2.6 Structure of DNA and RNA
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/12
Last updated 6:53 PM on 12/10/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
1
New cards
What are nucleic acids?
The genetic material of the cells and are composed of recurring monomeric units called nucleotides.
2
New cards
What is each nucleotide made of?
* 5-carbon pentose sugar
* Phosphate group
* Nitrogenous base
* Phosphate group
* Nitrogenous base
3
New cards
Structure of the nucleotide
* Nitrogenous base is attached to the 1’ - carbon atom
* Phosphate base is attached to the 5’ - carbon atom
* Phosphate base is attached to the 5’ - carbon atom
4
New cards
What are the two types of nucleic acids present in cells?
* DNA, a more stable double stranded form that stores the genetic blueprint for cells
* RNA, a more versatile single stranded form that transfers the genetic information for decoding
* RNA, a more versatile single stranded form that transfers the genetic information for decoding
5
New cards
Nitrogenous bases in RNA & number of strands
Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Uracil + single stranded
6
New cards
Nitrogenous bases in DNA & number of strands
Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine + Double stranded
7
New cards
Drawings of DNA and RNA (you need to know how to draw these)
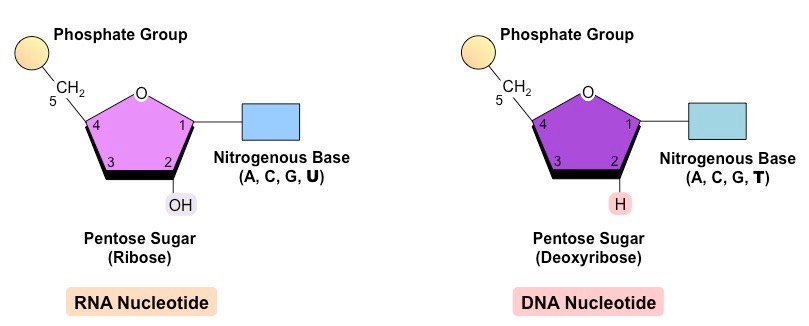
8
New cards
How the structure of DNA is formed
* Phosphate group of one nucleotide attaches to sugar of another nucleotide (at 3’)
* This is called a phosphodiester bond and water is produced as a by-product
* The two chains are held together through hydrogen bonding between complementary nitrogenous bases
* In order for the bases to be facing each other and thus able to pair, the strands must be running in opposite directions
* To be able to do this the strands must be antiparallel
\
* This is called a phosphodiester bond and water is produced as a by-product
* The two chains are held together through hydrogen bonding between complementary nitrogenous bases
* In order for the bases to be facing each other and thus able to pair, the strands must be running in opposite directions
* To be able to do this the strands must be antiparallel
\
9
New cards
10
New cards
Who proposed the correct structural organization of the DNA molecule?
James Watson and Francis Crick.
11
New cards
What were Watson and Crick able to find out?
* DNA strands are antiparallel and form a double helix
* DNA strands pair via complementary base pairing (A = T ; C Ξ G)
* Outer edges of bases remain exposed (allows access to replicative and transcriptional proteins)
* DNA strands pair via complementary base pairing (A = T ; C Ξ G)
* Outer edges of bases remain exposed (allows access to replicative and transcriptional proteins)
12
New cards
Errors in earlier versions of Watson and Crick DNA model
* The first model generated was a triple helix
* Early models had bases on the outside and sugar-phosphate residues in the centre
* Nitrogenous bases were not initially configured correctly and hence did not demonstrate complementarity
* Early models had bases on the outside and sugar-phosphate residues in the centre
* Nitrogenous bases were not initially configured correctly and hence did not demonstrate complementarity
13
New cards
Controversy with first DNA model
The final construction of a correct DNA molecule owed heavily to the X-ray crystallography data generated by Franklin
* This data confirmed the arrangement of the DNA strands into a helical structure
* The data was shared without Franklin’s knowledge or permission and contributed profoundly to the final design
* Hence, Franklin is now recognised as a key contributor to the elucidation of DNA structure
* This data confirmed the arrangement of the DNA strands into a helical structure
* The data was shared without Franklin’s knowledge or permission and contributed profoundly to the final design
* Hence, Franklin is now recognised as a key contributor to the elucidation of DNA structure