Life Processes (Descriptive)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Define Nutrition
Transfer of energy from an external source (food) to inside the body for to be utilised to perform life processes.
Define respiration
Acquiring oxygen from the outside environment and using it to break down food sources for energy needs.
What is a living thing?
What is a living thing?
Visible movement is usually used to define whether an organism is living or non living.
Yet , this does not suffice as for example in plants after they are done growing they might not show any visible movements but are still alive.
So we must also consider the movement happening at a very small scale or molecular level to define whether it is a living organisms.
Are viruses alive
The basic functions performed by living being to keep themselves alive.
Why do we need life processes?
Life processes are needed in order to prevent damage and breakdown and to repair the damaged cells as well as growth.
What are life processes?
The basic functions performed by living being to keep themselves alive and for growth.
Why do unicellular organisms not have separate transportation systems?
Their whole body is in contact with the outside environment.
Why is simple diffusion not enough in complex organisms.
Their whole body is not in contact with the outside environment and they have larger body sizes with separate areas with their specific functions so transport between the different sections becomes essential.
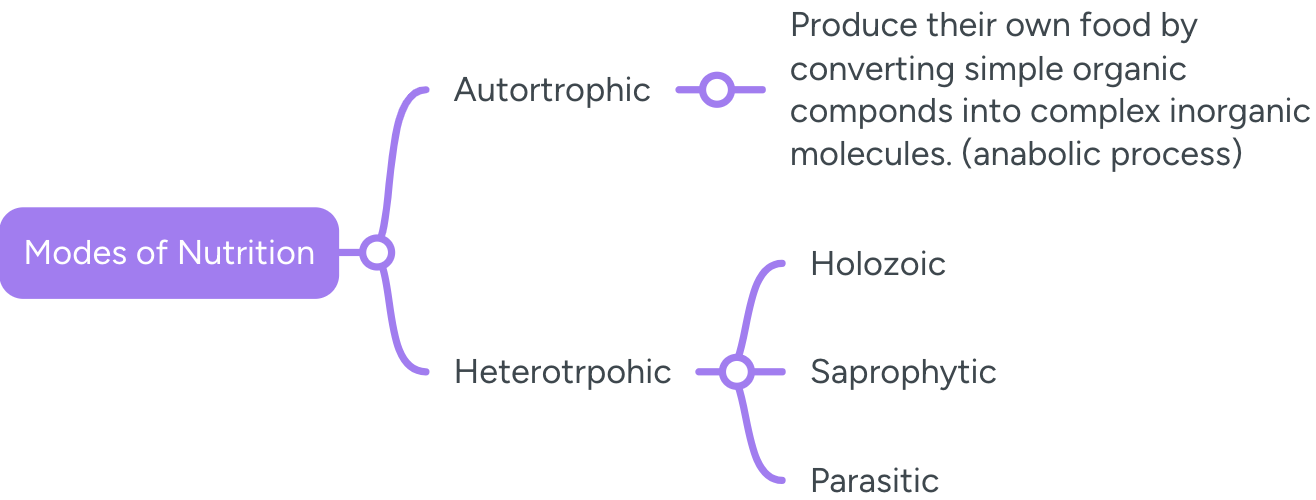
What are the different modes of nutrition?
Autotrophic Nutriton
Organisms are able to produce their own food.
Includes photosynthetic organisms like green plants , bacteria.
Anabolic Process - converting simple organic molecules into complex inorganic compounds is known as the anabolic process.
Heterotrophic Nutrition - derive their nutrition from other living or dead sources
Holozoic - They eat food as a whole and digest it. (Examples - humans , tigers , amoeba)
Parasitic - Depend on the host for nutrition , they harm but do not kill the host. (Examples - cuscuta , tapeworm , ringworm , leech)
Saprotrophic
Derive nutrition from dead and decaying organic matter.
Converts complex organic matter into simple inorganic forms by releasing chemicals
Also known as decomposers
Examples - bacteria , microorganisms and mushrooms
What is anabolic process?
Anabolic Process - converting simple organic molecules into complex inorganic compounds is known as the anabolic process.
Write a short note on chloroplasts
It is the site of photosynthesis.
It is present in the palisade mesophyll , spongy mesophyll and the guard cells in a leaf.
It contains chlorophyll which helps in the absorption of sunlight.
Explain the structure and the 3 function of stomata
They are tiny pores on the underside of the leaves that allows for the exchange of gases between the plant and the atmosphere.
It performs the functions of transpiration and controls the loss of excess water.
The opening and closing of stomata are done by changing the water content to change the turgidity of the cell.
The guard cells swell when the water flows causing the pores to open and the pore closes when the cell shrinks.
The guard cells have chloroplasts and perform photosynthesis.
What are the raw materials that are needed for photosynthesis
Carbon Dioxide is absorbed from the surroundings mainly through the stomata. Apart from this the stem , leaves and roots also help in gaseous exchange by diffusion.
Water is absorbed through the roots and is transported through the xylem to the leaves. The water molecule is split in the presence of water to form hydrogen ions and oxygen.
Sunlight is need for the breakdown of water (photolysis) and is absorbed by the chloroplasts.
Chlorophyll - it is the green coloured photosynthetic pigment that is found in chloroplasts of a plant that is responsible for trapping solar energy.
What are the 3 steps needed for photosynthesis?
Absorption of the light energy by the chlorophyll
Conversion of light energy into chemical energy for the splitting of water molecules into hydrogen ions and breathable oxygen.
Reduction of carbon dioxide into carbohydrates (glucose)
What is the difference in photosynthesis in desert plants
Stomata remains closed during daytime to prevent water loss and opens at night.
When the stomata opens at night , the exchange of gases occurs and an intermediate is formed.
During the daytime in the presence of sunlight , the intermediate is converted into carbohydrates or simple sugars.
What is the importance of transpiration?
It removes the excess water from the plant.
Helps in the cooling of the plan
Transpiration pull helps to uplift water from soil through roots and xylem.
Explain the 3 experiments used to show the need of sunlight , chlorophyll , and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis
Aim of the experiment | ||
To prove that chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis | To prove that carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis | To prove that sunlight is essential for photosynthesis |
Experimental Setup | ||
Take a potted plant with variegated leaves and destarch it for two days. | Take 2 similar plotted plants and destarch it for two days | Take a potted plant and destarch it for two days |
Cover it with a lid and seal the bottom , in only one of the plants keep a container containing KOH. | Apply a black tape covering some parts of the plant. | |
| ||
Result | ||
The test is positive in the parts of the leaf that had green patches while the white part is starch negative. | The leaf from the setup without KOH shows starch positive while the other shows negative. | The area of the leaf that was not covered by the strip shows starch positive while other shows negative |
How do plants absorb nitrogen?
Either as inorganic forms or nitrates or the organic forms produced by bacteria from atmospheric nitrogen.
How does Amoeba get its nutrition?
It ingests food particles by formed temporary finger like projections from the cell surface called pseudopodia.
These structures fuse over the food particles to form a food vacuole.
Inside the food vacuole the complex food substances are broken down into smaller soluble molecules and gets absorbed by the cytoplasm ie digestion and absorption.
The remaining undigested food material is removed by the cell membrane , which eliminates out the undigested food ie egestion.
How does nutrition occur in paramecium
Paramecium is another unicellular organism , which has a definite shape and intakes good at a specific spot.
Food is moved to this spot by the movement of cillia , which cover the entire surface of the cell
Explain in detail the Alimentary canal.
Mouth
Tongue - it is the highly muscular sensory organ present at the floor of buccal cavity. It bears taste buds which help in the tasting of food and helps to mix Saliva. It forms a bolus.
Teeth - they are hard structures present on both the lower and upper jaw. It usually consists of a crown , root and neck. It’s outer layer is made of a hard substance called enamel , inner to the enamel , dentine is present.
Pharynx - It is a small funnel shaped chamber that is present behind the oral cavity it contains both the oesophagus and trachea.
Oesophagus - it is a thin and long structural tube that transports food from the mouth to the stomach.
Peristalsis - it is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the oesophagus that helps move food all the gut , especially found in the oesophagus.
Salivary Glands - it produced saliva which contains an enzyme called salivary amylase that converts starch into simple sugars.
Stomach
It is the J-shaped organ that helps in the churning of food.
The gastric glands found in the stomach releace the following:-
Hydrochloric Acid - it kills the germs in the food and creates an acidic pH for the activation of pepsin.
Pepsin - breaks down proteins
Mucus - protects the inner lining of the stomach.
Exit of food from the stomach is controlled by the pyloric spinchter.
Small Intestine
The inner lining has numerous finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption.
The small intestine is the site of complete digestion of food.
Secretion from the liver and pancreas enter the intestine to help the digestion process.
Liver
It secretes bile juice which is stored in the gallbladder temporarily and is then released into the small intestine
The salts present in bile help in the emulsification of fats.
It creates an alkaline enviroment for the maximum activity of pancreatic enzymes
Intestinal Glands - walls of the small intestine contain numerous glands that secrete intestinal juice containing enzymes which convert proteins to amino acids , carbohydrates into glucose and fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Pancreas - pancreatic juice
Pancreatic amylase - digests carbohydrates
Trypsin - digests protein
Lipase - digestis lipids/fats
Large Intestine - the water from the food is absorbed here. Appendix is also part of the large intestine.
Rectum - pouch like structure that stores faecal matter temporarily.
Anus - it is the end point of the alimentary canal through which feces is eliminated. This is controlled by the anal spinchter.
What are the gastric juices?
The gastric glands found in the stomach releace the following:-
Hydrochloric Acid - it kills the germs in the food and creates an acidic pH for the activation of pepsin.
Pepsin - breaks down proteins
Mucus - protects the inner lining of the stomach.
What are the secretions by the liver?
Liver
It secretes bile juice which is stored in the gallbladder temporarily and is then released into the small intestine
The salts present in bile help in the emulsification of fats.
It creates an alkaline enviroment for the maximum activity of pancreatic enzymes
What are the secretions of the pancreas?
Pancreas - pancreatic juice
Pancreatic amylase - digests carbohydrates
Trypsin - digests protein
Lipase - digestis lipids/fats
Explain assimilation.
THe process of the distribution of the nutrients obtained from the digested food across various cells of the body is called assimilation.
It is used for the following needs:
Supplied to all cells for energy
Creation of new cells
Repair of cells and tissues
Explain the different types of respiration
Aerobic Respiration
Takes place in the presence of oxygen.
Glucose is complete oxidised to release carbon dioxide , water and large amounts of energy.
Glucose is first broken down into pyruvate in the cytoplasm and the in the mitochondria pyruvate (3 carbon molecule) is broken down into carbon dioxide , water and 38 ATP
Anaerobic Respiration in Yeast (Absence of Oxygen)
Takes place in the absence of oxygen.
Yeast cell performs an incomplete breakdown of glucose (which is initially converted into pyruvate)into ethanal , carbon dioxide
Anaerobic Respiration in Muscles (Lack of oxygen)
A lack of oxygen occurs due to the intensive activity.
In this case pyruvate breaks down to form lactic acid and energy.
The accumulation of lactic acid causes muscle cramps and fatigue
Write a short note on ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate is the energy currency of the cell
The energy released during cellular respiration is used to synthesise an ATP molecule from ADP and inorganic phosphate
The energy equivalent to 30.5 kJ/mole is released when the terminal phosphate bond is broken down using water.
Write a detailed note on respiration in green plants.
During the daytime the rate of photosynthesis is high , the carbon dioxide that is generated through cellular respiration is used up for photosynthesis , hence there is a large amount of oxygen released during the daytime.
During the nighttime , there is little to no photosynthesis taking place hence there is a large amount of carbon dioxide released.
There is gaseous exchange in the root by the process of diffusion , the gases diffuse in and out of the root hair.
There are small pores on stems called lenticels though which gaseous exchange occurs.
The hibiscus plants has stomata on the stem which aid in the exchange of respiratory gases.
How does gaseous exchange occur in aquatic organisms?
They use the oxygen dissolved in water for respiration
The concentration of oxygen in water is lower when compared to ai , thus the rate of breathing in aquatic animals is much higher than terrestrial organisms.
Fishes take in water through their mouths and force it through the gills where the dissolved water is absorbed into the blood stream
Explain the Human Respiratory System in detail.
Nostrils - the air is taken into the body from the external openings known as nostrils.
Nasal Passage - air entering the nostrils lead to the nasal passage , it is lined with fine hair and mucus which filters the entering air.
Pharynx - nasal chamber opens into the pharynx and passes air into the voice box (larynx)
Larynx - it is located in the neck region and has vocal chords which produce sound.
Trachea - it the windpipe , it has incomplete rings of cartilage to maintain it’s shape to ensure air passes through and prevent it from collapsing.
Bronchi - the trachea divides into two smaller tubes called bronchi which extend int each lung.
Bronchioles - bronchi subdivide into smaller tubes
Alveoli - they provide the surface area for the exchange of gases
Lungs - they are the primary organs for respiration , which allow for O2 to fill in them from the atmosphere which then diffuses into the alveoli and allows CO2 to diffuse out and expels it from the body
Diaphragm - it is a muscular partition present between the thorax and the abdomen which forms the base of the cheset cavity which allows the lungs to expand and conract
Ribs - 12 large pairs of bones that form a cage in the thoracic region that protects the lungs and heart.
Write a short note on Haemoglobin.
It is respiratory pigment found in the blood of human beings , it has very high affinity for oxygen and is present in RBCs.
It combines with oxygen and transports them in the form of oxy-haemoglobin and does the same with carbon dioxide to form carboxyhaemoglobin
What is blood? What are the components of blood?
Blood is a fluid connective tissue which circulates all across and body and performs transportive functions. It contains a red pigment for haemoglobin which allows it to transport many different materials.
Plasma
It is the fluid part of the blood that is made up mostly of water
Constitutes 55% of the blood volume.
Includes proteins , salts , glucose , nitrogenous compounds
It also transports food , water , oxygen , carbon dioxide and nitrogenous waste in its dissolved form.
What are the functions of blood
It helps in the transport of nutrients to all parts of the body for storage and synthesis of new substances.
It helps in the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide for respiration.
It is involved in the transport of excretory products like urea , uric acid and ammonia
It acts as a buffer system in our body and helps in the regulation of pH and body temperature
It is involved in the protection against disease by the WBC
Platelets present in the blood form a clot at the site of injury to prevent further loss of blood
Write a short note on plasma.
it has to components which is the serum and fibrinogen.
It comprises 55% of blood and consists of water , nutrients , waste products and hormones
Serum is everything in the plasma ecept for the clotting factors.
Explain the structure of the human heart.
Human heart is four chambered consisting of 2 atria and 2 ventricles.
Atria are the upper chambers and they are the receiving chambers.
Ventricles are the lower chamber and the distributing chambers.
The left ventricle has the thickest walls due to high pressure and it pumps the deoxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
What are the function of valves?
It prevents the backflow of blood in the opposite direction.
It prevents the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Explain double circulation in human beings.
(A) Pulmonary Circulation
Deoxygenated blood from right ventricle is carried to lungs by the pulmonary artery.
Oxygenation of blood takes place alveoli in lungs
Oxygenated blood is returned from lungs to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein
Blood is carried from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart.
(B) Systemic Circulation
Oxygenated blood from left ventricle is sent to idfferent parts of body by the aorta.
At the same time deoxygenated blood is collected from the veins and enters
Explain the process of blood clotting
In case of any injury when bleeding occurs the loss of blood has to be minimised.
TO prevent this the blood has platelet cells which circulate around the body and form a mesh like structure
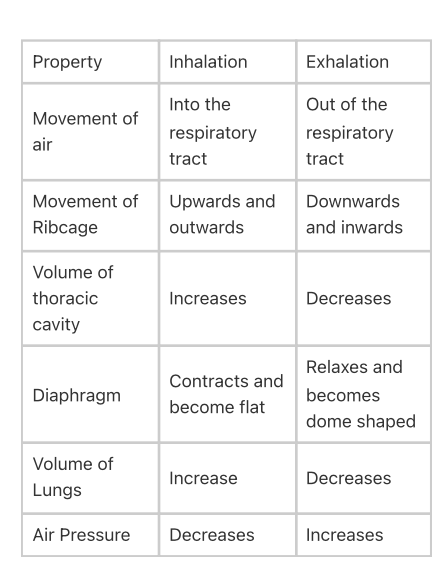
Differentiate between Inhalation and exhalation in humans
What is pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation
Pulmonary Circulation is the movement of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart.
Systemic Circulation is the movement of blood from the heart to the rest of the body and back to the heart for oxygenation.
Explain circulation is fishes
They have two chambered heart
The deoxygenated blood is pumped into the girlls where it is oxygenated and supplied directly to the rest of the body
They only have single circulation as blood only passes through the heart once in a cycle.
Explain circulation in reptiles and amphibians
They have three chambered heart containing two atria and a single ventricle.
They show double circulation but can tolerate the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
This is because they do not use energy to maintain their body temperatures.
They are cold blooded animals and they body temperature depends on the temperature of their surrounding
Crocodile is the only reptile with a four chambered heart.
What is lymph? What are the functions of lymph?
Lymph is a colourless extracellular liquid which connect all tissues. It consists of lymphatic vessels or capilaries
Functions of lymph
It is involved in the transportation of substances where blood vessels do not reach.
It carries digested and absorbed fat from the intestine
Drains excess fluids from tissue to the blood
It maintains the balance between tissue fluid and blood
Lymph nodes localise infections and produce antibodies
How is water transported in plants?
Xylem tissues of plant have interconnected network of tracheids and vessles present in the roots stem and leaves.
At the rot cell there is a difference in the concentration of ions in the root and soil causing water to enter the roots.
There is a steady upwards movement of water into the root that creates a column of upward moving water.
The process of transpiration creates a a transpirational pull moving water upwards.
What is transpiration? What is the importance of transpiration?
The loss of water in the form of vapours from the aerial parts of the plant is called transpiration.
It helps in the upward movement of water and dissolved minerals by the transpirational pull.
It helps in regulating temperature in the plant.
It maintains a constant supply of ions to the leaves.
It removes excess water from the plant
How does transportation of food happen in plants?
The movement of soluble products from photosynthesis from leaves to other parts of the plant is known as translocation.
It occurs in a set of vascular tissues known as phloem.
Phloem also transports amino acids and plant hormones.
It occurs with the help of sieve tubes , phloem vessels and companion cells.
It is an active form of transport and utilizes energy.
Materials like sucrose are transferred into phloem tissue using energy from ATP to increase the osmotic pressure.
What are the main functions of the kindey?
Removing excess water and nitrogenous waste in the form of urine.
Regulating pH of the blood
Maintaining the amount of water , ions and other substances in the blood.
Explain the structure of the kindey.
It is bean shaped organ situated towards the back of the abdominal cavity.
The left kidney is placed higher than the right kidney due to the liver.
Unfiltered blood enters through the renal artery and filtered blood exits through the renal vein.
It is connected to the urinary bladder by ureters.
Urine is temporarily stored in the bladder and exits through the urethra which is an opening in the penis.
The filtration units inside the kideys are called nephrons.
Explain the structure of nephrons.
Bowman’s Capsule is a cup like double walled structure which contains a network of blood capilaries called glomerulus.
Renal tubules are the coiled part of the nephron , they are long tubes within the kidney that allow for increased surface area for urine formation.
The collecting duct collects the filtered urine.
Explain in detail the process of urine formation.
Ultrafiltration occurs in the glomerulus under high pressure forcing dissolved substances into the bowman’s capsule.
This filtered liquid is known as glomerular filtrate.
The glomerular filtrate passes through the tubular part of the nephrons where selective reabsorbtion of glucose , amino aids and major amounts of water occurs.
The nitrogenous waste products are removed from the blood by the ubule forming urine.
The urine formed in each kindey enters long tube called ureter which connects the kindey to the unirnary bladder,
Urine stored in the muscular urinary bladder causes the urge to pass it out through urethra.
What does the amount of water reabsorbed depend on?
Amount of excess water present in the body
Amount of dissolved waste
Explain the process of dialysis.
Artificial kindey is a device used to remove nitrogenous waste from the blood through dialysis.
Artificial kidney contains a number of tubes with a semipermeable lining in a tank filled with dialysing fluid.
This fluid has the same osmotic pressure as blood.
A graft is made in the pateints veins and the blood is passes through these tubes.
As the blood passes the waste products from the blood move into dialysing fluid by diffusion and the purified blood is pumped back into the patients body.
Why is artificial kindey not as effective as the natural kindey
The artificial kidney does not allow for the process of selective reabsorption to occurs. Normally in humans around 180L of filterate is generated exeryday but only about 1-2 litres are excreted meaning there is large amounts of rebasoption which is not occurs during dialysis.
Explain excretion in Plants
Gaseous Waste
Water vapours , carbon dioxide and oxygen are released by the plant through stomata in the leaves and lenticels in the stems.
Liquid Waste
Excess water is removed by transpiration
Plants also store waste products in gums. GUms are the metabolic products of plants.
Resins are formed as the oxidation products of essential oils.
Rubber plants release latex which is used in the tire industry.
Solid Waste
Stored in vacuoles and tissues in dead cells.
Also stored in leaves and barks which fall off later to remove the waste.
Plants excrete some solid waste into the soil around the,.