ARHS Ancient-Medieval Midterm
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms

Twelve Votive Figures, Sumerian, c. 2600 BCE, from the temple of Abu at Eshnunna (Tell Aman, Iraq)
very geometric, relatively simplistic shapes, huge big eyes, rigid and stiff, simplified texture to hair and braids
small statues placed in temples to represent worshippers, meant to stand in perpetual prayer before the deities.

Bull headed harp from the royal cementary ar Ur, Sumerian, c. 2600 BCE
made of tar, shell
depicts one of the first recorded methods of stories, could be fictional, entirely a myth. Depicts a man and two bulls fighting (as noticed by the x shape)
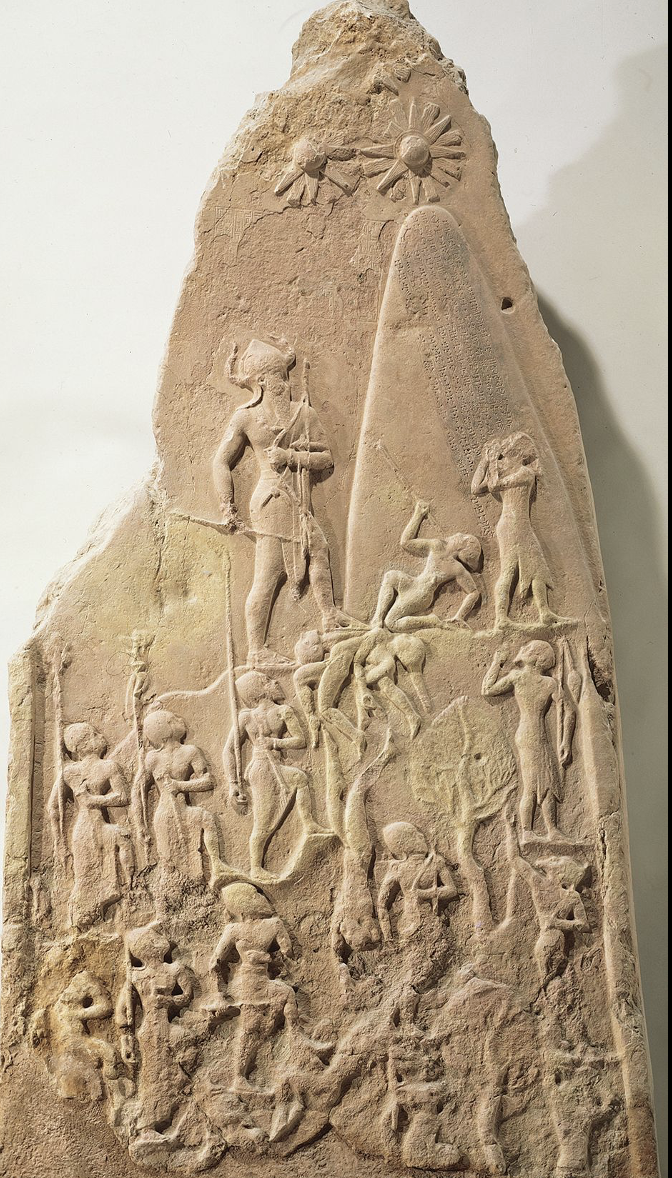

Victory Stele of Naram Sin, Akkaidian, found in Susa, Iran (originally from Sippar)
c. 2200 BCE, commemorating Naram-Sin's victory over the mountain people, displaying him as a god-like figure leading his army.
Utilizes hierarchy of scale, where the more important people are bigger/larger than everyone else. Bull horns on king’s head indicate he is godlike
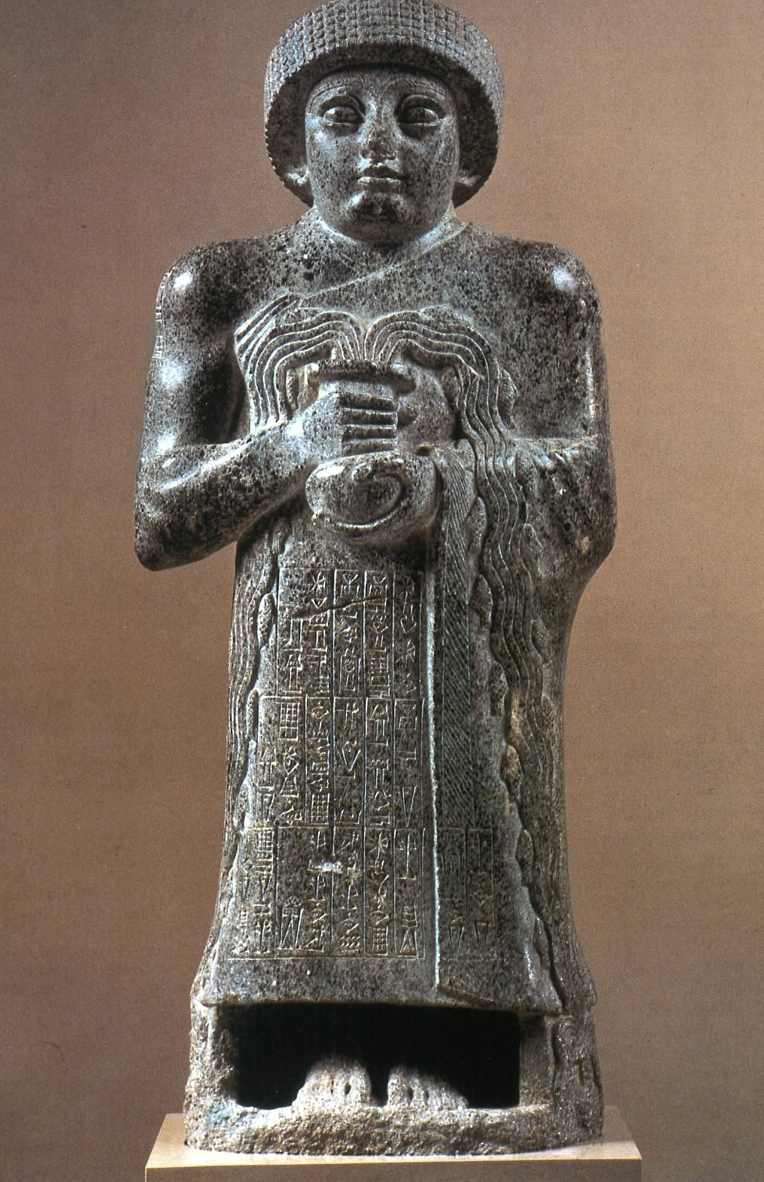

Votive statue of Gudea, Neo Sumerian, from Girsui (Telloh, Iraq), c. 2100 BCE
Made from diorite - because the rock is extremely solid, its harder to emphasize detail. Yet the statue has cuneiform along its clothing, and the design choices are purposeful - takes much more effort to carve this material. Surface of stone has high polish. Movement is centered, compact - is holding a vase with the waters of life.
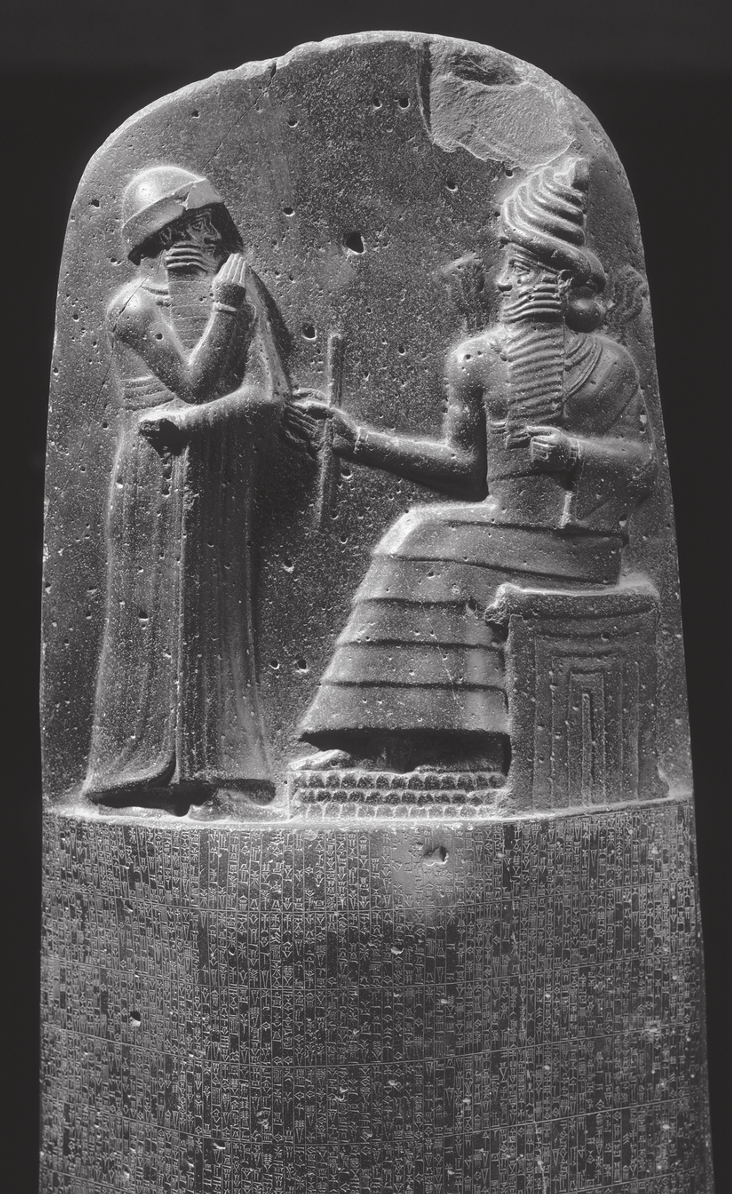

Stele of Hammurabi, Babylonian, c. 1750 BCE, found at Susa, probably from Sipper
scene portrays Hammurabi recieving the law from the throne of god, shamash (wearing a horned headress, symbolizes divinity)
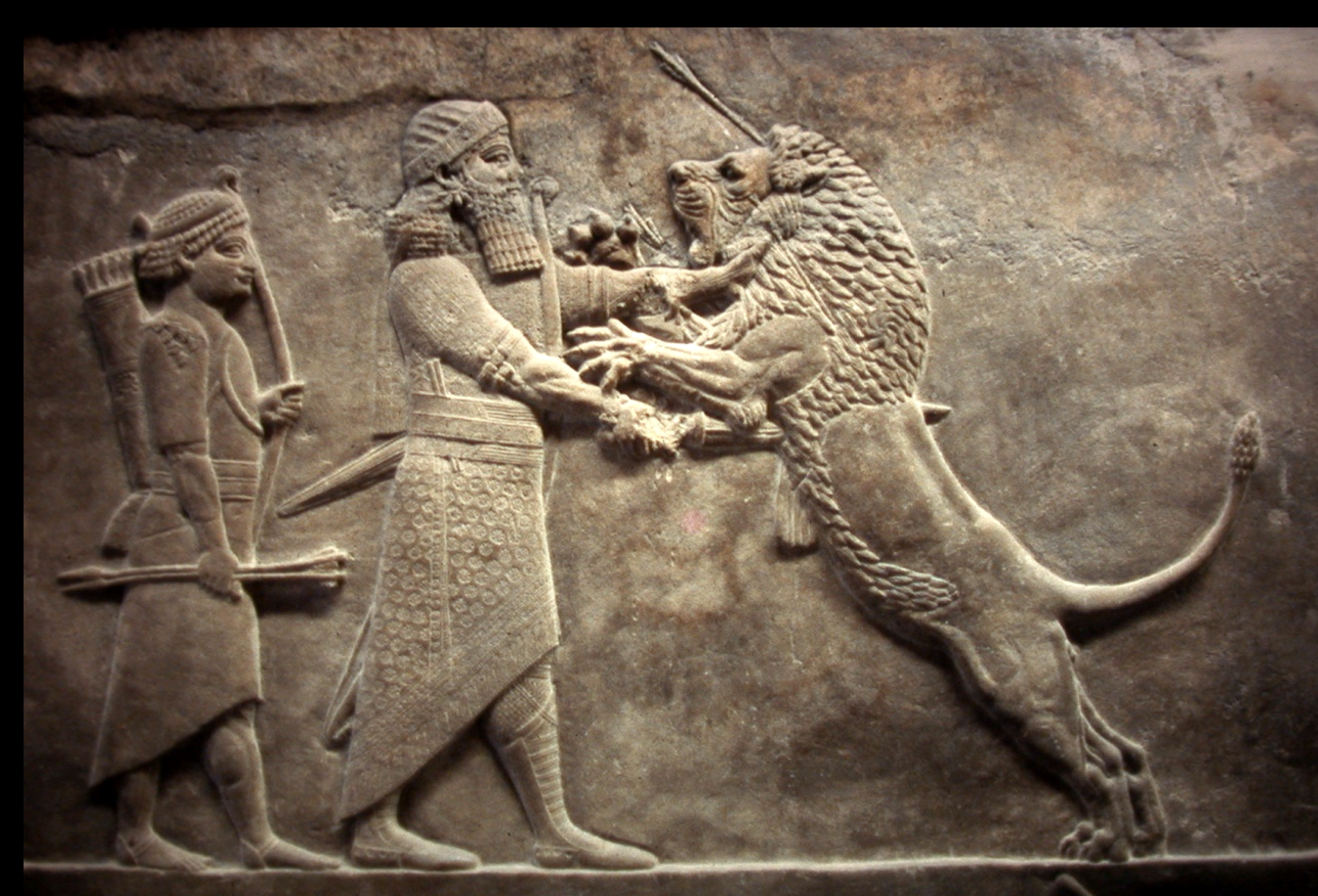

Assurbanipal killing a lion, Assyrian, from the palace at Nineveh (Iraq) c. 650 BCE
Assurbanipal II was a very learned king and a great patron of the arts and literature. His palace was decorated with many fine reliefs and included a library. Both of these are important sources on the Assyrians.
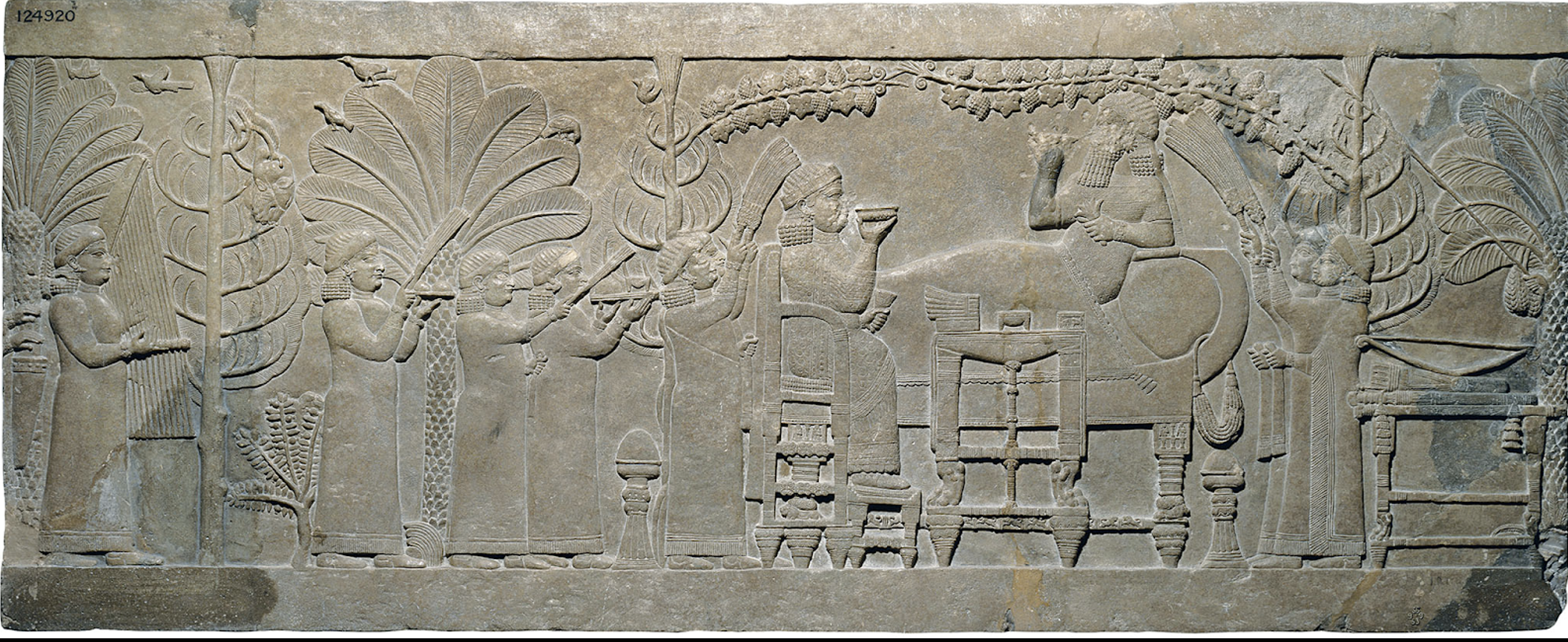

Assurbanipal and his queen in the garden, Assyrian, from the palace at Nineveh, c. 650 BCE
Purpose of Assyiran reliefs is highly propogandistic, meant to intimidate the viewer/remind them of kingly power. These reliefs are the earliest works of art that have attempted to depict real historical events. Contains realistic perspective + depth, geographic setting, necessary when depicting complex historical events
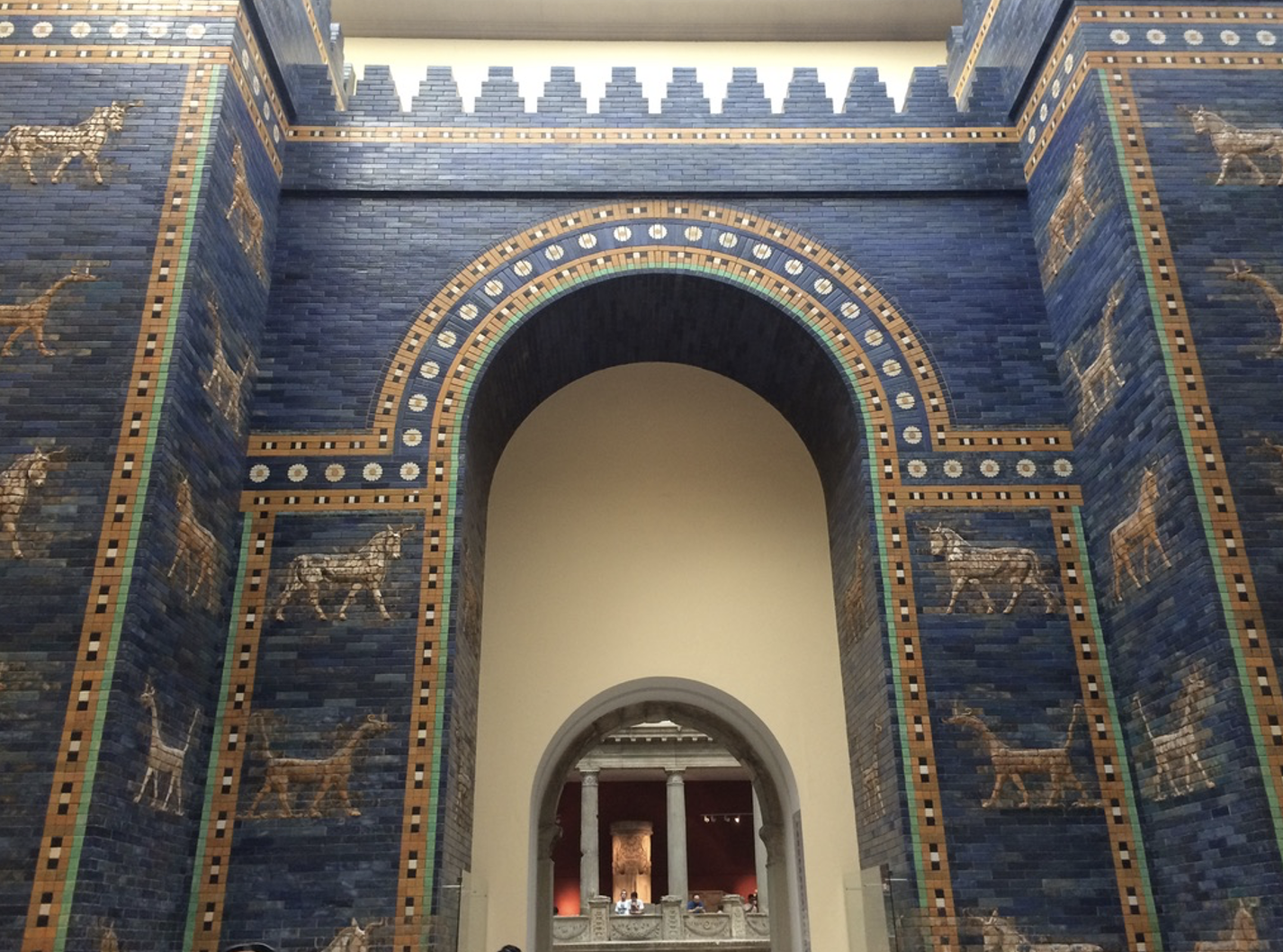

Ishtar Gate, Neo- Babylonian (built by Nebuchadnezzar II also built the hanging gardens), c 575 BCE, originally in Babylon, reconstructed in the Pergamon Museum
Made of glazed mudbricks — the animals are the authentic bricl. Blue glaze from lapis lazuli, imported from Afghanistan.
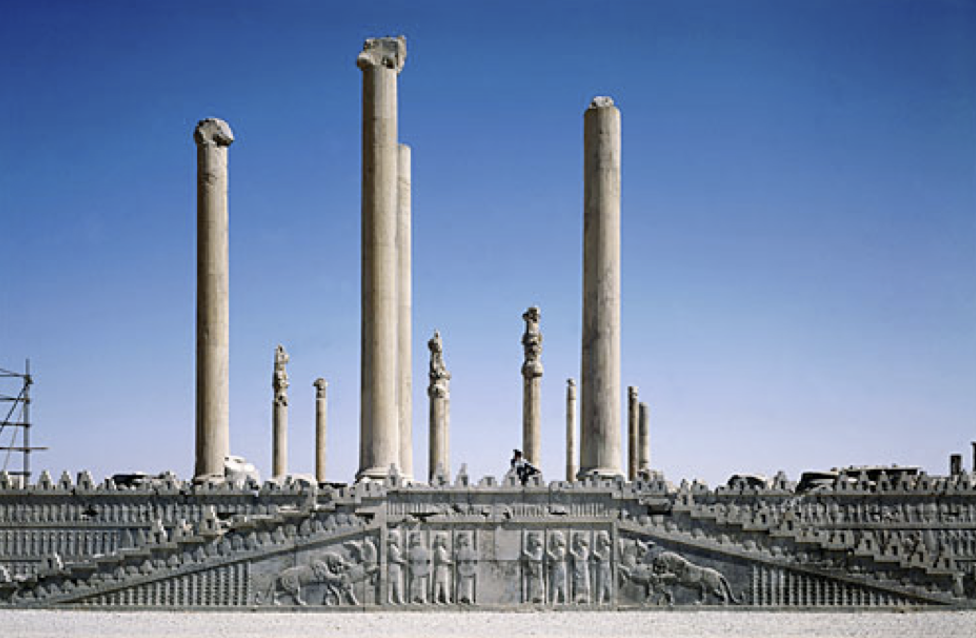

Apadana (audience hall) of Darius and Xerxes, Persian, c. 500 BCE, Persepolis, Iran
Persians created art that contained many influences from other cultures. Reliefs contain several people from various cultures bearing tribute (ex. Babylonians, Syrians, Armenians). Audience hall utilizes axial symmetry. Bulls on Persian reliefs are associated with divinity, demonstration of wealth and power
Ancient Egypt Period Dates
3500-3000 BCE - Predynastic period
3000-2100 BCE - Old kingdom
2100-1700 BCE - Middle kingdom
1600-1000 BCE - New kingdom
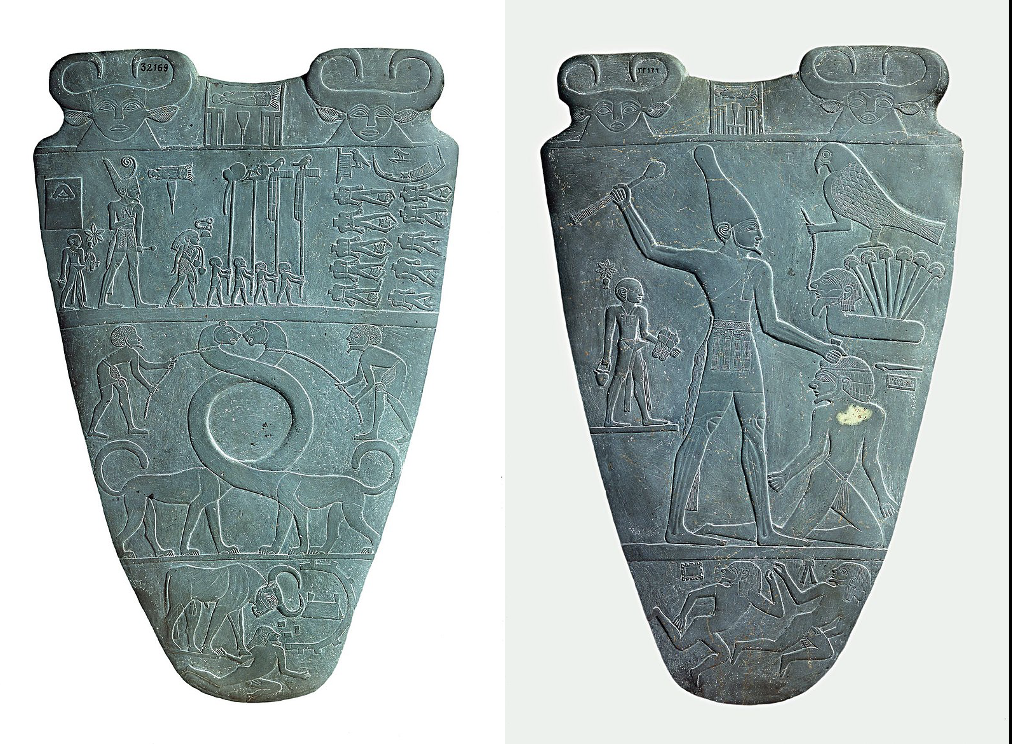

Palette of Narmer, c. 3000 BCE,
Back: Narmer is wearing the crown of Upper Egypt. Falcon symbolizes Horus, protector of phaorohs, sitting atop a lotus plant (Lower Egypt). Emphasizes his conquest of LE and now rules both lands, unifying Egypt.
Front: Narmer takes part of a royal procession, enemies are beheaded. At the bottom, a bull traples the enemy, and, with its horns, breaks the citadel wall.
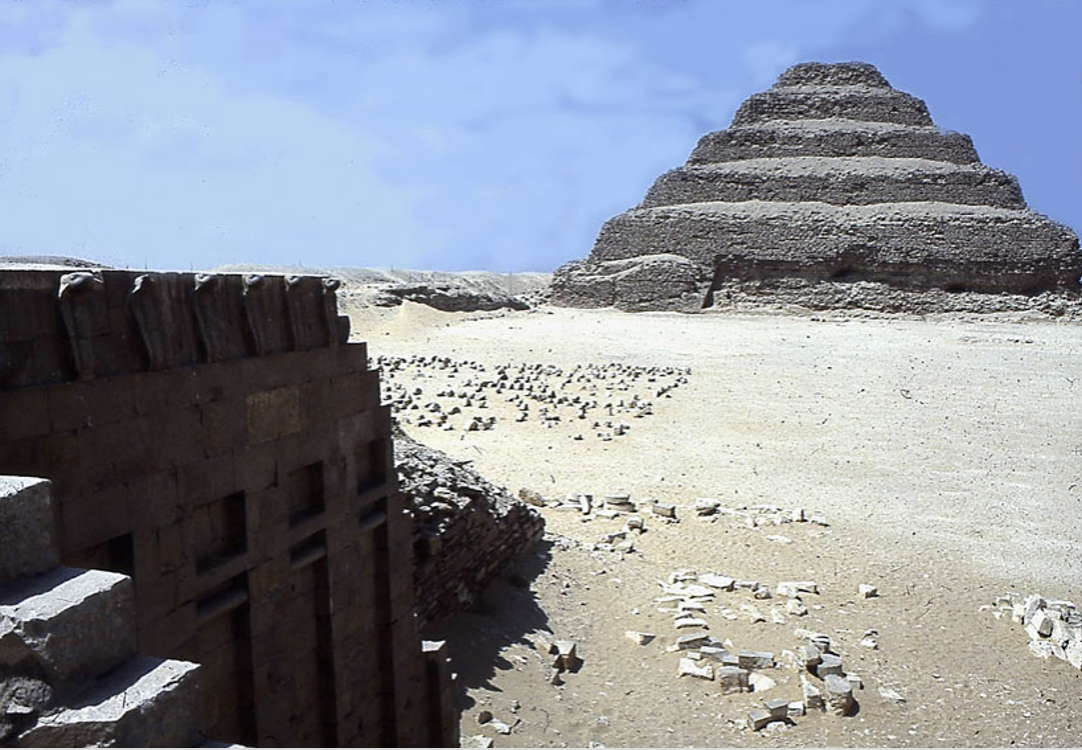

Pyramid of Djoser, by Imhotep, c. 2600 BCE, Saqqara, Egypt
Not an isolated structure, a part of a larger funerary complex including temples to worship the dead x
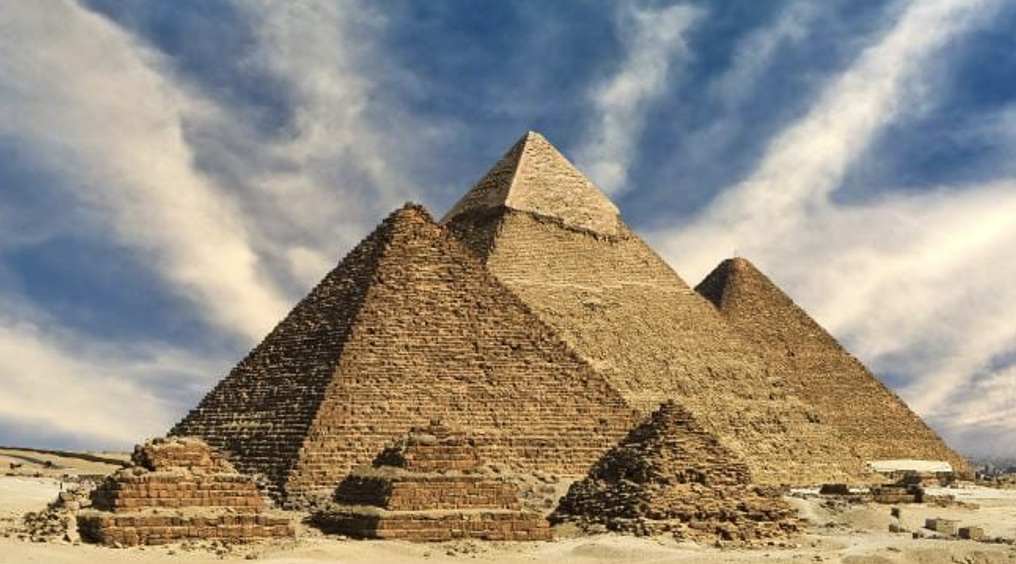

Great Pyramids of Giza c. 2550-2450 BCE,
From oldest to newest: built for the pharohs Khufu, Khafre, and Menkure.
Triangle shape: associated with the sun, stairway to heaven. Pyramids were originally covered in smooth, white limestone.
Alignment of the pyramids is the exact same alignment on Orions belt (to Egyptians was Osiris, god of death), the air shafts in pyramids might be star shafts from King’s chamber can see const. Osiris, from Queen chamber can see const. Isis.
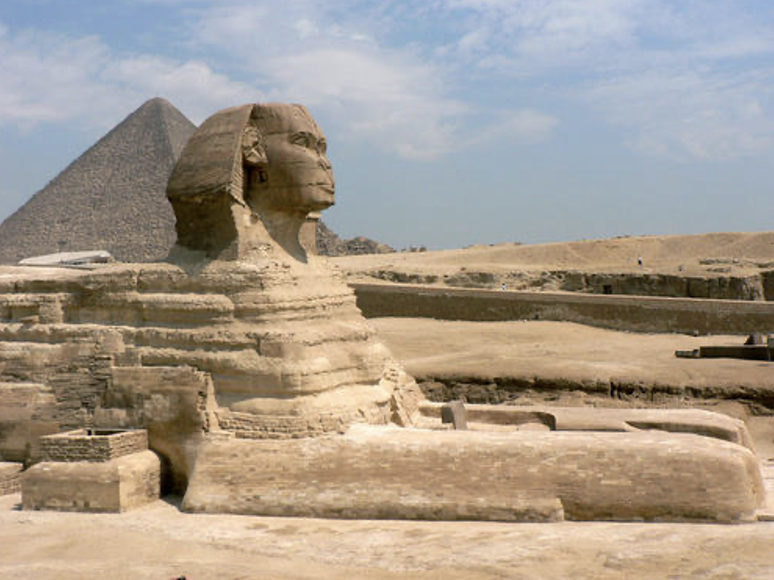

The Great Sphinx at Giza (built for Khafre, face is his portrait), c. 2550 BCE
Potentially idealized
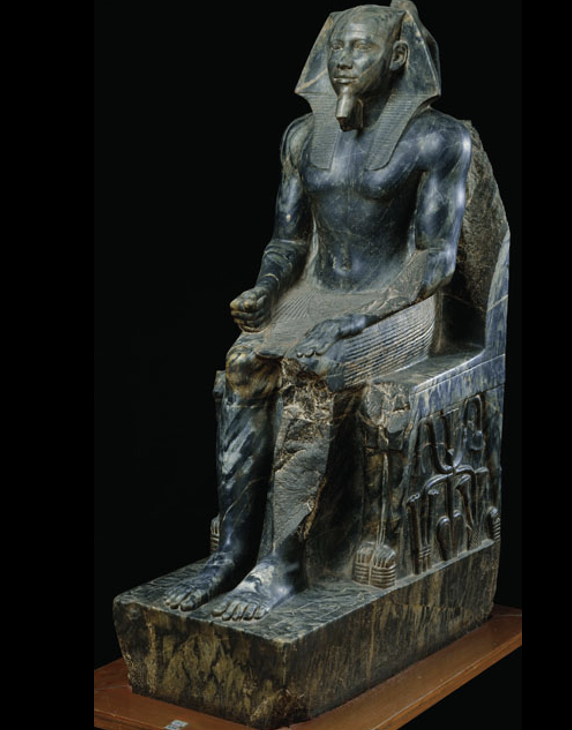

Statue of Khafre (from funerary complex), c. 2500 BCE
Made of extremely durable stone, meant to last an eternity. Figure is contained and compact, arms left to the sides — difficult to carve any unique pose. Face is rounder, softer features, smoothed over look creates idealization (soft, benelovent), contrasting his body posture (rigid, strong, powerful). Mix between realism and idealization.
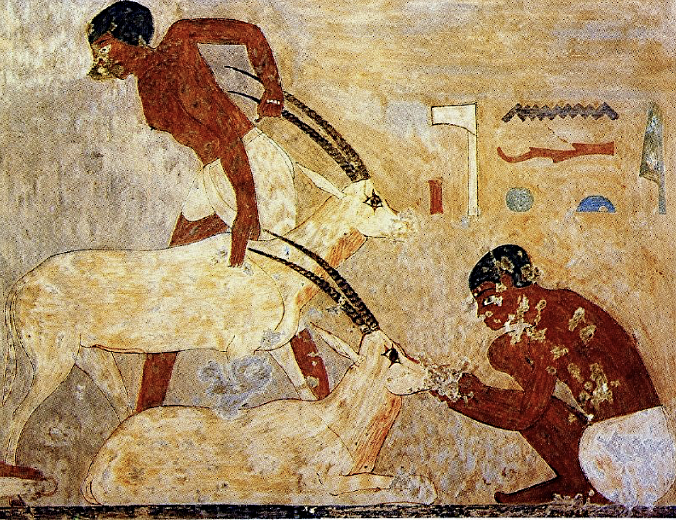

Paintings from rock cut tombs at Beni Hasan, c. 1900 BCE
Proportions are less rigid like Old Kingdom Egyptian art. Use of perspective (figures on different ground levels) and foreshortening + spatial depth (no mixed perspective). More natural posing, actually doing things, when before most figures would just standing.
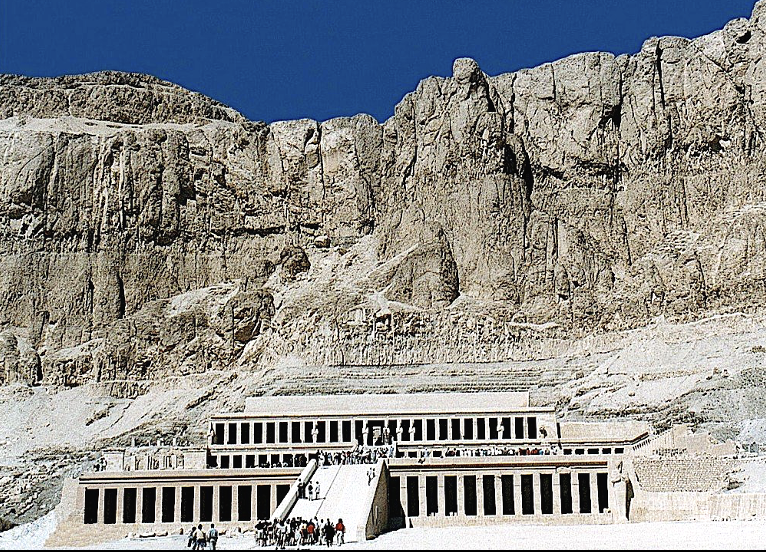

Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut, c. 1450 BCE
Temple for the first female Pharaoh, portrayed as both a man and a woman in art. Temple utilizes axial symmetry: when the ground plan of a structure is arranged logically along an axis.
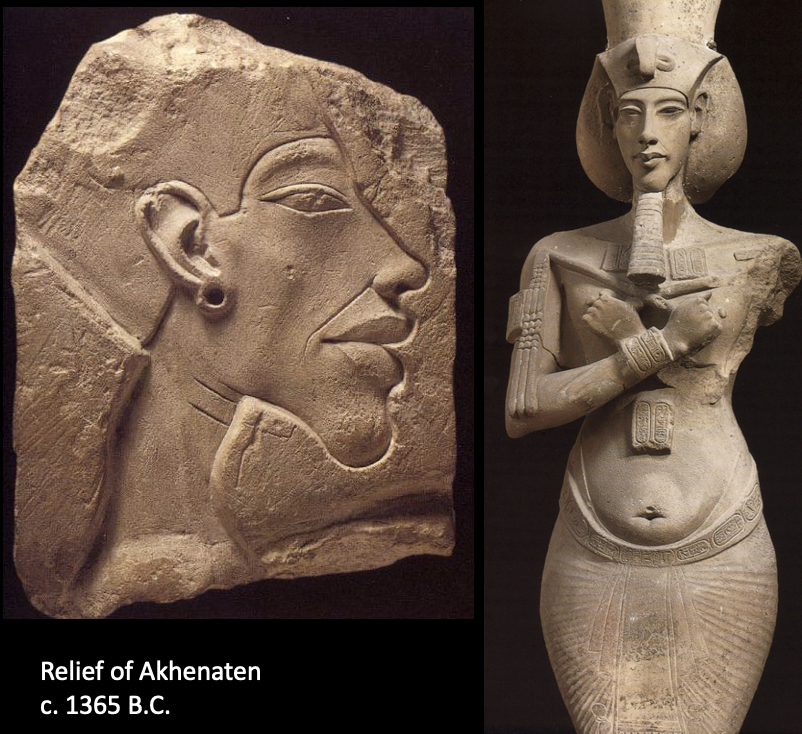

Relief of Akhenaten, c 1365 BCE
Akhenaten attempted to create Egyptian monotheism. Creation of the amarna style, pronounced, cartoonish features. Looks androgynous in art = meant to highlight both the masculine and feminine in the divine. Akenhaten was widely unpopular, worship of the Aten (the monotheistic sun god) died with him.
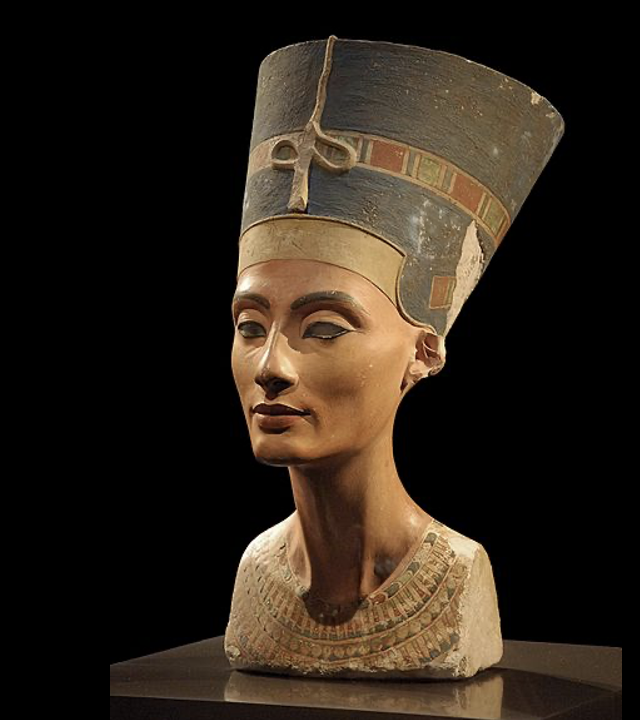

Bust of Queen Nefertiti, c. 1345
Other side of the amartna style, softer, more life-like.
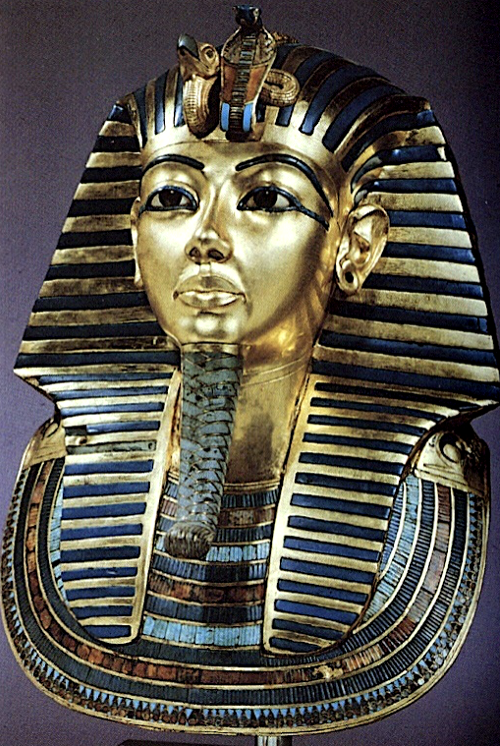

Funerary mask of King Tut, c. 1330 BCE
The return to “normal” Egyptian style. Tut is only extremely famous because his tomb is the only tomb that wasn’t robbed
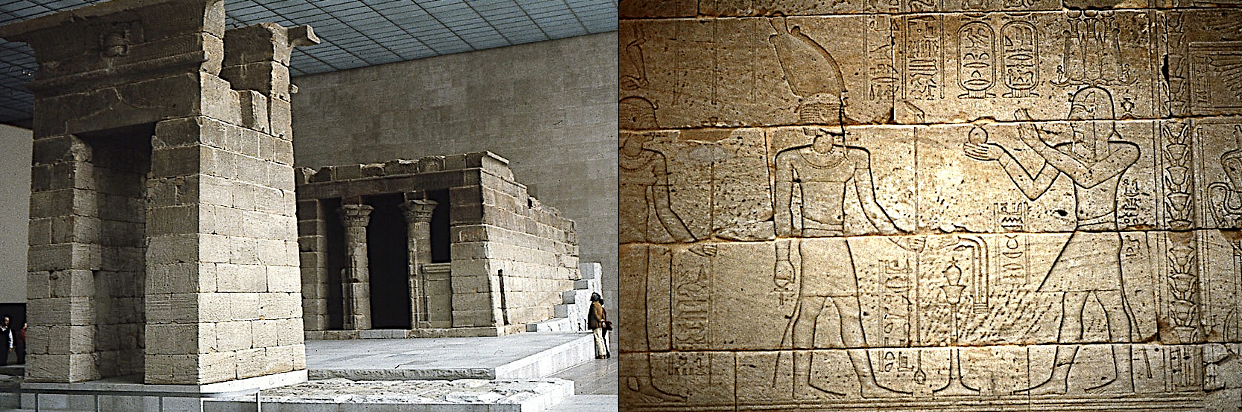

Dendur temple, c. 22 BCE.
Displays henotheism: polytheistic peoples had respect for other culture’s gods. Augustus Caesar (identifiable by inscription) is seen worshipping Egyptian gods
Bronze Age Greece Period dates
2800-2000 BCE - Cycladic
2000-1400 BCE - Minoan
1600-1100 BCE - Mycenaean
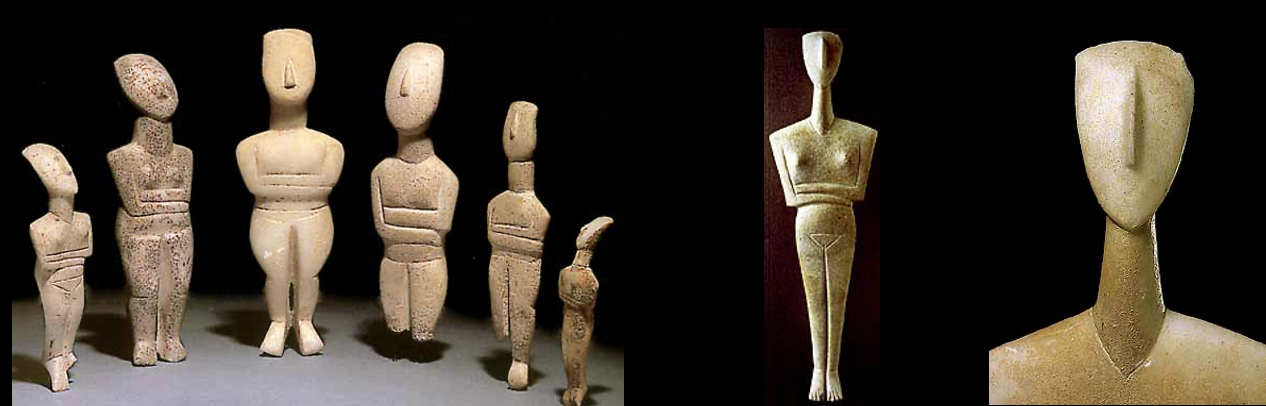

Cycladic Figurines, Cycladic, c. 2800-2000 BCE
Made of fine quality marble. Extremely stylized. Generally represent female figures, some male ones painted, found lying down in graves — extremely similar to prehistoric art Cyclades
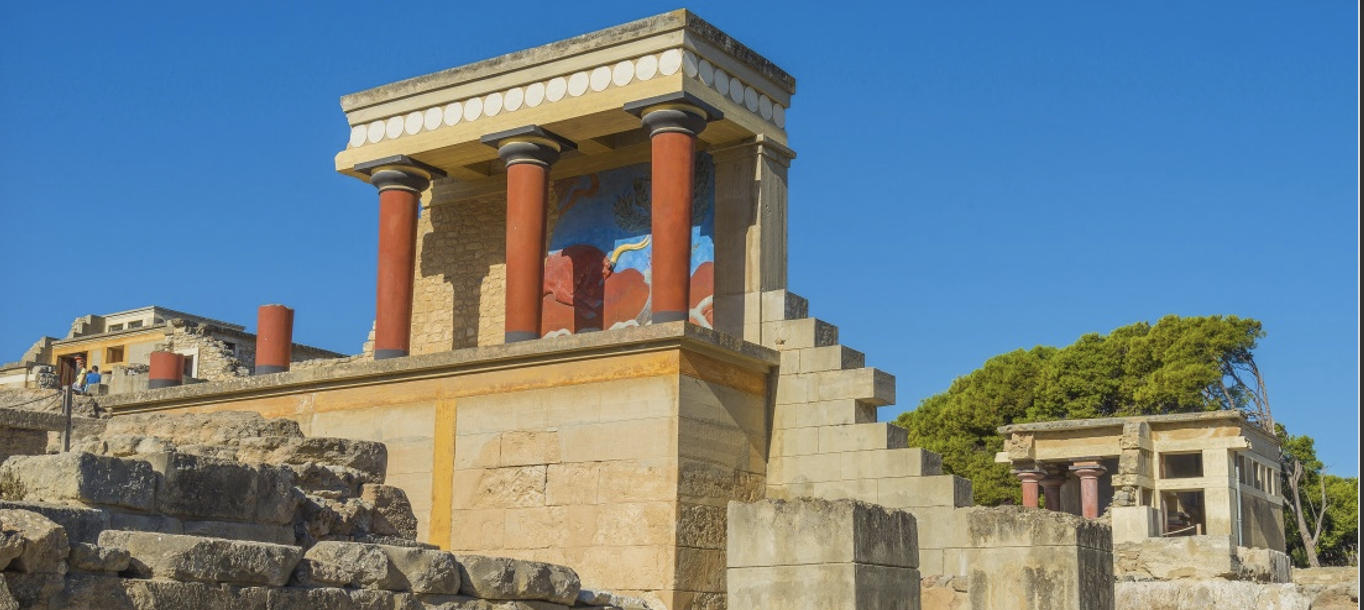

The palace at Knossos, Crete, Minoan, c. 1600-1500 BCE
Might not have been a palace — don’t know enough info. Sprawling architecture, no symmetry, plan centers around a large courtyard. Pretty accessible, very open, no fortifications or axial symmetry. Makes sense with Minoan culture — isolated on an island, did no engage in warfare.
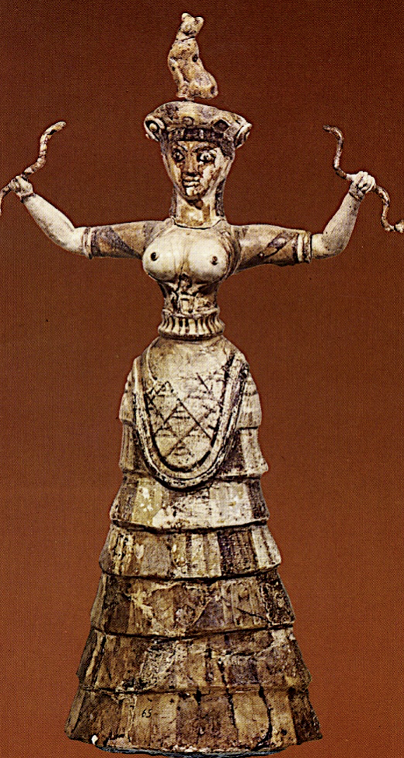

Snake goddess, from Knossos, Minoan, c. 1600 BCE
Snakes = positive associations in pre-Christian cultures
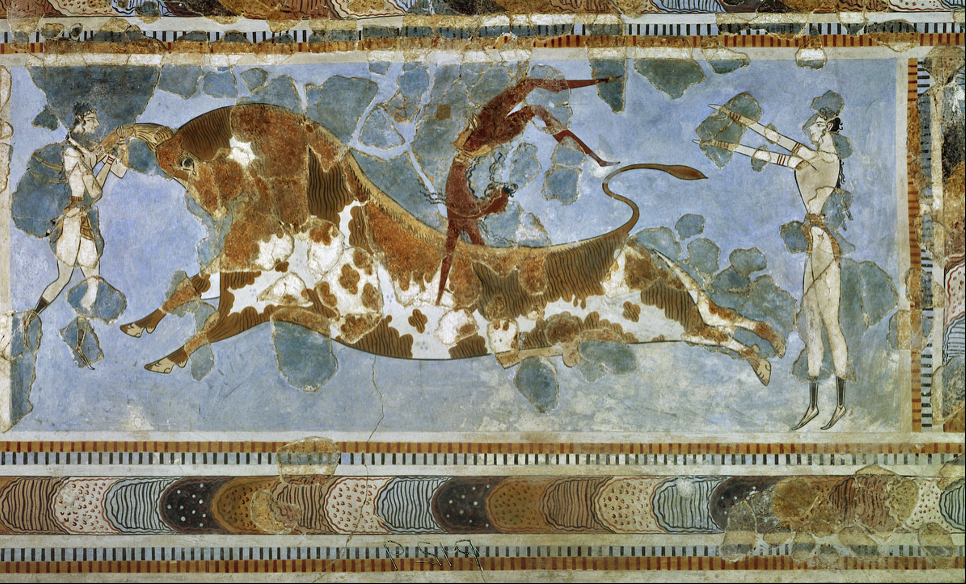

Bull-leaping fresco from Knossos, Minoan, c. 1500 BCE
First to use the art of the true fresco (painting done on wet plaster, stays bright + endures). Skin color is not related to race, but to show differences in sexes. 2 pale women are shown, one darker man. Carefully designed, interest in naturalism.

“kamares ware”, Minoan, c. 2000-1800 BCE
might be based on motifs of the sea, even though abstract

Octopus Jar, Minoan, c. 1600 BCE
Octopus looks lively and benevolent to hold respect for the sea. Not much use of negative space, the tentacles are evenly distributed.

Harvester vase from Hagia Triada, Minoan, c.1500 BCE
Carved, not painted. Features are homogenus, all facing the same direction. Very fluid, dynamic, expressive, figures aren’t stagnant or rigid. Anatomically correct, muscles + limbs distinc, naturalistic. Oftentimes when men are depicted in art, its related to warfare or violence, but Minoans aren’t a warmongering civilization. Artwork conveys this.
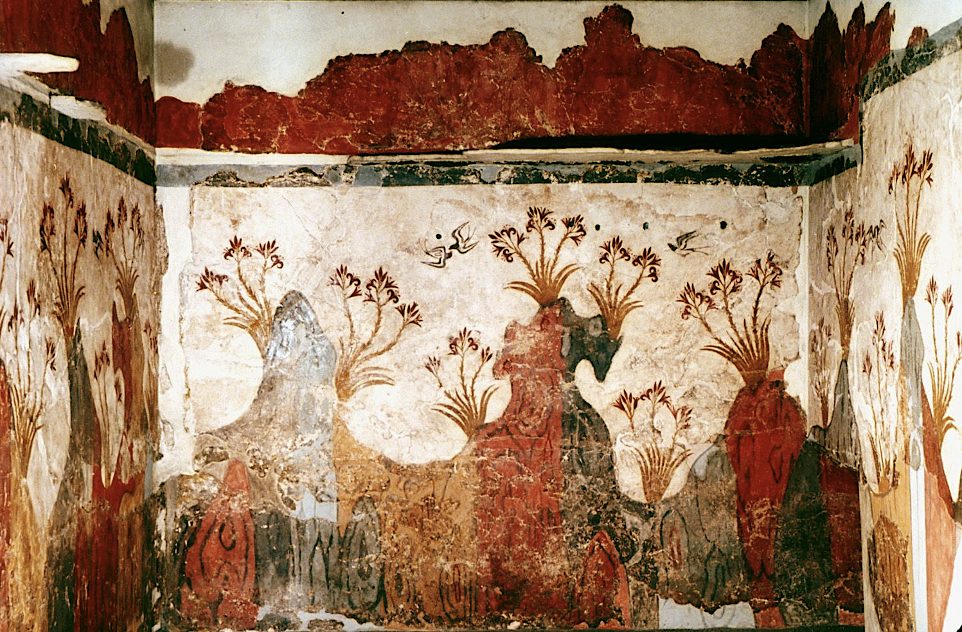

Springtime fresco from Thera, Minoan, c. 1500 BCE
First true landscape in art history? Not completely naturalistic looking
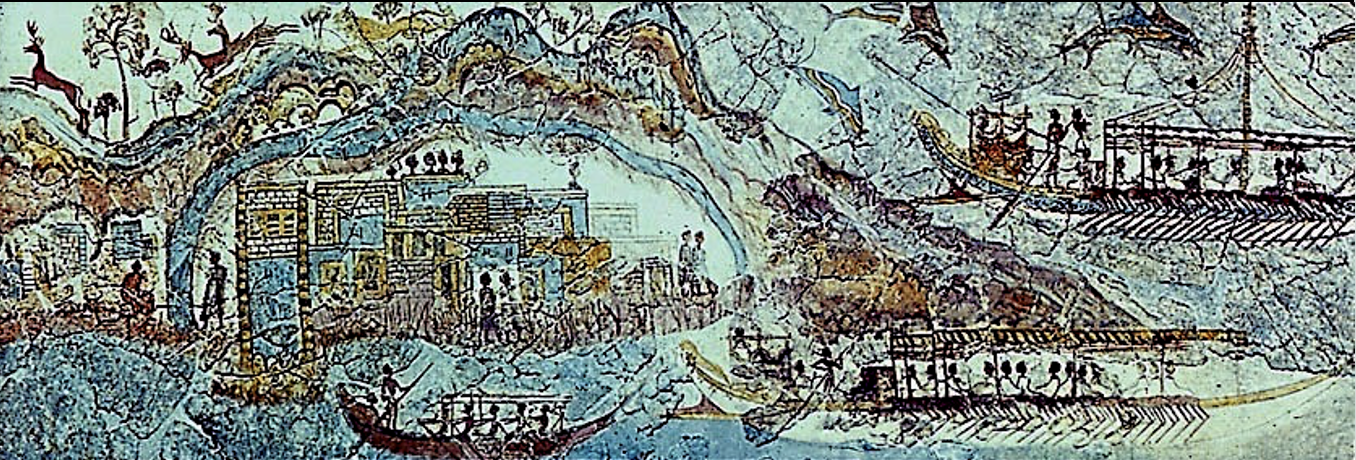

Flotilla Fresco from Thera, Minoan, c. 1500 BCE
“The first historical landscape scene”, shows people coming back from a fishing expedition/potentially founding a colony.
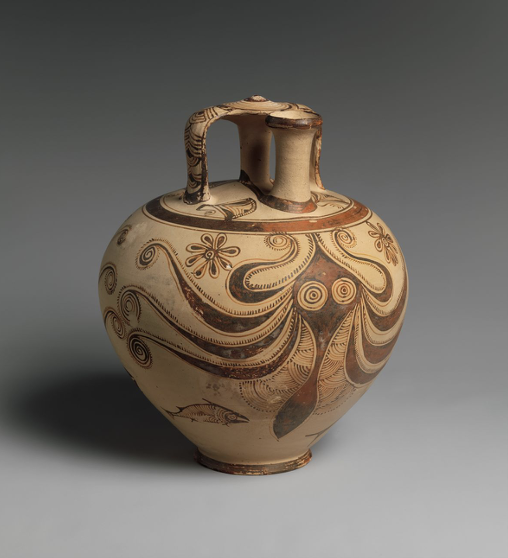

Stirrup Jar with Octopus, Helladic/Mycenean, c.1200-1100 BCE
Mycenean art is influenced by Minoan art. But Mycenean art has loss of vitality, motion. Very geometric + abstract, less realistic and more symmetrical.
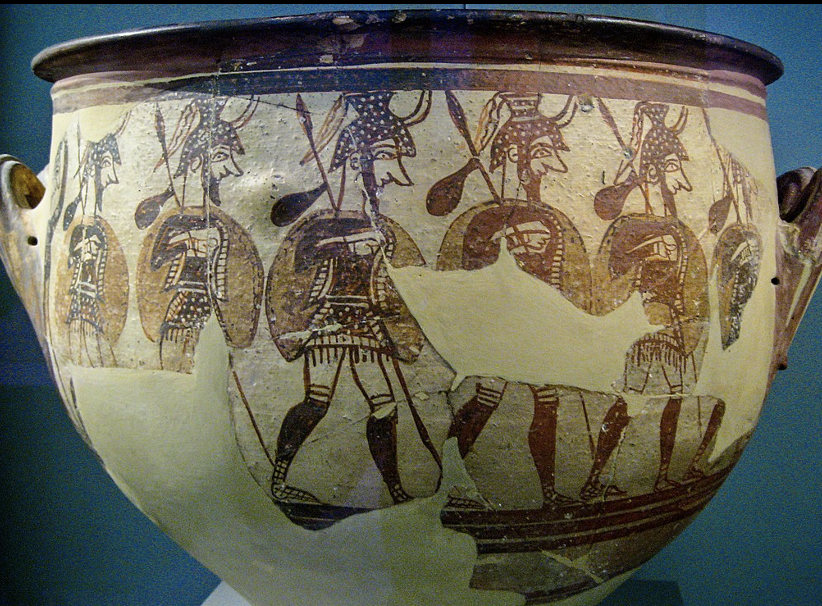

“Warrior Vase”, Mycenean, c. 1200 BCE
Figures are cartoonish, little difference in expression/features. Repetitive, not much depth.
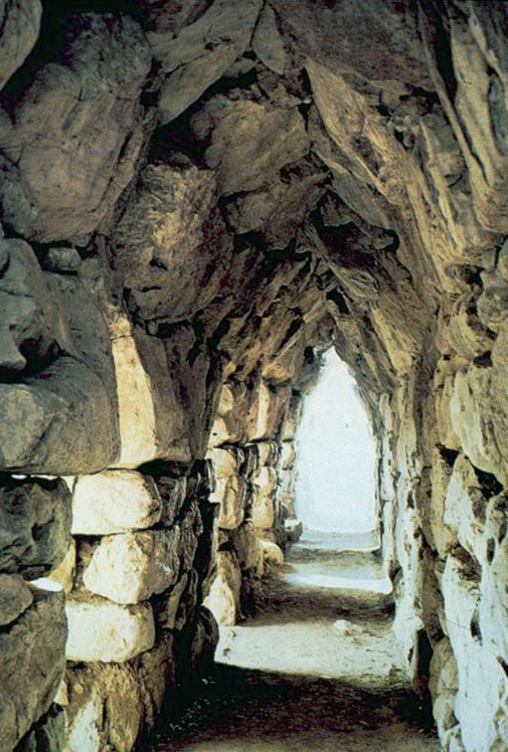

Cyclopean masonry from the citadel of Tiryns with a corbelled arch, c. 1400-1200 BCE
Heavily fortified cities, throne room/megaron (four columned hall, elaboratly painted, with a porch at front, hearth in middle) in each palace.

Beehive tomb (treasury of Atreus), at Mycenae, c. 1300 BCE
Greek Art Period dates
1100-700 BCE - Geometric
700-600 BCE - Orientalizing
600-480 BCE - Archaic
480-450 - Early Classical
479 BCE: Athens defeats Persia in the Persian wars, Persia sacks Athens and destroys the Acropolis 480
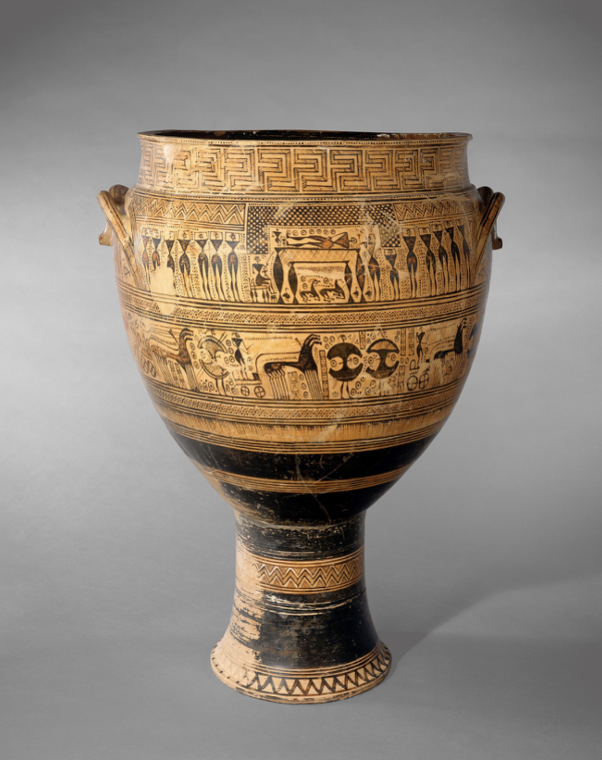

Attic Geometric Krater, c. 750-735 BCE
A funerary procession is depicted on the basin, highly schematized, very abstract, not much empty space. Extremely layered, objects are stacked on top of each other in rows.
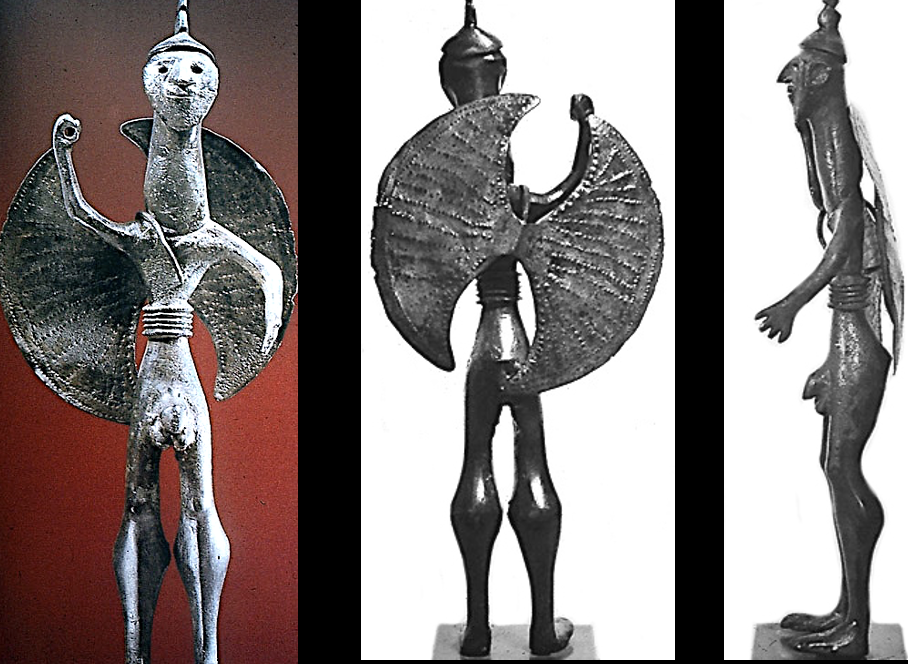

Thessalian Warrior, 8th century BCE

Attic amphora from Eleusis, c. 650 BCE
The amphora showcases first mythological scene (that survived), Odysseus stabbing Polyphemus’ eye.

“Lady of Auxerre”, c. 650-625 BCE
Made of limestone. Most likely a votive offering. Daedalic style - hair is wig like/blocky, posture similar to Egyptian sculpture, smooth/flat. Schematized body forms, exaggerated facial features.
Early Greek Temple Architecture
Peripteral = having columns on all sides
Naos/cella = the “living space” of the god, central chamber where the cult statue was placed. Megaron was a precursor to this
Temple of Hera I, Paestum, c. 550 BCE
Had entasis, a slight bulging of the columns prominent in the Archaic period, but less so in later temples. Most greek temples were complete structural masses, as opposed to Roman temples.
Archaic Period
Saw the rise of doric and ionic orders in STONE, probably developed in wood during orientalizing period. The freize = area above the pillars.
Orientalizing Period
Orientalizing period started via trading with the ancient near east. The pottery became less geometric and more curvaliniear.
Geometric Period
Geometric period held the earliest forms of famous greek pottery, “horror vacui”, fear of empty space.
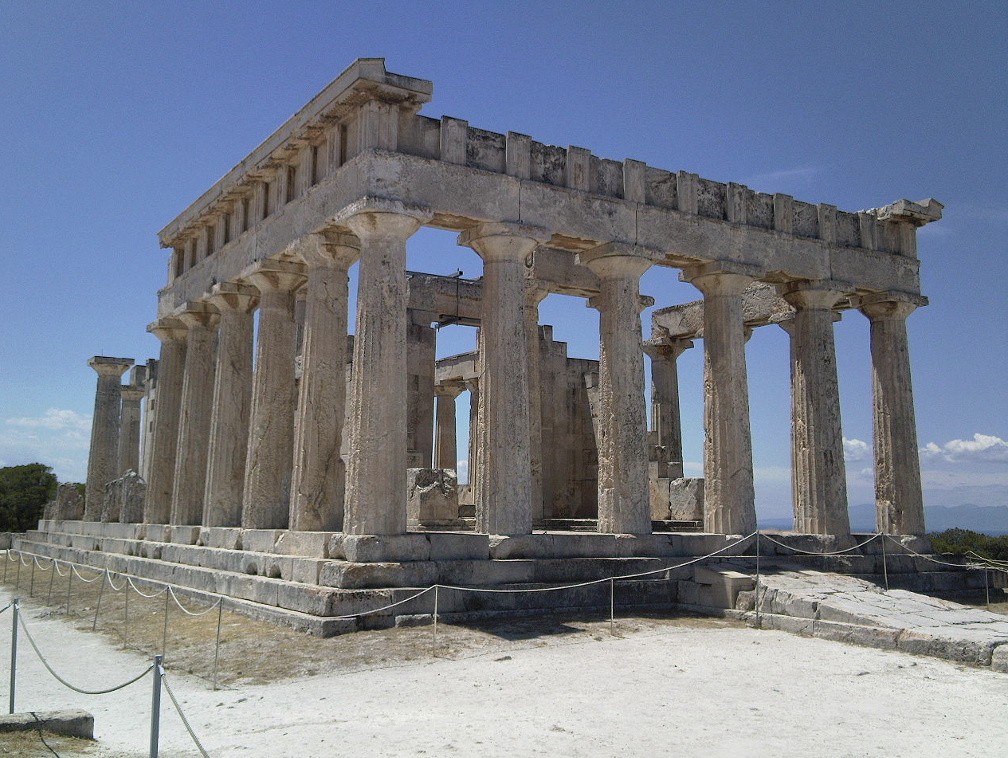

Temple of Aphaia, Aigina island, c. 500 BCE
Slimmer columns, doric capital gets smaller. Pediment figures utilize scale, all are the same size, just in different positions — looks more harmonious. East pediment warrior = more naturalistic, showcases struggle, muscles defined. West warrior = archaic face + smile, muscles less defined, pose lounging back while dying? Both are different artists
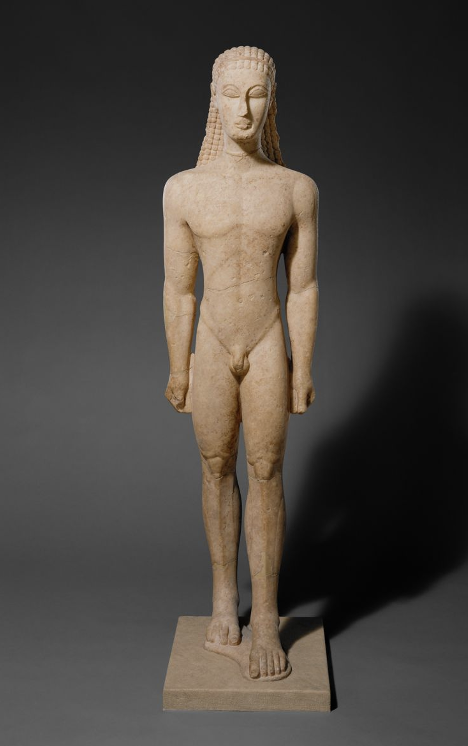

Metropolitan Kouros, c. 600 BCE, early Archaic
More schematization, less naturalistic. Slimmer body, almond shaped eyes.

Anavysos Kouros “Kroisos”, c. 540 BCE, later Archaic
Less schematization, muscles and facial features are more developed, life like. Hair is more textured but still schematized. Male nudity is unique to ancient greek culture in sculpture. Has the archaic smile - most sculptures have a closed lip smile, might be sculptors intent to add three dimensionality.

Kore 675, c. 510-500 BCE
Made of marble with polychromy. Lots of paint survived on this statue. Experiment with folding in drapery, although not completely realistic, is attempting for naturalism. Hair is fluid + more realistic. Has the classic archaic smile.
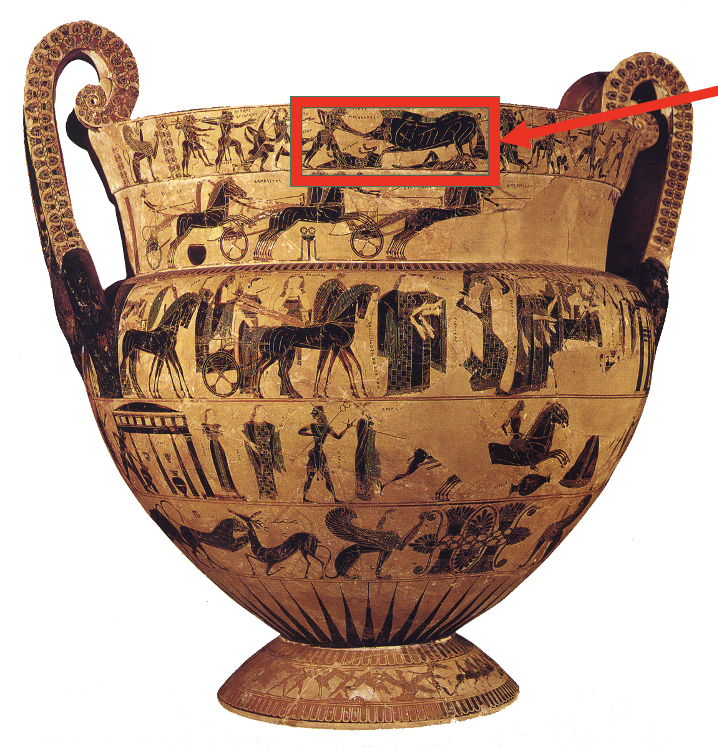

Francois Vase, c. 575 BCE. Has the hero melegar hunting the Calydonian boar

Achilles slaying the Amazon queen Penthisilea vase, artist: Exekias, c. 550 BCE
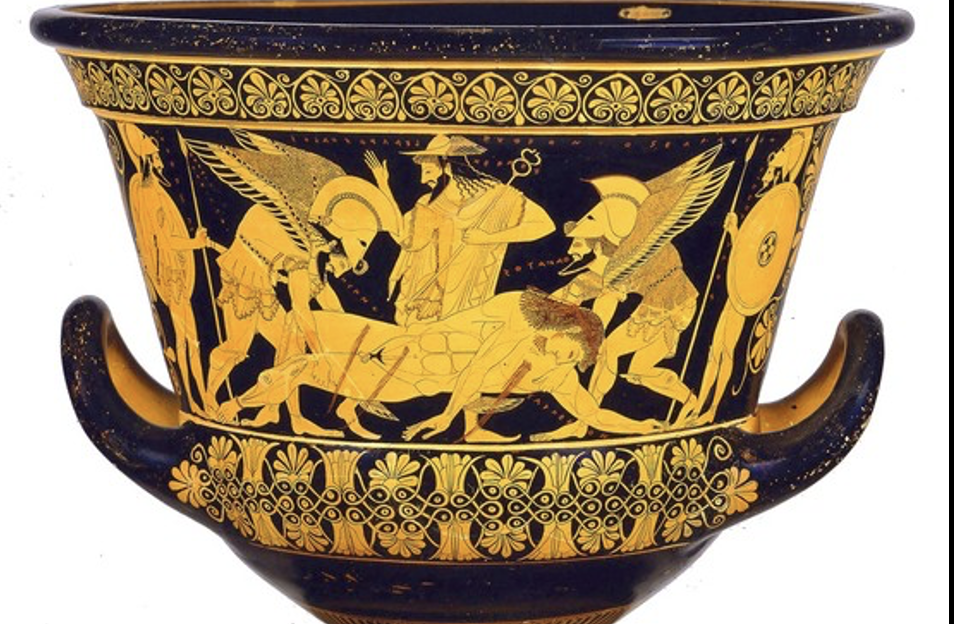

Death of Sarpedon by Euphronios, c. 520 BCE
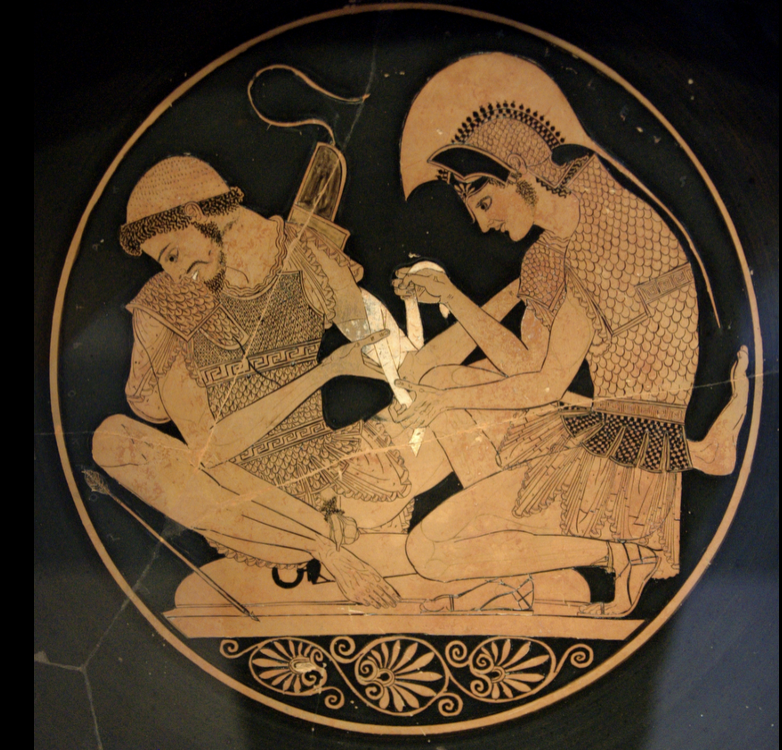

Red figure Kylix of Achilles and Patroclus by the Sosias painter, c. 500 BCE
Classical and Hellenistic Periods + important dates
480-450 BCE - Early Classical
450-400 BCE - High Classical
400-323 BCE - Low Classical
323-31 BCE - Hellenistic
250-50 BCE - Hellenistic Baroque
480 BCE - Persian War
450 BCE - Athens and Persia sign peace treaty
404 BCE - Sparta defeats Athens in Peloponnesian war
323 BCE - Death of Alexander the Great
31 BCE - Death of Cleopatra, the last Hellenistic monarch

Kritios Boy, c. 480 BCE
Earliest representation of the human body (to be the most realistic). Contrapposto stance: hips slightly uneven, weight shifted on one leg, more realistic.
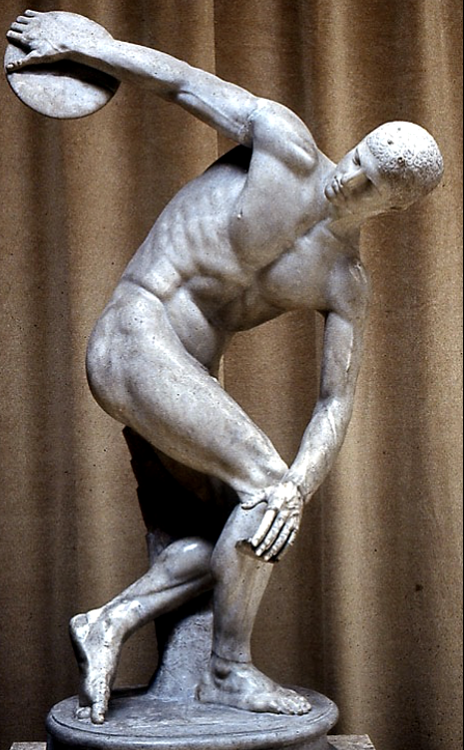

Myron, the diskobolos, c. 450 BCE
Shows action well, dynamic pose, contains neutral expression. Is a roman copy, was most likely a bronze sculpture that was destroyed/melted down.

statue from the Temple of Zeus at Olympia
finished c. 460 BCE
West Pediment shows the battle of Lapiths and Centaurs. The early classical style is also known as the “severe” style, very heavy features, thick eyelids, “doughy” drapery.

The Doryphoros (Roman copy) by Polykleitos, c. 440 BCE
Utilizes contrappasto stance, limbs tense in an x: one arm lax, other tense, opposite for legs. Sculpture thought to be an example piece of a treatise that the author wrote called the Canon, a composition lost to time detailing the anatomical rules for sculpture.
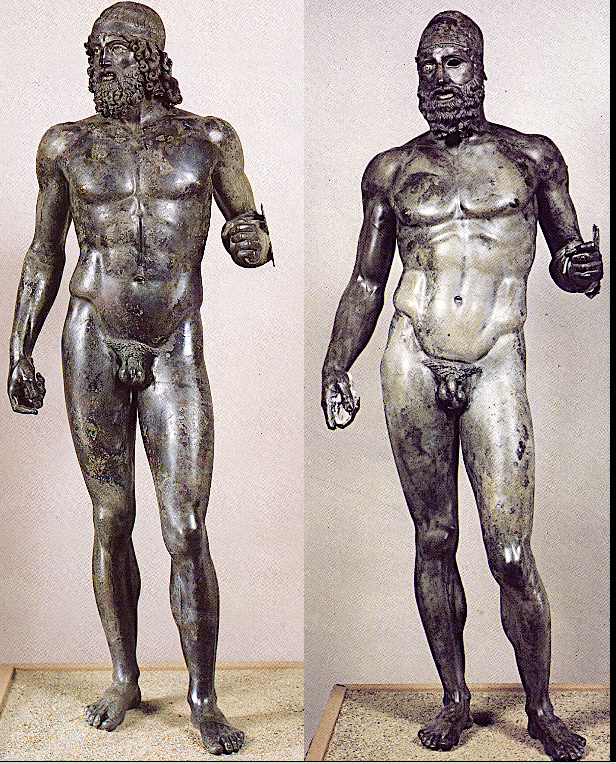

Riace warriors, c. 440 BCE
The only large, life size, bronze age high classical sculptures to survive. Were found off the coast of Riace. Ex. of contrappasto once more.
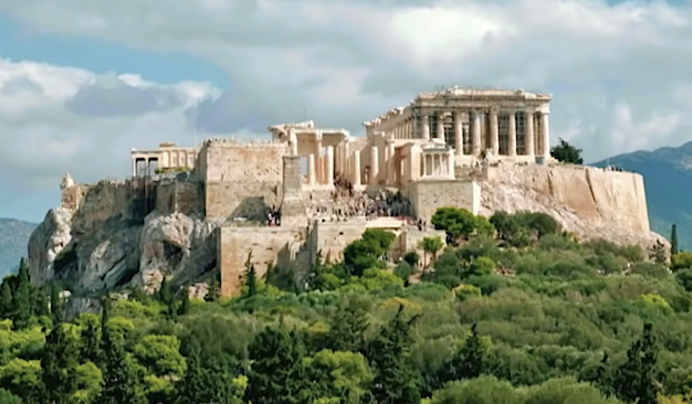

The Akropolis, Athens, architects are Illetinos and Kallikrates, scupltor, Phedias c. 447-432 BCE
Made of marble. Is NOT actually a real temple, no cult associated with Athena, more like a giant votive offering. View of Parthenon is meant to be seen from an angle, frames Parthenon from the side, unlike Egyptian temples which are symmetrical. Not a true Doric temple bc it has Ionic elements (shows Greek power) Utilizes both Ionic and Doric columns, has a doric frieze, but aroound the chamber for the cult statue, has an Ionic frieze.
There was a giant chryselephantine (gold and ivory) statue of Athena called Athena Parthenos, made by Phedias, 40 ft high.
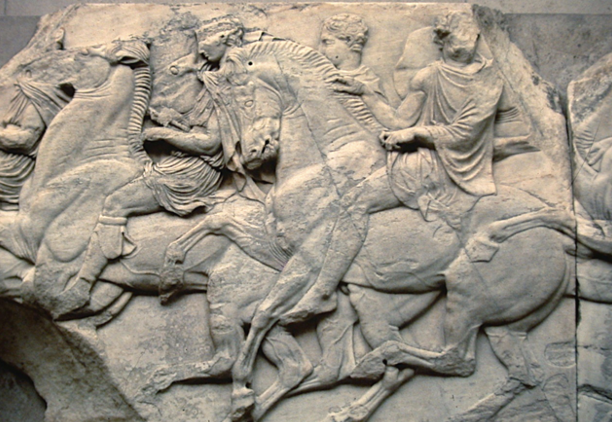

Parthenon frieze, 447-432 BCE
A continuous ionic style frieze around the outer walls of the naos/cella. Each of the 4 sides had different themes (lapiths vs. centaurs, gods vs. giants, greeks vs. amazons, greeks vs. trojans), these 4 mythical conflicts can be taken to symbolize civilizations conquest of “barbarism”
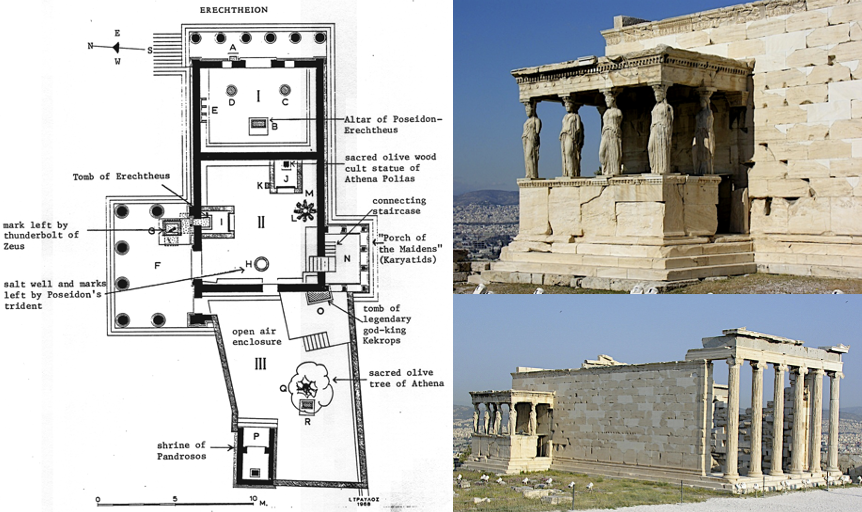
The Erechtheion (Erechtheum) 447-432 BCE
Holiest building on the Acropolis. Housed several sites, associated with earliest mythic history of Athens, including the ancient wooden image of Athenia, Athenia Polias, which was the focus of the Parathenieia festival.
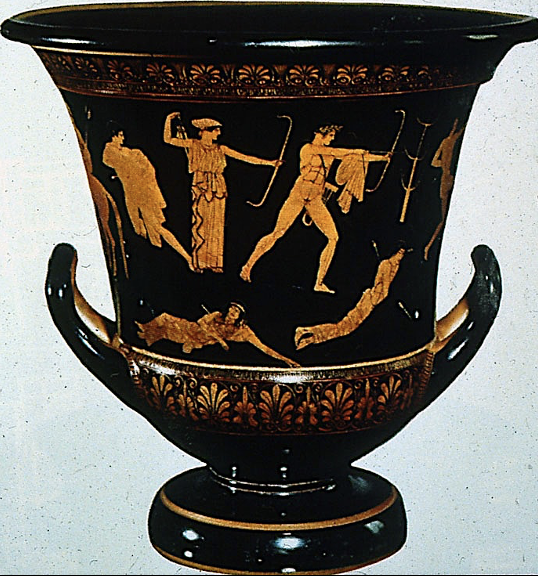

Calyx Krater, Niobid painter, c. 460-450 BCE
Archaic vase making exhausted — attempted to experiment with perspective. Paid less attention to sensitively modeling design/composition.
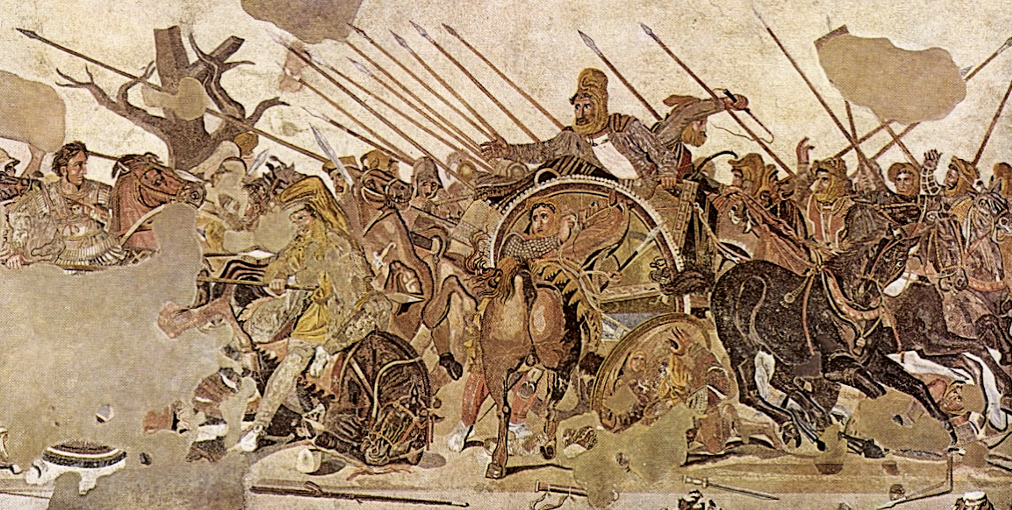

Alexander Mosaic, based on a painting of c. 300 BCE
Dead tree: impending death + doom (for the Persians)
Alexander is wearing a crorass and no helment, Persians wearing eastern armor. Is a dynamic scene, people thrown onto the ground, just Alexander alone, none of his army. King Darius has a worried expression, only the “barbarics” in classical art were allowed to show emotion, Greeks were supposed to be perfect

Apoxyomenos (Roman copy), Lyssipos, original c. 340 BCE
The new canon of proportions: is 8 heads tall, longer and lengthier bodies. Invites one to walk around the sculpture, very dynamic

Aphrodite of Knidos (Roman copy), Praxiteles, original c. 340 BCE
First major female nude in Greek art
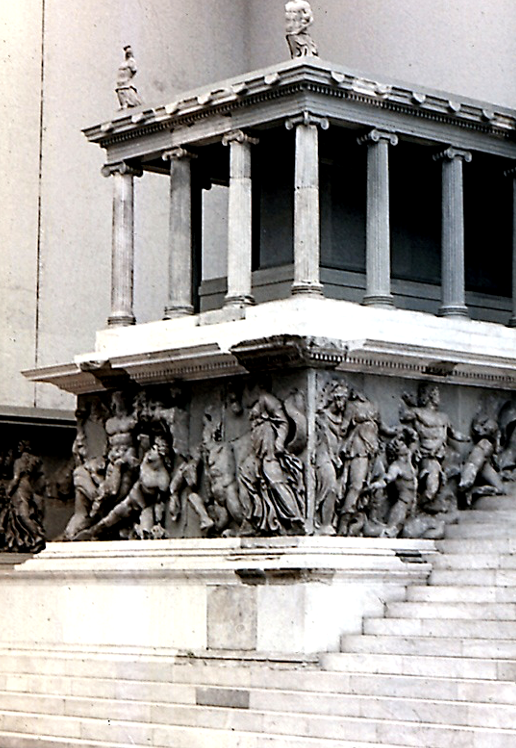

The Great Altar of Zeus at Pergamon, Asia Minor, c. 200-150 BCE
Vowed this to Zeus because Pergamon defeated the Gauls. King Eumenes compared his exploits with the gods. He is equating the golden age of Pergamon with the golden age of Athens, but attempting to do Athens at the same time.
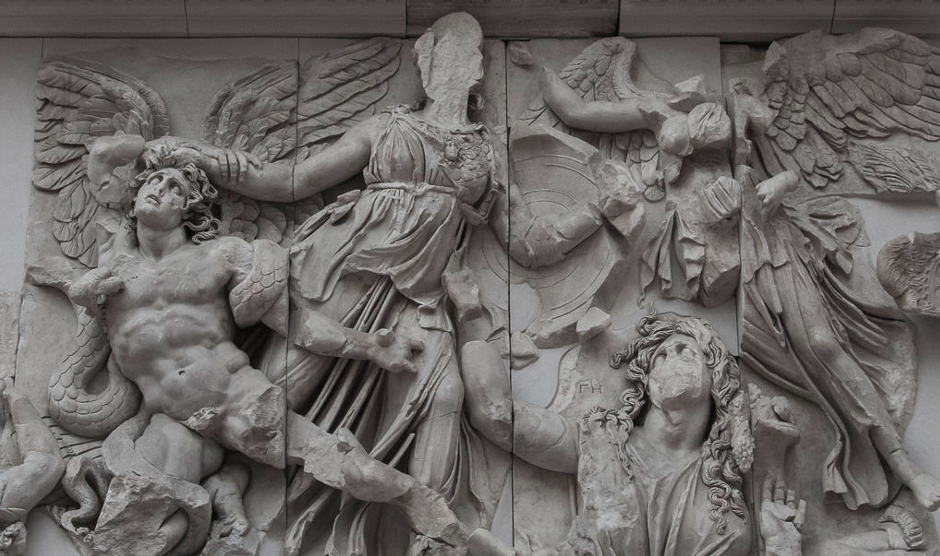

Relief of Athena battling Aponidus on the Great Altar of Zeus at Pergamon
The epitome of Hellenistic Baroque style, very dynamic, chaotic, emphasizes movement and fluidity. Baroque is complex as opposed to simple and still, like classical art. Utilizes chiaroscoro: shawos and high contrasts, seen in the sunken eyes, adds drama emotionality and complicates the piece.
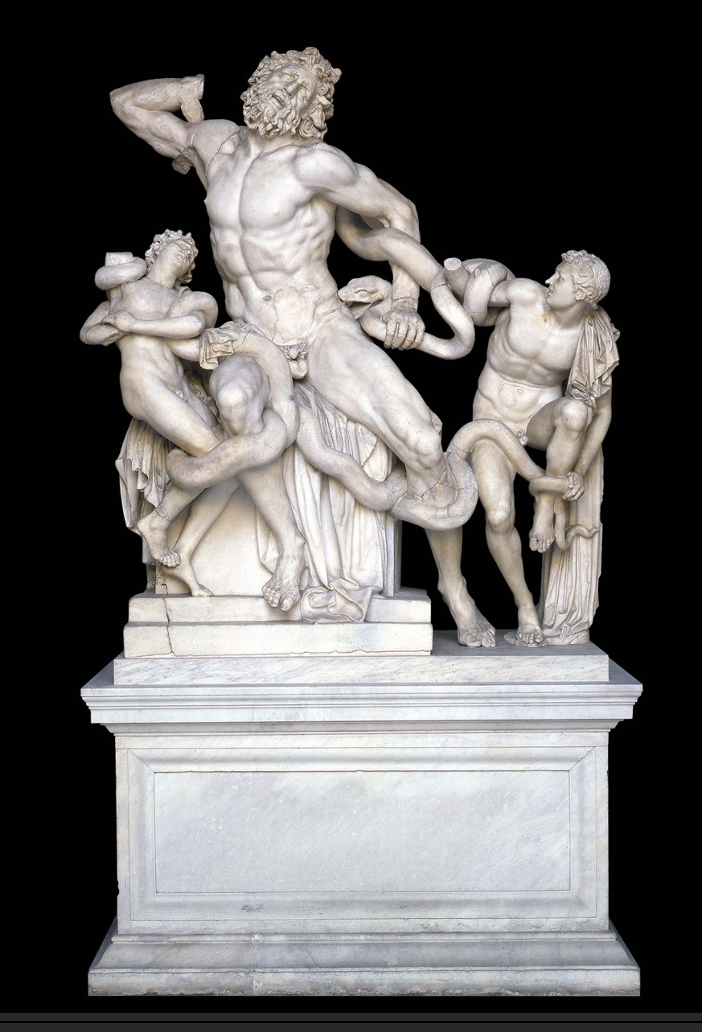

Laokoon, c. 150 BCE
Anguish and anxiety is clearly depicted from the facial features, eyebrows drawn up, sockets deeply carved, parted mouths, eyes turned up.

Aphrodite of Melos, aka Venus de Milo, original by Alexander of Antioch, c. 80 BCE
Her face is calm, not much expression - dreamy, far off look. Her body is stylized, not in depth, softer and less detailed. Has a contrappasto stance, languid body position. A slight return to classical style.
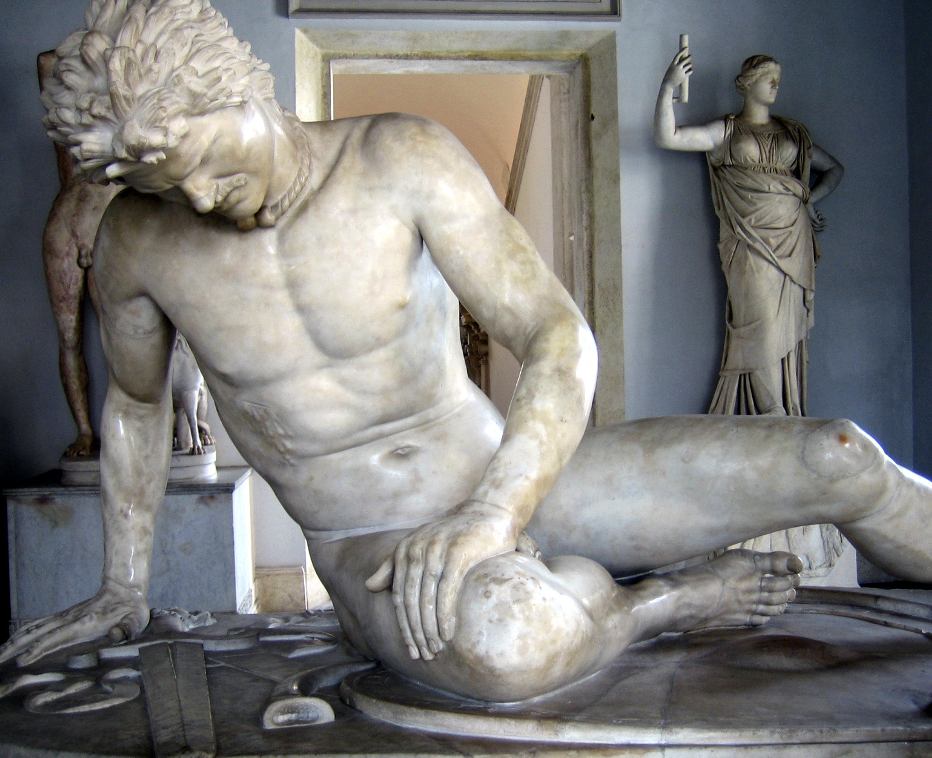

Dying Gaul, Roman copy, c. 200-150 BCE
Torque, mustache, spiked hair with line mark him as not Greek, use of pathos, empathizing with the “barbarians”
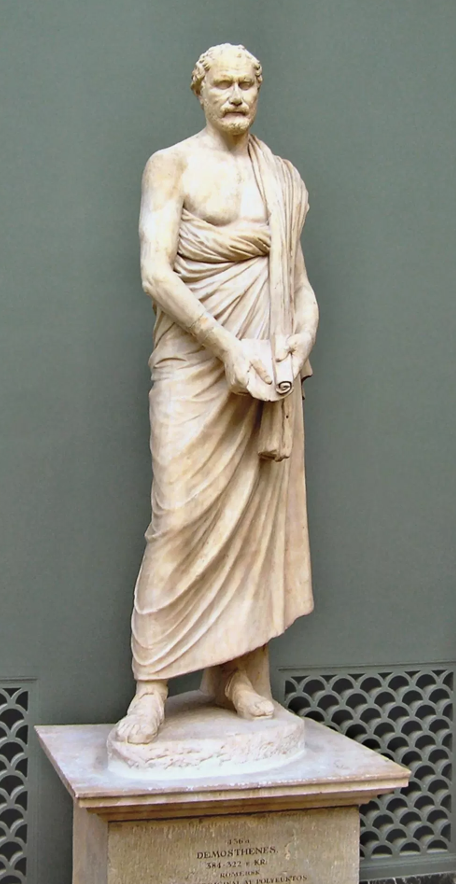

Roman copy of a posthumous portrait of the orator Demosthenes, original c. 280 BCE
Resigned expression, accepting his death. Appealed to Roman patrons due to his self marytrdom. Is NOT idealized, is clothed, body language is inward. Face is recognizable.
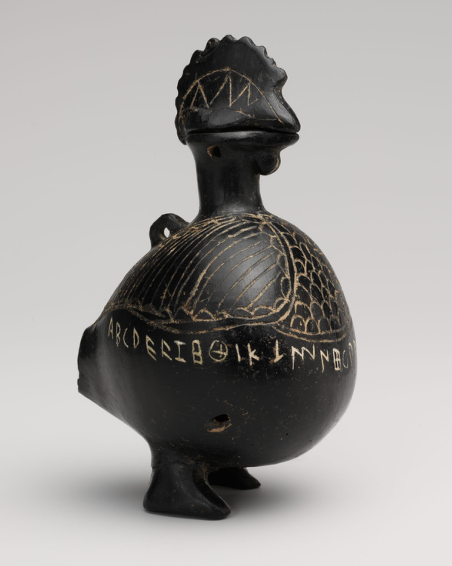

Terracotta vase in the form of a cockerel, Etruscan, c. 650-600 BCE
Might be Villanovan’s (iron age Italians) under Greek influence. Has the Etruscan alphabet on it, language is non indo-European.
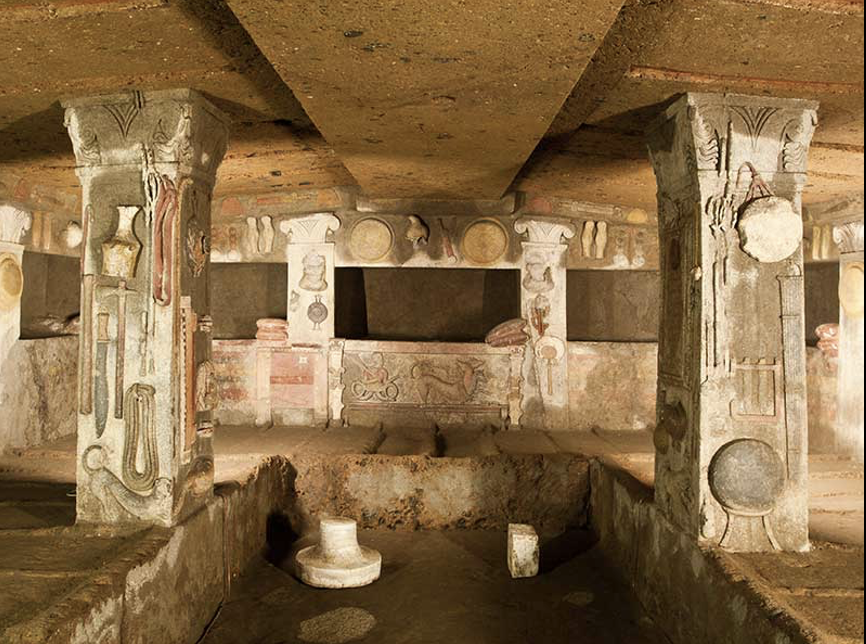

Tomb of the Reliefs, 3rd century BCE, Cerveteri Italy
Reliefs might mimic an Etruscan house, tomb focused culture, focus on the afterlife.
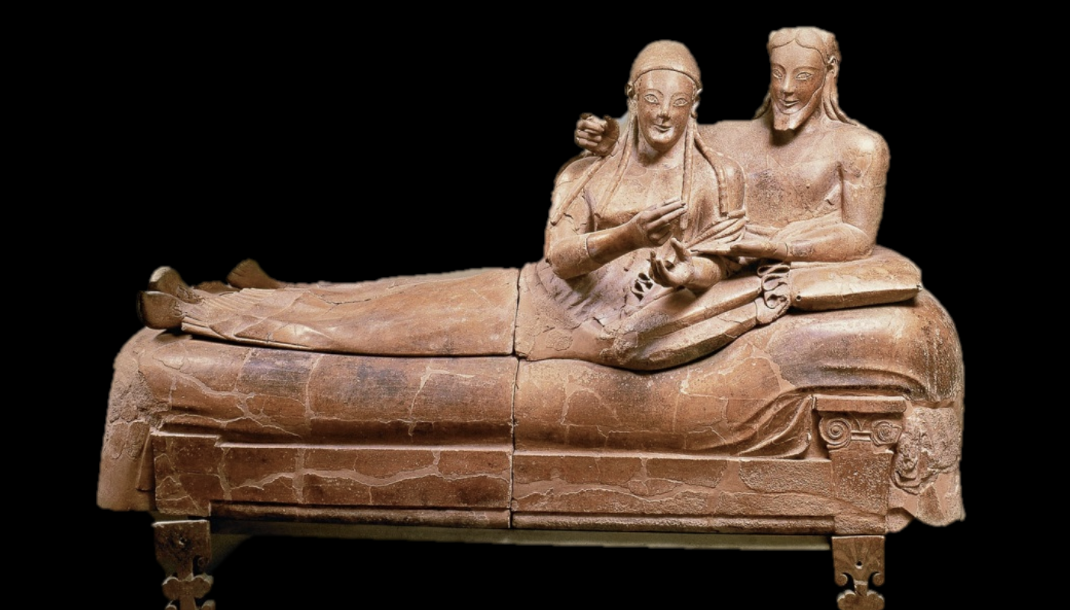

Husband and Wife Sarcophagus from Cerveteri, c. 520 BCE
Both have an archaic smile, almond shaped eyes. Lively, fluid pose, less stiff and formal than archaic art.
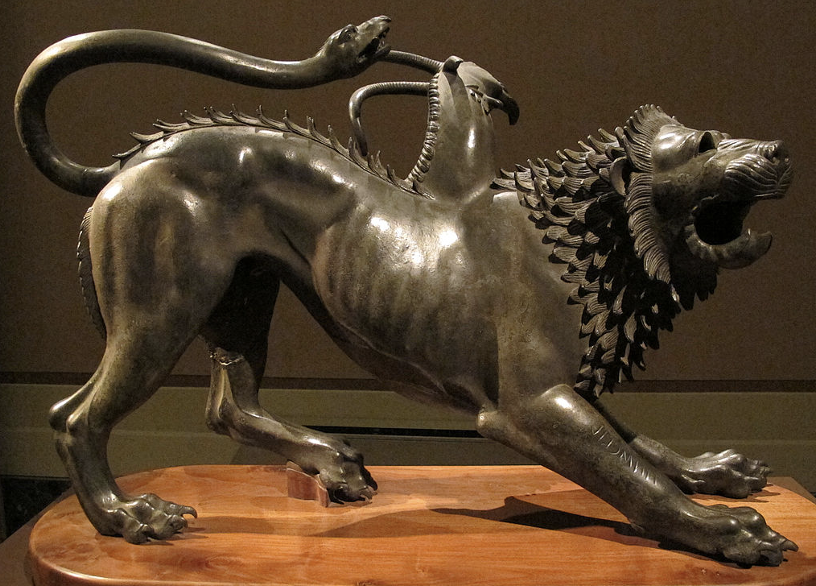

Bronze Chimera of Arezzo, Etruscan, c. 400 BCE
Highly naturalistic, is a genuine large scale Etruscan piece, unlike the capitoline wolf. Was a votive offering, still has that blend of stylization and realistic motifs.
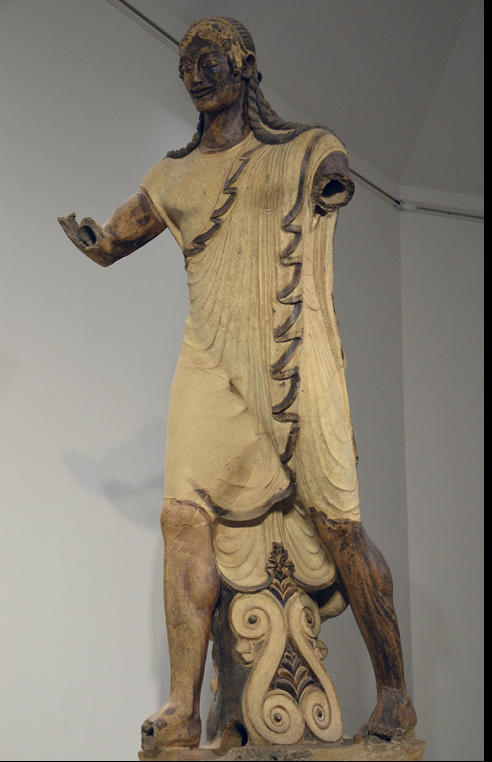

Apollo of Veii, Etruscan, c. 510-500 BCE
Made of terracotta. Hair is very stylized, like the archaic smile. More dynamic, the pose is fluid, is painted, anatomy less pronounced as he is wearing clothes.
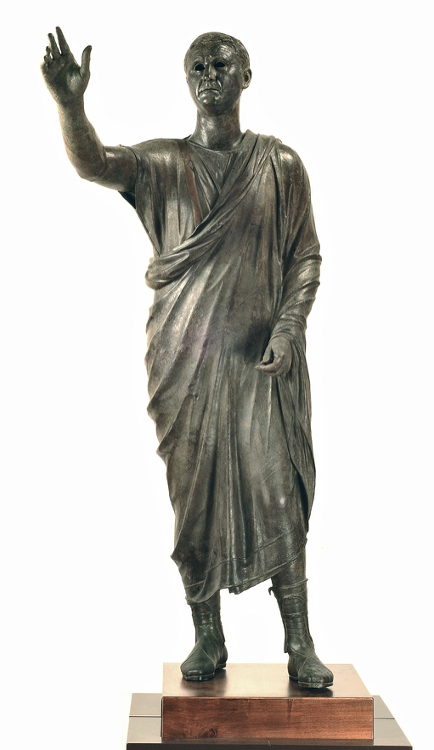

Statue of Aulus Metellus, the Arringatore, c. 80 BCE
Made of bronze. Came from an old Etruscan family on the helm of statue’s toga, is an inscription in Etruscan.
Roman Historical Periods
509-27 BCE - Republic
27 BC - 4th Century AD (?) - Empire
753 is when Romulus and Remus myth states when Rome was founded
509 is when Brutus kills the king, sets up a republic
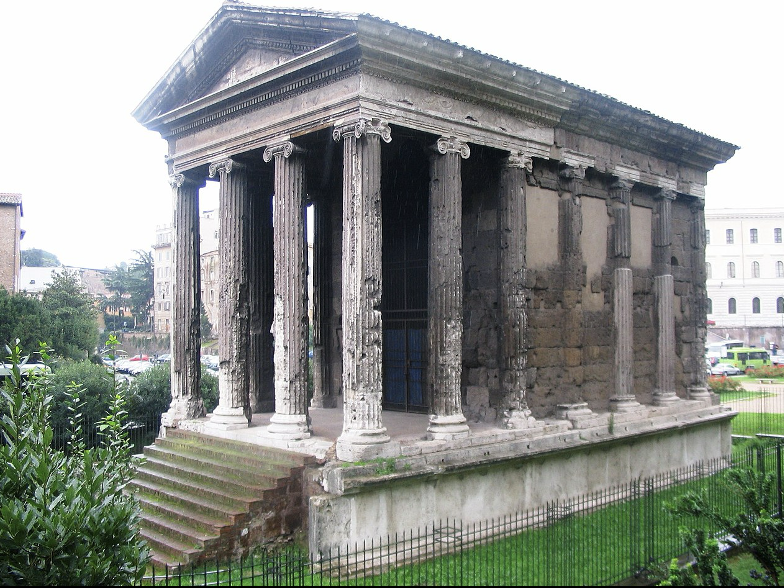

Temple of Portunus, Boarium, Rome, c. 100 BCE
Frontal, with half built columns on the side, Ionic pillars.
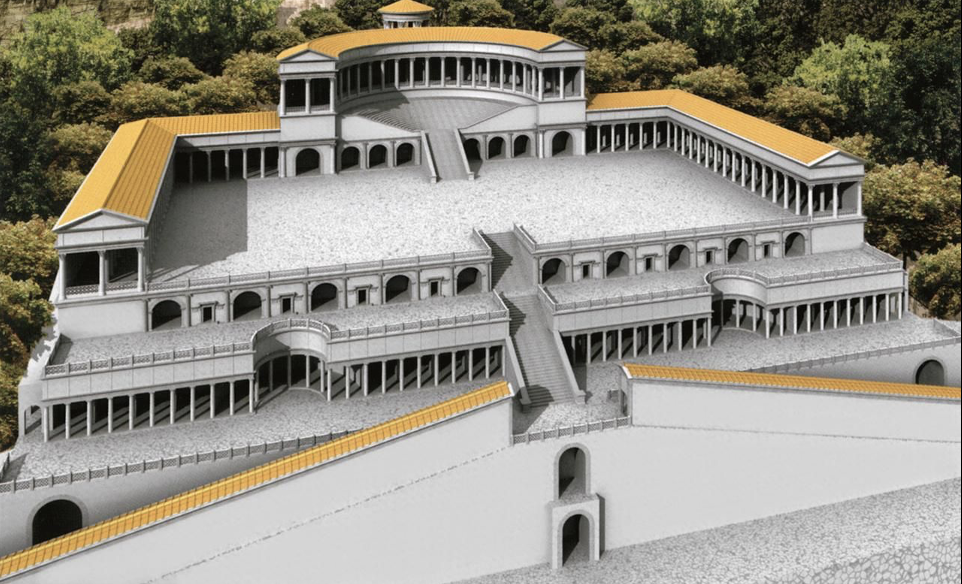

Sanctuary of Fortuna Primagenia at Praeneste, c. 100 BCE
Each floor up is essentially an element of surprise, utilizes axial symmetry
Roman Political System
Quaestor
Praetor
Consul (two positions that change every year)
Censor (only an ex. consul can hold the title)
Optional in case of emergency: Dictator (appointed for a limited amout of time, can override the power all other positions hold)

Portrait head of a man from Scopito, 1st Century B.C.

Marcus Licinius Crassus, Mid 1st Century B.C.

Head of a Patrician from Otricoli, c. 75 – 50 B.C
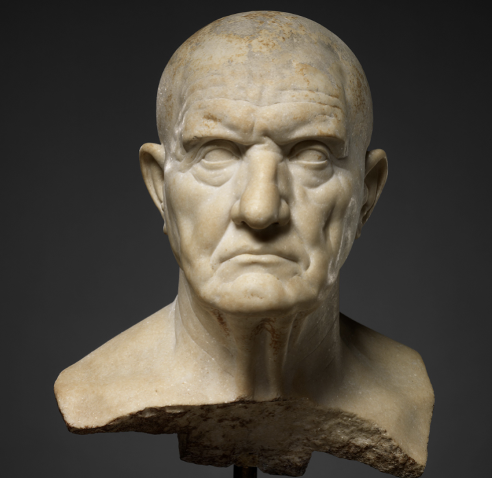

Bust of a Man, Mid 1st Century A.D
Unknown Roman man, c. 50-30 BCE
Can’t be sure if this is exactly what he looked like, slightly stylized but still veristic style.
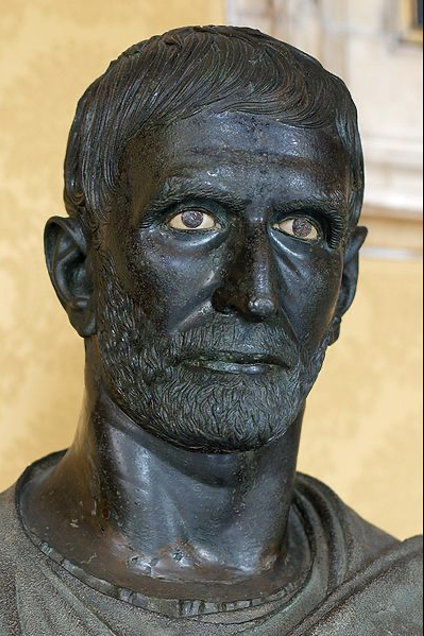

Capitoline “Brutus”, 2nd century BCE
Boring eyes detailed carving of hair and the beared, gaze is very intense. Prominent neck musculature and has some wrinkles. Stoic expression, serious face.
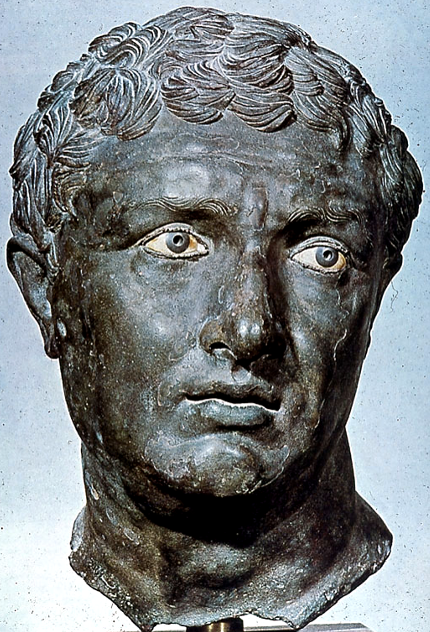

Hellenistic Greek portrait from Delos, 2nd century BCE
Rounder features, lips slightly parted, bigger, exaggerated eyes. Hair is slightly stylized, tons of muscles/textures in the skin to the point where it almost doesn’t seem realistic.
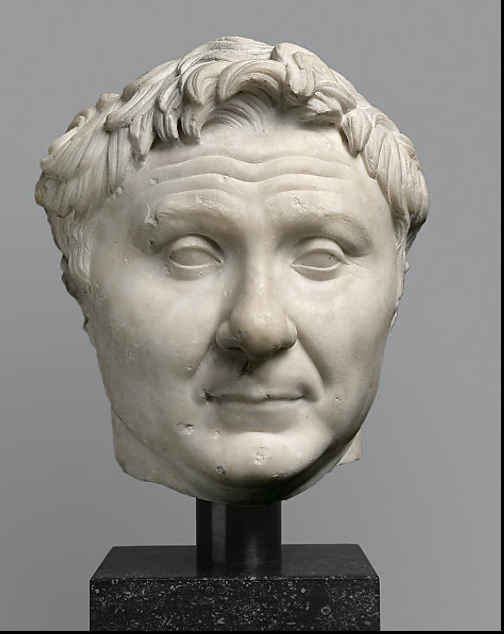

Pompey the Great, original c. 50 B.C.
Raised eyebrows, upturned lips, looks somewhat smug and unassuming/soft, not as stern or old-appearing.
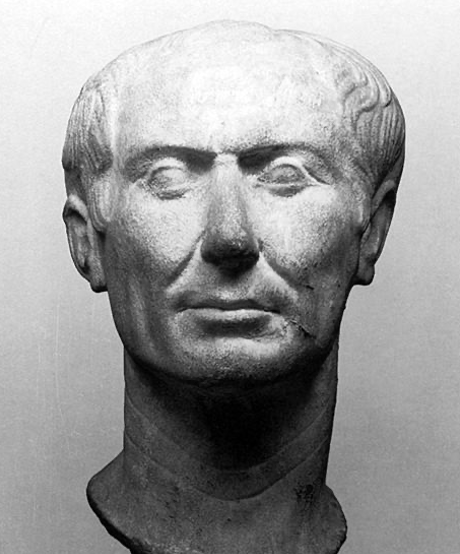

Portrait of Julius Caesar from Tusculum Italy, c. 44 B.C.
Most accurate representation of Caesar, right before his death.
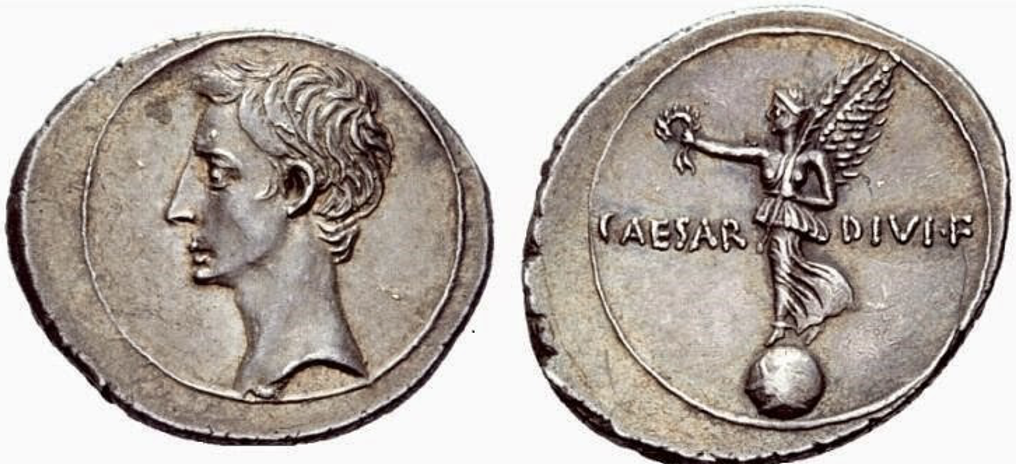

Silver denarius with portrait of Octavian, after 42 B.C.

Denarius of Marc Antony (left) and Octavian (right), 41 B.C.
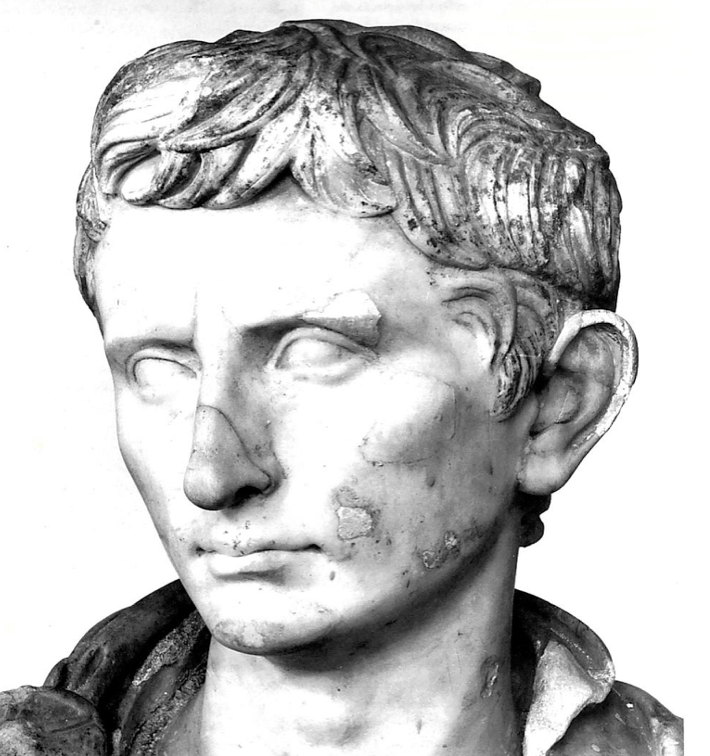

Portrait of Octavian, c. 30 BCE
Was a major political player at only 19, as such, statue looks young. Has furrowed eyeborws, stern, fierce expression. Fluffy agitated hair emphasizes youthfullness, meant to show him as achiever/busy person.
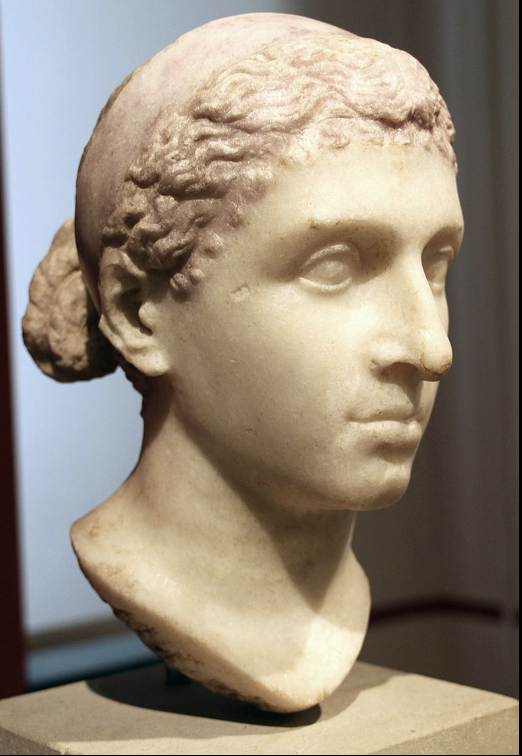

Portrait of Cleopatra, third quarter of the first century B.C.
Is not “egyptianized”. A pretty realistic portrait of her.
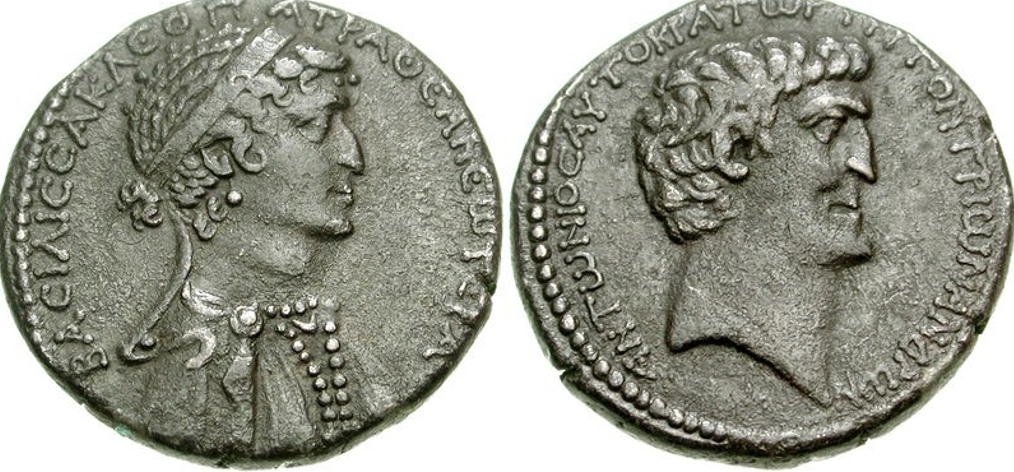

Tetradrachm of Cleopatra (left) and Antony (right), 36 B.C.
They both hold similar features, faces are the same, to symbolize unity.
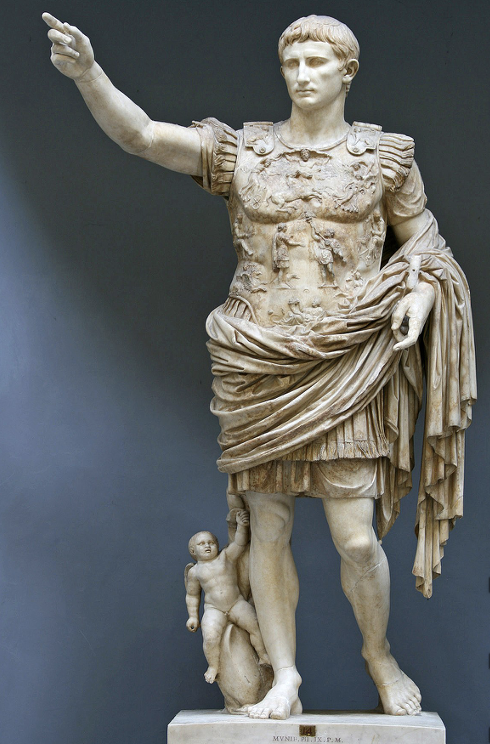

Primaporta Augustus, c. A.D. 15
Based on the forms of high classical greek art, chiastic composition. Is an idealized version of Octavian, now called Augustus as a monarch. Appears more sure of himself, eyebrows less furrowed than previous portrait, rounder, smoother features rather than the angular face in his Octavian appearance (which is possibly more truthful).
Curass has rich iconography basically shocasing how his rule is divinely sanctioned, has impact on entire universe
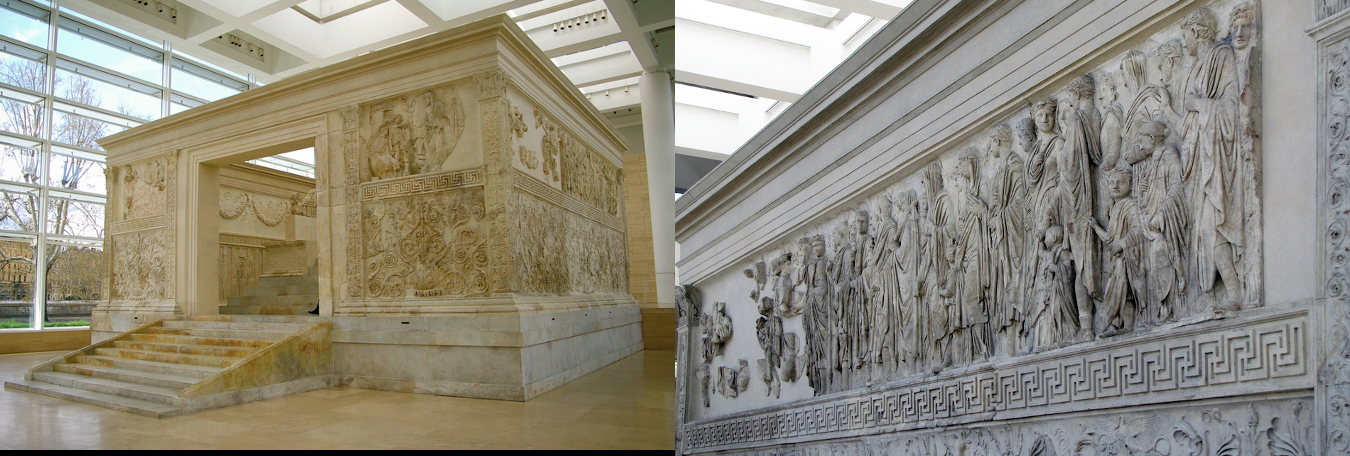

Ara Pacis Augustae, dedicated in 9 B.C, Rome, Italy
Two panel reliefs at front represent Aeneas and Romulus, Augustus appears on a separate relief in a similar position. Goddess in relief is intentionally left vague: mythic association that can appeal to different viewers
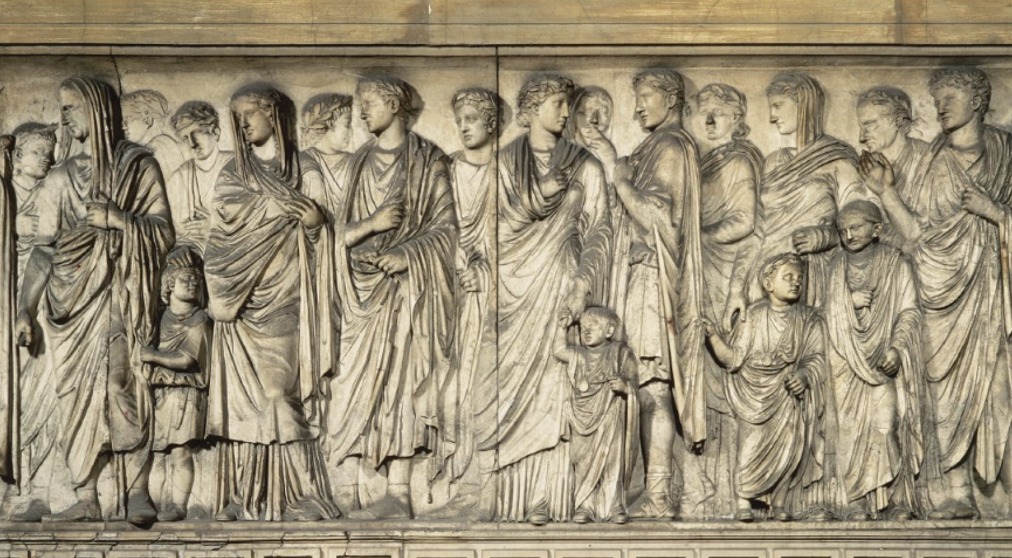

Procession of the Imperial family on the Ara Pacis Augustae, Rome,13-9 B.C.
Monumental because children appear in Roman state art. Very different from the Parthenon frieze because it isn’t generic and focuses on a specific event