chemical bonding
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
compound
a substance that is made up of two or more elements chemically combined
compound with -ide
compound with -ate
ide: contains two elements
ate: contains two or three elemts (one is an oxygen)
molecule
group of atoms joined together
def: Octet rule
when bonding occurs atoms tend to reach the electron arrangement with eight electron in their outermost energy level.
exceptions to the octet rule
transition metals
Hydrogen, Lithium and Beryllium (achieve two electrons in their energy level)
def: Ionic bonding
the force of attraction between oppositely charged ions in a compound
ionic bonding
transfer of electrons
between metals and nonmetals
def: ion
charged atom/group of atoms
about an ion
an atom becomes an ion when it gains or loses electrons
square brackets represent ions
elements in group 1,2 and 3: positive cations
Elements in Group | Lose | charge |
1 (I) | 1 electron | 1+ |
2 (II) | 2 electrons | 2+ |
3 (III) | 3 electrons | 3+ |
elements in group 6 and 7: negative anions
Elements in group | gain | charge |
6 (VI) | 2 electrons | 2- |
7(VII) | 1 electron | 1- |
formulas of ionic compounds
between non metals and metals
Group 1 and 2: metals - lose electrons
Group 6 and 7: non metals - gain electrons
complex ions
separate flashcards
metals are always__
non metals are always ___
metals - positive
non metals negative
when writing ionic compunds
Positive ion (metal) goes first
Negative ion (non-metal) goes second
Multiply by the smallest possible integer to make the + and - the same
If the ion is complex put it inside a bracket and put the subscript outside the bracket
crystal lattice structure
Three-dimensional arrangement of ions in a crystal.
Each single unit cell repeats itself in all directions to build up a crystal.
valency
the number of atoms of hydrogen that the element will combine with.
def: transition metal
one that forms at least one ion with a partially filled d sublevel.
Properties of Transition metals ***(applies to all transition metals except for scandium and zinc)
Have variable valency
Form coloured compounds
Widely used as catalysts
Covalent bonding
involves the sharing of electrons
overlap of orbitals
between nonmetals and nonmetals
single bond
double bond
triple bond
Single Bond- 2 electrons
Double Bond- 4 electrons
Triple Bond-6 electrons
molecule
group of atoms joined together
def: sigma bond
formed by the head on overlap of 2 circle or px orbitals
def: pi bond
formed by the sideways overlap of two pz or py orbitals
single bond:
double bond:
triple bond:
single bond: sigma bond
double bond: one sigma one pi bond
triple bond: one sigma and two pi bonds
properties of ionic and covalent bonds
Ionic | Covalent | |
1. | Contain a network of ions in crystals | Contains individual molecules |
2. | Usually hard and brittle | Usually soft |
3. | Have high melting and boiling points | Have low melting and boiling points |
4. | Solid at room temperature | Usually liquids, gases or soft solids at room temperature |
5. | Conduct electricity in molten state when dissolves in water | Do not conduct electricity. |
shapes of covalent molecules
tetrahedron
pyramidal
triagonal planar
v shapes/angular
linear
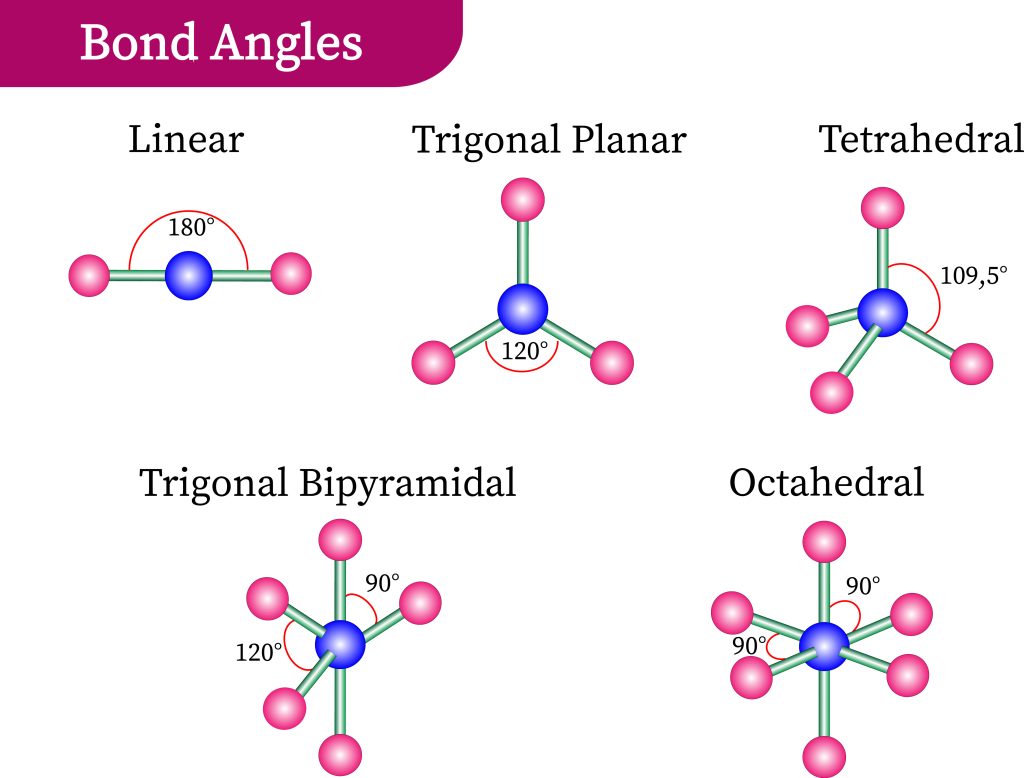
tetrahedron
bonding pairs: 4
lone pair: 0
bond angle: 109.5
no. of atoms: 5
pyramidal
bonding pairs: 3
lone pair: 1
bond angle: 17
no. of atoms: 4
triagonal planar
bonding pairs: 3
lone pairs:0
angles: 120
no. of atoms: 4
V shapes/ angular
bonding pairs: 2
lone pairs: 2
bond angle: 104.5
no. of atoms: 3
Linear
bonding pairs:2
lone pair: 0
bond angle: 180
no. of atoms: 3
exceptions
BF3 - Trigonal planar
BeCl - Linearexceptions regarding shapes of molecules
linear
tetrahedral
trigonal planar
(all non polar)
def: electronegativity
relative attraction that an atom in a molecule has for the shared pair of electrons in a single covalent bond
electronegativity in covalent bonds
one atom in a molecule has a greater pull - this means its more electronegative
non polar covalent
atoms in a molecule that share electrons equally
polar covalent
the atoms in a molecule that have an uneven distributin of electrons
use of electronegativity
to predict the polarity of covalent bonds
to predict which compounds are ionic and covalent
electronegativity values
Value | Bonding |
0 - 0.4 | Non polar covalent |
0.4 - 1.7 | Polar covalent |
Over 1.7 | Ionic bonding |
Equal or under 1.7 | Covalent bonding |
intramolecular bonding
bonding that takes place within a molecule
intermolecular forces
forces of attraction that exist between molecules
def: Van der Waals
weak attractive forces between molecules resulting from the temporary formation of temporary dipoles
between non polar molecules
the bigger and stronger the van der waal force
bigger - van der waal force gets bigger
stronger - higher boiling and melting point
def: dipole - dipole forces
forces of attraction between the negative pole of one molecule and the positive pole of another polar molecule
molecules with a permanent dipole
def: Hydrogen bonding
particular type of dipole-dipole bonding where the hydrogen atoms are bonded to Nitrogen, oxygen and Flourine.
hydrogen carries a partial positive charge and is attracted to the electrnegative atom (N,O or F)
how to tell which force it is
Van der Waals | Non- polar molecules (noble gases, hydrocarbons) |
Dipole-Dipole | Polar molecules |
Hydrogen Bonding | When hydrogen is bonded with an electronegative atom (N,O and F) |