Pharmacology; cardiovascular and pulmonary considerations; home health
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
polypharmacy
-excessive/inappropriate use of meds
2 factors that affect adverse drug rxn
-pattern of drug use that occurs in geriatrics
-altered response to drug tx
pharmacokinetic changes
-way the body handles the drug
pharmacodynamic changes
-way the drug affects the body
aspects of pharmacodynamics changes
-drug absorption
-drug distribution
-drug metabolism
-drug excretion
aspects of pharmacodynamic changes
-change in affinity
-change in way drug is linked to cells internal biochemistry
-change in biochemical response
Beers Criteria
-A list of medications that are generally considered inappropriate when given to elderly people
HTN essential
-no etiologic cause
HTN secondary
-occurs in presence of known causes
classification of hypertension
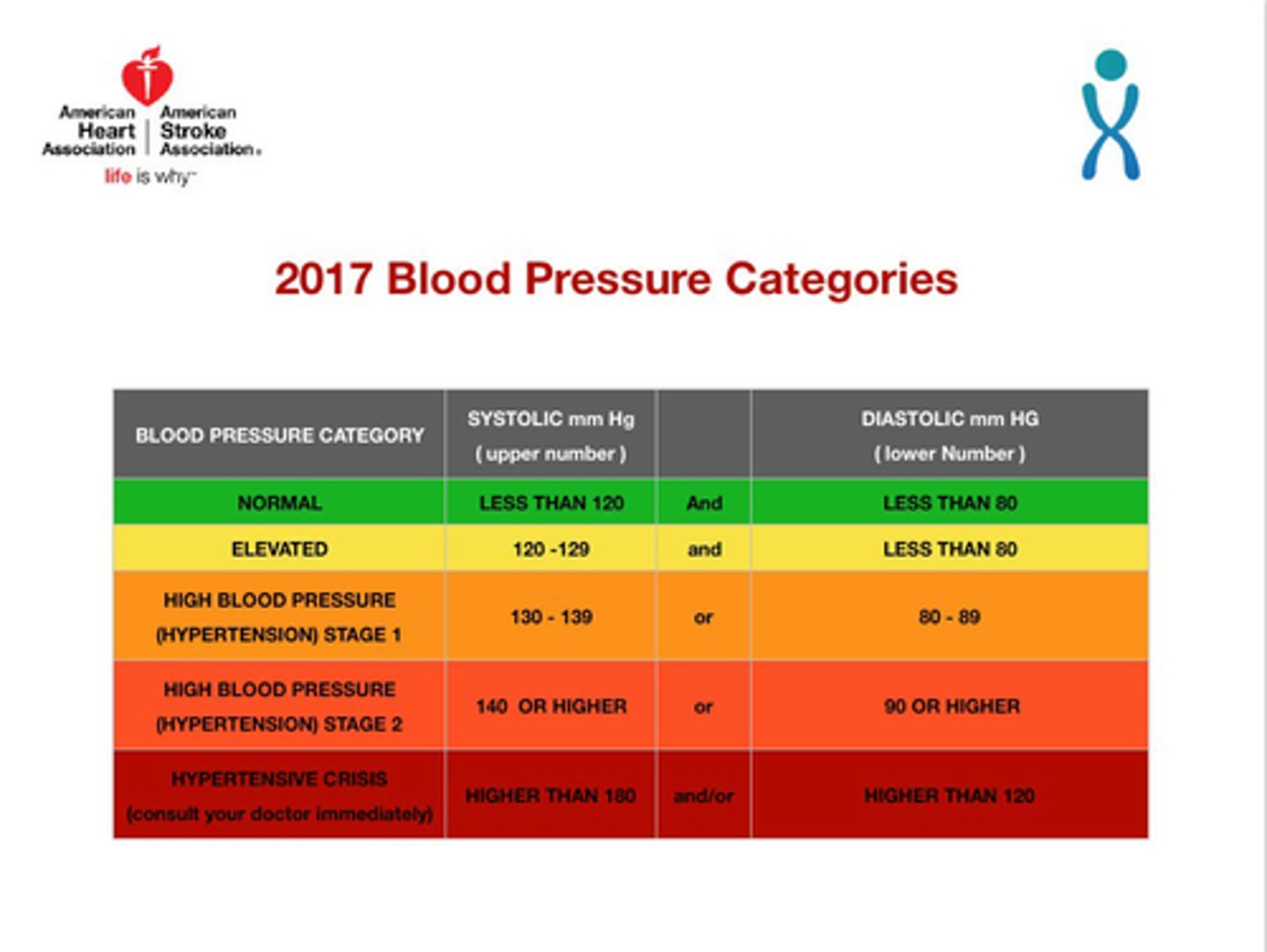
what might be impacted by HTN
-impaired exercise tolerance (need longer warm up and cool down)
how will education or HEP change for pt w/ HTN
-longer warm up and cool down
-regulate activity level
-adherence ot meds
-stress mgmt
-dietary modification
coronary artery disease
-progressive disease where a combination of atherosis and sclerosis of coronary aa creates myocardial ischemia
CAD effect on physiology
-angina pectoris (stable and unstable)
-imbalance btwn myocardial O2 supply and demand
CAD meds
-beta-blockers
-blood thinners
-nitroglycerin
what may be impacted by CAD
-HR
-VO2 max
-exercise tolerance
-endurance
stable angina
-predictable and consistent pain that occurs on exertion and is relieved by rest and/or nitroglycerin
unstable angina
-chest pain at rest or chest pain of increasing frequency
what can be used to assess exercise tolerance w/ CAD
-vital signs
-subjective reporting
-s/s
Overall tx w/ CAD should emphasize
-risk factor reduction
-exercise training
-self-management
how will education or HEP change with CAD
-resistance training should be used in addition to aerobic training
-safe dosages
-30-69% 1RM
A-fib
-most common arrhythmia
-conduction issue
-related to increased atrial pressures and enlargement
effect of A-fib on physiology
-decreased cardiac output
-clot formation
-decreased exercise tolerance
Can people with A-fib exercise safely
-yes but consideration needs to be paid to comorbidities
what can be used to assess
-ECG
-RPE
-pulse (60s)
how will education or HEP change w/ A-fib
-signs of DVT
-rest as needed
-graded exercise
-how to properly take pulse
congestive heart failure (CHF)
-complex clinical syndrome that results in a heart that is unable to provide sufficient output to meet perfusion and oxygenation needs of the body
CHF meds
-diurectics
effect on physiology
-pain
-orthopnea
-paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
-fluid retention
-activity intolerance
what can we do
-know where bathroom is
-exercise mild/mod HF
-check dyspnea
-check BP
-check wt
-check fatigue
when exercising pt w/ CHF
-check dyspnea
-check RPE
-low intensity, long duration
-more rest
-volume should increase overtime based on observable adaptations
pt ed for CHF
-volume monitoring
-med adherence
-dietary restrictions
-monitoring for s/s of decompensation
valvular disease
-valve defect that restricts or causes backflow
effect of valvular disease on physiology
-increased afterload-->concentric hypertrophy of ventricle
-HF
-decreased CO
exercise considerations with valvular disease
-decreased exercise tolerance
-dyspnea
-fatigue
pt ed or HEP changes with valvular disease
-check RPE
-energy conservation techniques
peripheral vascular disease
-atherosclerosis in peripheral arteries
ABI
-> 1.4 abnormal, incompressible tib aa
-1-1.4 normal
-0.9-0.99 borderline, acceptable
-0.80-0.89 mild disease
-0.5-0.79 moderate disease, specialist referral
-<0.3 severe limb disease
exercise considerations with PVD/PAD
-overcome fear of claudication pain and falling
-exercise only to mild or no sxs
-interval training better tolerated initially
-non-wt bearing activity is not as effective as wt bearing but can be used to supplement warm-ups
-longer warms ups
-sensory considerations and foot care emphasis
-exercise should be progressed in volume first THEN intensity
-evidence for unsupervised exercise training is mounting
-shifting culture toward tech driven tele coaching and tele monitoring
HR max calculation
-208 - (0.7 x age)
Cardiac output
-HRxSV
-5L/min at rest
-20-40 L/min during exercise
SV
-EDV-ESV
Ejection fraction
-% EDV
primary HTN
-no cause
secondary HTN
-Elevated BP with a specific cause
COPD
-Airway obstruction associated with emphysema and chronic bronchitis
effect on physiology (COPD)
-effortful inhalation-->hypertrophy of accy muscles
-air trapping
-increased effort on exhalation d/t
-decreased skeletal muscle endurance d/t
-shift from type I to type II muscle fibers
-reduced mitochondrial density
-reduced capillary density
-decreased exercise capacity
ed and HEP considerations in COPD
-tripod
-barrel chest
-inspiratory muscle training
-resistance training
-rib joint mobilizations
-stress management
pneumonia
-acute inflammation of the lungs caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal pathogen
-collection of edema, RBC, WBC leave lung tissue unable to perform ventilation or perfusion
effect on physiology pneumonia
-decreased cilia
-decreased oropharyngeal clearance-->aspiration
-decreased immune response
clincial presentation of pneumonia
-productive cough
-yellow, green, rust colored sputum
-dyspnea
-tachycardia
-tachypnesa
-hypoxemia
presentation of pneumonia in older adults
-change in mental status
-anorexia
-decrease in function and activity tolerance
-falls
-incontinence
-elevated HR
-changes in sleep cycle
how will ed and HEP change s/p pneumonia
-more rest breaks
-work on endurance
-refer for swallowing
Rehab for pulmonary conditions
-breathing control
-chest PT
-conditioning exercise
-pt ed
-helping ribcage mobilization
Rehab for cardiac conditions
-Pt ed
-appropriately dosed exercise
-breathing techniques and relaxation
-monitor vitals
-stress mgmt
-nutritional considerations