End of Chapters, FAA Questions, Exam Review, Kahoots
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
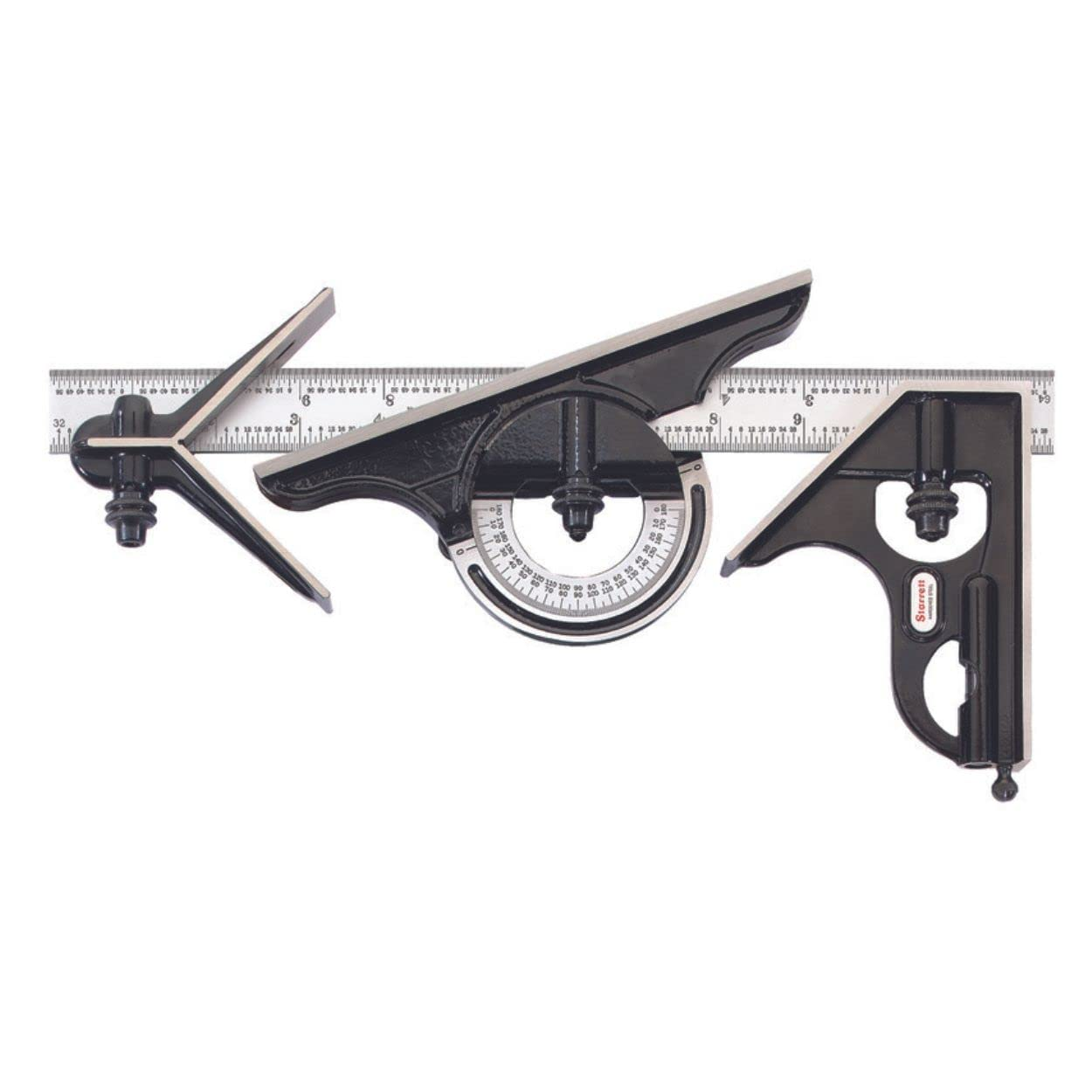

What does a combination set include? (5 things)
A combination set is a measuring device that includes a (1) center head, a (2) protractor head, a (3) stock head with level and (4)scribe, and a (5) steel scale.

What are thickness gauges used for?
Thickness gauges are thin steel or brass blades of varying thickness that measure small clearances, such as those in piston rings.
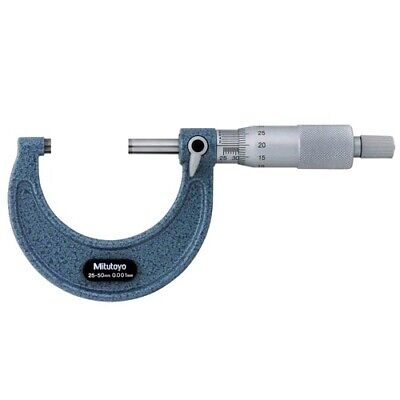

What is a micrometer caliper used for? (2 Things)
A micrometer caliper is used to measure the (1) thickness of numerous items, (2) including sheet metal and the out-of-roundness of cylindrical objects.
This type of caliper uses measurements in inches and millimeters.
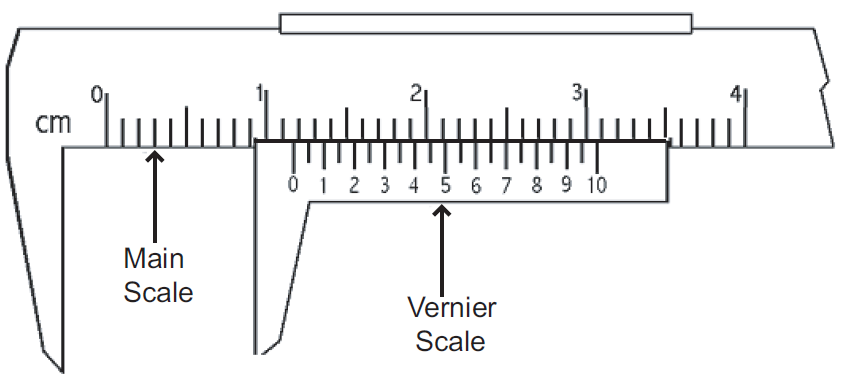
What does a vernier scale on a caliper allow?
Some calipers are manufactured with a vernier scale. This scale allows measurements to be taken to one ten-thousandth of an inch.
What is the use of a vernier caliper?
A vernier caliper is a precision instrument with a useful range of up to six inches. You can use it to measure both inside and outside dimensions.
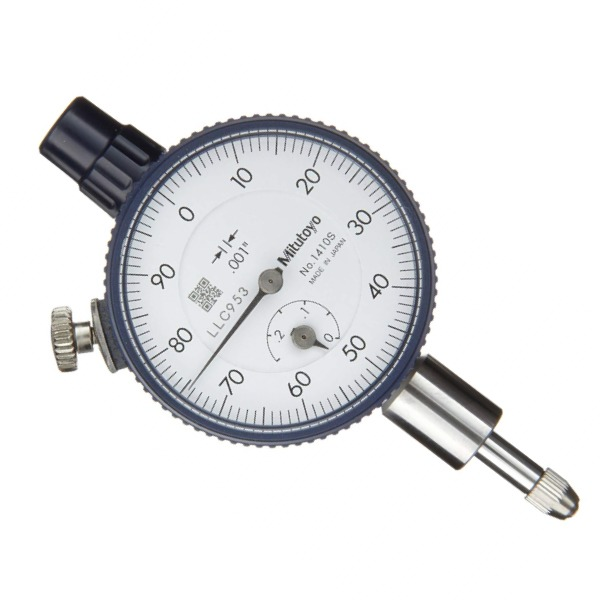

What do dial indicators measure? (2 Things)
Dial indicators measure the amount of (1) movement between parts and (2) out-of-round conditions.
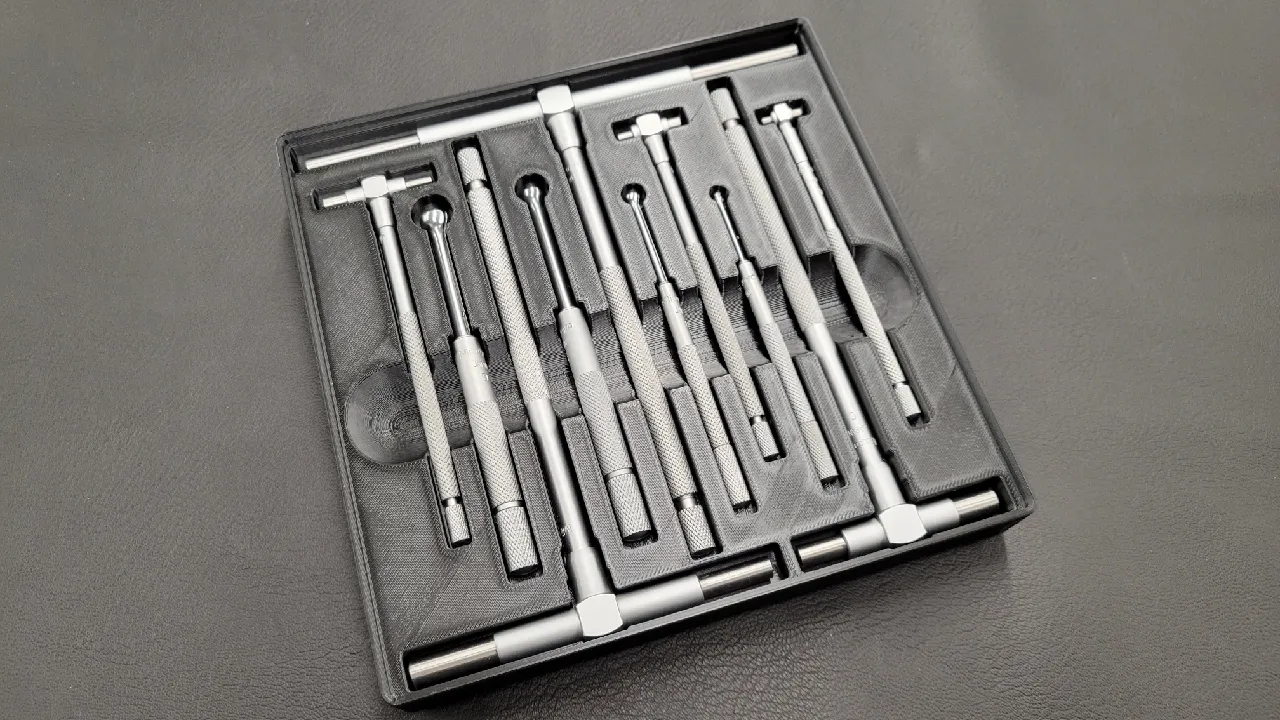

How are small hole gauges and telescoping gauges used?
Small hole gauges and telescoping gauges are used with a micrometer caliper. Place the gauge in a hole and lock it in place at the exact diameter of the hole; then remove the gauge and measure it with calipers.
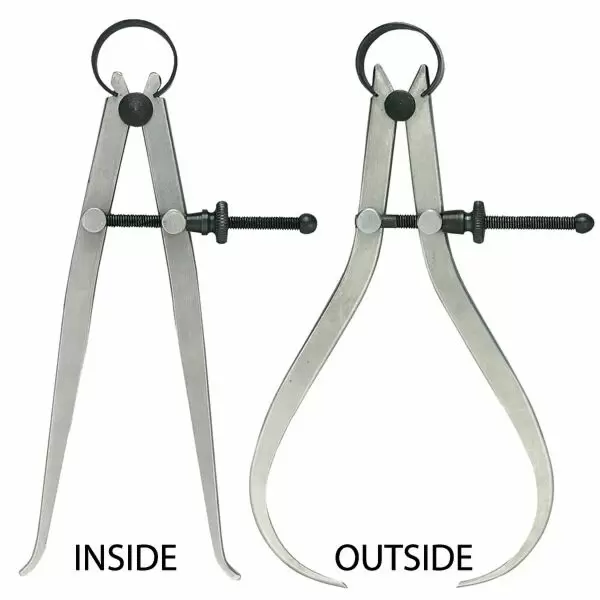

Define Calipers in General: (Not just Vernier Calipers)
A measuring instrument used to measure the distance between two opposite sides of an object. There are various types, including inside, outside, hermaphrodite, micrometer, and vernier calipers.
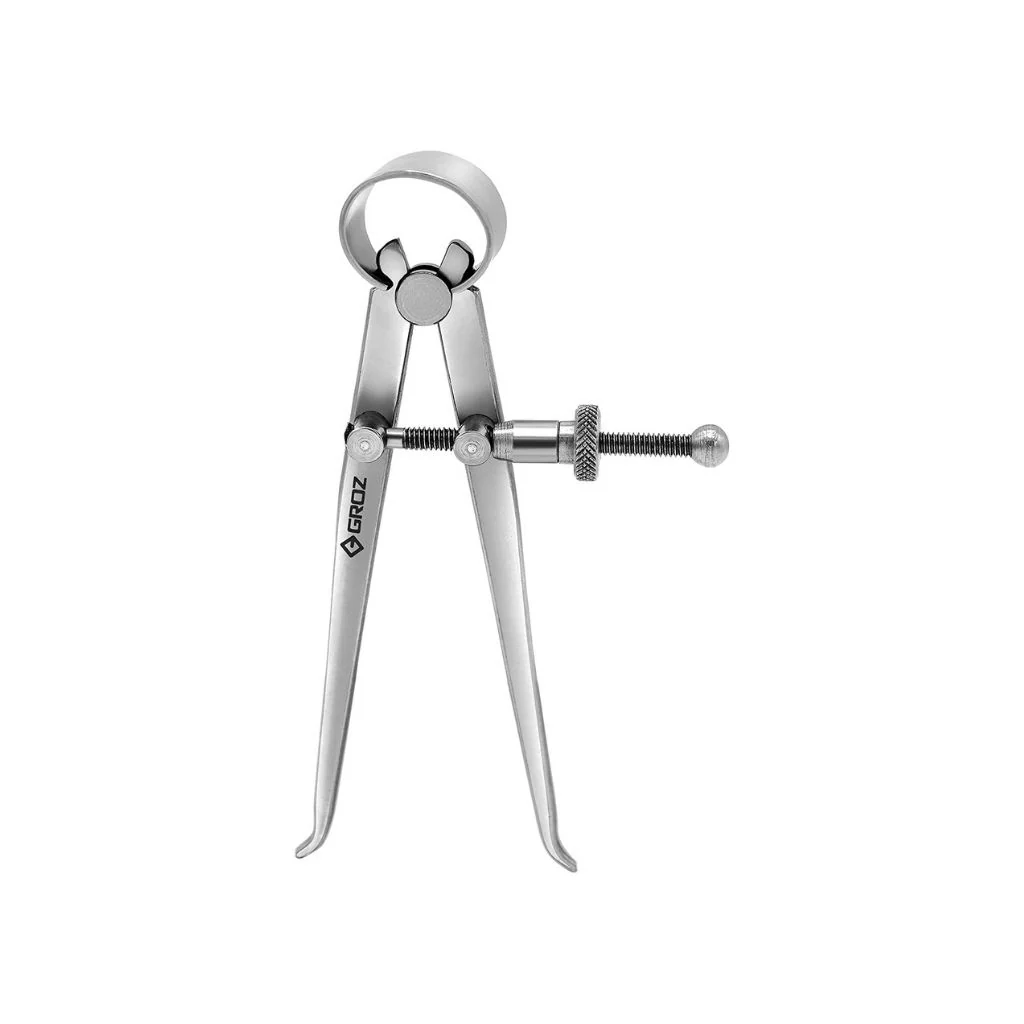

Define Inside Calipers in General:
A measuring instrument with two adjustable legs used to determine an inside measurement. Once set, the actual measurement is made with a steel scale, micrometer, or vernier caliper.
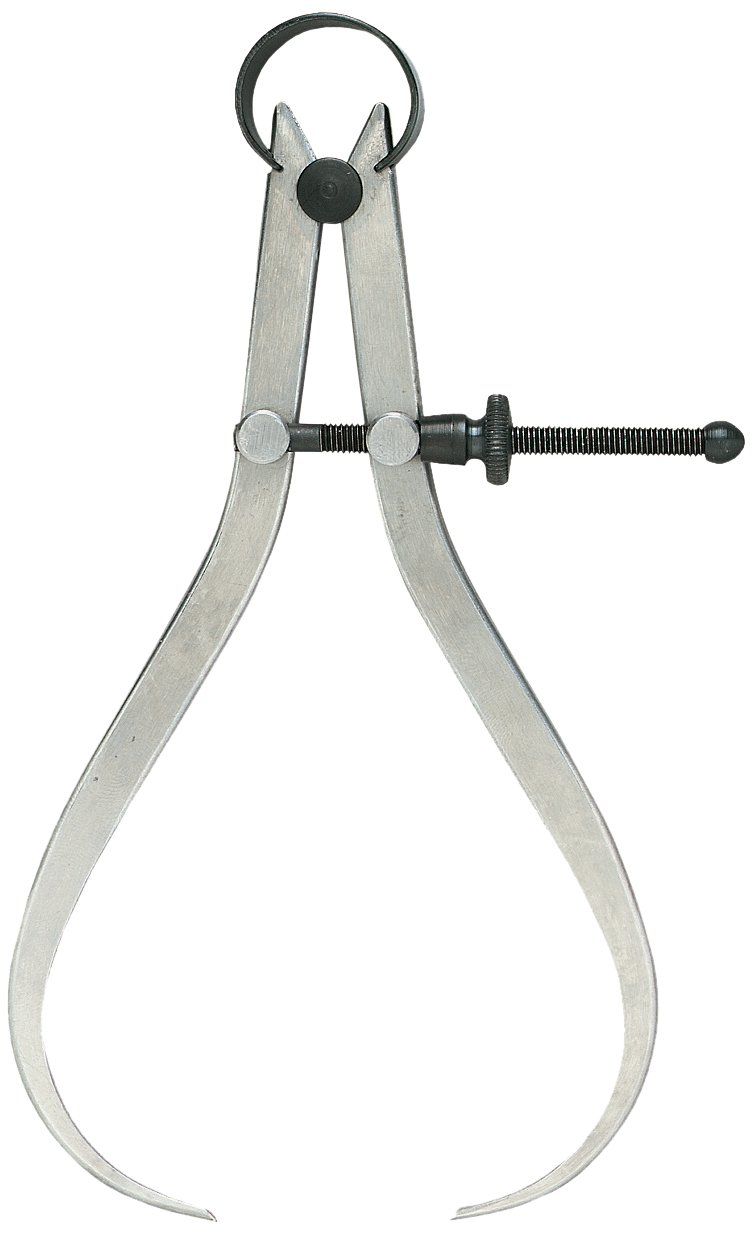
Define Outside Calipers in General:
A measuring device with two movable legs used to determine the distance across an object. Once set, the actual measurement is made with a steel scale or vernier caliper.
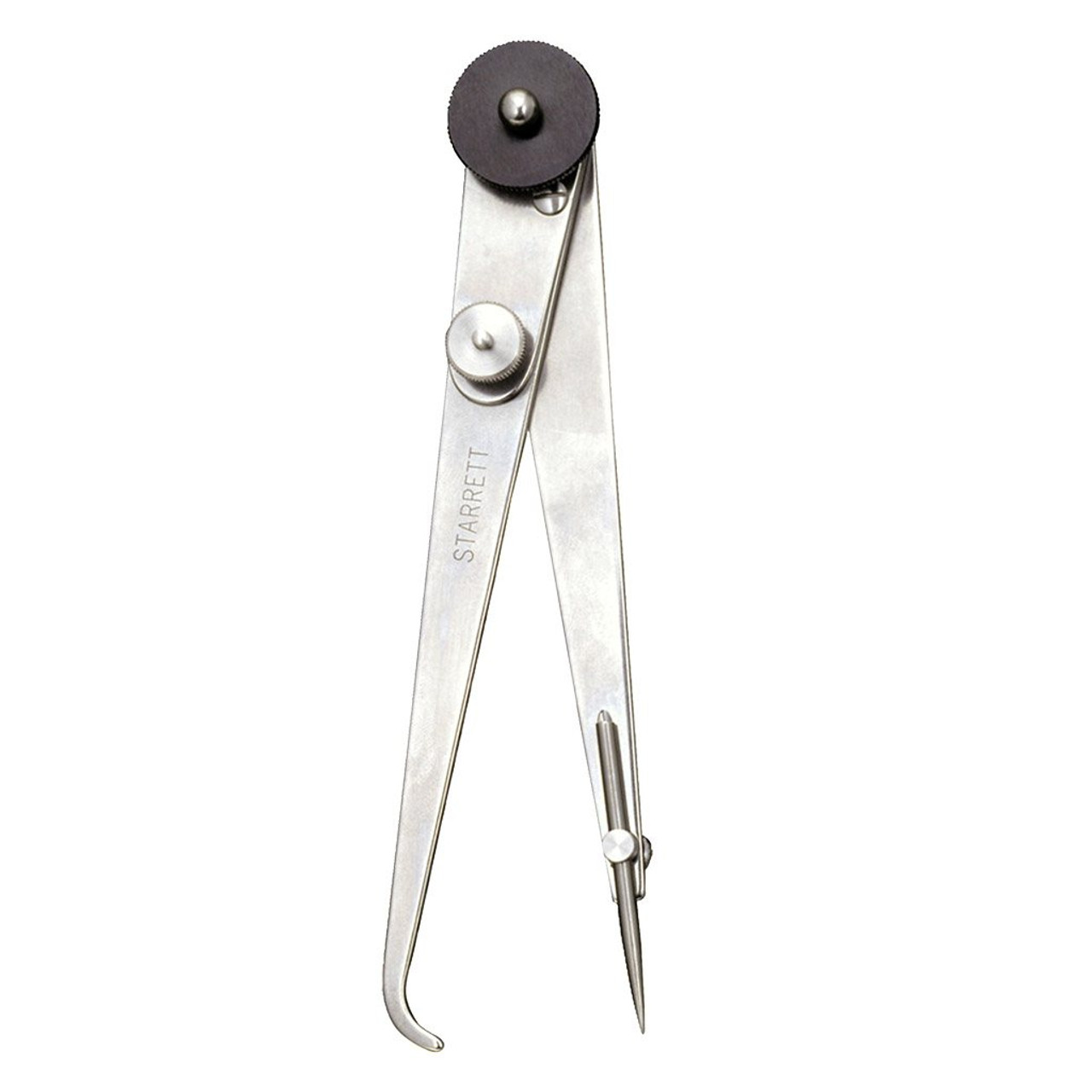

Define Hermaphrodite Calipers:
A tool used to scribe lines equidistant from an edge. It has one plain leg and one with a hook. The hook rests on the edge while the point scribes the line.
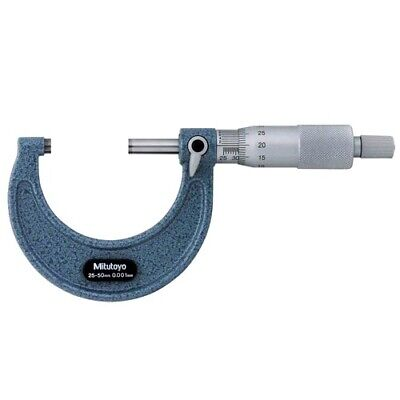

Define Micrometer Caliper: (In term of how it works and its revolutions.)
A precision measuring device with a single movable jaw advanced by a screw. One full revolution moves the jaw 0.025 inch.
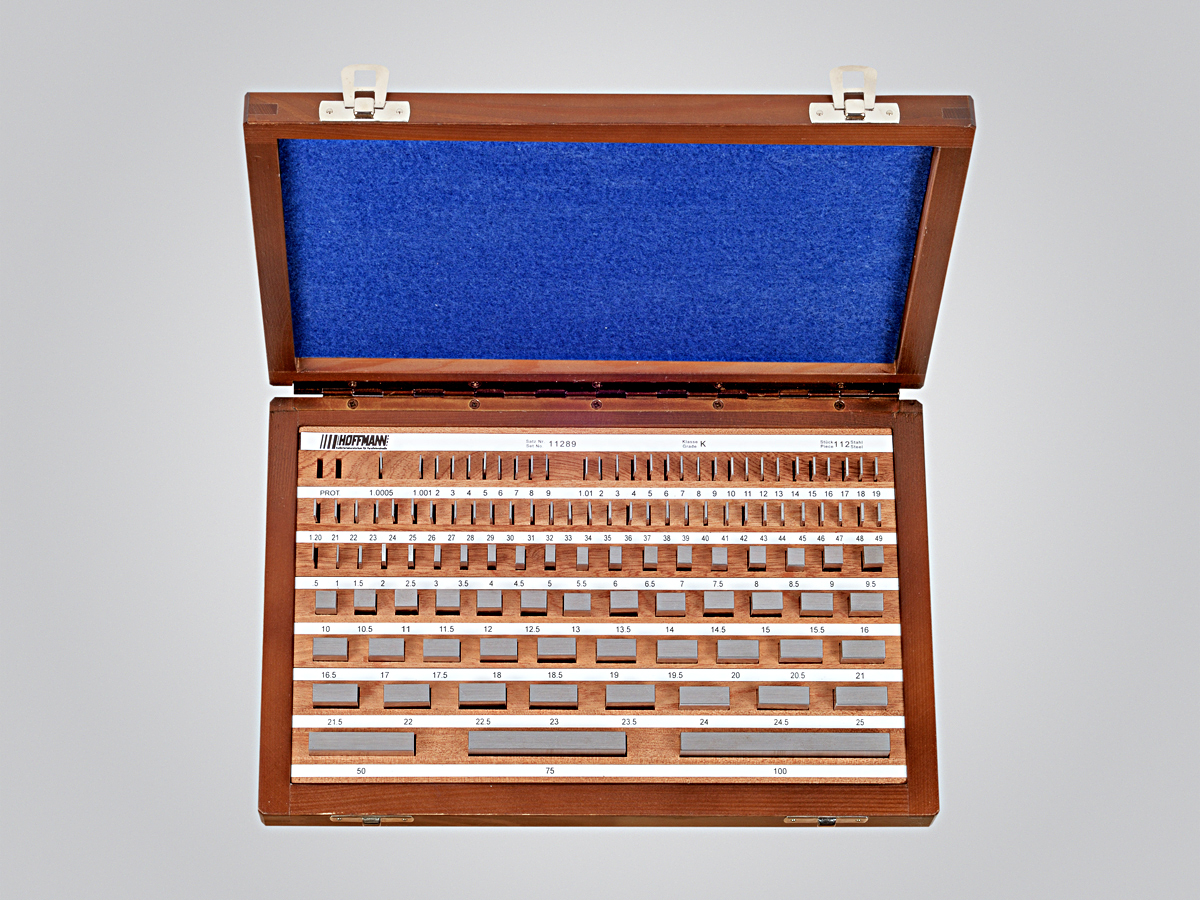

Define Gauge Block:
A precisely sized metal block used as a reference standard to calibrate measuring equipment. Commonly used to recalibrate a micrometer.
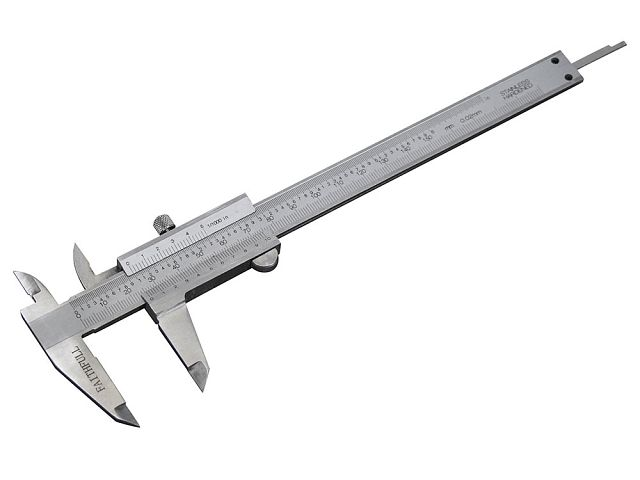

Define Vernier Caliper:
A precision tool used to measure inside or outside dimensions. It uses a vernier scale to divide increments of a regular scale accurately.
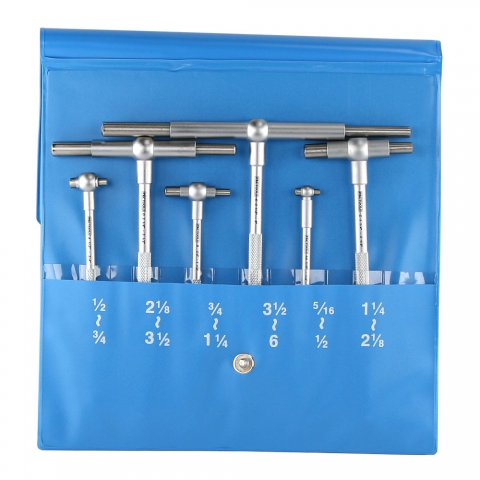

Define Telescoping Gauges:
A precision device with a spring-loaded rod inside a tube. It is expanded to fit the bore or hole, locked, removed, and then measured with a micrometer.
The three heads normally included in a combination set are the:
a. Stock
b. Protractor
c. Centering
What kind of calipers would be used to scribe a straight line a given distance from the edge of a piece of materials?
Hermaphrodite
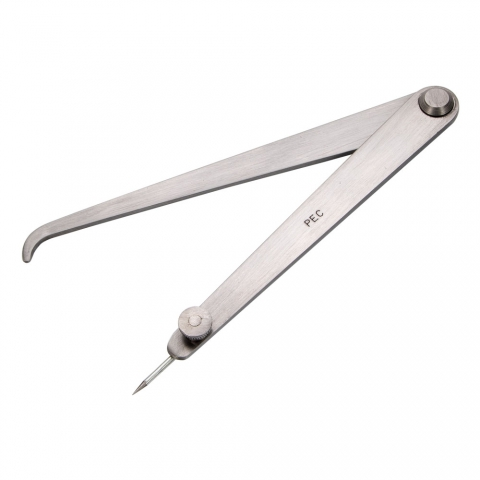

The threads in a micrometer caliper have a pitch of __________ threads per inch.
40
A standard micrometer will measure in increments of __________ inch(es).
.001
A vernier micrometer will measure in increments of __________ inch(es)
.0001
Read this micrometer caliper.
0.238
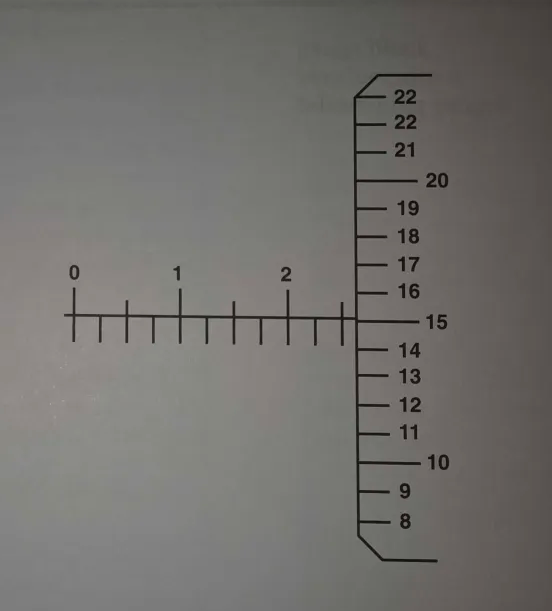
Read this micrometer caliper.
0.265
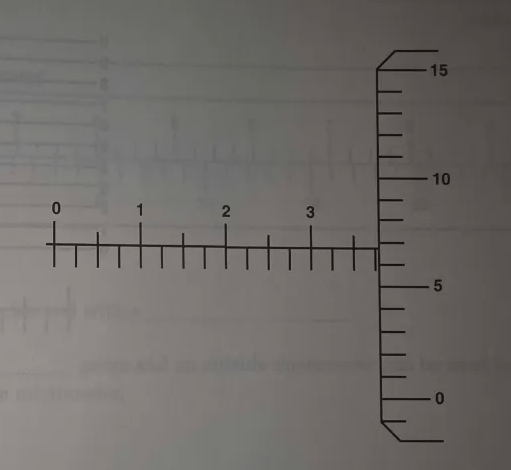
Read this micrometer caliper.
0.382
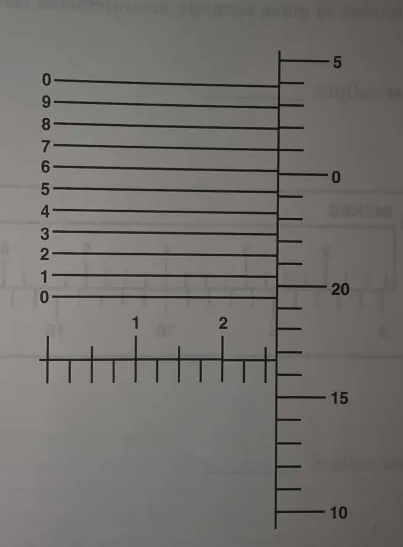
Read this vernier micrometer.
0.2667

Read this vernier micrometer.
0.1334
__________ calipers are used to make accurate measurements faster than can be made with micrometer caliper.
Vernier
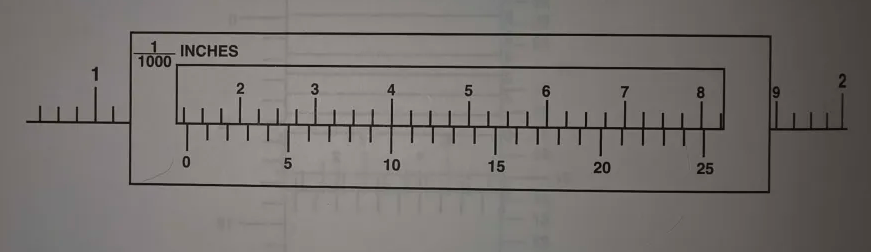
Read this English vernier caliper.
1.135 inches

Read this English vernier caliper.
1.310 inches

Read this English vernier caliper.
2.290 inches
Engine crankshaft runout can be check with a __________ __________
dial indicator
A __________ or __________ __________ gauge and an outside micrometer can be used to measure locations that are too small to use an inside micrometer.
telescoping, small hole
9-1 AMG057
Which tool can be used to measure the alignment of a rotor shaft or the plane of rotation of a disk?
A– Dial indicator
B– Shaft gauge
C– Protractor
9-1. Answer: A. JSGT 9B, AC 43.13-1B
Dial indicators are precision measuring instruments that are used to measure end-play and to check shaft alignments.
9-2 AMG057
Identify the correct statement.
A– An outside micrometer is limited to measuring diameters.
B– Tools used on certificated aircraft must be an approved type.
C– Dividers do not provide a reading when used as a measuring device.
9-2. Answer: C. JSGT 9B, FGH
Dividers are a layout tool consisting of two legs with sharp points. They are used to scribe circles and arcs, and for transferring measurements. However, dividers have no way of indicating a measurement.
9-3 AMG057
Which tool is used to measure the clearance between a surface plate and a relatively narrow surface being checked for flatness?
A– Depth gauge
B– Thickness gauge
C– Dial indicator
9-3. Answer: B. JSGT 9B, FPH
A thickness gauge, often referred to as a feeler gauge, is often used to determine the clearance between a surface plate and a surface being checked for flatness. A depth gauge indicates the depth of something and a dial indicator allows you to check for shaft alignment and end play.
9-4 AMG057
Which number represents the vernier scale graduation of a micrometer?
A– .00001
B– .001
C– .0001
9-4. Answer: C. JSGT 9B, FGH
A micrometer measures with a vernier scale on the barrel to the nearest ten-thousandths of an inch or .0001.
9-5 AMG057
Which tool is used to find the center of a shaft or other cylindrical work?
A– Combination set
B– Dial indicator
C– Micrometer caliper
9-5. Answer: A. JSGT 9B, FGH
A combination set consists of a steel scale, a stock head, a protractor head, and a centering head. The centering head is used to find the center of cylindrical pieces.
9-6 AMG057
If it is necessary to accurately measure the diameter of a hole approximately 1/4 inch in diameter, the mechanic should use a
A– telescoping gauge and determine the size of the hole by taking a micrometer reading of the adjustable end of the telescoping gauge.
B– 0- to 1-inch inside micrometer and read the measurement directly from the micrometer.
C– small-hole gauge and determine the size of the hole by taking a micrometer reading of the ball end of the gauge.
9-6. Answer: C. JSGT 9B, N/A
Small hole gauges are used to transfer the diameter measurement of a hole to a micrometer to determine the size. Telescoping gauges serve the same purpose, but are not generally available in sizes as small as 1/4".

9-7 AMG057
What tool is generally used to set a divider to an exact dimension?
A– Machinist scale
B– Surface gauge
C– Dial indicator
9-7. Answer: A. JSGT 9B, FGH
Dividers are a layout tool, not a precision measuring device. They are generally set using a machinist scale.
9-8 AMG057
What tool is generally used to calibrate a micrometer or check its accuracy?
A– Gauge block
B– Dial indicator
C– Machinist scale
9-8. Answer: A. JSGT 9B, N/A
Special gauge blocks are generally included when micrometers are purchased. They may be used to test the micrometer for accuracy, and to calibrate when required.
9-9 AMG057
What precision measuring tool is used for measuring crankpin and main bearing journals for out-of-round wear?
A– Dial gauge
B– Micrometer caliper
C– Depth gauge
9-9. Answer: B. JSGT 9B, AC 43.13-1B
In many cases, an outside micrometer is used to determine an out-of-round condition. To do this, take a measurement at one point and then rotate the micrometer 90 degrees and take a second measurement.
9-10 AMG057
The side clearances of piston rings are measured with a:
A– Micrometer caliper gauge
B– Thickness gauge
C– Dial gauge
9-10. Answer: B. JSGT 9B, FPH
Side clearance of piston rings is checked with a thickness gauge, or feeler gauge.
9-11 AMG057
How can the dimensional inspection of a bearing in a rocker arm be accomplished?
A– Depth gauge and micrometer
B– Thickness gauge and push-fit arbor
C– Telescopic gauge and micrometer
9-11. Answer: C. JSGT 9B, FPH
A telescoping gauge is used to transfer the diameter of the bearing to an outside micrometer.
9-12 AMG057
The twist of a connecting rod is checked by installing push-fit arbors in both ends, supported by parallel steel bars on a surface plate. Measurements are taken between the arbor and the parallel bar with a
A– Dial gauge
B– Height gauge
C– Thickness gauge
9-12. Answer: C. JSGT 9B, FPH
To check for twisting in a connecting rod, install arbors in both ends of the connecting rod and lay it across parallel blocks on a surface plate. Then, check the clearance at the points where the arbors rest on the blocks with a thickness gauge.
9-13 AMG057
The clearance between the piston rings and the ring lands is measured with a
A– Micrometer caliper
B– Thickness gauge
C– Depth gauge
9-13. Answer: B. JSGT 9B, FPH
The clearance between the piston rings and the ring lands is called side clearance and is easily checked using a thickness gauge.
9-14 AMG057
What may be used to check the stem on a poppet-type valve for stretch?
A– Dial indicator
B– Micrometer
C– Telescoping gauge
9-14. Answer: B. JSGT 9B, FPH
Valve stretch is indicated by a decrease in diameter near the neck of the valve stem. This is easily measured using a micrometer caliper.
9-15 AMG057
Which tool can be used to determine piston pin out-of-round wear?
A– Telescopic gauge
B– Micrometer caliper
C– Dial indicator
9-15. Answer: B. JSGT 9B
By taking measurements with an outside micrometer at 90 degrees to each other, an out-of-round condition may be determined.
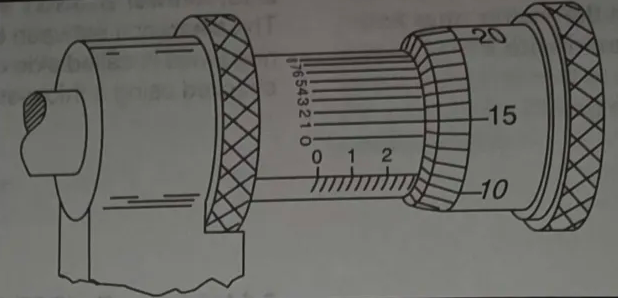
9-16 AMG057
(Refer to figure 46 on page 9-6.) The measurement reading on the illustrated micrometer is:
A– 0.2851
B– 0.2911
C– 0.2901
9-16. Answer: A. JSGT 9B, FGH
Each line on the barrel represents .025 inches. There are 11 lines showing, so you know the measurement is at least .275 (.025 x 11 = .275). Now look at the thimble. Each line represents .0010 inches. The line on the barrel is between the 10 and 11, which indicates the measurement is at least .010 inches longer, or .285 (.275 + .01 = .285). The number on the top of the barrel represents .0001 (ten-thousandth) inches. To identify the number of ten-thousandths, look for the line on the thimble that is aligned with a horizontal line on the barrel. In this case the line indicating 1 on the barrel is aligned with the 15 on the thimble. This means that .001 must be added to the measurement. The total measurement is (.285 + .0001 = .2851).

9-17 AMG057
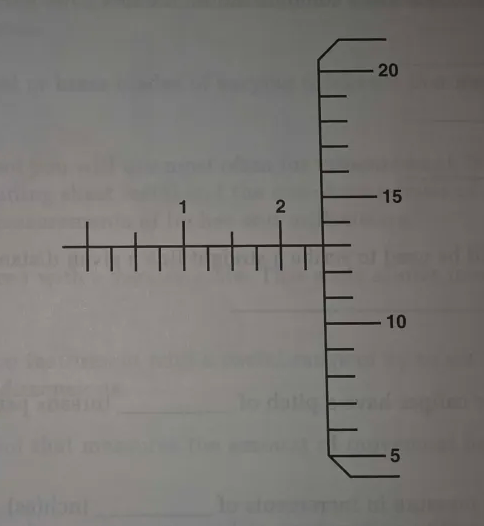
(Refer to figure 47.)
What is the measurement reading on the venier caliper scale
A– 1.411 inches
B– 1.436 inches
C– 1.700 inche
9-17. Answer: B. JSGT 9B, FGH
On a venier caliper inches, tenths of inches, and divisions of 25 thousandths of an inch are taken from the top scale. The bottom scale represents thousandths of an inch. In this example, the zero mark on the bottom scale is between the 1-inch and 2-inch mark on the top scale indicating the measurement is greater than 1 inch. The zero mark is also beyond the 4 indicating the measurement is greater than 1.4 inches (1 + .4 = 1.4). The top scale also indicates that more than 25 thousandths must be added. This results in a measurement that is at least 1.425 inches (1.4 + .025 = 1.425). To determine how many thousandths greater than 25 thousandths, identify the line on the top scale that is aligned with a line on the bottom scale and read the number of thousandths off the bottom scale. An additional 11 thousandths must be added. The total measurement of 1.436 is correct (1.425 + .011 = 1.436).

9-18 AMG057
(Refer to figure 48.)
What does the micrometer read?
A– .2974
B– .3004
C– .3108
9-19. Answer: C. JSGT 9B, FGH
The micrometer reading is interpreted as follows:
Component | Reading |
|---|---|
Barrel | 0.275 |
Thimble | 0.004 |
Vernier | 0.0002 |
Total | 0.2792 |
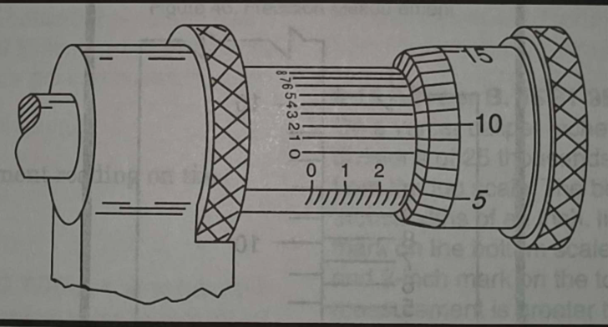
9-19 AMG057
(Refer to figure 49.)
The measurement reading on the micrometer is
A– .2758
B– .2702
C– .2792
9-19. Answer: C. JSGT 9B, FGH
The micrometer reading is interpreted as follows:
Component | Reading |
|---|---|
Barrel | 0.275 |
Thimble | 0.004 |
Vernier | 0.0002 |
Total | 0.2792 |
1 – Which tool is used to measure the clearance between a surface plate and a surface being checked for flatness?
a. Depth Gauge
b. Thickness gauge
c. Dial Indicator
b. Thickness gauge
2 – Which tool can be used to measure the alignment of a rotor shaft or the plane of rotation of a disk?
a. Dial Indicator
b. Shaft Gauge
c. Protractor
a. Dial Indicator
3 – Dividers do not provide a reading when used as a measuring device. (True or False)
True
4 – A combination square can be used to find the center of a shaft or other cylindrical work. (True or False)
True
5 – What tool is generally used to calibrate a micrometer or check its accuracy?
a. Dial Indicator
b. Gauge Block
c. Machinist Scale
b. Gauge Block
6 – Which number represents the vernier scale graduation of a micrometer?
a. .001
b. .00001
c. .0001
c. .0001
7 – Most vernier and dial calipers are capable of measuring the outside dimension, inside dimension, and depth of a part. (True or False)
True
8 – Gauge blocks are so precise that when stacked, they will adhere together and function as one larger block. (True or False)
True
9 – Telescopic gauges are used because a technician can measure a hole and take a direct reading off of the gauge. (True or False)
False
10 – What organization maintains the standards that we calibrate precision measuring instruments to in the United States?
a. ASNT
b. FAA
c. NIST
c. NIST
11 – What tool should be used to measure the diameter of a hole that is approximately 1/4" in diameter?
a. Telescoping Gauge
b. Small Hole Gauge
c. Inside Micrometer
b. Small Hole Gauge
12 – What precision measuring tool can be used for measuring crankpin out of round?
a. Micrometer Caliper
b. Dial Gauge
c. Depth Gauge
a. Micrometer Caliper
13 – Side clearance of piston rings are measured with?
a. Dial Gauge
b. Micrometer Caliper
c. Thickness Gauge
c. Thickness Gauge
14 – What may be used to check the stem on a poppet-type valve for stretch?
a. Dial Indicator
b. Micrometer
c. Telescoping Gauge
b. Micrometer
15 – Zeroing a caliper should always be the first step in taking a measurement. (True or False)
True
16 – Micrometers are a more accurate measuring tool than Calipers. (True or False)
True
17 – Measurements made with precision tools are temperature dependent. (True or False)
True
18 – Gauge blocks are accurate to ± 6 millionths and are typically used to calibrate other tooling. (True or False)
True
1. What does NIST stand for and why are they important for precision measuring instruments?
NIST – National Institute of Standards and Technology. The NIST is important because they are the organization that maintains the standards we use to measure everything with. All calibrated equipment used to approve aircraft and part must be traceable to NIST standards.
2. What are some of the reasons that a precision measuring instrument would be rejected and sent out for calibration or replaced?
Instruments should be calibrated at least once a year. Also, they must be inspected and calibrated if they are dropped or damaged in any way. Older instruments may show signs of age if the jaws are not parallel, scale alignment is off or have excessive backlash in the mechanism.
3. What is the finest resolution that a person can measure with the unaided eye?
Most people can measure to the nearest 1/32” or 1 mm with the unaided eye.
4. In general, how accurate are vernier and dial calipers?
Vernier and dial calipers are typically accurate to one thousandth of an inch. (0.001”)
5. What are the advantages of a vernier or dial caliper?
Calipers have several advantages. They can take a wide range of measurements so one tool can measure inside, outside and depth of an object. Also, unlike a micrometer, they have a wide range of adjustment.
6. In general, how accurate are micrometers?
Micrometers with a vernier scale are accurate to one ten thousandth of an inch. (0.0001”)
7. Why does a technician need to be careful when using electronic calipers and micrometers?
Electronic calipers and micrometers are great because they are the easiest to read. However, the resolution is often finer than their accuracy which can lead to a technician using a tool without enough precision for the measurement being taken.
8. How should a technician check the zero of an instrument before they take a measurement?
To check a zero of an instrument, first clean the jaws or anvils. Then close the tool and check that the indicator lines up with zero. On a vernier caliper, the zero marks should align. On a dial caliper, the bezel is rotated to align the 0 on the dial with the needle. On a micrometer the sleeve is rotated with a wrench to align the indicator line with the 0 on the thimble scale.
9. How do you read a vernier caliper?
First you would read the main scale. Digits typically represent whole inches (1.0”) or tenths of an inch (0.1”). Tic marks can be 0.025” or 0.05”, this will be dictated by the vernier scale. Then you look to see which vernier scale tic mark lines up with a tic mark on the main scale. That number represents how many thousandths of an inch (0.001”) that you need to add to the main scale reading.
10. How do you read a dial caliper?
First you would read the main scale. Digits typically represent whole inches (1.0”) or tenths of an inch (0.1”). Then you would read the dial. Typically, the needle will make one revolution for every tenth (0.1”) the jaws are moved. The dial indicates how many thousandths of an inch (0.001”) that you need to add to the main scale reading.
11. How do you read micrometer?
Micrometers typically come in whole inch frame sizes. First read the sleeve scale. The sleeve scale had digits for every tenth of an inch (0.1”) and tic marks every 0.025”. Then read the thimble scale to determine how many thousandths of an inch you need to add to the sleeve scale. Last you look at the vernier scale to see which tic mark on the thimble lines up. This indicates how many ten-thousandth of an inch (0.0001”) need to be added to the main reading.
12. How are dial indicators used?
Dial indicators and dial test indicators are often used to measure variation in a part. This can be out of round, choke, runout, end play or backlash. It is not an absolute measurement but a relative measurement. This means that it is measuring a range of variation not an exact size.
13. What is the primary function of a gauge block?
Gauge blocks are used to calibrate other precision measuring instruments and to set up other tooling.
14. What is wringing as related to gauge block?
Wringing is the process of stacking gauge blocks to achieve a precise height to setup or calibrate tooling. The blocks adhere together because of the precise fining and require a fair amount of force to pull them apart.
15. What indirect measurement tools are used in aviation?
Telescopic gauges, small hole gauges, and dividers are used to take indirect measurements. The tools size is adjusted to fit a part and then removed. Then a scale, caliper, or micrometer is used to measure the tool.
16. How are feeler gauges used?
Feeler gauges, also known as thickness gauges, are a set of gauges where each one is ground to precise dimensions. The gauges of an appropriate size are selected, and a process of elimination is used to determine the size. When slight drag is felt on the gauge as it’s being drawn through the gap, this indicates that it is the same size as the gap.
17. What are go / no-go gauges?
A go / no-go gauge is set up for quick inspection of certain parts. Often the gauge is designed for a specific inspection task. The “Go” represents one end of the allowable tolerance while the “No-Go” represents the other end of the tolerance. For example, if the “Go” gauge fits in a hole, then it is larger than the minimum specification. If the “No-Go” does not fit in a hole, then it is smaller than the maximum specification.
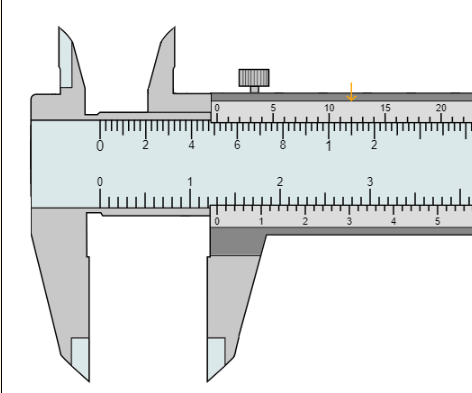
18. What is the measurement in inches?
0.512”
19. What is the measurement in inches?
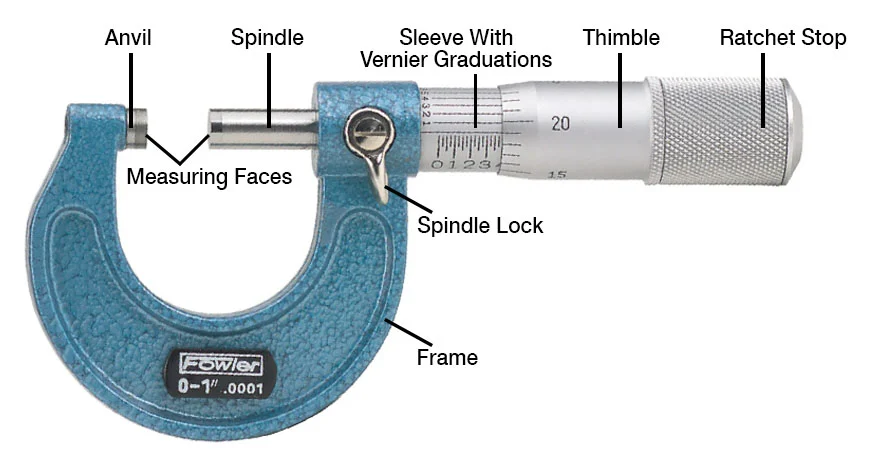
1.164”

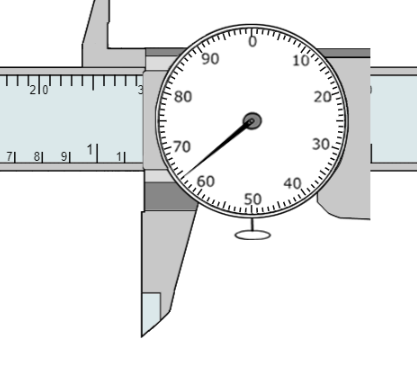
20. What is the measurement?
0.7187”
21. Identify the parts of an outside micrometer.