Microbiology Exam 5-mine
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
Wild-type strain
strain isolated from nature
Mutant
change in nucleotide sequence
mutant phenotype
altered phenotype relative to parental strain
What is a problem with the isolation of mutants
a specific mutation is a rare event and the mutant of interest will be outnumbered by the parent strain
selectable mutation
mutant has an advantage under certain environmental conditions and will overtake the wild strain
Non-selectable mutation
no growth advantage or disadvantage in any environment. Difficult to isolate
What is a screening strategy for identifying mutants?
selectable marker genes
A mutation during DNA replication will result in what two types of cells?
Wild type and mutant
Name one example of negative selection
Replica plating
Replica plating
method to screen nutritional mutants (leucine auxotrophs)
What are the point mutations?
silent, nonsense, missense
Silent mutation
no change in amino acid sequence
Nonsense mutation
codon becomes stop codon
Missense mutation
amino acid is changed
Transitions
purine to purine and pyrimidine to pyrimidine
Transversion
pyrimidines to purines
Frameshift mutation
one or more nucleotides are added or deleted from DNA
Back mutations
a mutation occurs at a previously mutated position, so it returns to original
Point mutations are typically reversible (True/False)
True
Mutagenesis
induced mutation
Ames Test
screen chemicals for potential mutagenicity
screen for increase rate of back mutations in auxotrophic bacteria in presence on chemical disc
Vertical gene transfer
genes passed from parent to offspring
Horizontal gene transfer
movement of genetic material between organisms that are not related by parent and offspring
What are the three types of horizontal gene transfer
Transformation, Transduction, Conjugation
Transformation definition
free DNA is incorporated into a recipient cell and brings about genetic change
Transduction definition
bacterial virus that transfers DNA from one cell to another
Conjugation definition
genetic transfer from a donor cell to a recipient cell requiring cell-to-cell contact
Transformation process
free DNA enters cell
homologous recombination
Generalized Transduction
any host gene packaged into virion
virion lacks viral genome
requires recombination for stabilization in new host
lytic or lysogenic
low frequency
Specialized Tranduction
only genes near viral integration site are packaged
virion carries most to all of viral genome
recombination not needed
lysogenic
high frequency
Conjugation process
sex pilus and then the DNA is sent into the other cell and replicated
Rolling circle replication
bacterial conjugation where transfer plasmid DNA from donor to recipient cell and then circular DNA just rolls and replicates
F plasmid
circular
~100k bp
contains genes that regulate DNA replication
contains transposable elements
contains tra genes that encode transfer functions
episome
Episome
can exist independently or integrate into host chromosome
F-
cell without F plasmid
F+
cell with non-integrated F plasmid
HFr
cells with integrated F plasmid
Transposable elements
mobile DNA
Are transposable elements found in all three domains of life?
yes
What are the two types of transposable elements in bacteria?
Insertion sequences and transposons
Insertion sequences
2 inverted repeats + transposase gene
Transposons
2 inverted repeats + transposase genes + other genes
Restriction enzymes
Recognize specific base sequences within DNA (recognition sequences) and cut the DNA at specific sites
Where are restriction enzymes found
prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea)
Recognition sequences
inverted repeats
methylation
defense mechanism against foreign DNA
Defenses against horizontal gene transfer
physical barriers and restriction enzymes
Type II restriction enzymes
cleavage site locate within the recognition sequences
What are the three types of ends that Type II forms
5’ overhang
3’ overhang
Blunt ends
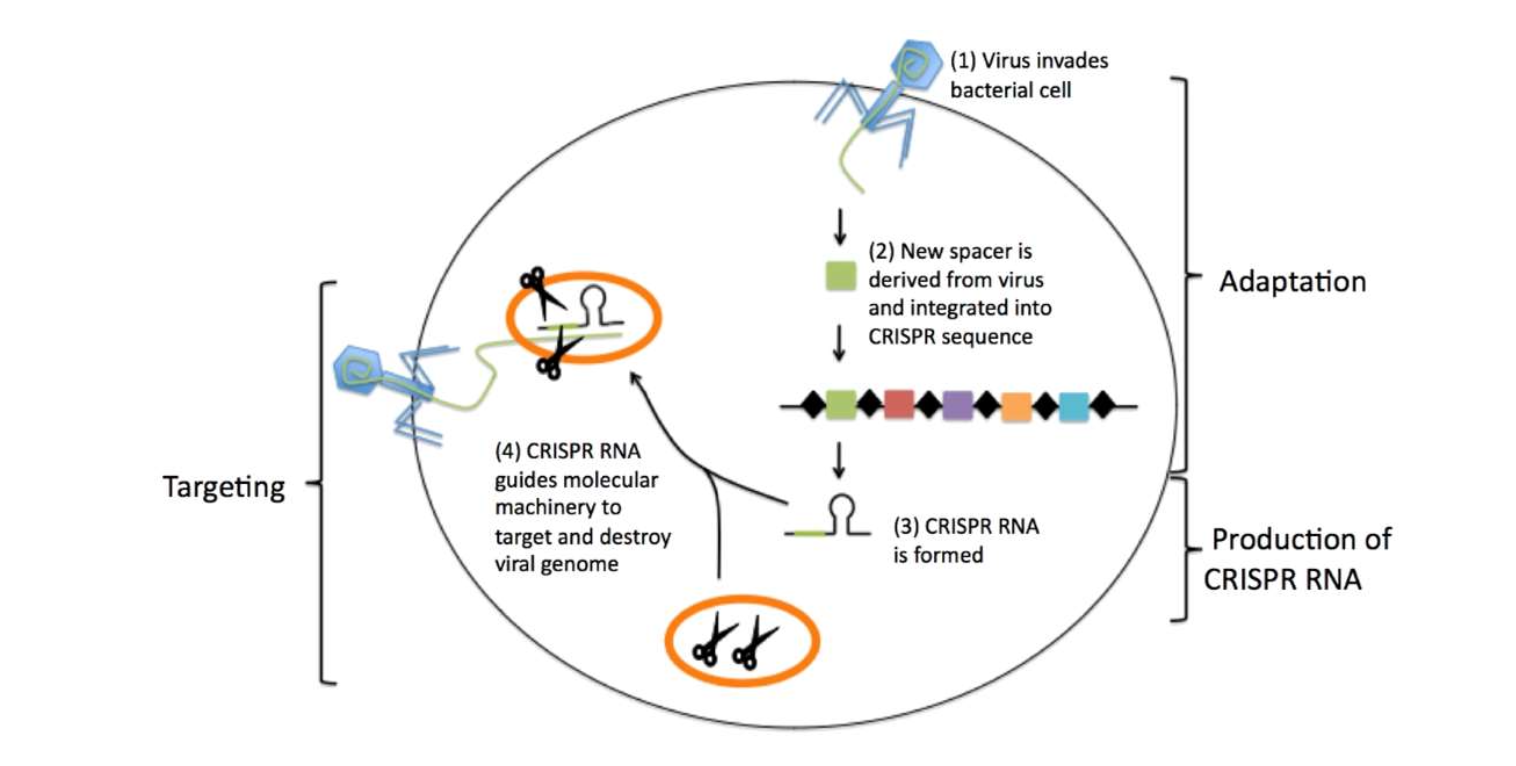
CRSPR
clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
CRSPR Process
segments of prokaryotic DNA containing short repetitions of base sequences
each repetition followed by short segments of spacer DNA from previous exposure to a bacterial virus or plasmid
CRSPR Cas-9
crRNA + tracrRNA + Cas9 endonuclease
How does CRSPR Cas-9 work?
binds to target viral dsDNA and cuts both strands (double stranded cleavage)
CRSPR Cas-9 process
virus invades bacterial cell
new spacer derived from from virus and integrated into CRSPR sequence
CRSPR RNA is formed
CRSPR RNA guides molecular machinery to target and destroy viral genome
What is also called magic scissors
CRSPR Cas-9
Gel electrophoresis separates cells by their
shape and size
How does size effect movement in gel electrophoresis
larger fragments move more slowly
How does shape effect movement in gel electrophoresis
compact shapes move faster
How does gel electrophoresis work?
the phosphodiester bond in DNA is negatively charged, so they migrate towards the positive pole. Fragments are then stained
Nucleic Acid hybridization
single stranded DNA or RNA used for screening homologous sequences by utilizing complementary base pairing (hybridization)
Nucleic Acid hybridization procedure
label know nucleic acid with radioactive/fluorescent dye
hybridize probes with unknown samples
if probe hybridizes it is positive
Southern blotting
DNA in the gel labeled with DNA or RNA probe
Northern blotting
RNA in gel labeled with DNA or RNA probe
Western blotting
protein in gel labeled with antibody
Splicing
introns are removed and exons are joined by spliceosome
Spliceosomes contain
small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs)
Reverse transcriptase
makes DNA copy of RNA (cDNA)
cDNA made from mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
What does reverse transcriptase allow for
a means of synthesizing eukaryotic genes from mRNA transcripts-synthesized gene free of introns
Polymerase Chain Reaction Purpose
rapidly increase the amount of DNA in a sample
For PCR, primers of known sequences are added to indicate where amplification will begin, along with
special heat tolerant DNA polymerase and nucleotides
PCR is repetitively cycled through
denaturation, priming, and extension
Every cycle of PCR increases the amount of DNA by much
double
What is PCR essential for
gene mapping, genetic deficits, cancer, forensics, taxonomy, evolutionary studies
DNA sequencing
isolate unknown DNA fragment
DNA is denatured to produce single template strand
strand labeled with specific primer molecule
DNA polymerase and all nucleotides added to a tube. Each tube contains one type of dideoxy nucleotide that stop chain lengthening reaction
newly replicated strands are terminated at the point of addition of a dd nucleotide
a schematic view illustrating how each fragment will end with a labeled dideoxy nucleotide, after all four tubes are mixed
a gel showing the results of a sequencing run for six different strands of DNA. Location and color of the band provide the correct identity and order of the bases
Pyrosequencing
whole-genome shotgun sequencing
Benefits of pyrosequencing
fast and cost effective analysis
pyrosequencing procedure
DNA fragmentation
separate and sequence small DNA fragments
Assemble pieces of DNA sequences together
Annotation, finding ORF
Microarray
track the expression of thousands of genes to identify diseases and treatments
Plasmids can be used as
cloning vectors
Why is it easy to isolate DNA in plasmids?
small size
Do plasmids have an independent origin or replication?
yes
Polylinker within plasmid
multiple cloning site, single cut made by restriction enzymes
Vector transfer is normally carried out by
chemical transformation or electroporation
Desirable features in a cloning host
fast growth rate
grown in large quantities
nonpathogenic
genome is well delineated
capable of accepting plasmid or bacteriophages
maintains foreign genes through multiple generations
will secrete a high yield or proteins from expressed foreign genes
Types of cloning vectors
simple cloning vectors
Shuttle vectors
Expression vectors
TI plasmid vector
simple cloning vectors
replicates in narrow range of host cells
Shuttle vectors
replicates in wide range of hosts
easily move genes between multiple hosts
multiple selection markers
multiple origins of replication
Expression Vector
transcriptional control
multiple cloning sites downstream of promoter region
high levels of protein expression
promoter is repressed unless activated by an inducer
strong transcription terminator sites prevent read-through
TI plasmid vector
used to introduce foreign DNA into plants
Example of TI plasmid vector
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
What DNA is transferred to the plant in TI vectors
T-DNA
Cloning steps
Isolation and fragmentation of source DNA
Inserting DNA fragment into cloning vector
Introduction of cloned DNA into host organism
Where/when is DNA usually inserted
in vitro
DNA ligase
enzyme that joins two DNA molecules. sticky and blunt ends
Introduction of clones DNA into host organism. ___ is often used to get recombinant DNA into host
Transformation
X-gal
colorless substrate used to detect activity of ß-galactose
No vector screening (plasmids as cloning vectors)
AMP: sensitive
Lac Z: no gene
X-gal: no colony on AMP plate
Vector without insert screening (plasmids as cloning vectors)
AMP: resistant
Lac Z: intact gene
X-gal: processed by lac Z protein. Blue colony
Vector with insert
AMP: resistant
Lac Z: damaged gene (interrupted by an insert)
X-gal: not processed (no color) White colony
Expression of mammalian genes in bacteria
different codon usage
presence of introns in eukaryotes
degradation by host intracellular proteases
toxicity to prokaryotic host
formation of inclusion bodies
improper protein folding
lack of post-translational modification
Advantages using bacterial system
quick replication and cheap production cost