Ren R 210 Module 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
1
New cards
Physical Properties of SOM
* water holding capacity (can hold up to 10x it’s weight)
* soil structure and aggregation (↑ SOM, ↓ bulk density, ↑ porosity)
* soil structure and aggregation (↑ SOM, ↓ bulk density, ↑ porosity)
2
New cards
Chemical Properties of SOM
* absorptive capacity = CEC (↑ SOM, ↑ CEC for pH dependant charges)
* buffering capacity (↑ SOM, ↑ resistance to pH changes)
* buffering capacity (↑ SOM, ↑ resistance to pH changes)
3
New cards
Biological Properties of SOM
* ↑ SOM, ↑ fertility of soil
* acts as slow release fertilizer (source nutrients: N, P, K, S for plants and biota)
* supports large and varied microbial population (↑ SOM, ↑ biological biomass)
* acts as slow release fertilizer (source nutrients: N, P, K, S for plants and biota)
* supports large and varied microbial population (↑ SOM, ↑ biological biomass)
4
New cards
Chemical Forms of Carbon
Inorganic C (CO2, CO, CH4)
Organic C (SOM, SOC)
Organic C (SOM, SOC)
5
New cards
Labile
(refers to soil C quality) easy and fast decomposition → low C/N ratio → excess N
6
New cards
Recalcitrant
(refers to Soil C quality) hard and slow decomposition → high C/N → limited N availability
7
New cards
Human Alterations to Carbon Cycle
CO2 Emissions
* combustion of fossil fuels
* deforestation
CH4 Emissions
* rice paddies
* cows
(CH4 emissions are several orders of magnitude lower than soil stocks, and therefore can be offset by SOM accumulation)
* combustion of fossil fuels
* deforestation
CH4 Emissions
* rice paddies
* cows
(CH4 emissions are several orders of magnitude lower than soil stocks, and therefore can be offset by SOM accumulation)
8
New cards
Carbon Use Efficiency (CUE)
33%
for every 1 C assimilated, 2 C are respired
for every 1 C assimilated, 2 C are respired
9
New cards
C/N Ratio of Forests vs. Agricultural Soils
forest → between 20-30
agriculture soils → < 20
agriculture soils → < 20
10
New cards
SOM Composition
Living Biomass (0.5-3%)
* roots
* microbes
* animals
Residues/Detritus → LF (5-40%)
* dead roots
* feces
* litter
**Humus (H, black greasy material) divided into 2 groups**
Non-Humic Substances (5-10%)
* biopolymers
* low MW
* known chemically
Humic Substances (40-90%)
* biopolymers
* *high MW*
* \*\*unknown chemically\*\*
* roots
* microbes
* animals
Residues/Detritus → LF (5-40%)
* dead roots
* feces
* litter
**Humus (H, black greasy material) divided into 2 groups**
Non-Humic Substances (5-10%)
* biopolymers
* low MW
* known chemically
Humic Substances (40-90%)
* biopolymers
* *high MW*
* \*\*unknown chemically\*\*
11
New cards
Decomposition Definition
* chemical reaction occurring during decay of plant/animal remains
* altered chemical composition → produce energy
* altered chemical composition → produce energy
12
New cards
Mineralization Definition
* release of soluble or gaseous inorganic constitutes during decomposition
* SOC → CO2
* SON → NH4^-
* SOC → CO2
* SON → NH4^-
13
New cards
Humification Definition
* decomposition results in black greasy OM
* old theory - condensation reaction: low MW biopolymer → high MW biopolymer
* new theory - stabilization of SOC by three mechanisms…
* chemical
* aggregate
* mineral associated OM
* old theory - condensation reaction: low MW biopolymer → high MW biopolymer
* new theory - stabilization of SOC by three mechanisms…
* chemical
* aggregate
* mineral associated OM
14
New cards
Non-Humic Substances
**Cellulose** (\~30% of plant material, cell walls) → linear polymer of glucose units (polysaccharides, carbs)
**Hemi-Cellulose** (\~20% of plant material) → branched polymer of diff sugars (glucose, fructose: polysaccharide)
**Lignin** (\~20% of plant material, woody material) → branched, aromatic polymer (volatile)
**Lipids** (\~20% of plant material, cellular material) → fats and waxes
**Protein** (\~5% of plant material) → amino acids (N is present), biochemical machine, photosynthesis
\
Protein → Hemi-Cellulose → Cellulose → Lignin → Fats
Easy to decompose → Hard to decompose
**Hemi-Cellulose** (\~20% of plant material) → branched polymer of diff sugars (glucose, fructose: polysaccharide)
**Lignin** (\~20% of plant material, woody material) → branched, aromatic polymer (volatile)
**Lipids** (\~20% of plant material, cellular material) → fats and waxes
**Protein** (\~5% of plant material) → amino acids (N is present), biochemical machine, photosynthesis
\
Protein → Hemi-Cellulose → Cellulose → Lignin → Fats
Easy to decompose → Hard to decompose
15
New cards
New Humic Fractions
INSOLUBLE ORGANIC
* Humin (highly condensed, complexed with clays)
SOLUBLE ORGANIC
* Humic acids (dark brown to black, high MW)
* Fulvic acids (yellow to red, lower MW)
\
*Microbes use enzymes to cleave off functional groups. No such thing as Humin, HA, and FA in nature*
* Humin (highly condensed, complexed with clays)
SOLUBLE ORGANIC
* Humic acids (dark brown to black, high MW)
* Fulvic acids (yellow to red, lower MW)
\
*Microbes use enzymes to cleave off functional groups. No such thing as Humin, HA, and FA in nature*
16
New cards
SOM Stabilization
* contemporary theory
* based on decreasing molecular size
* stabilization in aggregates and mineral surfaces
* based on decreasing molecular size
* stabilization in aggregates and mineral surfaces
17
New cards
SOM Theoretical Pools
Chemical protection → structural C and charcoal C
Physical protection → aggregation
Organo-mineral associations → MAOM
Physical protection → aggregation
Organo-mineral associations → MAOM
18
New cards
Autotrophs
Use CO2 as carbon source
19
New cards
Heterotrophs
Use organic C as carbon source
20
New cards
Photo-
Use sun as energy source
21
New cards
Chemo-
Use organic C as energy source
22
New cards
Litho-
Uses energy from soil redox reaction
23
New cards
Chemoheterotroph example
People
24
New cards
Photoautotroph example
Plants
25
New cards
Chemoheterotroph example
Fungi
26
New cards
Nitrogen Fixation
chemical/biological conversion of N2 to R-NH2
chemical → lighting, humans
biological → symbiotic (bacteria and plant sharing C + N), mutualistic, free-living bacteria in soil
chemical → lighting, humans
biological → symbiotic (bacteria and plant sharing C + N), mutualistic, free-living bacteria in soil
27
New cards
Bacteria Genera and Associated Plant Family
Rhizobium → Pea Family
Frankia → Alder Family
Frankia → Alder Family
28
New cards
Nitrogenase
Enzyme that catalyzes N fixation
29
New cards
N Cycle
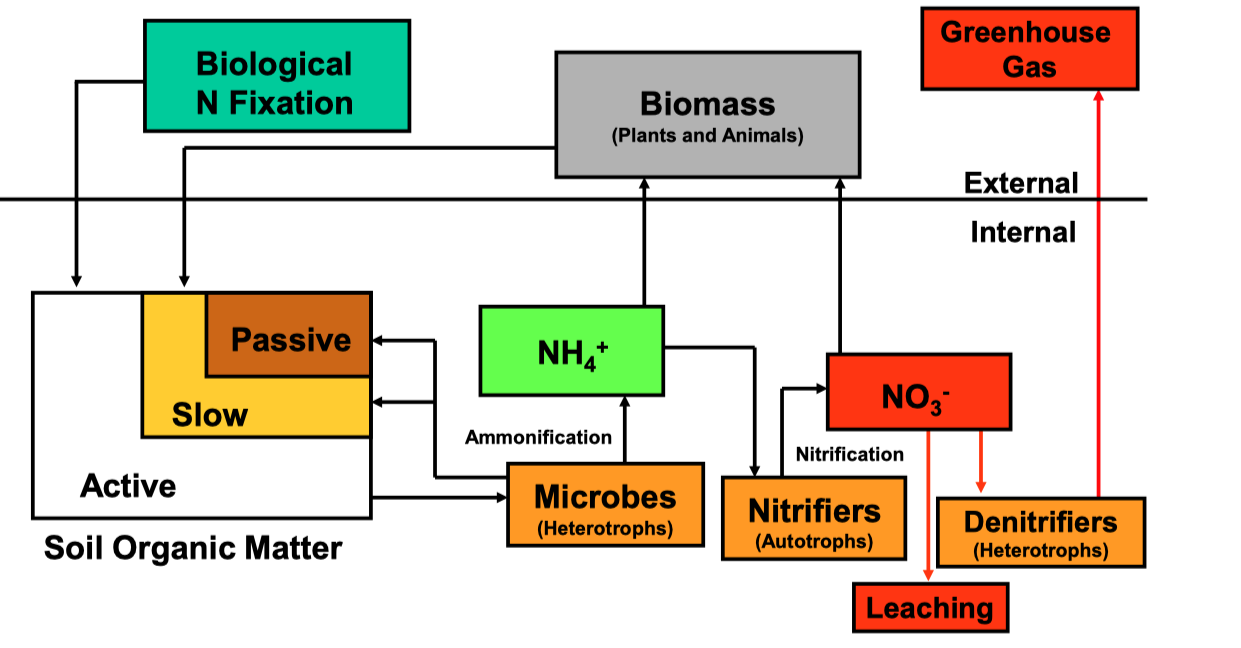
30
New cards
REDOX Reactions
Ao + Dr → Ar + Do
A → e- acceptor
D → e- donor
o → oxidized (lose e-, becomes less negative)
r → reduced (gain e-, becomes more negative)
A → e- acceptor
D → e- donor
o → oxidized (lose e-, becomes less negative)
r → reduced (gain e-, becomes more negative)
31
New cards
Human Alteration of N Cycle
Human N fixation
* fertilizers
* leguminous crops
* combustion of fossil fuels
* land clearing
* burning of forests
* draining of wetlands
* fertilizers
* leguminous crops
* combustion of fossil fuels
* land clearing
* burning of forests
* draining of wetlands
32
New cards
Chemical N fixation
Haber Bosch process → need lots of natural gas to break triple bond in N2
33
New cards
Eutrophication
Increase in nutrients (N+P) in surface waters
* causes algae growth → kills fish
* ↑ turbidity, ↓ light
* ↓ water quality
* causes algae growth → kills fish
* ↑ turbidity, ↓ light
* ↓ water quality
34
New cards
Phosphorus Cycle
* very different form N
* no REDOX potiential
* all from lithosphere
* no organic form
* overtime all P precipitates out of the solution into insoluble forms → availability ↓ over time
* no REDOX potiential
* all from lithosphere
* no organic form
* overtime all P precipitates out of the solution into insoluble forms → availability ↓ over time
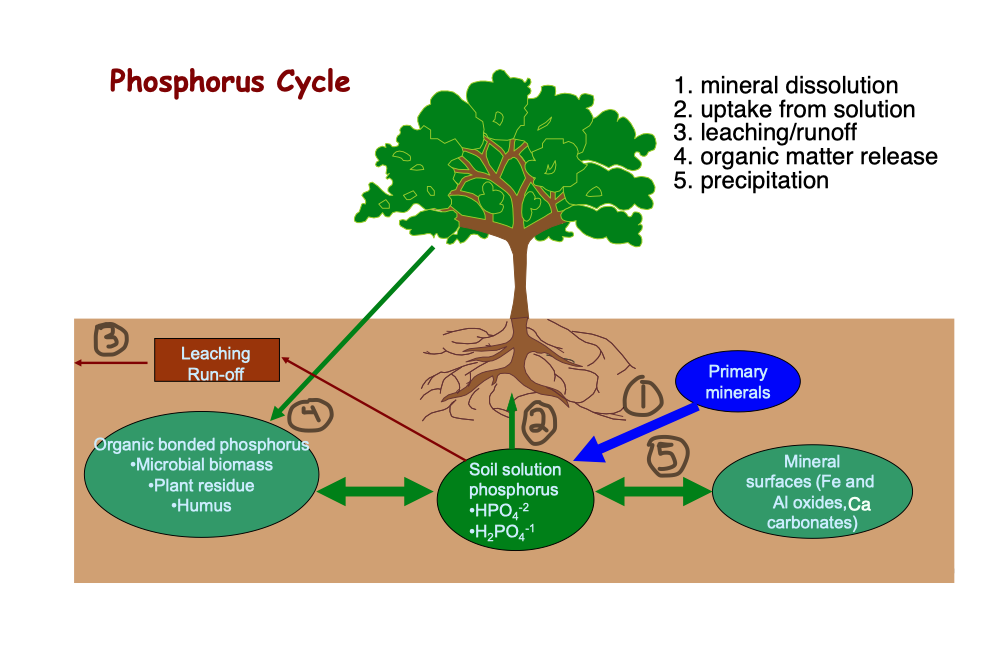
35
New cards
Potassium Cycle
* no REDOX
* from lithosphere
* macronutrients: N, P, K, S, Ca, Mg
* from lithosphere
* macronutrients: N, P, K, S, Ca, Mg
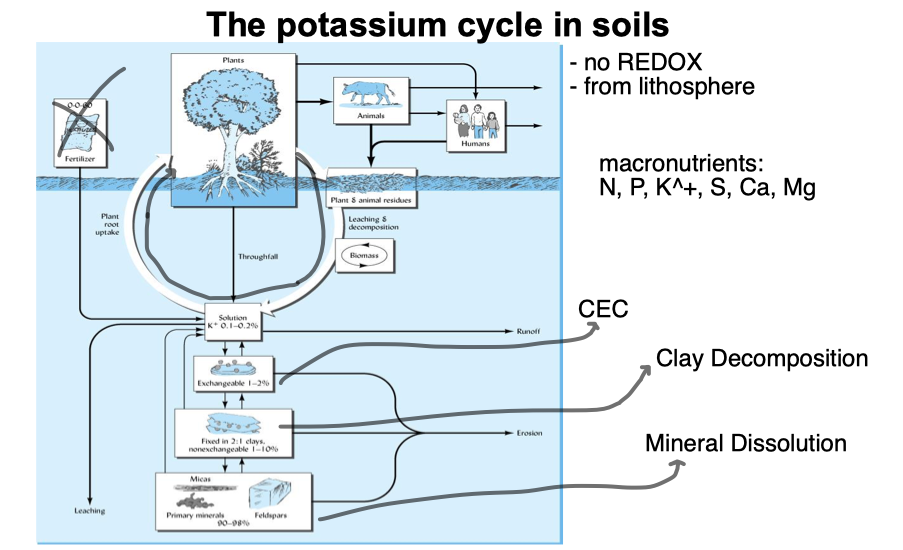
36
New cards
Sulfur Cycle
* like N, have REDOX potential
* unlike N, from lithosphere
* organic forms of S → C-S, C-O-S
* e- acceptor in anaerobic environments
* unlike N, from lithosphere
* organic forms of S → C-S, C-O-S
* e- acceptor in anaerobic environments
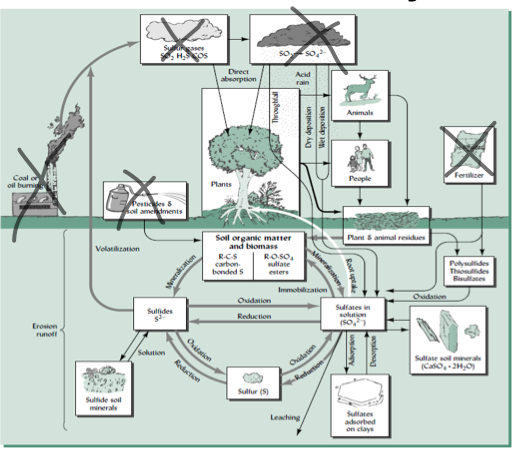
37
New cards
Micronutrients
Fe, Cu, Ni, Mo, B, Zn
Trace metals → require chelates (elements that make these metals more soluble)
Trace metals → require chelates (elements that make these metals more soluble)
38
New cards
Plant Nutrients
evolving, new concept includes functional nutrients
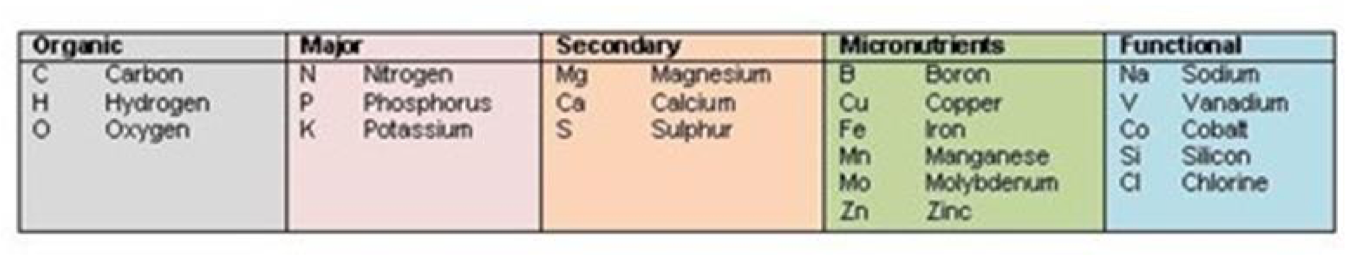
39
New cards
Law of the Minimum
Agricultural idea → appropriate for agroecosystems
crop growth is limited by one factor
crop growth is limited by one factor
40
New cards
Concept of Fertility in Agriculture
* monoculture, known plant requirements
* possible to measure limitations
* NPKS, maximize yield
* possible to measure limitations
* NPKS, maximize yield
41
New cards
Concept of Fertility in Wildlands
* multiple species, funstional types
* not possible to know of define limitations
* microbial function, bioavailable nutrient profile, SOM quality all contribute to ecosystem function
* not possible to know of define limitations
* microbial function, bioavailable nutrient profile, SOM quality all contribute to ecosystem function
42
New cards
Soil Food Web
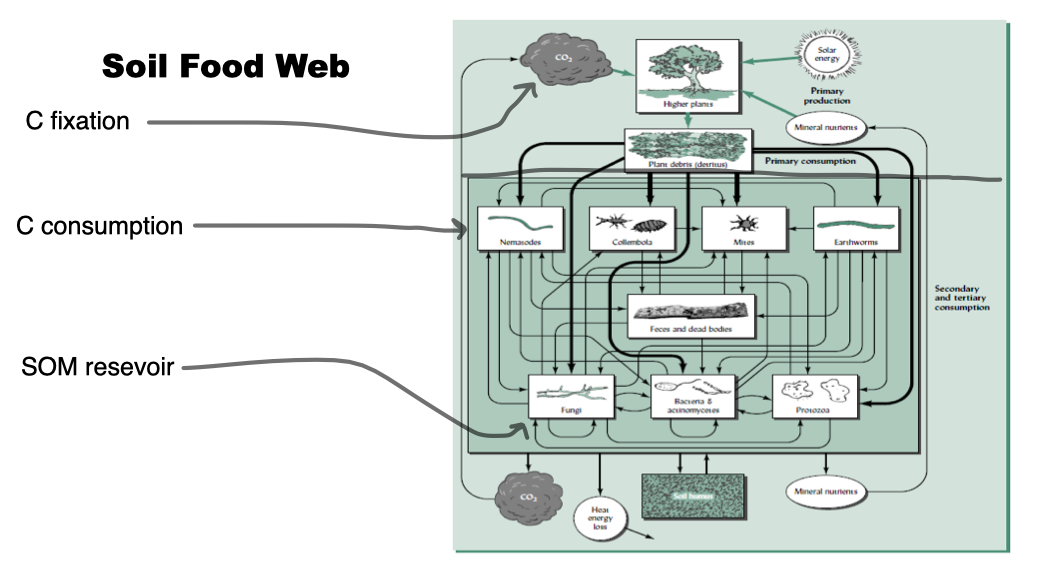
43
New cards
Meagfauna
* mostly rodents
* bioturbation → soil mixing/predation
* bioturbation → soil mixing/predation
44
New cards
Macrofauna
* ants, millipedes, termites, earthworms, beetles, etc.
* bioturbation
* predatory, but smaller size
* OM shedders (↓ particle size)
* bioturbation
* predatory, but smaller size
* OM shedders (↓ particle size)
45
New cards
Mesofauna
* mites and other small insects (0.1-1.0 mm)
* shedders
* OM consumers
* predators
* invertebrates
* shedders
* OM consumers
* predators
* invertebrates
46
New cards
Mite Diversity
* very high in grasslands and forests
* diversity indicates ecosystem function
* diversity indicates ecosystem function
47
New cards
Microfauna
* Nematodes
* Protozoa → largest to smallest: ciliates (hair), amoebae (flowing cytoplasm), flagellates (whip-like appendages)
* Protozoa → largest to smallest: ciliates (hair), amoebae (flowing cytoplasm), flagellates (whip-like appendages)
48
New cards
Microflora
* fungi
* bacteria
* archaea
* bacteria
* archaea
49
New cards
Types of Mycorrihiza
* echo → outside cell, gymnosperms
* erricoid → species specific
* arbuscular → inside cell, angiosperms
* orchid → species specific
* erricoid → species specific
* arbuscular → inside cell, angiosperms
* orchid → species specific
50
New cards
Soil-Plant Relations Lab
Phase 1 - Soil Quality Monitoring
\
Phase 2 - DASH/DIRTS Health App
Phase 3 - Regenerative Agriculture
\
Phase 2 - DASH/DIRTS Health App
Phase 3 - Regenerative Agriculture