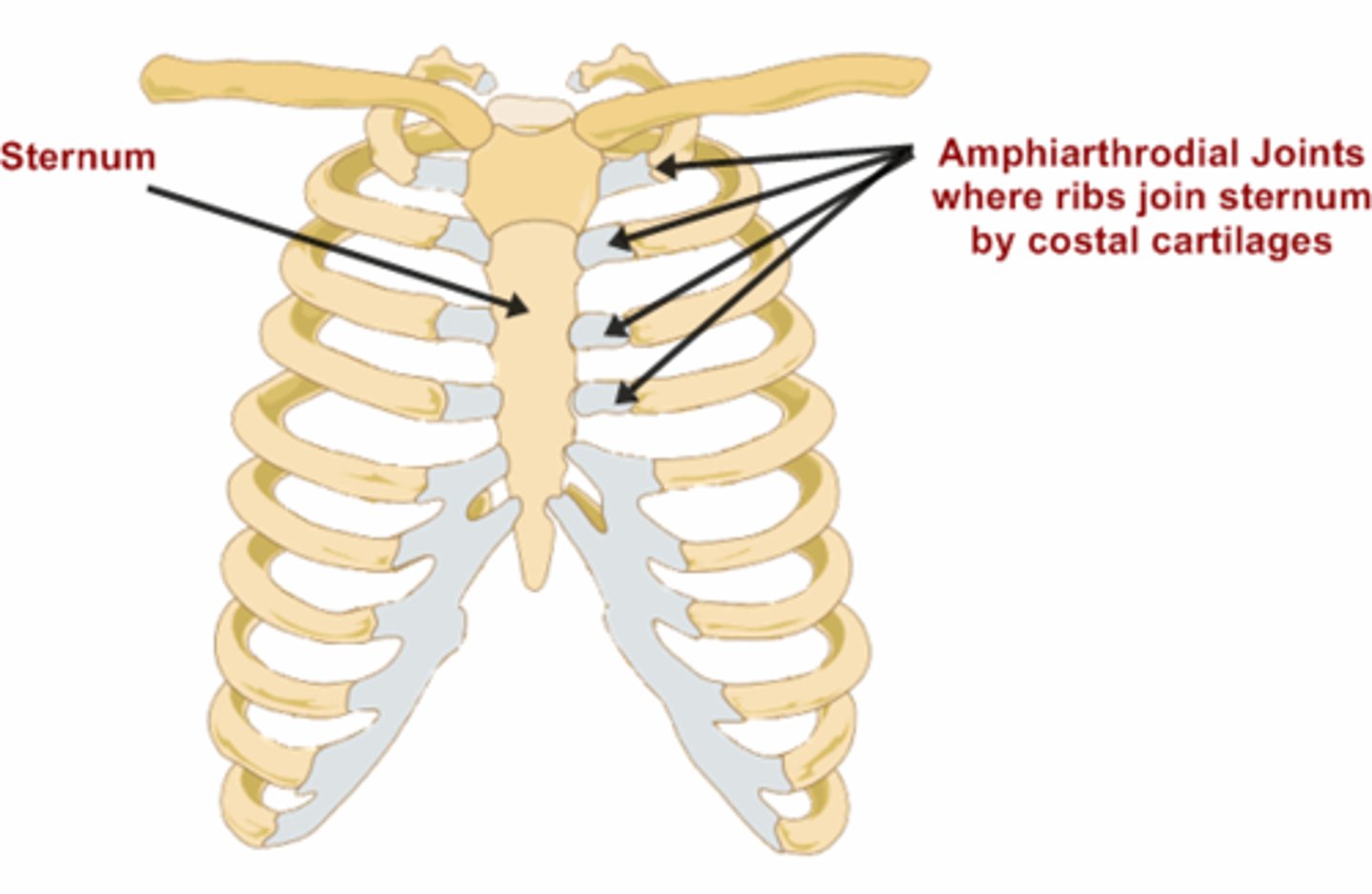
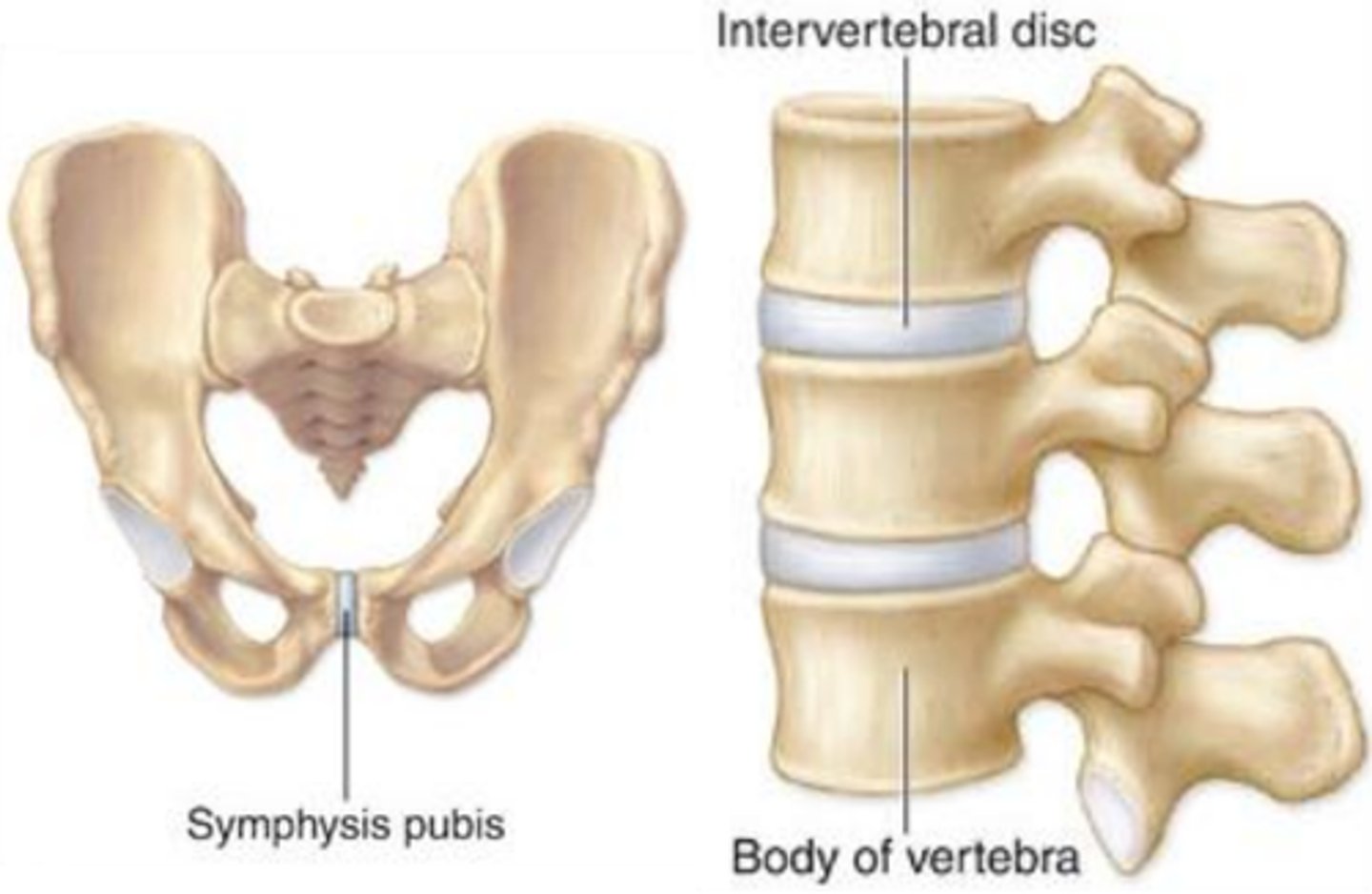
Amphiarthrosis
slightly movable joint
ex. pubic symphysis
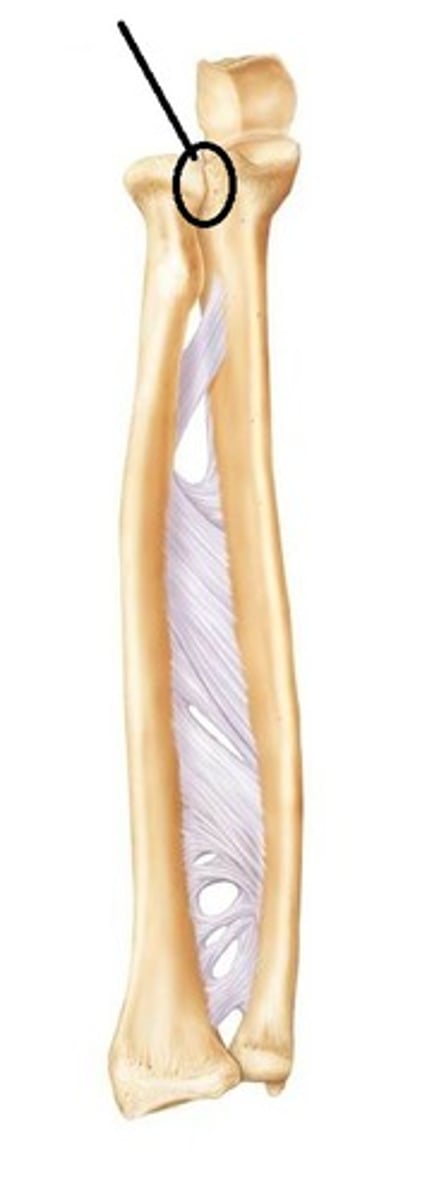
sydesmosis joint (fibrous)
a fibrous joint at which two bones are bound by relatively long collagenous fibers

symphysis joint (cartilaginous)
bones grow together with cartilage and function as one
diarthrosis joint (synovial)
freely movable joint
synovial fluid
joint-lubricating fluid secreted by the synovial membrane
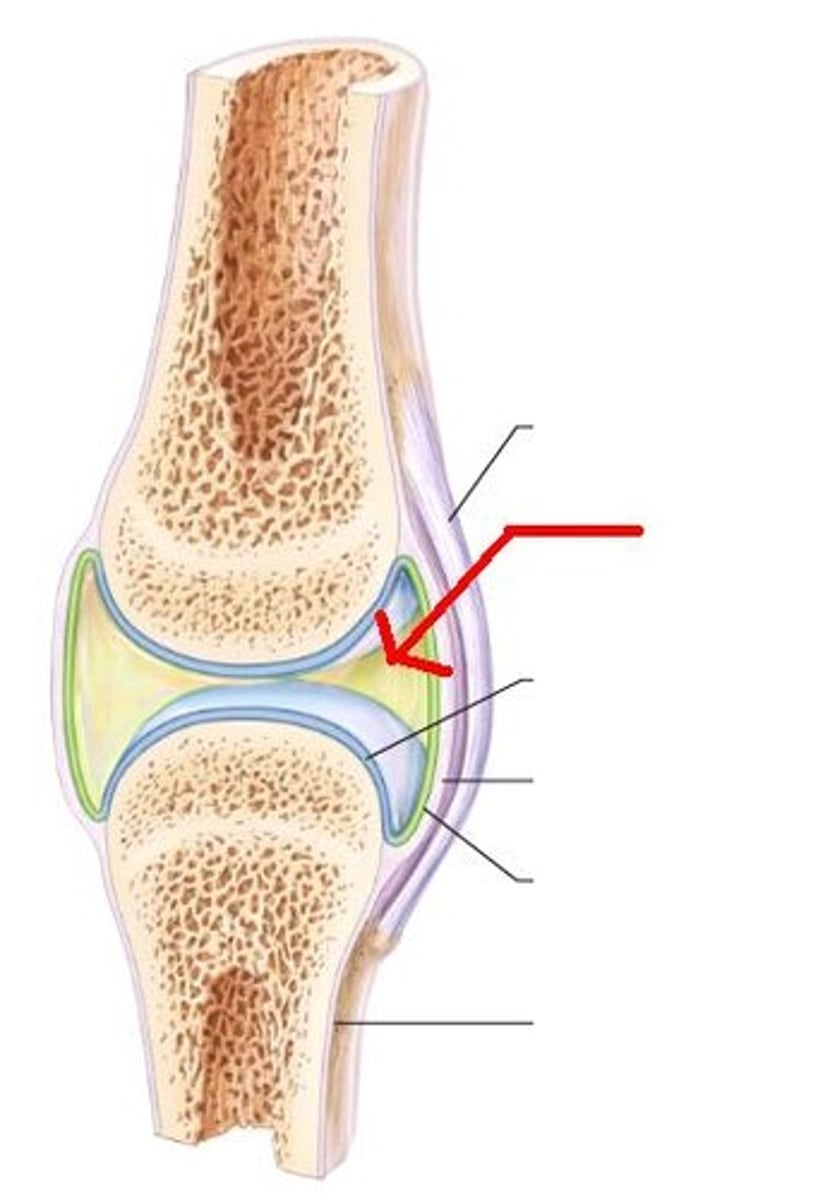
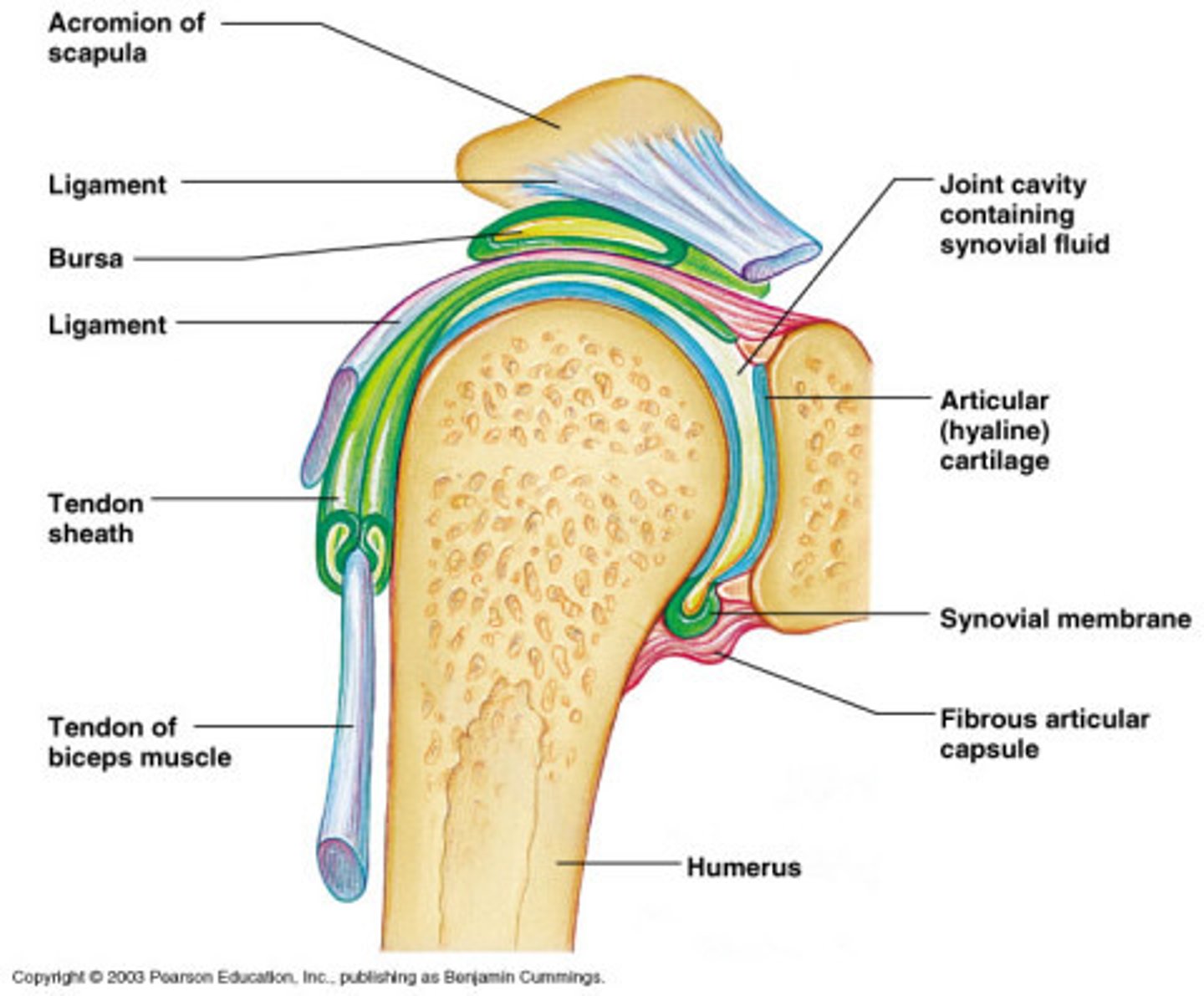
articular capsule of synovial joint
connects bones and encloses synovial cavity
2 layers:
fibrous capsule - outer layer; dense irregular connective tissue; attaches to periosteum; flexible yet strong; some portions form bundles called
ligaments
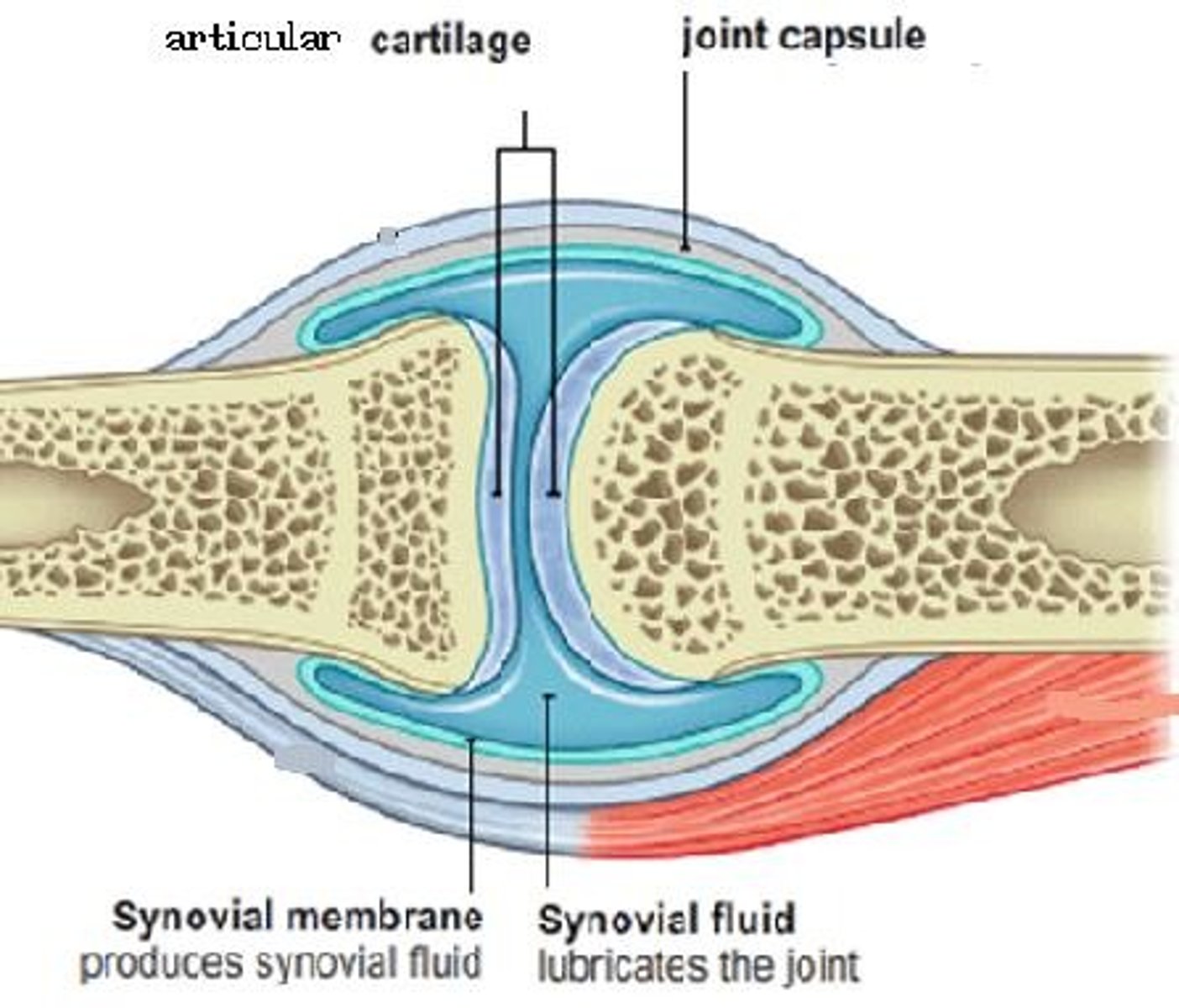
synovial membrane
membrane lining the capsule of a joint, secretes synovial fluid
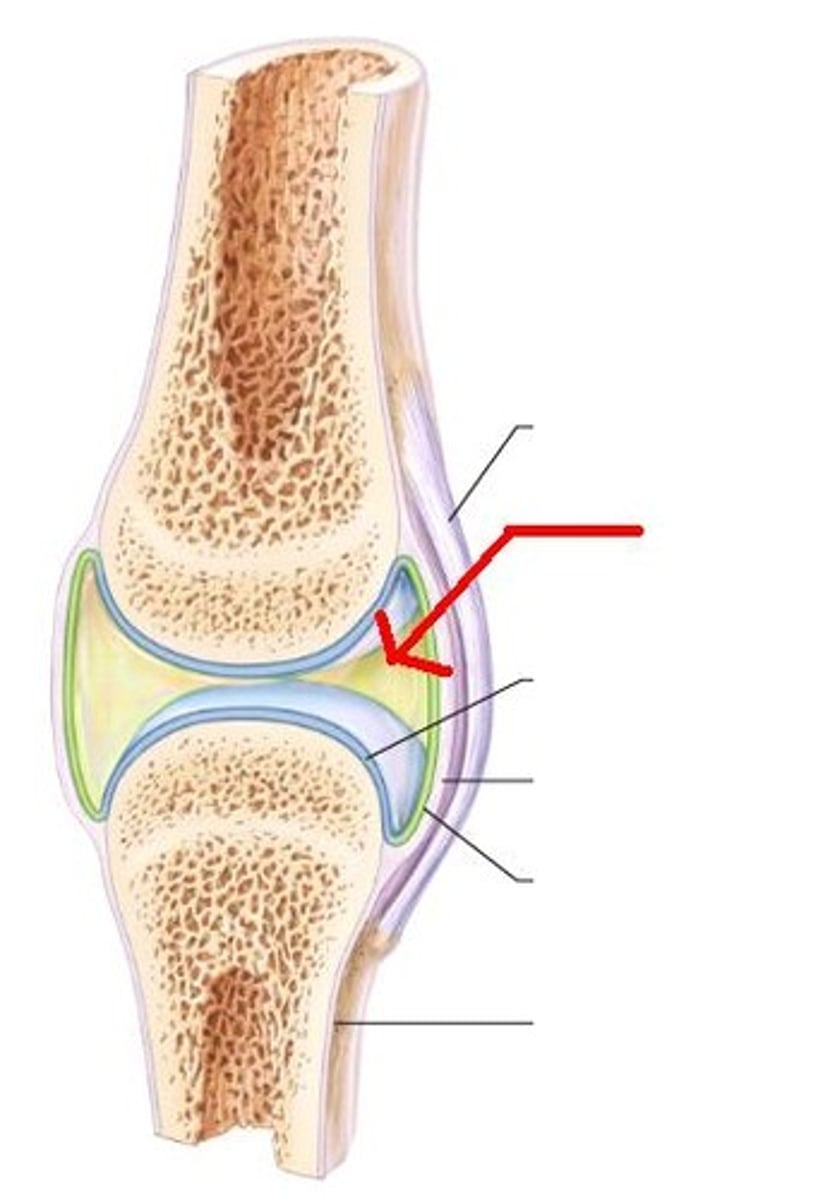
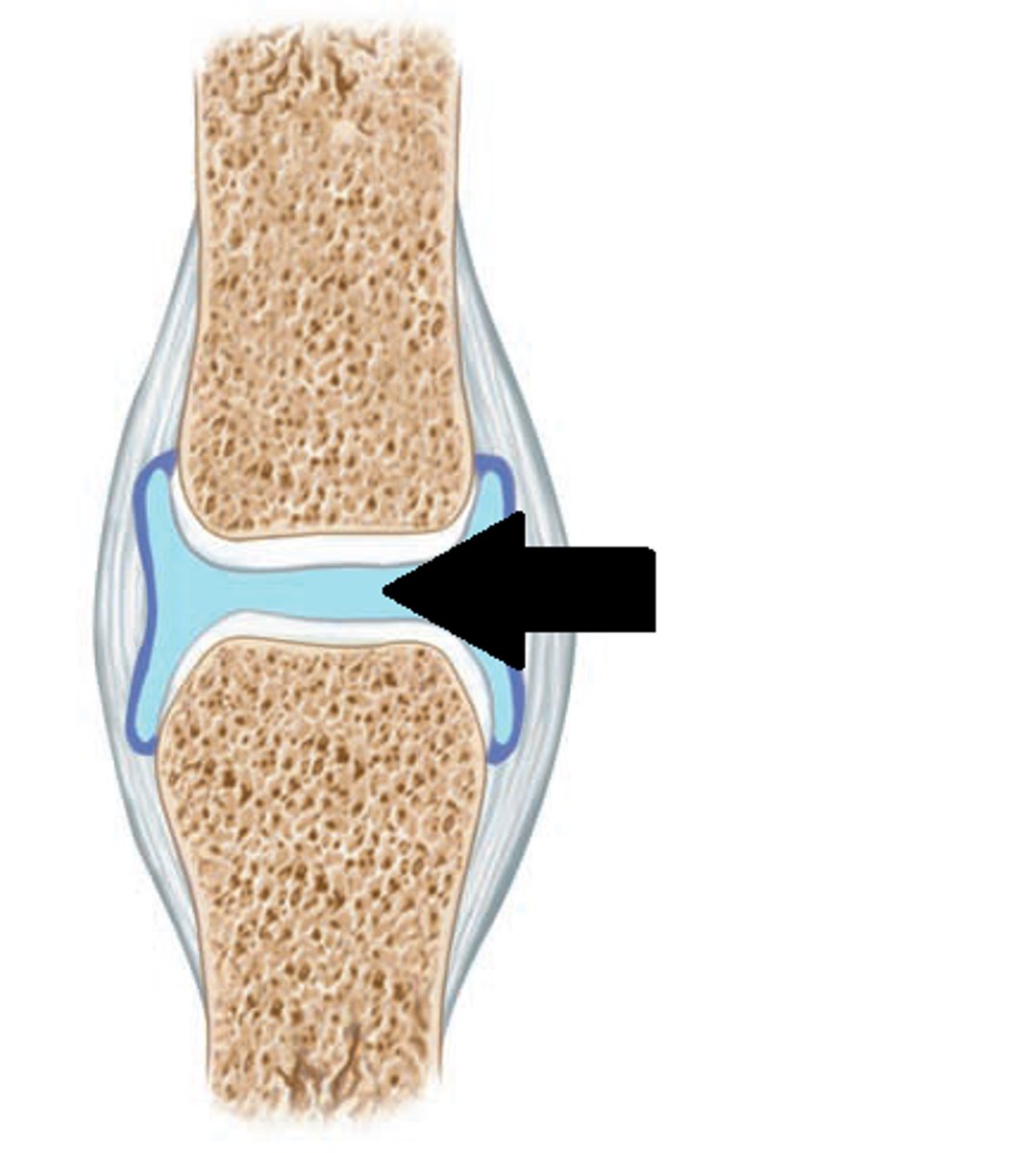
synovial cavity
space between bones at a synovial joint; contains synovial fluid produced by the synovial membrane
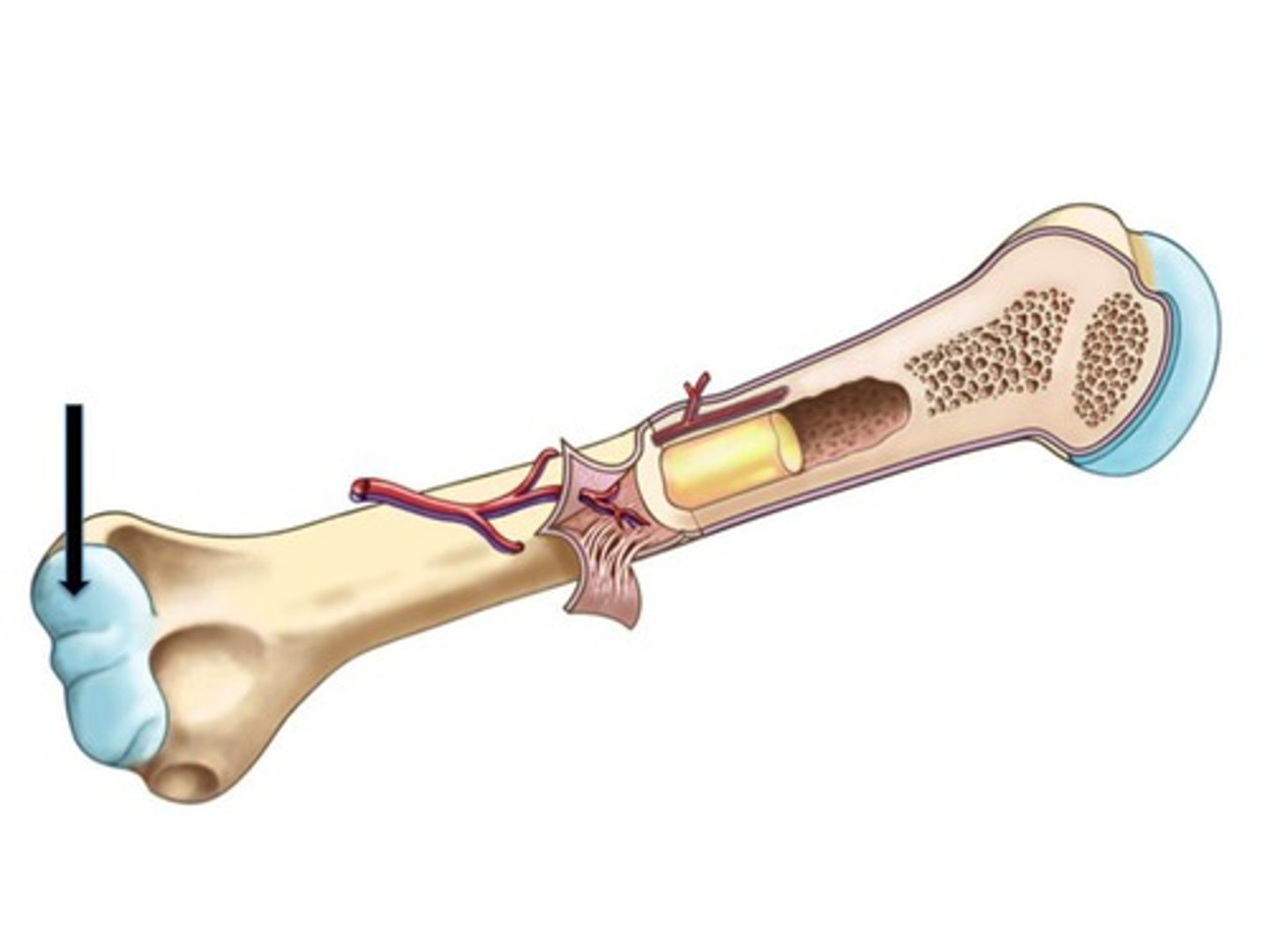
articular cartilage
covers the surfaces of bones where they come together to form joints
fat pads
superficial to the joint capsule, protect articular cartilages
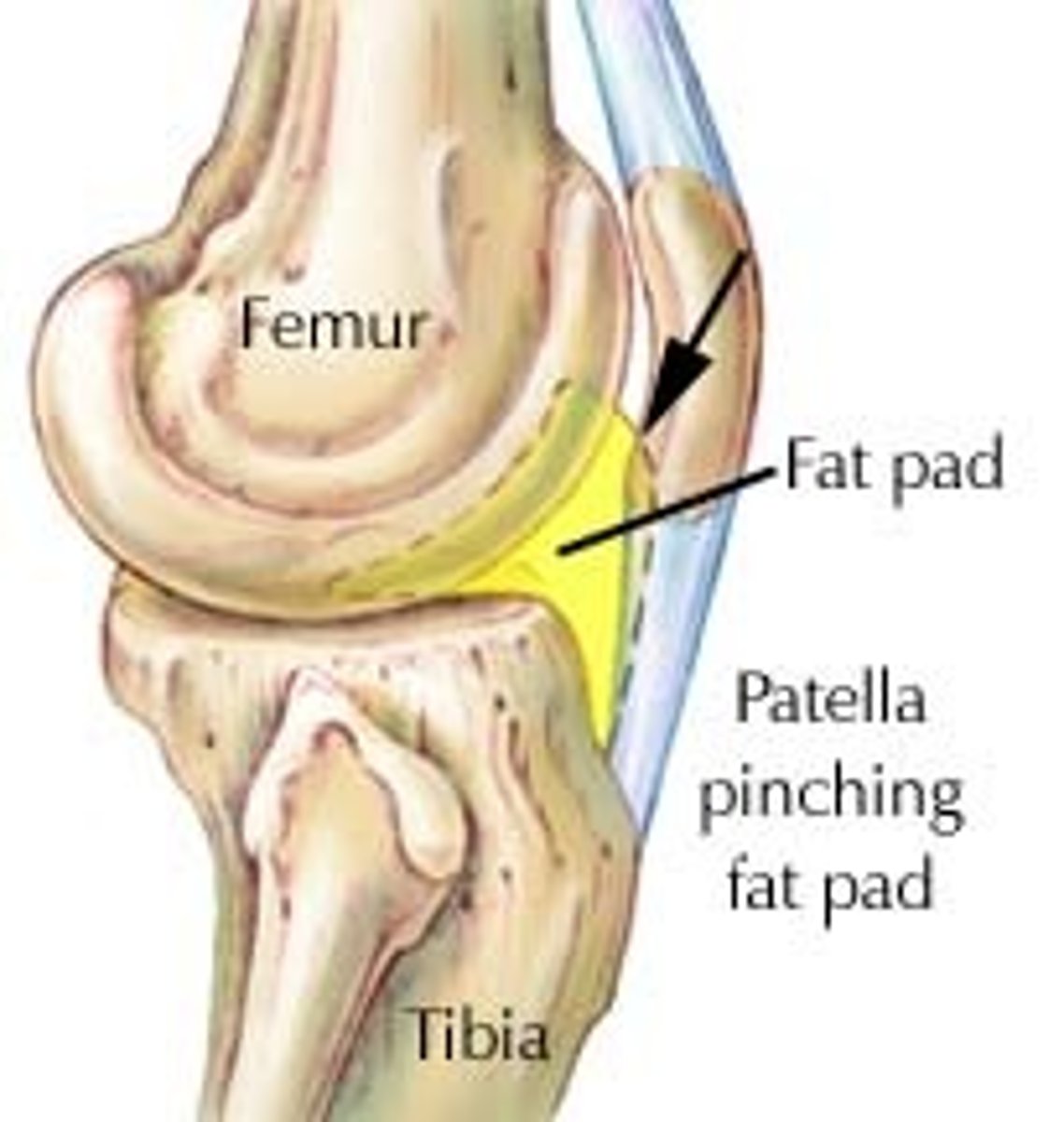
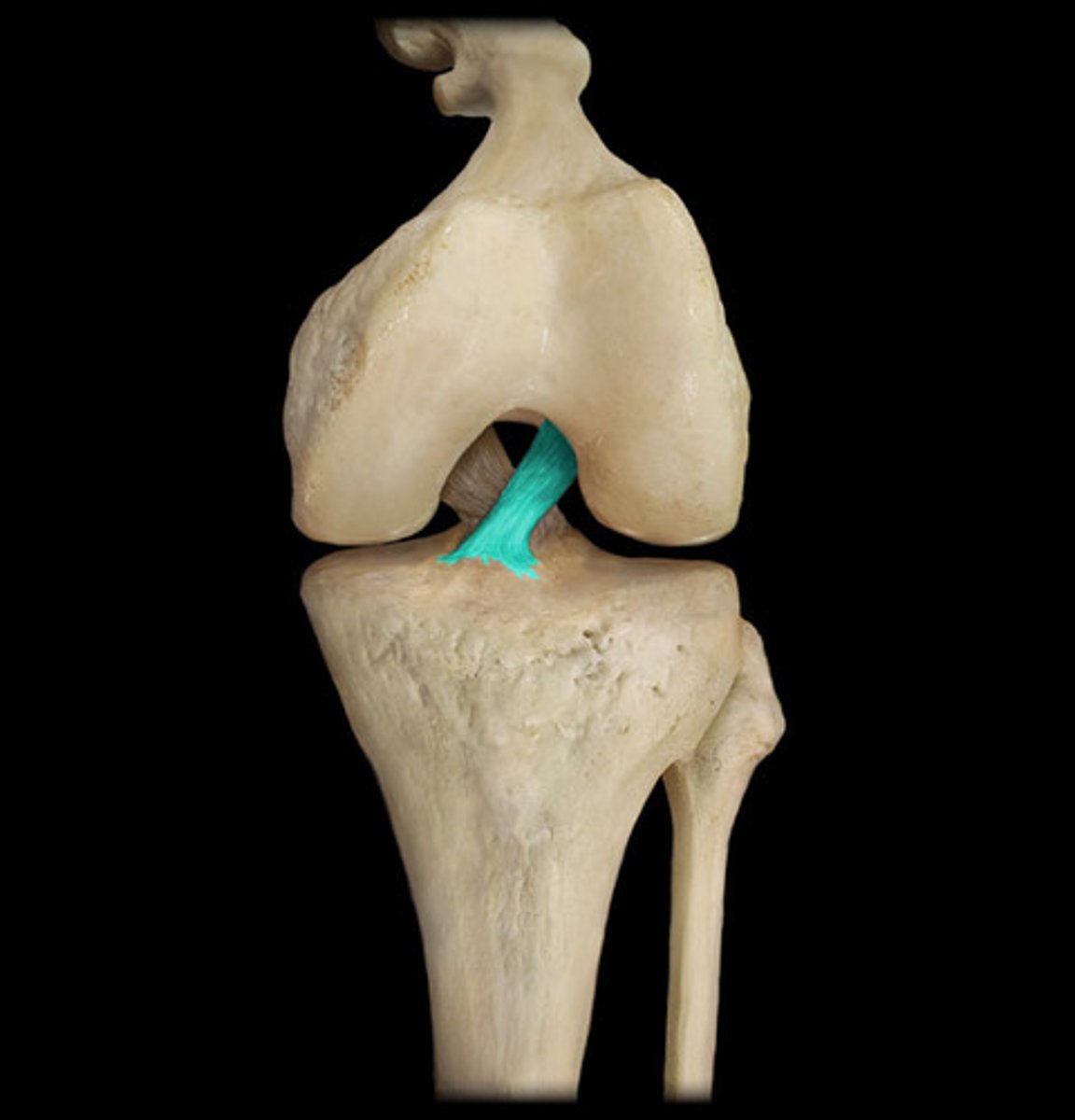
meniscus (disc)
plate of fibrocartilage partially or completely dividing a joint cavity
Bursae
flattened fibrous sacs lined with synovial membrane and containing a thin film of synovial fluid
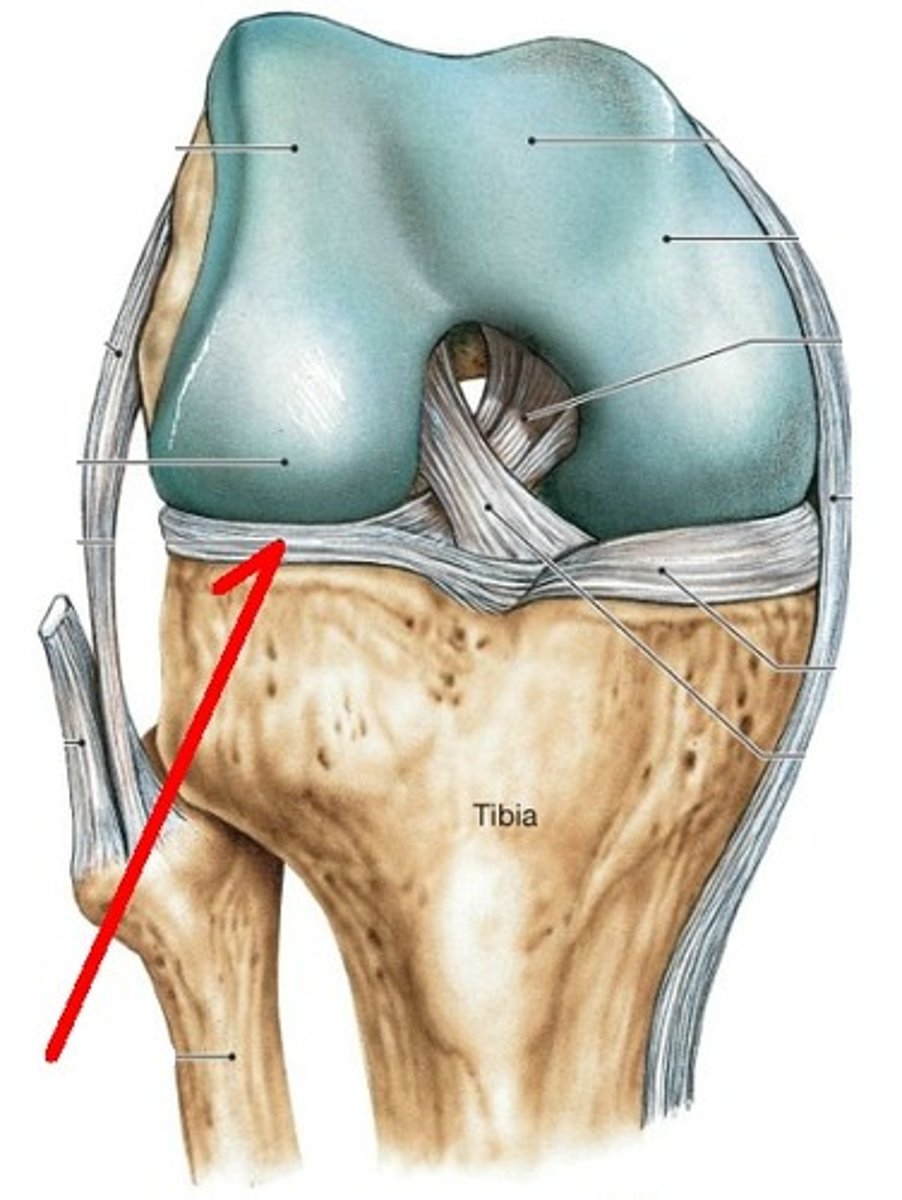
Ligaments
Connect bone to bone
Tendons
Connect muscle to bone
synovial joint movements
flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, rotation, circumduction
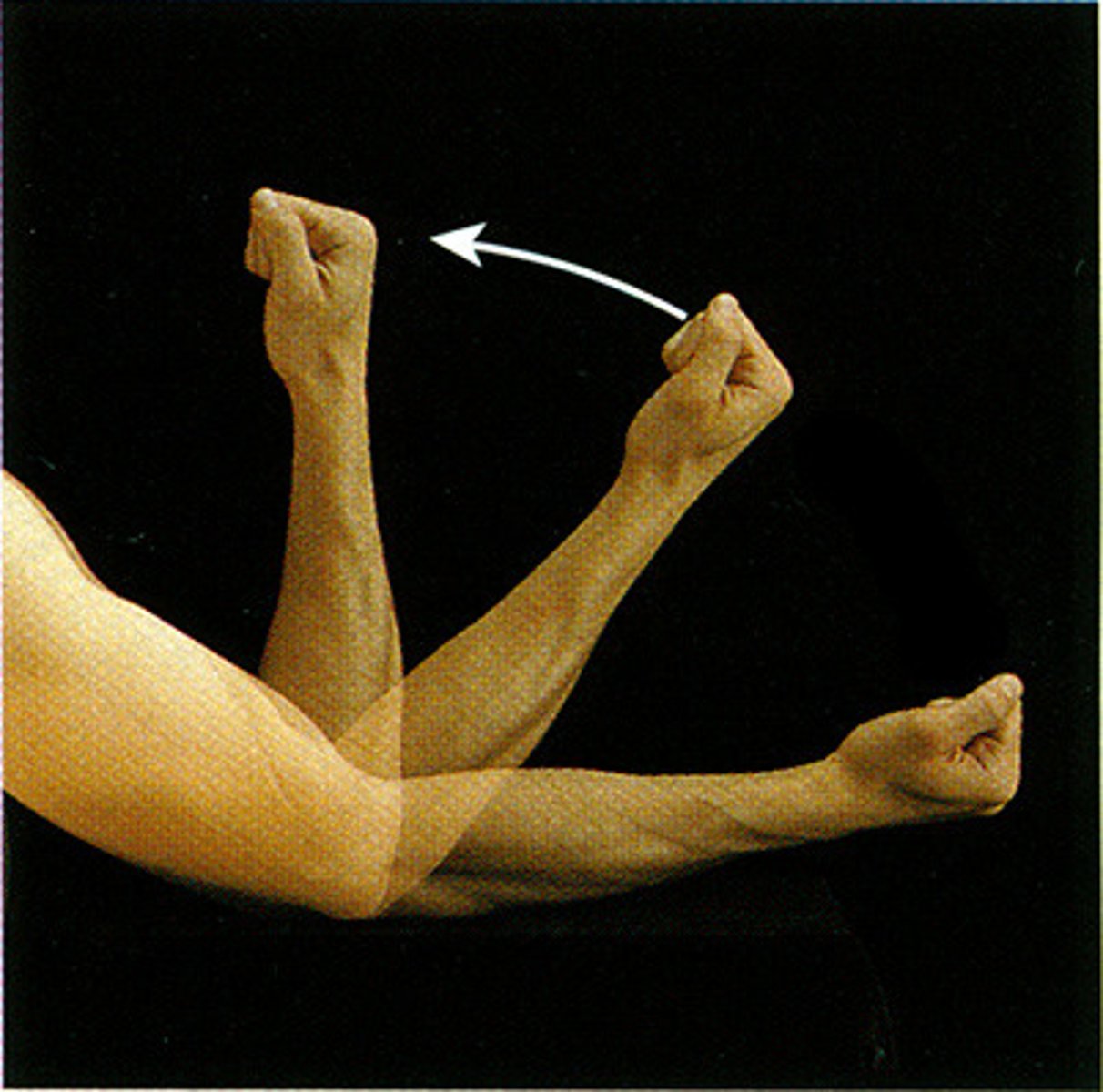
Flexion
Decreases the angle of a joint
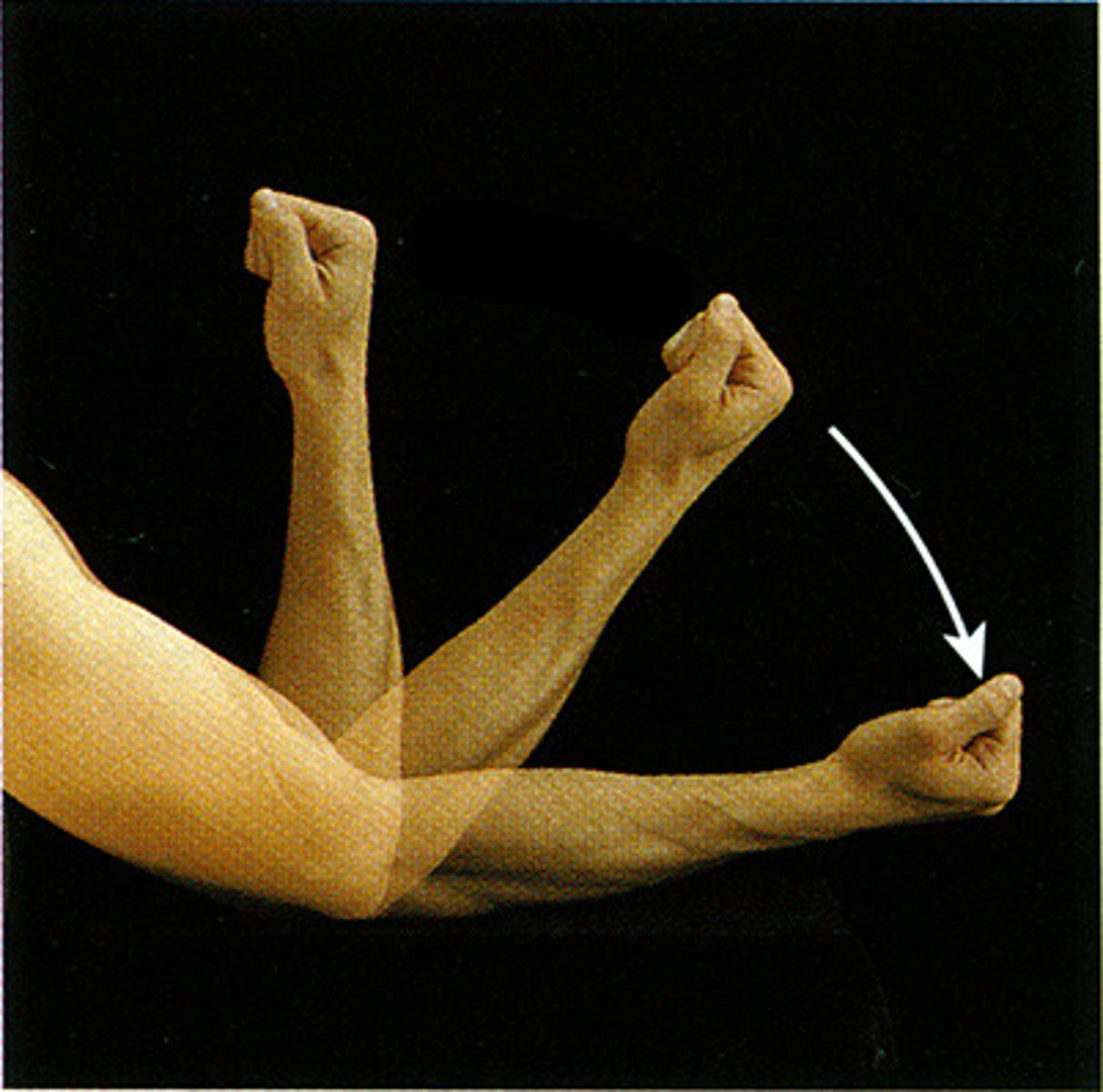
extension
increases the angle of a joint
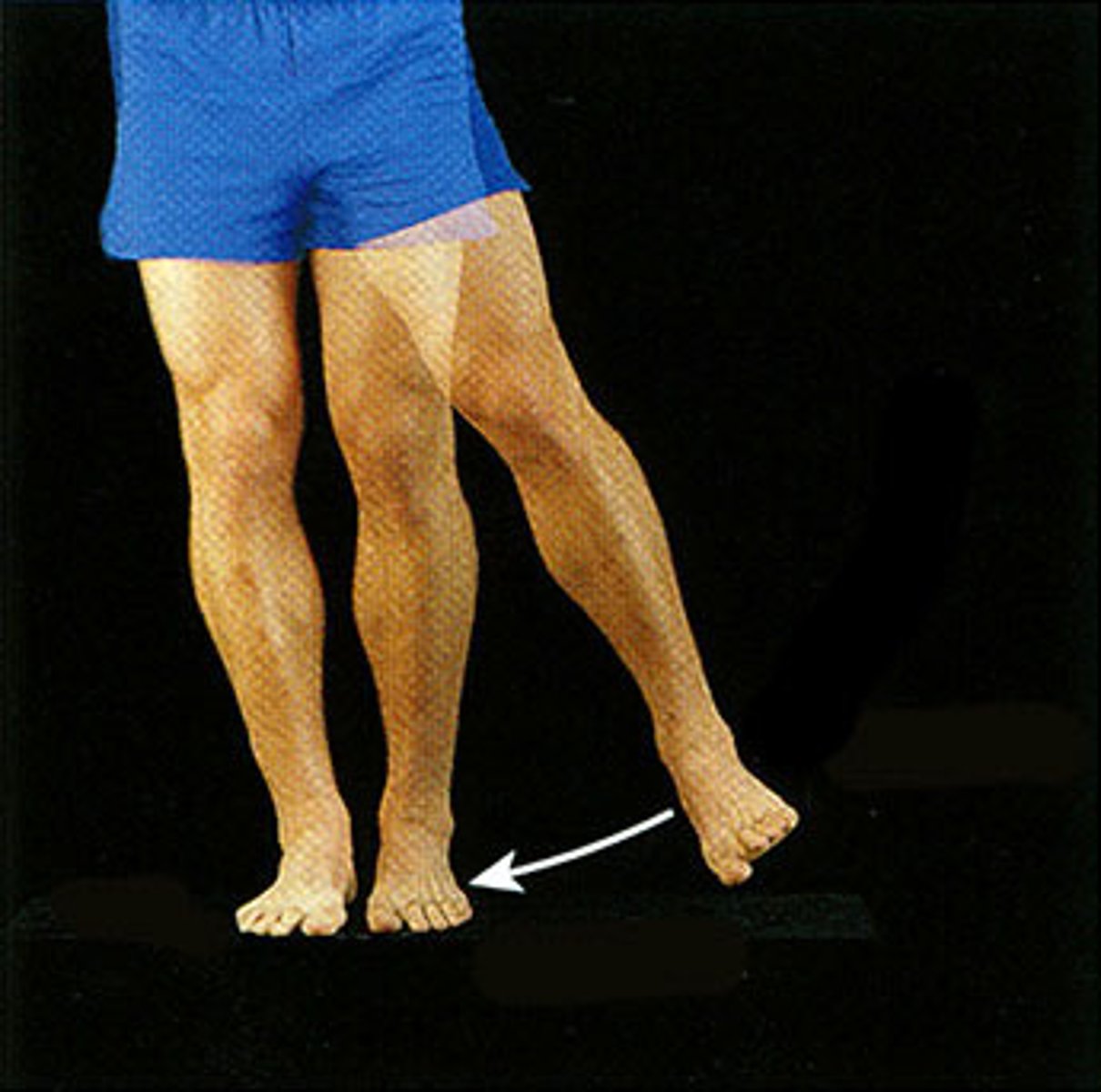
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
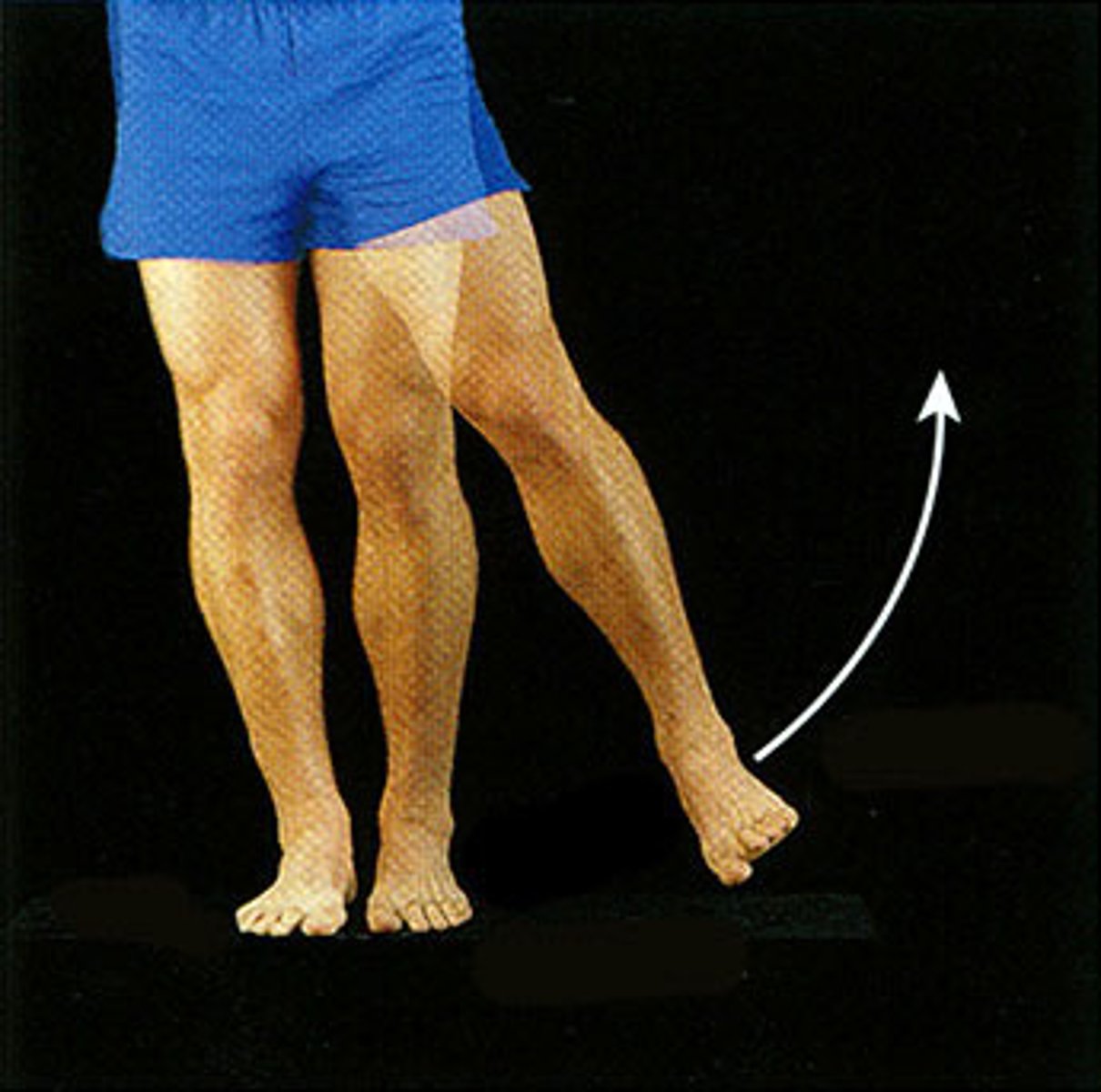
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
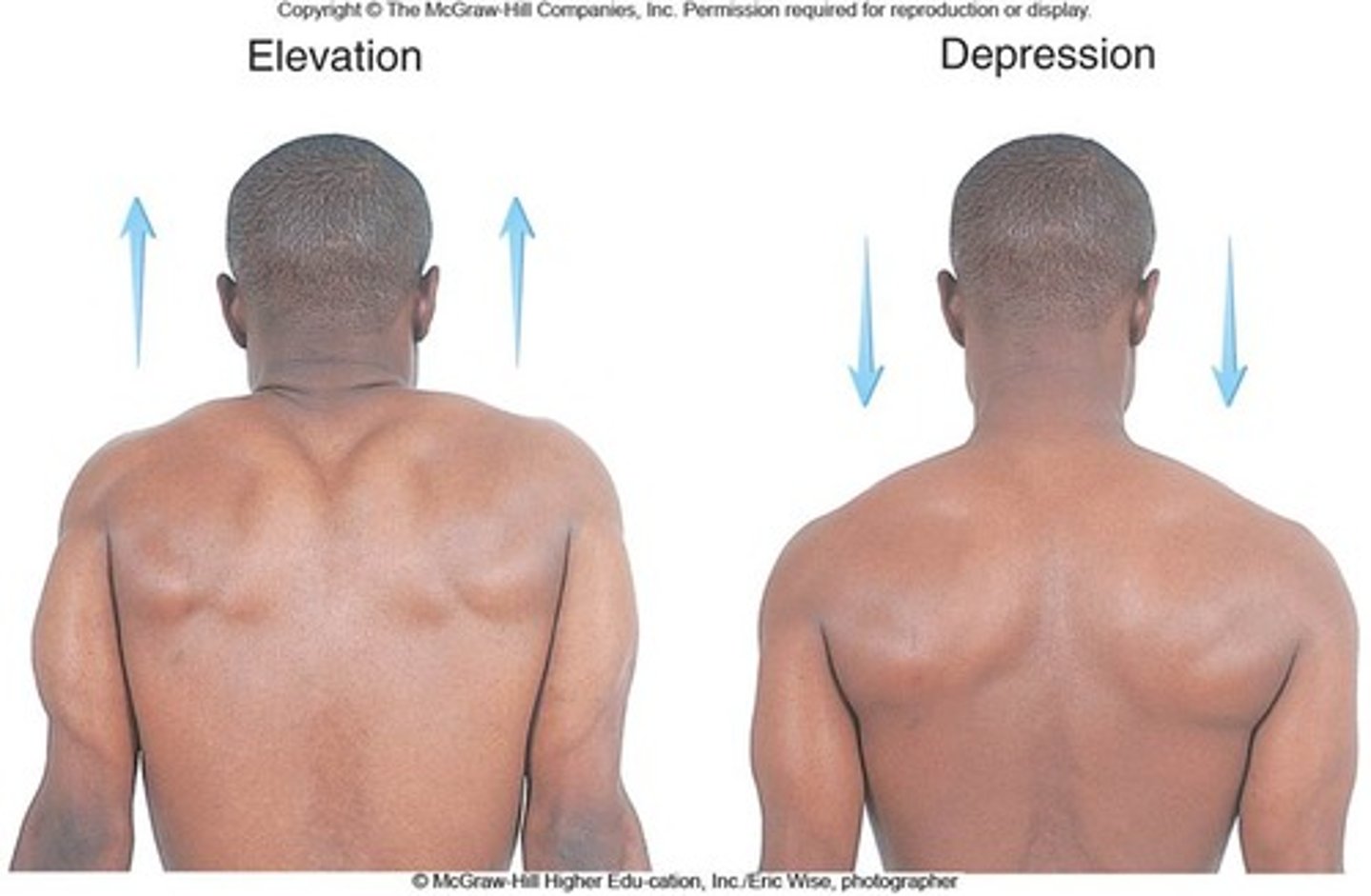
Elevation
raising a body part superiorly
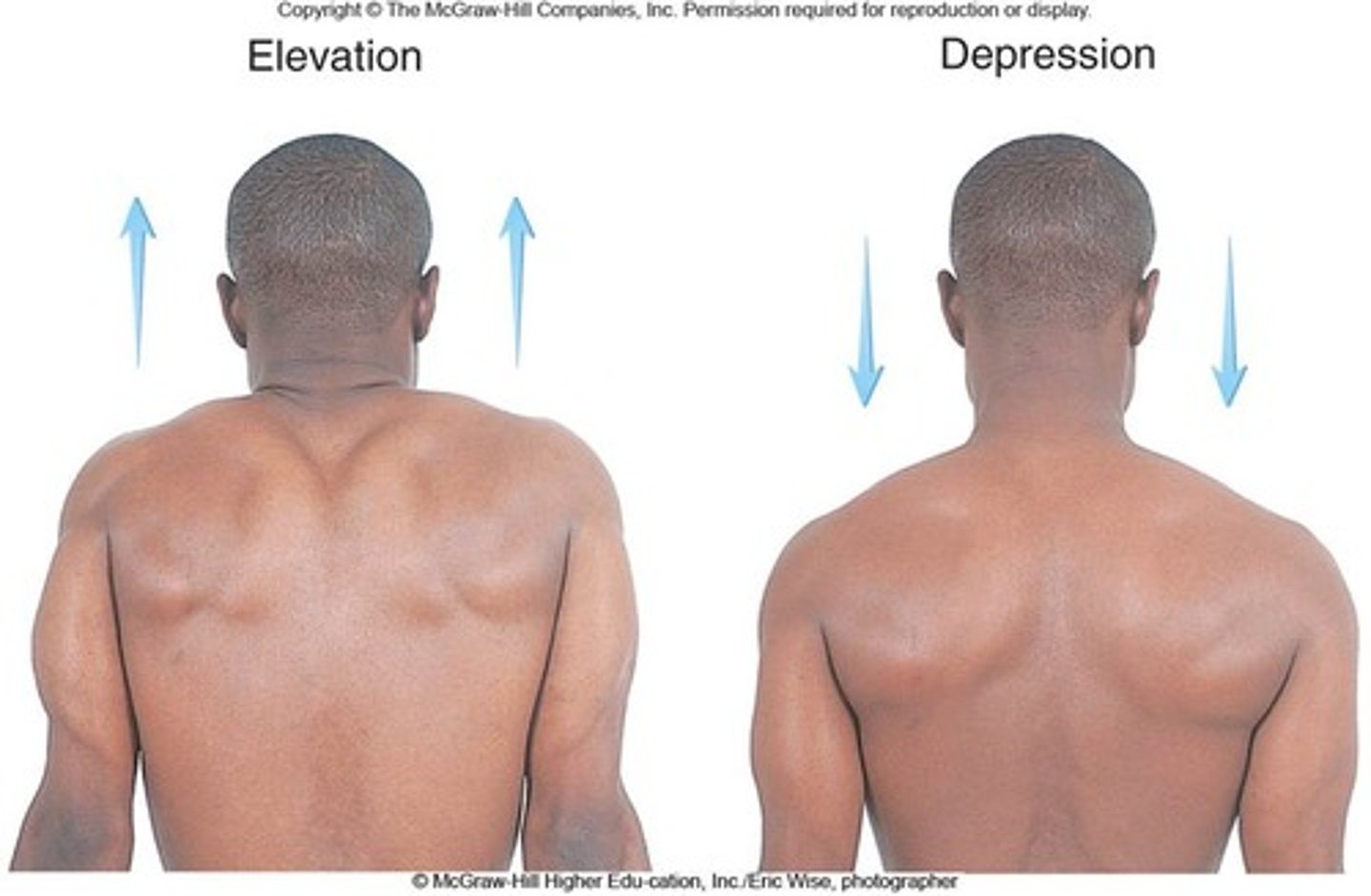
Depression
lowering a body part inferiorly
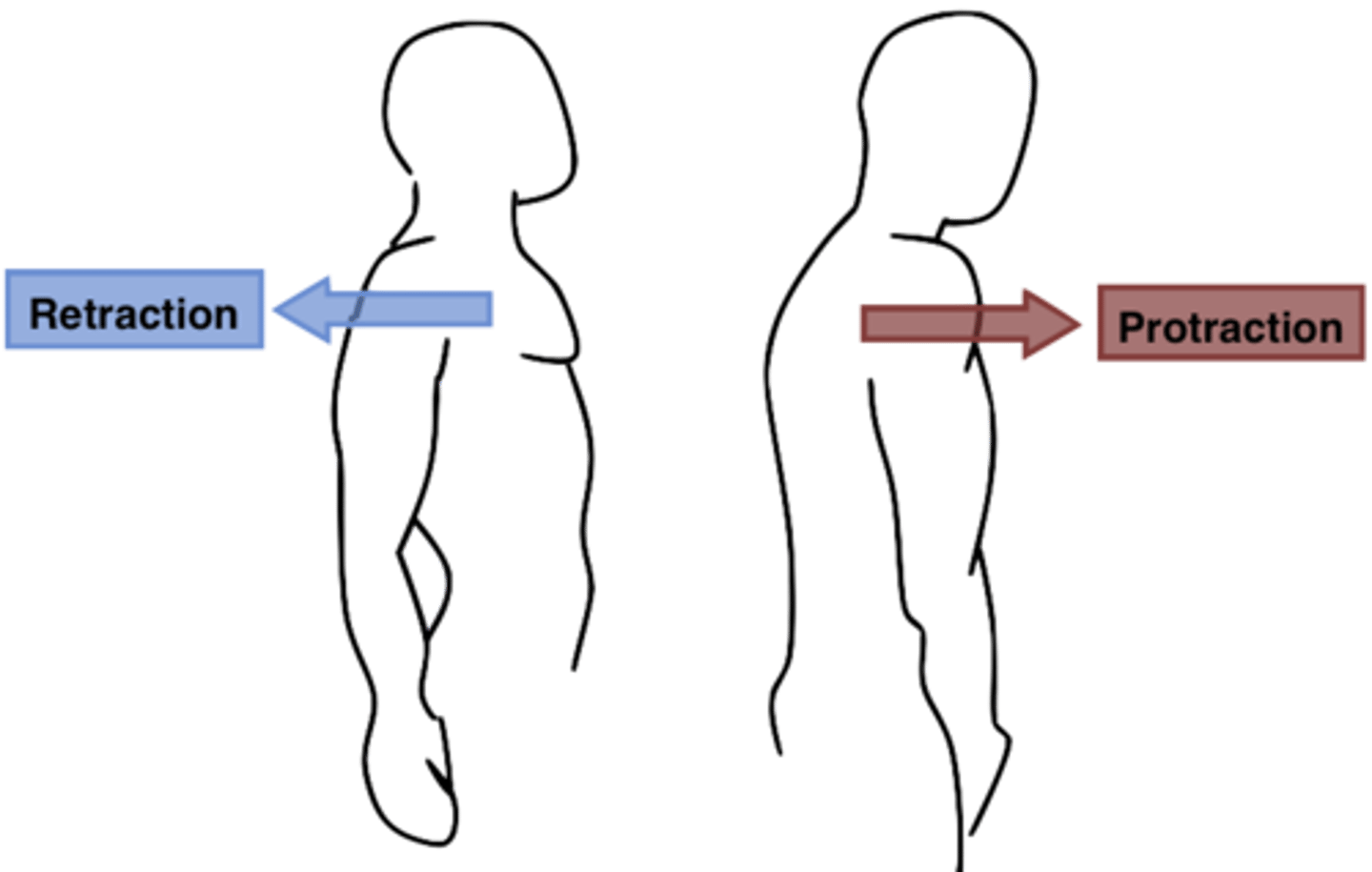
Protraction
moving a body part forward and parallel to the ground
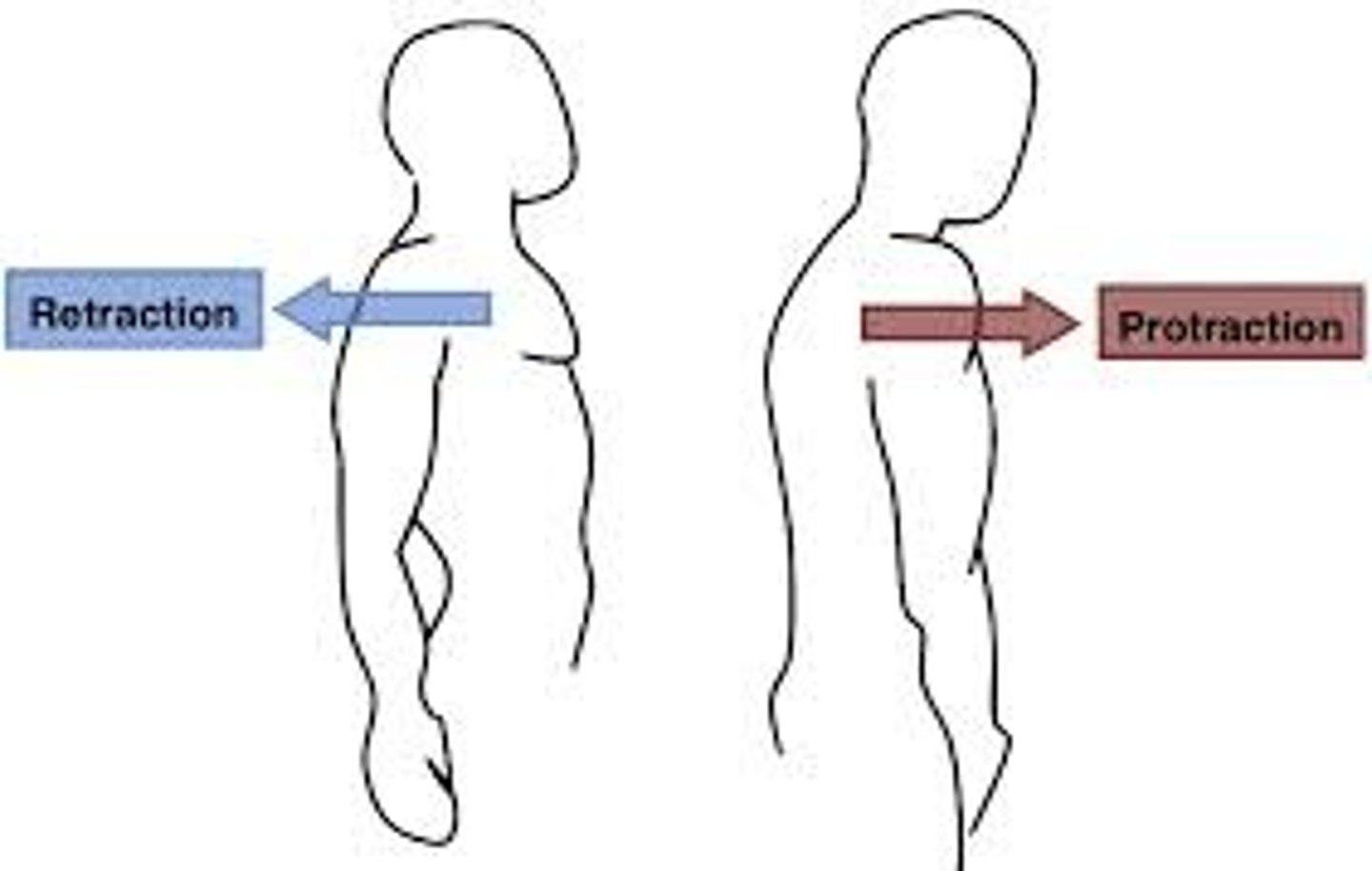
Retraction
moving a body part backward and parallel to the ground
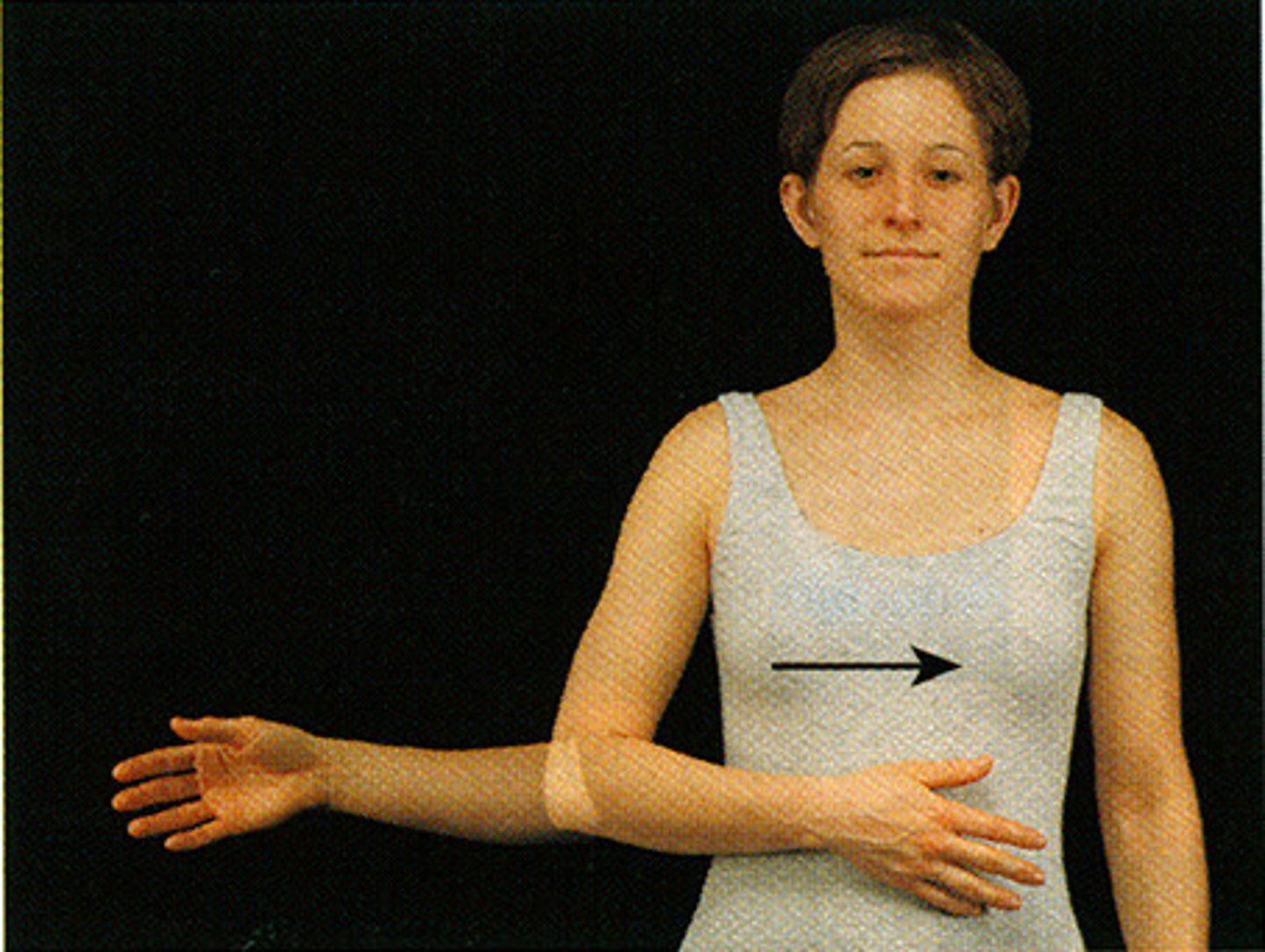
medial rotation
rotation toward the midline of the body
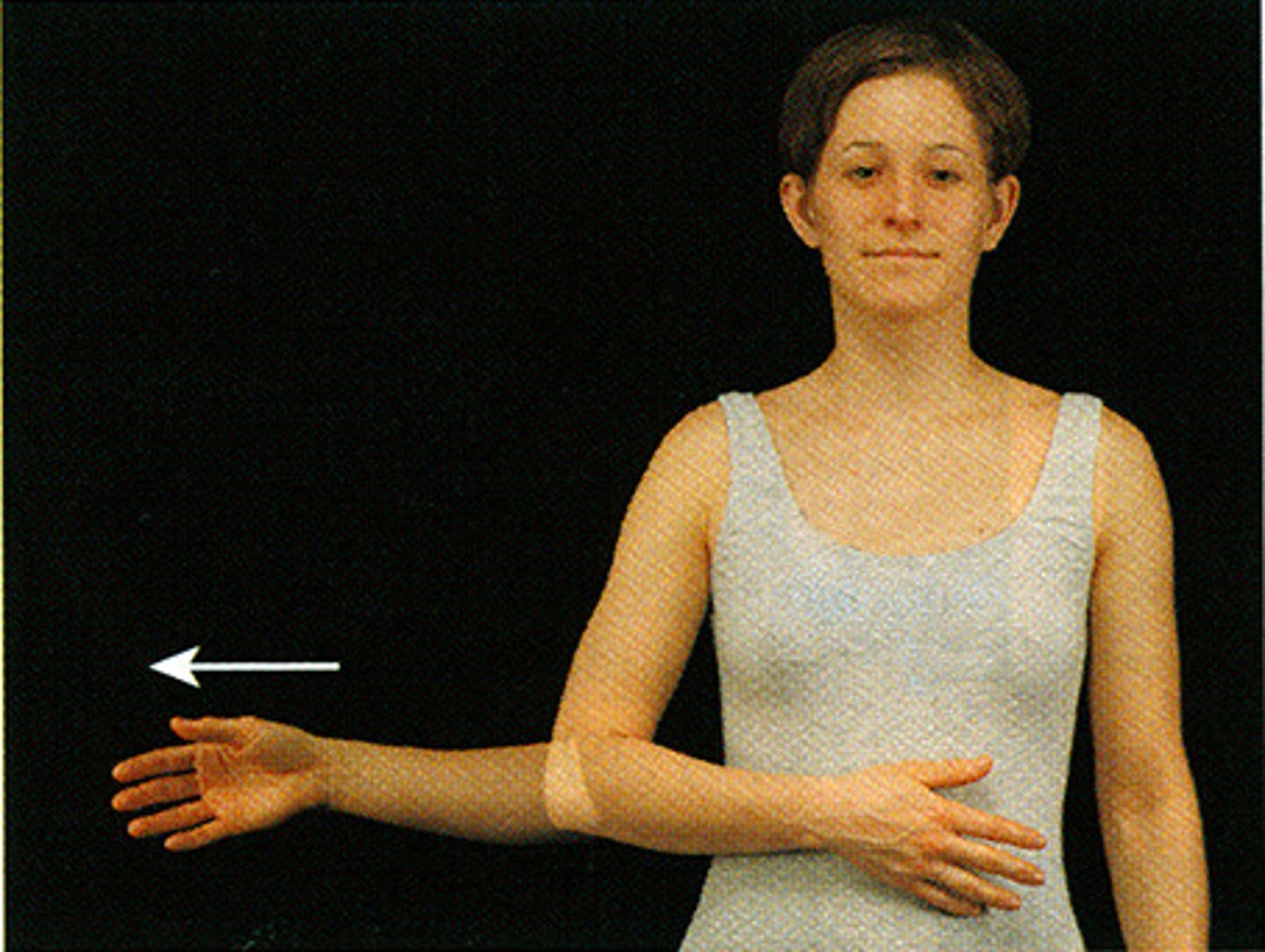
lateral rotation
rotation away from the midline
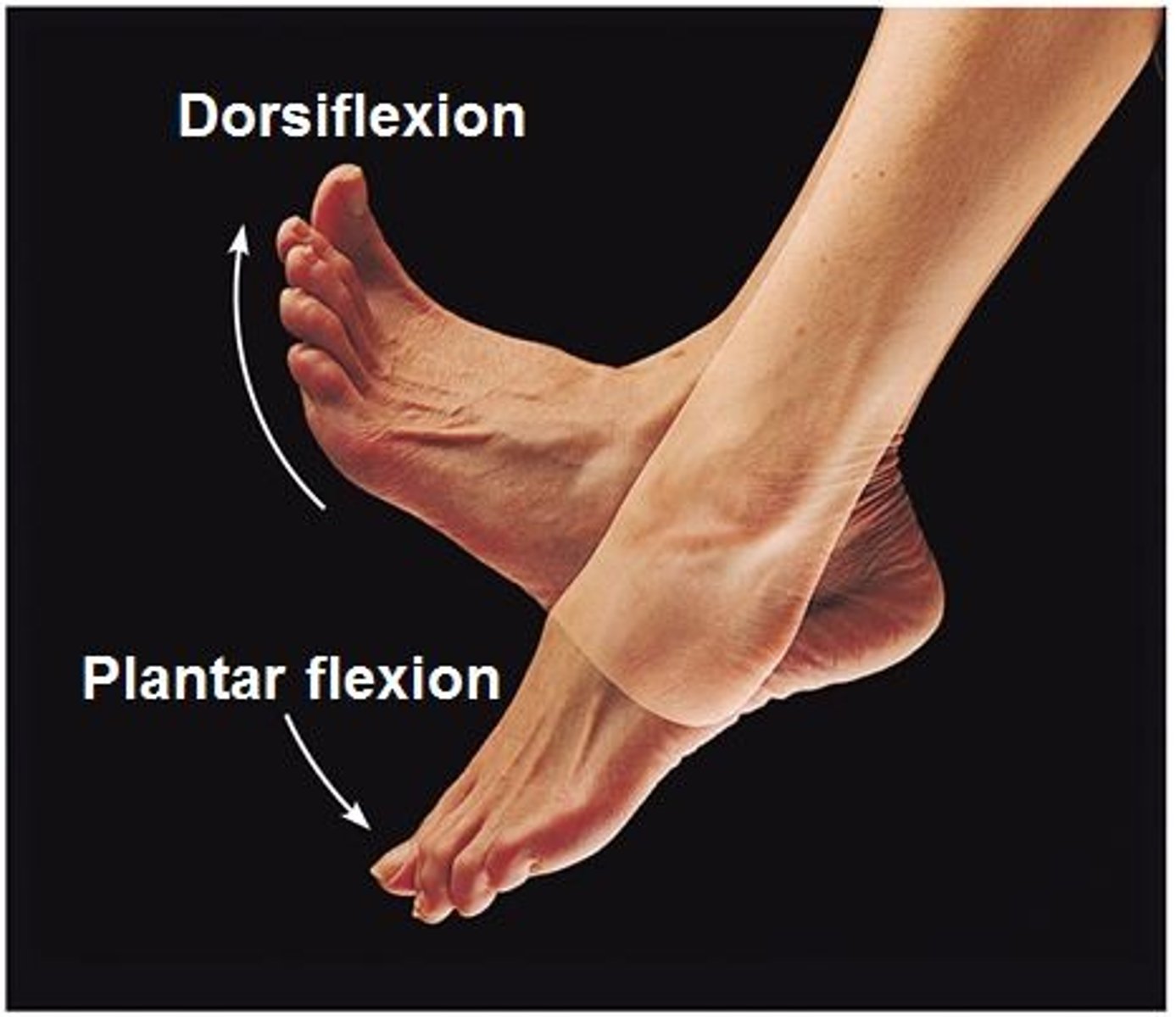
Dorsiflexion
bending of the foot or the toes upward
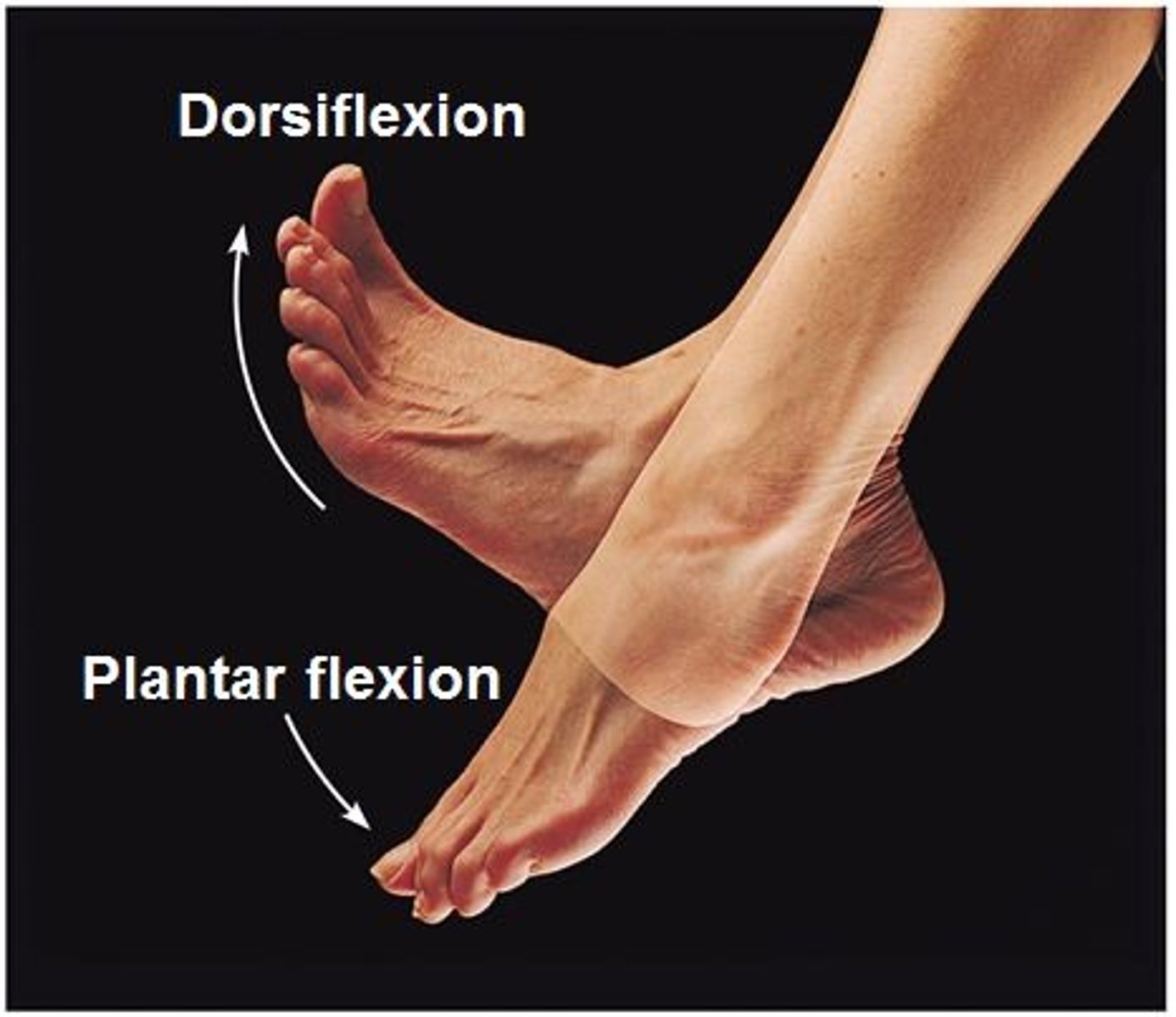
plantar flexion
bending of the sole of the foot by curling the toes toward the ground
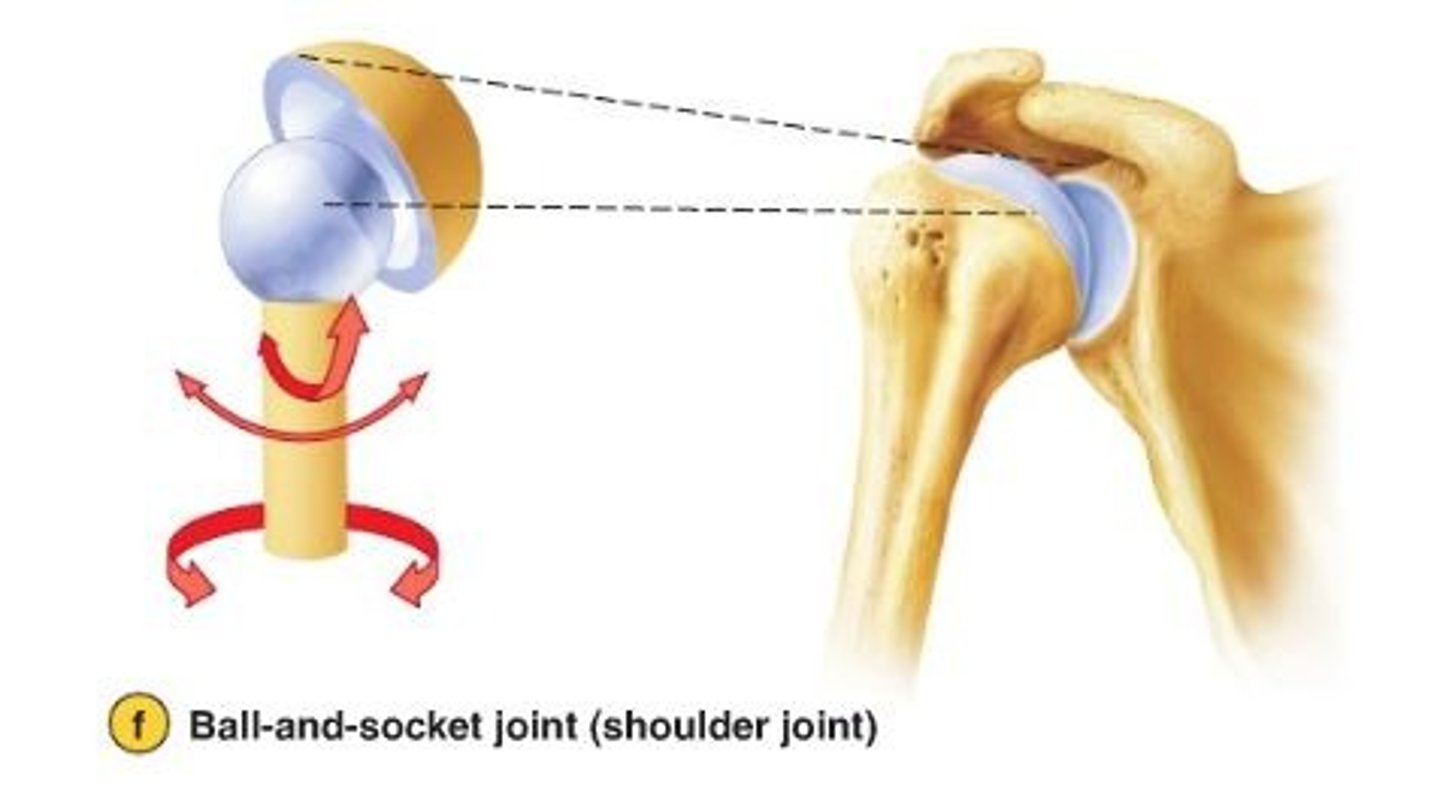
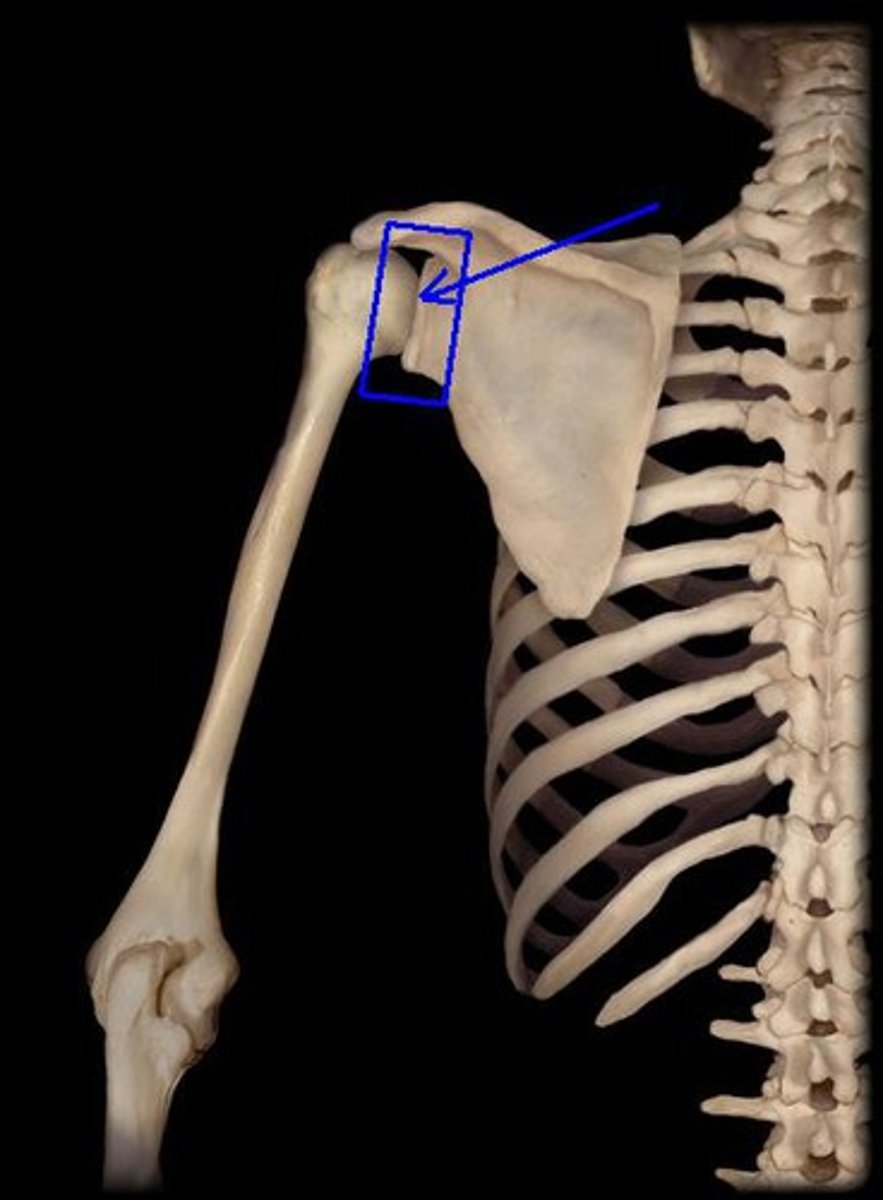
glenohumeral joint
shoulder joint; articulation between the glenoid cavity of the scapula and head of the humerus, ball and socket joint
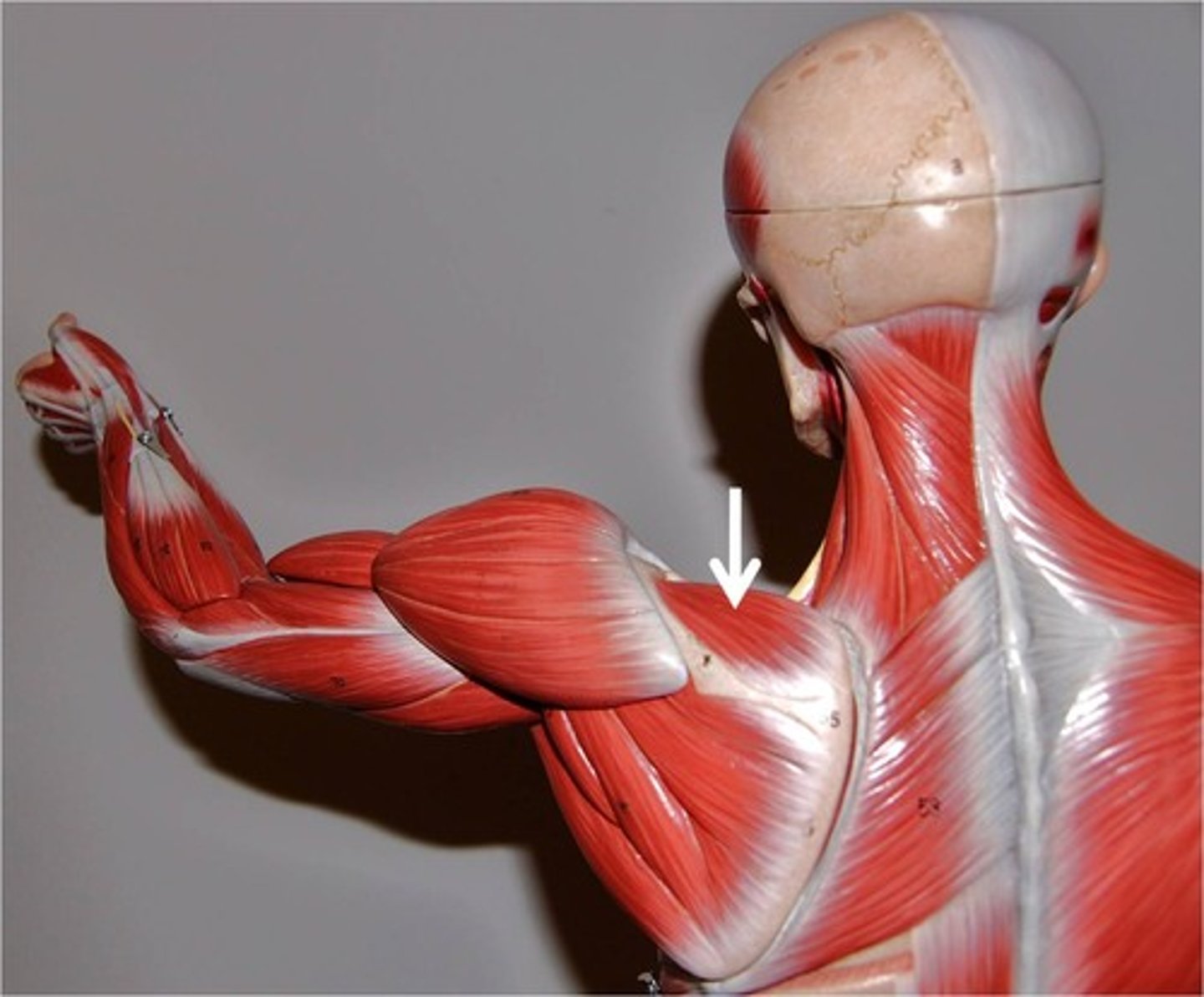
Supraspinatus
Abducts arm; stabilizes the head of the humerus in glenoid cavity; one of the "rotator cuff" muscles
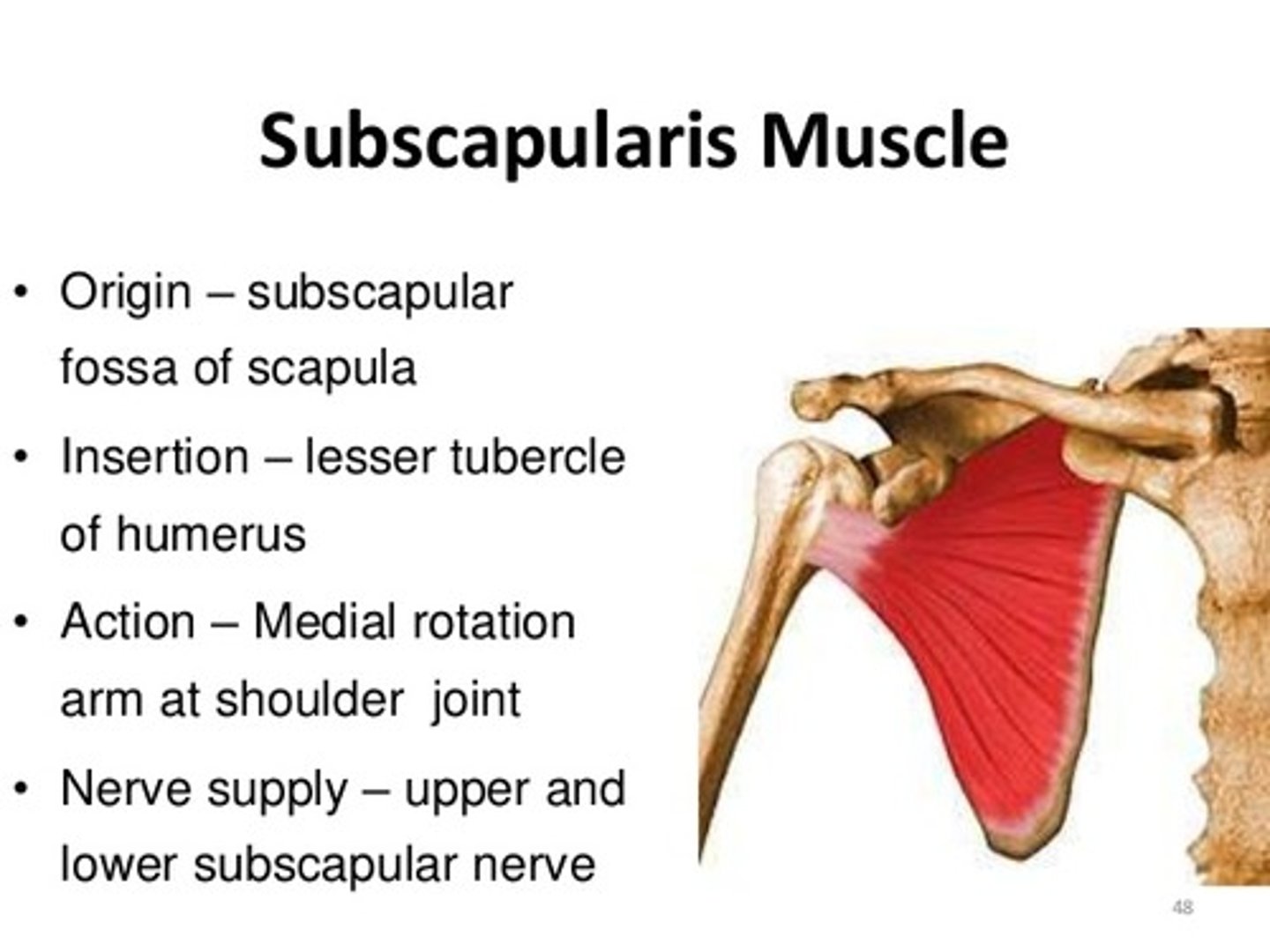
Subcapularis
rotates arm medially
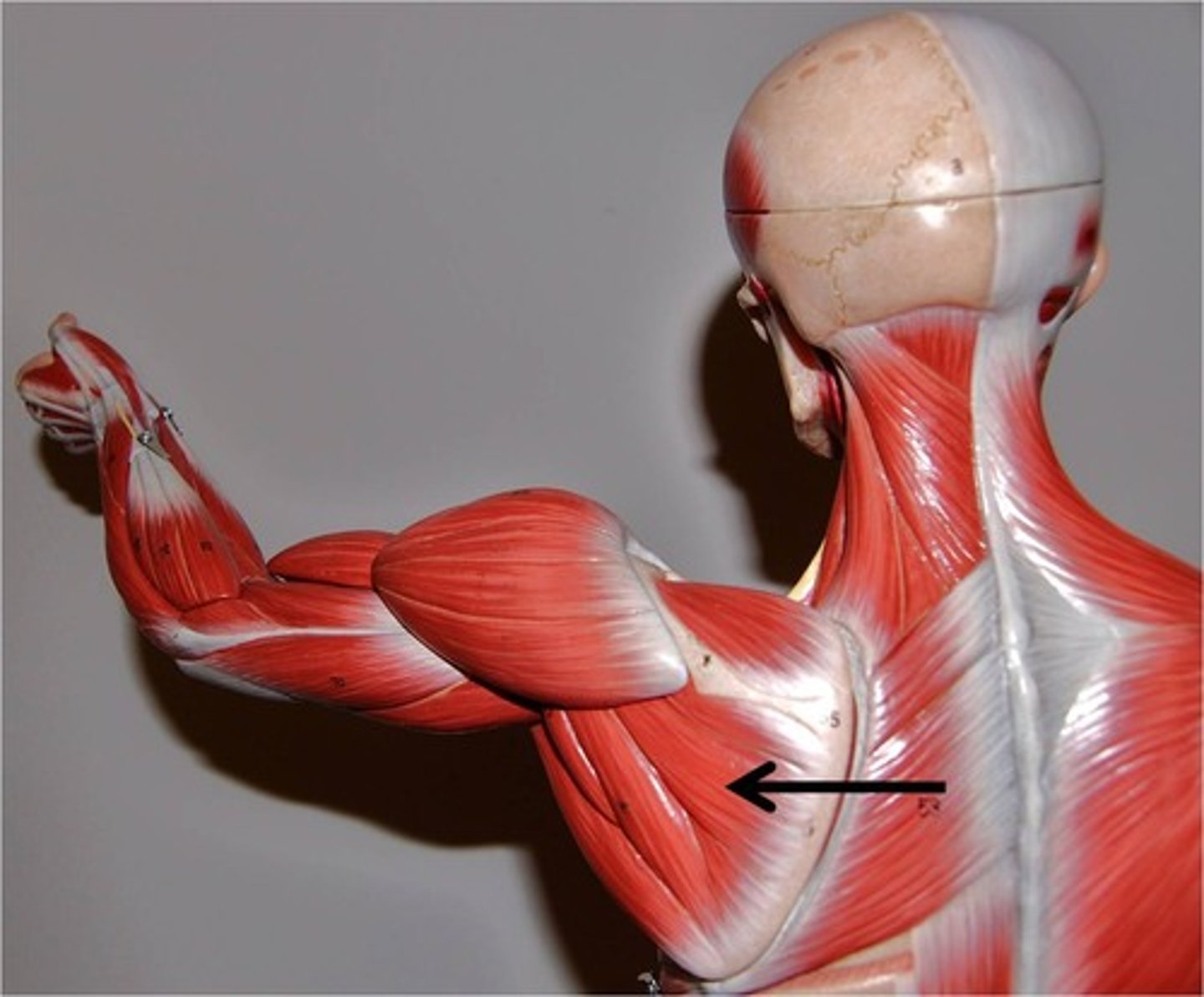
Infraspinatus
rotates arm laterally, stabilizes shoulder joint
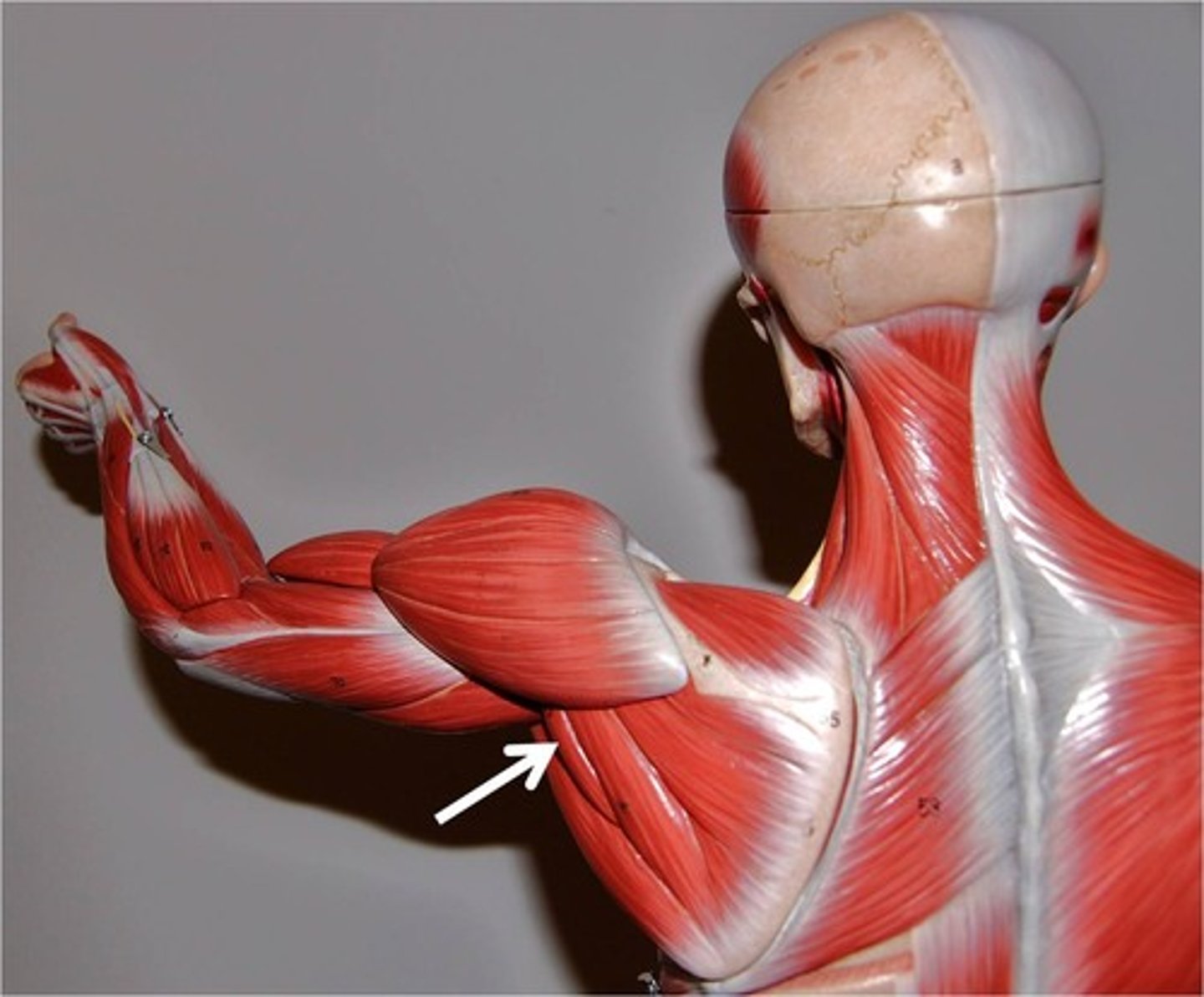
teres minor
rotates arm laterally, stabilizes shoulder joint
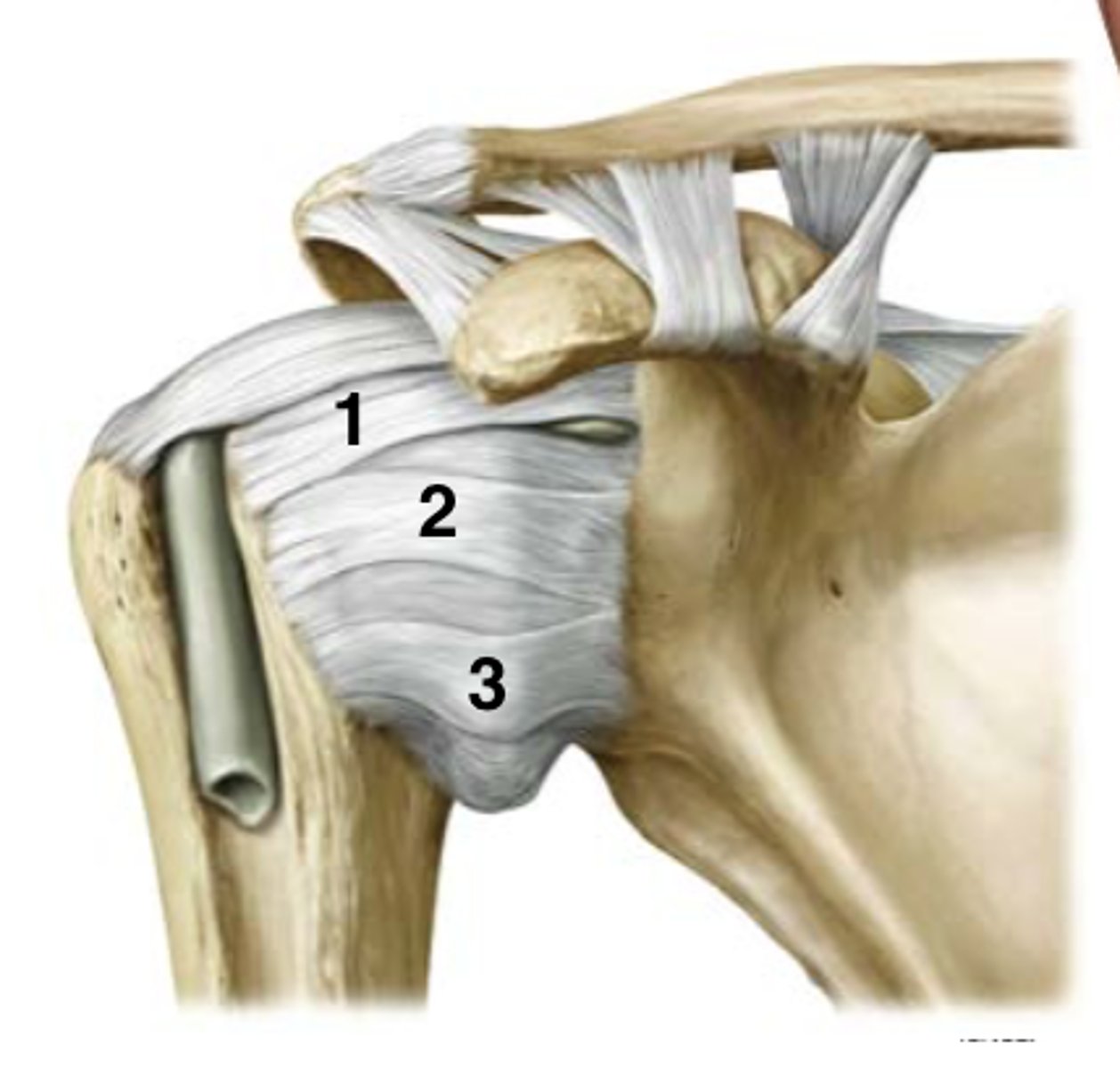
glenohumeral ligament
3 bands which run from the glenoid cavity to the humerus
coracoacromial ligament
Makes a connection between the coracoid process and the acromion
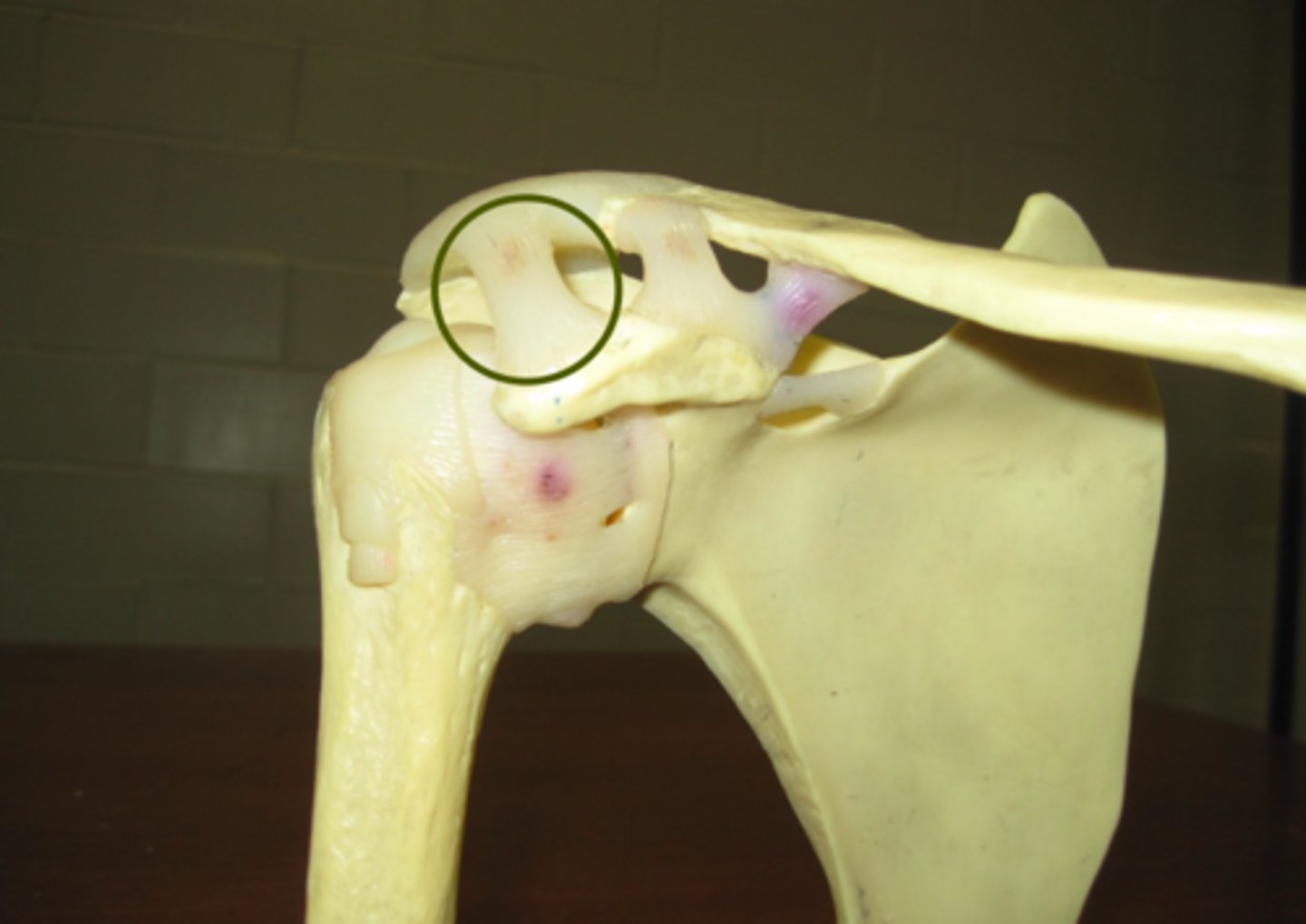
coracohumeral ligament
Connects head of humerus to the coracoid process
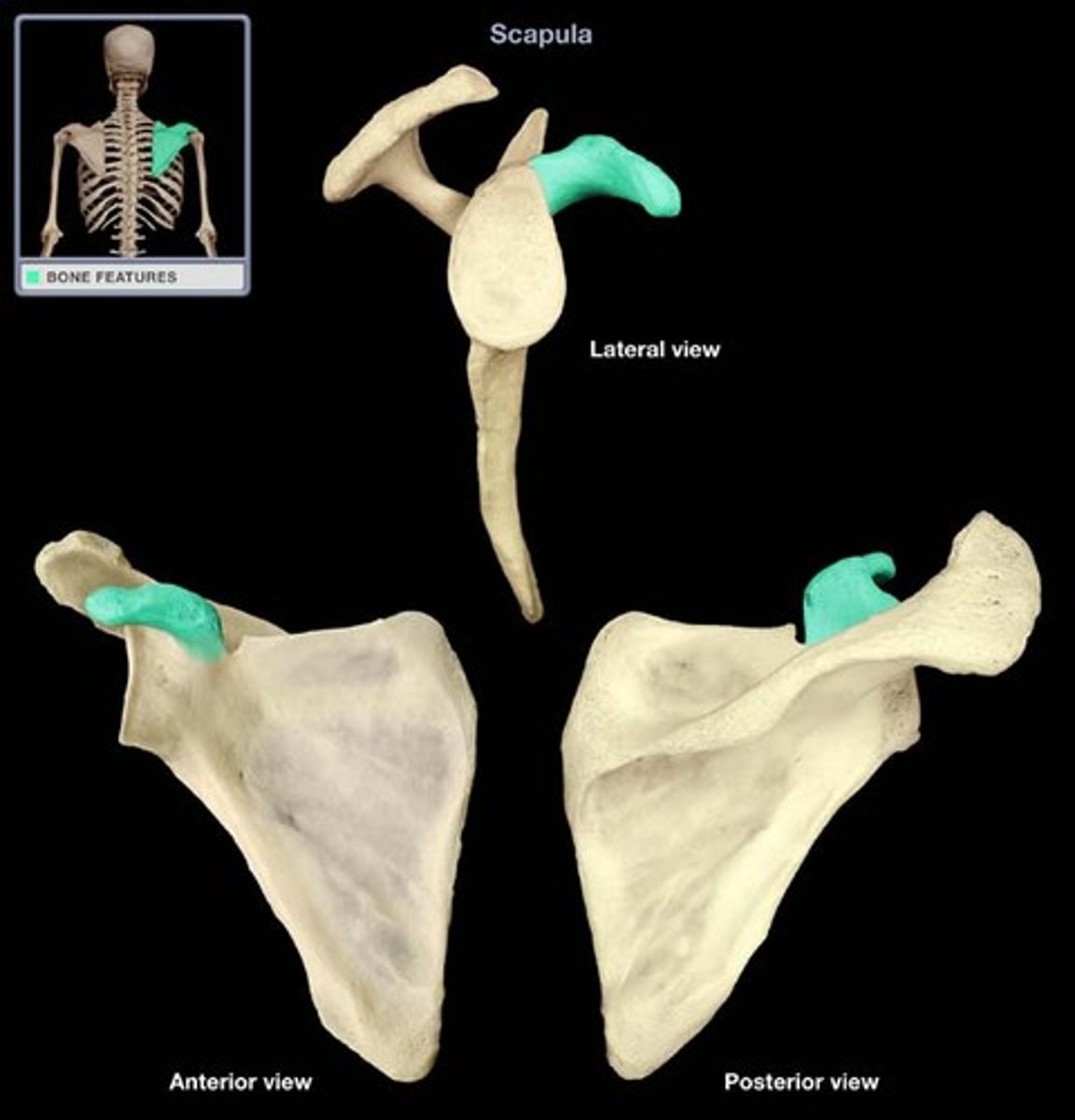
coracoid process
process above the glenoid cavity that permits muscle attachment
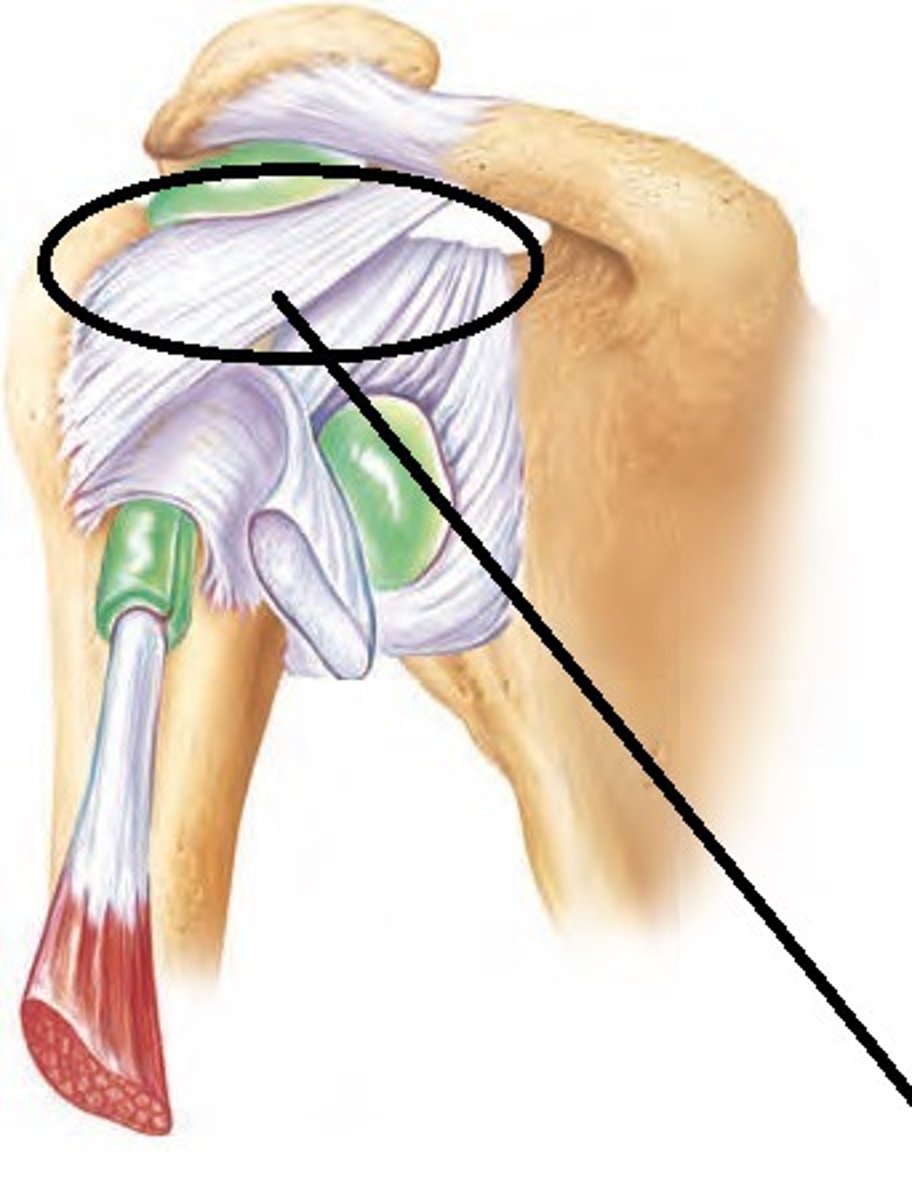
coraclavicular ligament
connects the clavicle to the coracoid process
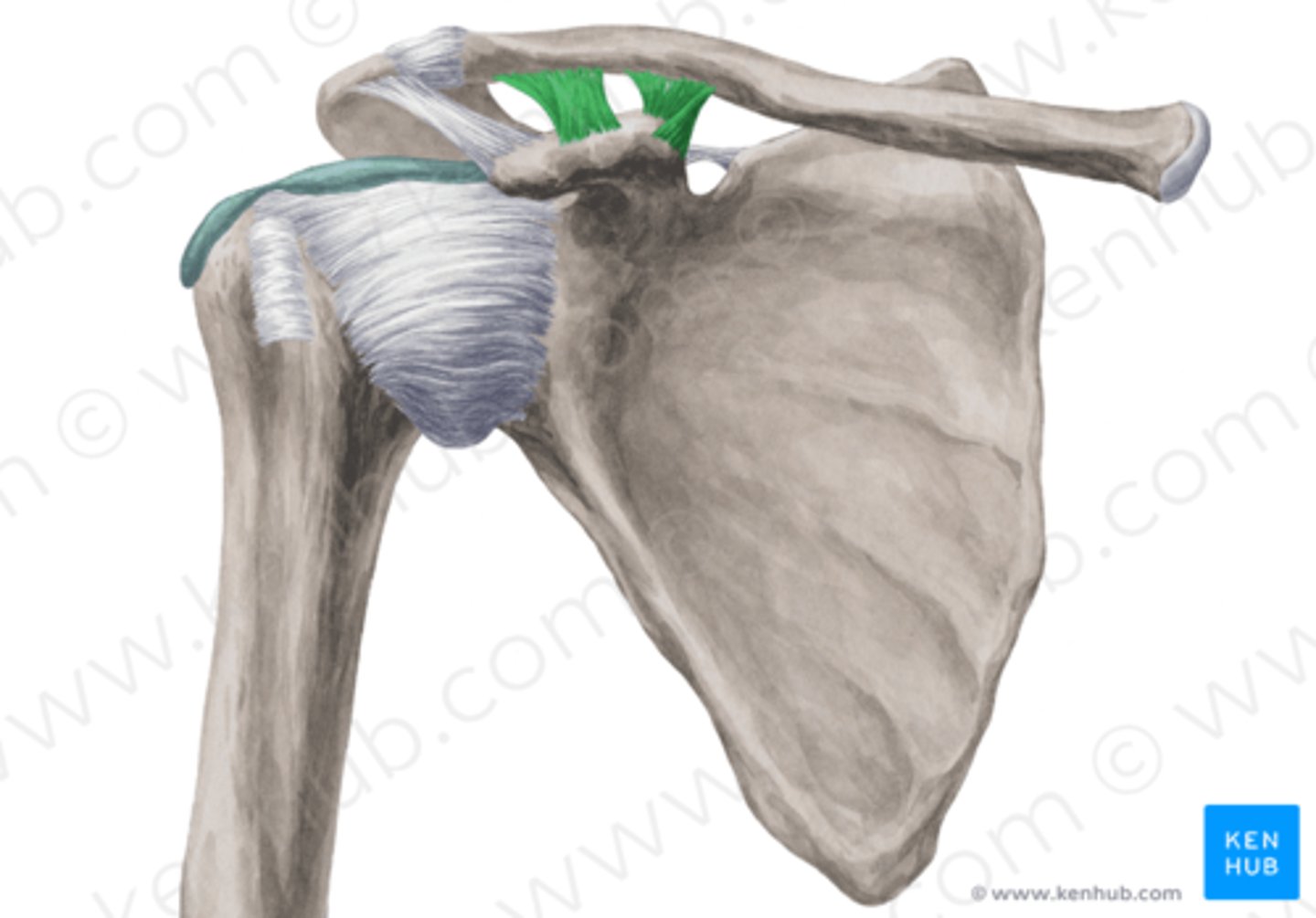
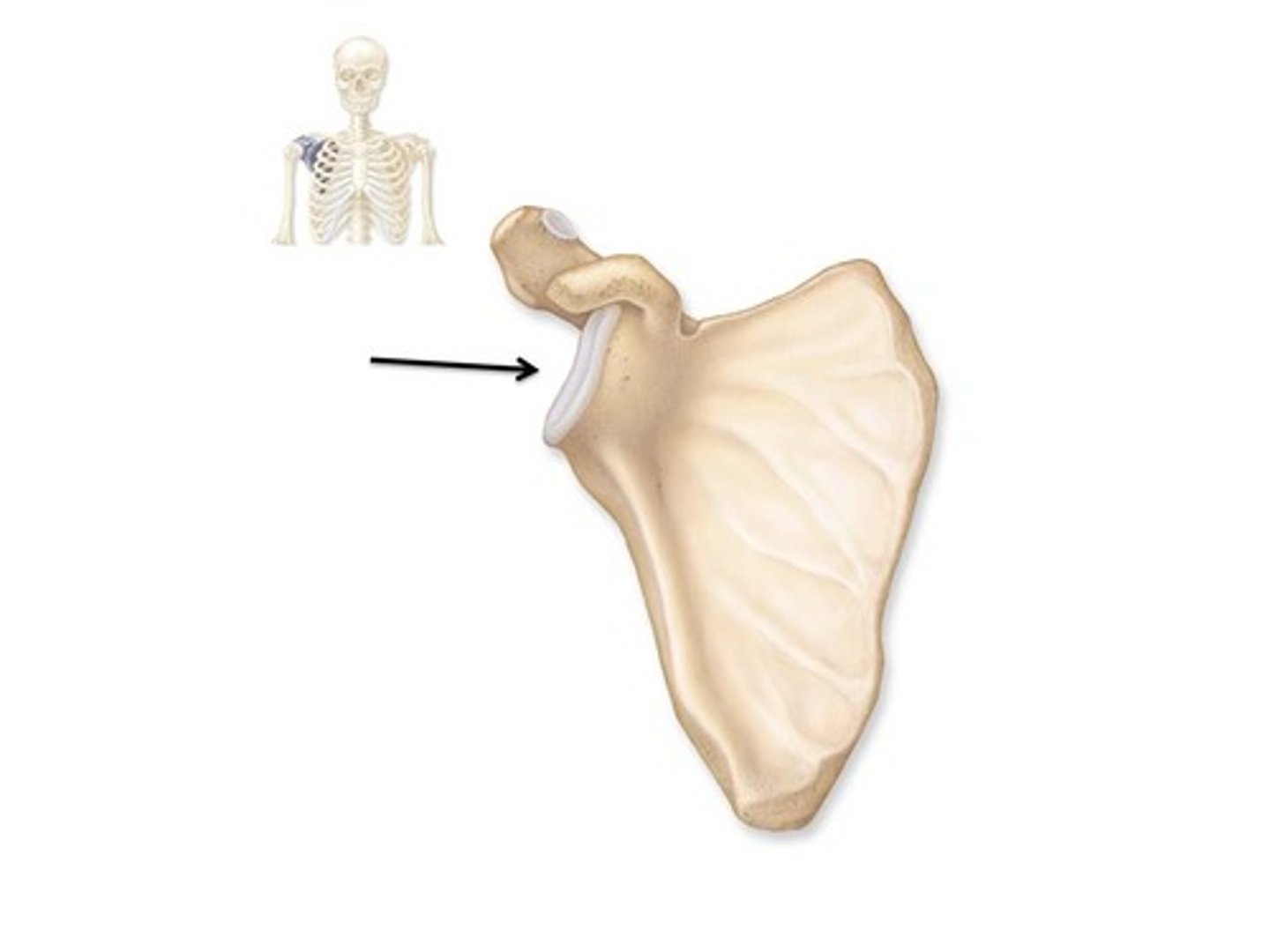
acromioclavicular joint
the joint formed by the acromion of the scapula and the clavicle
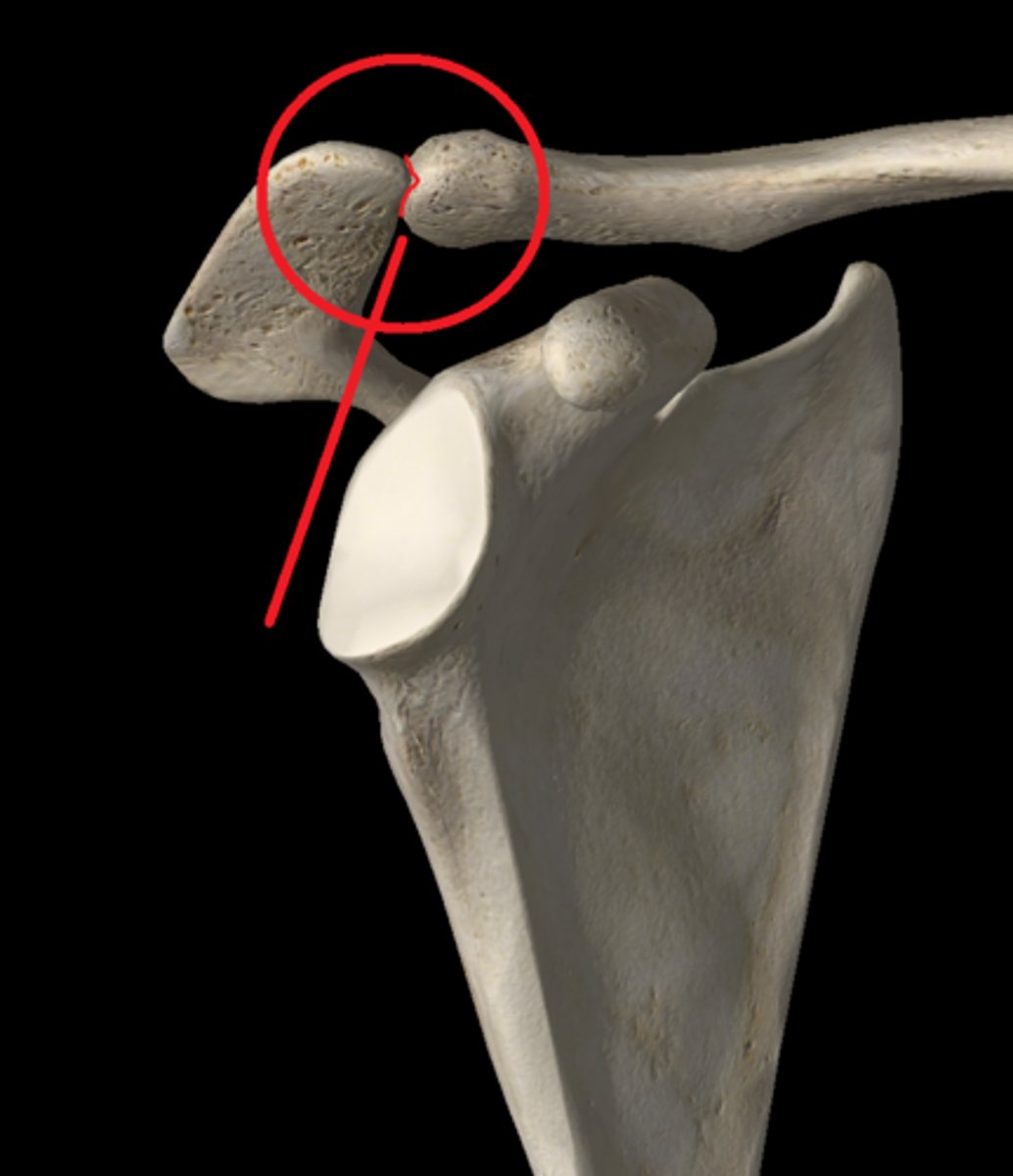
acromion process
extension of the scapula, which forms the high point of the shoulder
subacromial bursa
bursa that protects the supraspinatus muscle tendon and superior end of the humerus from rubbing against the acromion of the scapula
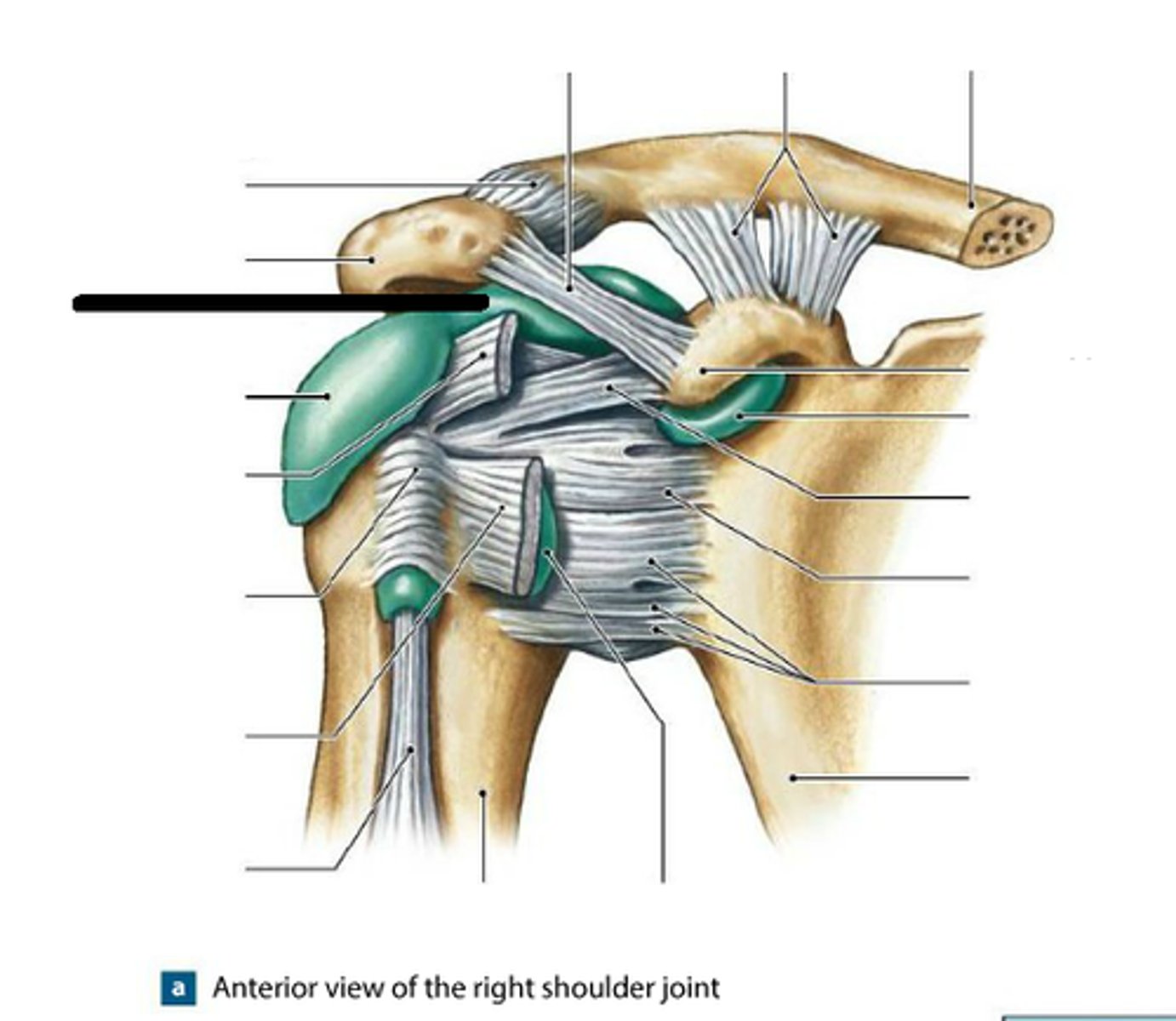
subcoracoid bursa
between the joint capsule and the coracoid process of the scapula
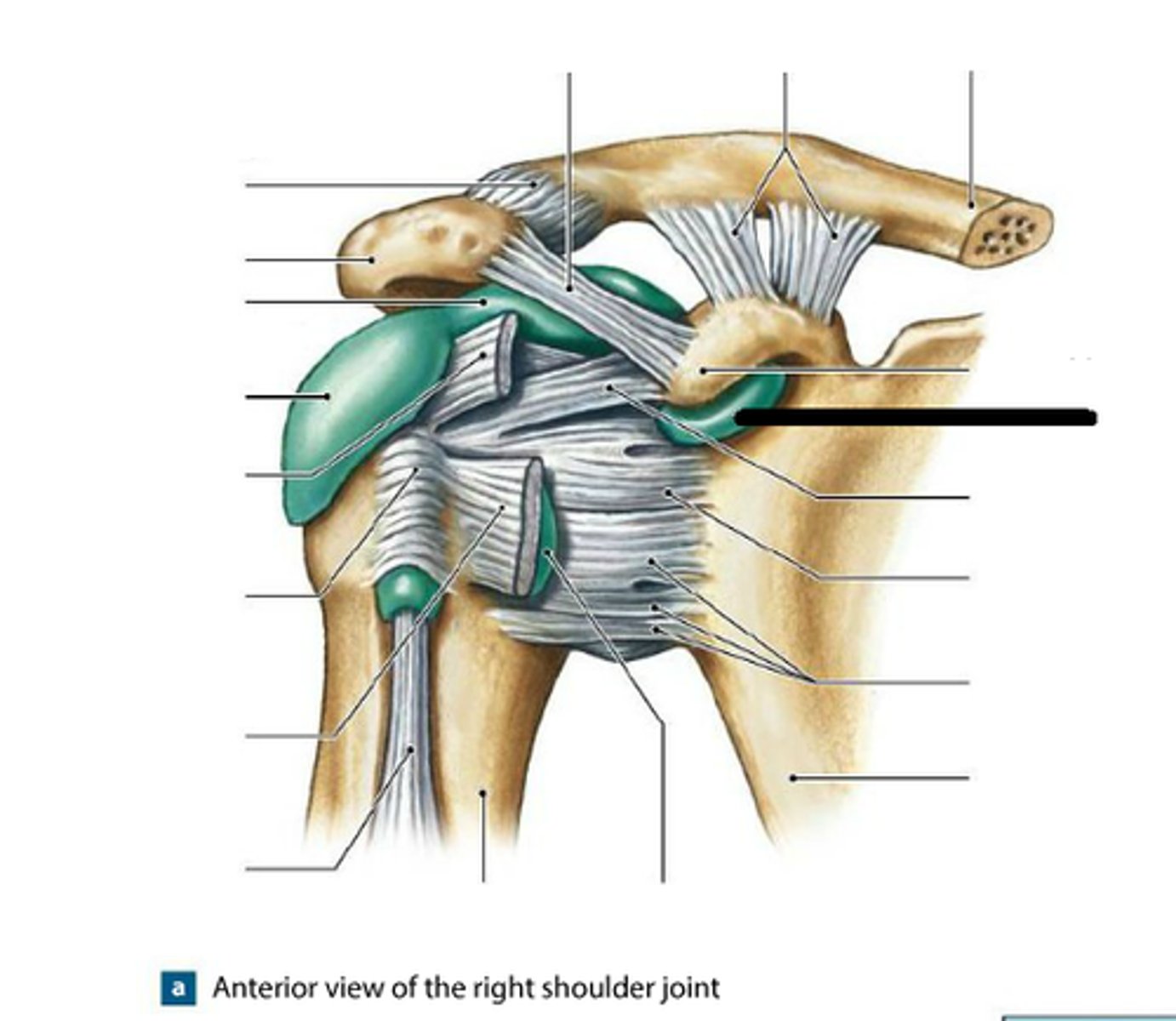
subdeltoid bursa
Forms a cushion between the deltoid muscle and the greater trochanter when the arm is abducted
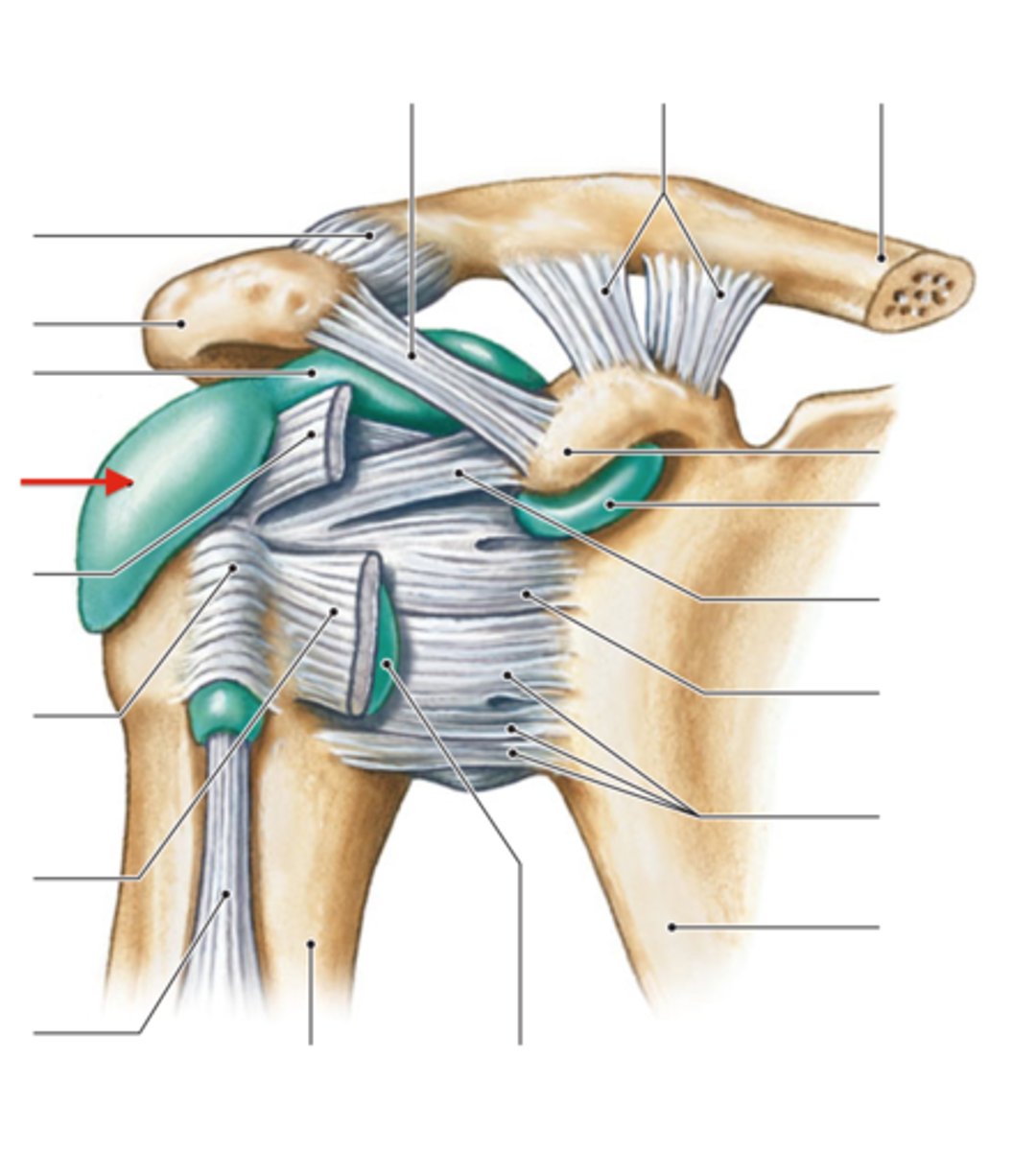
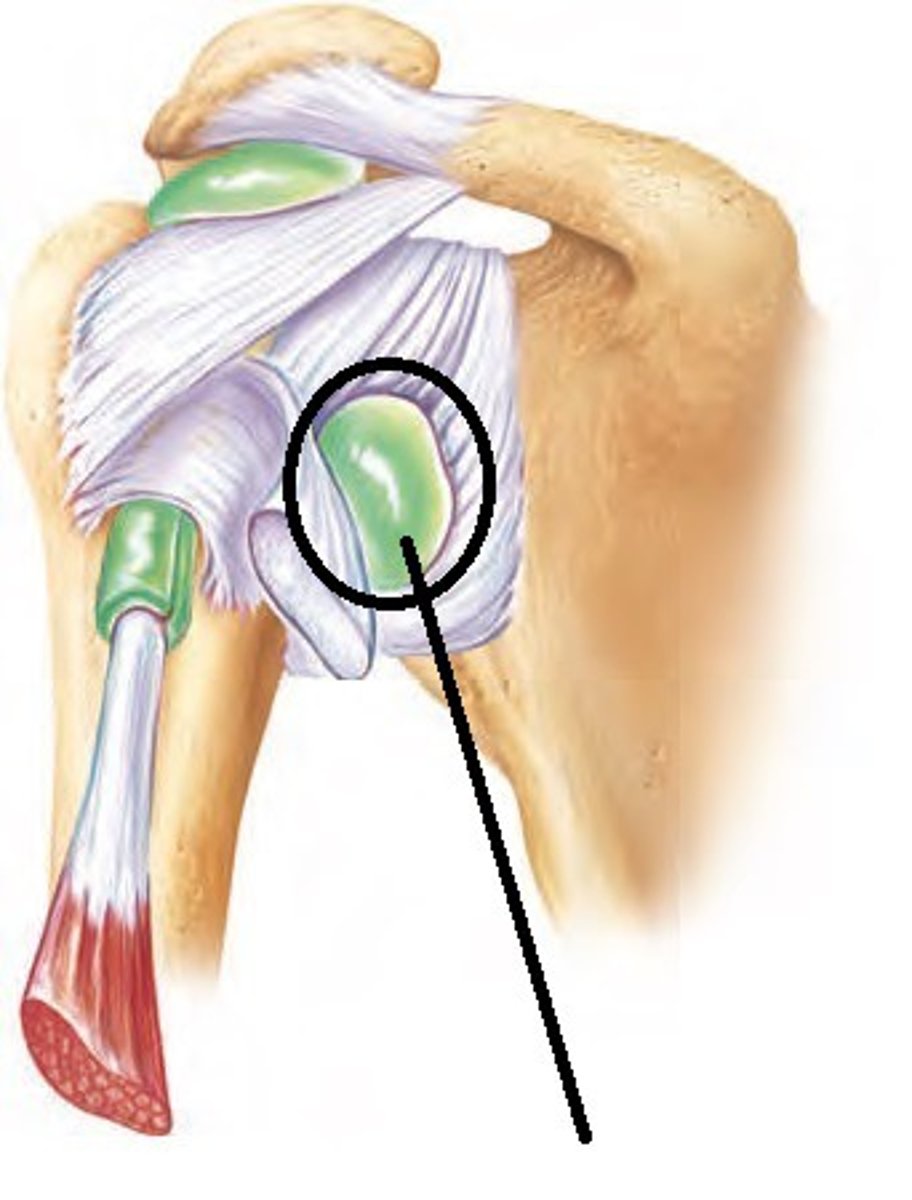
subscapular bursa
bursa that prevents rubbing of the subscapularis muscle tendon against the scapula
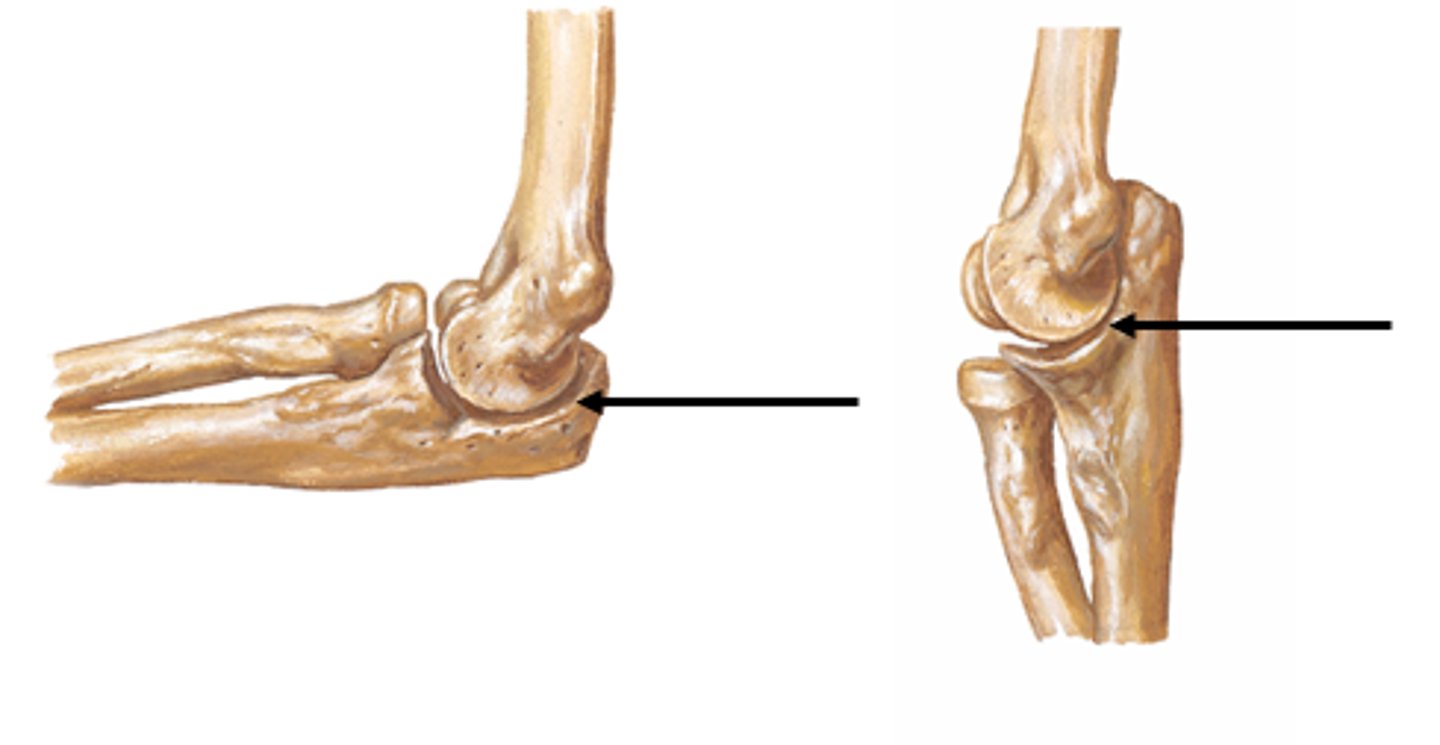
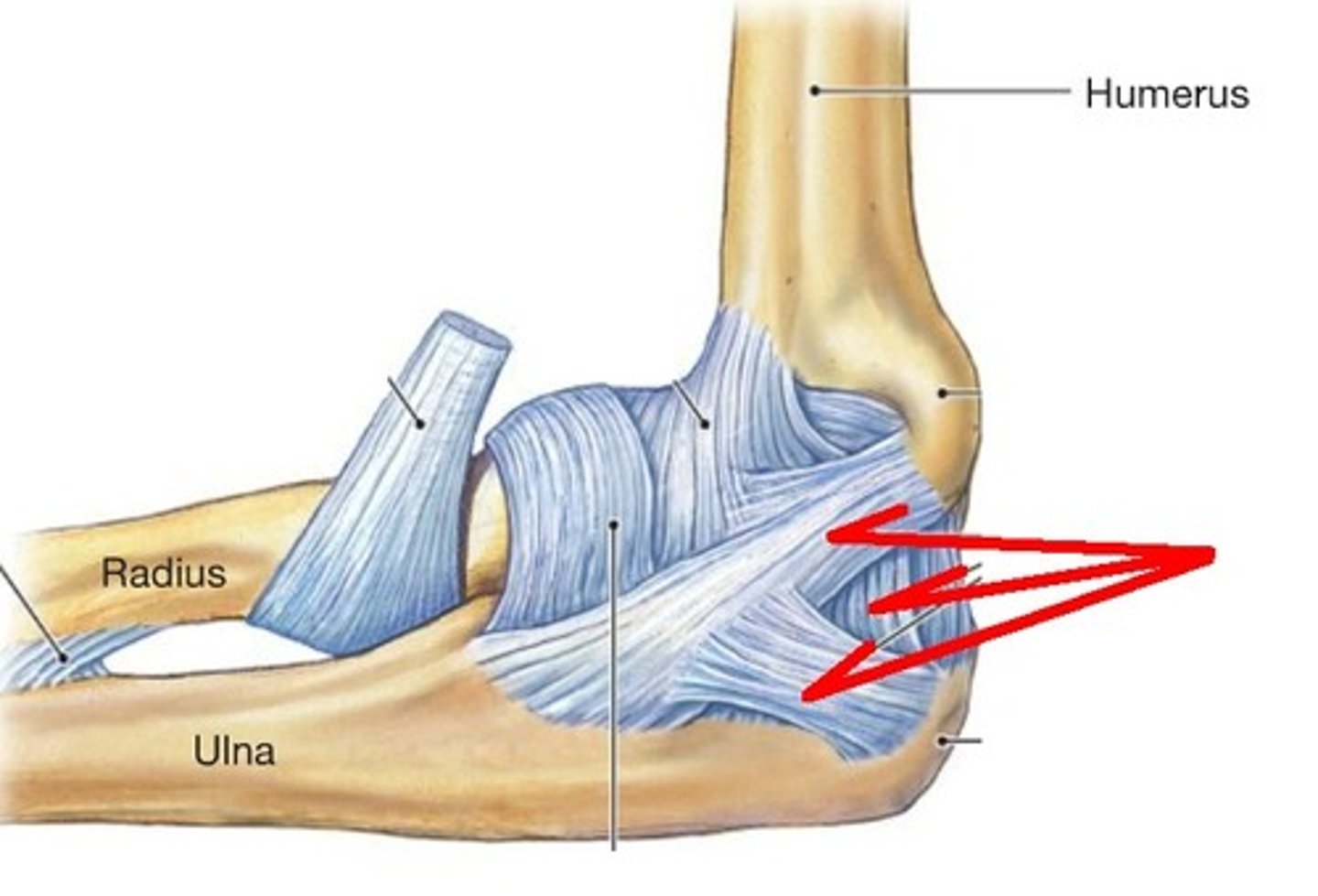
humeroulnar joint
trochlea of humerus and trochlear notch of ulna
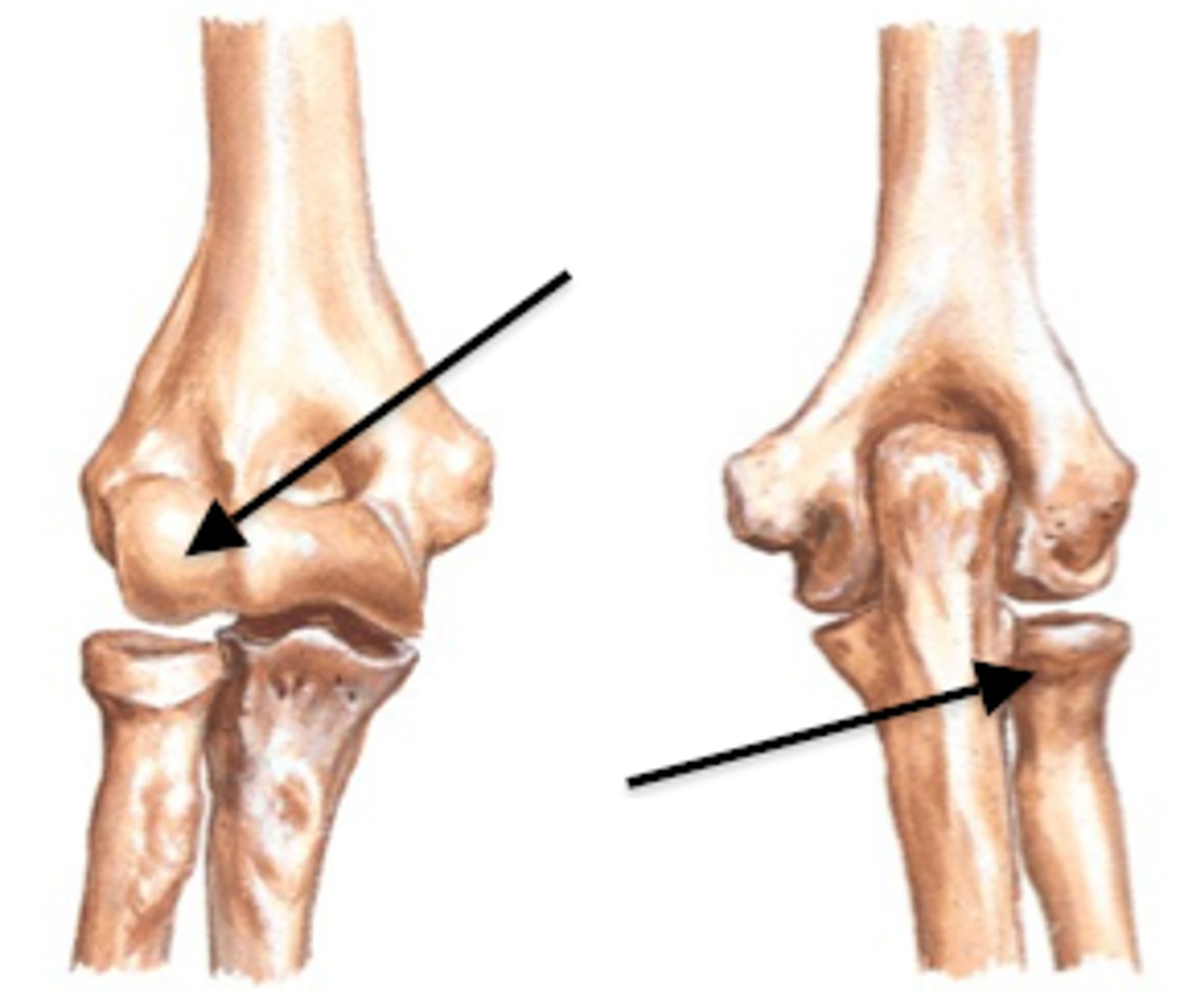
humeroradial joint
articulation between the capitulum of the humerus and head of the radius
radial collateral ligament
connects the lateral epicondyle of the humerus to the radius
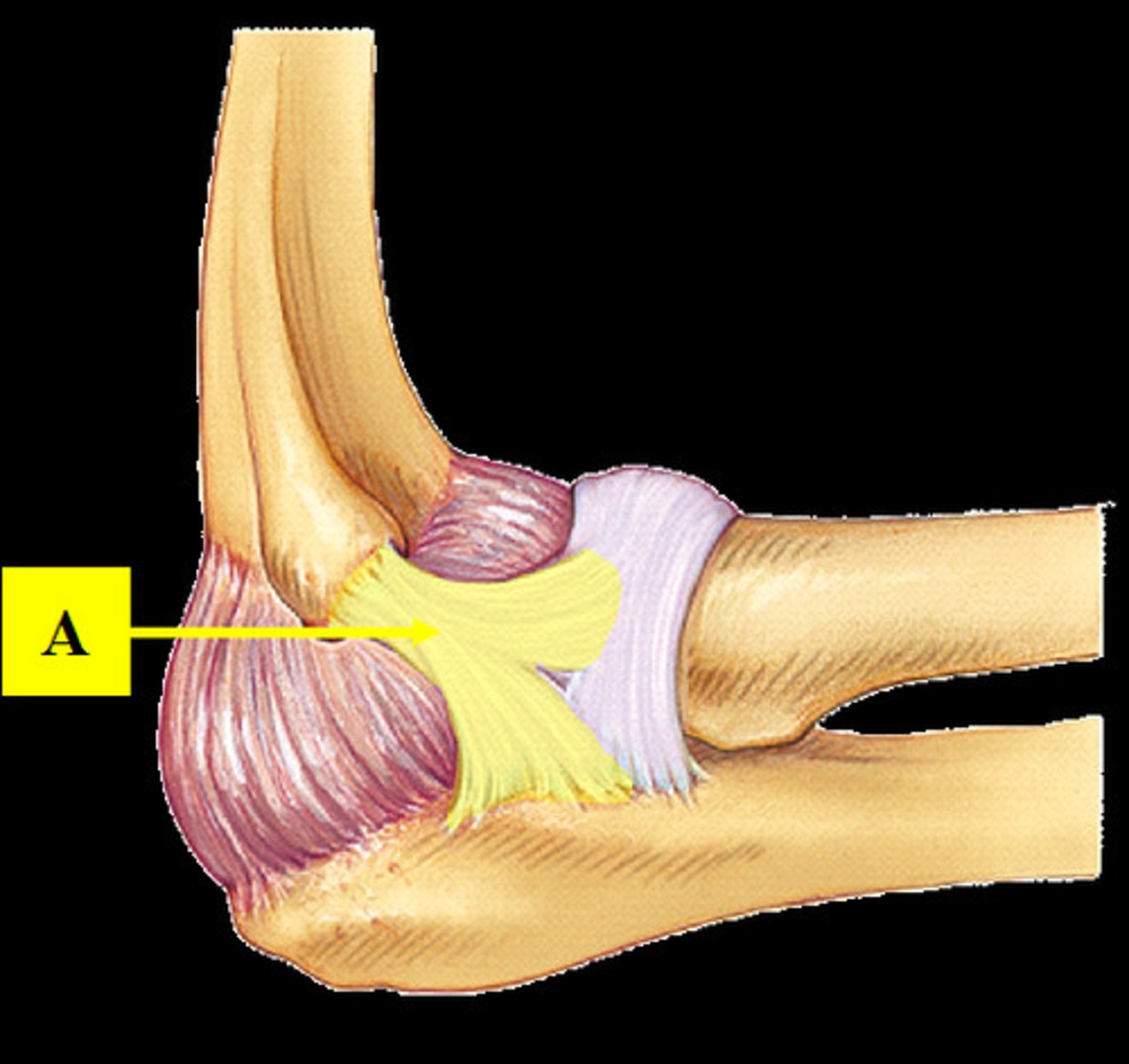
annular ligament
binds the head of the radius to the ulna
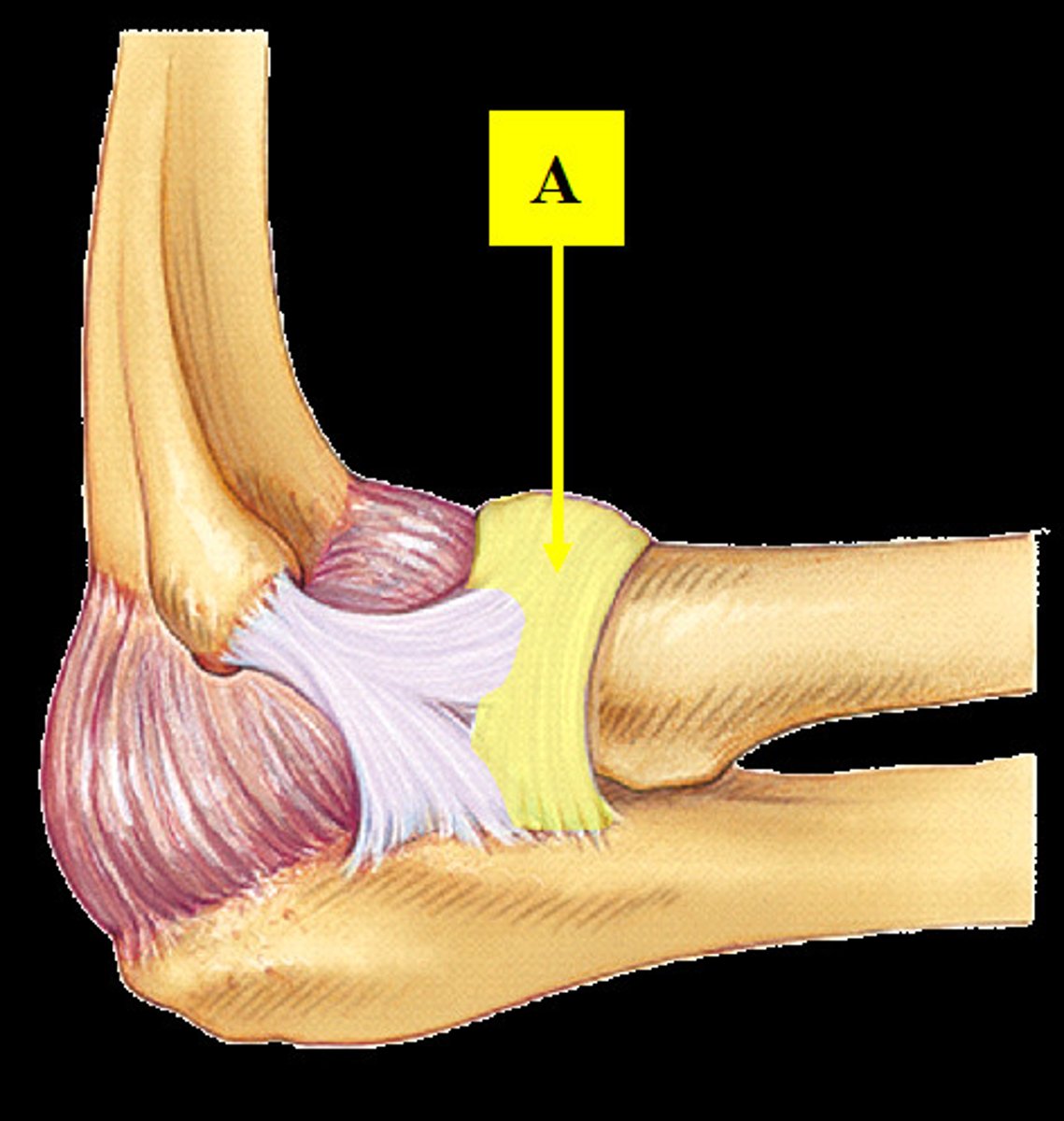
ulnar (medial) collateral ligament
- stabilizes the medial side of the joint
- connects the humerus with the ulna
coxal joint
hip joint
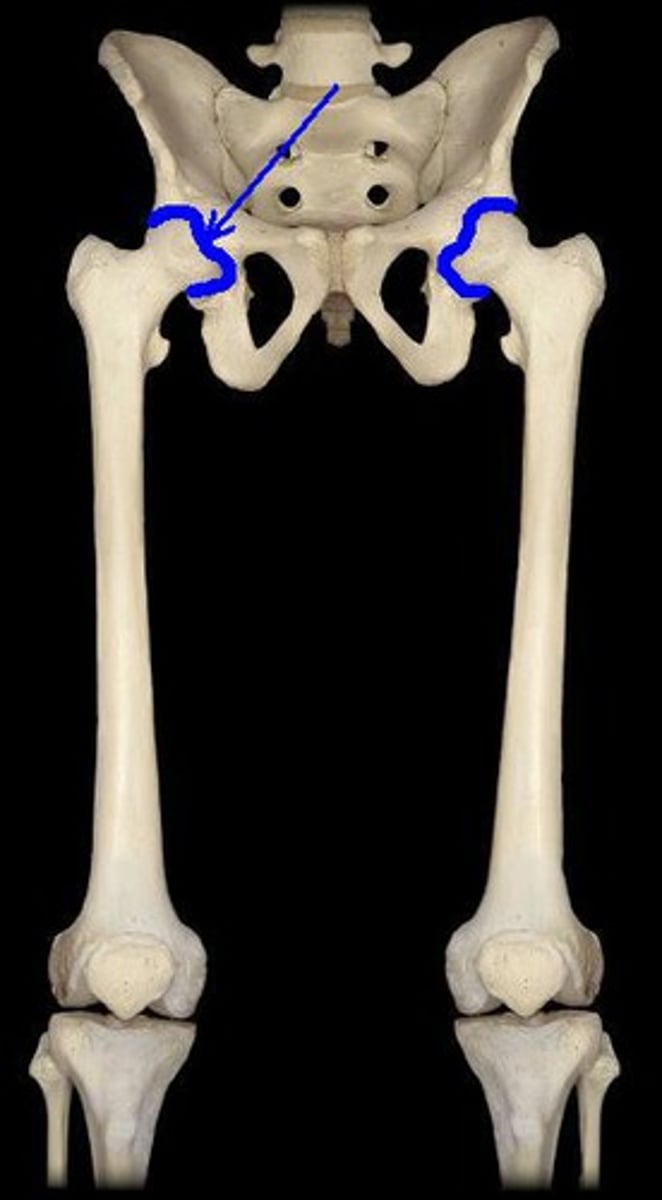
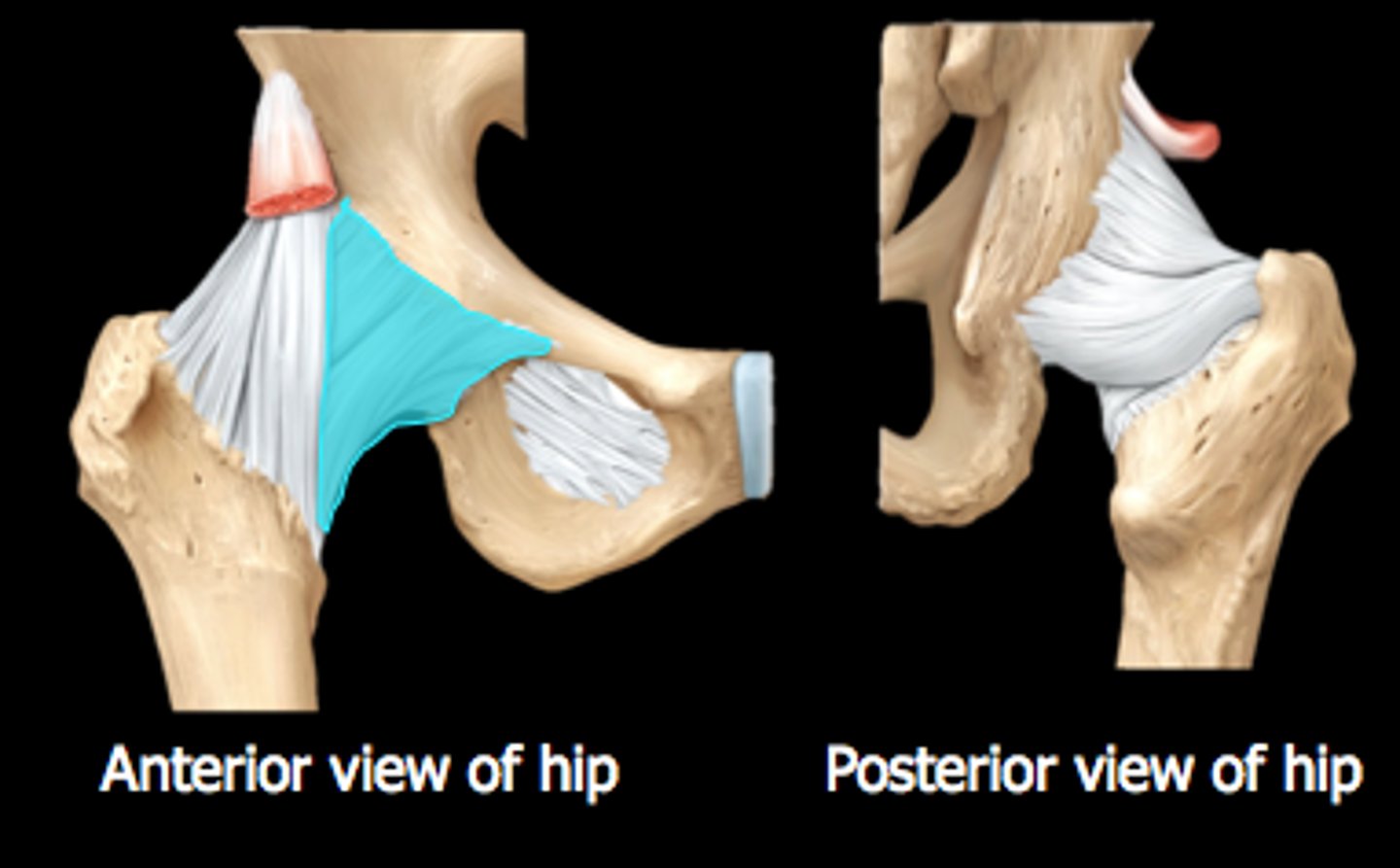
iliofemoral ligament
connects ilium to femur
strongest ligament in the body
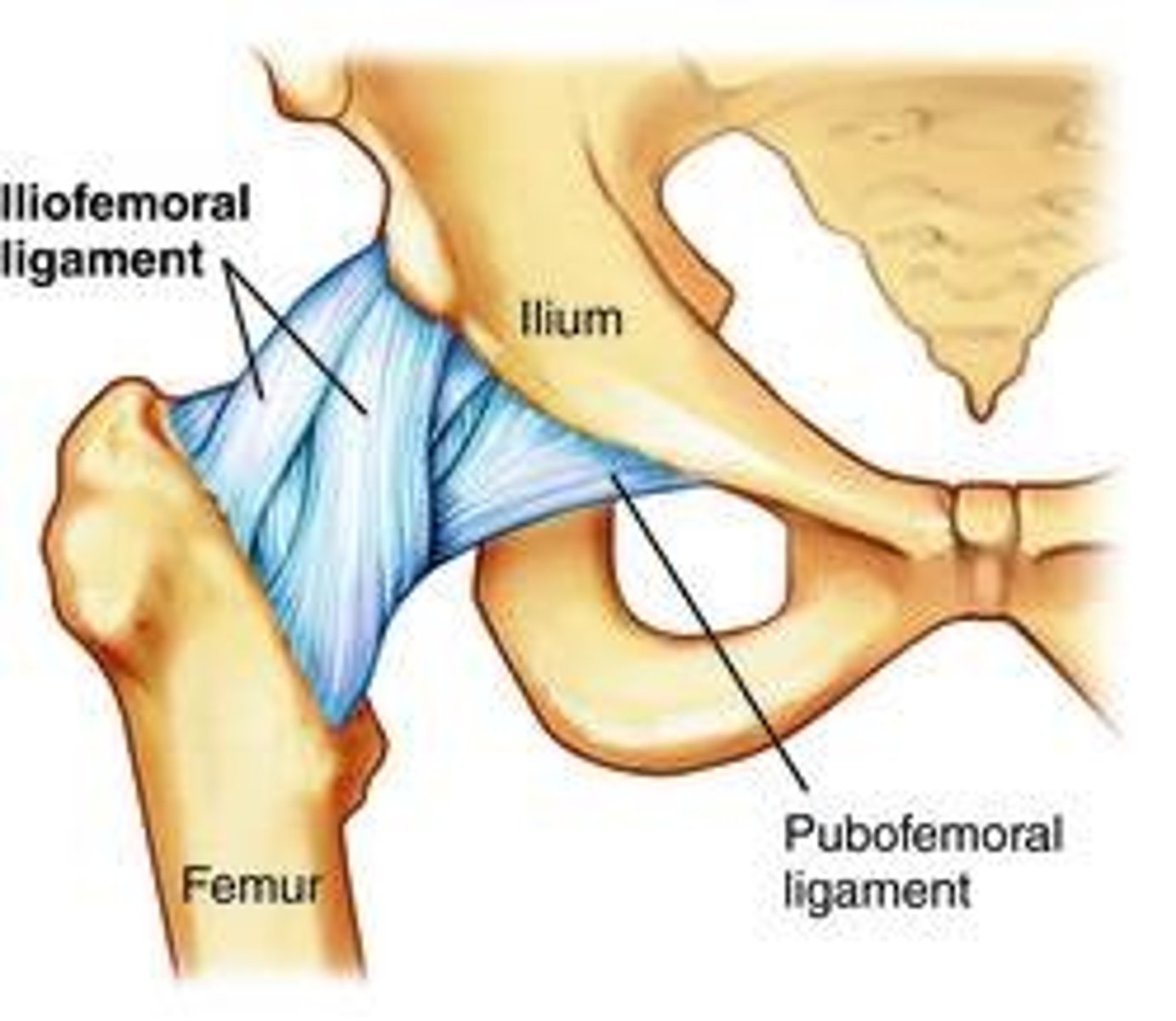
pubofemoral ligament
connects pubis to femur
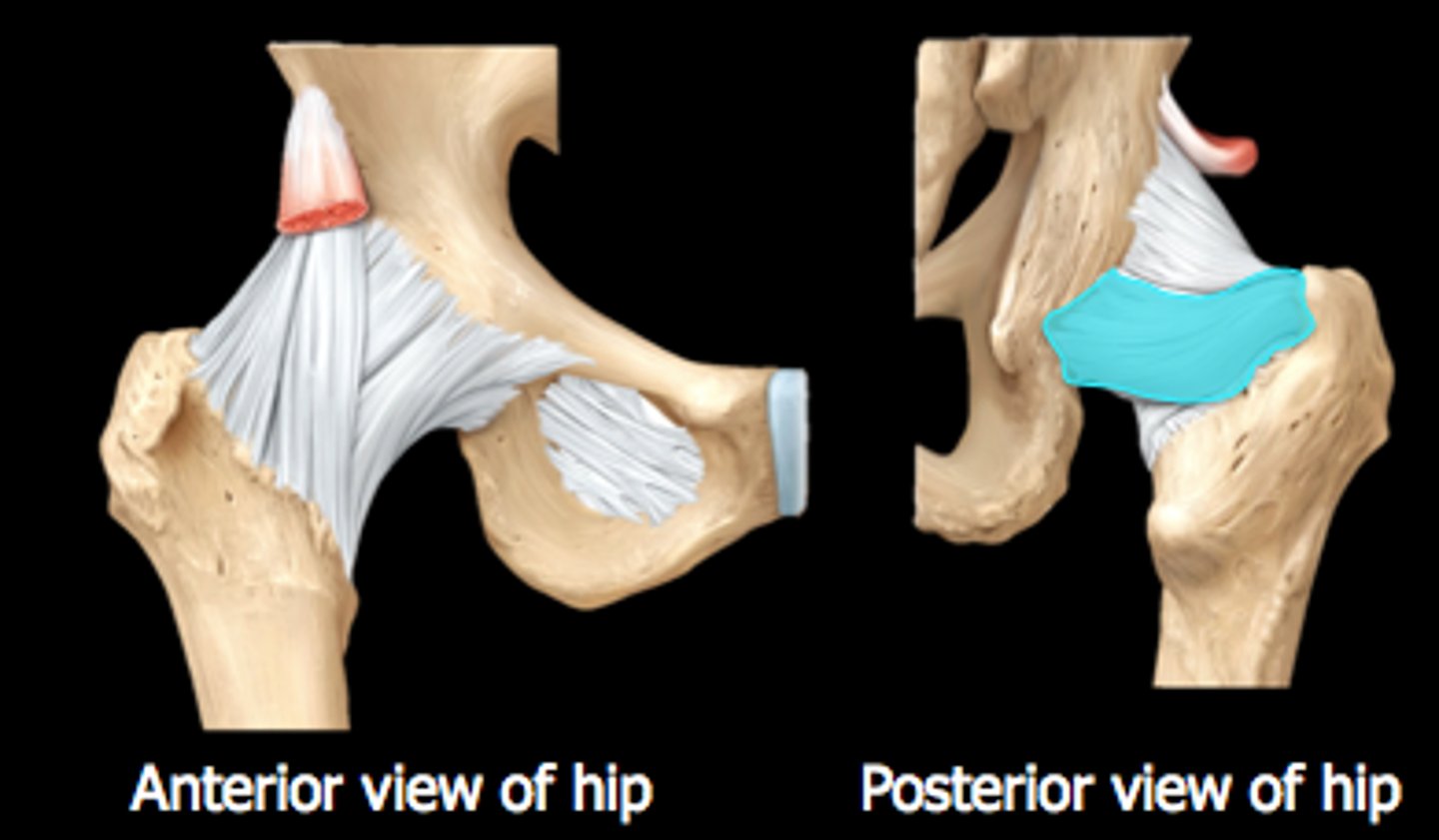
ischiofemoral ligament
connects ischium to femur
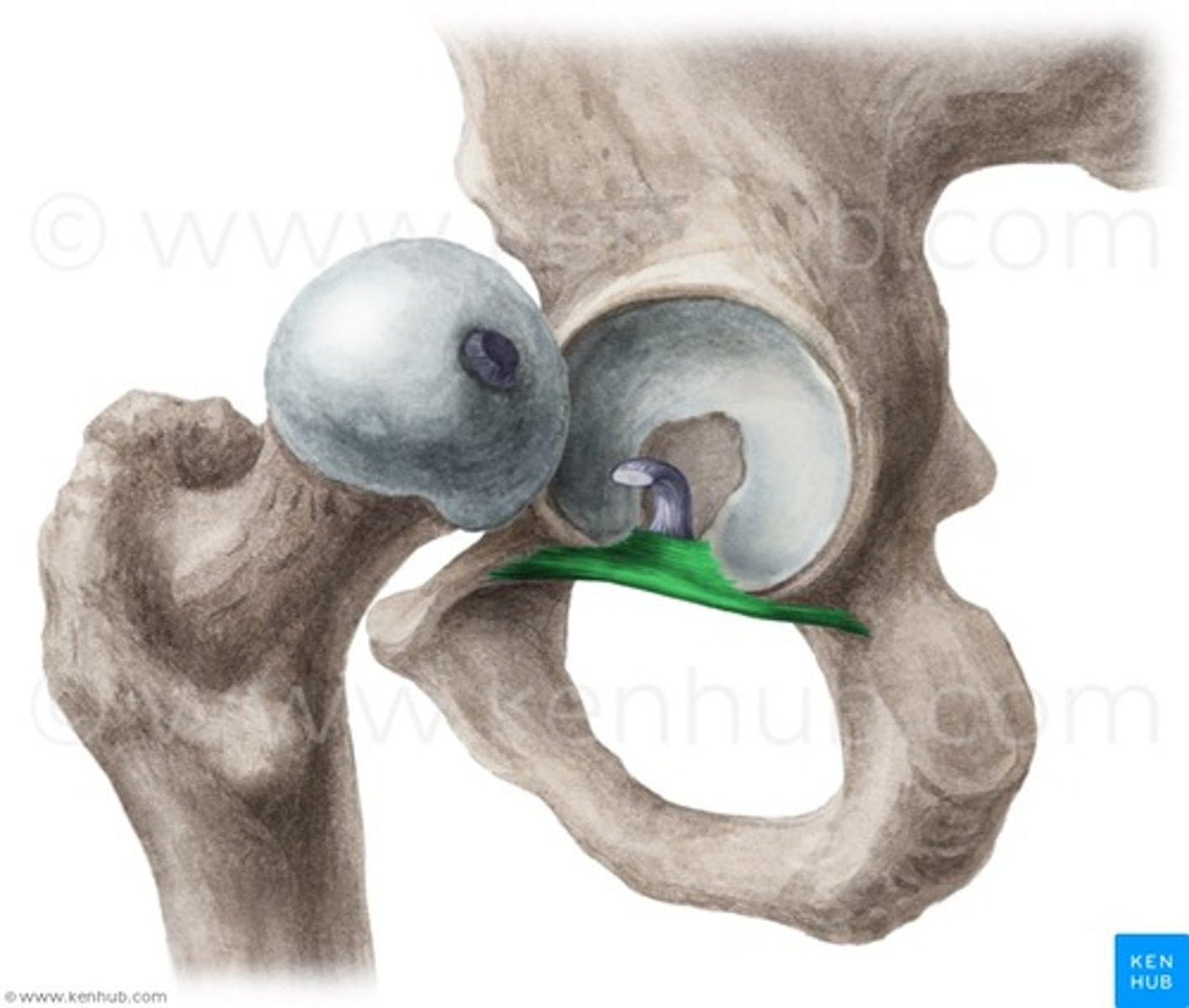
transverse acetabular ligament
Connects the femur to the inferior acetabular rim
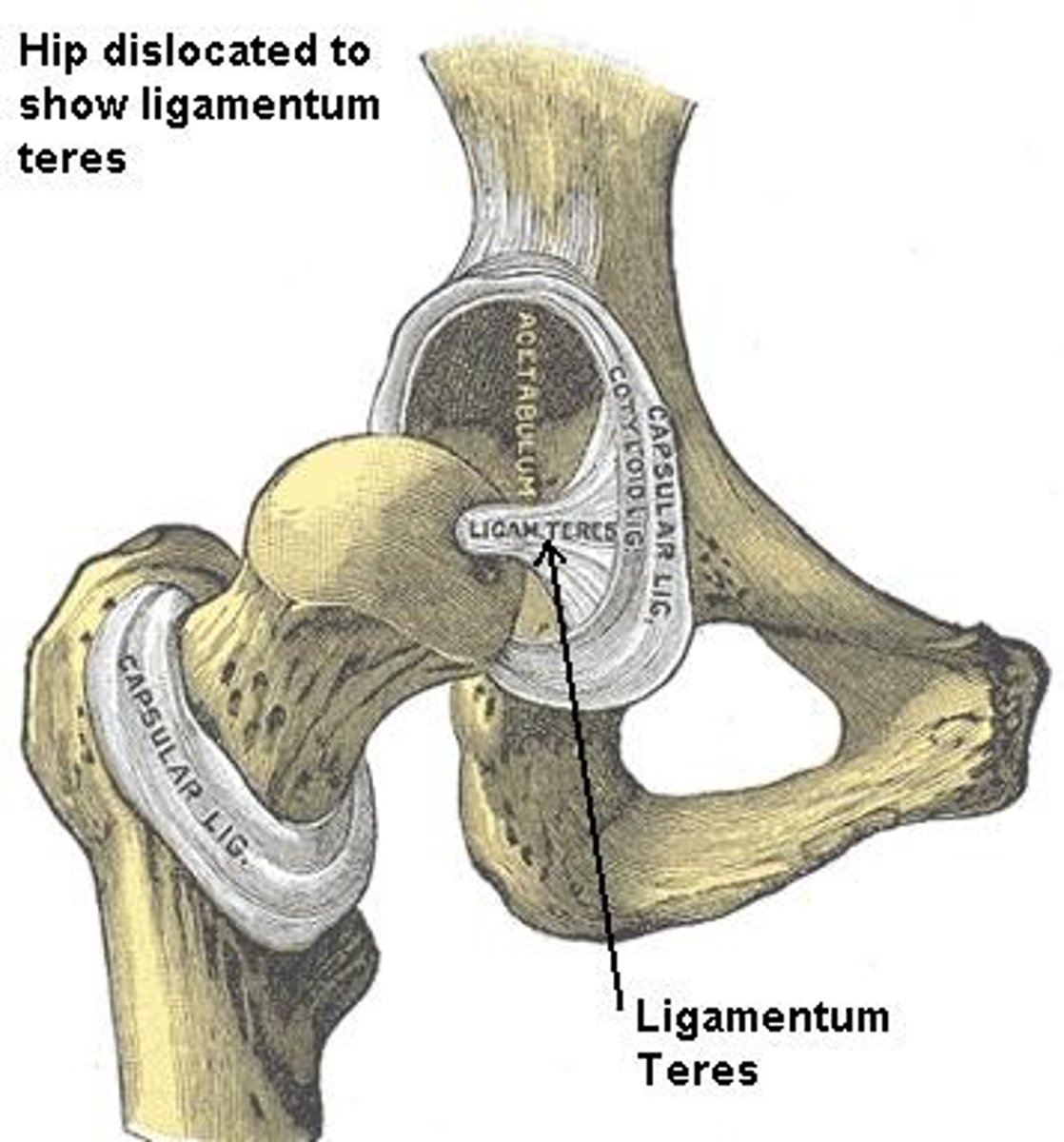
ligamentum teres
Ligament head of femur
Intra-articular ligament
Carries small artery to the femoral head
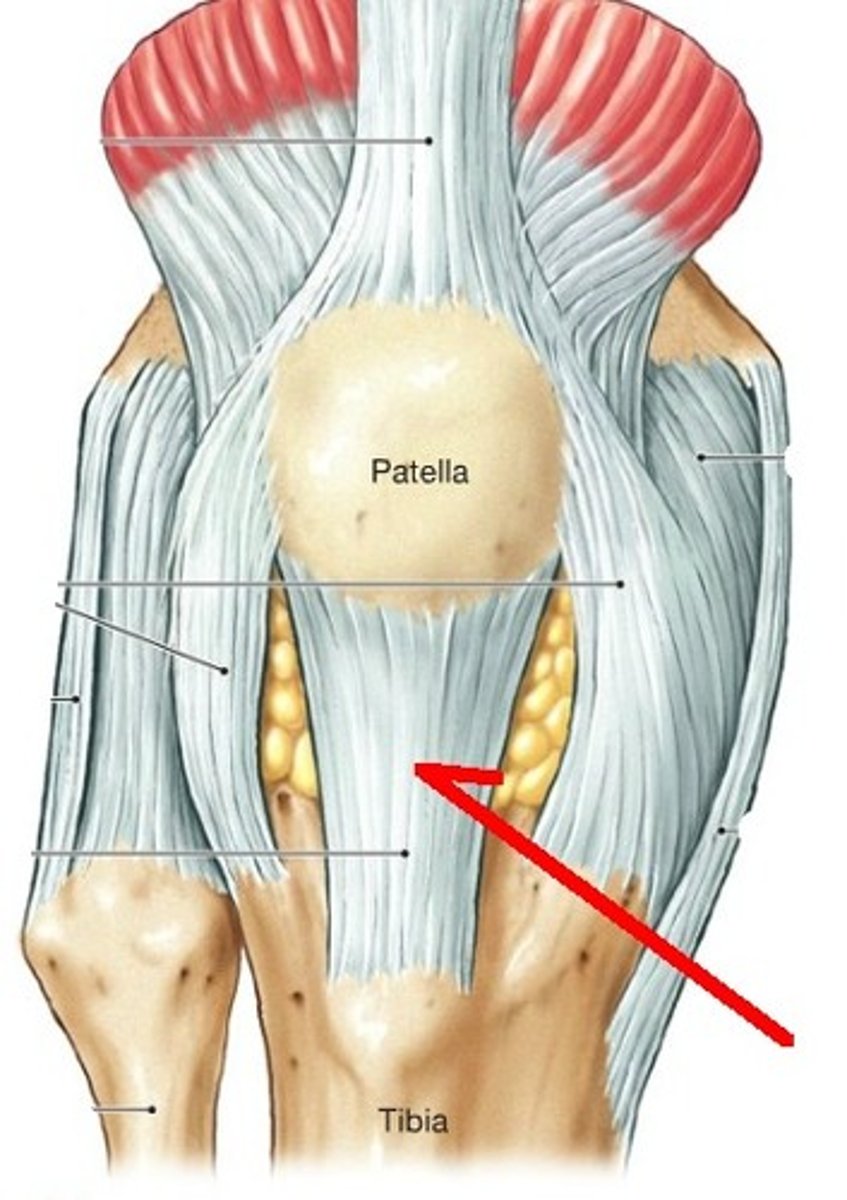
patellar ligament
connects the tibial tuberosity to the quadriceps tendon
popliteal ligaments
Run between the femur and heads of the tibia and fibula
tibial collateral ligament
connects the medial epicondyle of the femur to the tibia
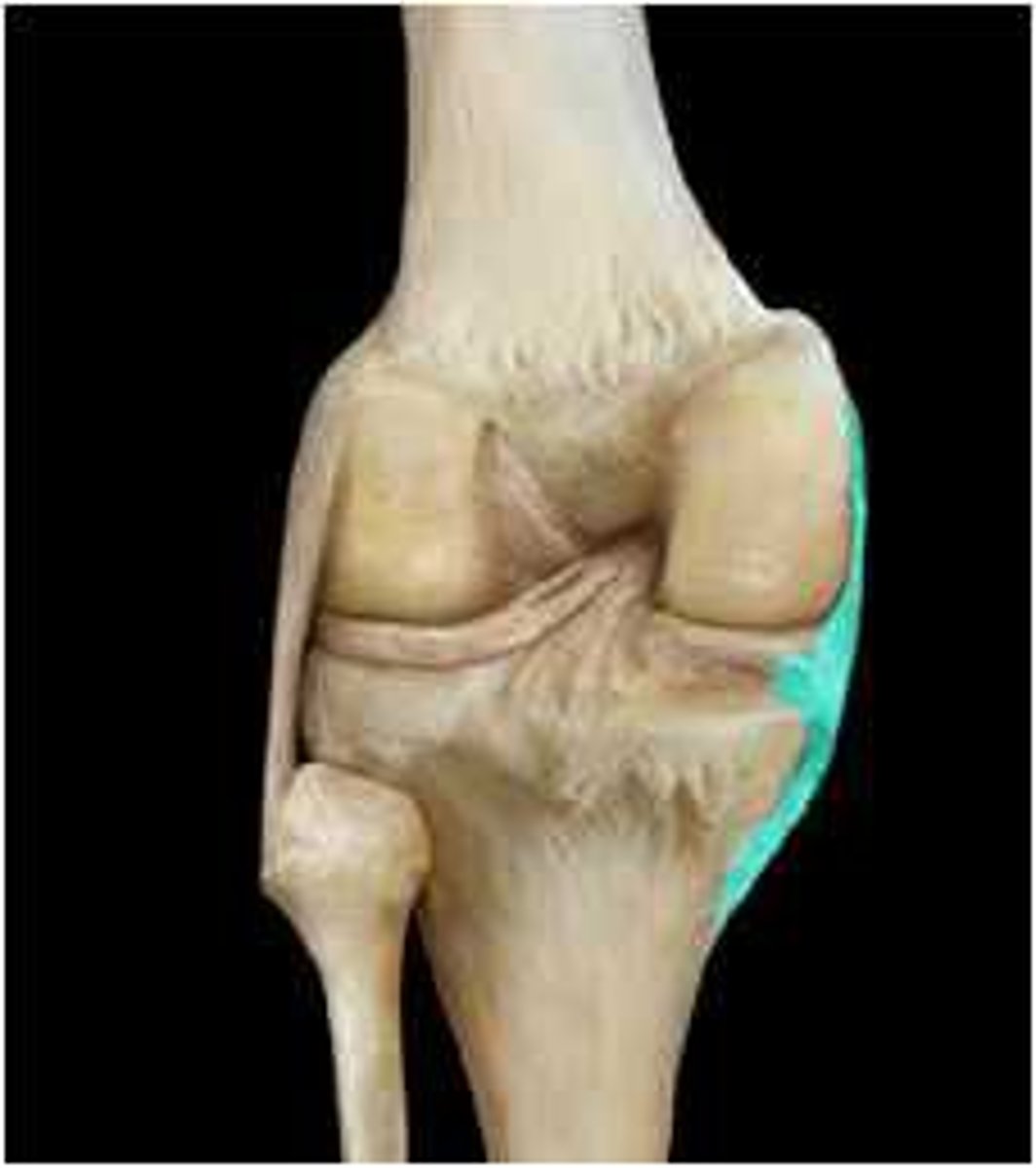
fibular collateral ligament
connects the lateral epicondyle of the femur to the fibula
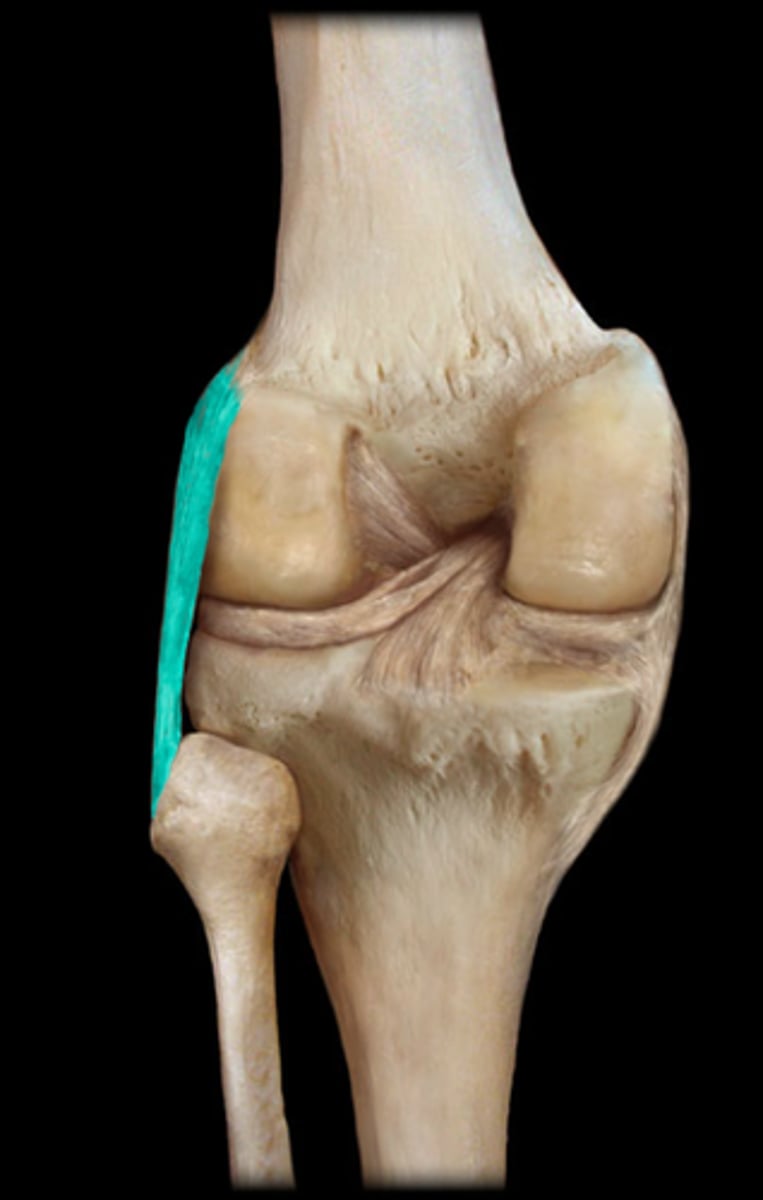
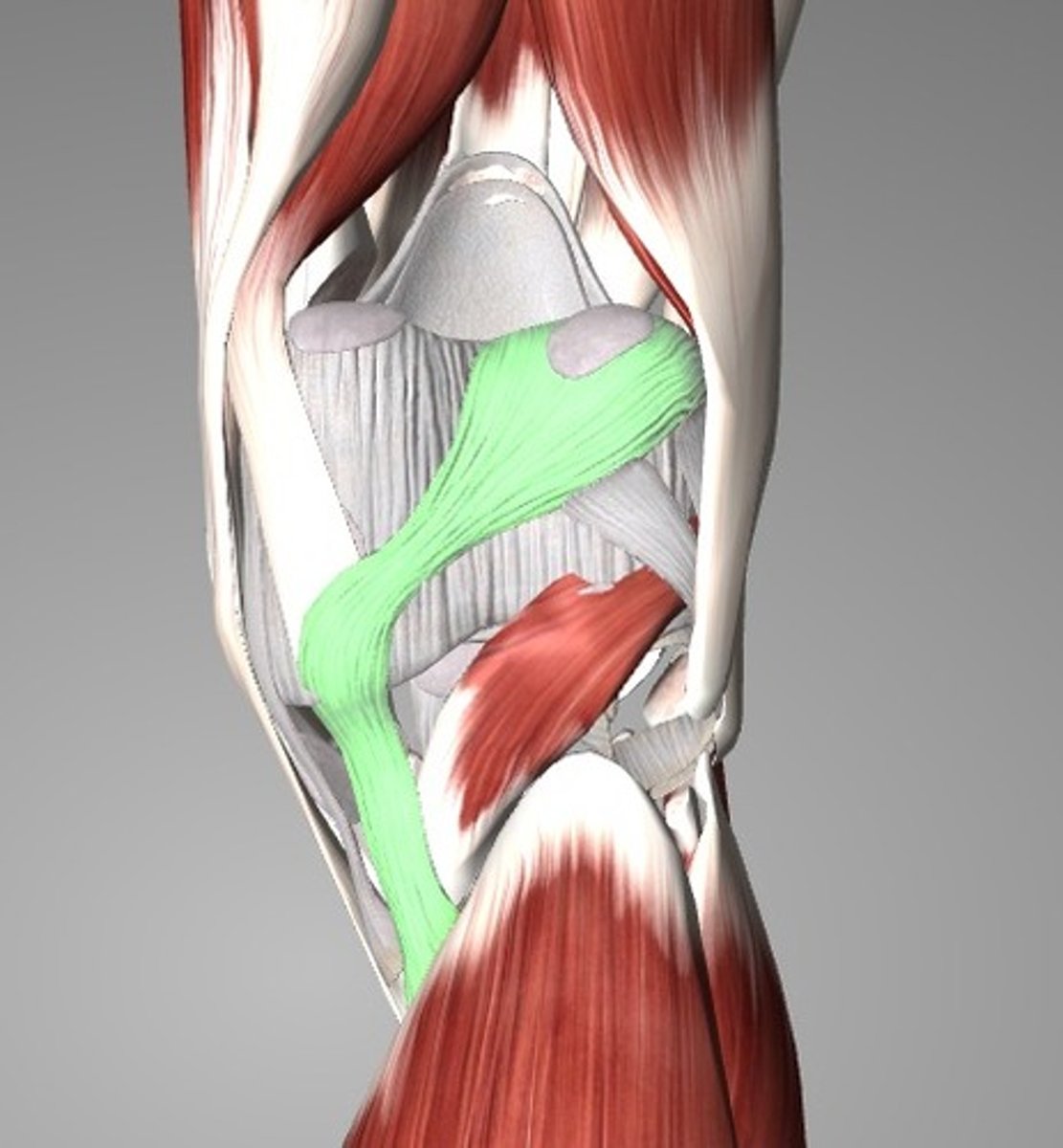
anterior cruciate ligament
(ACL) Attaches to anterior tibia
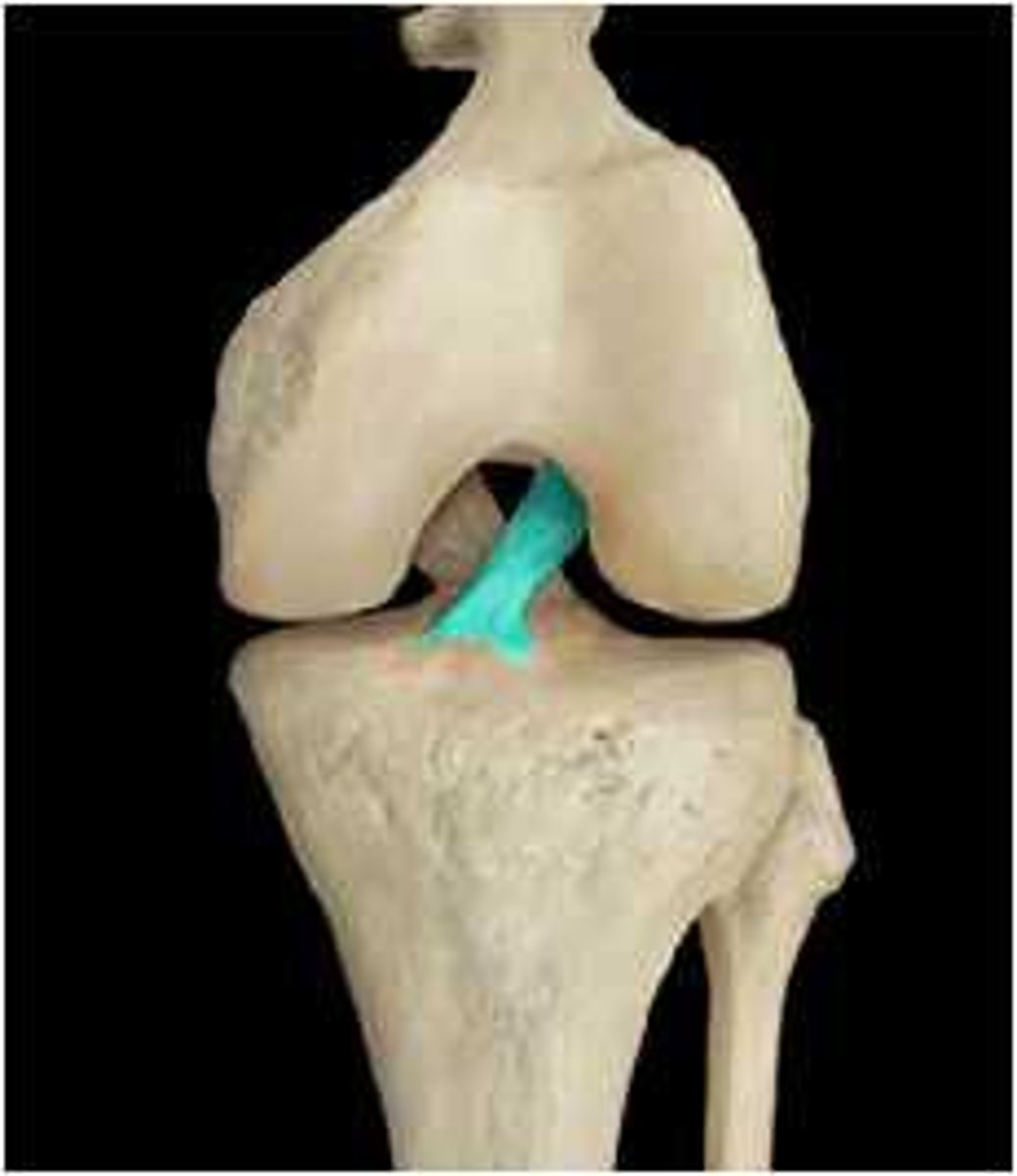
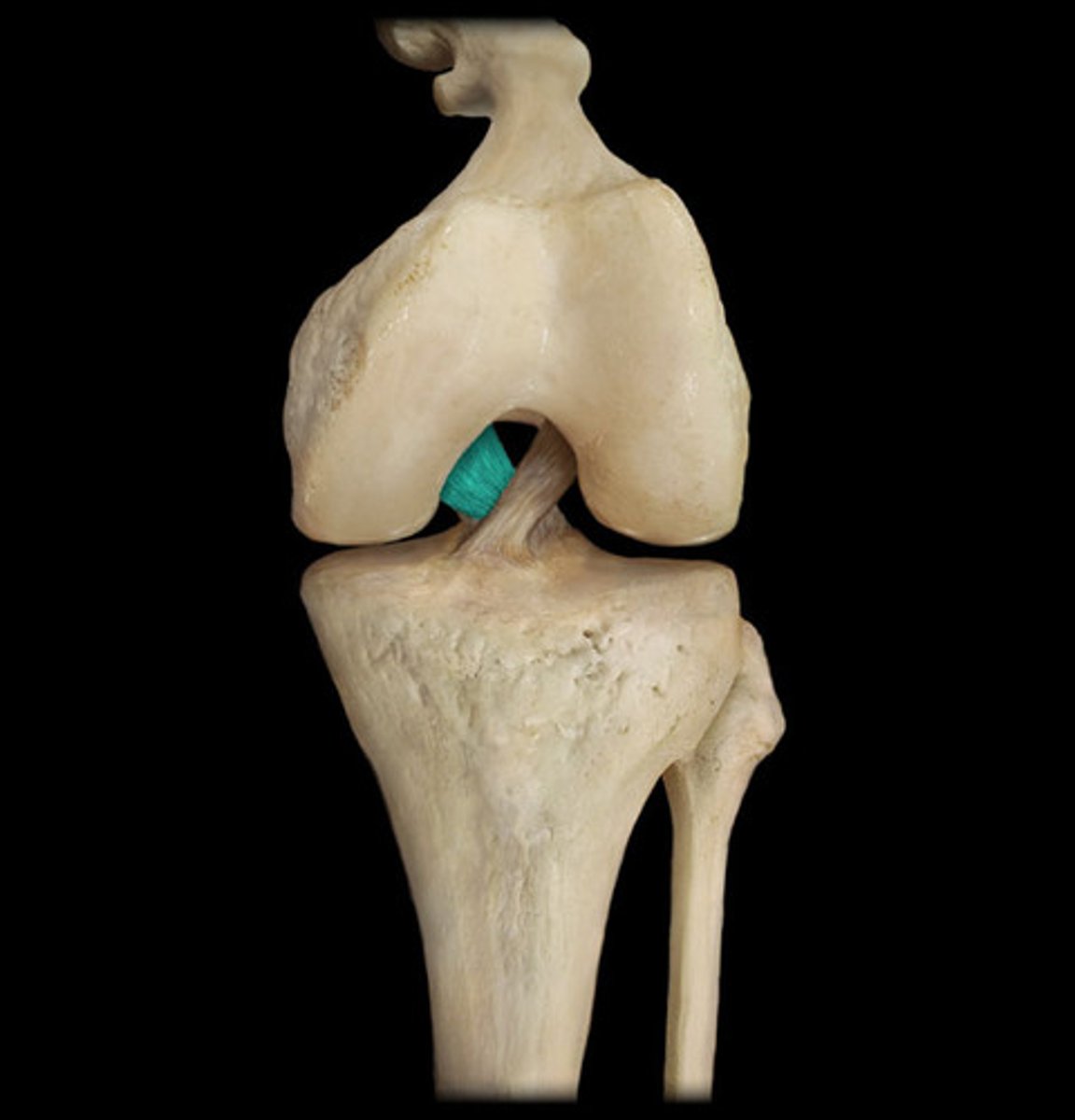
posterior cruciate ligament
PCL: connects the intercondylar eminence of the tibia to the medial side of the intercondylar fossa
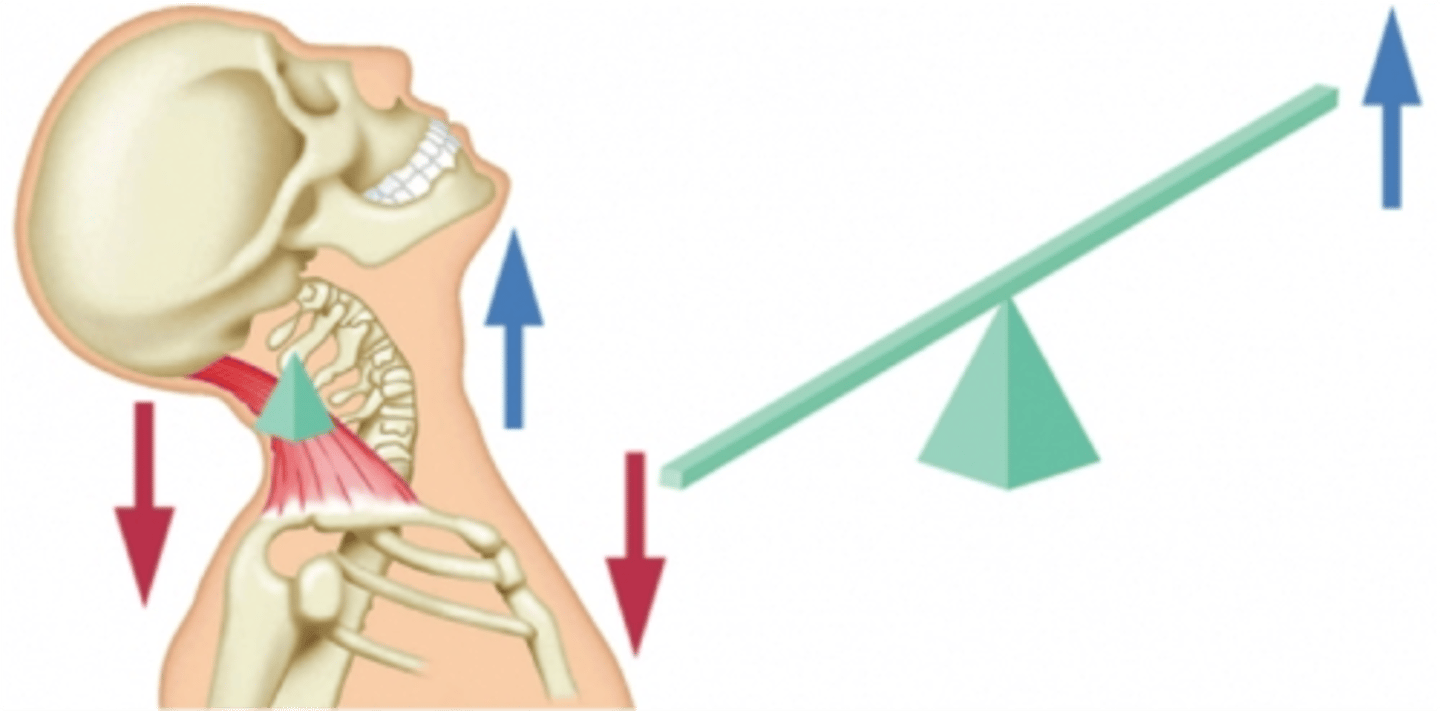
first class lever
a lever for which the muscle force and resistive force act on opposite sides of the fulcrum, example the neck
second class lever
the load is between the fulcrum and the input force; never changes the direction of the input force, example the hip
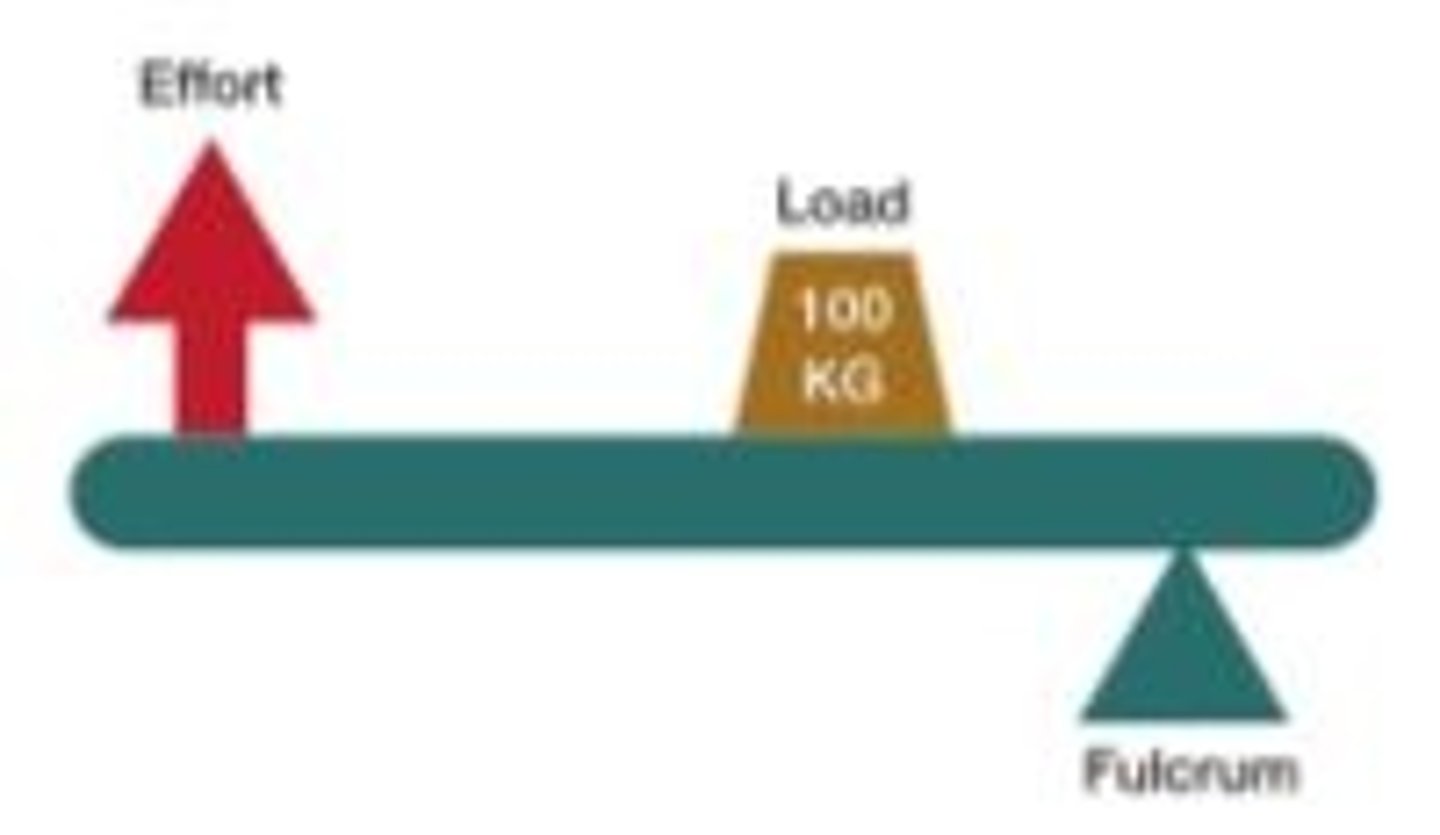
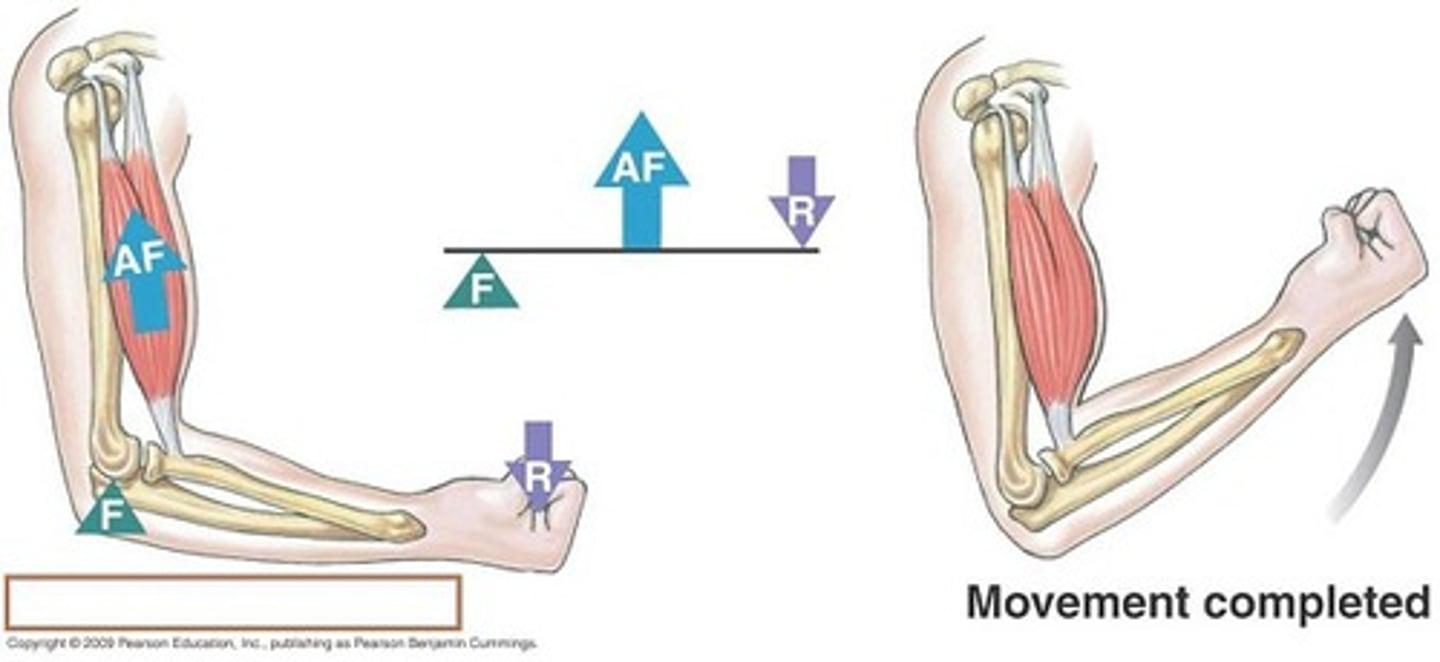
third class lever
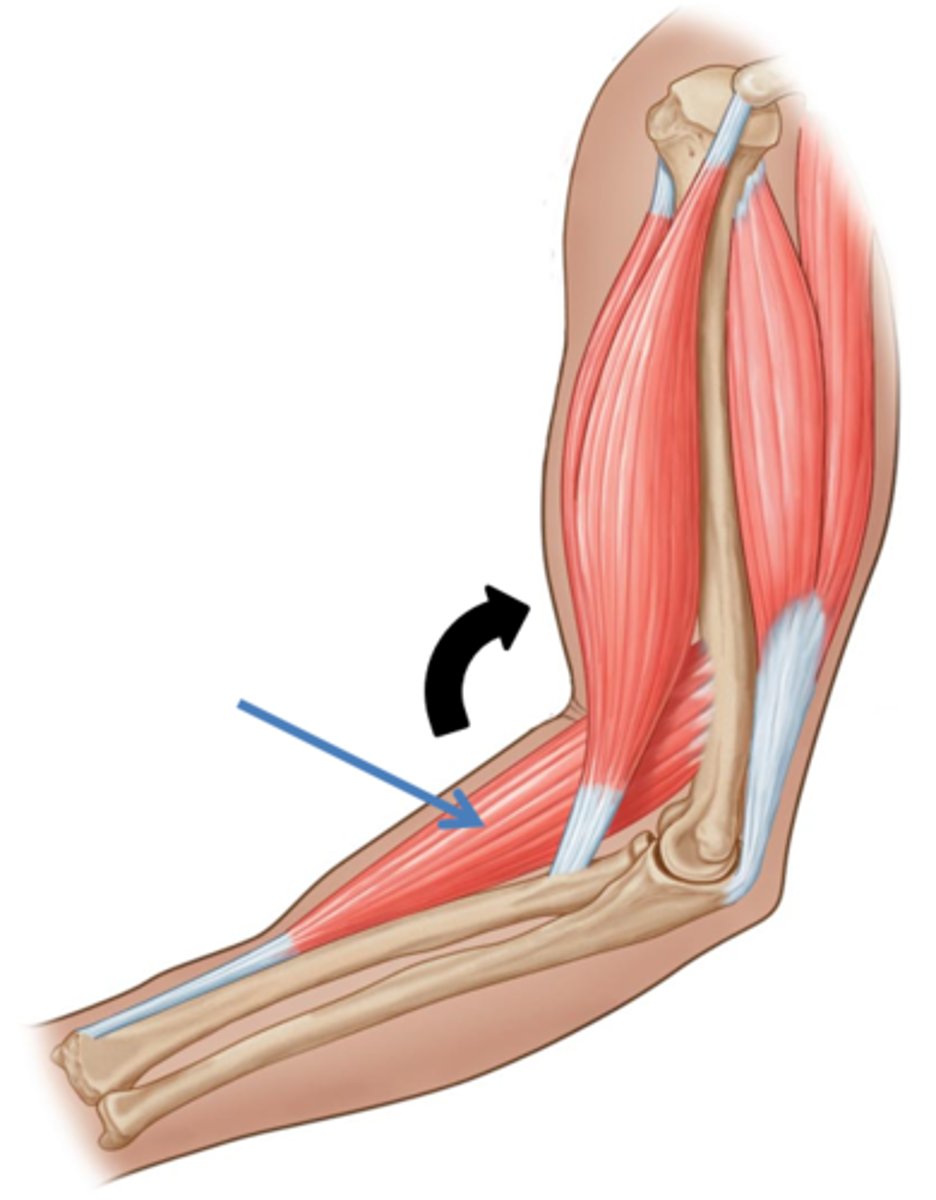
The fulcrum is at one end of the bar and the effort is between the fulcrum and the resistance, example the elbow
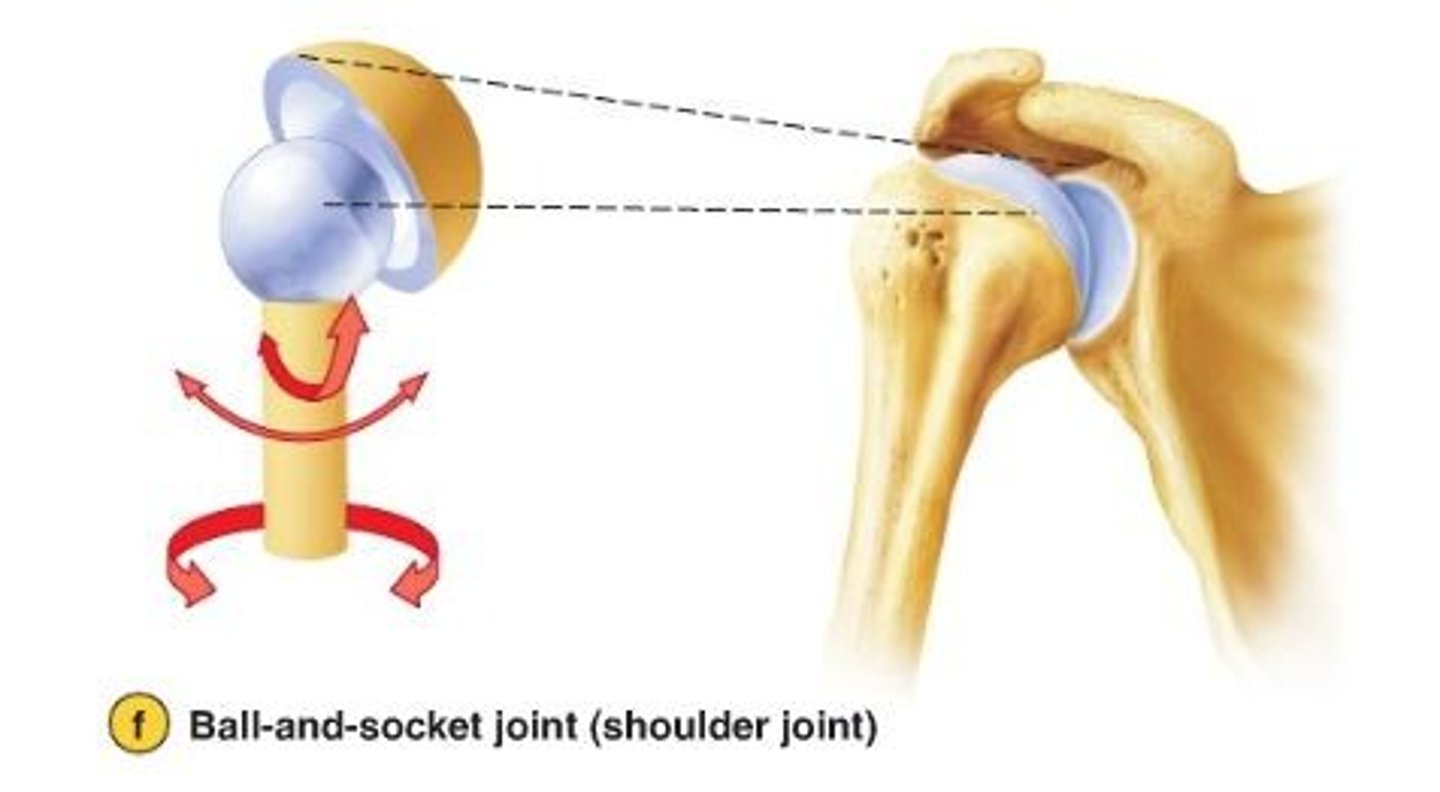
ball and socket joint
shoulder and hip
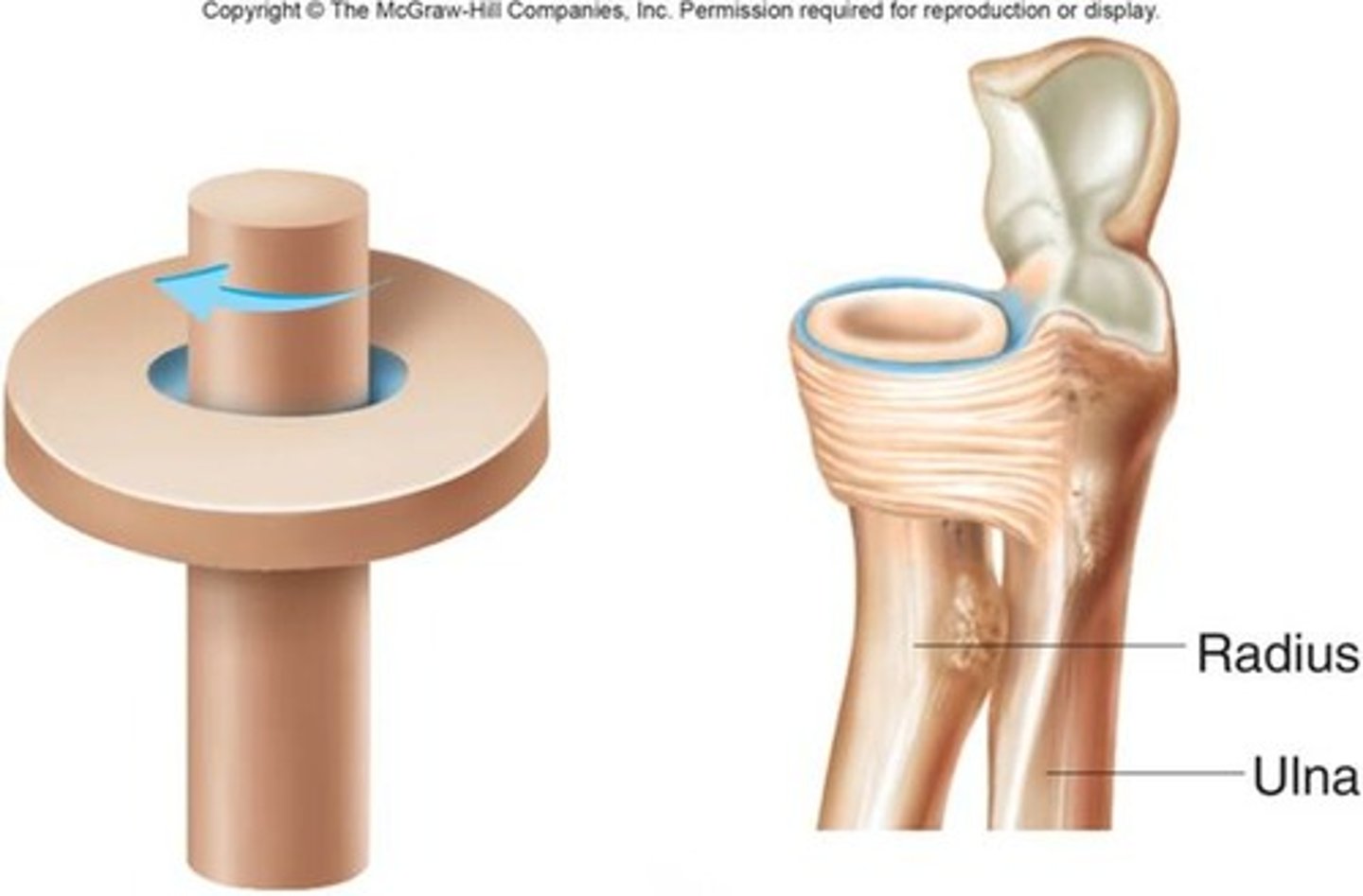
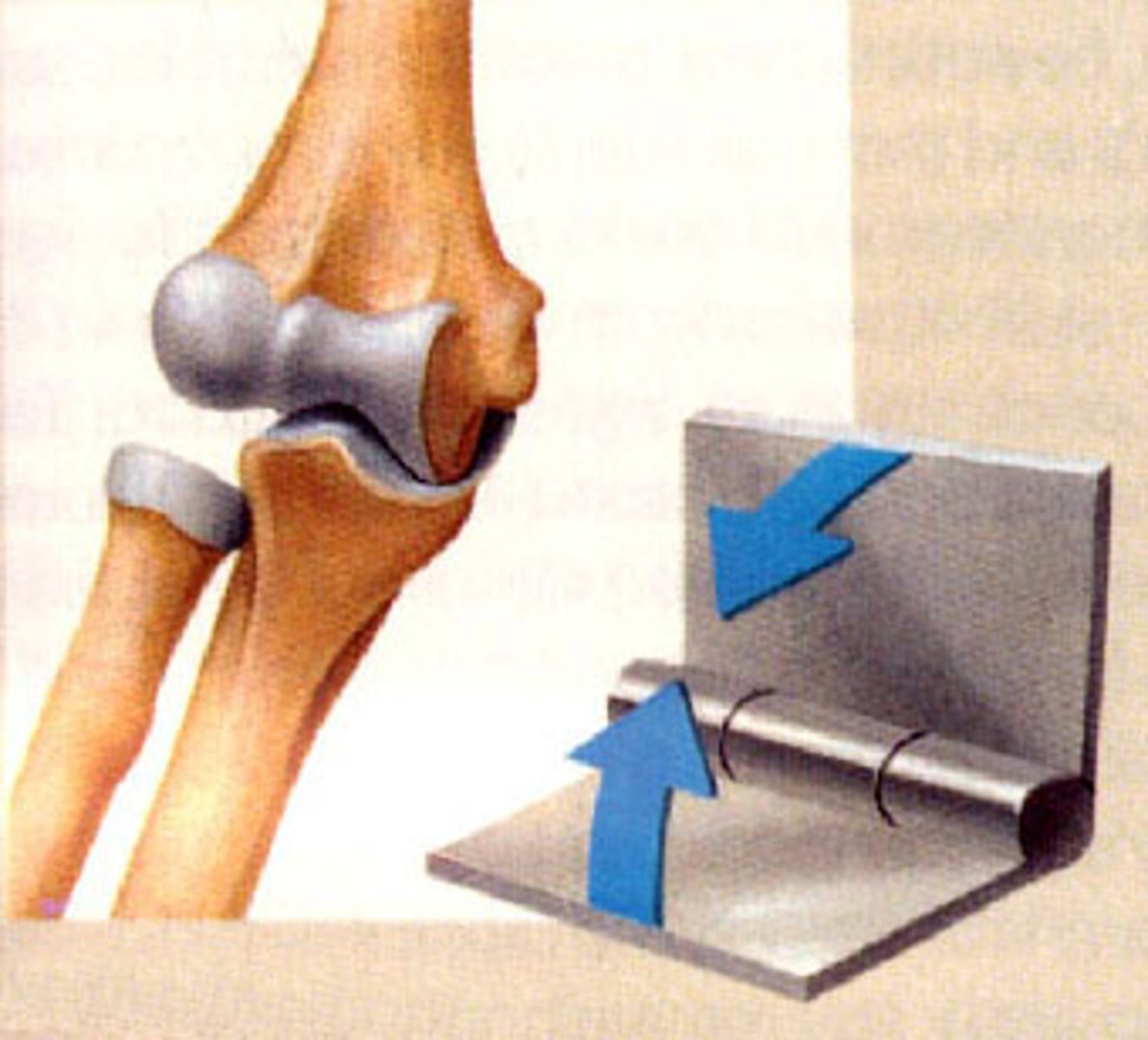
pivot joint
rotating bone turns around an axis; i.e. connection between radius/ulna and humerus
saddle joint
type of joint found at the base of each thumb; allows grasping and rotation
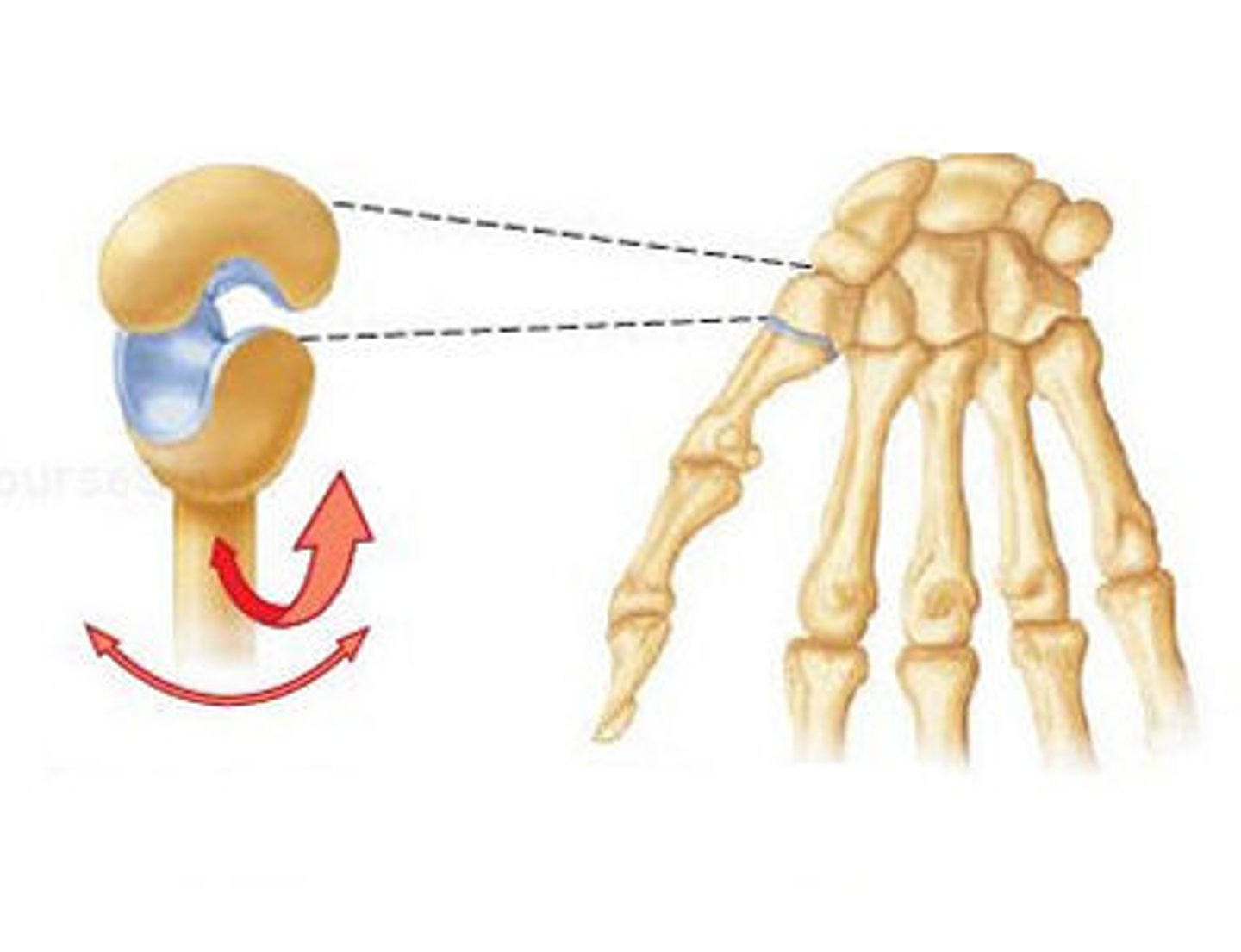
hinge joint
Joint between bones (as at the elbow or knee) that permits motion in only one plane
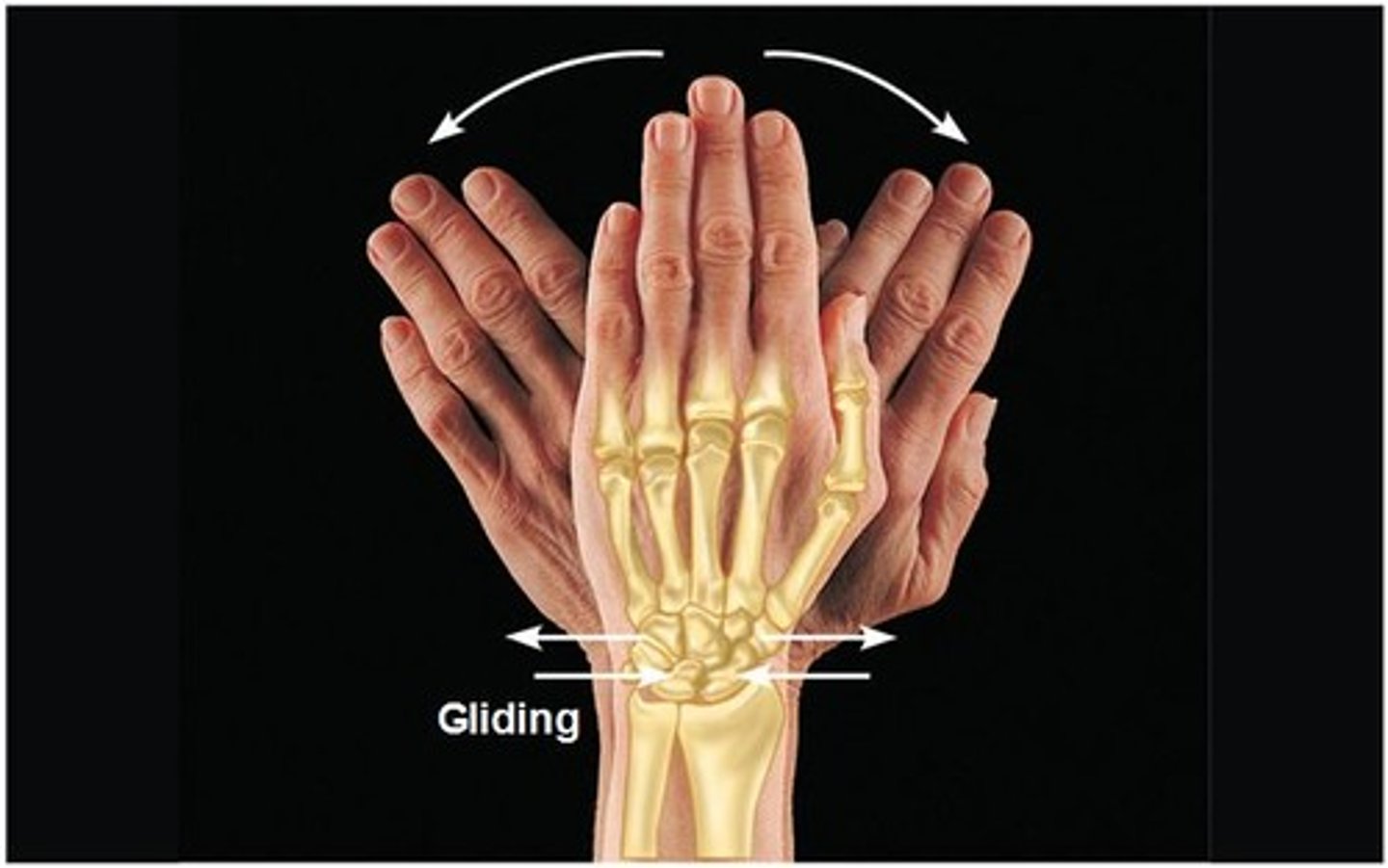
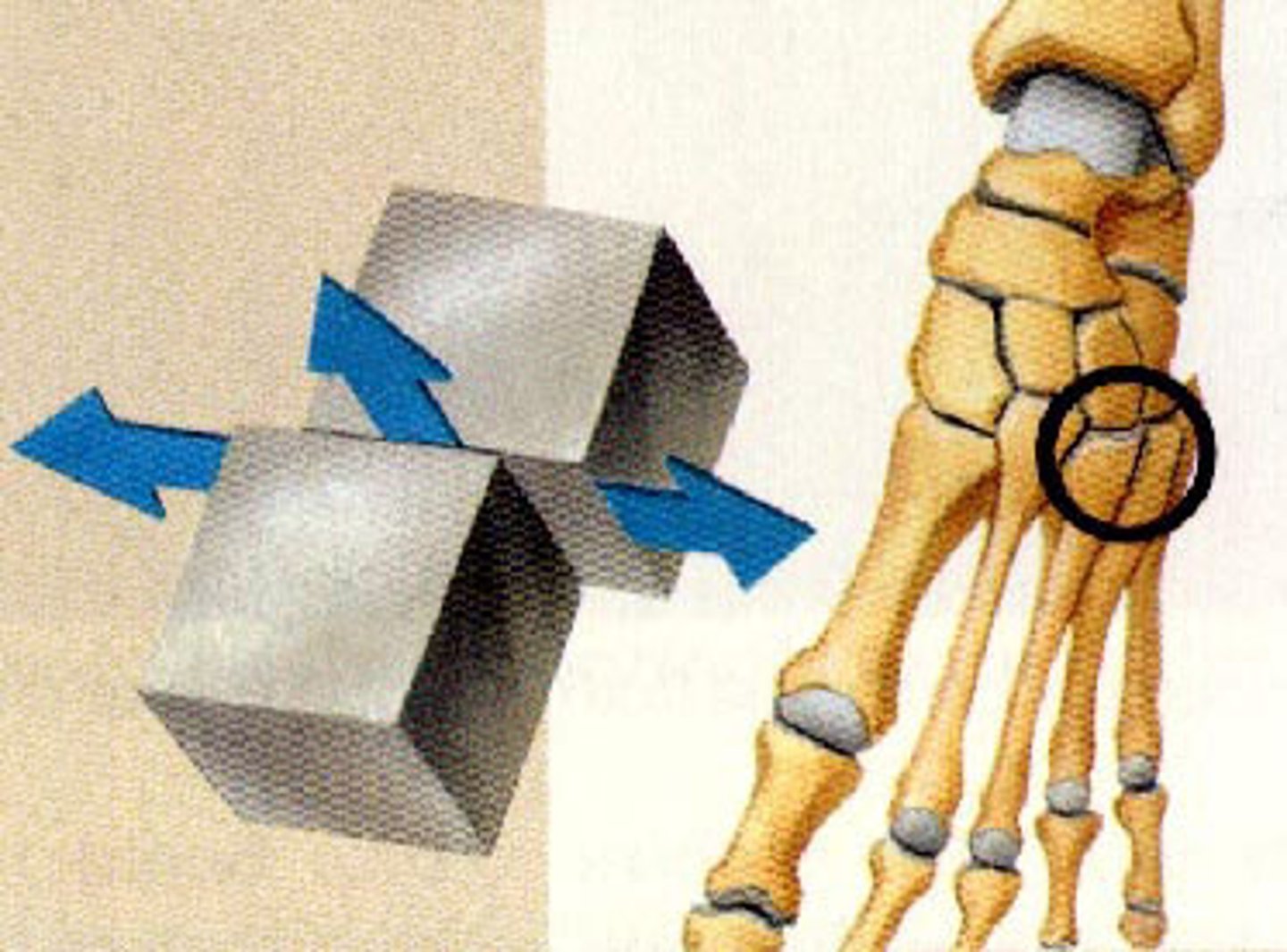
plane joint
allows only gliding movement (carpals)
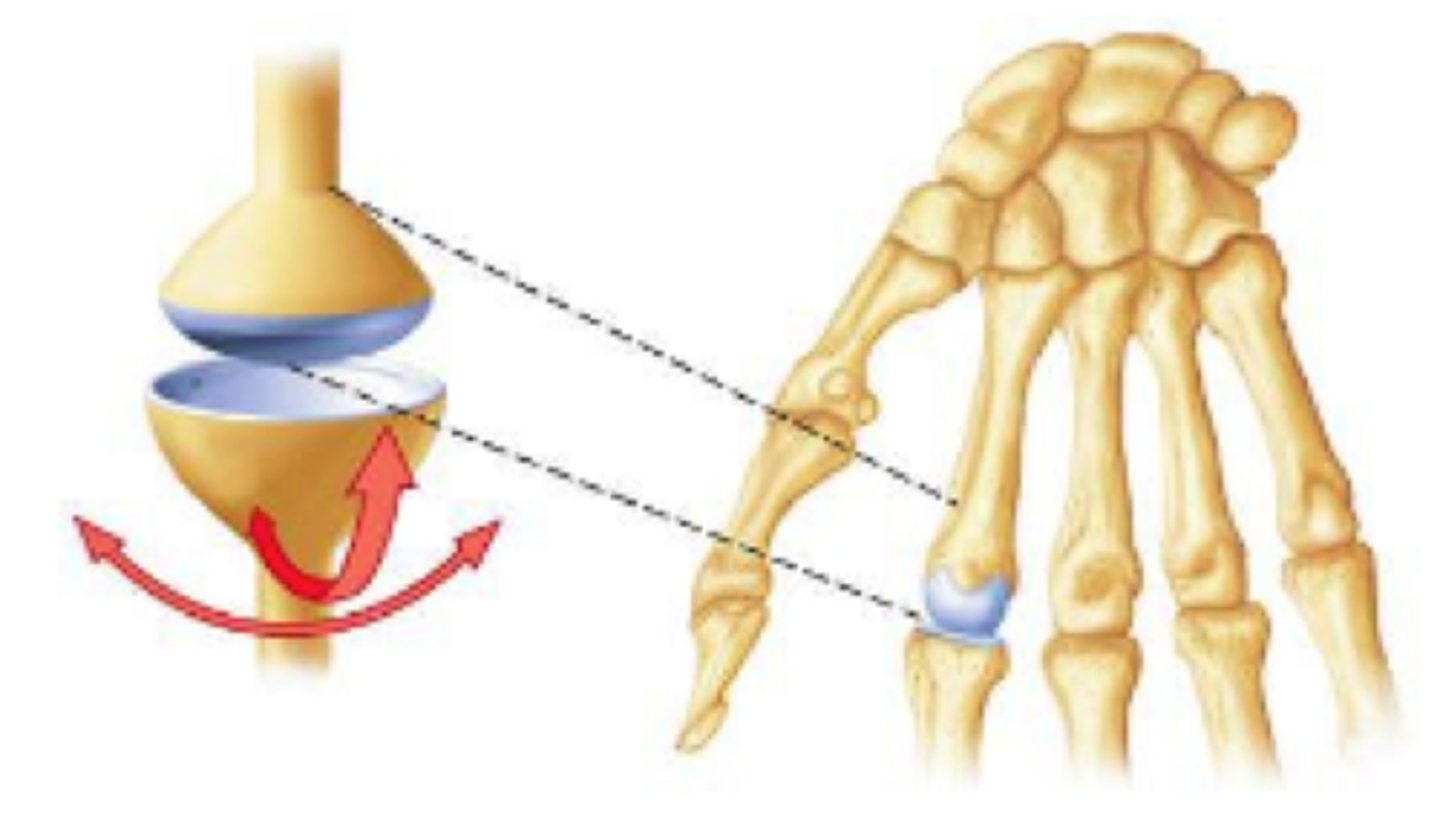
condylar joint
a shallow ball-and-socket joint with limited mobility
glenoid cavity
socket in scapular that receives head of humerus
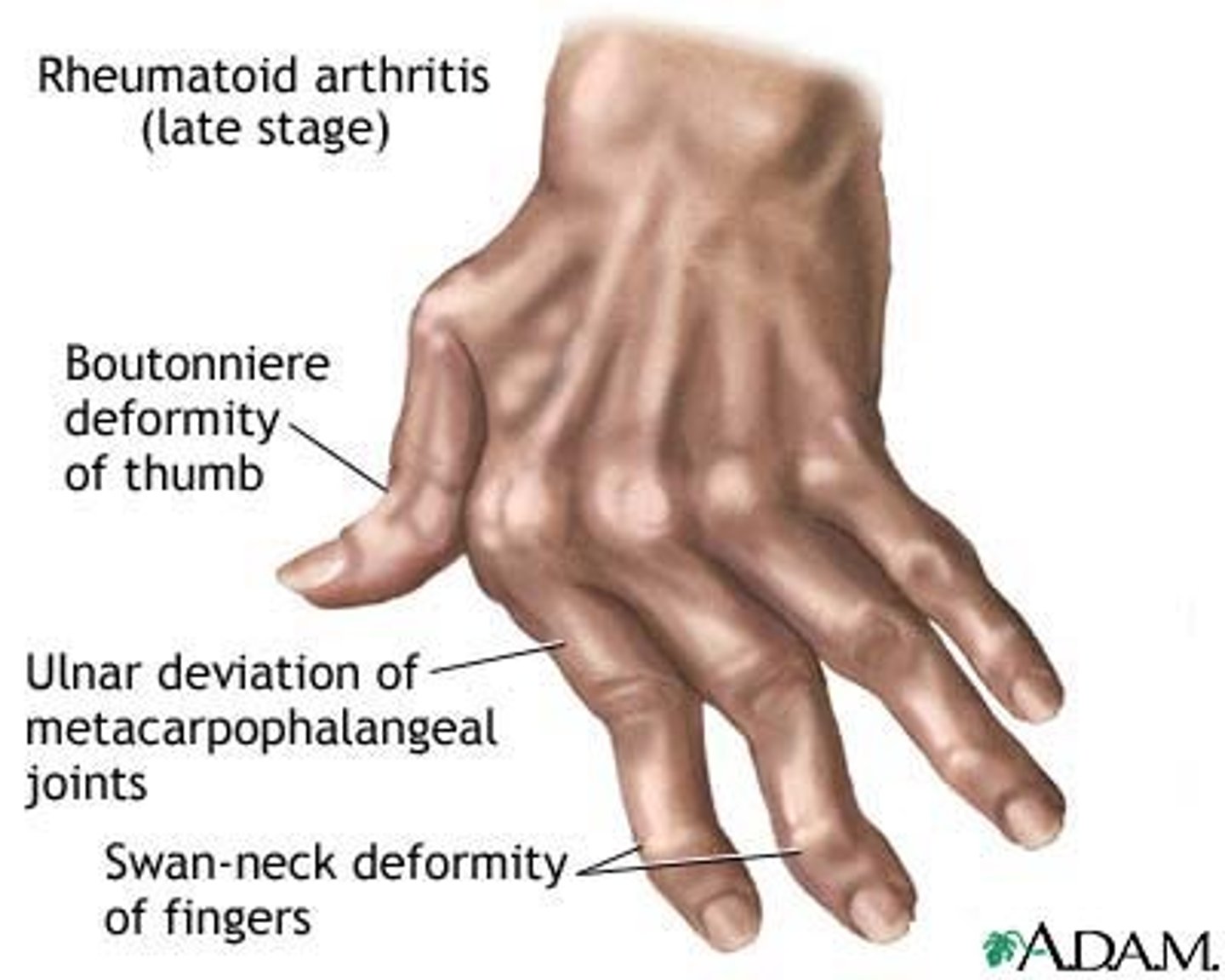
rheumatoid arthritis
A chronic systemic disease characterized by inflammation of the joints, stiffness, pain, and swelling that results in crippling deformities
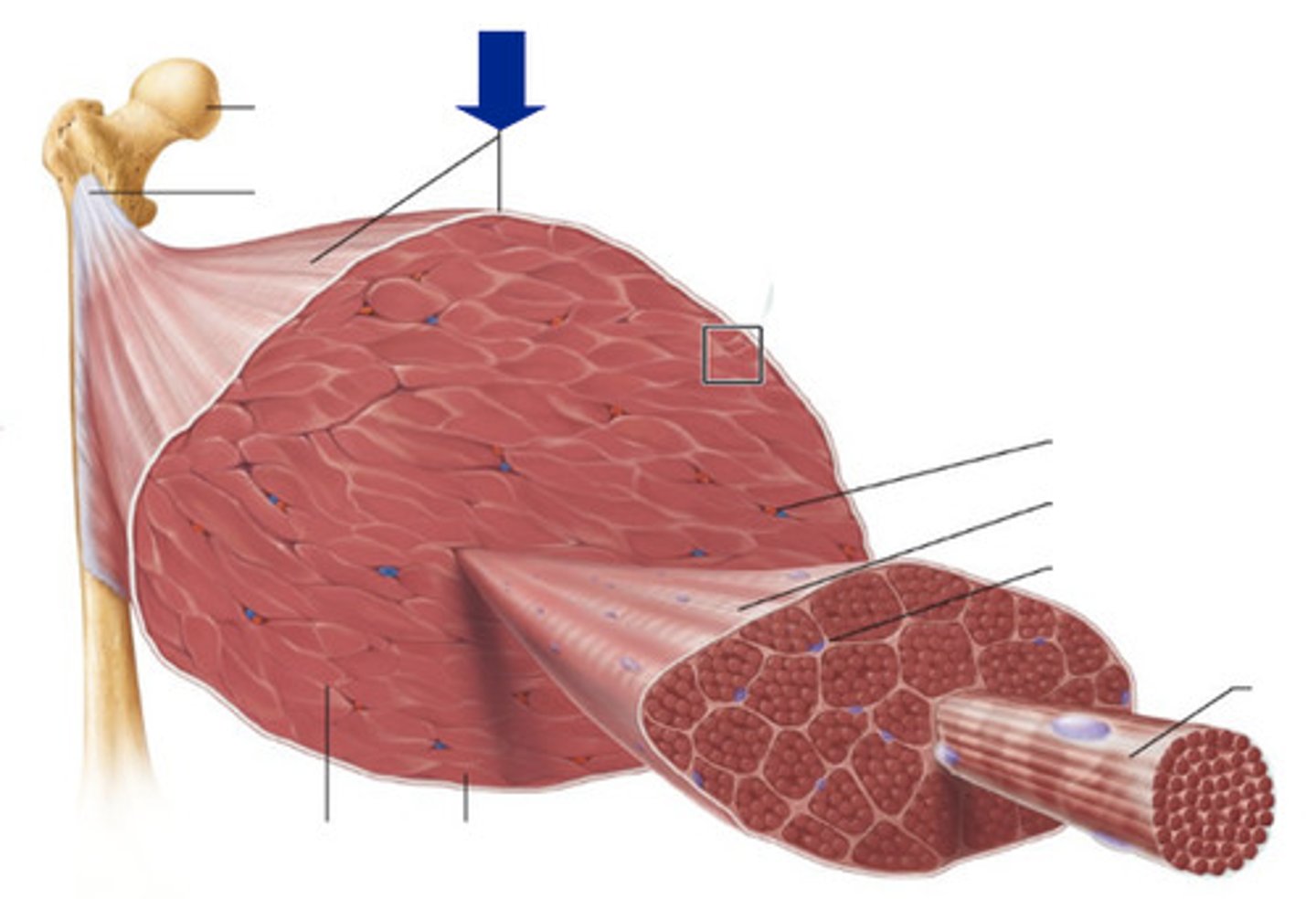
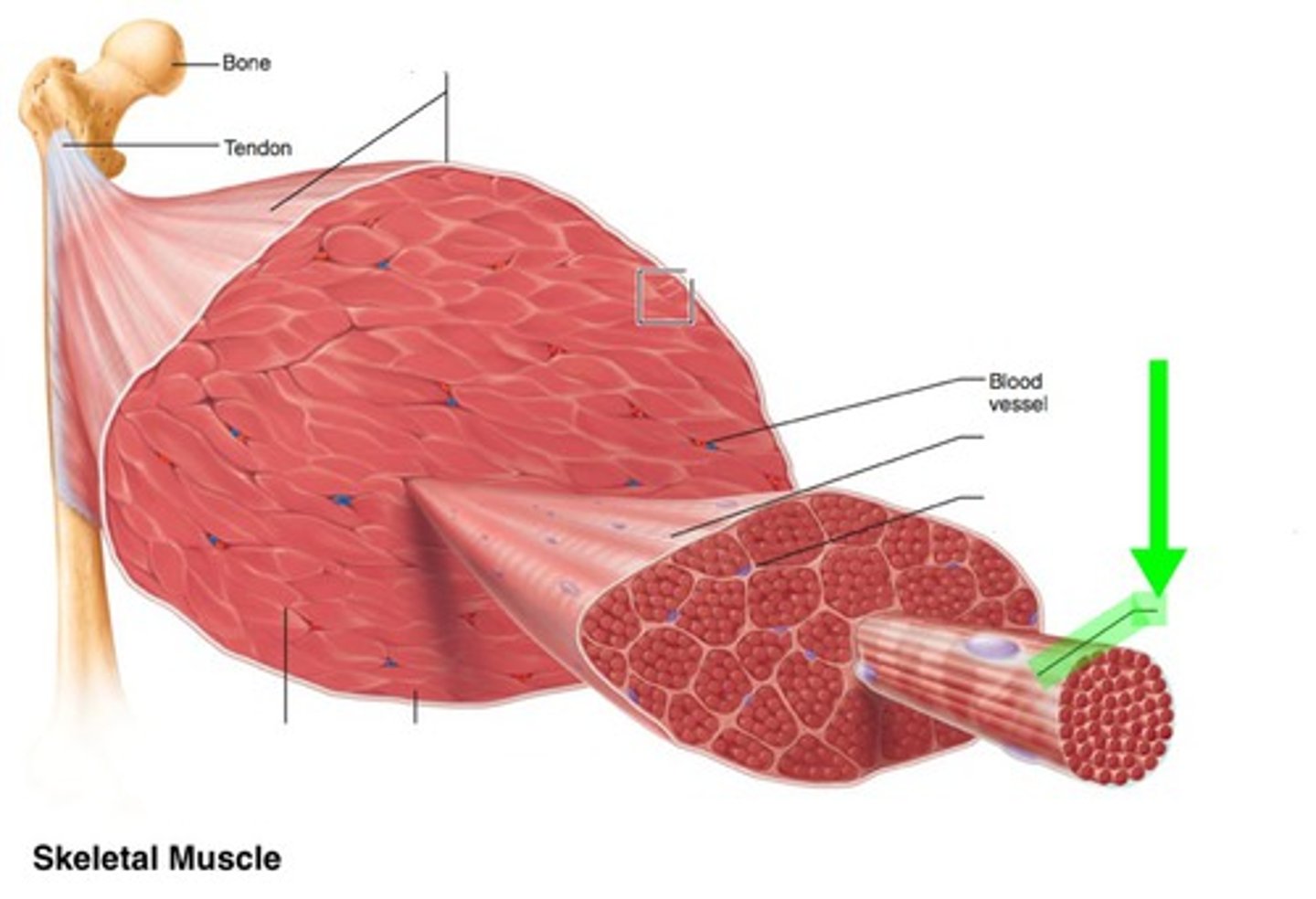
Epimysium
covers the entire skeletal muscle
muscle
tissue composed of fibers that can contract, causing movement of an organ or part of the body
fascile
bundle of muscle fibers surrounded by perimysium
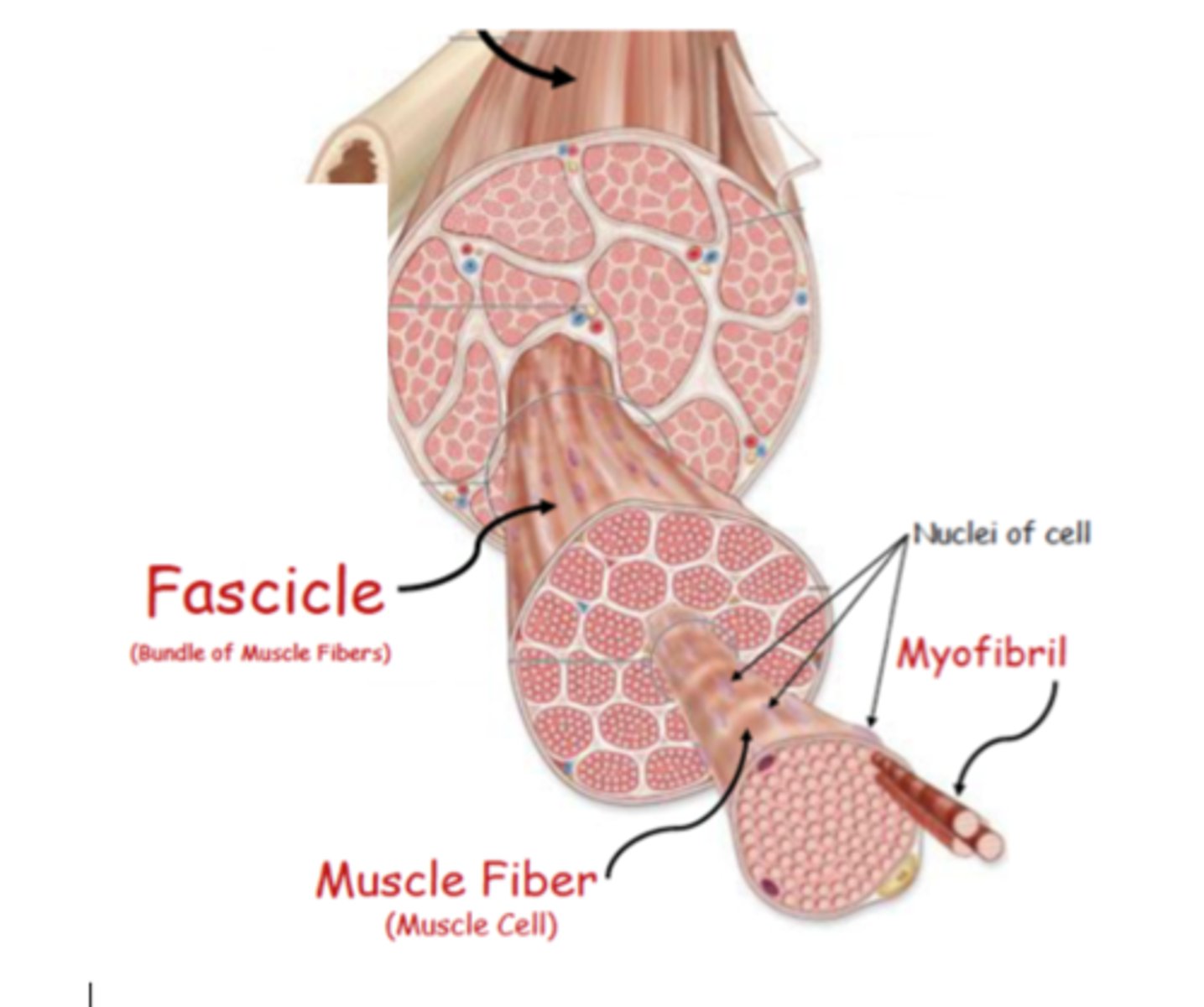
Perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding a fascicle (bundle of muscle fibers)
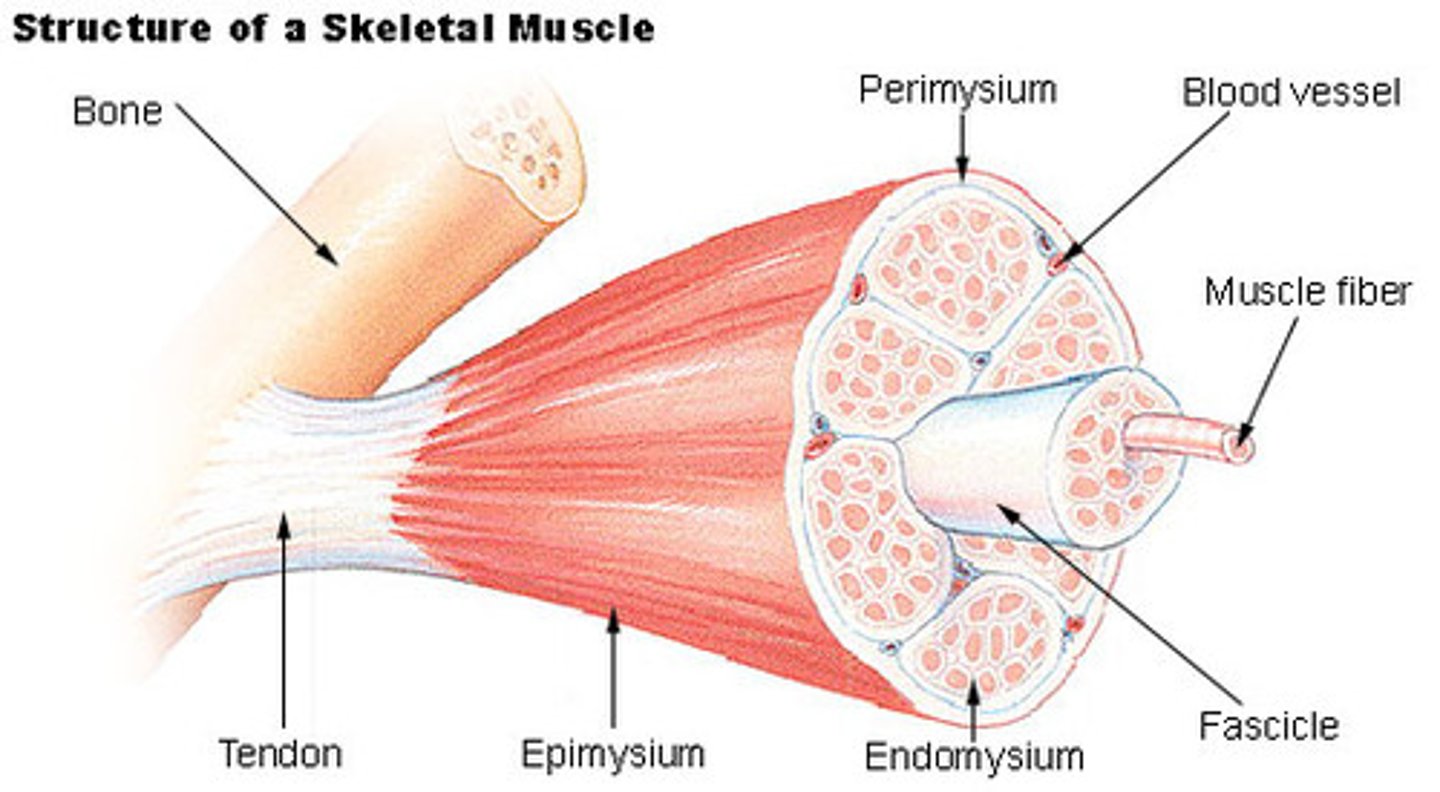
muscle fiber
long slender skeletal muscle cells
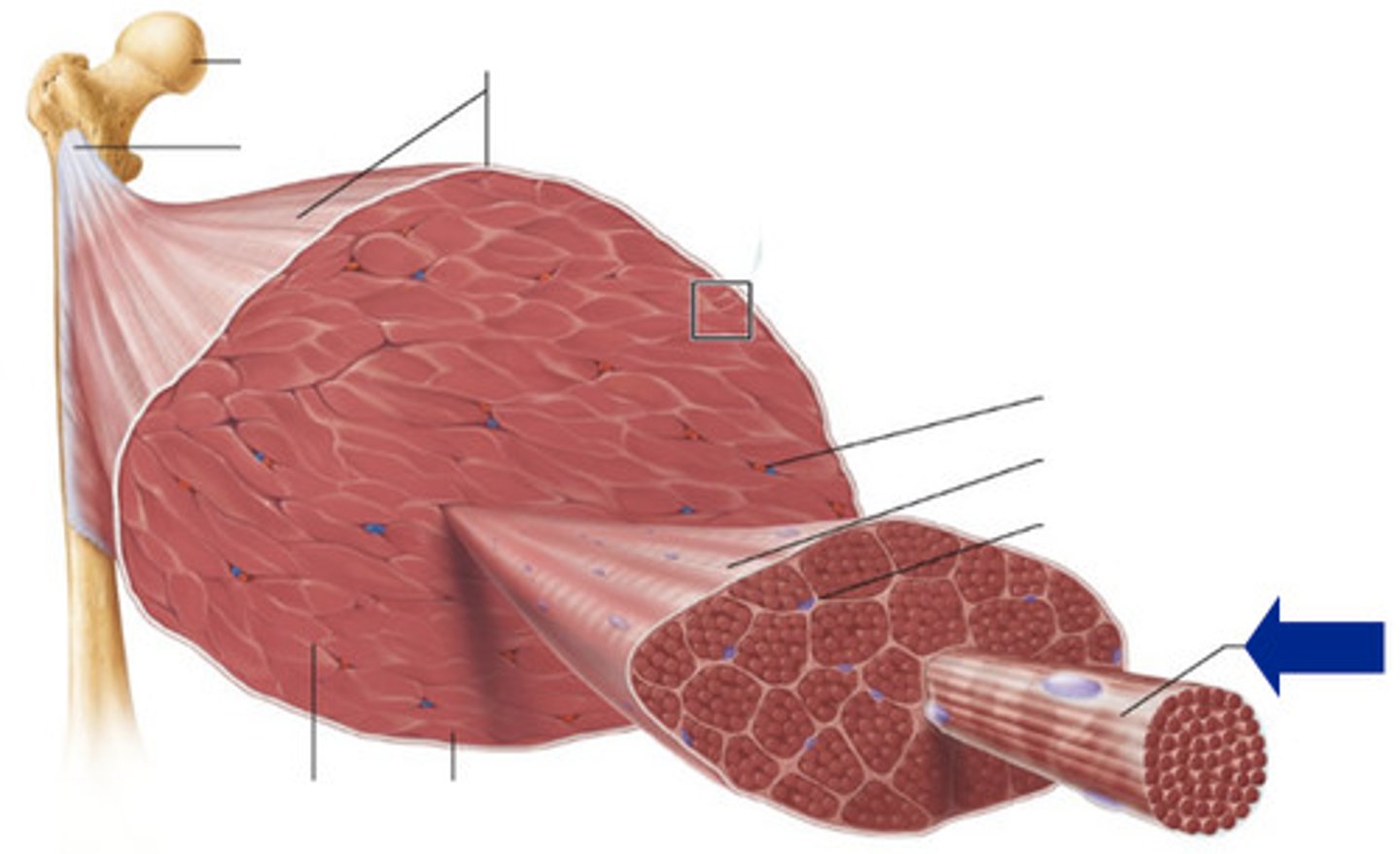
Endomysium
Surrounds individual muscle fibers
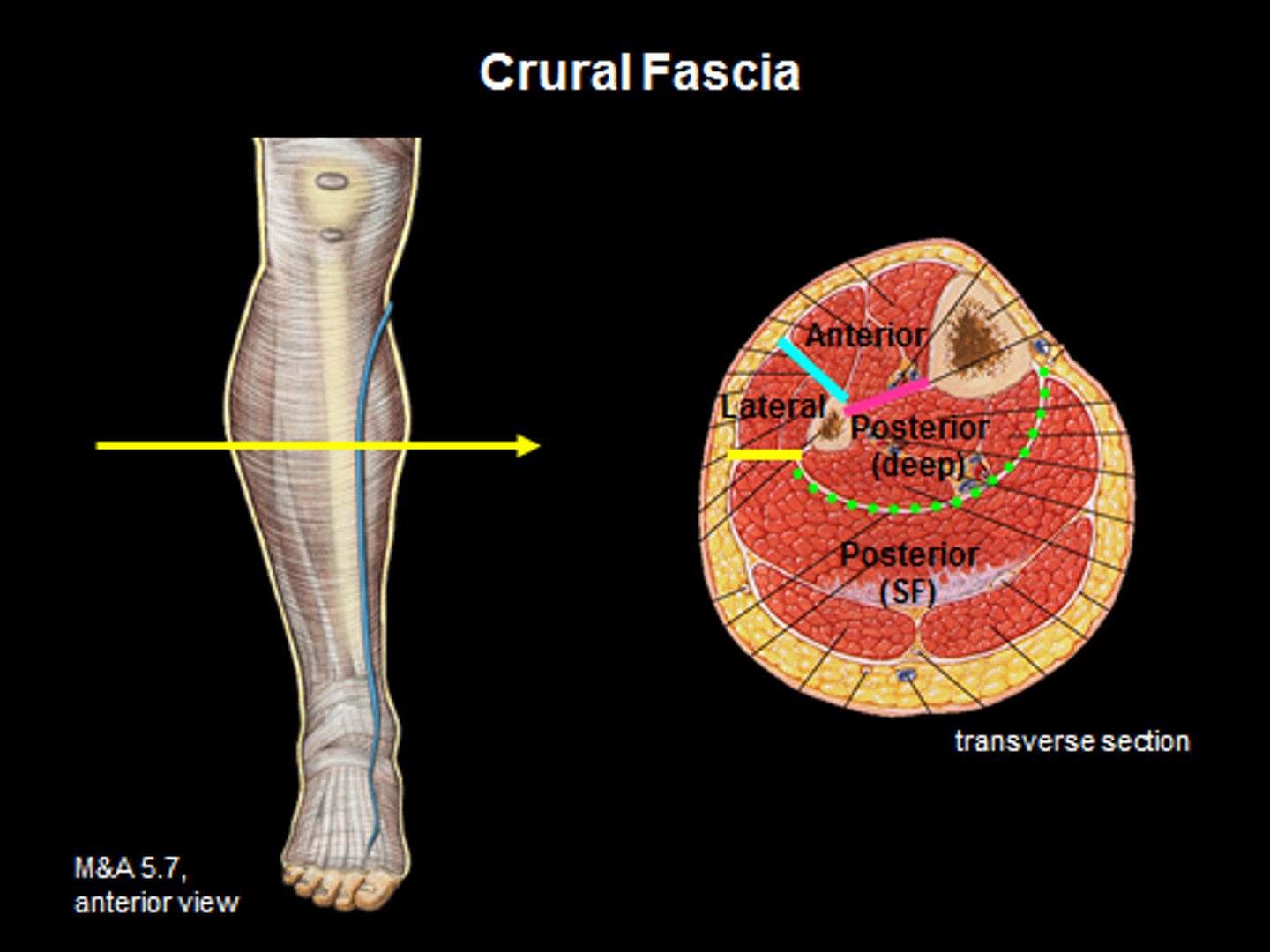
fascia
a band or sheet of fibrous connective tissue that covers, supports, and separates muscle
fascia compartments
fascial systems that enclose muscles in compartments
origin
attachment of a muscle that remains relatively fixed during muscular contraction

insert
the attachment of a muscle that is most distal and moves during contraction
Agonist muscle
The muscle primarily responsible for movement of a bone.
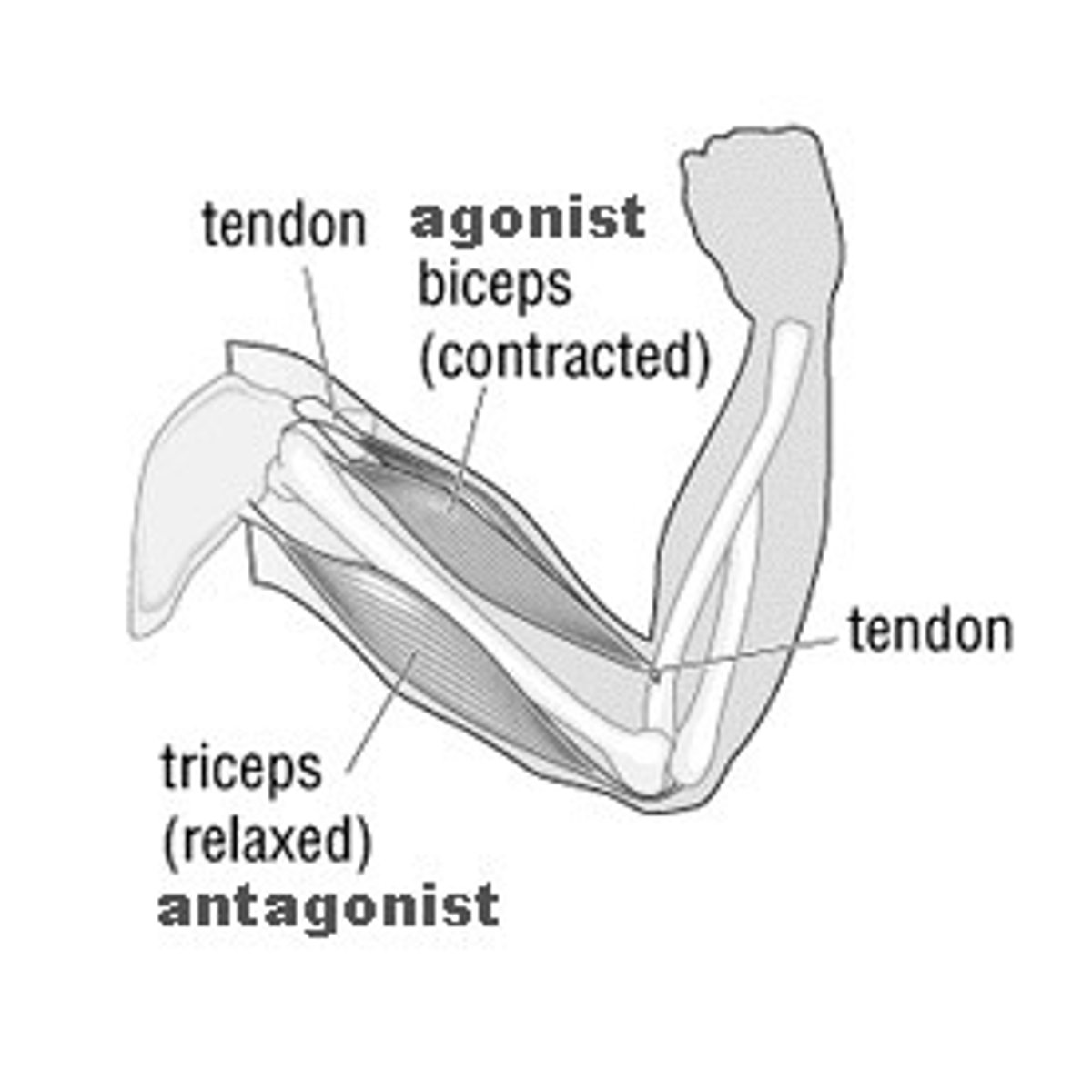
Synergist
muscle that aids a prime mover in a movement and helps prevent rotation