Atomic structure
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are isotopes?
Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons.
What is first ionisation energy?
The first ionisation energy is the energy required when one mole of gaseous atoms forms one mole of gaseous ions with a single positive charge.
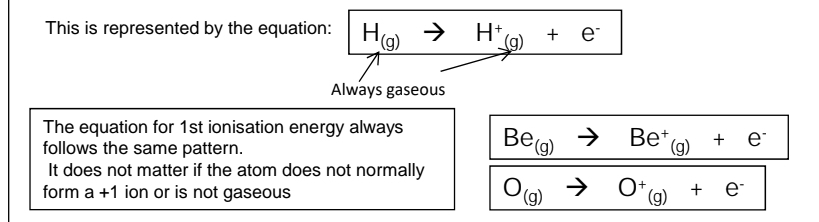
What are the factors that affect ionisation energy?
1.The attraction of the nucleus(The more protons in the nucleus the greater the attraction)
2. The distance of the electrons from the nucleus(The bigger the atom the further the outer electrons are from the nucleus andthe weaker the attraction to the nucleus)
3. Shielding of the attraction of the nucleus(An electron in an outer shell is repelled by electrons in complete inner shells,weakening the attraction of the nucleus)
How many electrons can the orbitals s,p,d,f orbitals have
s holds up to 2 electrons
p holds up to 6 electrons
d holds up to 10 electrons
f holds up to 14 electrons
What is the charge in a proton, neutron and electron?
Proton +1
Neutron 0
Electron -1
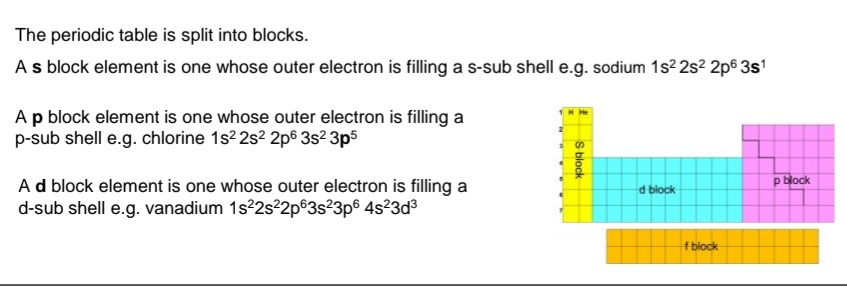
Where are s block, p block and d blocks and f blocks on the peridic table
What are the three main subatomic particles?
A: Protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Where are protons and neutrons located in an atom?
A: In the nucleus.
What is the relative charge and mass of an electron?
A: Charge: –1, Mass: ~0 (very small).
Q: What is the relative charge and mass of a neutron?
A: Charge: 0, Mass: 1.
In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of...?
A: Protons.
Q: What is the atomic number (Z) of an element?
A: The number of protons in its nucleus.
What is the mass number (A) of an atom?
A: The total number of protons and neutrons.
Define an isotope.
A: Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
Do isotopes have the same chemical properties? Why?
A: Yes, because they have the same electron configuration.
Q: What trend does atomic radius follow across a period?
A: It decreases from left to right.
Q: Why does atomic radius decrease across a period?
A: Increasing nuclear charge pulls electrons closer.
What happens to atomic radius down a group?
A: It increases due to more shells and shielding.
What is the maximum number of electrons in an orbital?
A: 2.
What is the order of filling sublevels (Aufbau Principle)?
A: 1s → 2s → 2p → 3s → 3p → 4s → 3d → 4p...
Which sublevel fills before 3d?
A: 4s.
When forming ions, which orbital loses electrons first — 4s or 3d?
A: 4s electrons are lost before 3d.
Why does ionisation energy increase across a period?
A: More protons (higher nuclear charge) = stronger attraction to outer electrons.
Why does ionisation energy decrease down a group?
A: More shielding and larger atomic radius weaken attraction.
What does a large jump in successive ionisation energies indicate?
A: That an electron is being removed from an inner shell.
How can you determine the group number from ionisation energy data?
A: Count the number of electrons removed before the big jump — that’s the group number.
An element has a big jump between the 2nd and 3rd ionisation energies. Which group is it in?
A: Group 2.