AP BIO Unit 5
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Gamete
haploid reproductive cell or sex cell (sperm, pollen grain, or egg)
Zygote
Fusion of the gametes gives rise to a fertilized egg cell, or zygote.
Haploid
cell, nucleus, or organism containing one set of chromosomes (n)
Diploid
cell, nucleus, or organism containing two sets of chromosomes (2n)
Meiosis I
first round of meiotic cell division; referred to as reduction division because the ploidy level is reduced from diploid to haploid
Meiosis II
second round of meiotic cell division following meiosis I; sister chromatids are separated into individual chromosomes, and the result is four unique haploid cells
Crossing Over
exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids resulting in chromosomes that incorporate genes from both parents of the organism
Chiasmata/chiasma
a point at which paired chromosomes remain in contact during the first metaphase of meiosis, and at which crossing over and exchange of genetic material occur between the strands.
How does meiosis increase genetic diversity?
crossing over (P1)
independent assortment (M1)
fertilization
mutations
How does crossing over/recombination increase genetic diversity?
Homologous chromosomes exchange segments of DNA in prophase 1. This creates new chromosome combinations with a mix of alleles from both parents.
How does independent assortment increase genetic diversity?
During metaphase 1, the homologous chromosomes line up randomly, creating over 8 million possible results.
How does fertilization of gametes increase genetic diversity?
The random fusion of any one sperm with any one egg further increases genetic diversity.
Law of Segregation
paired unit factors (i.e., genes) segregate equally into gametes such that offspring have an equal likelihood of inheriting any combination of factors
Law of Independent Assortment
genes do not influence each other with regard to sorting of alleles into gametes; every possible combination of alleles is equally likely to occur
Genotype
underlying genetic makeup, consisting of both physically visible and non-expressed alleles, of an organism
Phenotype
observable traits expressed by an organism
P Generation
parental generation in a cross
F1 Generation
first filial generation in a cross; the offspring of the parental generation
F2 Generation
second filial generation produced when F1 individuals are self-crossed or fertilized with each other
How to determine probability if A and B are mutually exclusive?
Sum rule
P ( X ) + P ( Y )
OR
How to determine probability if A and B are independent?
Product rule
P ( X ) ⋅ P ( Y )
AND
Incomplete dominance
in a heterozygote, expression of two contrasting alleles such that the individual displays an intermediate phenotype
Codominance
in a heterozygote, complete and simultaneous expression of both alleles for the same characteristic
Multiple alleles
the many different versions of an allele present in a population
Pleiotrpy
the production by a single gene of two or more apparently unrelated effects (phenotypic traits)
sex linkage
genes on either the X or Y chromosome (23rd chromosome)
mitochondrial DNA
Circular DNA located within the mitochondria of a cell. Only inherited from the mother.
Map Distance
the relative distance between two genes on a chromosome
Phenotypic plasticity
the property of organisms to produce distinct phenotypes in response to environmental conditions
How can the environment influence gene expression?
Through epigenetic modifications. External factors such as temperature can chemically alter the DNA structure and thereby impacting an organism’s traits.
Nondisjunction
failure of synapsed homologs to completely separate and migrate to separate poles during the first cell division of meiosis
causes trisomy or monosomy and increases with maternal age
If it happened in M1, 100% are abnormal. If it happened in M2, 50% are abnormal.
Trisomy 21
Down’s Syndrome
Monosomy X
Turner’s Syndrome
XXY
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
5p deletion
Cri Du Chat
chi-square
Calculate chi-square
Find critical value
Degrees of freedom= categories - 1
P-value 0.05 if not specified
If chi-square is > critical value = reject
If chi-square is < critical value = fail to reject
mutagens
a physical or chemical agent that can cause a permanent change in the genetic material, usually DNA, leading to mutations (mutagenesis), not reversible
Physical: heat, radiation; breaks the phosphodiesterase bonds in DNA
Chemical: base-analog, base-modifying; often mimic a base and bonds in its place
Biological: bacteria, viruses; increase the chance of cancer
epigenetics
the study of how behaviors and environments affect the way genes are expressed, heritable changes that do not involve changes in the DNA sequence, most are reversible
Ex. identical twins
autosomal traits
on somatic chromosomes (pedigrees)
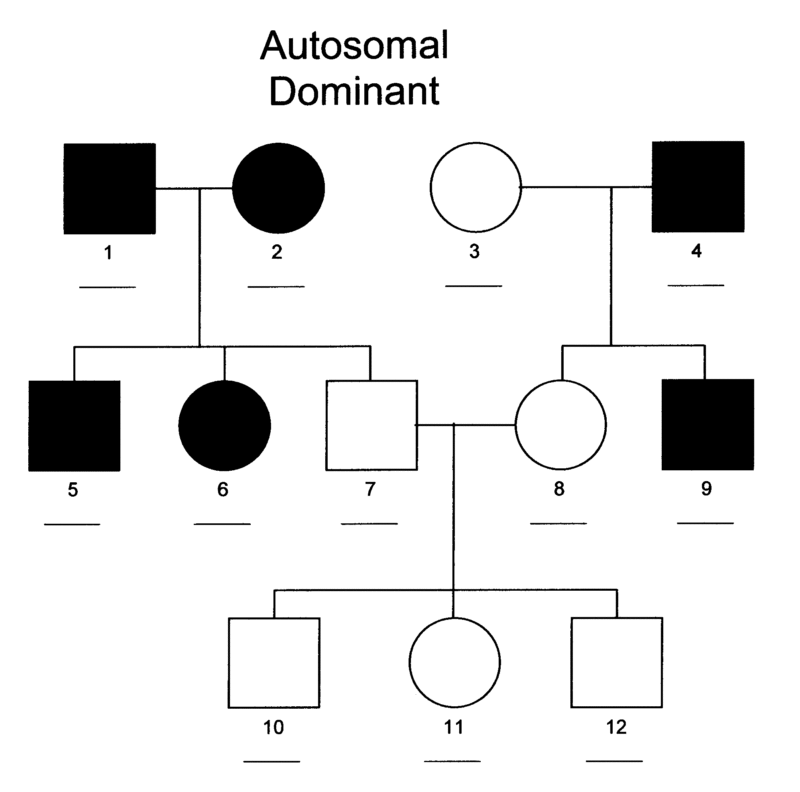
autosomal dominant
appears in males and females with same frequency
affected offspring must have an affected parent
rarely skips a generation
if one parent is heterozygous ~50% of offspring will be affected
Ex. Huntington’s Disease
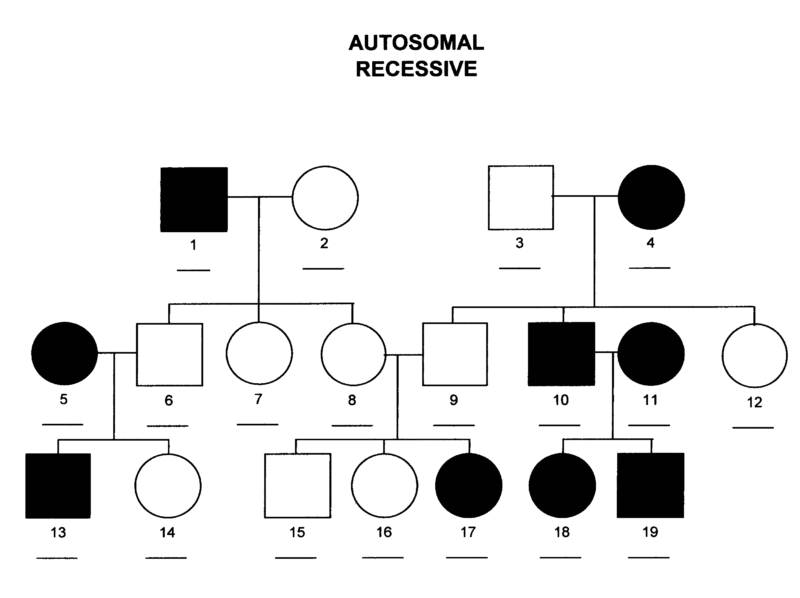
autosomal recessive
appears in males and females with same frequency
affected offspring usually have an unaffected parent
often skips a generation
if both parents are heterozygous ~25% of offspring will be affected
Ex. Cystic fibrosis
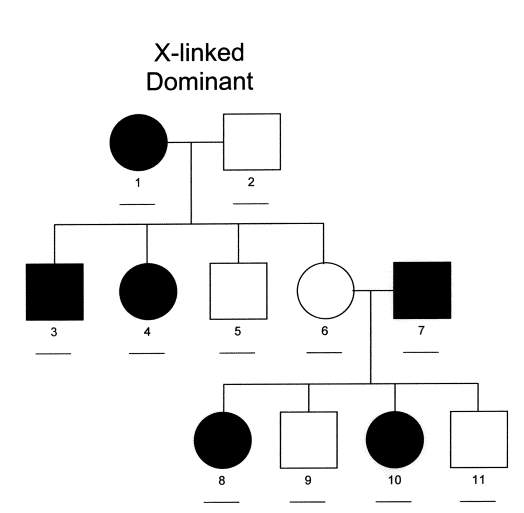
x-linked dominant
appears more often in females than males
affected sons must have an affected mother
affected fathers will pass the trait to all their daughters
hard to say it’s 100% x-linked
Ex. fragile X syndrome
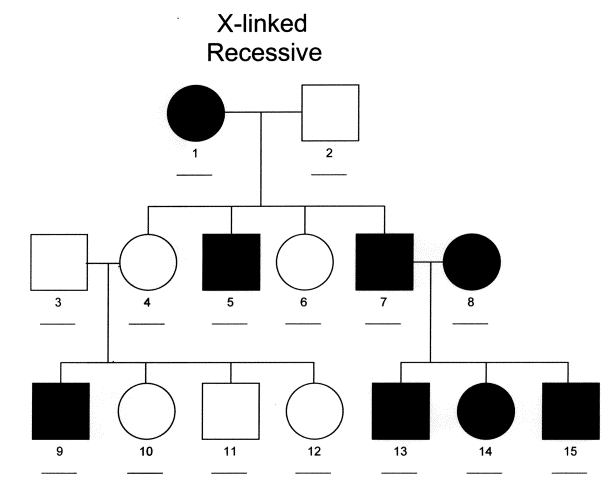
x-linked recessive
appears more often in males than females
affected sons must have an unaffected mother
all daughters of affected fathers are carriers
hard to say it’s 100% x-linked
Ex. red green color blindness
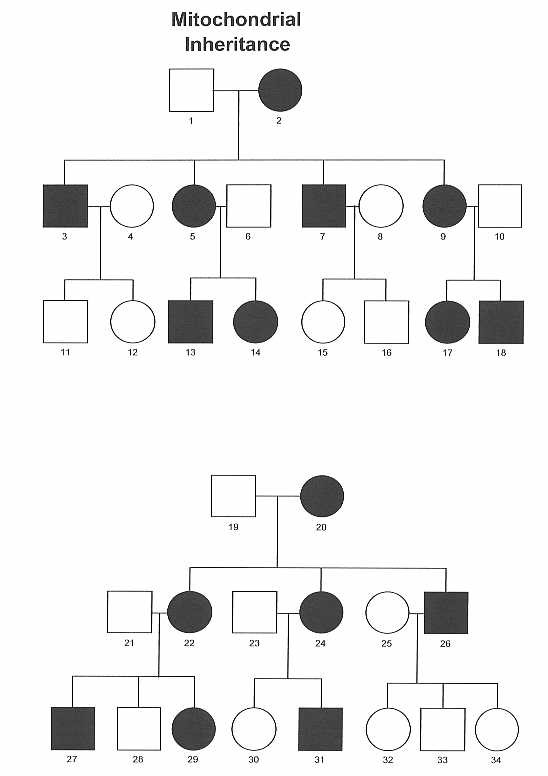
mitochondrial inheritance
trait comes from the mother only
all children are at risk of being affected/carrier
Ex. Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy
linked genes
genes located near each other on the same chromosome and are often inherited together
some gametes are only possible with crossing over
actual outcomes for recombinant phenotypes is less than 25%/25%, and is statistically different than the expected outcome
locus (plural loci)
position of a gene on a chromosome
unlinked genes
genes located on separate chromosomes or more than 50 map units apart
all gametes are equally possible (with or without crossing over), consistent with the Law of Independent Assortment
actual outcome (phenotypic ratio) is not statistically different from the expected outcome (each 25%)
recombinant phenotypes
the results of crossing over, different from the parental phenotypes
recombinant frequency
total percentage of recombinants
map units apart on a chromosome
higher recombination frequency = higher occurrence of crossing over = greater distance apart
polygenics
phenotypic characteristic caused by two or more genes, can also be influenced by environmental factors
Ex. hair color, skin color, height
non-nuclear inheritance
occurs when genetic material (DNA) in the cytoplasm is inherited; often from the mitochondria or chloroplasts of only the female parent
bacterial conjugation
bacteria exchange genes, sex pilus is a projection that initiates contact between bacterial cells
plasmids
small circular DNA molecules, can move between bacterial cells during conjugation
test cross
used to determine the unknown genotype of an individual by crossing the unknown parent with a homozygous recessive individual to observe the phenotypes of the offspring
Heterozygous Dihybrid Cross
AaBb x AaBb
9 - dominant traits
3 - dominant, recessive
3 - recessive, dominant
1 - recessive traits
epistasis
a gene at one locus alters the effects of a gene at another locus
polygenic inheritance
phenotypic characteristic caused by two or more genes
X inactivation
condensation of X chromosomes through a process called methylation into Barr bodies during embryonic development in females to compensate for the double genetic dose
linkage map
a diagrammatic representation of the relative positions of genes or genetic markers on a chromosome, determined by their recombination frequencies during meiosis
polyploid
individual with an incorrect number of chromosome sets
gametes with extra chromosomes
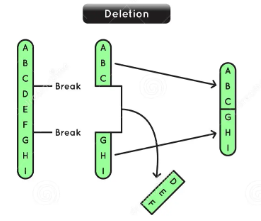
deletion
a portion of a chromosome is lost or removed
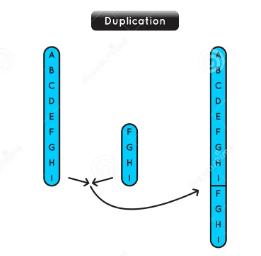
duplication
a segment of a chromosome is copied, resulting in multiple copies of that segment
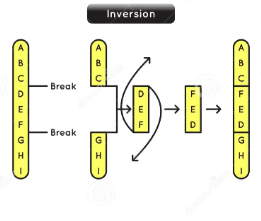
inversion
a segment of a chromosome is flipped or reversed, and then reinserted into the same location
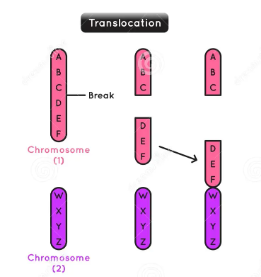
translocation
a piece of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome