micro OSPE NMU
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
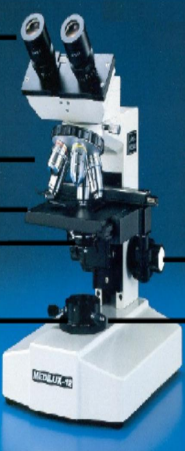
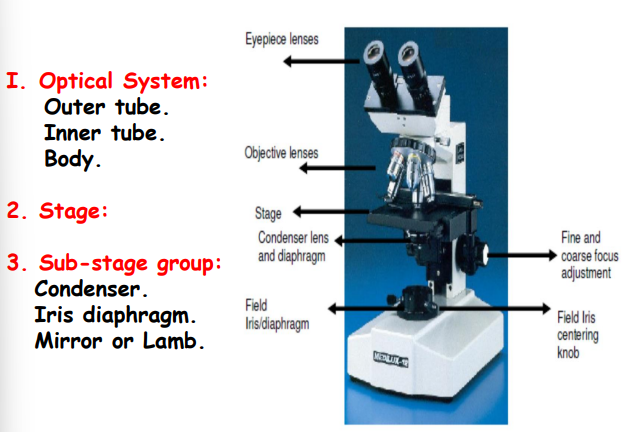
identify + all arrows :)
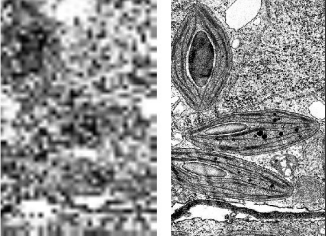
what does this picture indicate ?
what makes the photo look better ?
microscopic resolution
the shorter wavelengths the better resolution
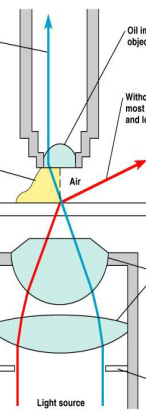
identify ? (name the substance)
what does it do ?
what special character does it have (to be used here)
cedar oil
.
The oil enhances resolution by preventing light rays from dispersing after passing through the specimen
.
it have the same refractive index as the glass

identify ?
used to ?
dark field microscope
used to identify delicate refractile organisms (spirochaetes)
special condenser > oblique light only
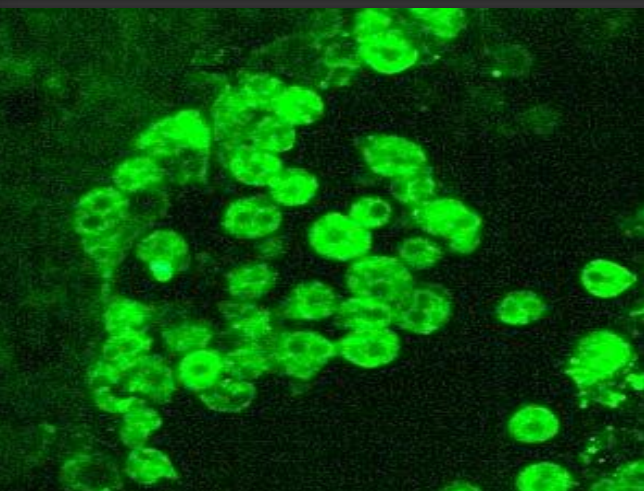
identify ?
stain ?
light used ?
ex ?
fluorescence (UV) microscope
acridine orange
uv
• Example: Immunofluorescent microscope.

identify ?
what beam is used ?
resolution power ?
disadvantages ? (3)
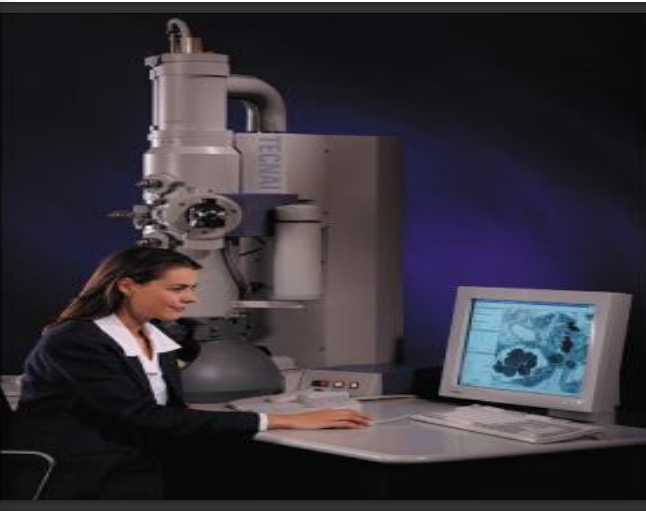
EM
• Electron beam ‘very short wave length’ instead of light.
• Resolution power = 1 nm viruses.
• Disadvantages:
1- Expensive
2- Experience
3- Ultra-thin sections.
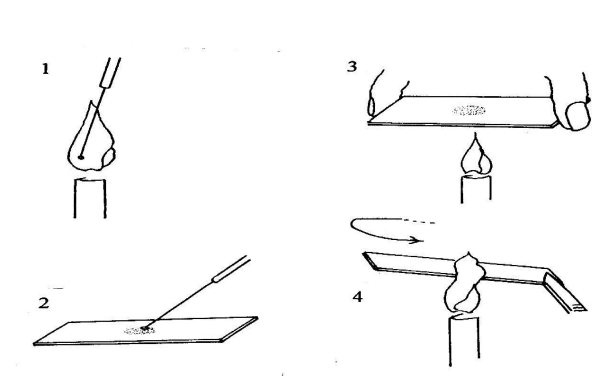
what is this ?
steps ? 6 افوره مني غالبا
Film (Smear) Preparation
.
1- Sterilization of the bacteriological loop.
2- Pick a pure colony in a drop of water or bacterial culture drop.
3- Spread on a slide.
4- Drying of the smear.
5- Fixation of the smear: (Why! & How!).
6- Staining.
identify all pls
ty
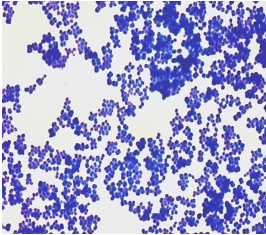
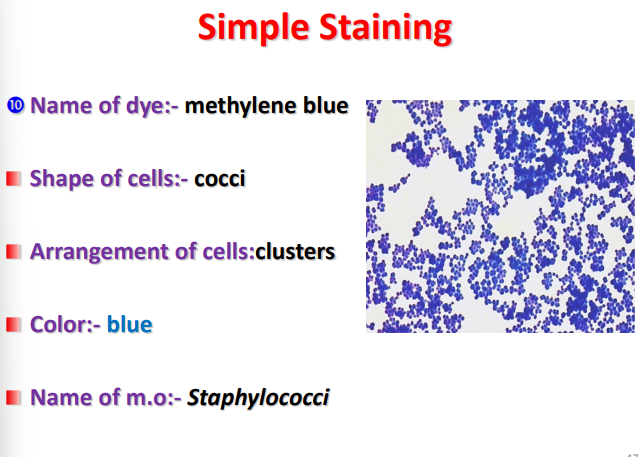
dye name ?
shape of cells ?
arrangement of cells ?
color ?
name of m.o.
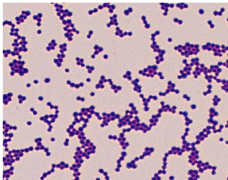
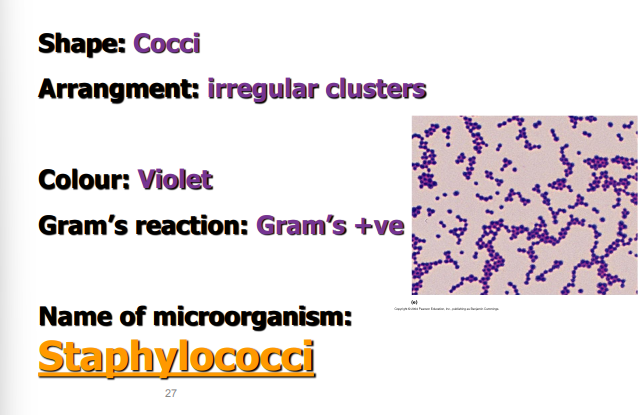
shape ?
arrangement ?
colour ?
gram’s reaction ?
name of microorganism ?
how to make gram stain ?
Crystal violet —> Iodine —> Alcohol —> Dil carbol fuchsin (Safranin)
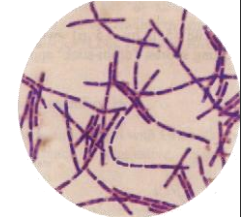
shape ?
arrangement ?
colour ?
gram’s reaction ?
name of microorganism ?
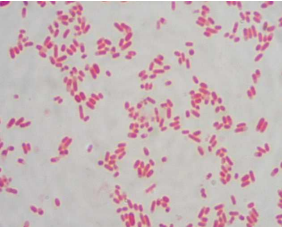
shape ?
arrangement ?
colour ?
gram’s reaction ?
name of microorganism ?
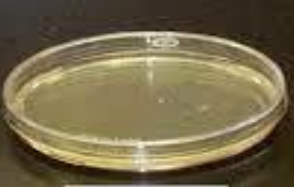
?
used to ?
nutrient agar plate
used for primary culture of many microorganisms

?
used to ?
Deep agar is used for culture of anaerobic bacteria.

?
used to ?
nutrient broth
its the base of nutrient agar
used for culture of non fastidious bacteria
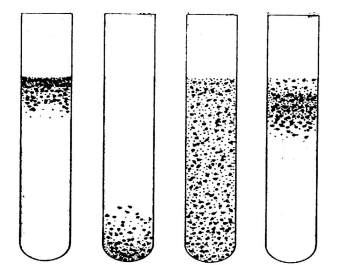
name each ..

arrow ?
pellicle

arrow ?
turbidity

arrow ?
sediment

identify ?
for ?
indicator of ?
media type ?
blood agar
- For the fastidious bacteria. (enriched media)
- An indicator medium i.e. help in the identification of bacteria by their haemolytic action on the red cells

identify ?
media type ?
used to ?
Chocolate agar
enriched media
used to Culture of Neisseria and Haemophilus groups.

اسف عالصور البشعه دي
identify ?
media type ?
used to ?
loffler’s serum
used in culture of diphtheria bacilli

identify ?
media type ?
used to ?
dorset egg
enriched media
used in culture of tubercle bacilli from NOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOON contaminated pathological samples (C.S.F)
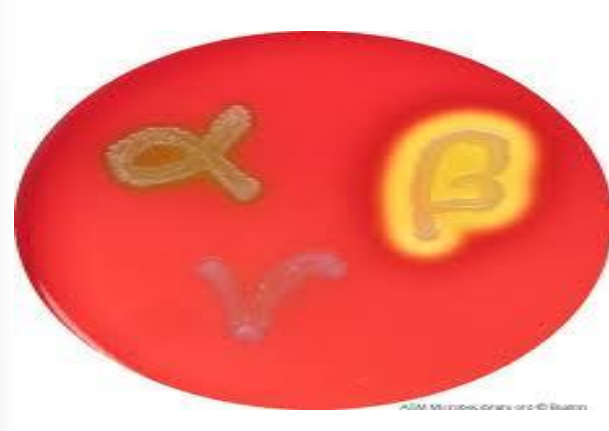

explain the 3 types of haemolysis on blood agar with examples !!!!
a) alpha- haemolysis (partial haemolysis):
It occurs due to partial destruction of R B Cs with release of biliverdin (green) e.g. Strept. viridans and Pneumococci.
b) beta- haemolysis (complete):
The colonies are surrounded by zones of clear haemolysis due to the complete destruction of RBCs by the toxins released bacteria e.g. Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
c) γ-haemolysis (no haemolysis): e.g. Strept. faecalis

identify ?
selective component ?
uses ?
TB colonies in lowenstein jensen medium
.
malachite green which inhibits the growth of any other bacteria other than TB
used for caltivation of TB bacilli from CONTAMINATED sample (sputum)
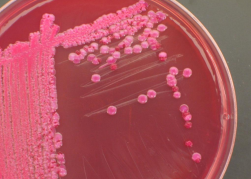
identify ?
contains what ?
used for ?
indicator media
media usually contains an indicator which changes its colour as a result of metabolic activation كدا
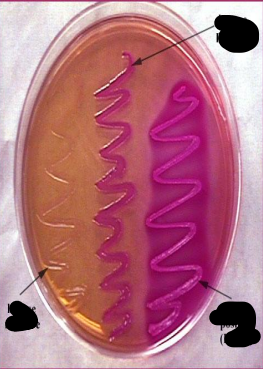
arrows ?
identify ?
indicator ?
uses ?
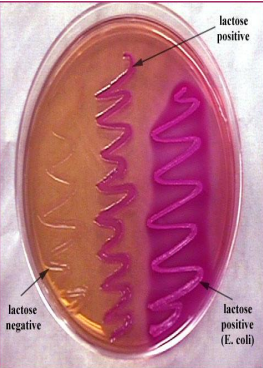
macconkey medium
indicator is neutral red which changed to pink in presence of acis which is produced from lactose fermentation
used in cultivation of enteric bacteria
and it differentiate between two major group of bacteria LF (rose) and NLF (pale)
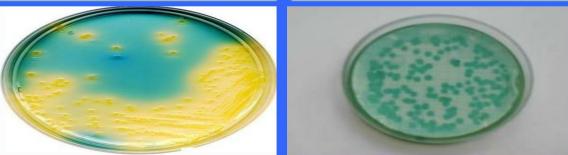
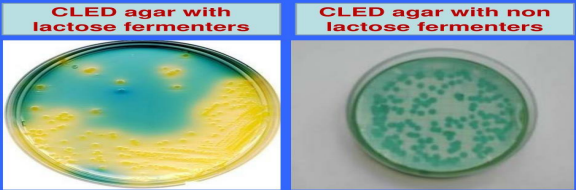
identify both
indicator ?
uses ?
bromothymol blue
used in culture of urine samples LF (yellow) NLF (pale yellow)
its an indicator media

identify ?
media type ?
mech ?
ex ?
selenite broth used for isolation of shigella and salmonella from feaces
stim . growth of some on expense of others
its a type of enrichment media

identify ?
stuarts transport medium
and it maintains high viability of gonococci on swabs during their transmission to the lab
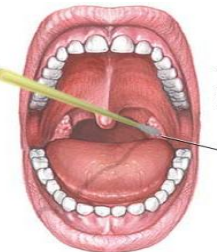
identify ?
used in ?
timing ?
throat swab
used in sore throat (respiratory tract infection)
timing : in the morning before eating,drinking or tooth brush
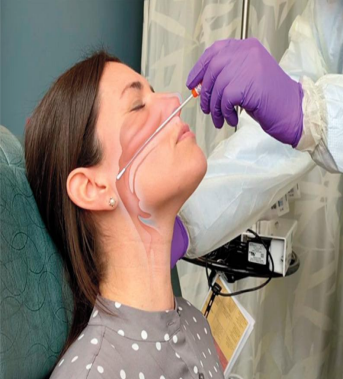
identify ?
used in ?
nasopharyngeal swab
commonly with meningitis and viral infection
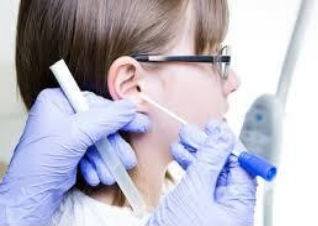
identify ?
used in ?
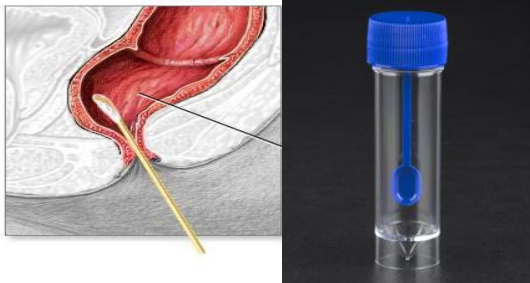
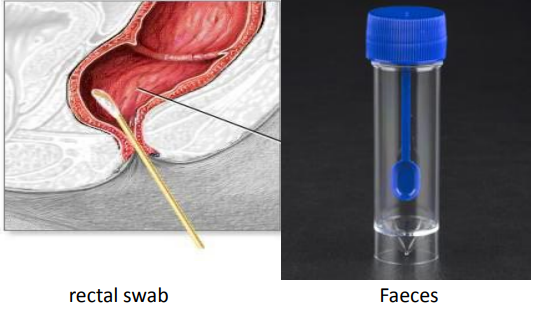
identify ?
used in ?
rectal swap used in cases of infective diarrhea, cholera chronic diarrhea
faeces (much better specimen than a rectal swap) used in acute intestinal infection
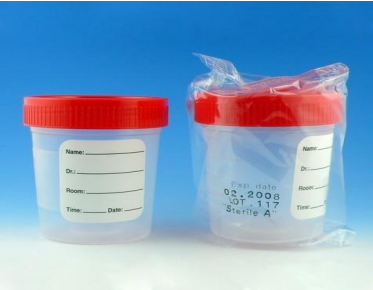
identify ?
used in ?
when should specimen be collected ?
methods of urine sample collection (mid stream specimen)
Urinary tract infection
collected as a clean catch-mid-stream after cleaning external genitalia with soap and water

identify ?
used in ?
Adhesive bags:
Used for collection of urine specimen specially in children.
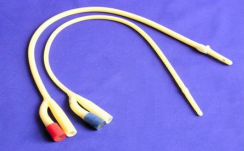
identify ?
used in ?
urethral catheter (foley)
collection of urine السؤال مش مظبوط
لو حد عندهحاجه احسن يقول

identify ?
used in ?
urethral catheter (nelaton)
collection of urine السؤال مش مظبوط
لو حد عندهحاجه احسن يقول
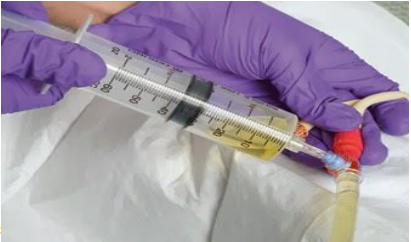
identify ?
collection of urine in a catheterized patient
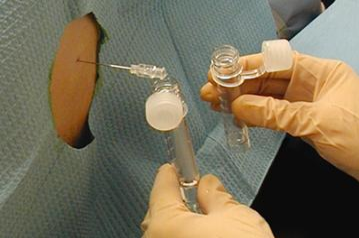
identify ?
used in ?
the sample is collected in ?
CSF sample
taken by lumbar puncture. Under strict aseptic precautions in meningitis
.
sample is collected in screw-capped bottles and sent to the laboratory at once
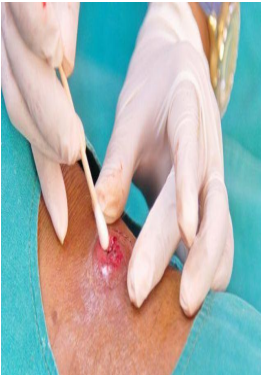
identify ?
used in ?
ordinary swap
used in taking pus or exudate from infected wounds (must be soaked well in the exudates)
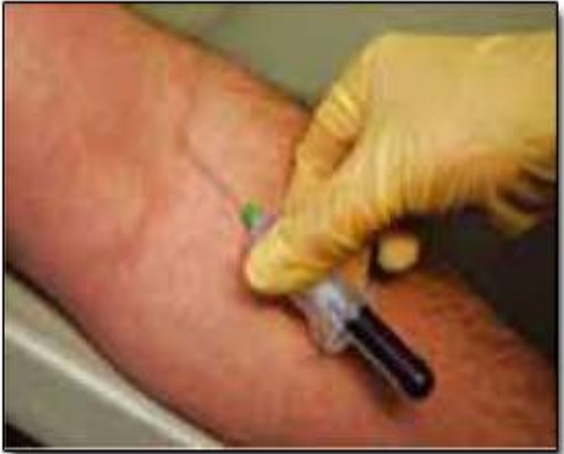
collected sample ?
in cases of ?
steps ?
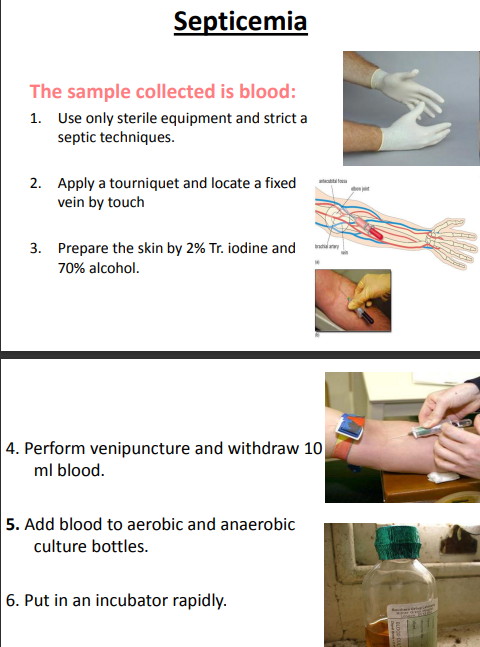
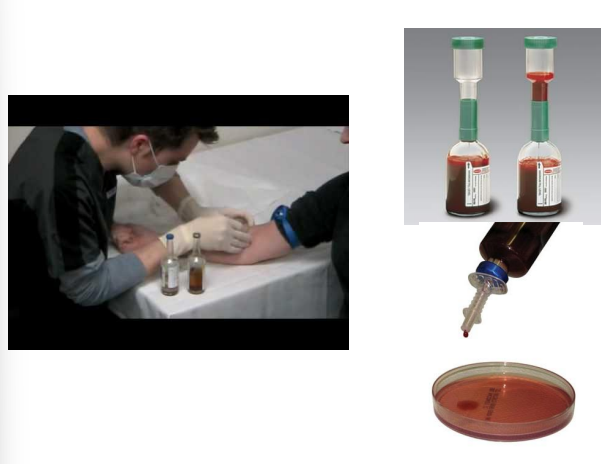
identify ?
procedure ? اعتقد صعبه اوي تيجي بس مش عارف اي تاني ممكن يجي
blood culture technique

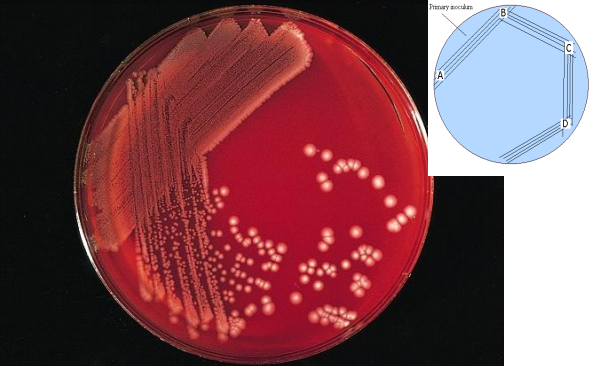
identify ?
plating out technique
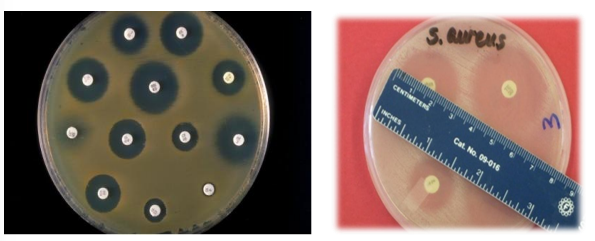
identify ?
method used ?
anti biotic sensitivity testing
kirby-bauer disk-diffusion method