Facial Bones, CNS, Sinuses
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
What are the largest immovable facial bones?
maxillary bones
Each maxilla assists in the formation of what three cavities?
1. mouth
2. nasal
3. one orbit
Where would you find maxillary sinuses?
body of maxilla
What is a cleft palate?
an opening between the two palatine processes
What two parts form the zygomatic arch?
posterior portion of zygomatic bone and zygomatic process of temporal bone
What are the thinnest and most fragile bones in the entire body?
lacrimal and nasal
Where are the lacrimal bones located?
anteriorly on medial side of each orbit
Where are the nasal bones located?
anterior and superior to frontal process of maxillae
Which of the nasal conchae is part of the facial bones?
inferior nasal conchae
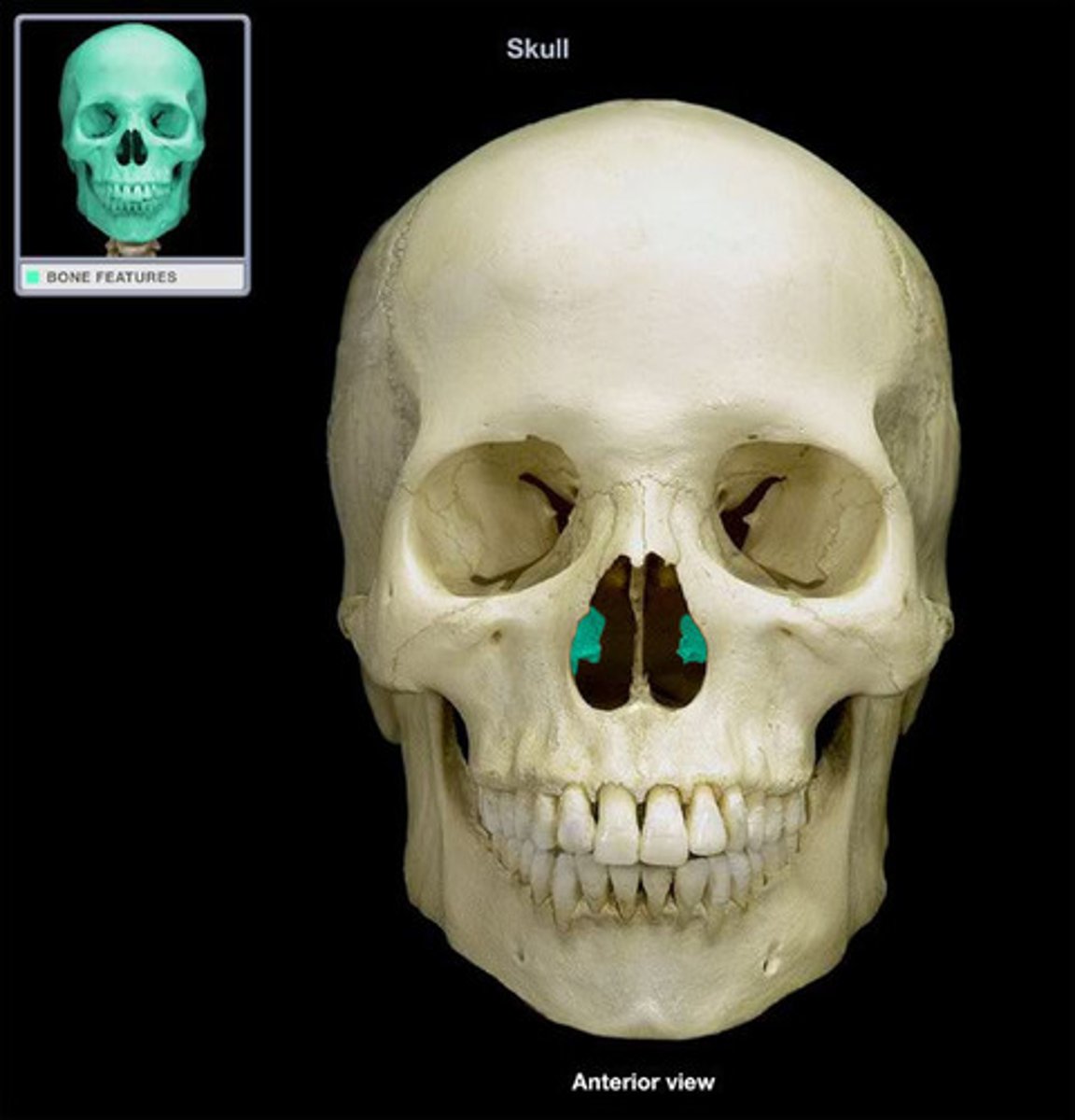
The three nasal conchae divide the nasal cavity into compartments which do what?
clean and warm air before it reaches lungs
Which portion of the palatine bones helps to form the posterior portion of the hard palate?
horizontal portion
This bone, together with the ethmoid bone, forms the nasal septum
vomer
Where at in the facial bones does a deviated septum occur?
vomer
What is the largest moveable facial bone?
mandible
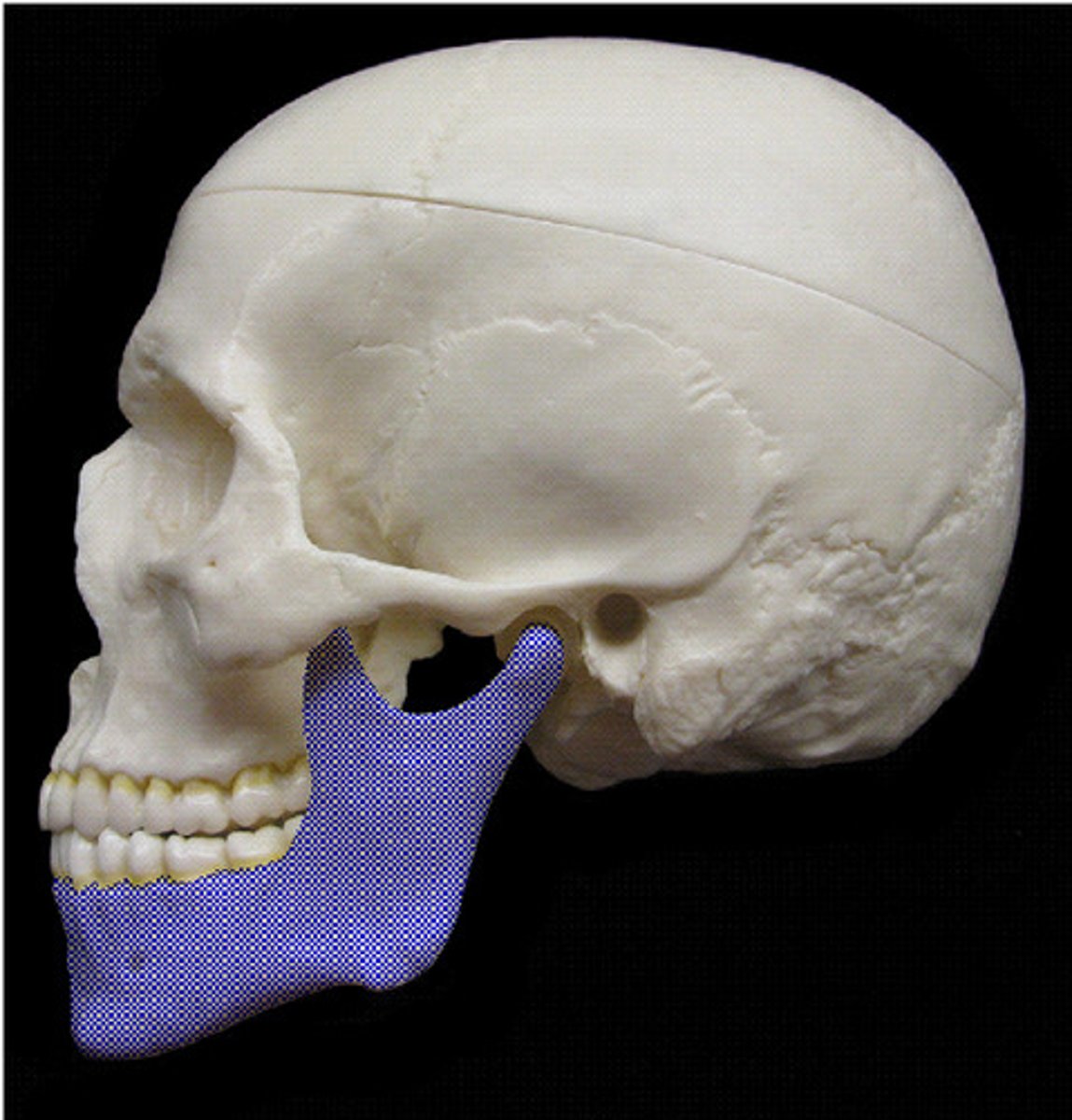
What is the angle of the mandible?
gonion, divides mandible into two main parts
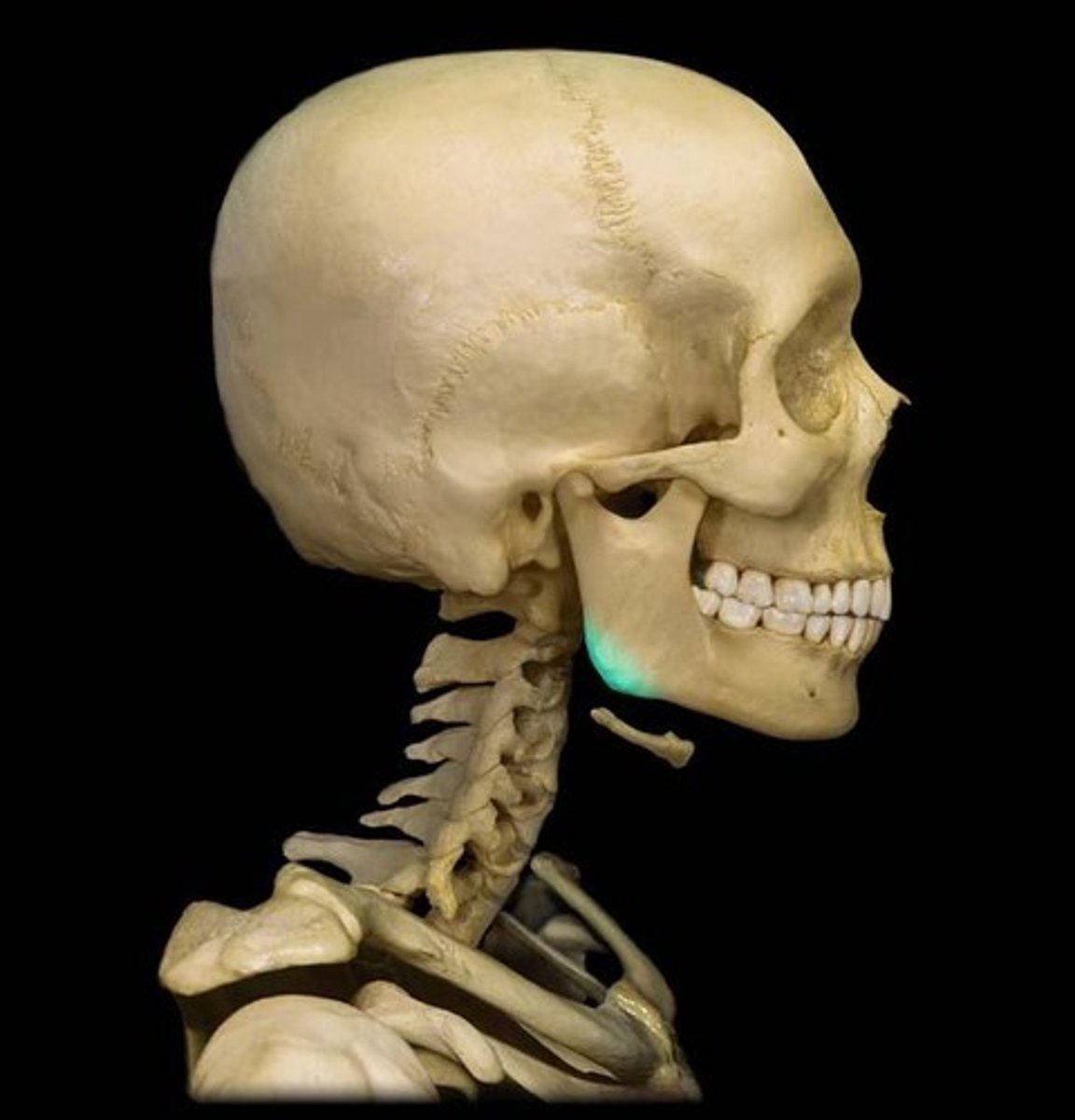
What is the body of the mandible?
area anterior to angle (all the way to other angle)
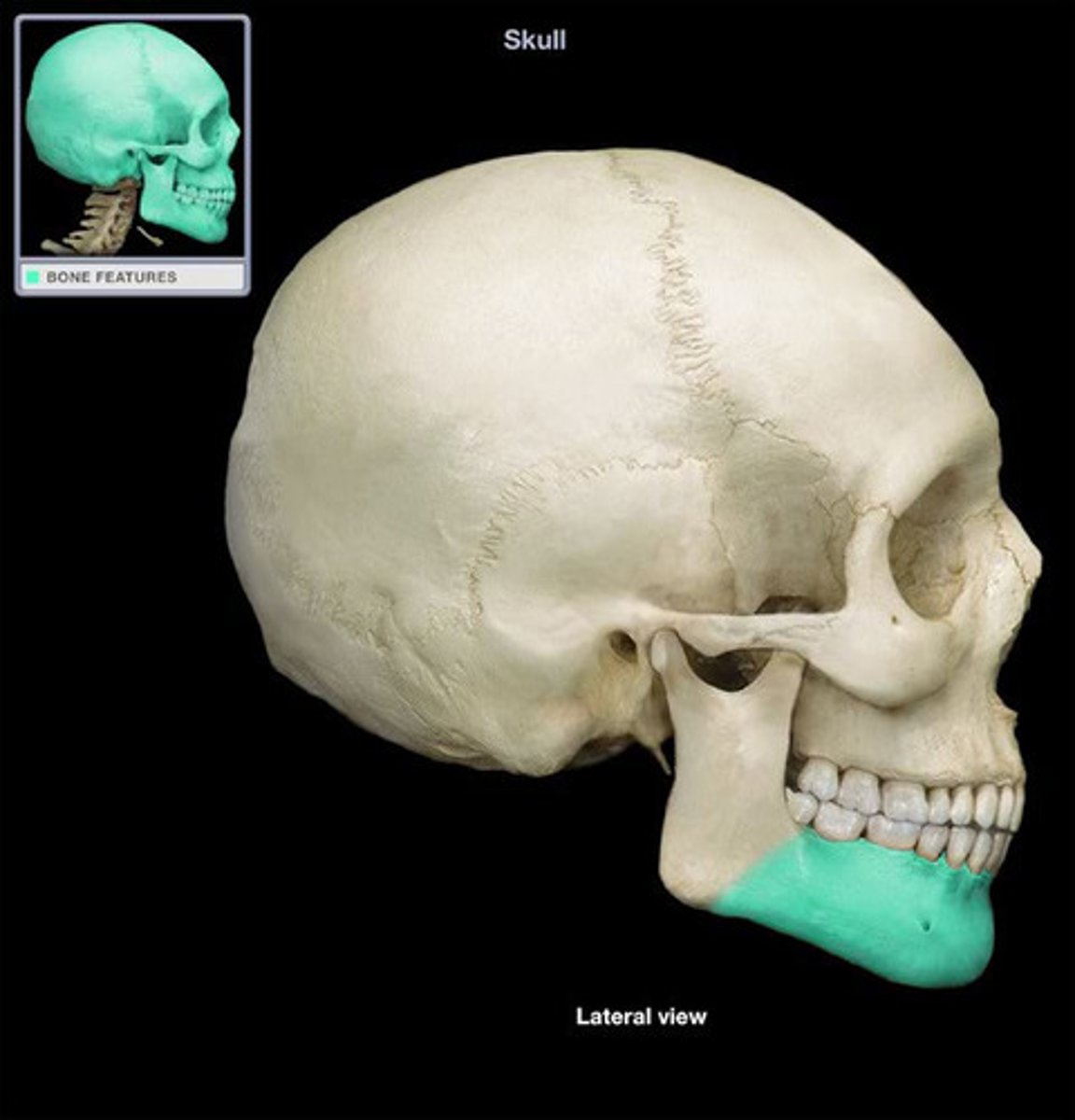
What is the ramus of the mandible?
area superior to angle
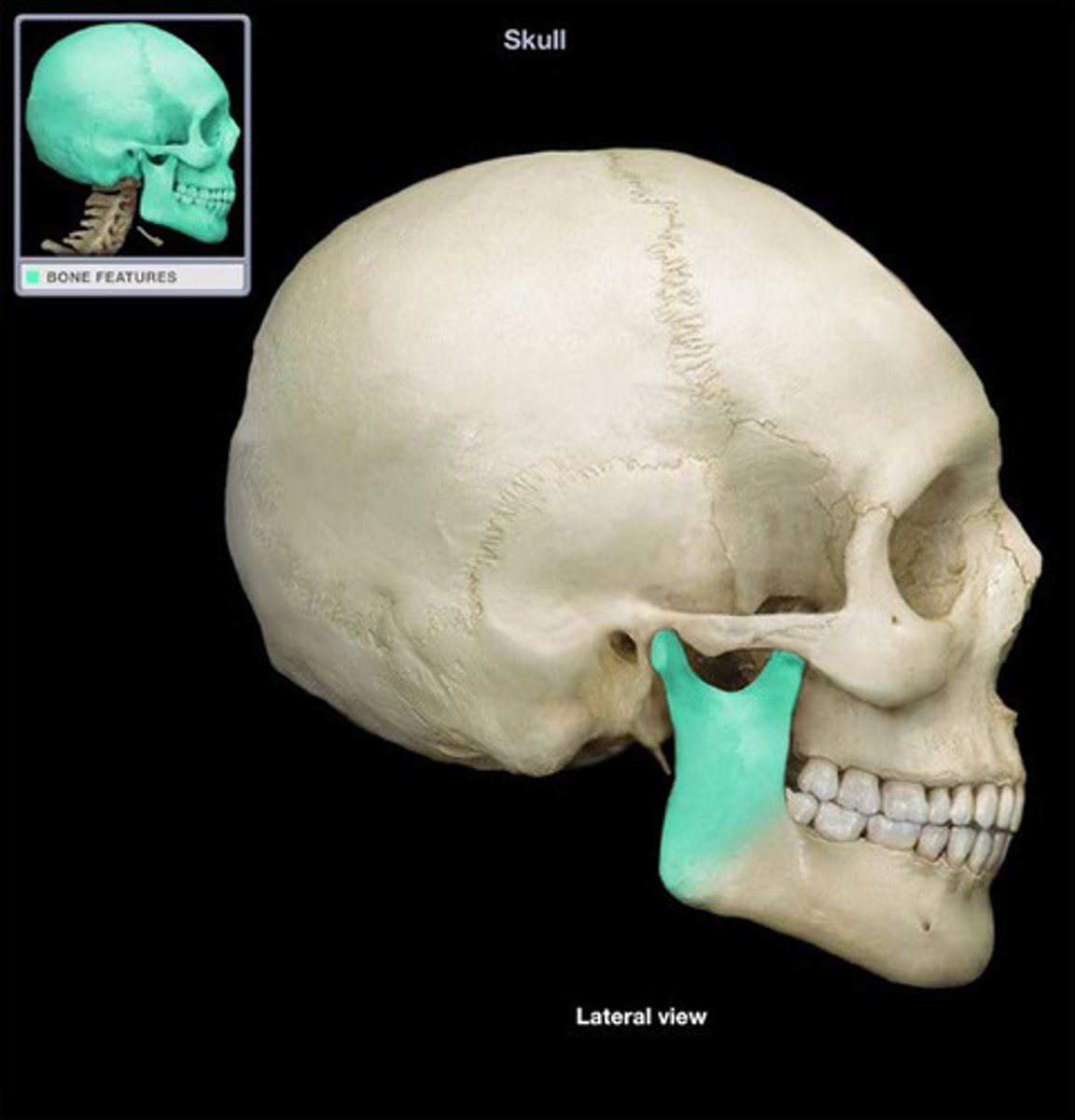
What is the alveolar process?
ridges that extends along entire superior portion of body
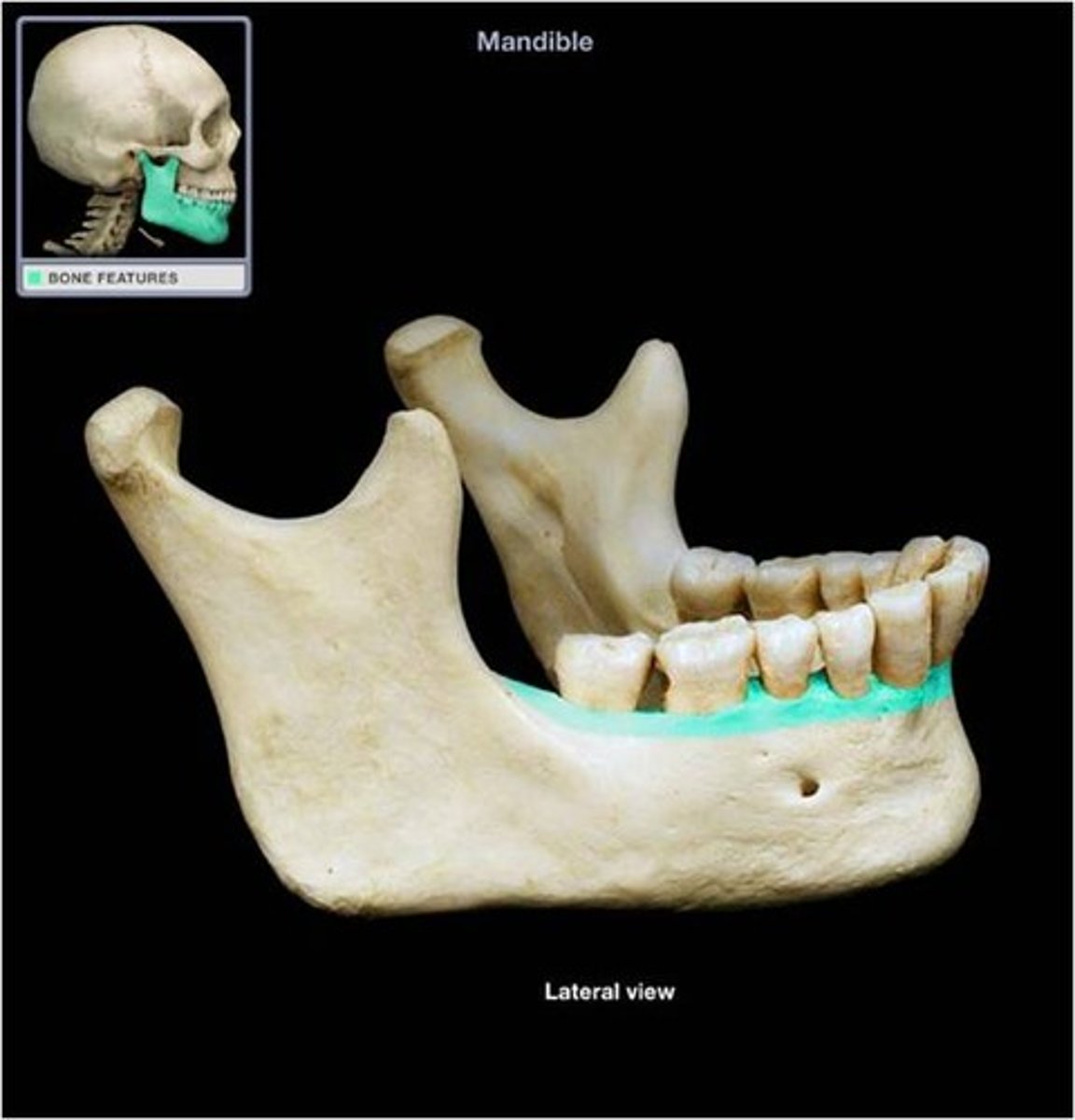
What is the mentum?
chin
The optic foramen allow passage for what?
passage of cranial nerves
Where is the optic foramen located?
apex of the orbit
Where is the superior orbital fissure located?
lateral to optic foramen (between greater and lesser wings)
Where is the inferior orbital fissure located?
between maxilla, zygoma, greater wing
What is sphenoid strut?
small root of bone separating the superior orbital fissure and optic canal
What are the two types of joints in the skull?
1. synovial (diarthrodial)
2. fibrous joints (synarthrodial)
What is a tripod fracture?
blow to the cheek resulting in the zygoma being fractured in 3 places
What is a leforte fracture?
severe bilateral horizontal fractures of maxillae
What is a countre-coup fracture?
injury/fracture to one side caused by impact to opposite side
Go through the STAMPSBC list for Lateral Facial Bones:
S - around waist
T - center cell @ 75 kVp
A - no angle
M - correct marker by mandible
P - PT side hugs bucky w/ side of interest closest to board, IPL perp & CR enters mid zygoma
S - 40"
B - suspension
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise
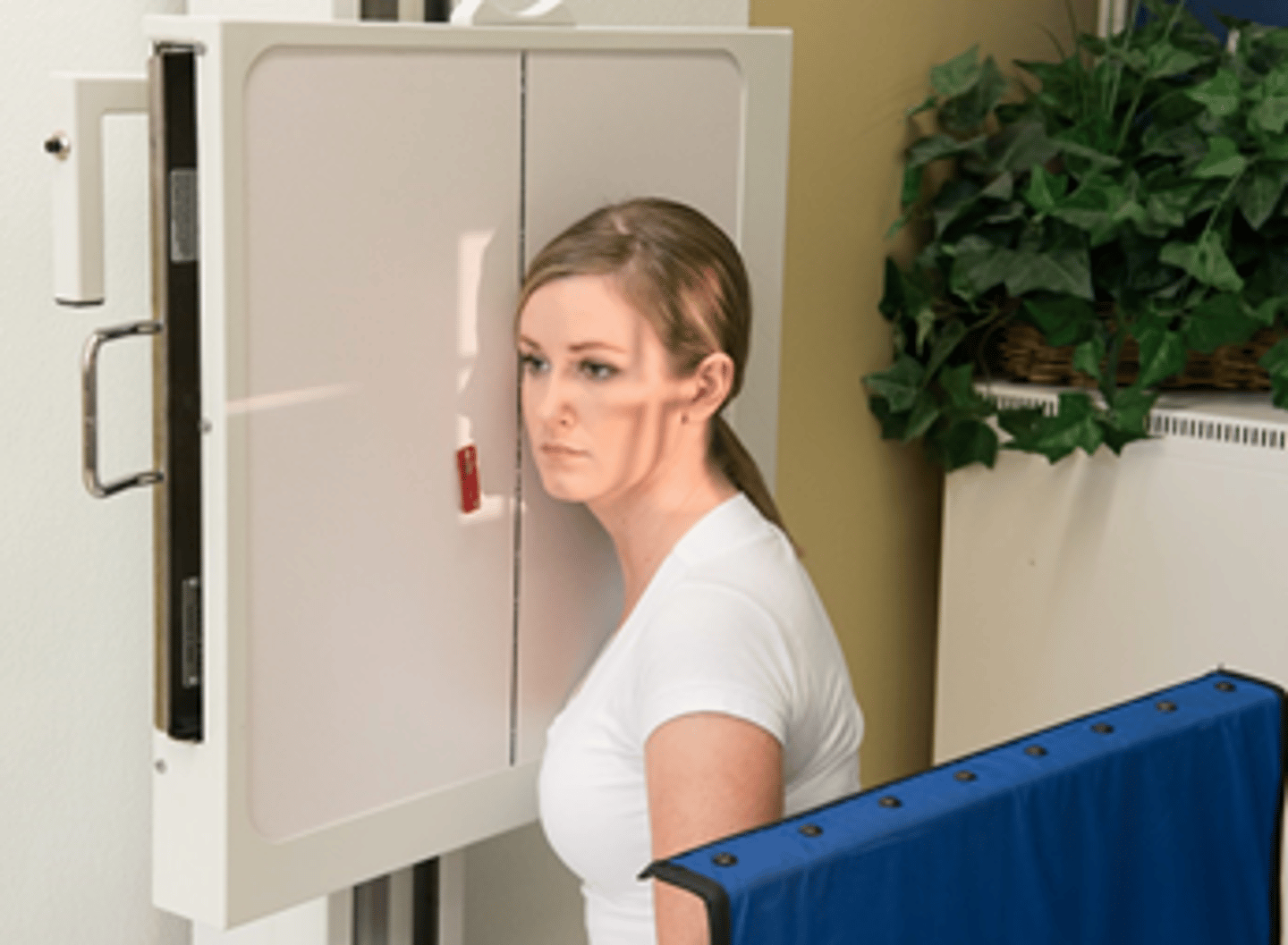

Go through STAMPSBC list for PA Waters facial bones:
S - around waist
T - center cell @ 75 kVp
A - no angle
M - correct marker in bottom corner
P - PT has chin to bucky w/ MML perp, CR exits acanthion
S - 40"
B - suspension
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise
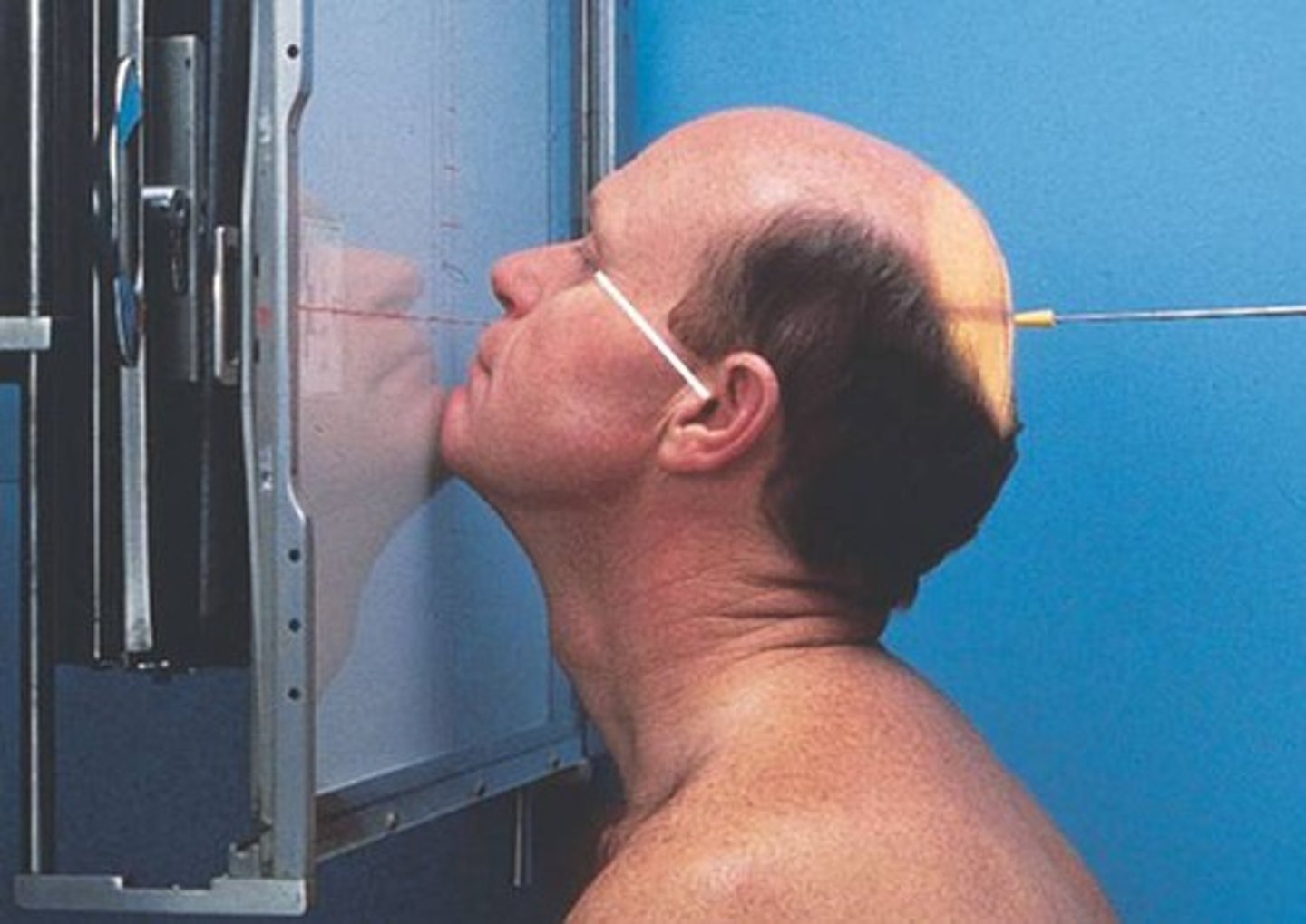
Go through STAMPSBC list for PA Modified Waters facial bones:
S - around waist
T - center cell @ 75 kVp
A - no angle
M - correct marker in bottom corner
P - PT has chin/nose to bucky w/ LML perp, CR exits acanthion
S - 40"
B - suspension
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise
Go through STAMPSBC for PA Caldwell facial bones:
S - around waist
T - center cell @ 75 kVp
A - 15 degree caudad
M - correct marker in bottom corner
P - PT has forehead to board w/ OML perp, CR exits nasion
S - 40"
B - suspension
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise
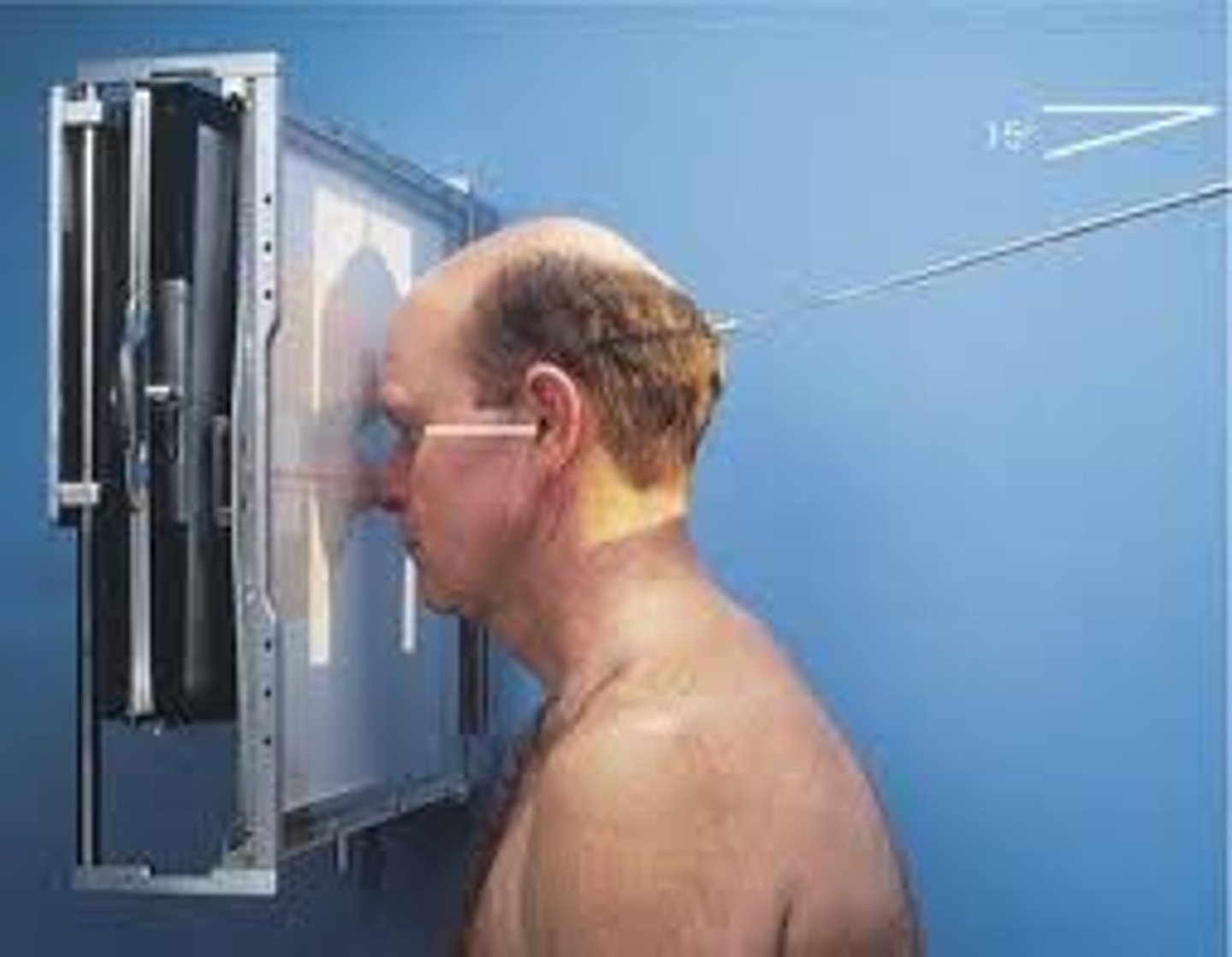
Go through STAMPSBC list for Lateral Nasal Bones:
S - around waist
T - 3.2 mAs @ 55 kVp
A - no angle
M - correct markers labelling correct side of body
P - PT helps hold cassette to board w/ IOML parallel, CR enters 1/2" below nasion
S - 40"
B - suspension
C - 10 x 12 crosswise, 5 x 7 collimation
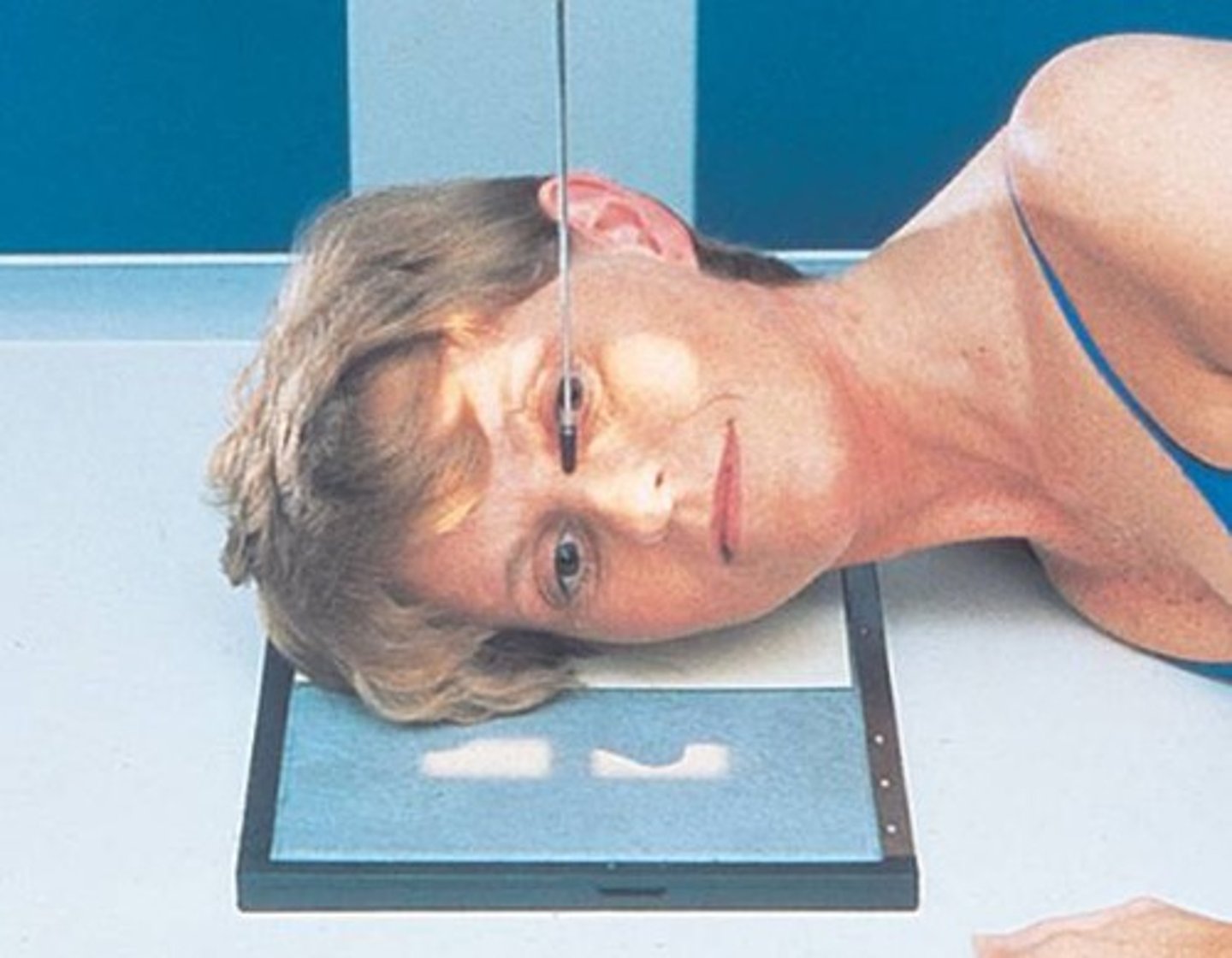
Go through STAMPSBC list for Rheese Method (parietoorbital):
S - around waist
T - center cell @ 75 kVp
A - no angle
M - correct marker for correct foramen on correct side
P - PT stands w/ chin, cheek, nose to bucky & eye over crosshairs, AML perp
S - 40"
B - suspension
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise, 7 x 7 collimation
Go through STAMPSBC list for AP Modified Axial Townes:
S - on lap
T - center cell @ 75 kVp
A - 30 caudad (OML), 37 caudad (IOML)
M - correct marker in bottom corner
P - PT seated w/ back to bucky, CR 1" above glabella (through zygoma)
S - 40"
B - suspension
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise
Go through STAMPSBC list for SMV:
S - on lap
T - center cell @ 75 kVp
A - no angle
M - correct marker in top corner
P - PT seated w/ vertex on board, IOML parallel & CR mid zygoma
S - 40"
B - suspension
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise
Go through STAMPSBC list for Oblique Inferosuperior (tangetial):
S - on lap
T - 6 mAs @ 60 kVp
A - no angle
M - correct marker in top corner
P - PT in SMV w/ head 15 degrees toward affected side & chin 15 degrees toward affected side, IOML parallel
S - 40"
B - suspension
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise, 5 x 7 collimation
What is the process leading AWAY FROM the cell body?
axon
What are the processes that conduct impulses TOWARD the cell body?
dendrites
What makes up the gray matter of the brain and spinal cord?
dendrites
What makes up the white matter of the brain and spinal cord?
axons
What is a multipolar neuron?
neuron w/ only one axons and several dendrites
What are the two main divisions of the CNS?
brain and spinal cord
The brain and spinal cord are both enclosed by three protective coverings termed ________
meninges
What are the three meninges from most internal to most external?
1. pia mater
2. arachnoid
3. dura mater
What are the three meningeal spaces?
1. epidural
2. subdural
3. subarachnoid
Where is the epidural space located?
between dura and inner table of skull
Where is the subdural space located?
between dura and arachnoid
Where is the subarachnoid space located?
between arachnoid and pia mater
What is a cisternal puncture done for? Where is it done?
- to introduce anesthesia
- done between C1 and occipital bone
What are the three general divisions of the brain?
forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
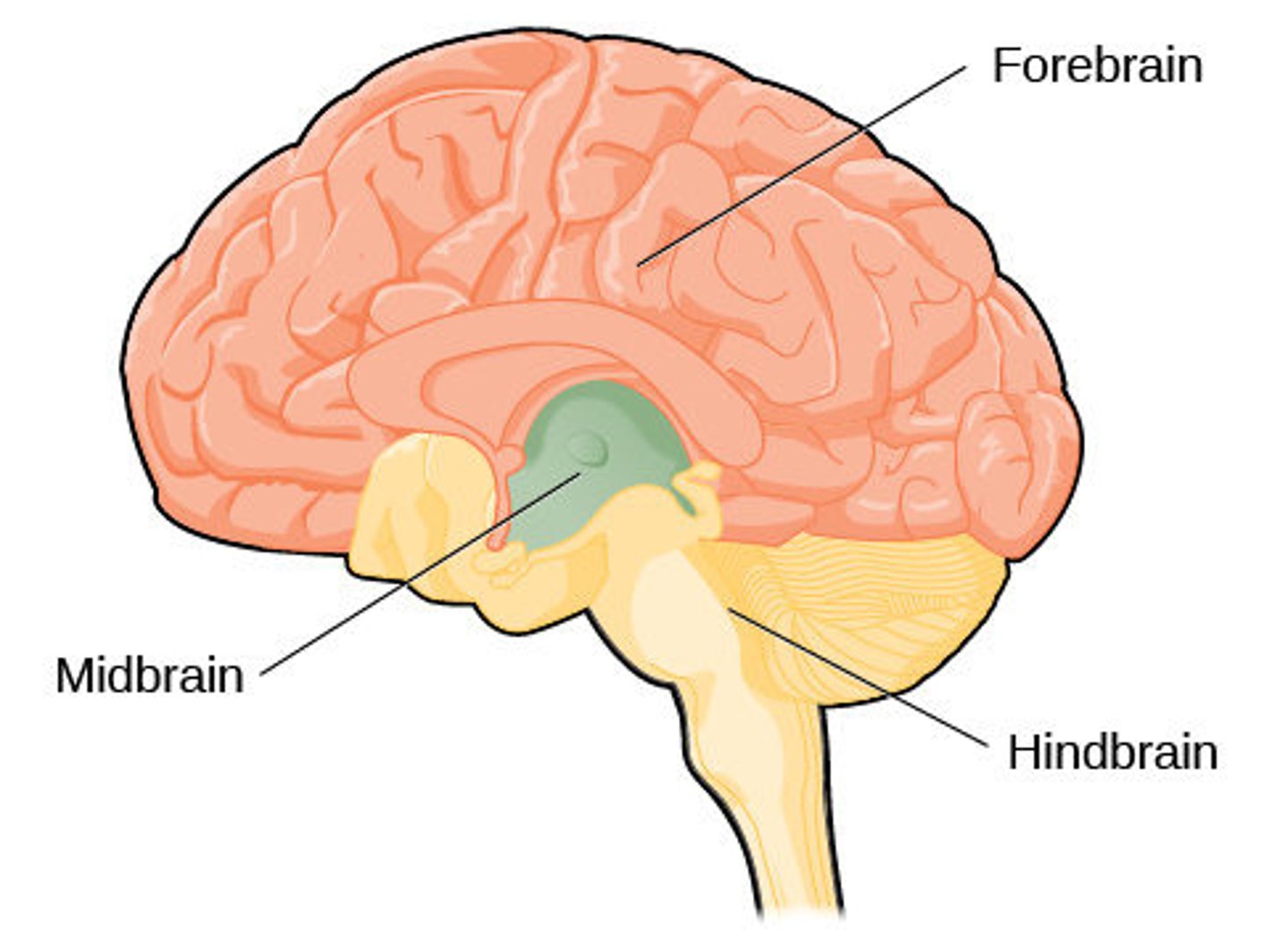
What are the three divisions of the forebrain?
1. cerebrum
2. thalamus
3. hypothalamus
What is the largest portion of the brain?
cerebrum
What divides the cerebrum into right and left hemispheres?
longitudinal fissure
What are the five lobes of the cerebrum?
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, insula/central
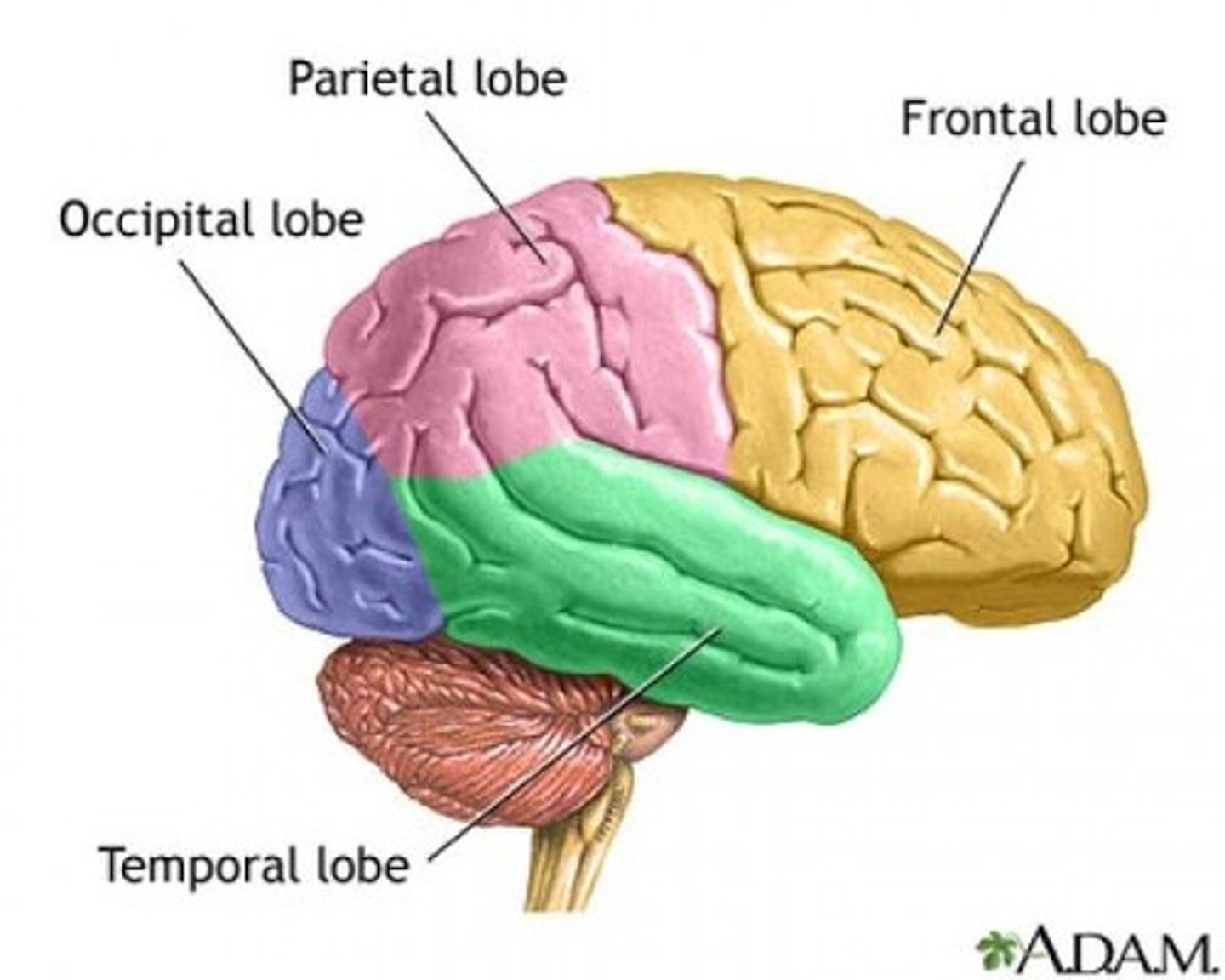
Each hemisphere of the cerebrum has folds called _____
gyri/gyrus
Each hemisphere of the cerebrum has grooves called ______
sulci/sulcus
What is located deep w/in the longitudinal fissure?
corpus callosum
The cerebral ventricle system is connected w/ the ____________ space
subarachnoid
Where is CSF formed?
lateral ventricles
What color is CSF?
clear
How much CSF is produced a day? How much is actually present?
- 500 mL
- 140 mL
The thalamus serves as an interpretation center for what impulses?
pain, temperature, touch, emotions, memory
What makes up the diencephalon portion of the forebrain?
thalamus and hypothalamus
What are the important body activities that the hypothalamus controls?
homeostasis (ability of the body to stabilize its normal body states)
True/False: the hypothalamus is connected to the pituitary gland by the infundibulum
true
The ________ is seen as a short, constricted portion of the upper brain stem connecting the forebrain to the hindbrain
midbrain
What are the three divisions of the hindbrain?
cerebellum, pons, medulla (oblongata)
What connects the right and left hemispheres of the cerebellum?
vermis
What does the cerebellum primarily control?
motor functions such as coordination, posture, balance
What is the bridge between the cerebrum, cerebellum, and medulla?
pons
Where is the medulla located?
level of the foramen magnum
What pass through the medulla?
fiber tracts between brain and spinal cord
What three things does the brain stem include?
midbrain, pons, medulla
What is the pineal gland?
small endocrine gland which aids in regulating certain secretions
What are the other names for the pituitary gland?
master gland, hypophysis
What does the pituitary gland control?
growth and reproductive functions
What is white matter?
tracts which consist of bundles of myelinated axons
What is gray matter?
composed mainly of neuron dendrites and cell bodies
What are cerebral nuclei also called?
basal ganglia
What are the four specific groupings of cerebral nuclei?
1. caudate nucleus
2. lentiform nucleus
3. claustrum
4. amygdaloid nucleus
Olfactory =
smell
Optic =
vision
What are sinuses?
large, air-filled cavities lined w/ mucous membranes
How many maxillary sinuses are there?
2
How many frontal sinuses are there?
usually 2
How many ethmoid sinuses are there?
many
How many sphenoid sinuses are there?
1 or 2
Which of the sinuses are visible at birth?
maxillary
Which of the sinuses can be seen around age 6 or 7?
frontal and sphenoid
When are all sinuses fully developed?
late teen years
Which of the sinuses is the largest?
maxillary
True/False: the maxillary sinuses are always paired and fairly uniform in size and shape
true
True/False: the frontal sinuses are rarely uniform in size and shape
true
Are the frontal sinuses larger in men or in women?
men
Where are the ethmoid sinuses located?
within the lateral masses of the ethmoid bone
What are the three groups of the ethmoid sinuses?
anterior, middle, posterior
True/False: if you see sphenoid effusion usually means there's a basal skull fracture
true
What is the osteomeatal complex?
drainage pathways of the frontal, maxillary, and ethmoid sinuses
What is the order in which the maxillary sinuses drain?
1.) infundibulum drains into 2.) middle nasal meatus which drains into 3.) inferior nasal meatus