Anatomy Exam 3 (Peripheral Nervous System)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
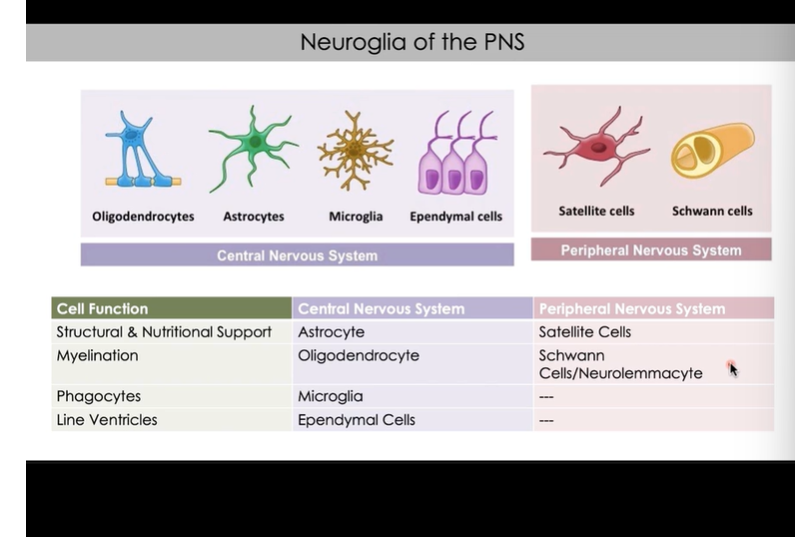
Spinal Cord
Begins at foramen magnum
Functions:
sensory and motor innervation of body
2-way conduction of signals between body and brain
major center for reflexes
Terminates at L1/l2 as Conus Medullaris
Filium terminate extends from conus
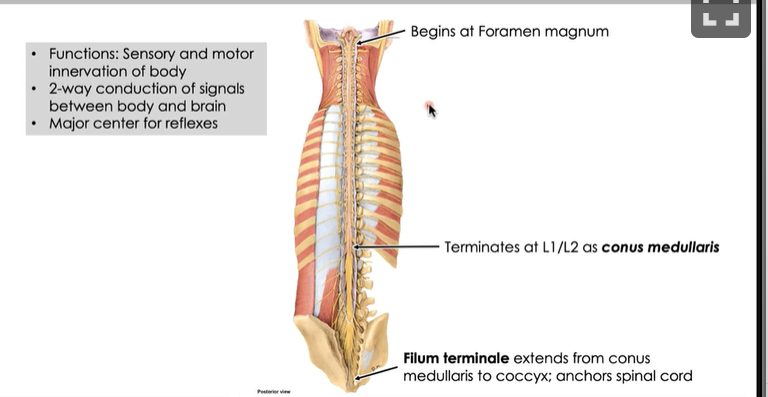
Spinal Cord
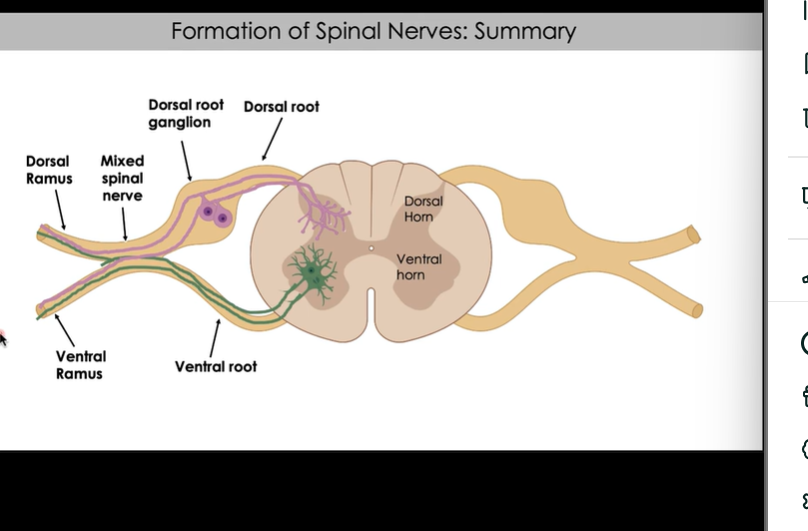
Each spinal cord segment has a mixed spinal nerve with dorsal and ventral roots
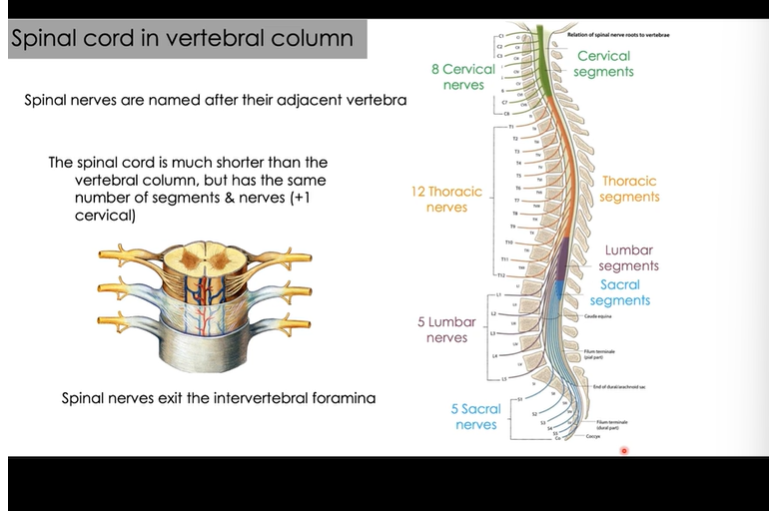
Cauda equina is the collection of spinal nerves traveling inferiorly to exit at associated intervertebral foramen
Spinal cord meninges
Epidural Space: filled with fat and veins
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
pia mater
Biggest difference between this and cranial cavity is that there is one extra space before DURA.
Spinal Cord segment
The spinal cord transmits nerve signals from motor cortex to the body, and from afferent fibers of sensory neruons to sensory cortex of the brain
The spinal cord is divided into SEGEMENTS. each segment pair of spinals nerves is formed
There are 31 spinal cordsegments
Gray Matter and white matter
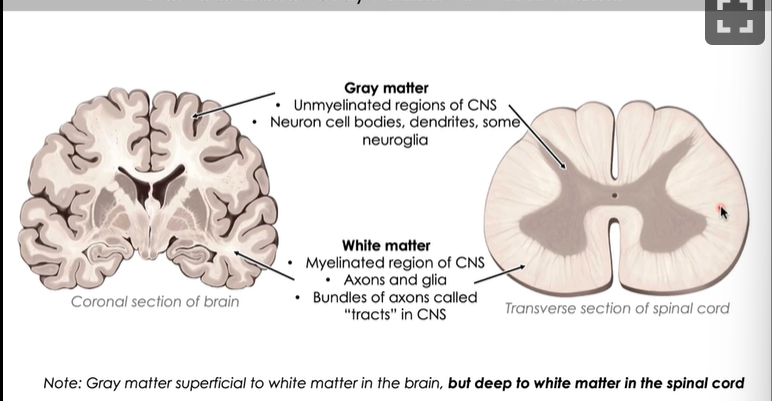
Spinal cord Gray matter
Organized into two (or three) “horns”
Anteriror/ ventral horn: houses somatic motor cell bodies
Posterior/Dorsal Horn: recives sensory neuronal input
Sometimes- Lateral Horn: houses visceral motor cell bodies
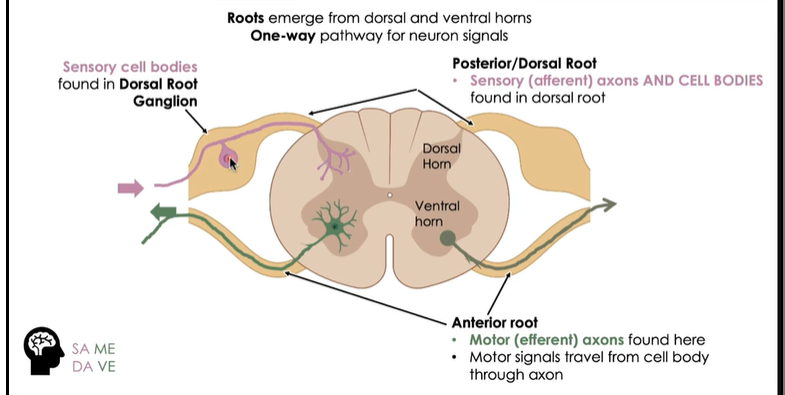
Spinal Cordroots
Roots emerge from dorsal and ventral horns
One-way pathway for neuron signals
Anterior root(down by ventral horn):
motor (efferent) axons found here
motor signals travel from cell body through axon
Posterior/ Dorsal root:
sensory (afferent) axons and Cell bodies
Sensory cell bodies found in dorsal root ganglion
SA = Sensory Afferent
ME = Motor Efferent
DA = Dorsal Afferent
VE = Ventral Efferent
Mixed spinal Nerve
like a highway, as we aproach the spinal cord we start to have one way highways
Nerve Plexuses
A nerve plexus is a network of nerves formed by VENTRAL rami only
All spinal Nerves except T2-T12 branch rejoin
Each muscle in a limb receives its nerve supply from more than one spinal nerve… damage to one spinal nerve cannot completely paralyze any limb muscle
Cervical Plexuses
The cervical plexuses innervate the muscles of the neck and the diaphragm
Phrenic Nerve: innervates the diagrpham
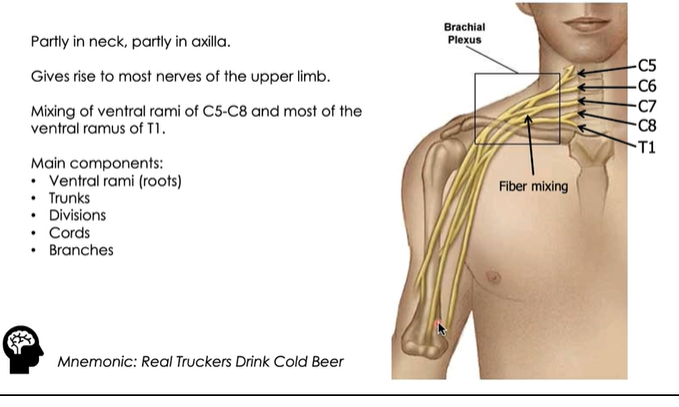
Brachial Plexus
Partly in neck, partly in axilla
Gives rise to most nerves of the upper limb
Real Truckers Drink Cold Beer
Terminal Branches of Brachial Plexus
Axillary Nerve: innervates deltoid muscle
Musculocutaneous nerveL innervates anterior compartment of arm
Radial Nerve: innervates posterious compartment of arm and forearm
Ulnar nerve: innervates ulnar side of anterior forearm
Median Nerve: innervates radial side of anterior forearm
Axillary: Shoulder (Deltoid) - Think “Axe swings”.
Musculocutaneous: Anterior Arm (Biceps) - Think “Flexing”.
Radial: Posterior Arm & Forearm - Think “Radical skateboard tricks”.
Median: Thumb Side of Forearm - Think “Middle, precision grip”.
Ulnar: Pinky Side of Forearm - Think “Under, funny bone”.
Axillary Nerve
Sensory innervation: shoulder joint and skin on part of deltiod
Motor innervation: treres minor and deltioid
Musculocutaneous nerve
Sensory innervation: skin sensation for lateral forearm
Motor innervation: anterior compartment of arm
Radial Nerve
Sensory innervation: skin over dorso-lateral arm and forearm and hand
Motor innervation: posterior compartment of arm and forearm (extensor compartment)
Median Nerve
Sensory innevration: skin of lateral palm and digits 1-3 and lateral side of digit 4
motor innervation: anterior compartment of forearm. intrisic muscle of the thumb
Ulnar nerve
Sensory information: skin of medial hand medial side
Motor innervation: hand muscles on ulnar side of anterior forearm
Lumbar Plexus
Femoral nerve:
Sensory innervation: skin of anteror medial thigh, skin of medial leg and foot
Motor innervation: muscles of anterior thigh, thigh flecors and leg extensors
Obturator Nerve:
Sensroy innervation: skin of medial thigh
Motor innervation: muscles of medial thigh (adductors)
Sacral Plexus
Gluteal nerves:
Superior gluteal nerve
motor innervation: gluteus medius and minimus tensor fascia lata
Inferior gluteal nerve:
motor innervation
Gluteus maximus
Sciatic Nerve
Innervation to most posterior side of leg. Splits in two different nerves
Tibial nerve: postero and lateral leg. musclesof posterior thigh
Common fibular nerve: anterior lateral leg. Muscles of anterior leg
Pudendal Nerve
Innervates gential region
Muscles of perineum