Neuroanatomy: Brain Structures, Functions, and Key Regions
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
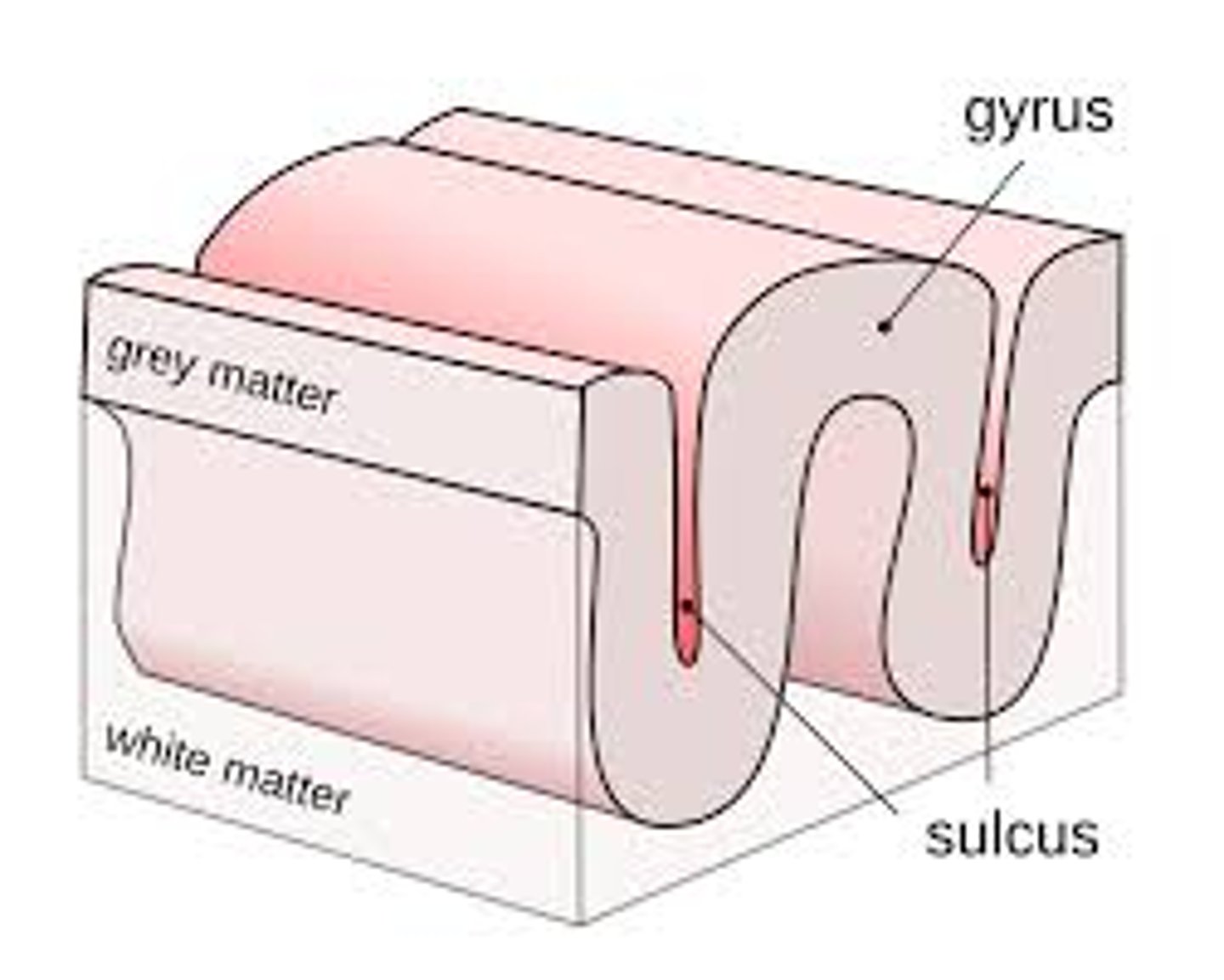
gyrus
a ridge of fold on the brain's surface
sulcus
a shallow groove between gyri
fissure
a deep groove or fissure in the brain
cerebral cortex
the outer gray layer of the cerebrum responsible for thinking and processing information
cerebral white matter
inner brain tissue made of myelinated nerve fibers that connect brain areas
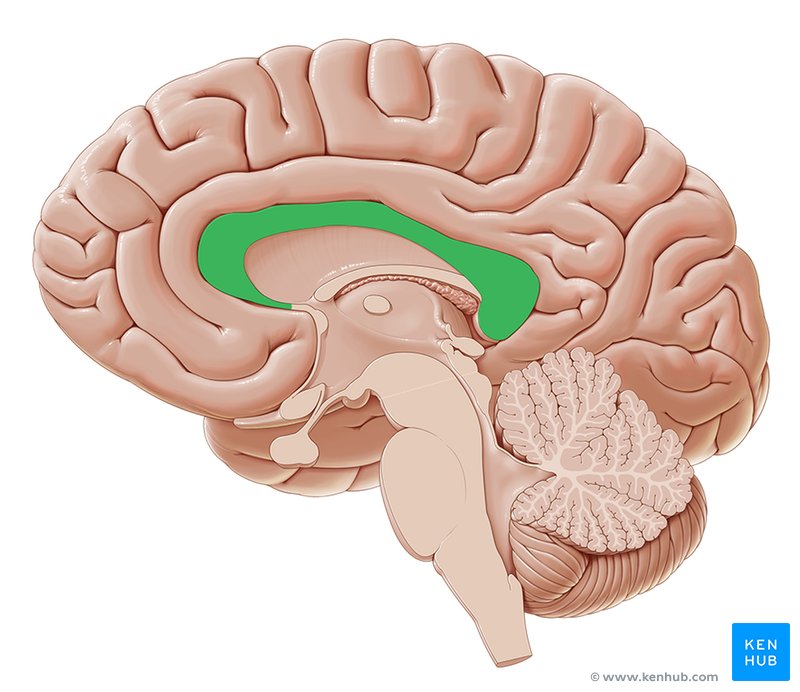
corpus callosum
nerve fibers connecting the left and right hemispheres
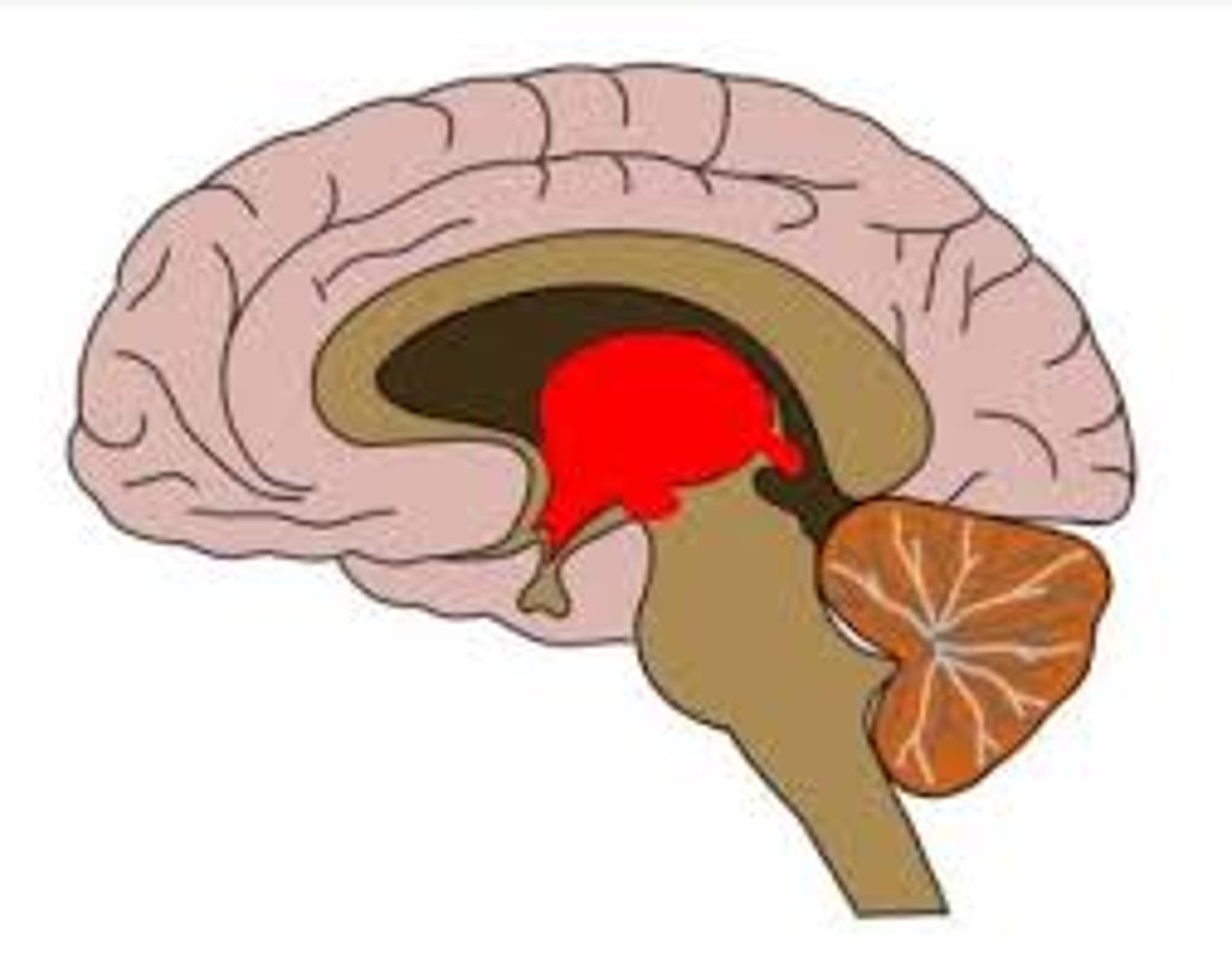
diencephalon
brain region containing the thalamus and hypothalamus, and pineal body
limbic system
controls emotions, memory, and motivation
meninges
three protective membranes around the brain and spinal cord
dura mater
tough outer layer of meninges
arachnoid mater
middle, web-like layer of the meninges
pia mater
thin inner layer that covers the brain surface
cerebrospinal fluid
fluid that cushions and protects the brain and spinal cord
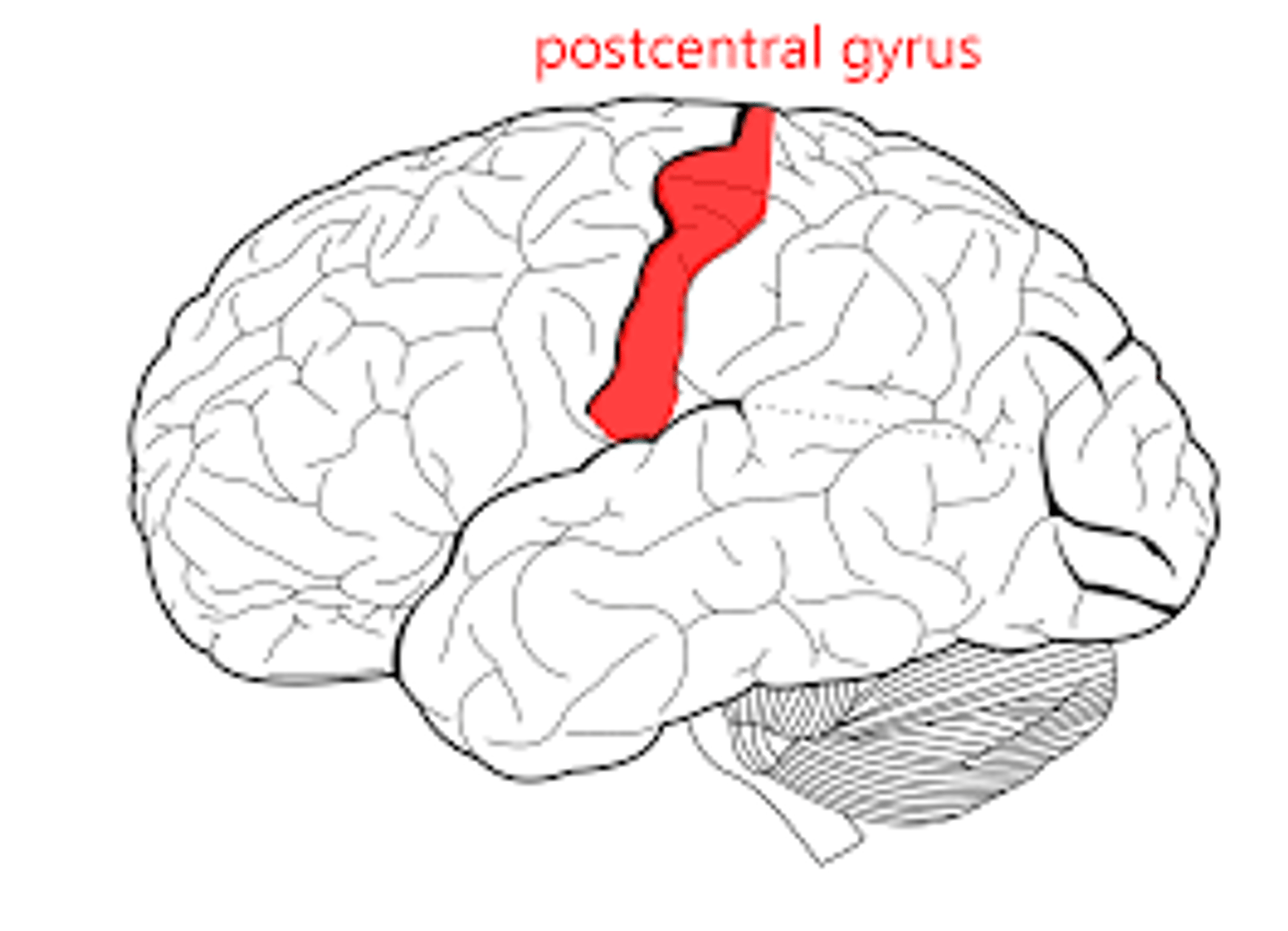
primary somatic sensory area
receives sensory information like touch, pain, and temperature
primary motor area
controls voluntary muscle movement
Broca's area
controls speech production
Wernicke's area
involved in understanding language
gray matter
brain tissue with neuron cell bodies; processes information
thalamus
relays sensory signals to the cerebral cortex
hypothalamus
regulates hunger, thirst, temperature, hormones, and metabolism.
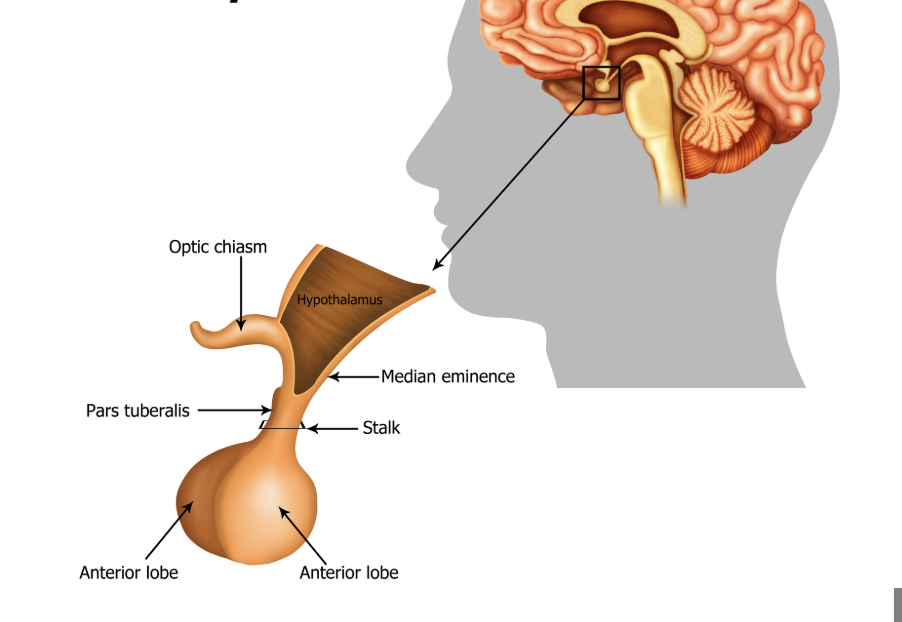
pituitary gland
secretes hormones that control other glands
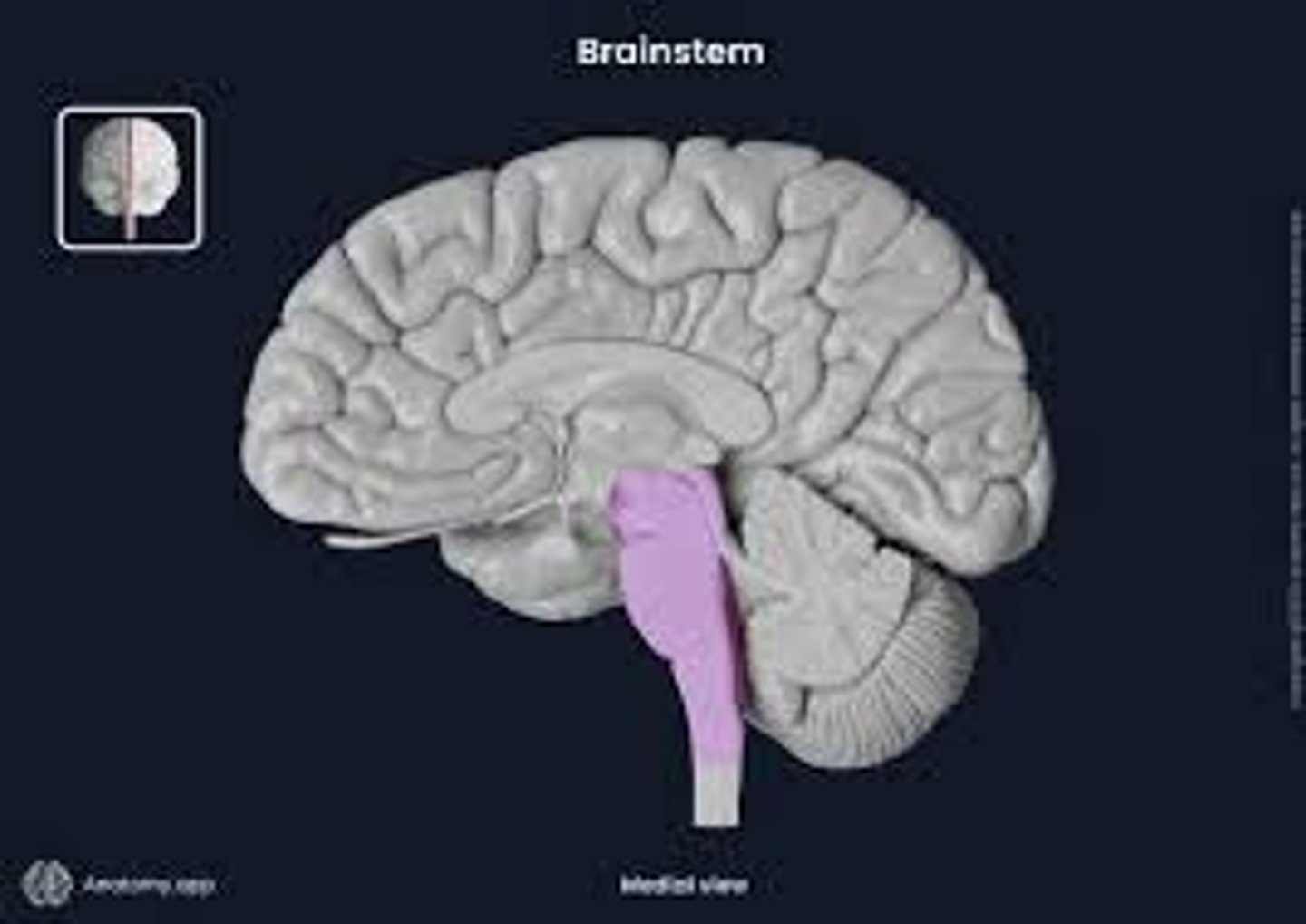
brain stem
connects brain and spinal cord, controls vital functions
midbrain
part of the brainstem involved in vision, hearing, and motor control
pons
links brain parts; helps control breathing
medulla oblongata
controls heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure
reticular activating system
maintains alertness and wakefulness
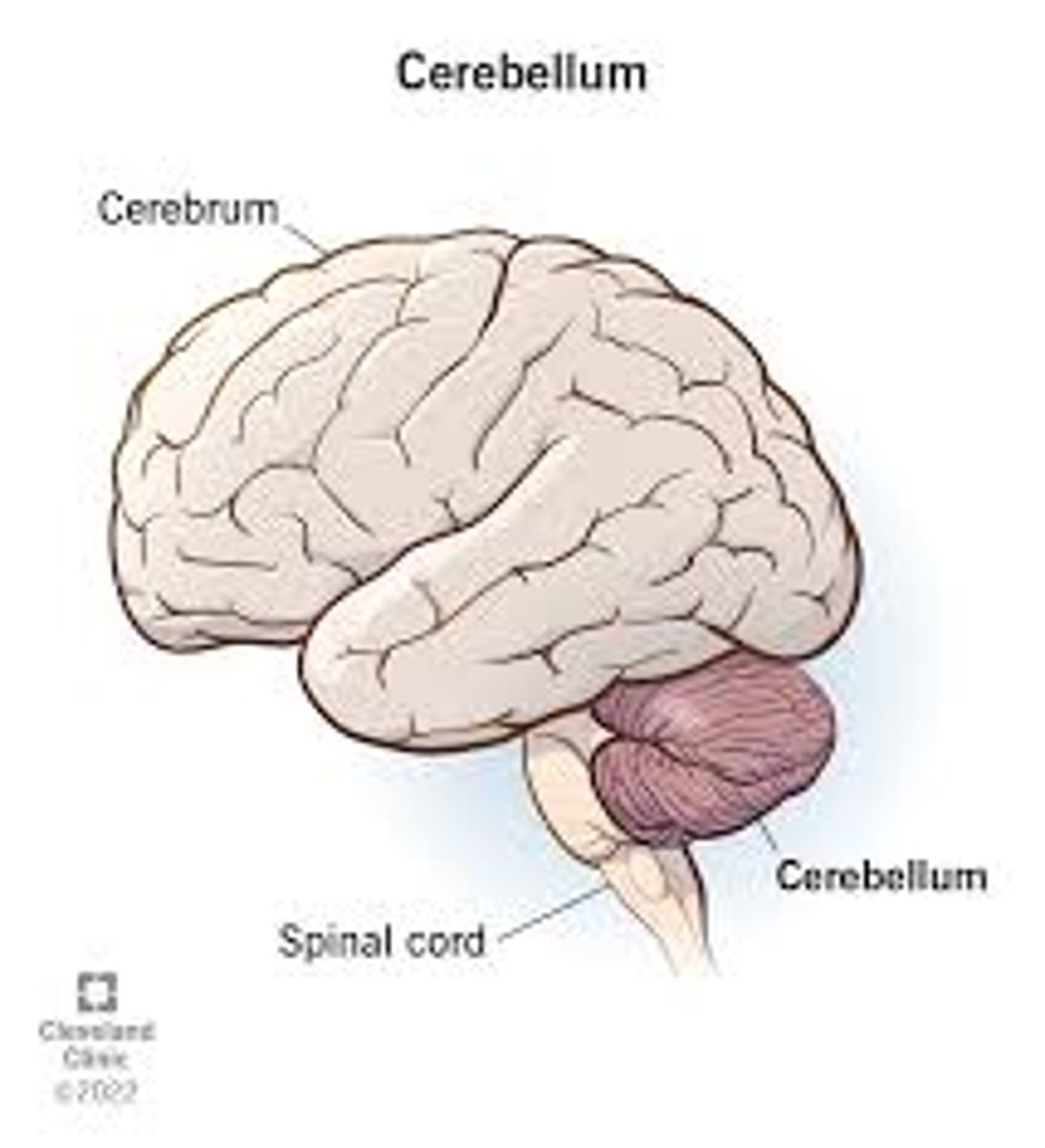
cerebellum
coordinates balance, posture, and movement
cerebral cortex
outer brain layer for higher thought and reasoning
cerebrum
Diencephalon
Cerebellum
Brainstem
midbrain
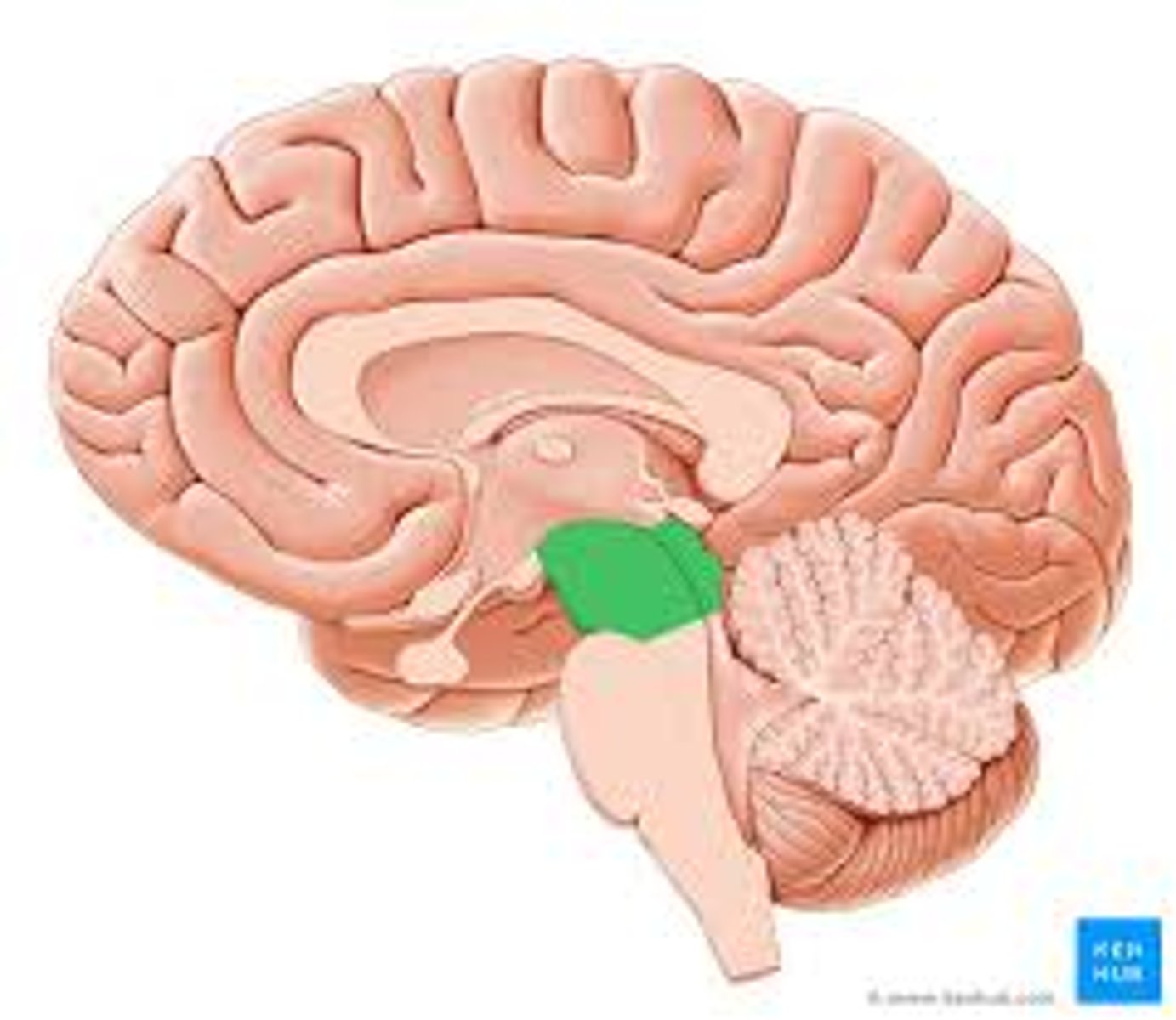
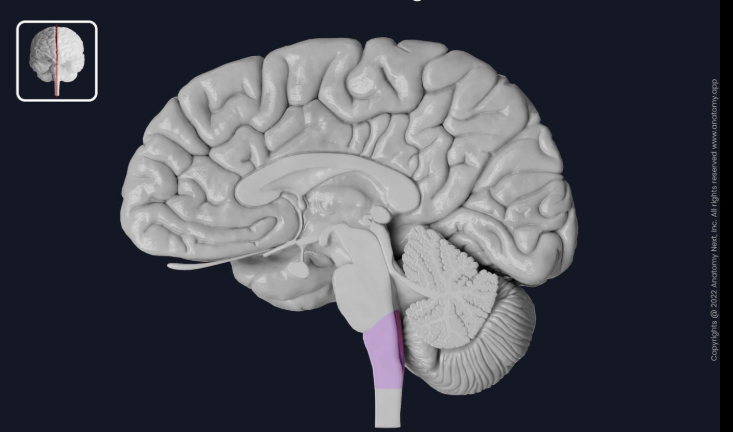
Pons
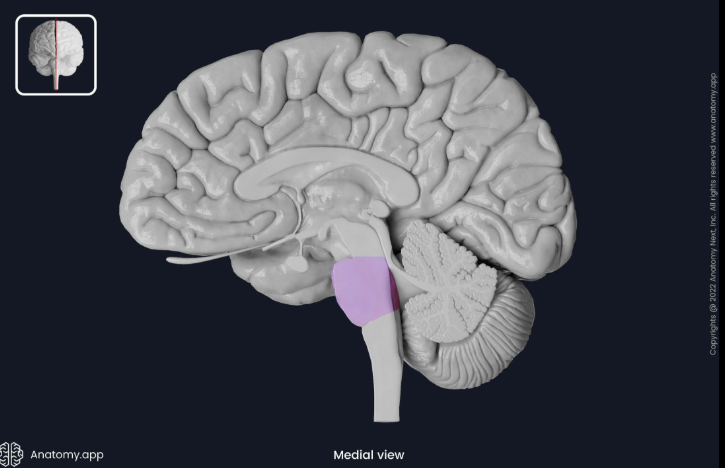
medulla oblongata
cerebral cortex
gyrus
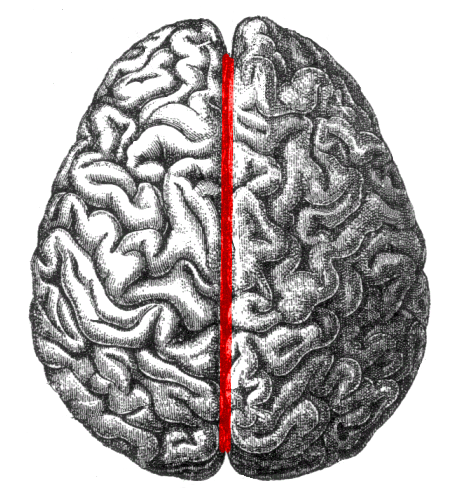
longitudinal fissure
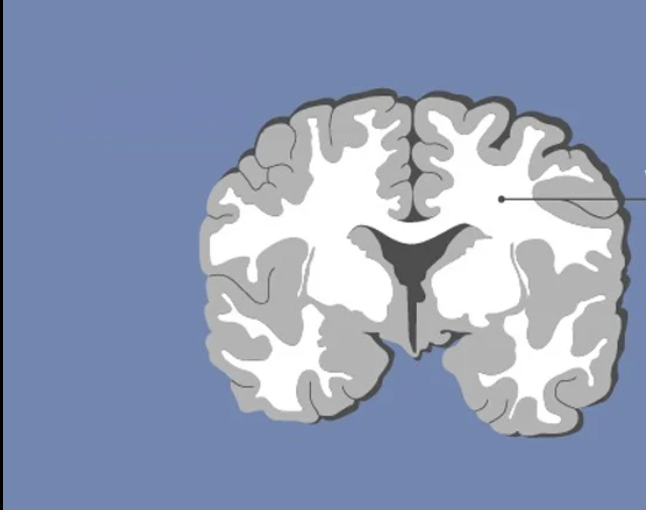
white matter
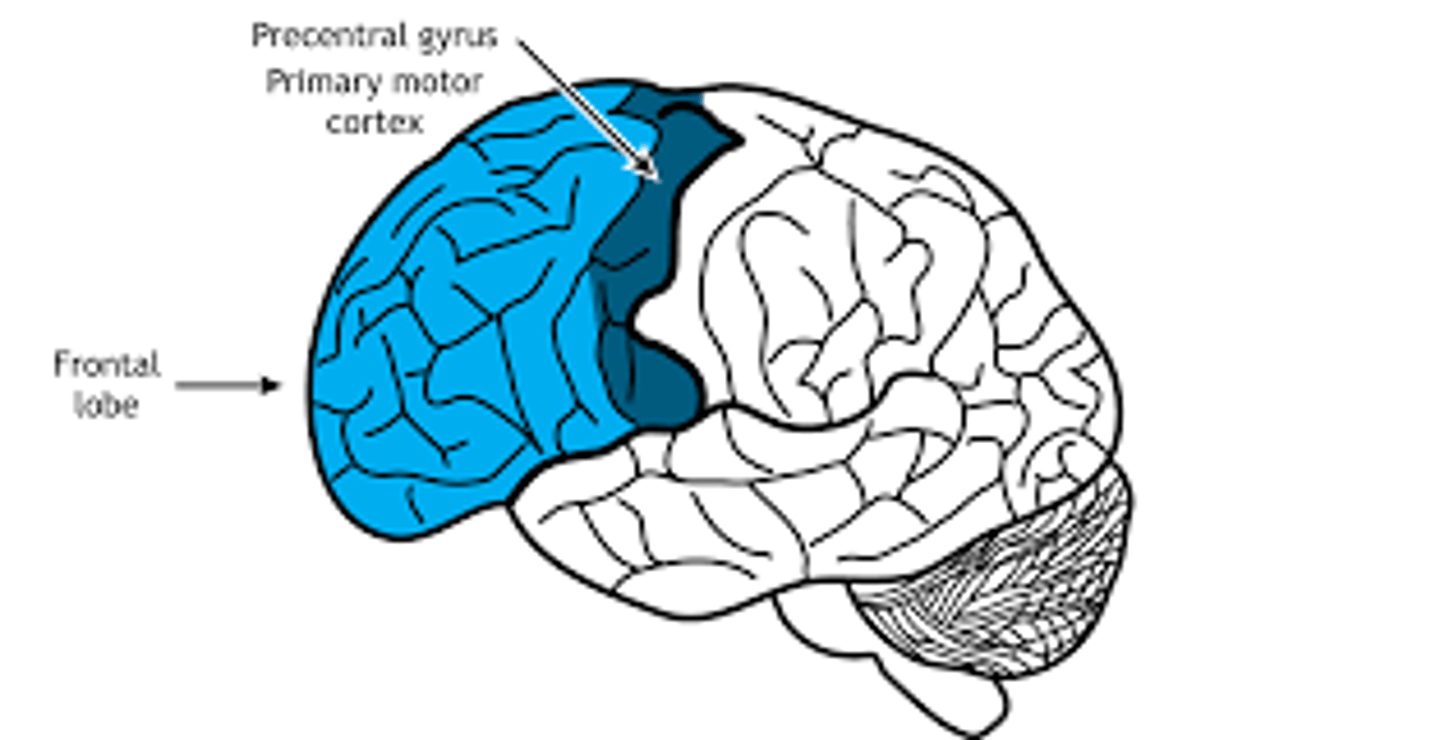
Frontal lobe
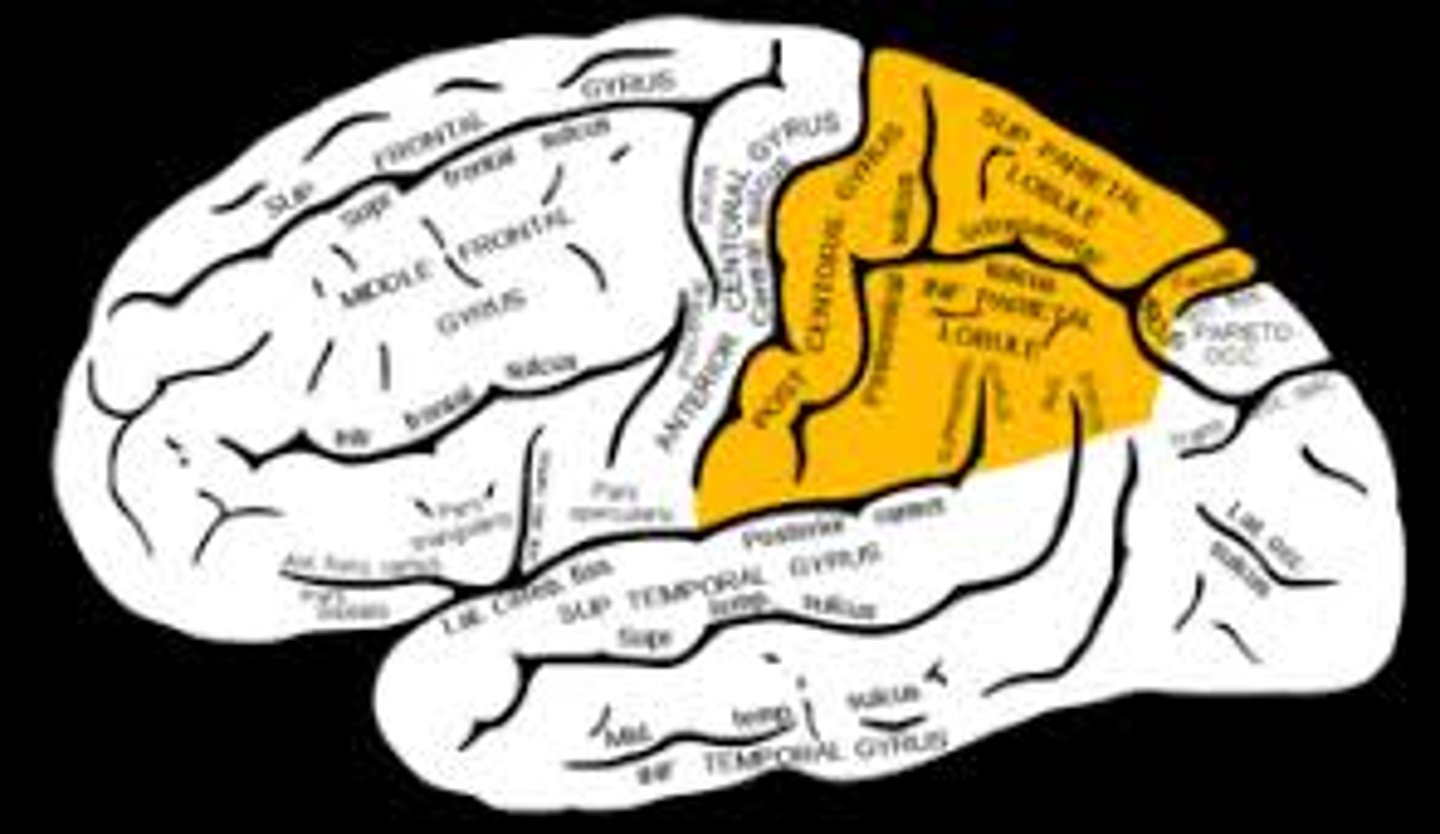
Parietal lobe
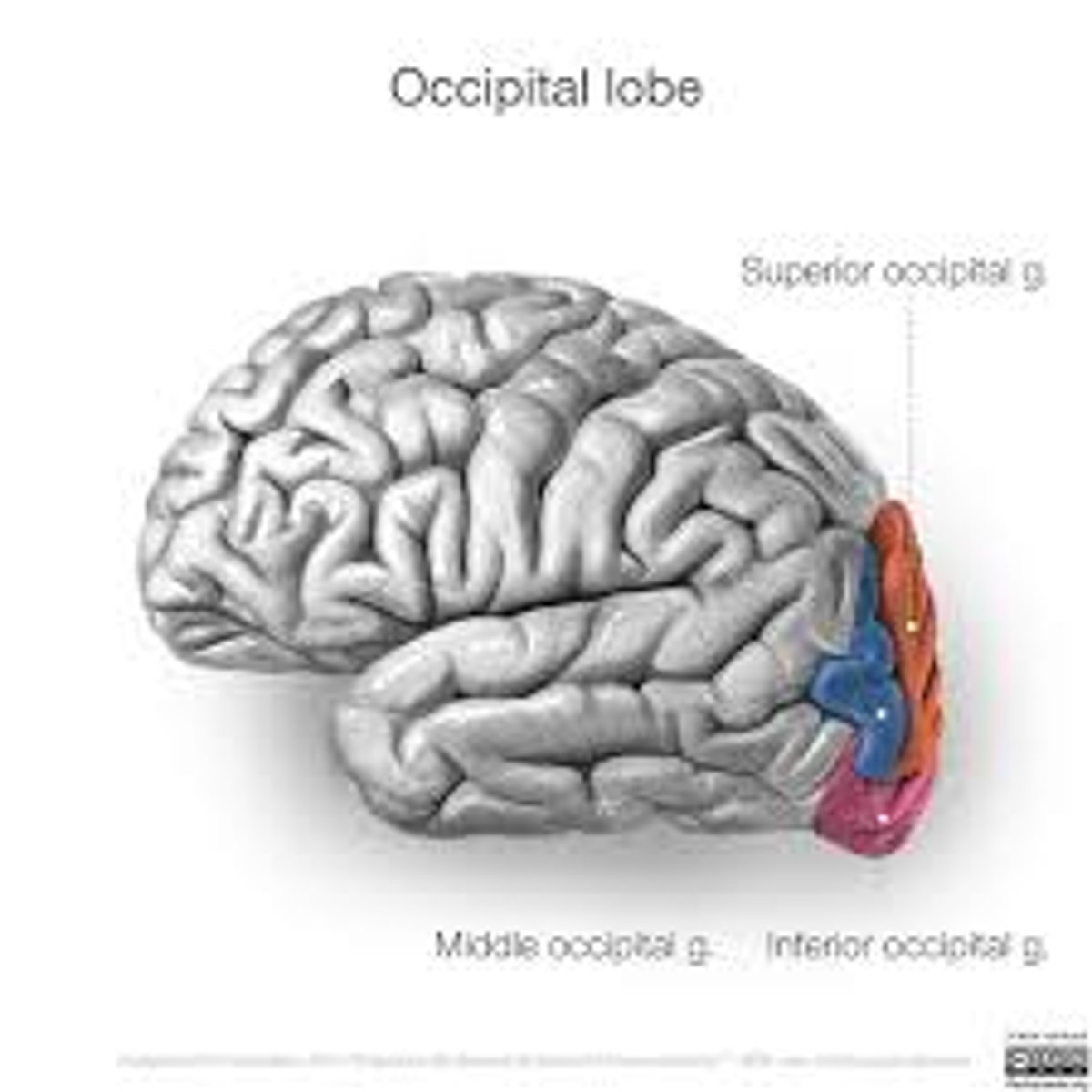
occipital lobe
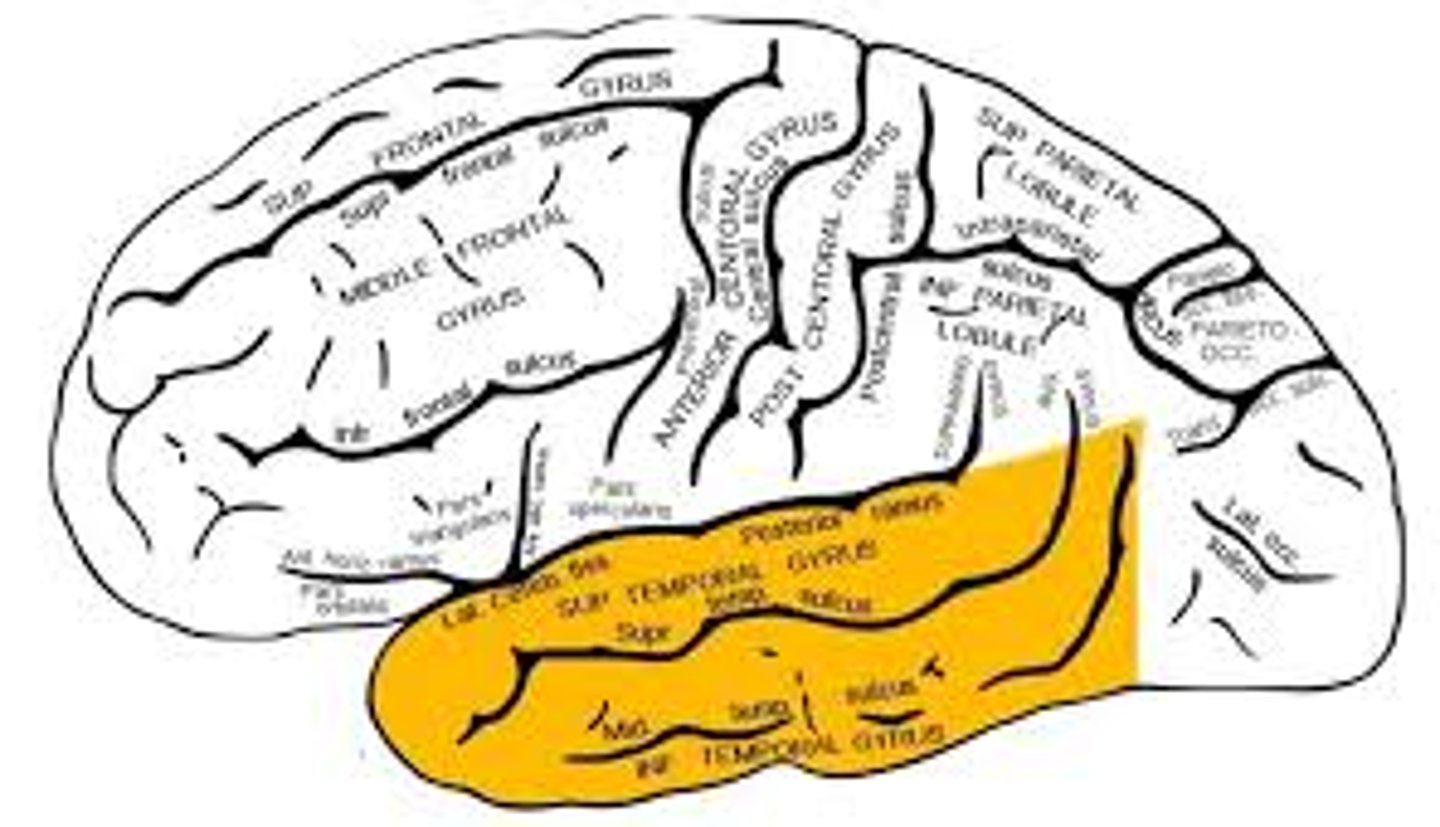
Temporal lobe
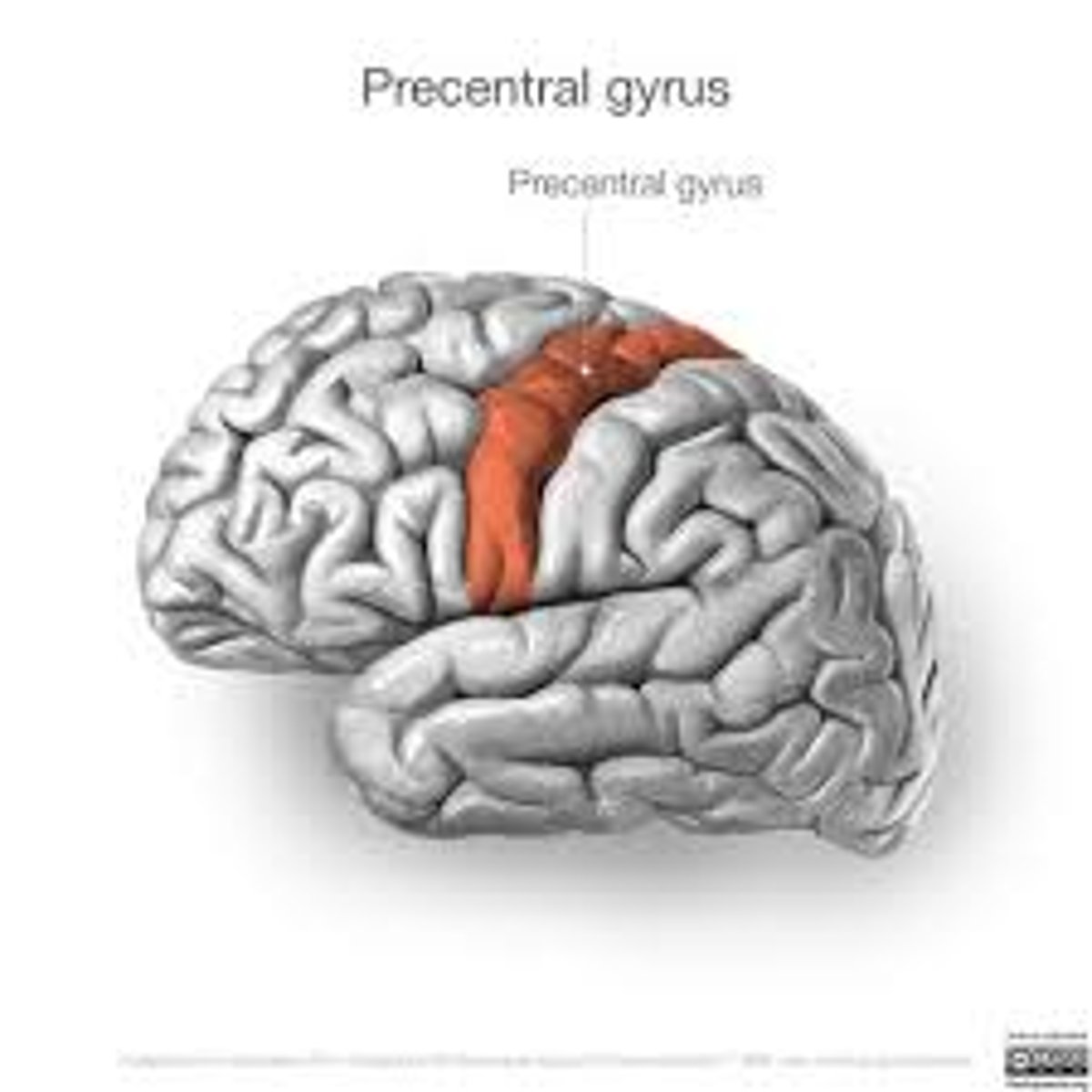
precentral gyrus
Postcentral Gyrus
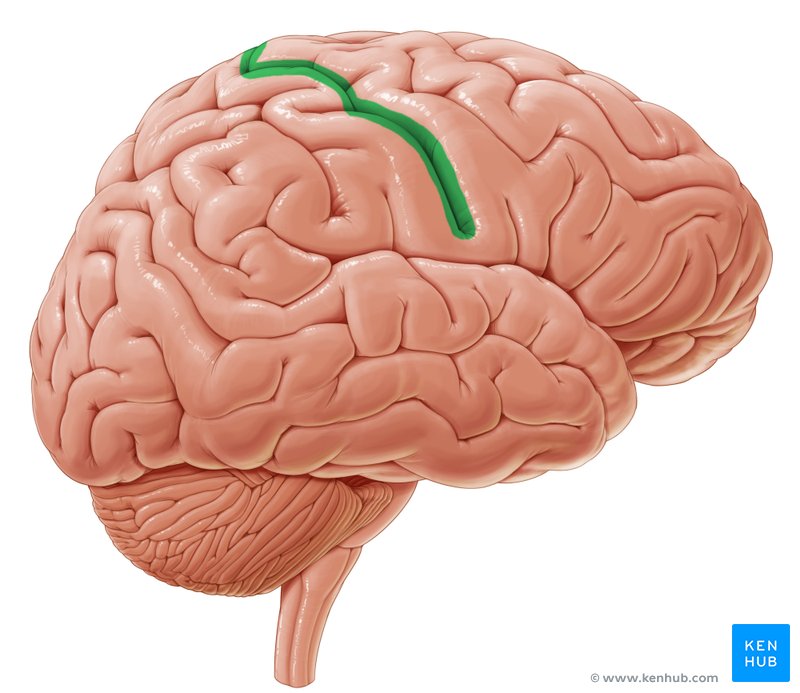
central sulcus
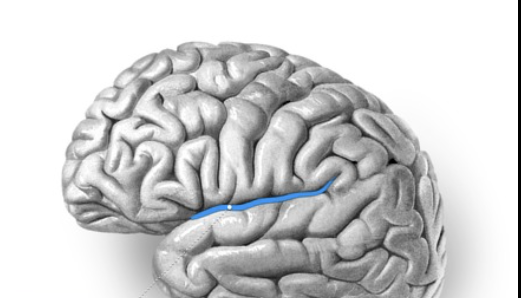
lateral sulcus
hypothalamus
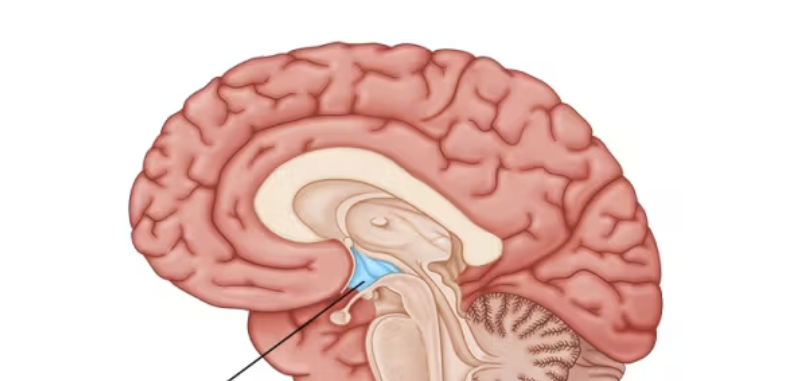
thalamus
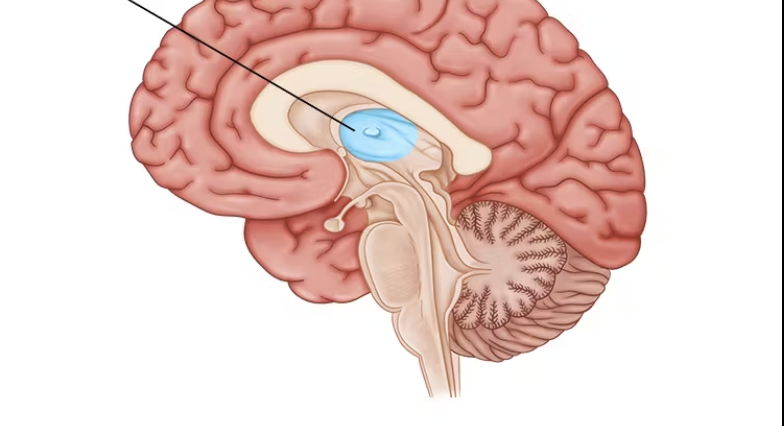
pineal body
pituitary gland
corpus callosum
brocas area
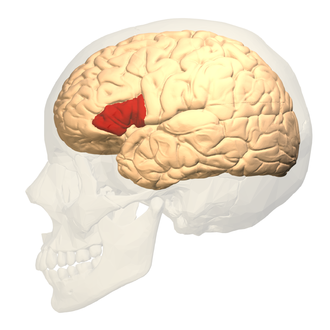
Wernicke's area
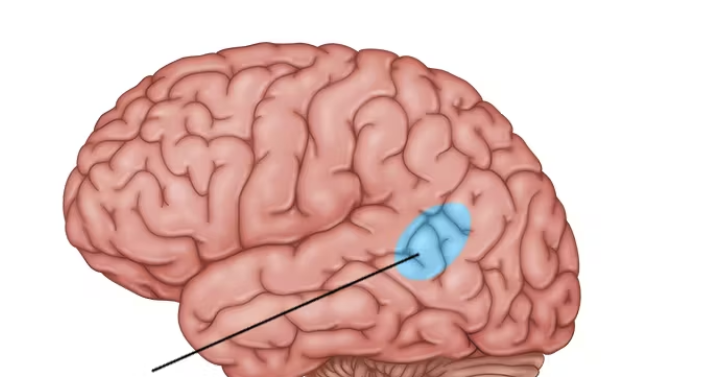
primary motor cortex
cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brain stem, cerebellum
4 main parts of brain
frontal lobe
Contains the primary motor area —allows us to move our skeletal muscles consciously, engage in higher-order thinking, comprehend language, and store some memories.
parietal lobes
Contains the primary somatic sensory area, which recognizes pain, coldness, or a light touch.
temporal lobe
auditory and olfactory regions
occipital lobe
visual area
epithalamus
Contains the pineal body, part of the endocrine system, and the choroid plexus, which forms cerebrospinal fluid.