Online Lab - Electrical and Mechanical Events of the Cardiac Cycle
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Cannulation of the trachea
Small hole is made in the trachea, and a plastic cannula is inserted so that secretions from the upper respiratory tract can be removed so the animal can be artificially ventilated
Where is the common carotid artery
Common carotid artery is in the neck behind the vagus nerve
Cannulation of common carotid artery
It is separated from the nerve and a clip is placed on it on the side closest to the heart. A hole is placed part way through the wall in the carotid artery and a catheter is introduced
What is the second tie used for during cannulation of the common carotid artery?
To secure the catheter in place
What is the catheter for?
To measure the animal’s blood pressure
Where is the external jugular vein
Side of the neck close to the skin
Where is the catheter advanced during cannulation of external jugular vein?
Past the clip, so that the tip lies in or close to the right atrium
What is the catheter used for when cannulating external jugular vein?
To measure right atrial pressure
Why do electrodes need to be placed via needles in the skin?
The dog’s fur prevents electrical contact
What is the carotid artery catheter connected to, and what is that connected to?
Pressure transducer; Grass polygraph
What are the ECG electrodes connected to? and what is that connected to?
Junction box; grass polygraph
Lead 1 combines electrodes on the…
Right arm and left arm
Lead II combines electrodes on the…
Right arm and left leg
Lead III combines electrodes on the…
Left arm and left leg
What does the P wave represent
Arterial depolarisation
What does the QRS represent
Ventricular depolarisation or commencement of ventricular systole (contraction)
What does the T wave represent?
ventricular repolarisation
What does the upstroke of the pressure wave in the carotid artery represent?
The commencement of systole
What is the first factor that contributes to the delay between the onset of the QRS and the onset of the rise in arterial pressure in the carotid artery?
Time taken for excitation-contraction coupling to occur - takes time for APs to travel down T-tubules
What is the second factor that contributes to the delay between the onset of the QRS and the onset of the rise in arterial pressure in the carotid artery?
Time of isovolumetric contraction, which lasts about 0.05 seconds
What is the third factor that contributes to the delay between the onset of the QRS and the onset of the rise in arterial pressure in the carotid artery?
Time taken for the pulse wave to travel along the wall of the arteries to the point of recording in the carotid
What is typical of a femoral arterial pulse?
High systolic peak and a secondary diastolic wave
As the recording site moves further from the heart, what are the 6 changes that occur?
Longer delay in the onset of the initial rise in pressure
There is an increase in the amplitude of the systolic peak
The pulse pressure (difference between systolic and diastolic pressure) becomes greater
The systolic portion narrows and the time to peak pressure is reduced
High frequency components like the incisura are damped out and disappeared
A hump or secondary wave may become prominent on the diastolic portion of the wave
What causes these changes in arterial pressure wave shape?
Resonance of arterial tree, tapering of vessels and reflection of the wave at branch points or when the arterial dimension changes
When arteries are less compliant…
the shape of the pressure wave changes (e.g., arteriosclerosis)
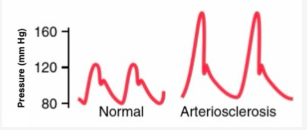
What happens to the catheter tip when measuring left arterial pressure?
It is advanced so that it lies within the left ventricle in the thorax
Does contraction of the left ventricle cause a wide or narrow pressure pulse?
Wide
What type of beats occasionally occur when the catheter tip in the ventricle irritates it?
Ectopic beats
Carotid sinus reflex
Causes a drop in blood pressure in branches upstream of the occlusion
Cause of carotid sinus reflex
Common carotid artery is occluded with a clip
What happens to heart rate and blood pressure when the carotid is occluded?
They rise
What is the carotid sinus?
Dilation of the internal carotid artery just above the bifurcation of the common carotid artery.
What are baroreceptors re the carotid sinus reflex?
Branched, coiled bare ends of sensory nerve fibres located in the adventitia of the carotid sinus. They act as stretch receptors, detecting stretch of the wall due to changes in arterial pressure.
How is the output from baroreceptors transmitted?
Via afferents in the carotid sinus nerve to the glossopharyngeal nerve (Cranial Nerve IX) and then to the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) in the medulla.
What happens when blood pressure rises?
Increased afferent impulses lead to decreased sympathetic discharge and increased vagal discharge. This causes vasodilation, reduced heart rate and cardiac output, returning blood pressure to normal
Occlusion of the carotid simulates…
A fall in blood pressure, causing a reduction in stretch of the carotid sinus, so afferent impulses are reduced. This results in a compensatory increase in sympathetic discharge to the heart, blood vessels and a decrease in vagal discharge
How is right atrial pressure measured?
Via the catheter in the external jugular
Tracheal occlusion causes…
Right atrial pressure
What causes the rise in arterial pressure when the trachea is occluded?
Intrathoracic pressure becomes more negative → increase in venous return to right side of heart → corresponding rise in right ventricular output → increases venous return to left side of heart
How can a positive pressure be produced?
Attaching a rubber tube to the tracheal canula and blowing into the tube
What effect does positive pressure have
increases right atrial pressure, decreases venous return on both sides of the heart
What wave is the p wave associated with?
The a wave of atrial contraction
What wave is the QRS wave associated with?
Small c wave which represents bulging of the tricuspid valves when the ventricles contract
What does the v wave represent?
Venous return to atrium when triscuspid valve is closed
What happens when the vagus nerve is stimulated at 20Hz?
The heart stops completely and then resumes beating at a slower rate
Vagal escape
Phenomenon where the heart resumes beating after a period of complete cessation due to vagal stimulation, often resulting in a slower heart rate.
Mechanism of vagal escape
Spontaneous discharge of the SA node is abolished and transmission of the cardiac impulse from the atria to ventricles is abolished - allows different conduction pathway with slower rate to take over as pacemaker.
What pressure range would you expect to record from the catheter in the right atrium
0 - -4 mmHg
What pressure range would you expect to record from the catheter in the left ventricle?
0-130