DAT- Chapter 1: Molecules and Fundamentals of Biology
1/121
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
matter
anything that takes up space and has mass.
Element
a pure substance that has specific physical/chemical properties and can’t be broken down into a simpler substance
Atom
the smallest unit of matter that still retains the chemical properties of the element
Molecule
two or more atoms joined together
Intramolecular forces
attractive forces that act on atoms within a molecule.
Intermolecular forces
forces that exist between molecules and affect physical properties of the substance.
Monomers
single molecules that can potentially polymerize.
Polymers
substances made up of many monomers joined together in chains.
Carbohydrates contain
contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
Monosaccharides
are carbohydrate monomers with an empirical formula of (CH2 O)n . “n” represents the number of carbons.
isomers
same chemical formula, different arrangement of atoms
Disaccharides contain two monosaccharides joined together by a
glycosidic bond
dehydration (condensation) reaction
where a water molecule leaves and a covalent bond forms.
hydrolysis
a covalent bond is broken by the addition of water.
Sucrose
disaccharide made of glucose + fructose
Lactose
disaccharide made of galactose + glucose
Maltose
disaccharide made of glucose + glucose.
Polysaccharides contain
contain multiple monosaccharides connected by glycosidic bonds to form long polymers.
Starch
form of energy storage for plants and is an alpha (α) bonded polysaccharide.
amylose
Linear starch
amylopectin.
the branched form of starch
Glycogen
form of energy storage in animals and is an alpha (α) bonded polysaccharide. It has much more branching than starch
Cellulose
structural component in plant cell walls, and is a beta (β) bonded polysaccharide. Linear strands packed rigidly in parallel
Chitin
structural component in fungi cell walls and insect exoskeletons. It is a beta (β) bonded polysaccharide with nitrogen added to each monomer.
Proteins contain 1.—————
These atoms combine to form 2.———-,
which link together to build 3—————
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms (CHON)
amino acids
polypeptides (or proteins)
A proteome refers to
all the proteins expressed by one type of cell under one set of conditions.
Amino acids
are the monomers of proteins
Amino acid structure includes…
Amino group (NH3), Hydrogen, Carboxyl group (O-C=O), and R-group connected to a central Carbon
Polypeptides are
polymers of amino acids
Polypeptides are joined by ————
peptide bonds
polypeptides are joined by what kind of reaction?
through dehydration (condensation) reactions
The polypeptide becomes an amino acid chain that contains two end terminals on opposite sides.
what are the end terminals called?
N-terminus (amino terminus)
C-terminus (carboxyl terminus)
N-terminus (amino terminus) of a polypeptide is the side that
ends with the last amino acid’s amino group.
The C-terminus (carboxyl terminus) of a polypeptide is the side that
ends with the last amino acid’s carboxyl group.
Conjugated proteins are?
proteins that are composed of amino acids and non-protein components
2 types of Conjugated proteins are?
Metalloproteins (ex. hemoglobin)
Glycoprotein (ex. mucin)
Metalloproteins (ex. hemoglobin)
proteins that contain a metal ion cofactor.
Glycoprotein (ex. mucin)
proteins that contain a carbohydrate group.
Protein structure includes
1. Primary structure
2. Secondary structure
3. Tertiary structure
4. Quaternary structure
Primary structure
sequence of amino acids connected through peptide bonds.
Secondary structure
intermolecular forces between the polypeptide backbone (not R-groups) due to hydrogen bonding. Forms α-helices or β-pleated sheets
3. Tertiary structure
three-dimensional structure due to interactions between R-groups. Can create hydrophobic interactions based on the R-groups. Disulfide bonds are created by covalent bonding between the R-groups of two cysteine amino acids. Hydrogen bonding and ionic bonding between R groups also hold together the tertiary structure.
4. Quaternary structure
multiple polypeptide chains come together to form one protein
Protein denaturation
the loss of protein function and higher order structures. Only the primary structure is unaffected.
Proteins will denature as a result of…
high or low temperatures, pH changes, and salt concentrations
Protein functions (there are 6)
Storage = Reserve of amino acids
Hormones = Signaling molecules that regulate physiological processes
Receptors = Proteins in cell membranes which bind to signal molecules
Structure = Provide strength and support to tissues (hair, spider silk)
Immunity = Antibodies that protect against foreign substances
Enzymes = Regulate rate of chemical reactions
Catalysts do what to reaction rates?
increase reaction rates
How do catalysts increase reaction rates?
by lowering activation energy of a reaction
The transition state is
the unstable conformation between the reactants and the products.
Catalysts reduce the energy of
the transition state.
Catalysts do NOT what?
shift a chemical reaction or affect spontaneity.
Enzymes act as biological catalysts by
binding to substrates (reactants) and converting them into products.
Active site
Where enzymes bind to substrates and is specific for the substrate that it acts upon
Most enzymes are
proteins
The specificity constant measures
how efficient an enzyme is at binding to the substrate and converting it to a product
The induced fit theory describes
how the active site molds itself and changes shape to fit the substrate when it binds. The “lock and key” model is an outdated theory of how substrates bind.
A ribozyme is
an RNA molecule that can act as an enzyme (a non-protein enzyme).
A cofactor
is a non-protein molecule that helps enzymes perform reactions
A coenzyme is
an organic cofactor (i.e. vitamins). Inorganic cofactors are usually metal ions
Holoenzymes
are enzymes that are bound to their cofactors
apoenzymes
are enzymes that are not bound to their cofactors.
Prosthetic groups
are cofactors that are tightly or covalently bonded to their enzymes.
Enzymes catalyze reactions in the following ways:
● Conformational changes that bring reactive groups closer.
● The presence of acidic or basic groups.
● Induced fit of the enzyme-substrate complex.
● Electrostatic attractions between the enzyme and substrate.
Phosphatase
Cleaves a phosphate group off of a substrate molecule
Phosphorylase
Directly adds a phosphate group to a substrate molecule by breaking bonds within a substrate molecule
Kinase
Indirectly adds a phosphate group to a substrate molecule by transferring a phosphate group from an ATP molecule. These enzymes do not break bonds to add the phosphate group.
Feedback regulation of enzymes
the end product of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction inhibits the enzyme’s activity by binding to an allosteric site.
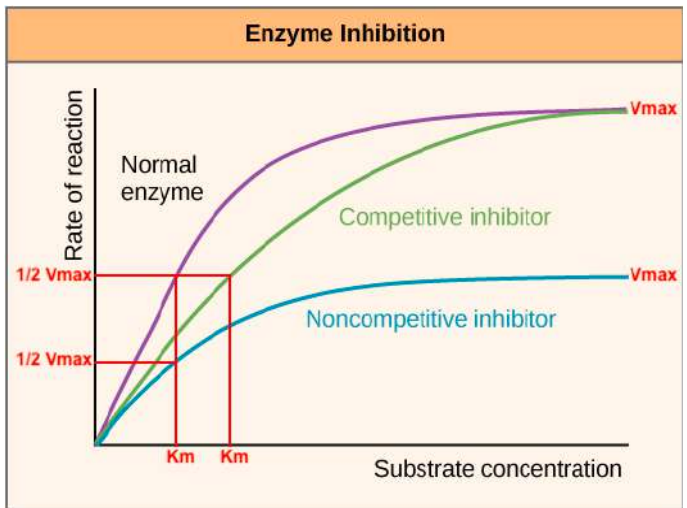
Competitive inhibition occurs when
an inhibitor competes directly with the substrate for active site binding. Adding more substrate can increase enzyme action.
Noncompetitive inhibition occurs when
the noncompetitive inhibitor binds to an allosteric site (a location on an enzyme that is different from the active site) that modifies the active site. In noncompetitive inhibition, the rate of enzyme action cannot be increased by adding more substrate.
Vmax is
the maximum reaction velocity
Michaelis Constant (KM )
is the substrate concentration [X] at which the velocity (V) is 50% of the maximum reaction velocity (Vmax).
Saturation occurs when
all active sites are occupied, so the rate of reaction does not increase anymore despite increasing substrate concentration (causes graph plateaus).
Competitive inhibition → KM ———, while Vmax ———
Km increases
stays the same
Noncompetitive inhibition → KM ———, while Vmax ———-?
KM stays the same,
while Vmax decreases
enzyme kinetics plot
Lipids contain…
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (CHO), like carbohydrates
Lipids have long hydrocarbon tails that make them what?
make them very hydrophobic.
Triacylglycerol (triglyceride) is a lipid molecule with a ———- backbone and ———-
a glycerol backbone (three carbons and three hydroxyl groups)
and three fatty acids (long hydrocarbon tails).
Glycerol and the three fatty acids are connected by
ester linkages
Unsaturated fatty acids
have double bonds.
Saturated fatty acids
have NO double bonds and as a result pack tightly (solid at room temperature).
What is the difference between monounsaturated fatty acids and polyunsaturated fatty acids?
one has 1 double bond while the other fatty acid have has 2 or more double bonds.
what is the difference between cis-unsaturated fatty acids and trans-unsaturated fatty acids?
Cis-unsaturated fatty acids have kinks that cause the hydrocarbon tails to bend. As a result, they do not pack tightly.
Trans-unsaturated fatty acids have straighter hydrocarbon tails, so they pack tightly.
Phospholipids are lipid molecules that have
glycerol backbone, one phosphate group, and two fatty acid tails
Phospholipids have a phosphate group that is polar, while the fatty acids are nonpolar therefore
amphipathic (both hydrophobic and hydrophilic)
Cholesterol is an amphipathic lipid molecule that is a component of the cell membranes. It is the most common precursor to
It is also the starting material for
steroid hormones (lipids with four hydrocarbon rings)
vitamin D and bile acids
What are the factors that influence membrane fluidity:
Temperature - ↑ temperatures increase fluidity while ↓ temperatures decrease it.
Cholesterol - holds membrane together at high temperatures and keeps membrane fluid at low temperatures. (acts kind of as a buffer to counteract temp)
Degrees of unsaturation - saturated fatty acids pack more tightly than unsaturated fatty acids, which have double bonds that may introduce kinks
Lipoproteins
allow the transport of lipid molecules in the bloodstream due to an outer coat of phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins.
Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) is also called “Bad cholesterol ”, why is this?
can cause vessel blockage and heart disease.
Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)
have low protein density and work to deliver cholesterol to peripheral tissues.
High-density lipoproteins (HDLs)
have high protein density and take cholesterol away from peripheral tissues
High-density lipoproteins (HDLs) is also called “Good cholesterol ” because why?
they deliver cholesterol to the liver to make bile (reduces blood lipid levels).
what is used mainly as hydrophobic protective coatings? and what are there composition?
Waxes which are simple lipids with long fatty acid chains connected to monohydroxy alcohols (contain a single hydroxyl group) through ester linkages
Carotenoids
lipid derivatives containing long carbon chains with conjugated double bonds and six-membered rings at each end. They function mainly as pigments.
Sphingolipids
have a backbone with aliphatic (non-aromatic) amino alcohols and have important functions in structural support, signal transduction, and cell recognition.
Glycolipids
are lipids found in the cell membrane with a carbohydrate group attached instead of a phosphate group in phospholipids. Like phospholipids, they are amphipathic and contain a polar head and a fatty acid chain.
Nucleic acids contain what elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus atoms (CHONP)
Nucleic acids contain
nucleotide monomers that build into DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) polymers
Nucleosides
contain a five-carbon sugar and a nitrogenous base.
Nucleotides
contain a five-carbon sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group.