Chapter 13- Anatomy and physiology of pregnancy
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Gestation
Pregnancy. lasts 40 weeks or 280 days measured from last menstrual period. Described in terms of trimesters
Trimesters
First: first day of last menstrual period-13 weeks
Second: 14 weeks- 27 weeks
Third: 28 weeks- 40 weeks
Significant uterine growth in the first trimester
high levels of estrogen and progestrone
Early uterine enlargement
increased vascularity, dilation of blood vessels, hyperplasia, and hypertrophy, and development of the decidua
Uterine weight
increases dramatically. 4-70 g to 1200 g at term gestation.
Volume increase
10 mL to 5 L at term
Size of uterus
7 weeks- size of a large hen’s egg
10 weeks- orange
12 weeks- grapefruit
After the third month, uterine enlargement is primarily the result of mechanical pressure of the growing fetus
Lightening
fetus begins to descend into the pelvis in preparation for birth. occurs in nullipara approx 2 weeks before the onset of labor and in multipara at the start of labor
Hegar sign
at approx 6 weeks. softening and compressibily of the lower uterine segment
Factors that decrease uterine blood flow
low maternal arterial pressure, uterine contractions, and maternal supine position. Estrogen stimulation can increase uterine blood flow
Conditions associated with decreased placental perfusion
hypertension, intrauterine growth restriction, diabetes melitus, multiple gestations
Uterine souffle
bruit. rushing or blowing sound of maternal blood flowing through uterine arteries to the placement that is synchronous with the maternal pulse.
Funic souffle
synchronous with the fetal heart rate and is caused by fetal blood coursing through the umbilical cord
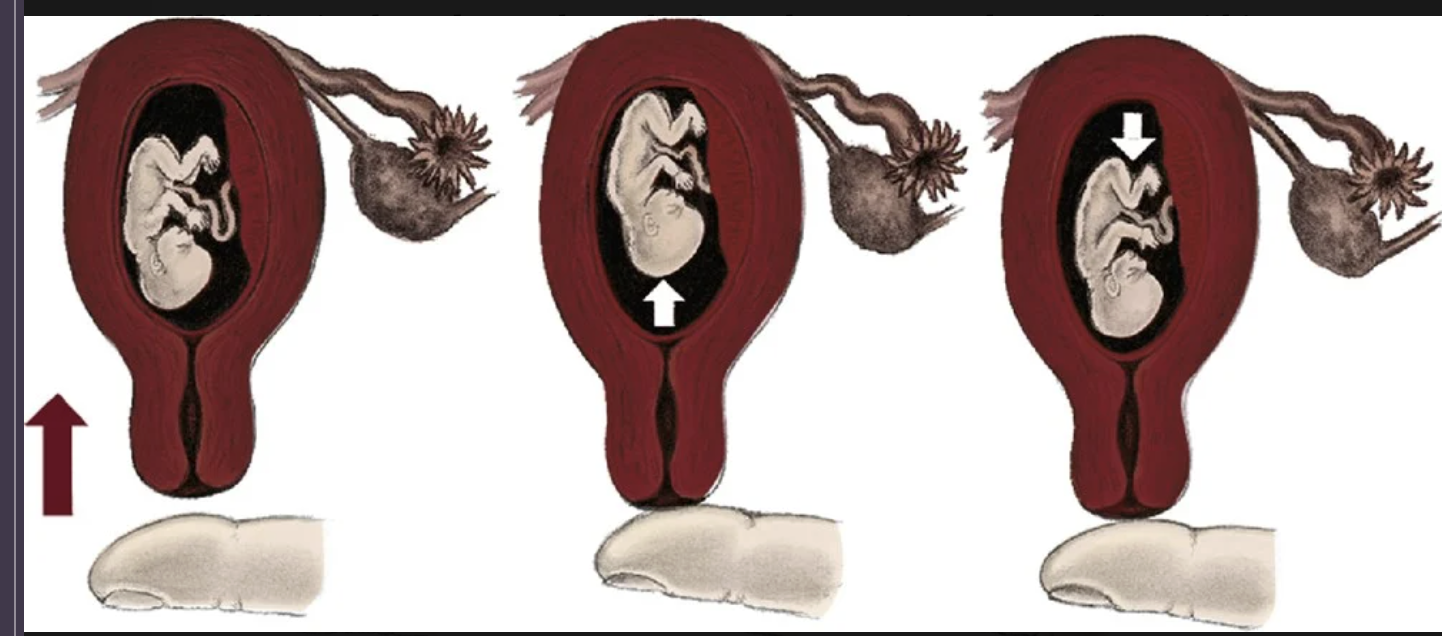
Ballottement
16-18 weeks of gestatio. palpating a floating structure by bouncing it gently and feeling it rebound. examiner places a finger within the vagina and taps gently upward on the cervix causing the fetus to rise. The fetus then sinks, and a gentle tap is felt on the finger
Quickening
first recognition of fetal movements or feeling life. detected by multiparaus woman as early as 14-16 weeks of gestation. nulliparious woman may not notice till 18th week or later. commonly described as fluttter
Cervix change during pregnancy
firm, nondistensible, closed structure that maintains the pregnancy/fetus within the uterus and changes to a soft, highly elastic tissue that dilates and becomes almost indistinguisable during labor for birth
Goodell sign
probable sign. softening of the cervical tip by 6th week. due to increased vascularity, slight hypertrophy, and hyperplasia
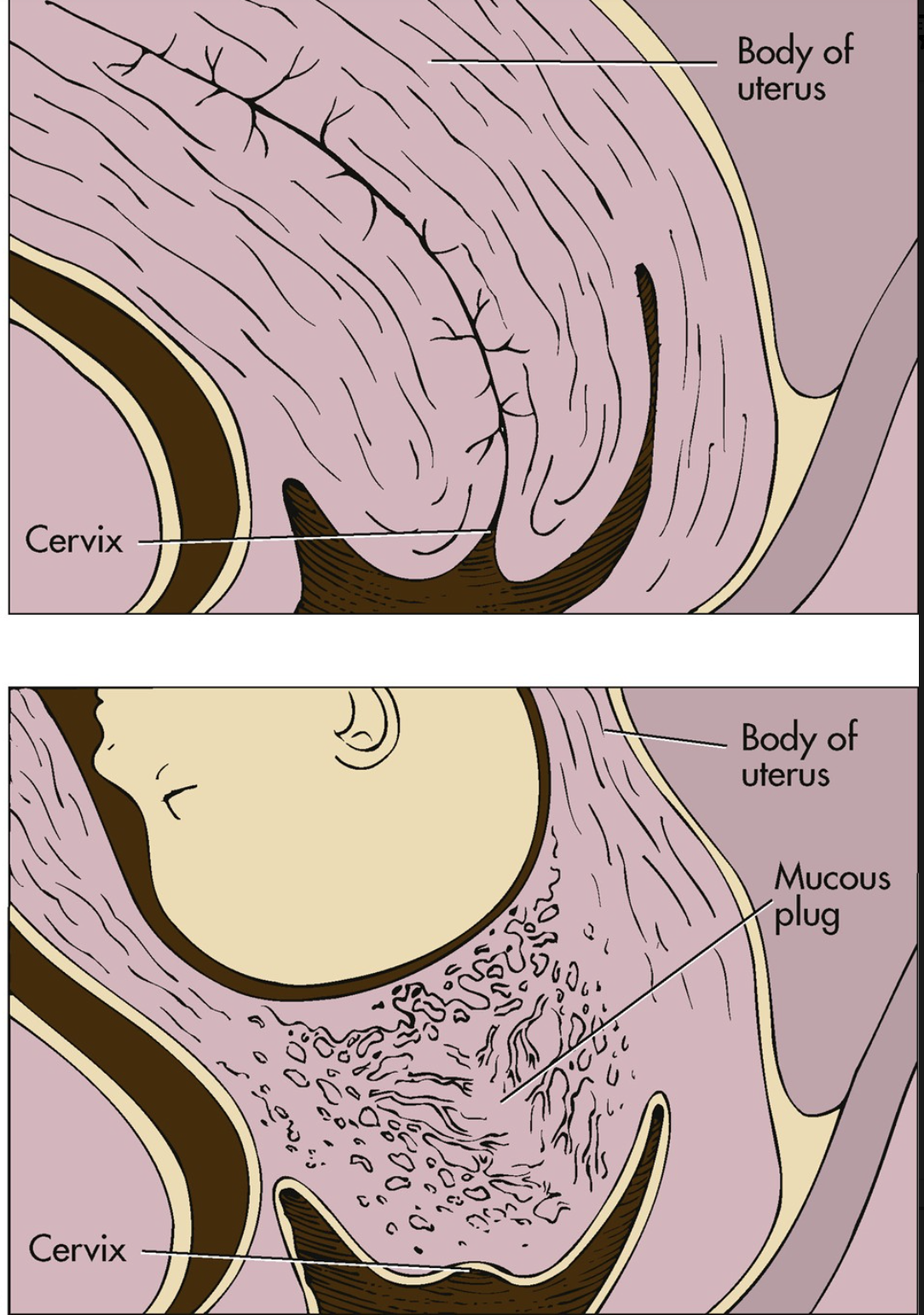
Operculum
muscous plug. mucus is rich in immunoglobulins and acts as a barrier against bacterial invasion of the uterus
Ovulation
does not occur. estrogen and progrestrone suppress FSH and LH. corpus luteum produces estrogen and progestrone for the first 6-10 weeks of pregnancy until the placenta becomes the primary source of these hormones
Chadwick sign
increased vascularity results in the violet-blue color of the vaginal mucusa and cervix. 6-8 weeks of pregnancy
Leukorrhea
white or slightly gray mucoid vaginal discharge with a faint musty odor. in response to cervical stimulation by estrogen and progrestrone
Early pregnancy lactation
estrogen stimulates the growth and proliferation of milk ducts while progrestrone causes growth and development of the mammary lobes. Lactation inhibited until the progestrone level decreases after birth
Blood pressure
maternal BP remains the same or decreases slightly even though CO increaes significantly. due to reduced systemic vascular resistance caused by the vasodilatory effects of progestrone, prostaglandins, and relaxin
Supine hypotensive syndrome or vena cava syndrome
CO is reduced by as much as 25-30% when woman is turned from lateral recumbent to supine. after 4-5 mins reflex bradycardia is noted, CO reduced by half, and woman feels faint.
Compression of the iliac veins and inferior vena cava by the uterus
causes increased venous pressure and reduced blood flow in the legs except when the woman is in the lateral position. leads to edema, varicose veins in the legs and vulva, and hemorrhoids that can develop in latter part of term pregnancy and contribute to the increased risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Physiologic anemia of pregnancy
hemodilution. plasma increase is greater than the increase in RBC production which causes decrease in nomal H&H values. considered anemic if H&H is less than 11 g/dL and 33% in first trimester. second 10.5 g/dL and 32% second. H&H higher in woman living in high altitudes and among woman with tobacco abuse
Pregnancy-related dyspnea
common. beg in first or second trimester. occurs with mild exertion or at rest. mechanical pressures can increase dyspnea.
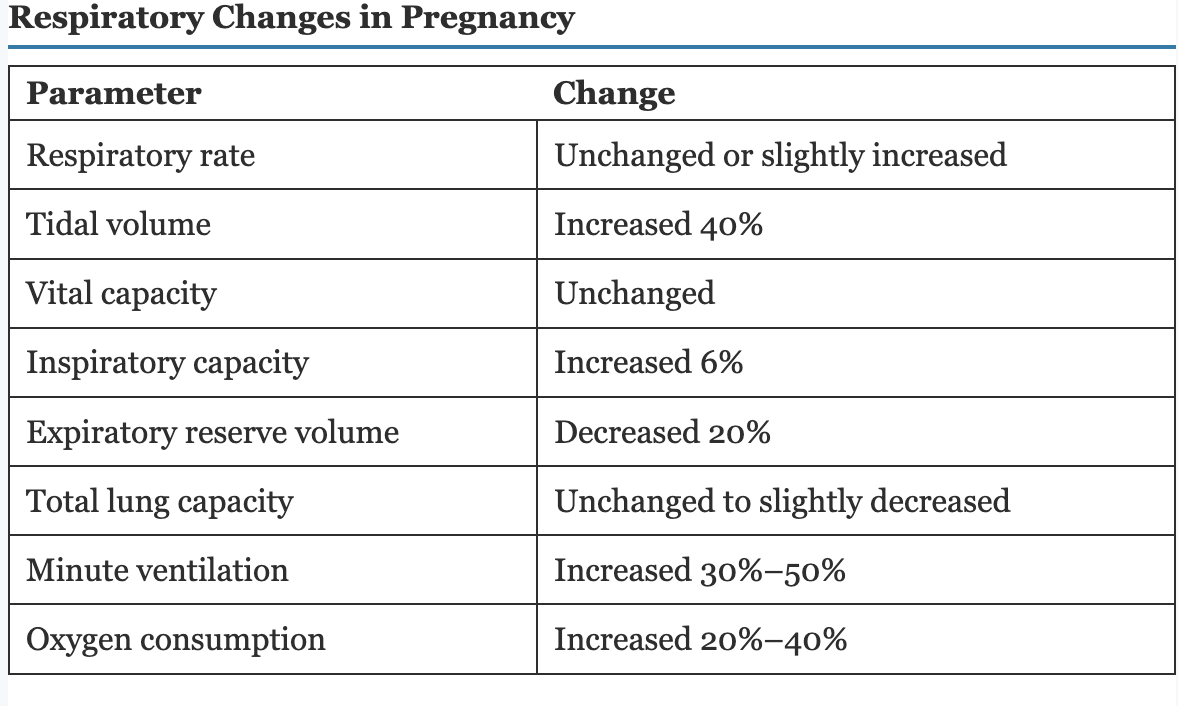
Respiratory changes in pregnancy
Epulis
red, raised nodule on the gums that bleeds easily. develop around the third onth and often enlarge as the pregnancy progresses.
Ptyalism
excessive salivation. caused by the unconsicous decrease in swallowing by the woman when nauseated. can also be caused by stimulation of the salivary glands when eating starchy foods
Increase in GFR
results in increased creatinine clearance and a reduction in serum creatinine, BUN, and uric acid levels
Physiologic or dependent edema
pooling of fluid in the legs in the latter part of pregnancy decreases renal blood flow and GFR
Hyperpigmentation
stimulation by the anterior pituirary hormone melanotropin. darkening of the nipples, areolae, axillae, and vulva approx 16 weeks.
Melasma
choasma or mask of pregnancy. blotchy, brownish hyperpigmentation of the skin over the cheeks, nose, and forehead.
Linea nigra
pigmented line extenting from the symphysis pubis to the top of the fundus in the midline. linea alba before hormone-induced pigmentation
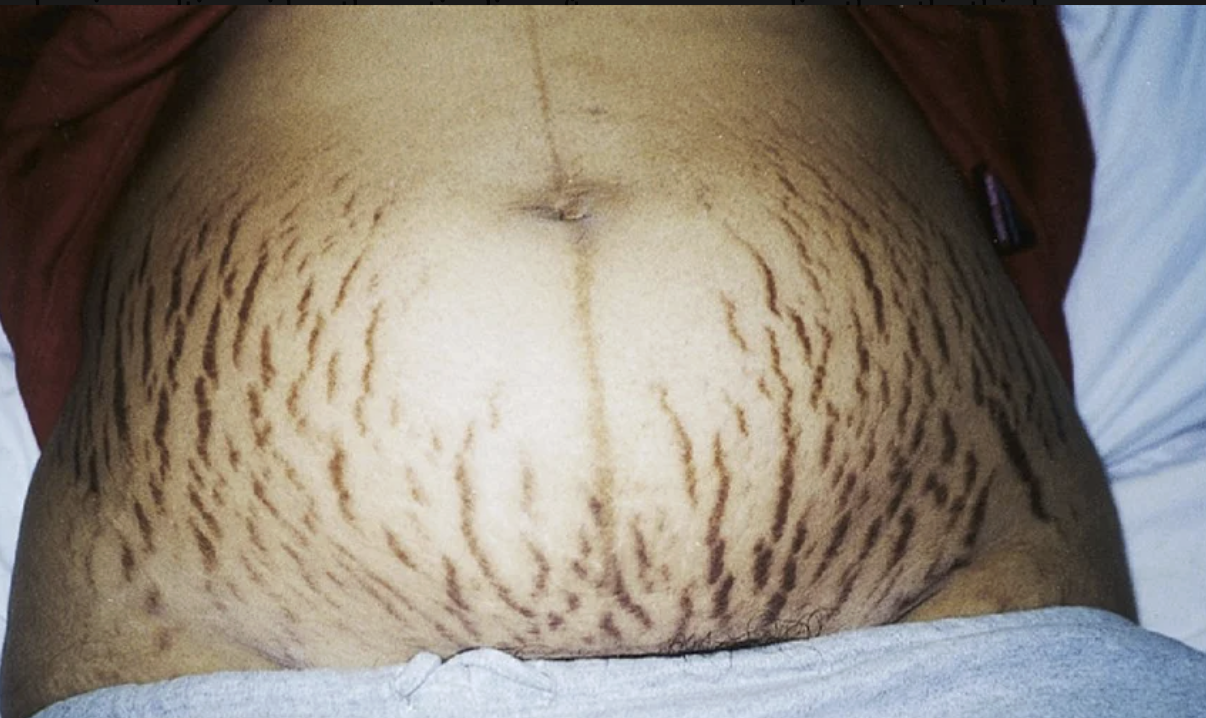
Striae gravidarum
stretch marks. tend to occur over abdomen, thighs, and breasts
Angiomata
vascular spiders. tiny star-shaped or branched, slighthly raised, and pulsating end arterioles usually found on the neck, thorax, face, and arms
Palmar erythema
pinkish red, diffusely mottled, or well-defined blotches are seen over the palmar surfaces. related to increased estrogen levels
Diastasis recti abdominis
rectus abdominis muscles can seperate. abdominal contents protrude at the midline. umbilicus flattens or protrudes.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
parasthesia and pain in hand, radiating to the elbow. caused by edema that compresses the median nerve beneath the carpal ligament of the wrist. smoking and alcohol consumption can make it worse
Human chorionic gonadtropin (hCG)
Maintains corpus luteum production of estrogen and progesterone until the placenta takes over the function.
Progrestrone
Suppresses secretion of FSH and LH by the anterior pituitary gland; maintains pregnancy by relaxing smooth muscles, decreasing uterine contractility; causes fat to deposit in subcutaneous tissues over the maternal abdomen, back, and upper thighs; decreases mother’s ability to use insulin
Estrogen
Suppresses secretion of FSH and LH by the anterior pituitary gland; causes fat to deposit in subcutaneous tissues over the maternal abdomen, back, and upper thighs; promotes enlargement of genitals, uterus, and breasts; increases vascularity; relaxes pelvic ligaments and joints; interferes with folic acid metabolism; increases the level of total body proteins; promotes retention of sodium and water; decreases secretion of hydrochloric acid and pepsin; decreases mother’s ability to use insulin
Serum prolactin
Prepares breasts for lactation.
Oxytocin
Stimulates uterine contractions; stimulates milk ejection from breasts after birth
Human chorionic somtommaotropin
Acts as a growth hormone; contributes to breast development; decreases maternal metabolism of glucose; increases the amount of fatty acids for metabolic needs
T3 and T4
Increase in thyroid hormones supports maternal metabolism and fetal growth and development
Parathyroid
Controls calcium and magnesium metabolism
Insulin
Increases production of insulin to compensate for insulin antagonism caused by placental hormones; effect of insulin antagonists is to decrease tissue sensitivity to insulin or ability to use insulin
Cortisol
Stimulates production of insulin; increases peripheral resistance to insulin
Aldosterone
Stimulates reabsorption of excess sodium from the renal tubules
HCG levels in pregnancy
earliest biological marker for pregnancy. double approx every 2 days for the first 4 weeks. later placenta becomes the primary source of estrogen and progestrone. higher than normal levels are associated with abnormal gestation or multiple gestations. lower or slow increase can indicate impending miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy
Medications during pregnancy testing
anticonvulsants and tranquilizers- false positive results
diurectics and promethazine- false negative results