IB Biology HL : energy transfers ecosystems- C4.2
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
food
nutrients which are broken down for energy
fundamentral concepts
energy is lost as they go up the food chain
ecosystems are affected by changes in the availability of energy and matter
biological processes depend on energy flow through earth’s system
the sun is the main source of fuel for ecosystems
food is a biofuel required by organisms to acquire energy for internal living processes
energy available to do useful work decreases as it’s transferred from organism to organism
energy flows though food webs in one direction from producers to consumers to decomposers
ecosystems are affected by changes in the availability of energy and matter.
humans are part of the earth ecosystem and influence energy flows through these systems
why does the total biomass of organisms higher up in the foodchain higher
some parts are not consummable; bones, hooves, horns
not all biomass is used; some isn’t consummed
some is lost to respiration
chemoautotrophs
oxidation of non-organic molecules, in unhospital conditions, eg sewers, geothermal vents
biomass
dry mass of organisms
pyramid of biomass advantages or disadvantages
gram m^-2
good
takes into account mass
bad
doesn’t take account of variation around year
some of the mass doesn’t get used up
pyramid of energy
kcal m^-2 yr^-1;
takes into account year on year variation
always are pyramid shaped
adaptations of maram grass
high resistance
fine, narrow leaves resisting strong winds and sandblasting
thick outer layer of waxy cuticle resists water loss
rolled leaves reduce SA for evaporation, conserving water
hairs inn the inner leaf epidermis reduce evaporation and air flow over the stomata to tolerate dessication
sunken stomata and rolled leaves decrease the humidity gradient and reduce water loss
extensive root systel allows for coping with moving sand and low nitrate in top soil
maram grass in embryo dunes
few odd plants
maram grass primary dune
larger tufts
little water
more biomatter
maram grass in mature dunes
less; more competition
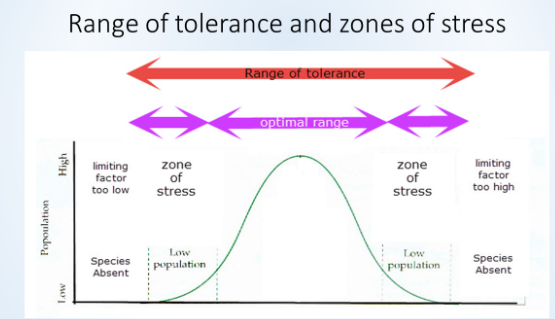
range of tolerance and zones of stress
zones of stress; end of zone of tolerance
mangroves conditions
brackish water: not salty nor fresh
constant flooding
little light
mangroves/ Rhizophora apiculata adaptations
stilt roots; gives structural integrity
halophyte; can survive in salty water
specialised roots; pneumatocytes; they respire even in waterlogged soil
seeds start to germinate while still attached to parent plant
coral reef conditions
warm water
sunlight for zooxanthellae
salt water; won’t growth at mouth of rivers
clear water; so no farming/freshwater treatment. no sediment
moderate wave action; not too strong
need inundation