Early Childhood Exam
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
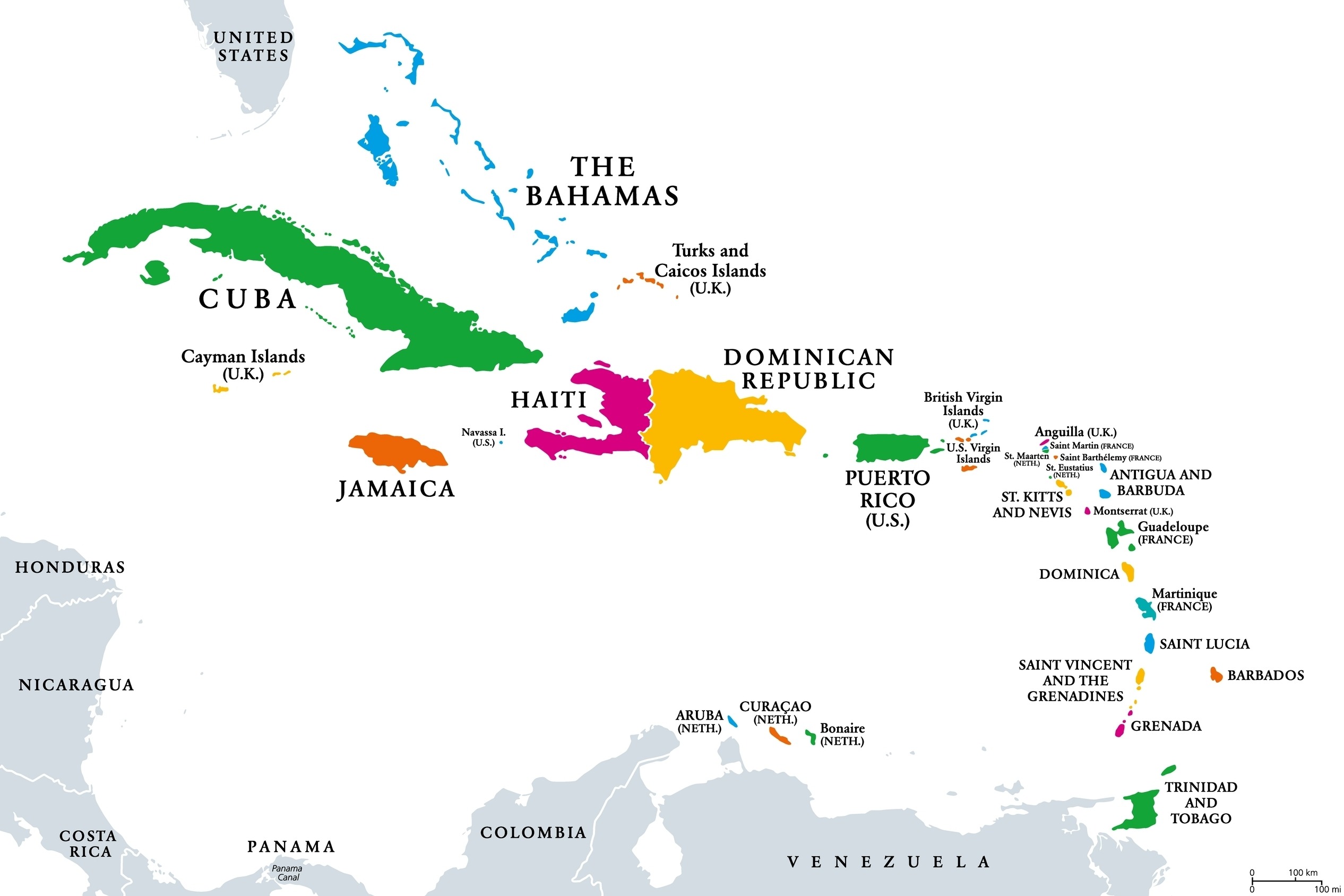
West Indes
collection of islands in the caribeian including Haiti, Cuba, the Bahamas, Jamaica, Barbados, etc. Seperates the Caribean Sea from the Atlantic Ocean
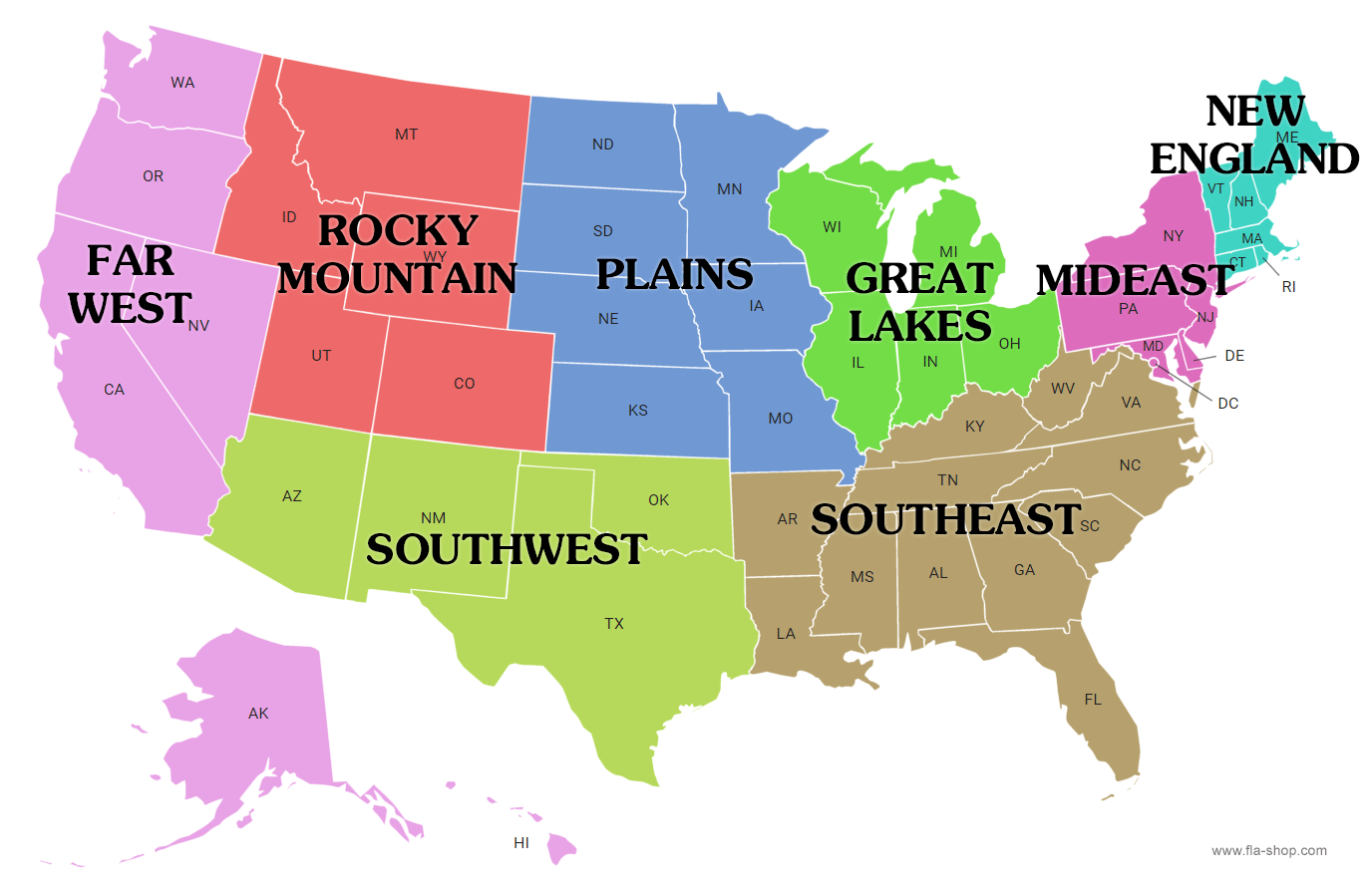
Subregions of the US
Far west/pacific Coast
Rocky Mountains
Southwest
Southeast
Great Plains
Great Lakes
Mideast
New England
the 5 Oceans
Indian
Atlantic
Pacific
Arctic
Southern (Antarctic)

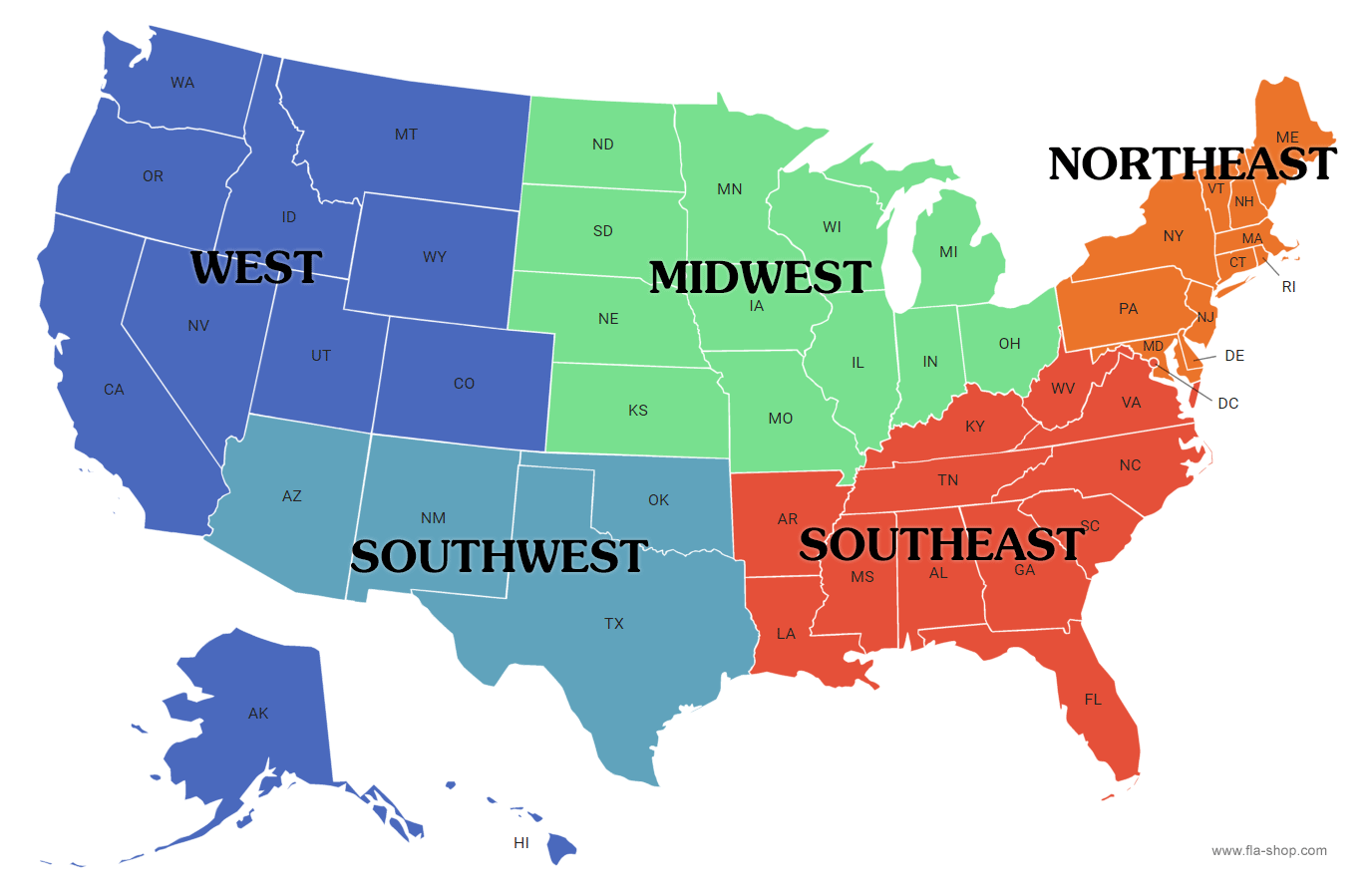
Regions of the US
North East
Midwest
West
South West
South East
X ∩ Y?
intersection aka all common items
X U Y?
union, aka combination, all items in both x and y
Piaget
cognitive constructivist, focused on individual discovery
Sensorimotor (0-2) senses
Pre operational (2-7) develops language, uses symbols
Concrete Operational (7-11) thinks logically about concrete events
Formal Operational (12+) abstract thinking
Vygostsky
Sociocultural, learn through more knowledgeable others (ZPD)
Erickson
psychosocial
trust vs mistrust (0-1)
Autonomy vs shame (1-3)
Initiative vs guilt (3-6)
Industry vs inferiority (7-11)
Identity vs confusion (12-18)
Intimacy vs isolation (19-29)
Generativity vs stagnation (30-64)
Integrity vs despair (65+)
Freud
psychosexual
Oral (0-2)
Anal (2-3)
Phallic (3-6)
Latency (6-puberty)
Genital (puberty)
Bandura
social learning theory, cognitive processes alongside experiences
Bobo doll experiment
Brofenbrenner
Ecological Systems theory

Kohlberg
moral development
Pre conventional—
Obedience & Punishment- fear of trouble
Self Interest
Conventional—
Interpersonal Accord & Conformity- what do other ppl think?
Authority & Social Order- what are the rules?
Post Conventional—
Social Contract- do the rules serve everyone fairly?
Universal Ethical Principles- abstract self chosen principles
Lewis Carroll
Alice and Wonderland
Hans Christian Anderson
Fairytales (Thumbelina, The Little Mermaid, The Ugly Duckling)
Beatrix potter
Peter Rabbit
C.S Lewis
Narnia
EB White
Charlottes Web
Jan Brett
The Mitten, The Hat
Mitsumasa Anno
Annos counting book
Margaret Wise Brown
Good night moon
Carlo Collodi
Pinocchio
L Frank Baum
Wizard of OZ
Robert Louis Stevenson
Treasure Island
Rudyard Kipling
Jungle Book
Fable vs Folktale
Folktale is the broad category of traditional stories passed down orally reflecting a lesson or custom.
Fables are brief and often use talking animals to display a universal moral
fables ALWAYS have a clear moral, folktales SOMETIMES do and fantasy’s RARELY do
Fantasy
A genre that includes magical elements and imaginative settings
IEP- purpose and procedure
purpose- to provide a legally binding educational plan, ensuring they receive free appropriate public education and outlines goals, supports etc.
Procedure- referral, evaluation, determining eligibility, developing plan with the IEP team (parents, special ed teacher, general ed teacher,rep of school system, eval interpreter), implementation, review, reevaluate
IFSP Individualized Family Service Plan- purpose and procedure
purpose- family centered approach to support children birth-3 by outlining goals and supports in a written plan
Procedure- referral, evaluation, team assembly, assessment, planning, documentation, implementation and review, transition planning to pre k as the approach 3 years old
504 plan
ensures equal access to education through providing supports and accommodations
IEP vs 504 plan
an IEP is more specific, intensive focusing on education while a 504 plan is more broad (IEP is under education act and 504 is civil rights)
To have an IEP you must have one of the 13 disabilities, while a 504 can apply for any disability
Threshold of responsiveness
how intense a stimulus must be for a child to react
Cognitive dissonance
mental discomfort from holding two or more conflicting beliefs (ex I know smoking is bad yet I still smoke)
oppositional identity
identity that emerges as a response to going against the norm/mainstream
social co-construction
Collaborative process of creating shared meaning or knowledge with others
identification
adopting another’s traits, behaviors or beliefs
induction
(aka generalization) the process where we draw a general conclusion from individual instances
Jargoning vs babbling
Babbling is when babies at 4-6 months make respective sounds (ba ba ba) Jargoning is when at 10-12 months babies will mimick adult speech, yet it is still nonsense words
Fragile X syndrome
genetic disorder, affects behavior and health
Links to autistic behavior, trouble with number sense
Turners Syndrome
missing or partially missing X chromosome, affecting health and growth
Symptoms: short stature, delayed puberty, webbed neck, learning disabilities, heart defect, verbal issues
Reye’s syndrome
swelling of the liver and brain due to an illness such as chickenpox
Cerebral palsy
cause by abnormal brain development or damage to the brain, affects muscle coordination and movement (static/ doesn’t worsen over time)
Absence seizure disorder
sudden brief blanking out spells caused by abnormal brain activity
Muscular dystrophy
muscle weakness and loss of muscle mass (worsens over time)
Cystic fibrosis
damage to the lungs and other organs (does not directly impact intellect)
dyspraxia
neurological condition affecting motor skills, orginization and coordination
spina bifida
spinal cord exposes, causing lower body paralysis
Intellectual challenges include difficulty with planning, attention and memory
Area formula- square/rectangle
A= l x w
Area formula- triangle
A= ½ b x h
area formula- circle
A= pie r squared
Area formula- parallelogram
A= b x h
Area formula- trapezoid
A= (a+b)/2 times h
Circle circumference formula
C= pie d
Surface Area formula- cube
SA= 6s squared
Surface Area formula- rectangular prism
SA= 2 (lw+ lh + wh)
Surface Area- cone
SA= pie x r squared+ pie x r x slant height
Surface Area- triangular pyramid and square prism
SA= sum of all face areas
Paralleogram
a four sided shape w two pairs of parallel sides
Surface area- triangular prism
SA= add up the areas of all the faces
Congruent
identical, in size and shape ( with angles and sides they have equal measure)
Perpendicular vs intersecting lines
perpendicular lines are a type of intersecting lines that must meet at a right angle, intersecting lines can meet at any point
Scalene triangle
No equal sides or angles
Isosceles triangle
2 equal sides and 2 equal angles
Median
Middle value from numerical order
Mode
most frequent value
Responsibilities shared by federal and state govt.
Taxation, establishing banks, administering courts, spending money for general welfare, establishing laws
Longitude vs Latitude
longitude is vertical (think LONG) latitude is horizontal (think lateral)
Cellular respiration
Process where cells turn nutrients and oxygen into energy (ATP) and release water and co2 as waste
Continents in Northern hemisphere
ALL OF North America, Europe MOST OF Africa and Asia SOME OF South America
Continents in Southern Hemisphere
ALL OF Antarctica, Australia, MOST OF South America SOME OF Africa
Continents in Western Hemisphere
ALL OF North and South America, SOME OF Africa, Antarctica, Europe and Asia
Continents in Eastern Hemisphere
ALL OF Australia MOST OF Europe, Asia and Africa SOME OF Antarctica
Direct vs representative democracy
direct democracy is where the people directly vote on laws vs a representiave democracy where the people vote on elected officials to then vote on laws on the peoples behalf
Popular Sovernity
the principle that the people hold the political authority (officals must serve the interest of the public)
Market Economy
A system where the production and distribution of goods are guided by individuals interaction with businesses rather than by a central government
Federal/enumerated powers
tariffs, borrowing money, commerce, naturalization rules, bankruptcy rules, coining money, creating post roads and offices, declaring war
State/reserved powers
Education, public health and safety, elections, family law,
Naturalization rules
18+
Permanent resident for at least 5 years
How does a bill become a law?
an idea is crafted (bill) and presented to either HOR or the senate
The bill is sent for a committee review
The bill is debated and voted on, then sent to the other chamber (HOR or senate)
Is house and senate disagree, a conference committee with members from both chambers is held and they come to a compromise (conference report)
Both house and senate must approve in a final vote
Presidential action takes place
Pervasive Development Disorder
category of neurodevelopmental disorders primarily encompassed by autism disorders, characterized by social and communicative impairments and repetitive behaviors and interests
ASD
Retts syndrome
Childhood Disintegrated Disorder
Childhood Disintegrated Disorder
Late onset (3-4 years) delays in language, social skills, and motor dev.
Resembles autism, reject social interaction
Rett Syndrome
Normal early development followed at 6-18 months where skills are lost, affects motor and language skills
Mostly occurs in girls, characterized by hand wringing and prolonged eye contact
Stages of Play
Unoccupied (0-3 months)
Solitary (0-2)
Onlooker (2)
Parallel (2+)
Associate (3-4)
Cooperative (4+)
Renaissance
1300-1500
Rebirth of art science and culture after the classical Antiguity period
Bridged Middle Ages and early modern era
Classical Antiguity
Greece and Roman ancient civilizations, built upon Bronze Age civilization, ended upon the fall of the western Roman Empire
Middle Ages/ Medevial
Characterized by feudalism (land for service), rise of the church, spread of the black plague
The Scientific Revolution
16-17th century, focus on natural laws in the universe, big on discoveries
Enlightenment
the scientific era 18th century where discoveries were applied to politics, reform,etc
Copernicus
Found the heliocentric model (places the sun not earth at the center of the universe)
Kepler
discovered laws of planetary motion (elliptical orbits, equal areas in equal times, and orbital period/distance relationship)
Galileo
Improved the telescope to then discover jupiters moons and the phases of Venus
Vesalius
Made anatomical disocvereis based on dissection
Boyles laws
Pressure and volume for gas is inversely proportional
Harvey
descibed circulation of blood
Leewenhoek
The microscope, discovered microorganisms
French Indian war/seven years war
French+native allies fought against Britain for expansion of colonization
Treaty of Paris
Britain secured all French territory east of Mississippi River
Britain heavily taxed the 13 colonies
Boston Massacre
British troops sent to Boston over tension over taxes
Boston tea party
sons of liberty/patriots disguised as natives, threw tea overboard on British ships
Second Continental congress
militias reorganized to form the continental army to follow Washington into battle