Ch.21: Biochemical Energy
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
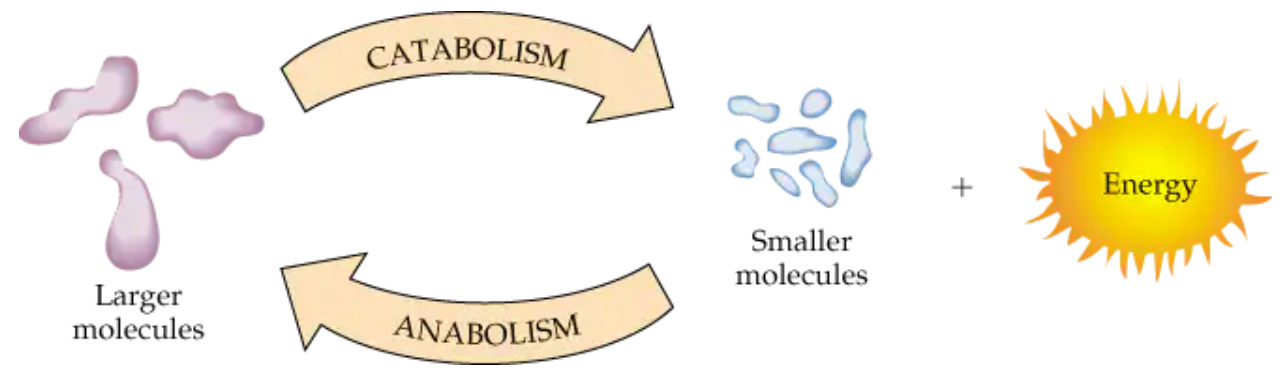
What is catabolism?
metabolic reaction pathway to break down food and release energy
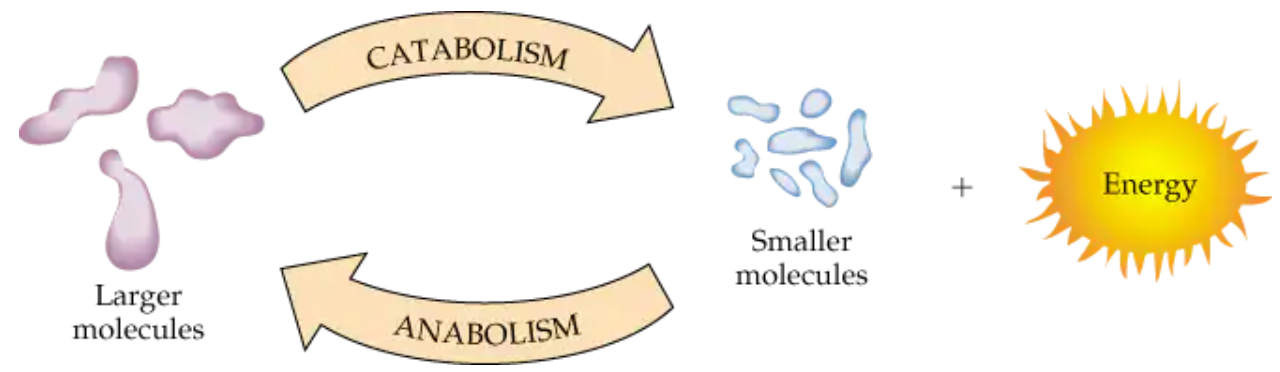
What is anabolism?
metabolic reaction pathway to build larger biological molecules from smaller things
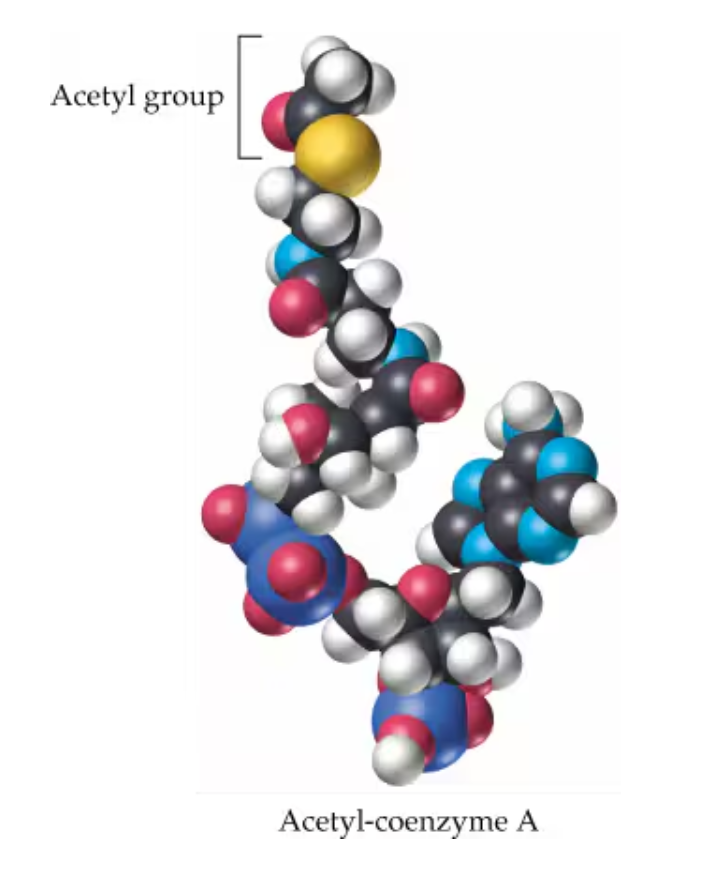
What is acetyl-CoA (acetyl-coenzyme A)?
the common intermediate that carries acetyl groups into the citric acid cycle
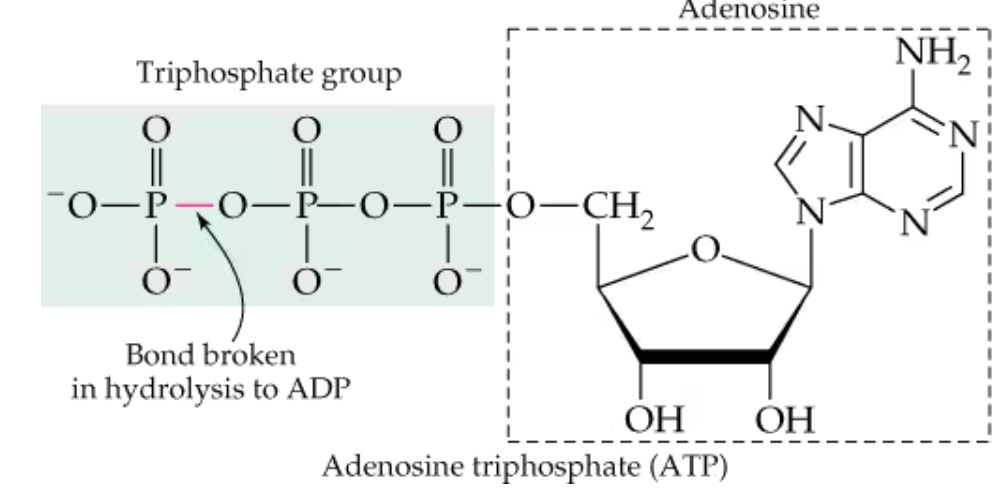
How is ADP made from ATP?
removal of the terminal -PO3-2 group from ATP via hydrolysis
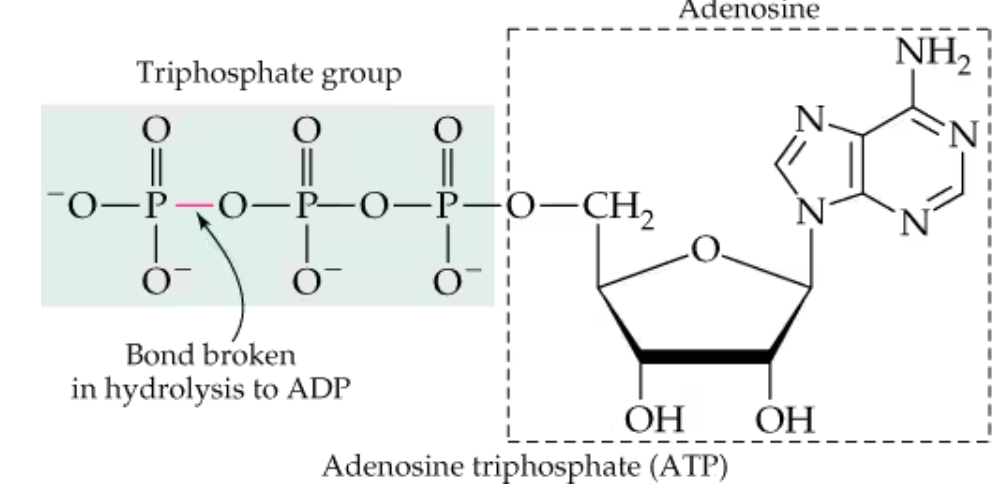
Is this reaction exergonic or endogenic (ATP to ADP)?
exergonic
What does the phosphorylation of ADP yield?
ATP
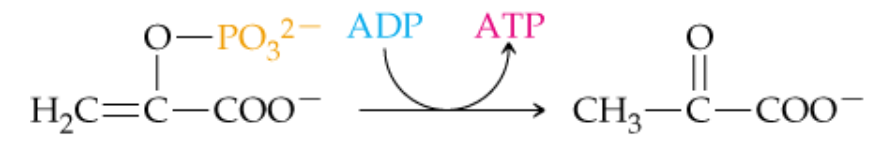
What does a curved arrow signify in biochem?
connects the reactants and products in one of the two chemical changes
What is the oxidized form of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide?
NAD+
What is the reduced form of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide?
NADH/H+
What is the oxidized form of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate?
NADP+
What’s the reduced form of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate?
NADPH/H+
What’s the oxidized form of Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide?
FAD
What’s the reduced form of Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide?
FADH2
What can oxidation be?
loss of electrons, loss of hydrogen, or addition of oxygen
What can reduction be?
gain of electrons, gain of hydrogen, or loss of oxygen
How many coenzyme molecules are produced from the citric acid cycle?
4
Are the coenzymes produced by the citric acid cycle in their reduced or oxidized form?
reduced
Name the 4 reduced coenzymes produced from the citric acid cycle?
3NADH and 1FADH2
What happens to the acetyl group that goes into the Krebs cycle?
converts into 2CO2 molecules
How many coenzymes enter the citric acid cycle?
4
Are the coenzymes that enter the Krebs cycle in their reduced or oxidized form?
oxidized
Name all of the coenzymes that enter the Krebs cycle?
3NAD+ and 1FAD
Name each molecule that goes into the Krebs cycle?
Acetyl-CoA, 3NAD+ , 1FAD, GDP, HOPO32-, H2O
Name all the molecules that are produced from the citric acid cycle?
HSCoA, 3NADH, 1FADH2, 3H+, GTP, 2CO2
What’s the Electron Transport Chain (ETC)?
chain of mitochondrial proteins that takes electrons from NADH/FADH₂ and passes them to oxygen, using the released energy to pump protons that drive ATP synthase to make ATP
For oxidative phosphorylation, what goes in?
ADP and HOPO32
For oxidative phosphorylation, what is produced?
ATP and H2O
What is a exergonic reaction?
one which releases free energy and is favorable
What is an endergonic reaction?
one which requires external free energy and is unfavorable
What is the importance of reaction coupling?
makes an otherwise unfavorable reaction happen through a net release of free energy which makes it exergonic
Where does the ETC occur?
inner membranes of the mitochondria