Nervous System Structures
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
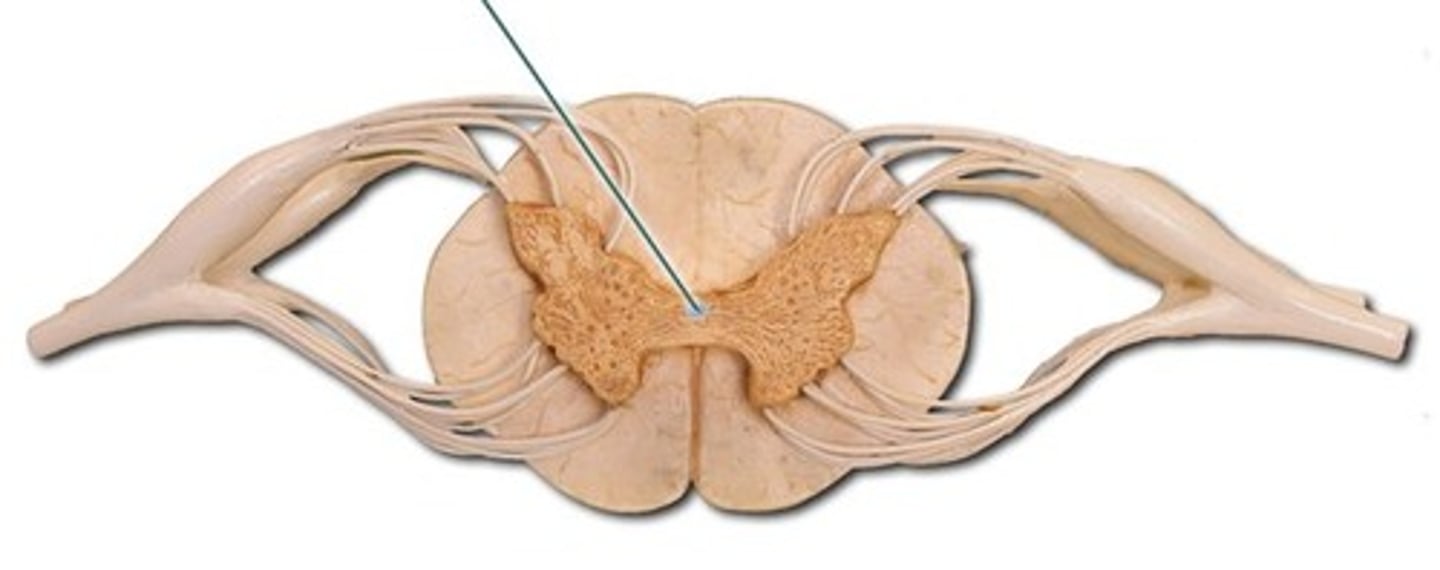
anterior horn
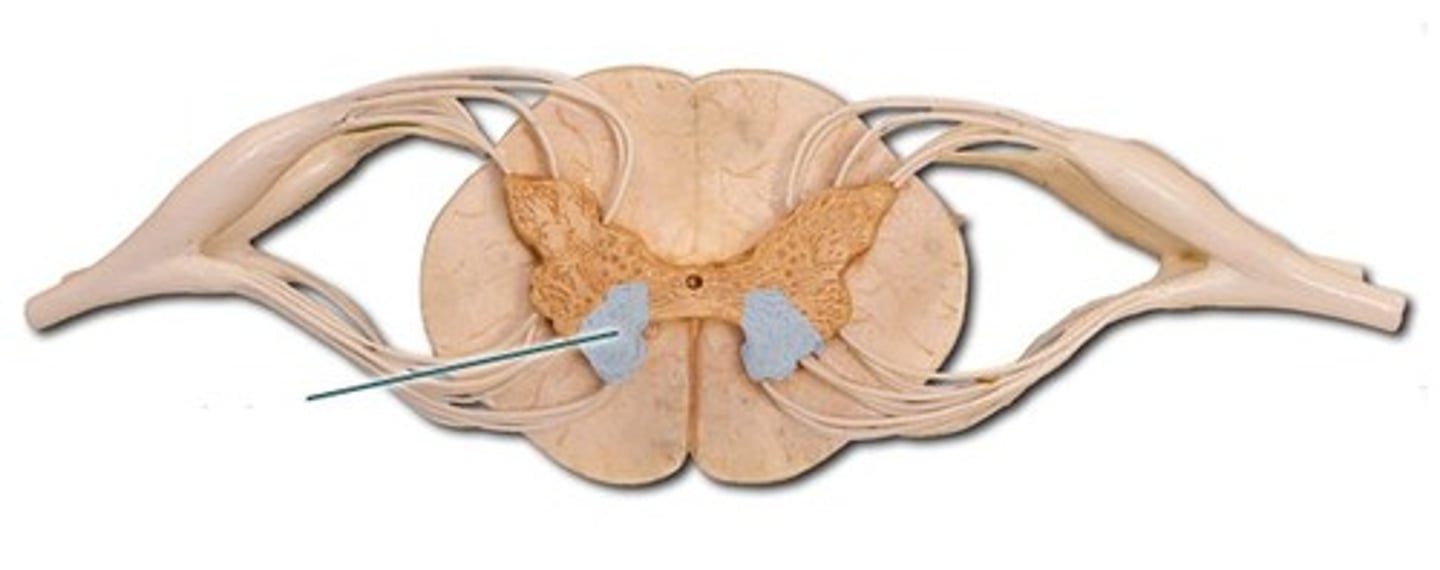
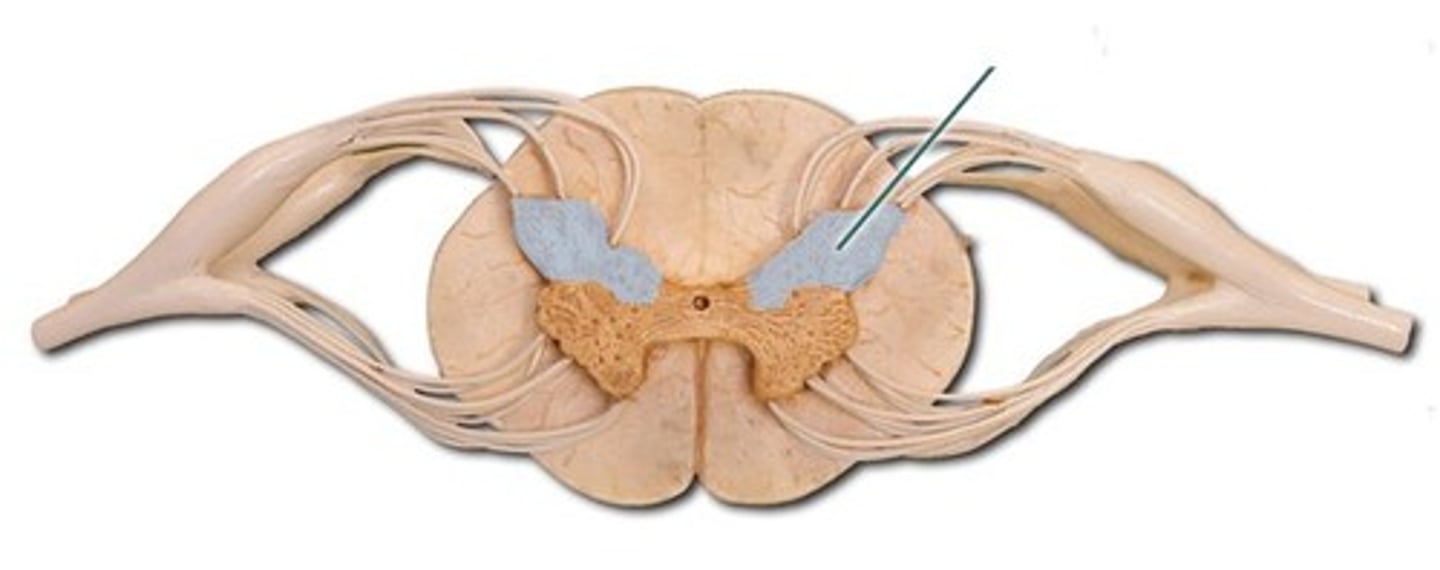
Posterior Horn
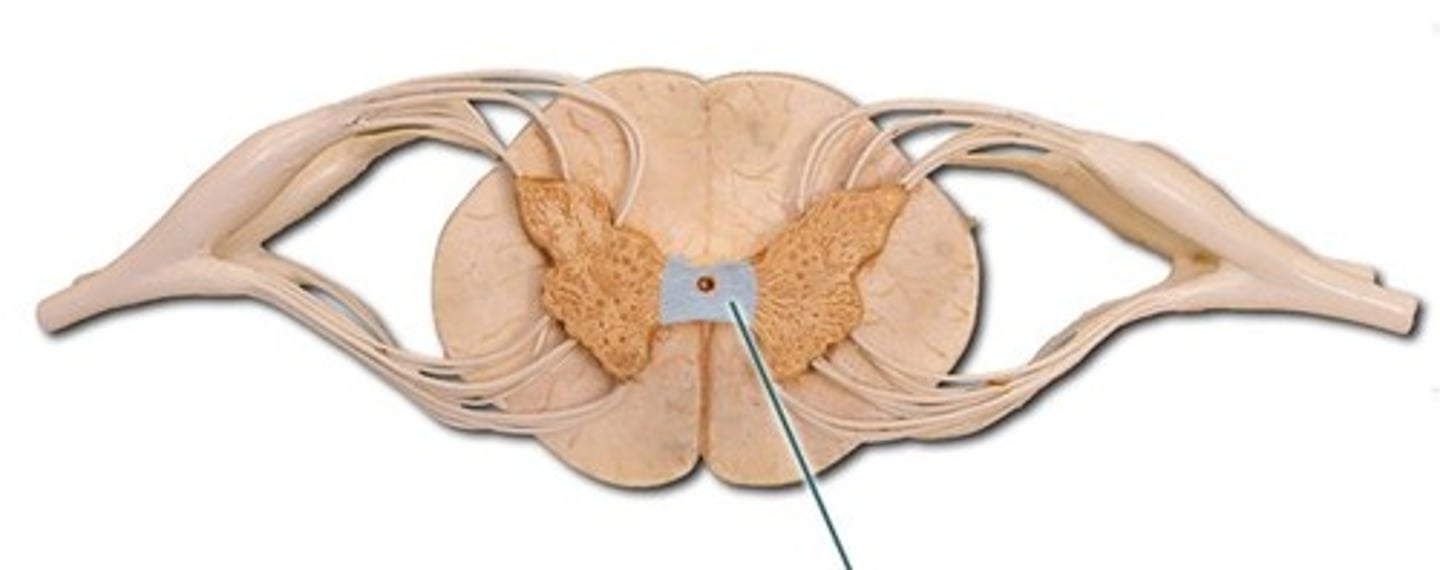
Gray Commissure
Gray Matter
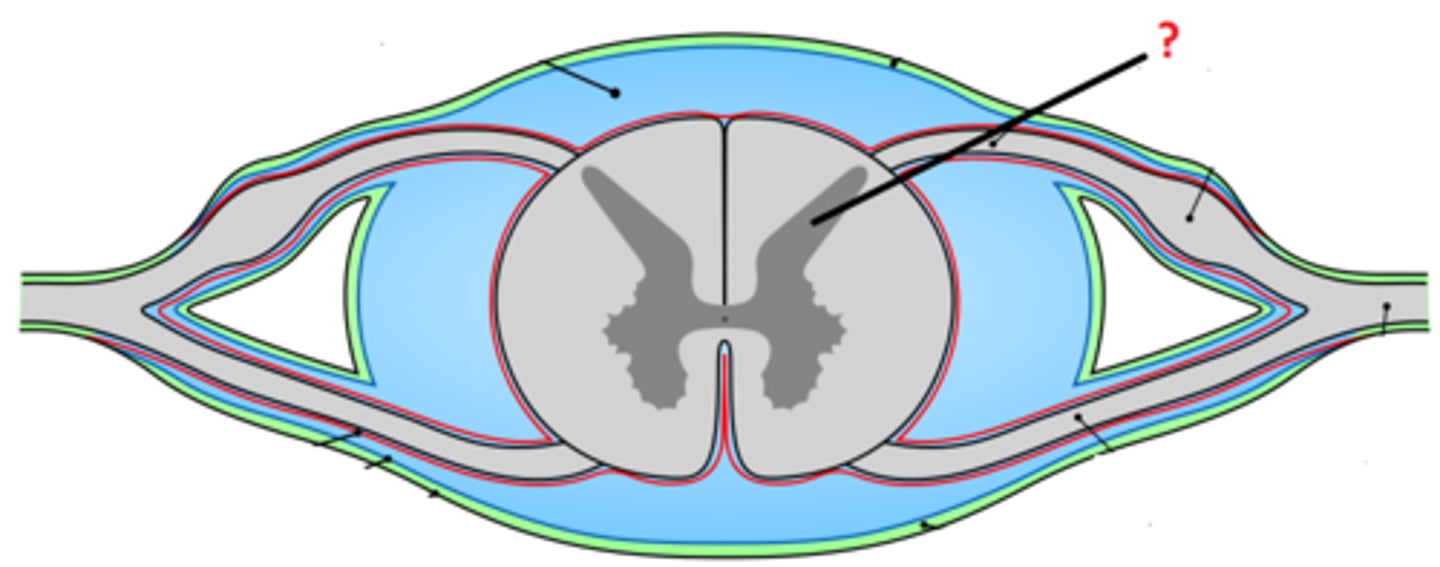
White Matter
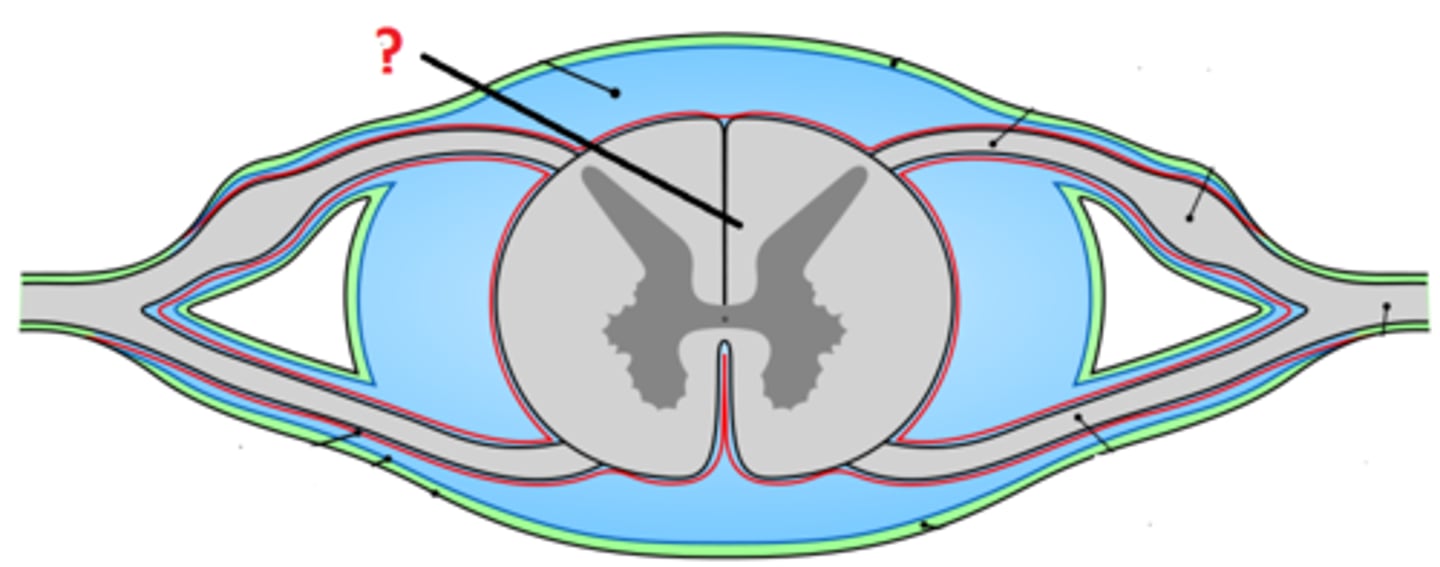
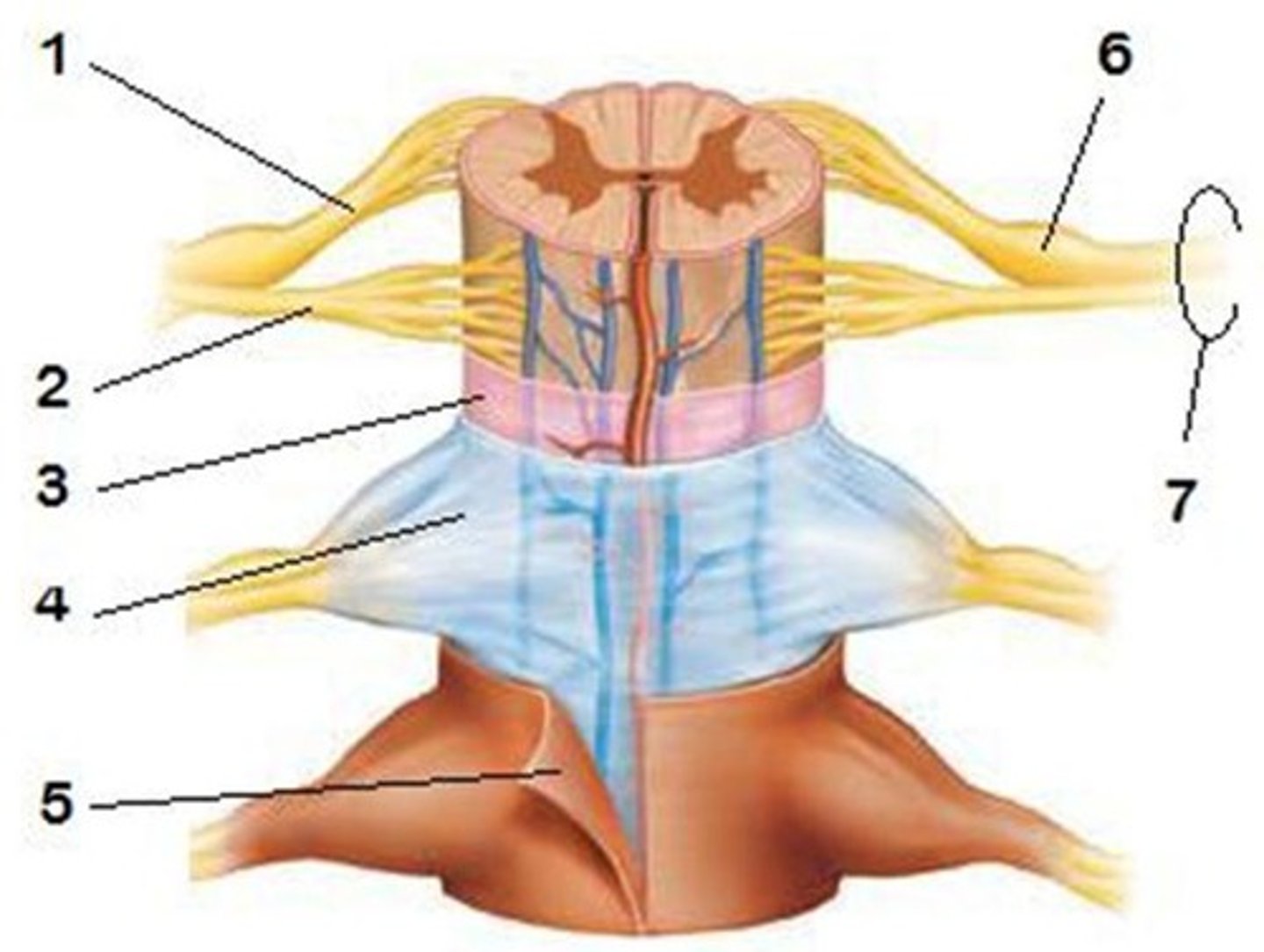
Dorsal Root Ganglion
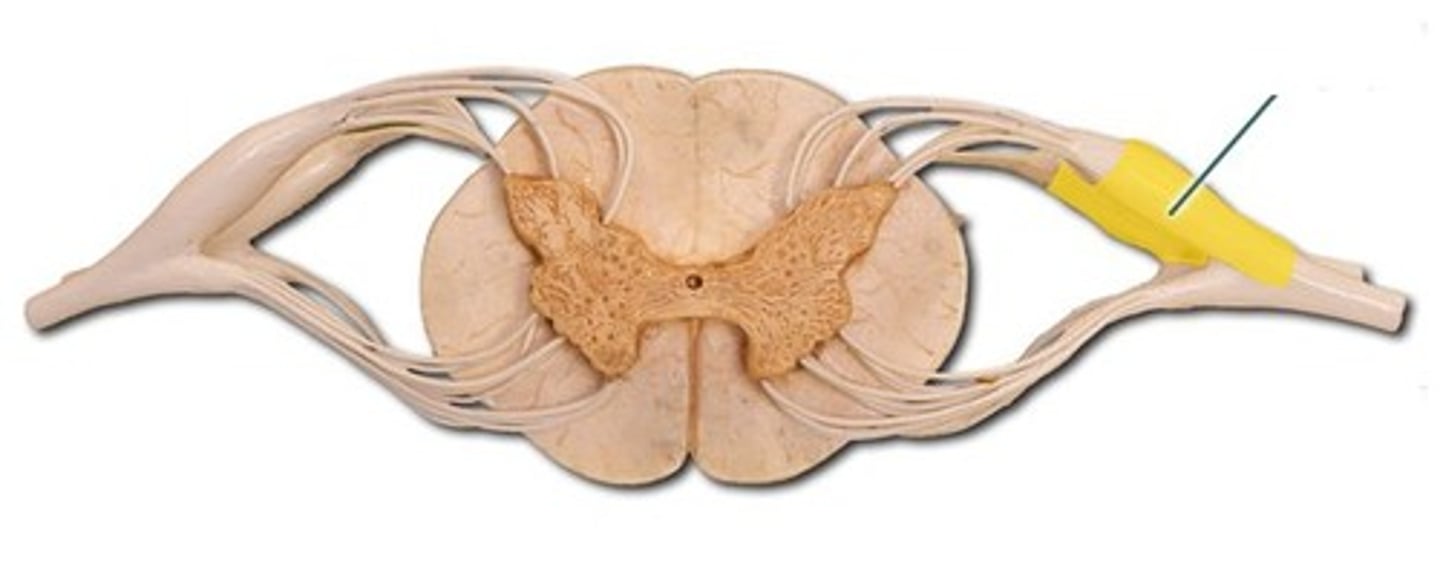
Ventral Root
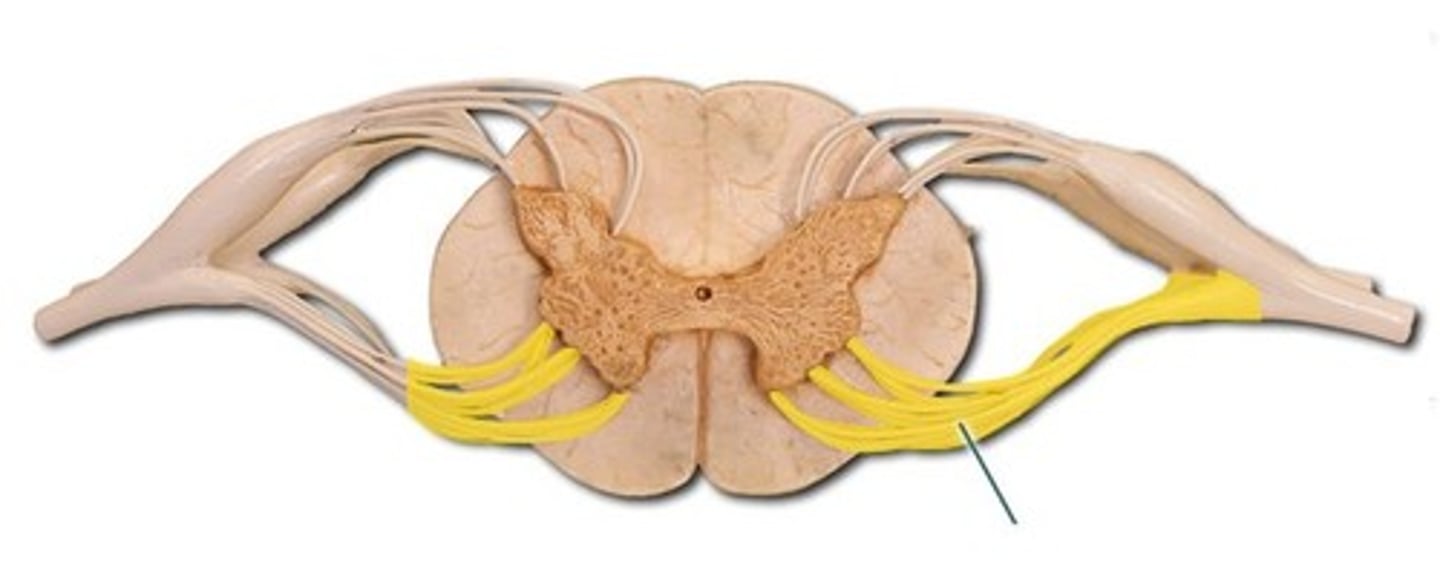
Central Canal
Epidural Space
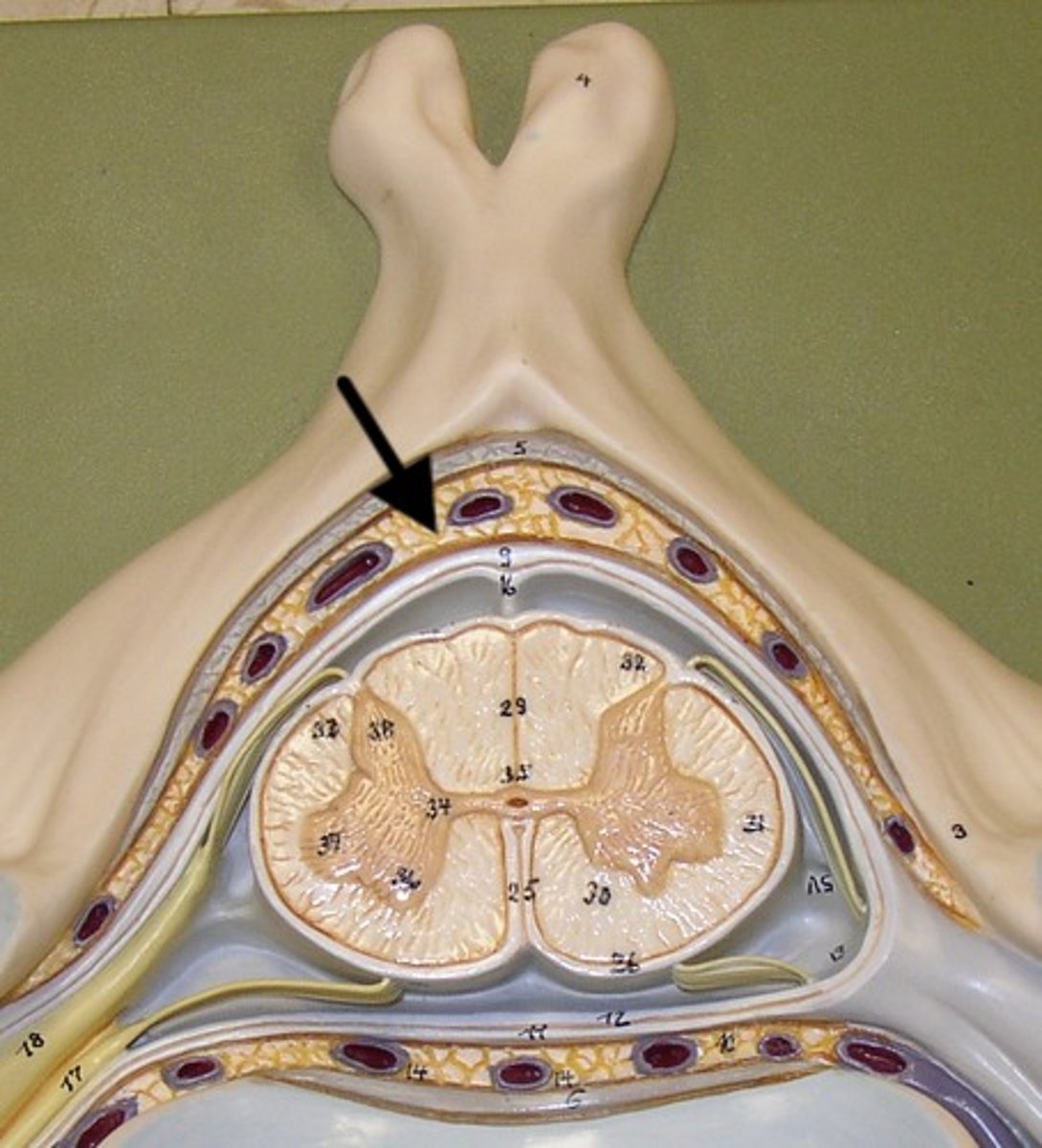
Dura Mater
5
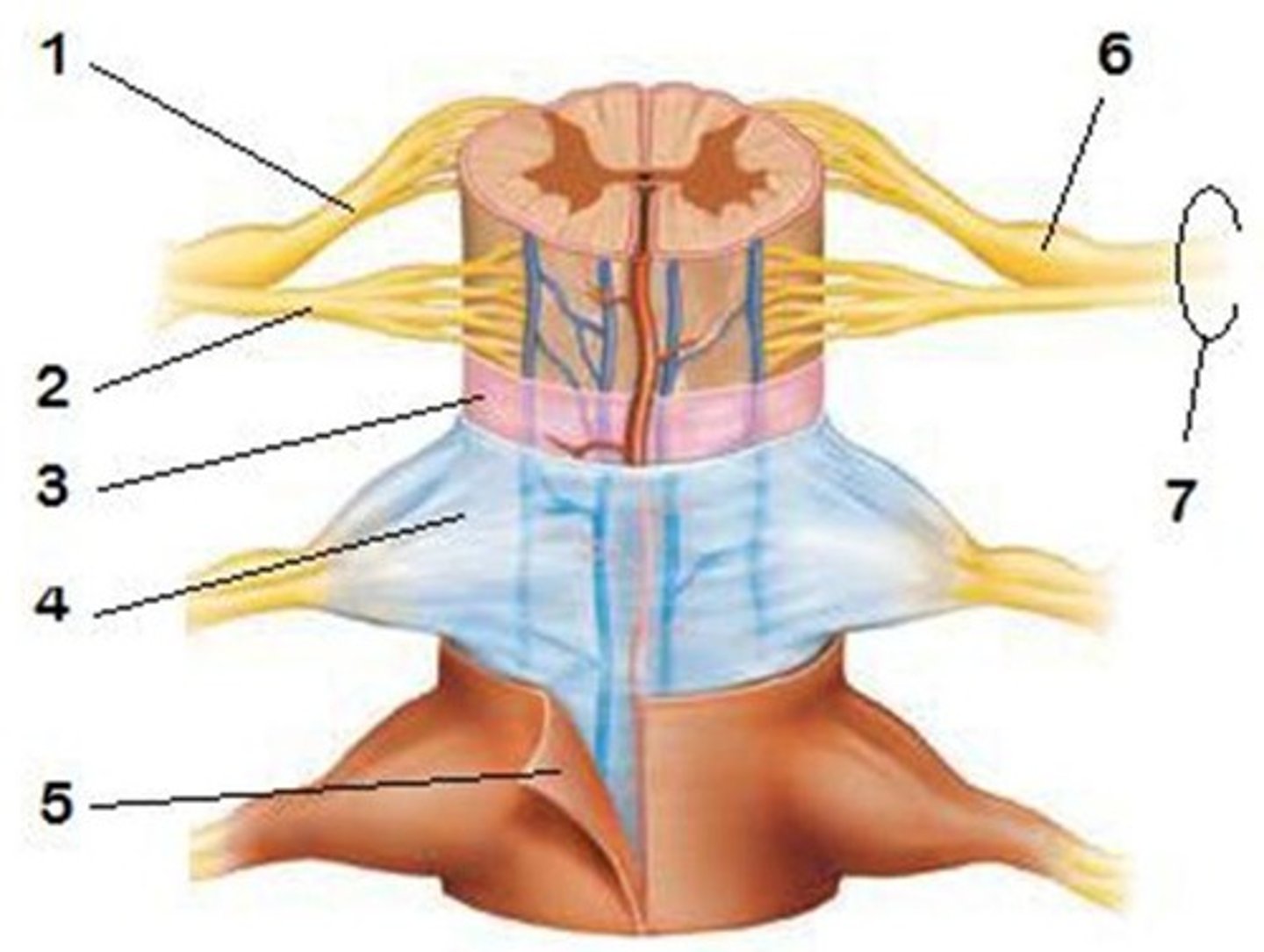
Arachnoid Mater
4
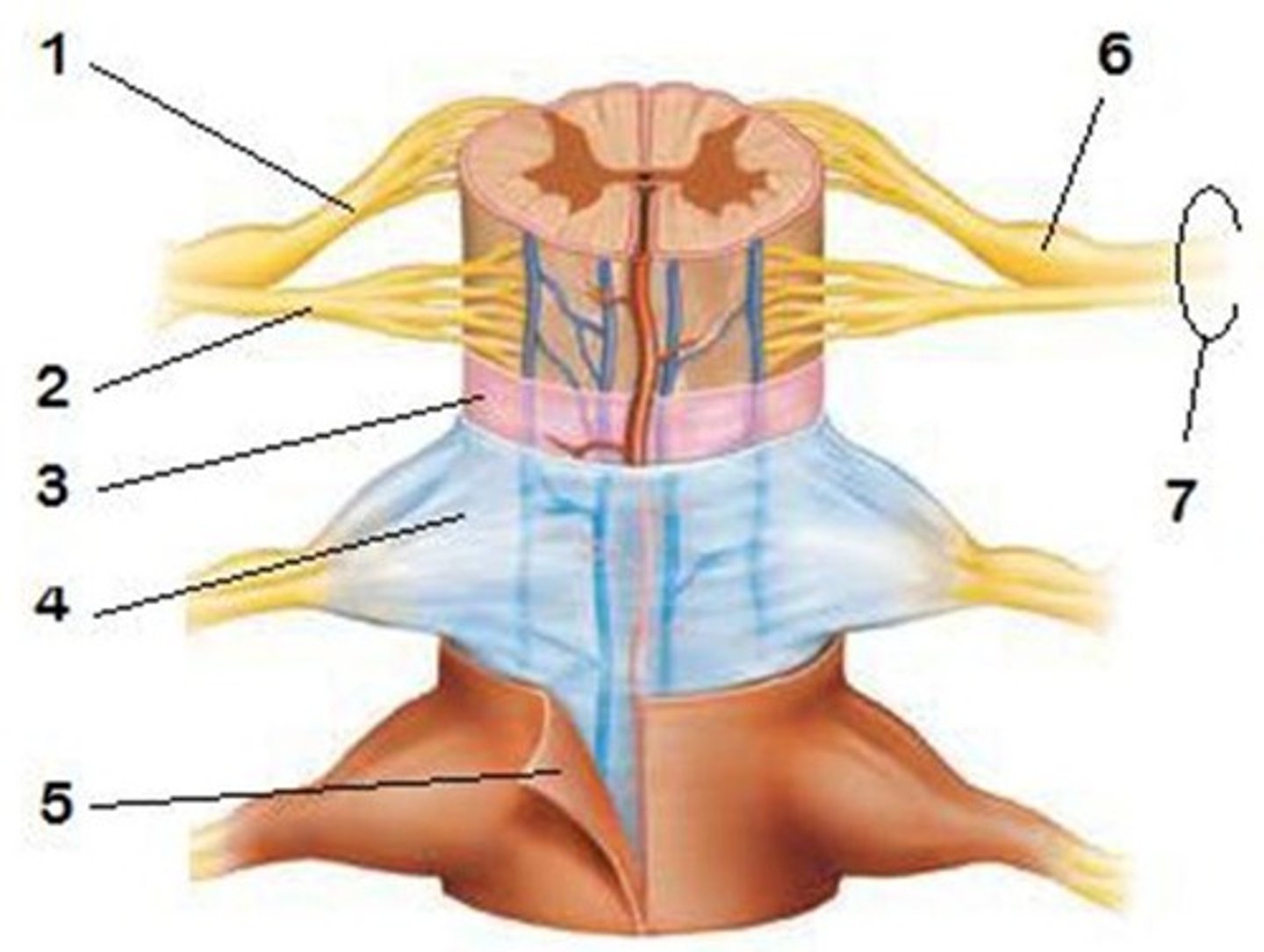
Subarachnoid Space
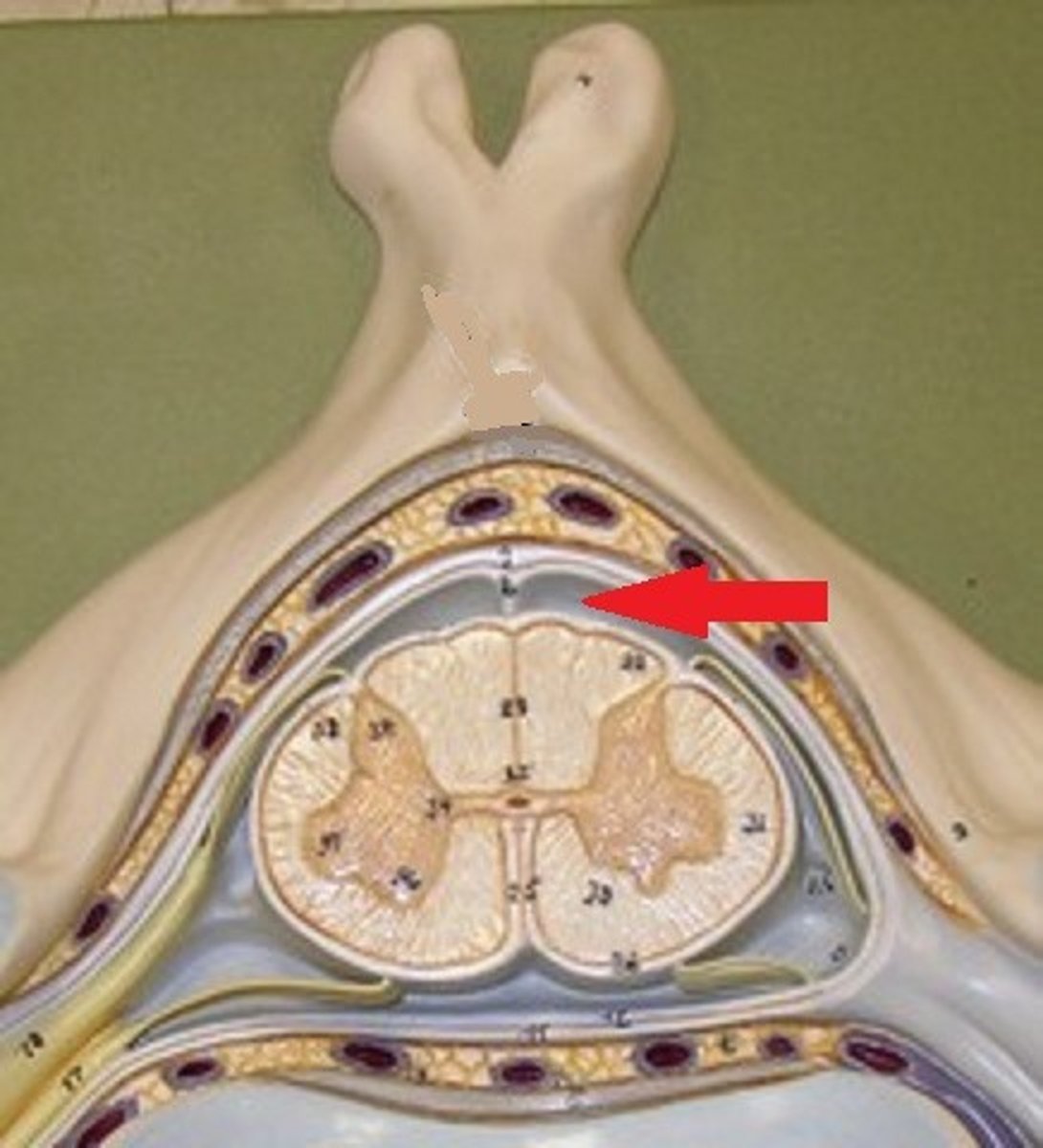
Pia Mater
3
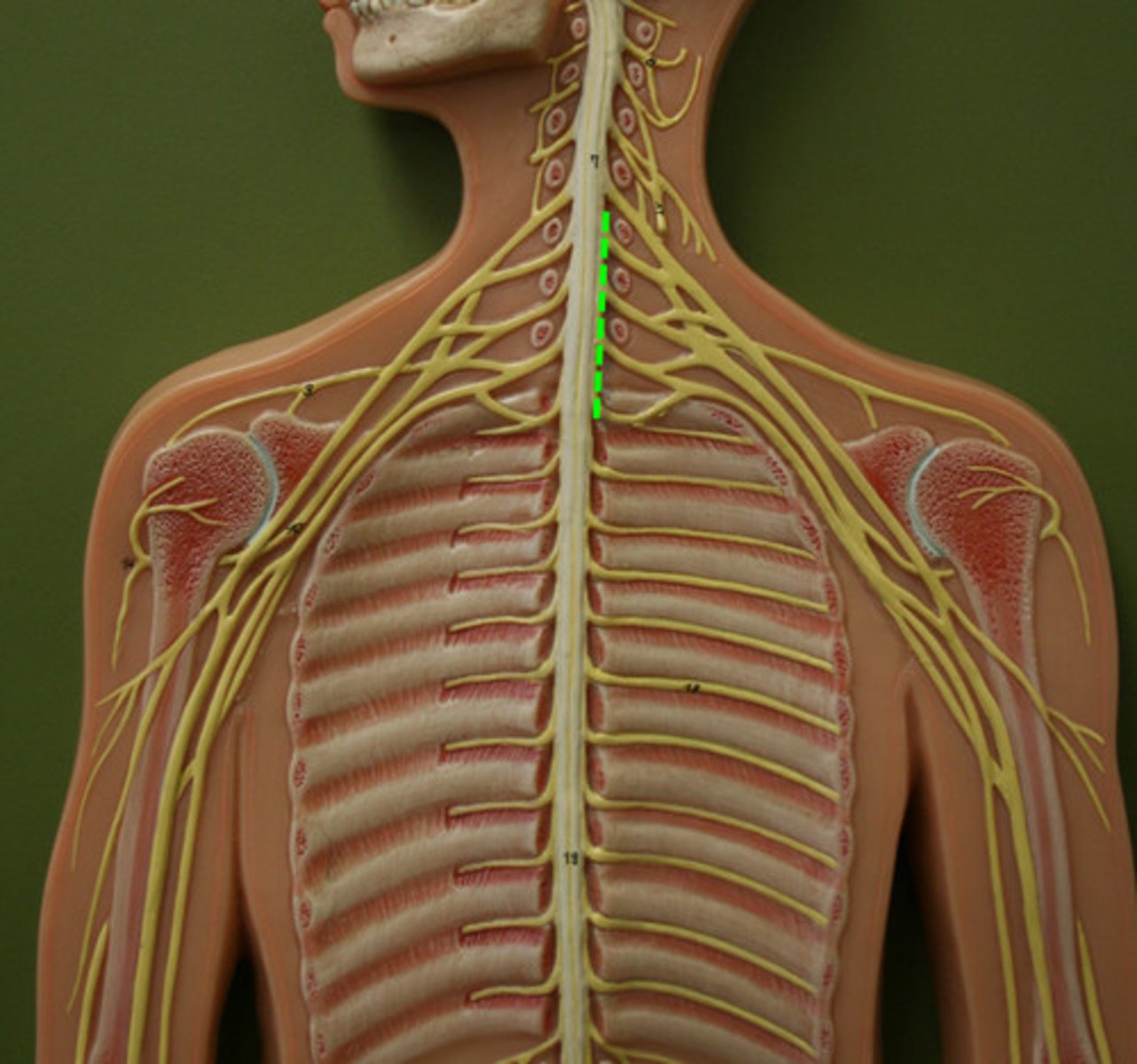
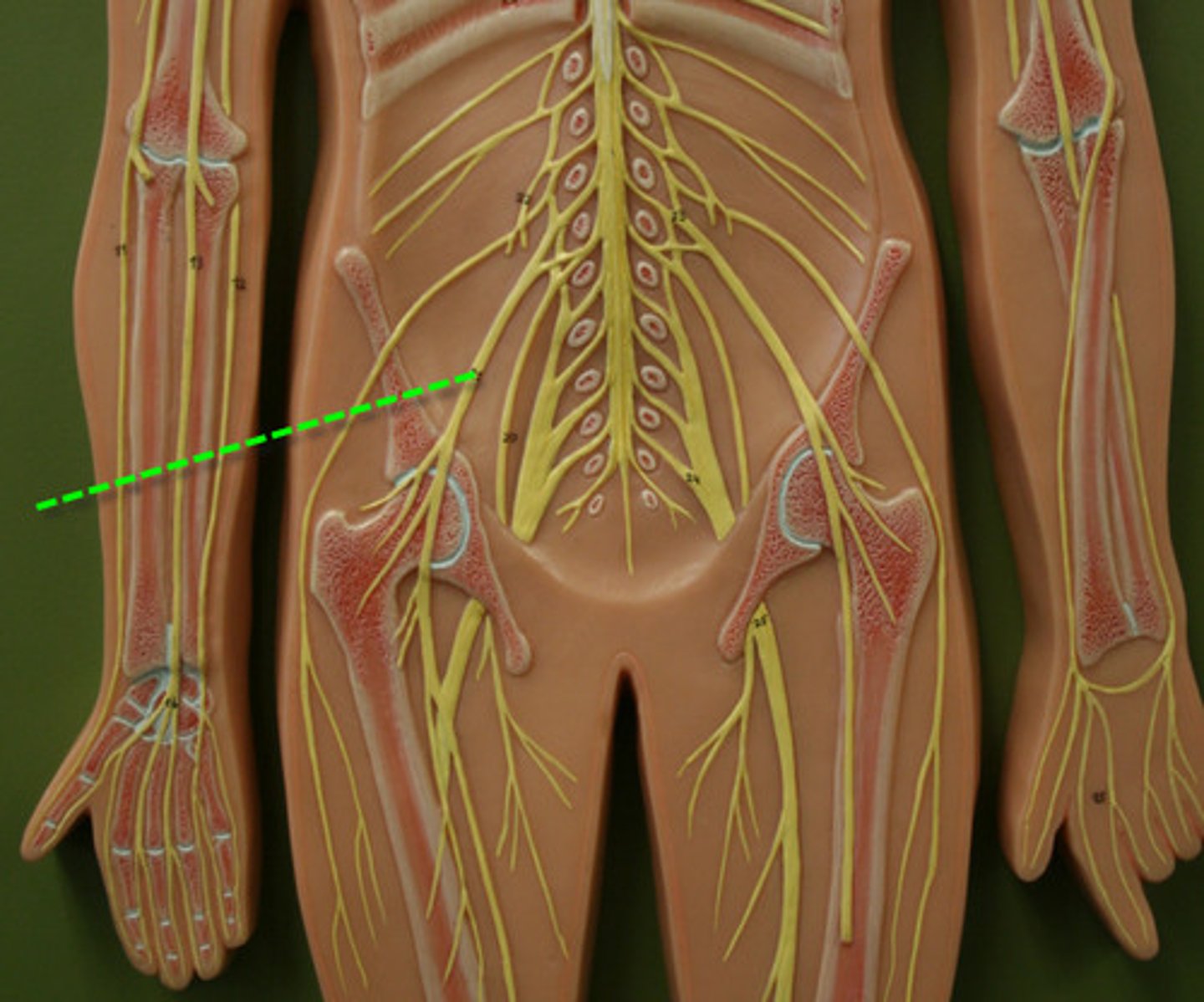
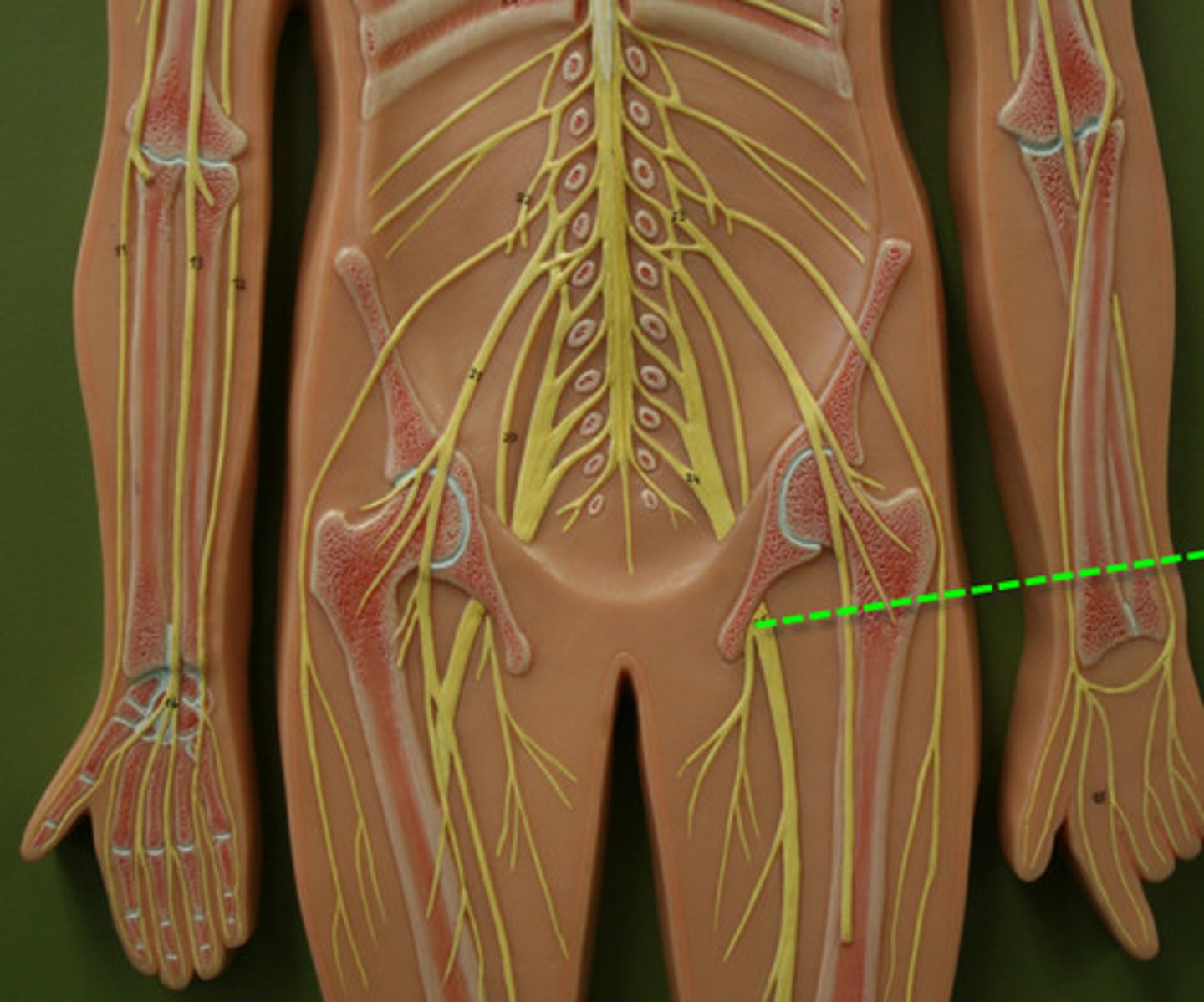
Cervical Plexus
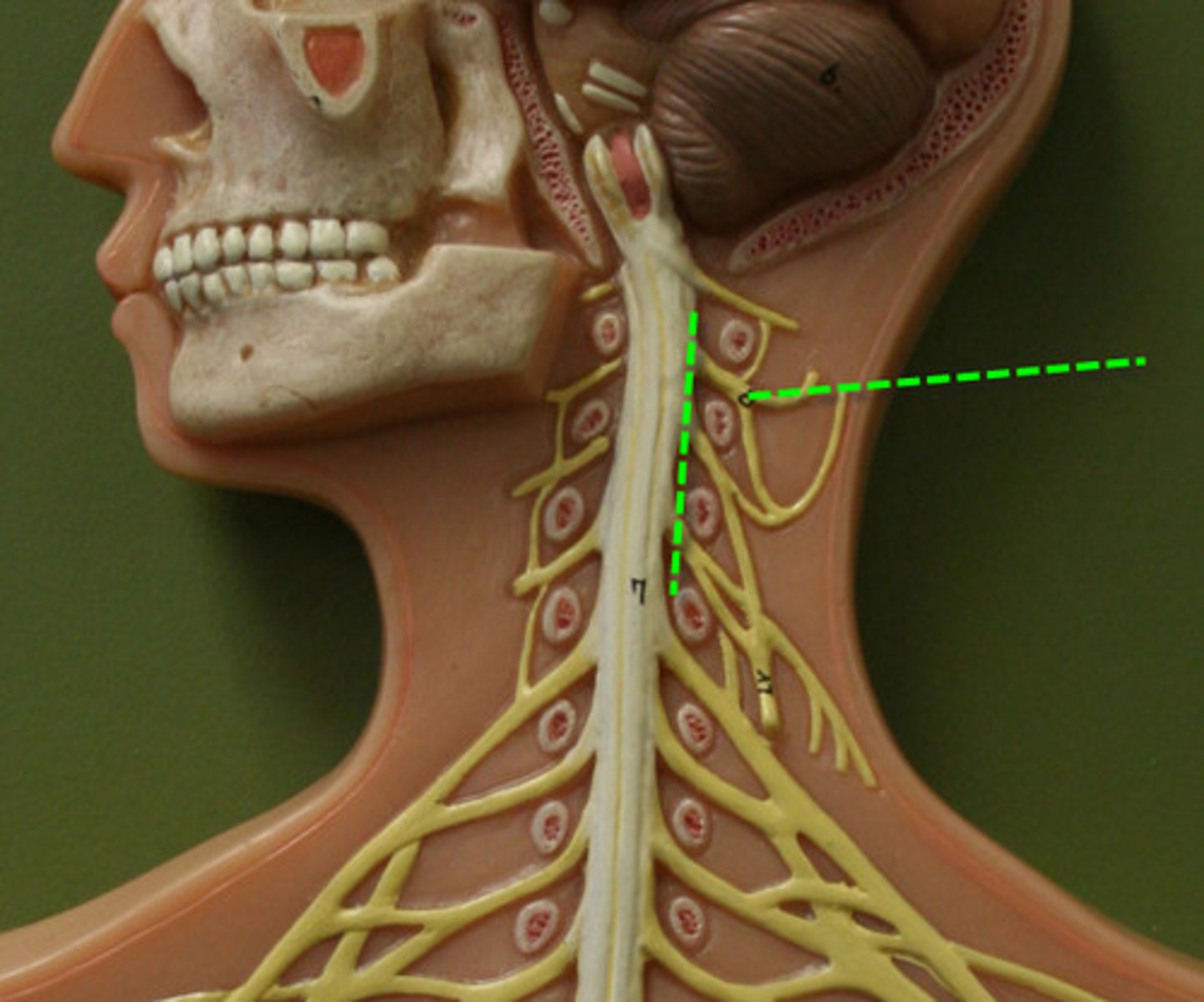
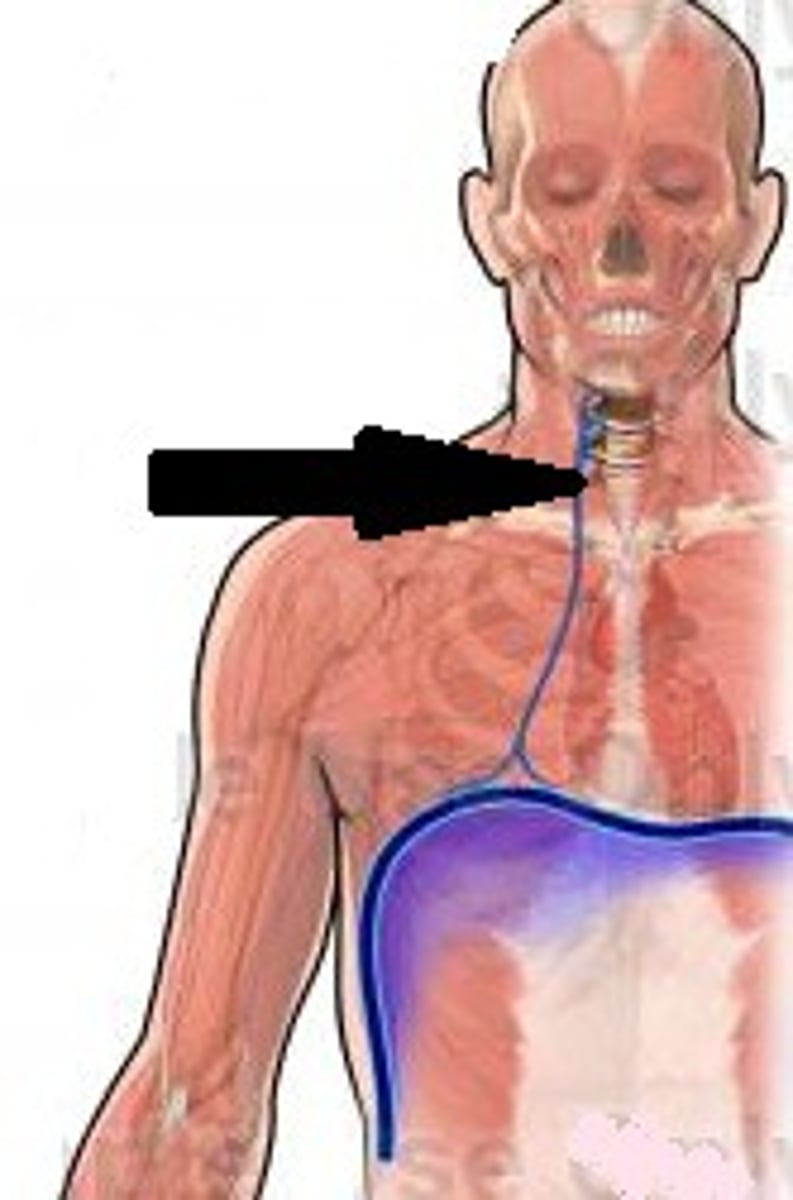
Phrenic Nerve
Brachial Plexus
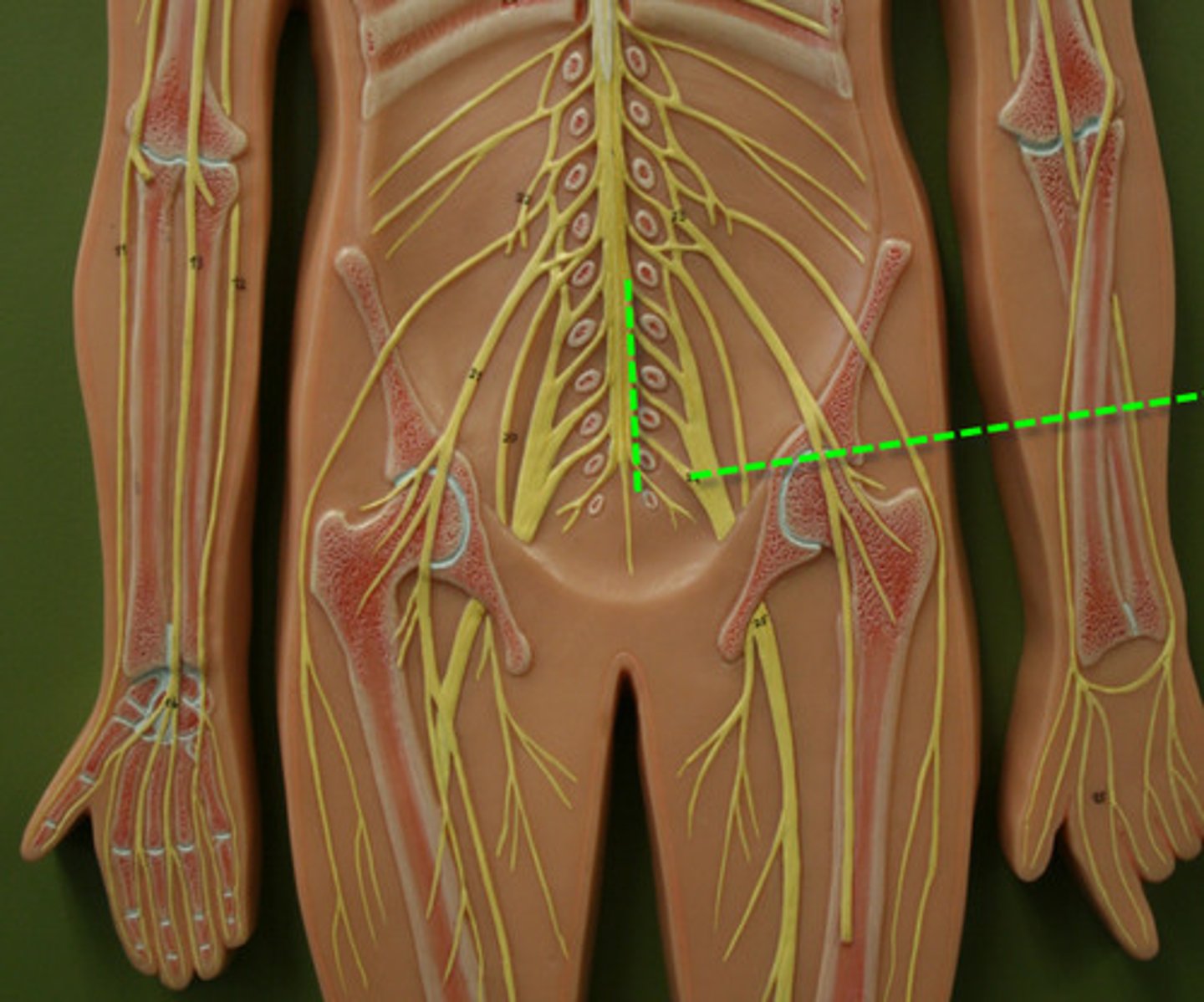
Lumbar Plexus
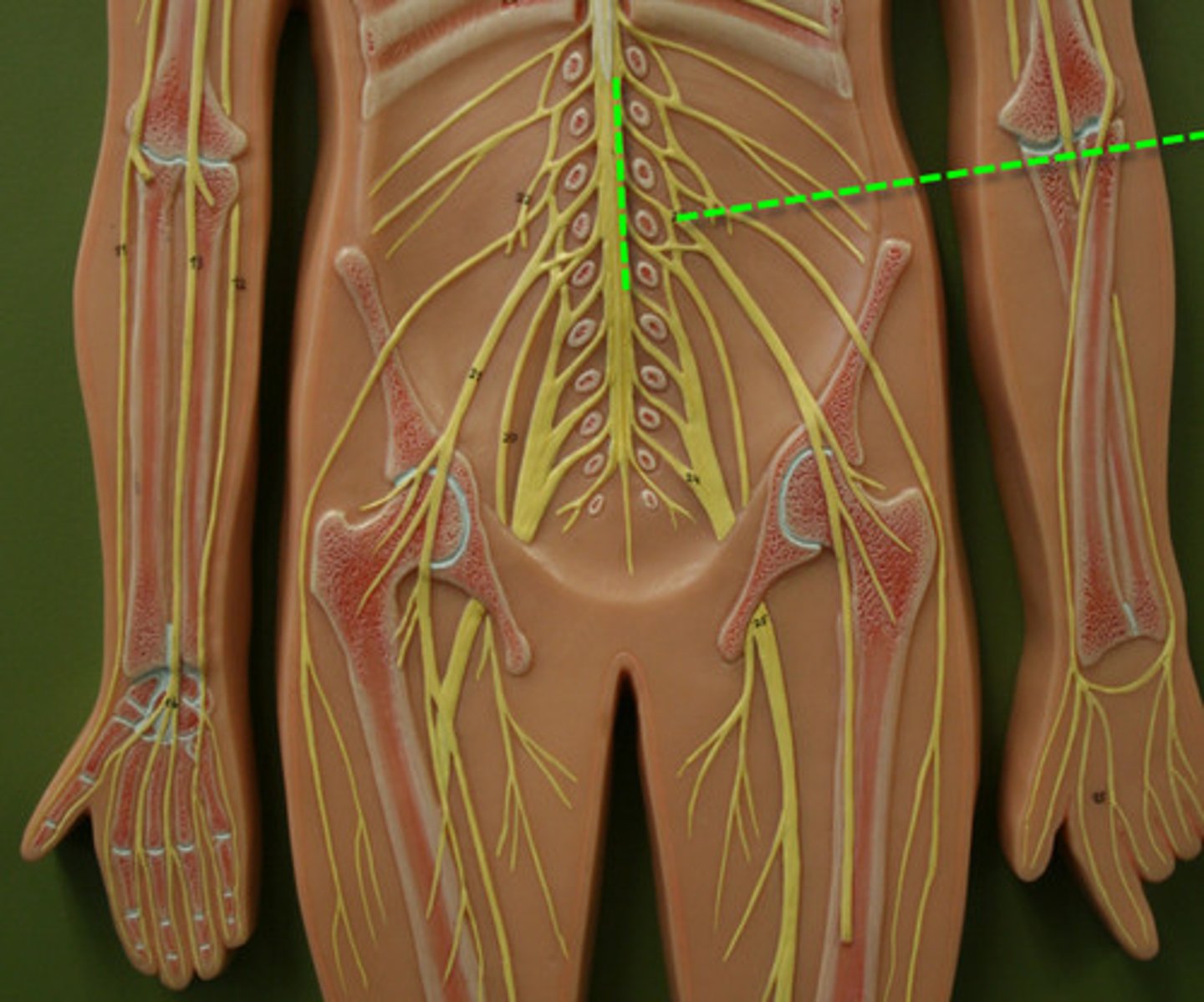
Sacral Plexus
Musculocutaneous Nerve
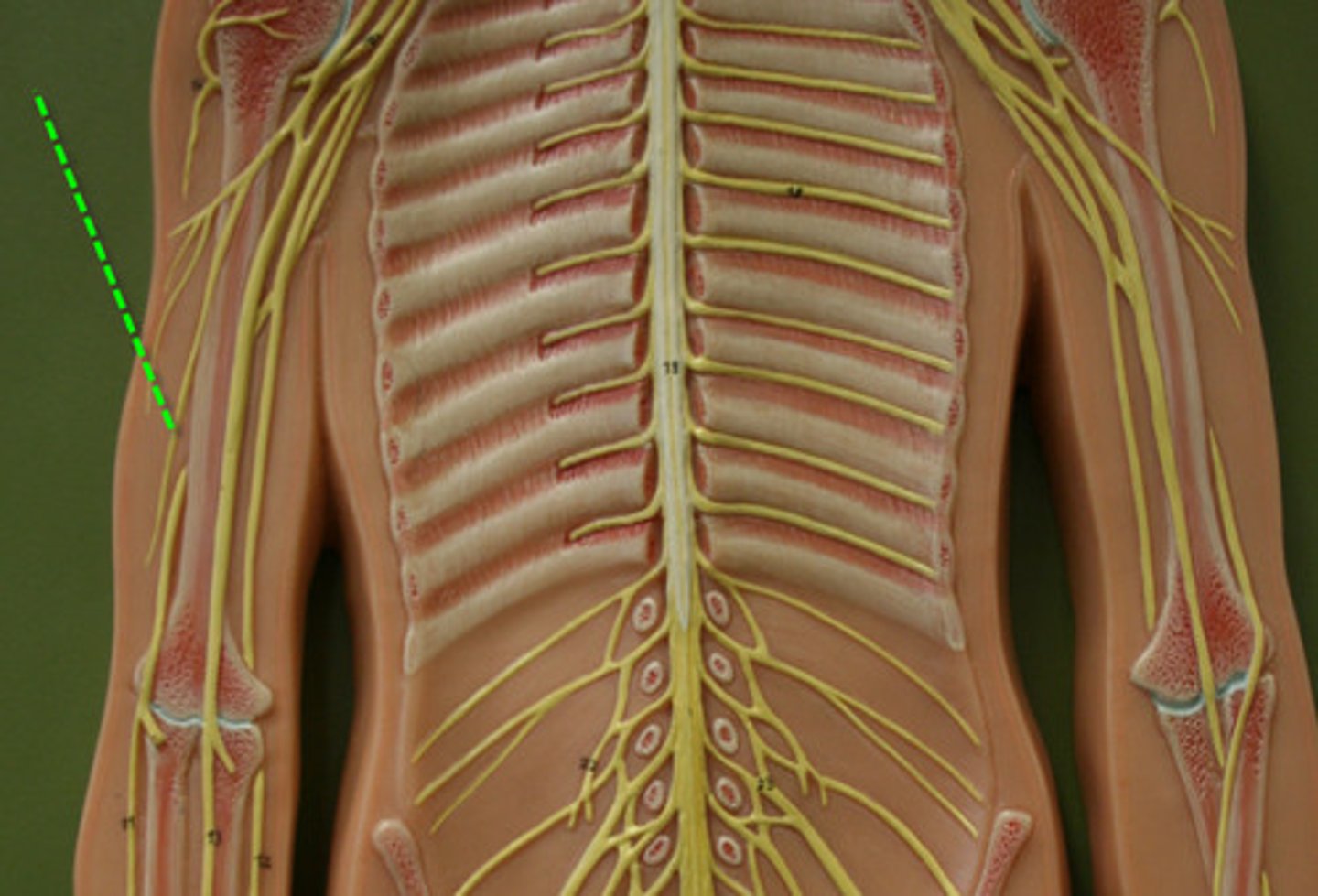
Ulnar Nerve
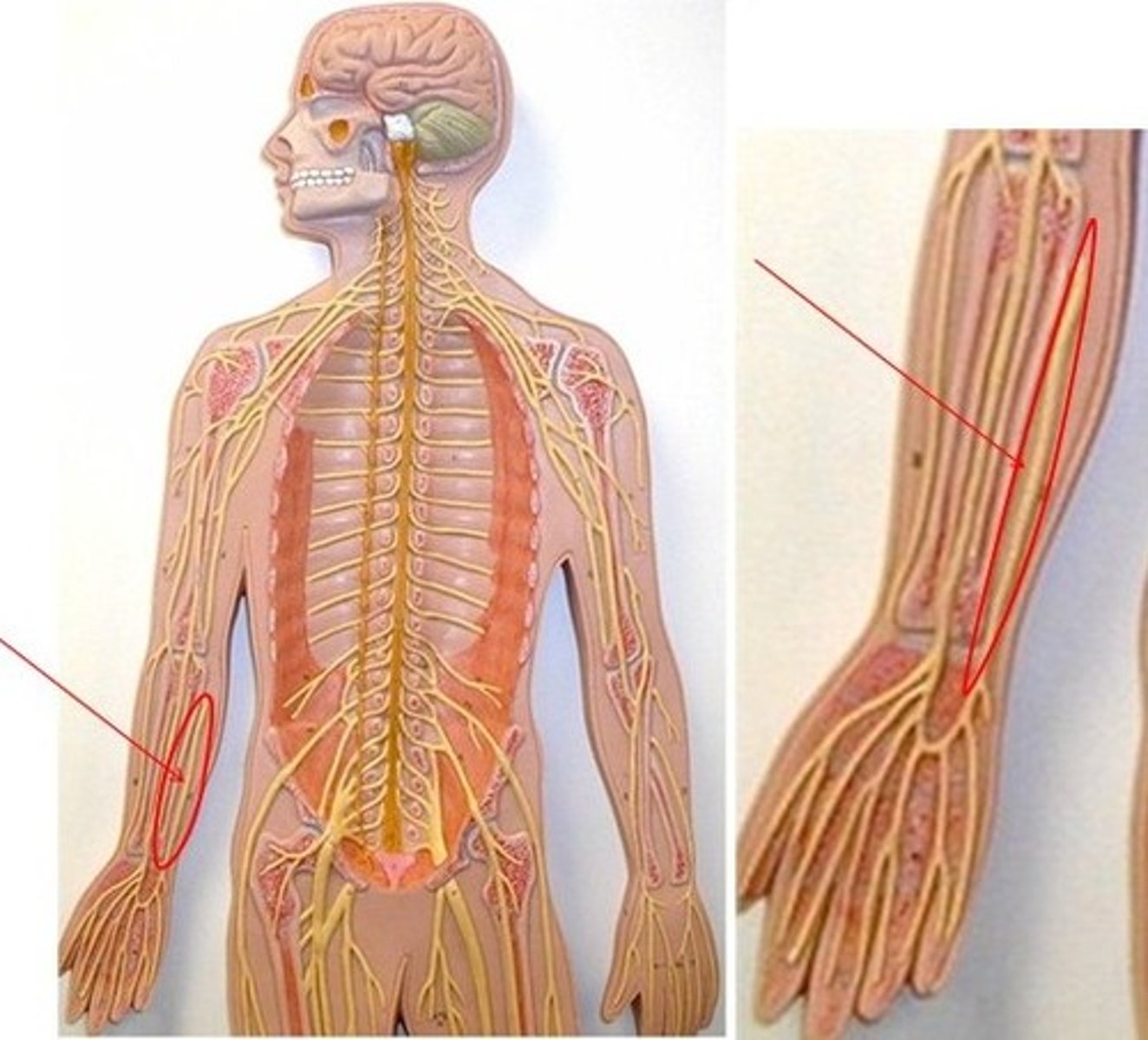
Median Nerve
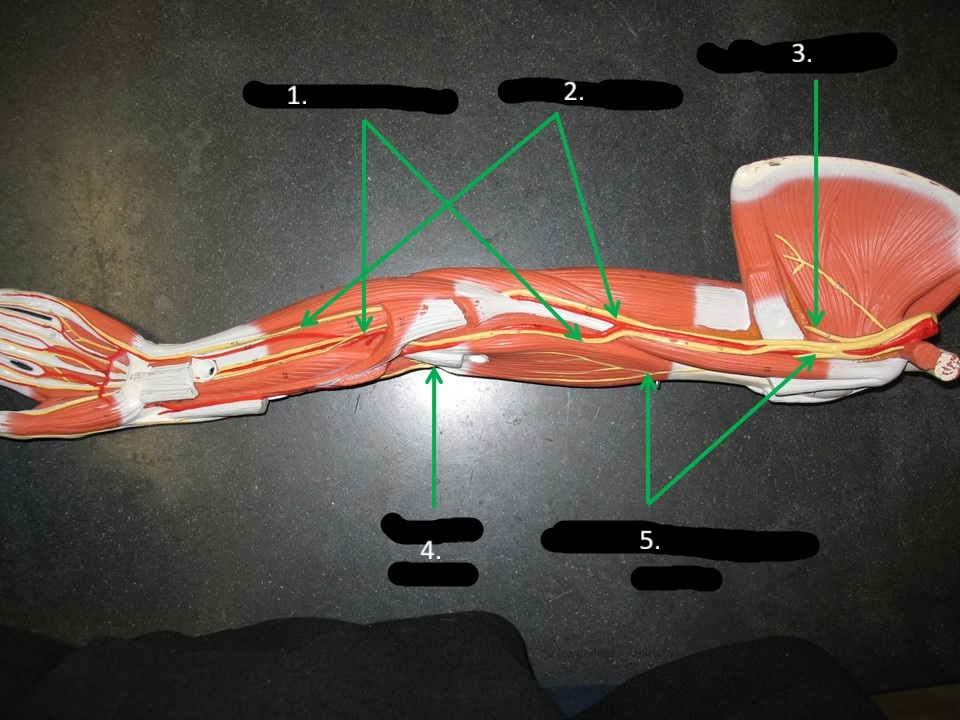
1.
Radial Nerve
Femoral Nerve
Sciatic Nerve
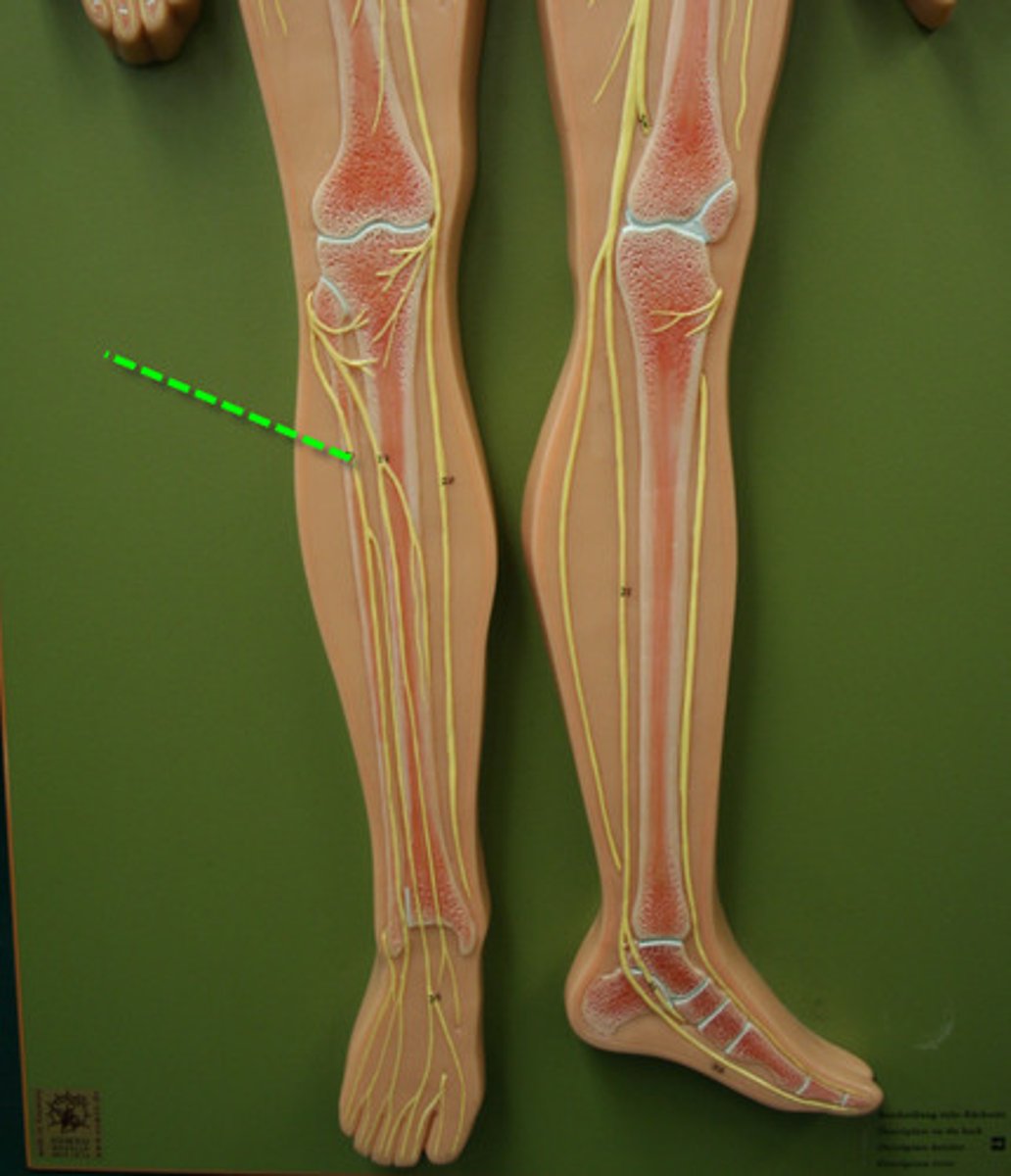
Tibial Nerve
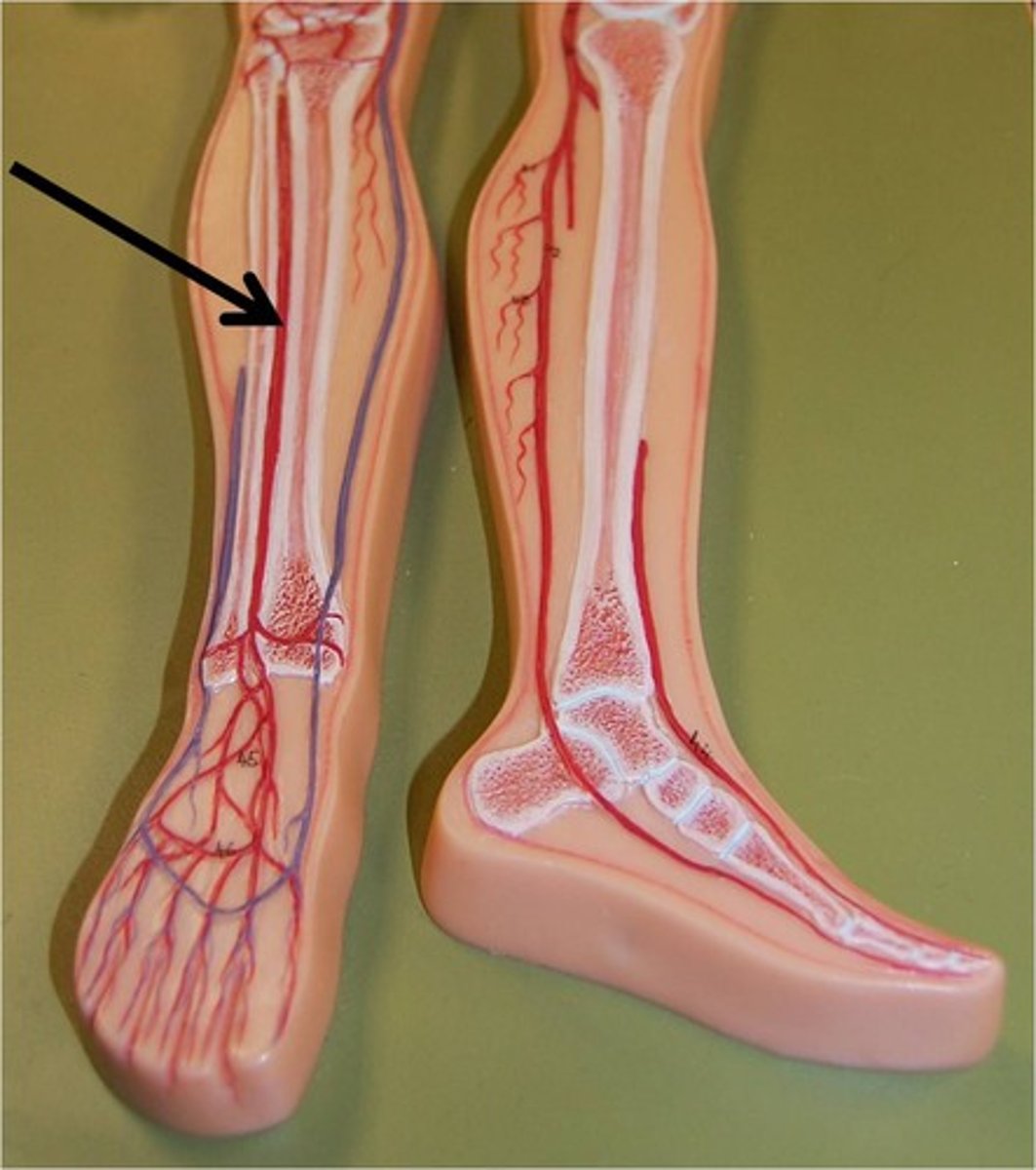
Peroneal Nerve
Cauda Equina
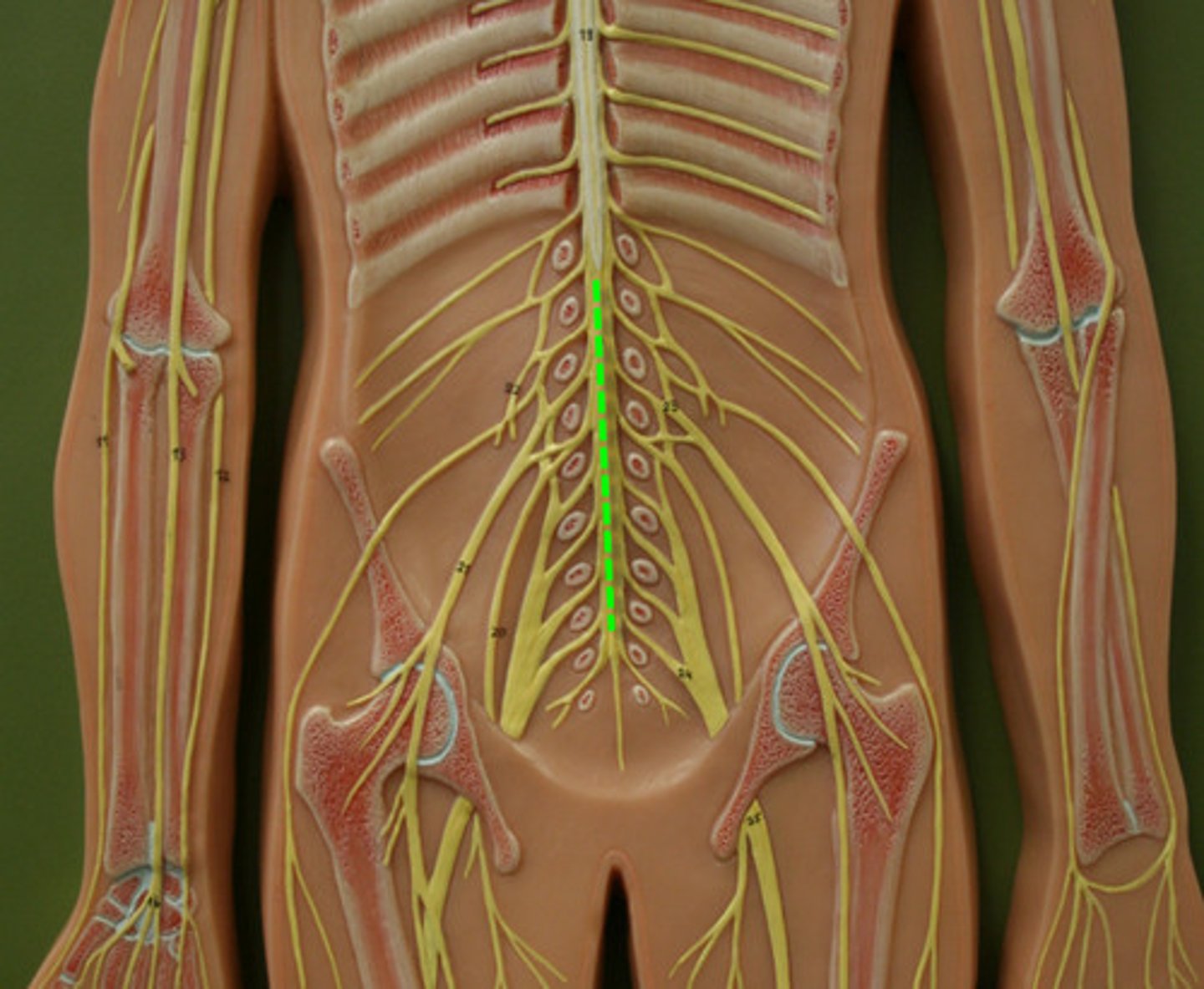
Filum Terminale
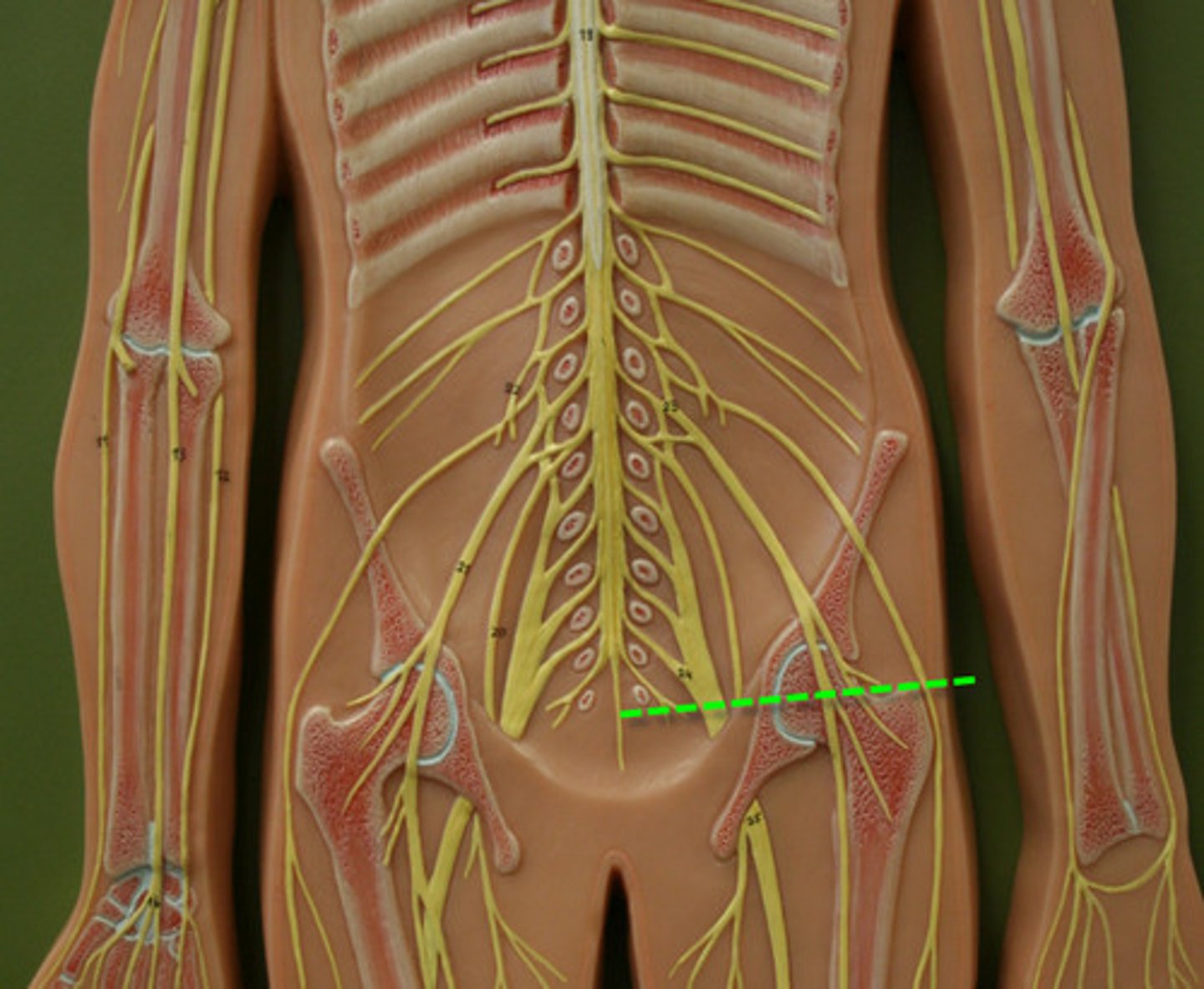
Sympathetic Chain
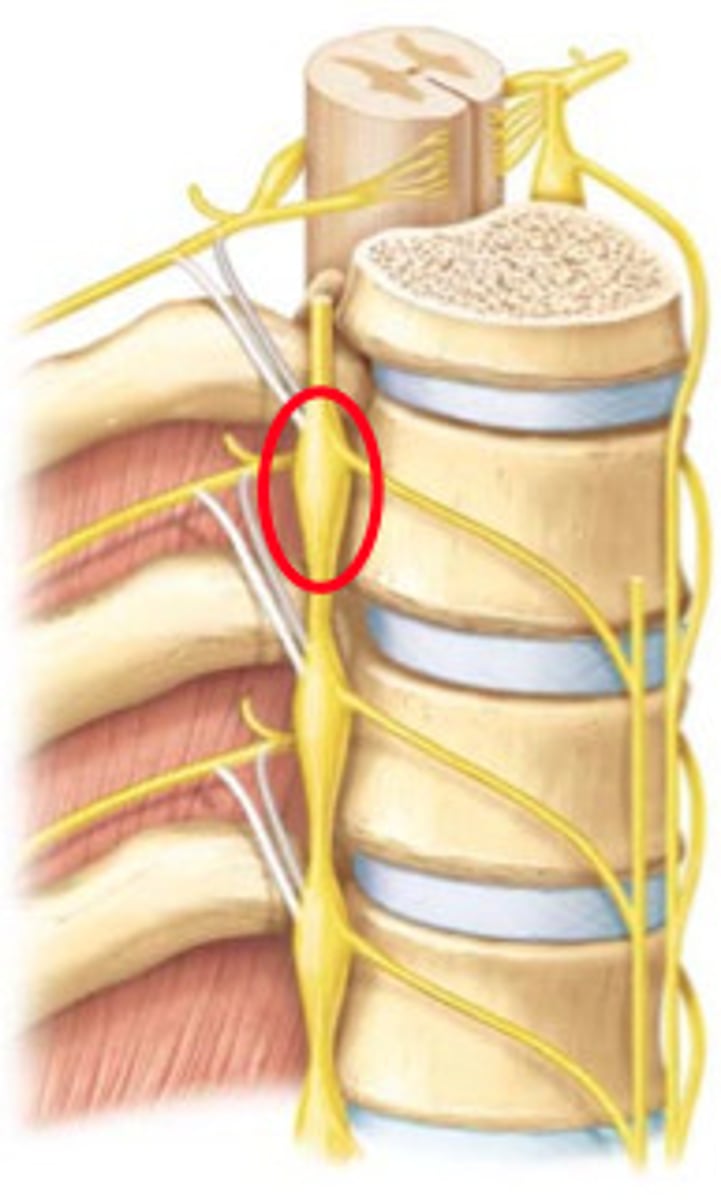
Collateral Ganglia
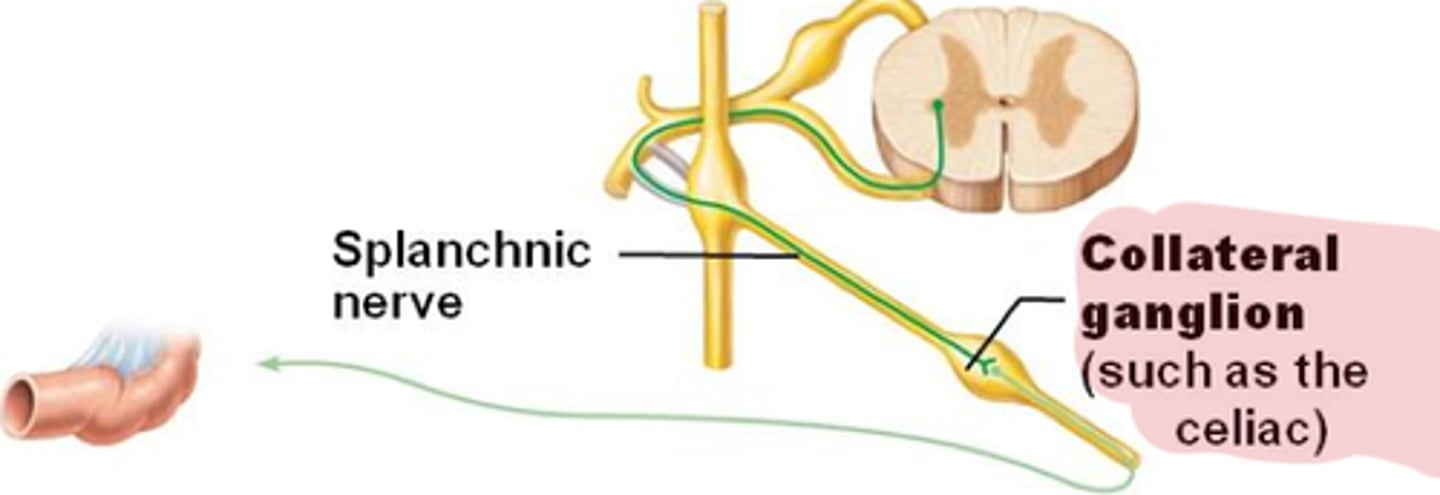
Splanchnic Nerves
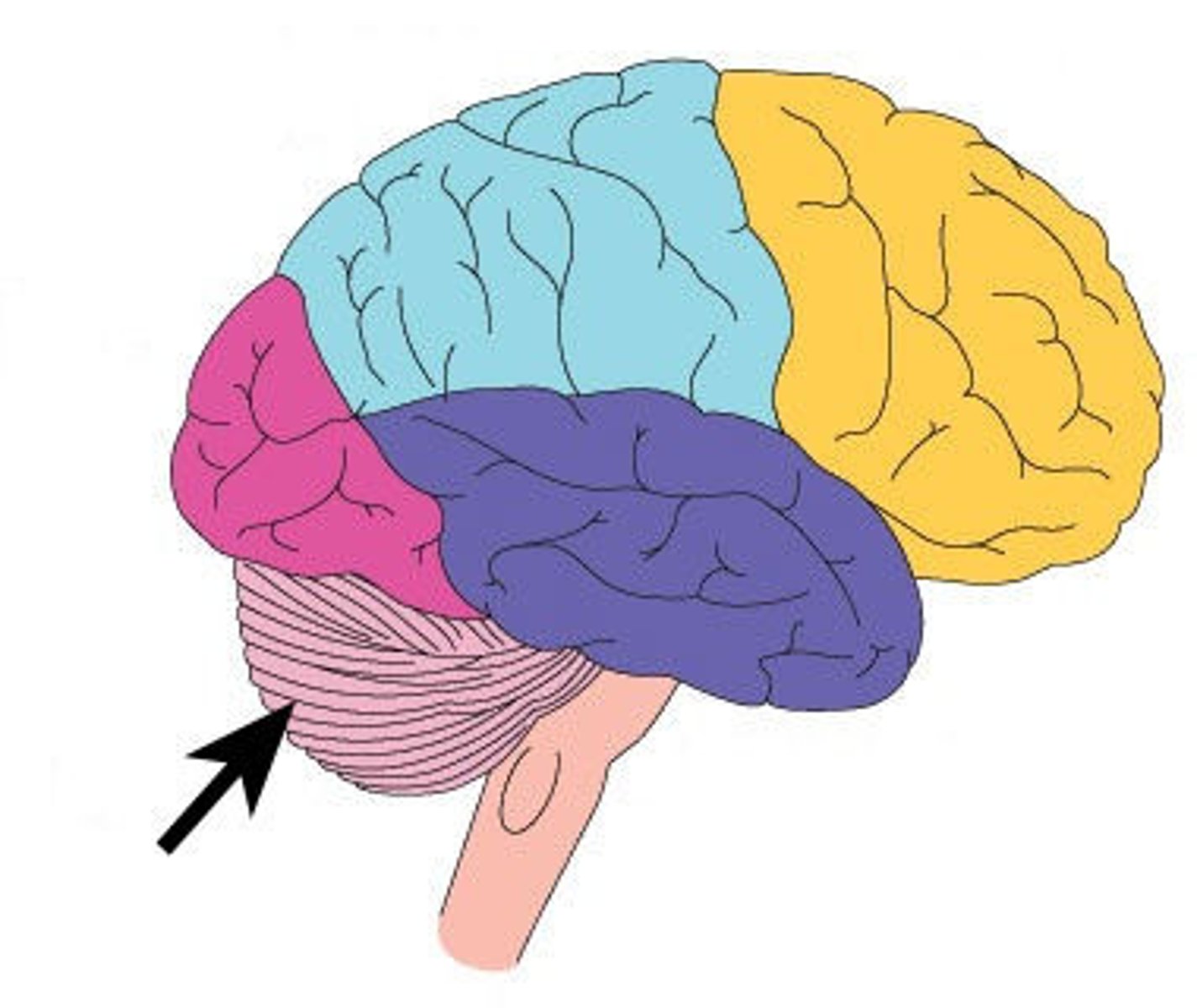
Cerebellum
a large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills
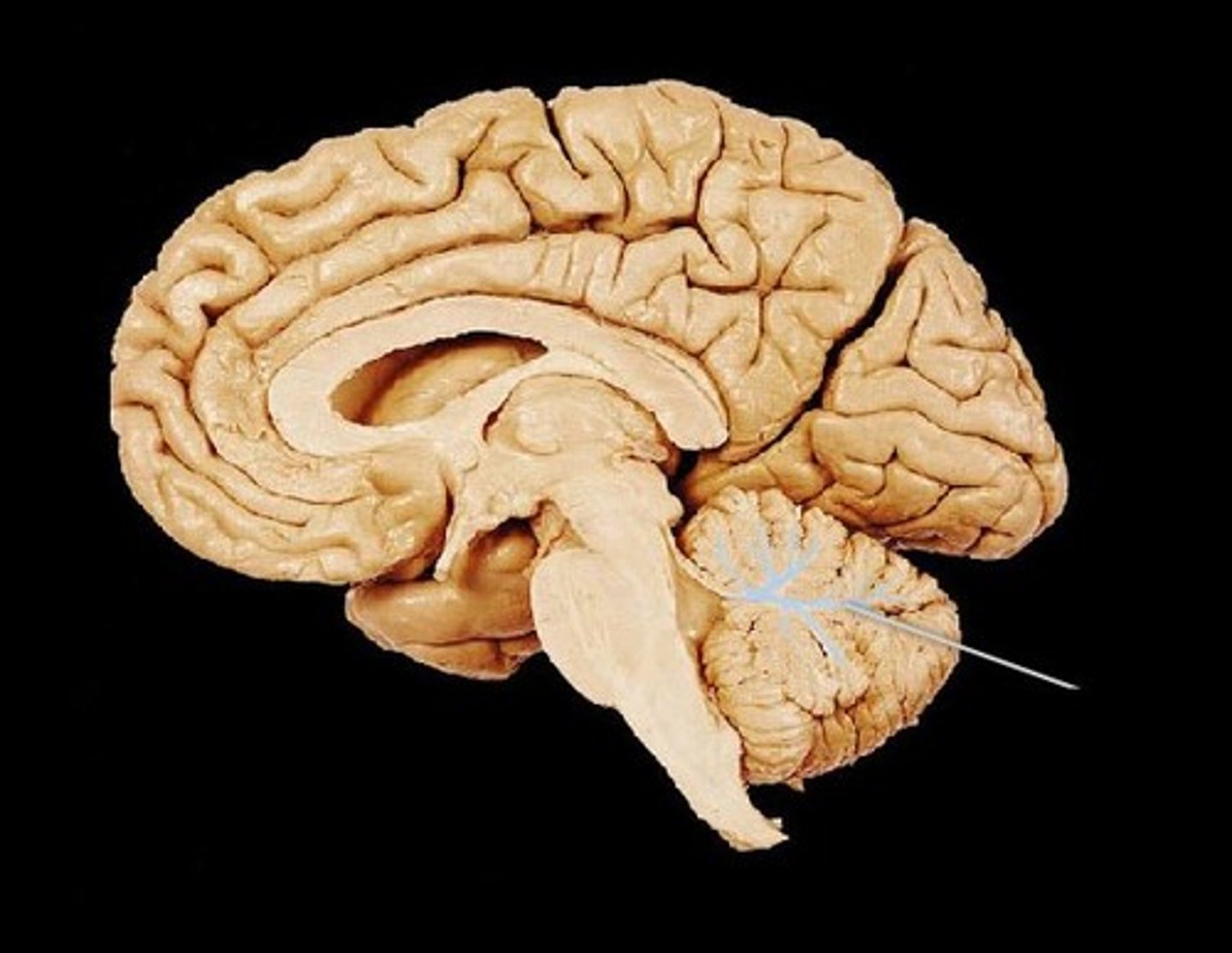
Arbor Vitae
white matter of the cerebellum
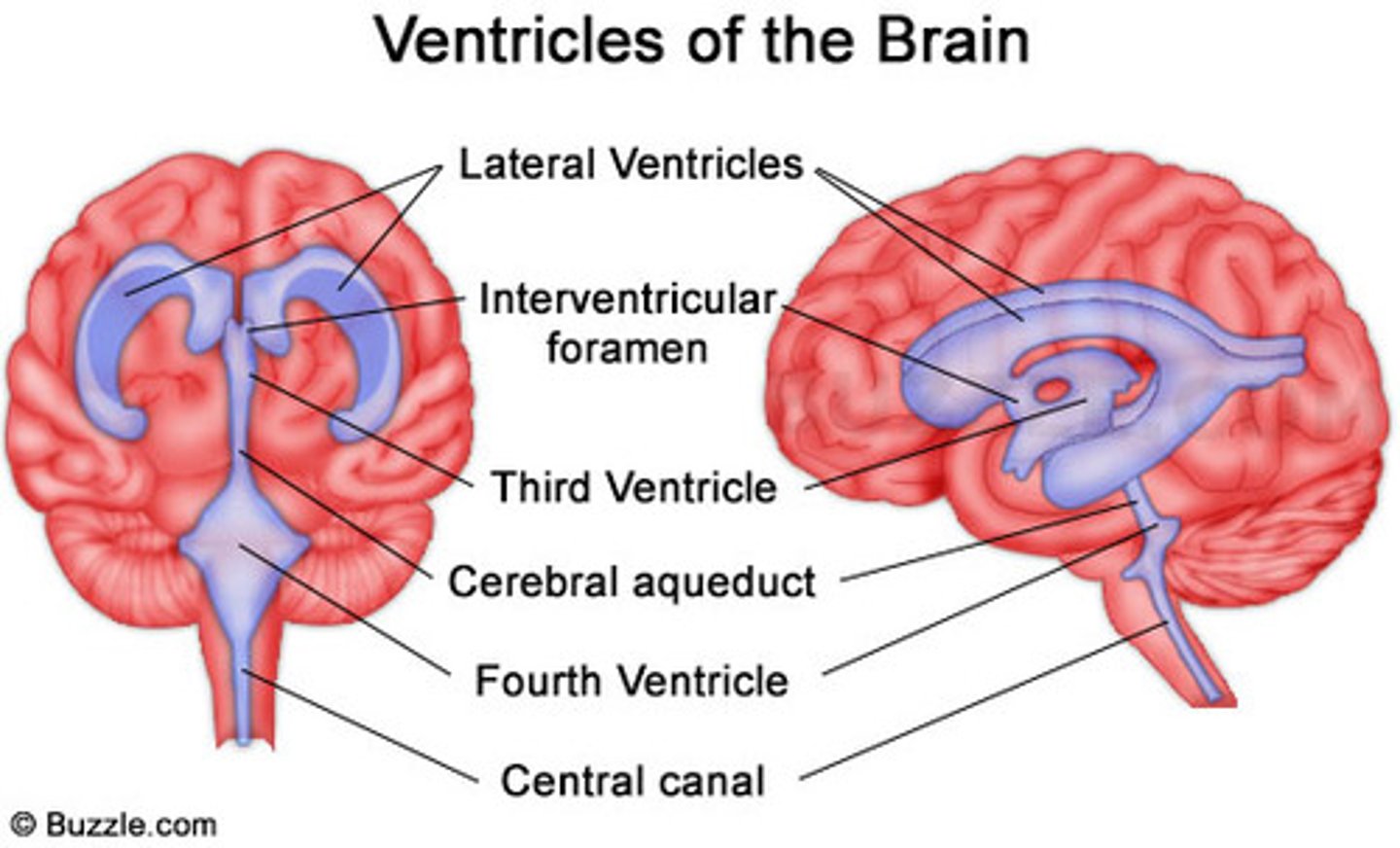
Lateral Ventricles
ventricles found in each cerebral hemisphere
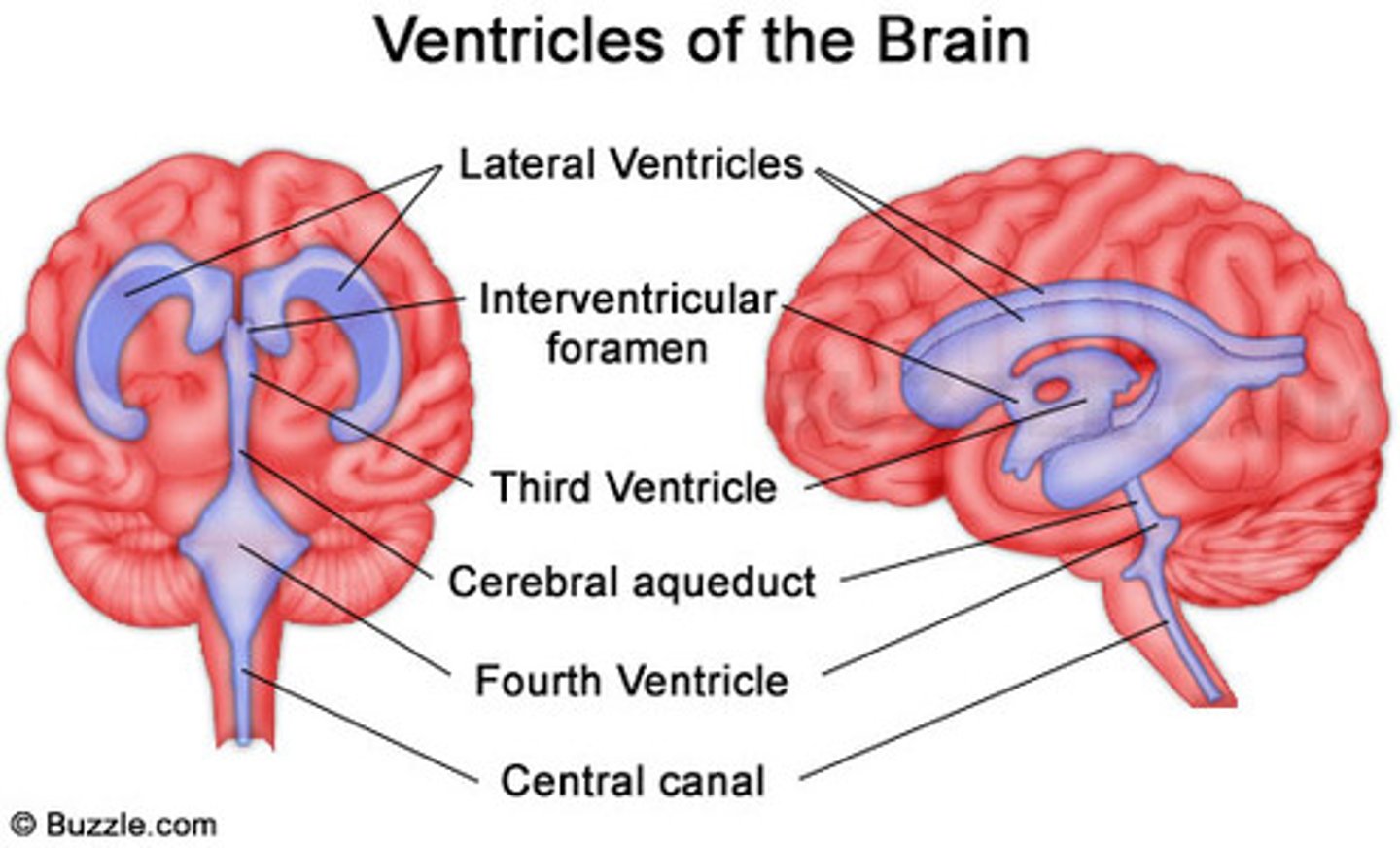
Third Ventricle
inferior to the corpus callosum
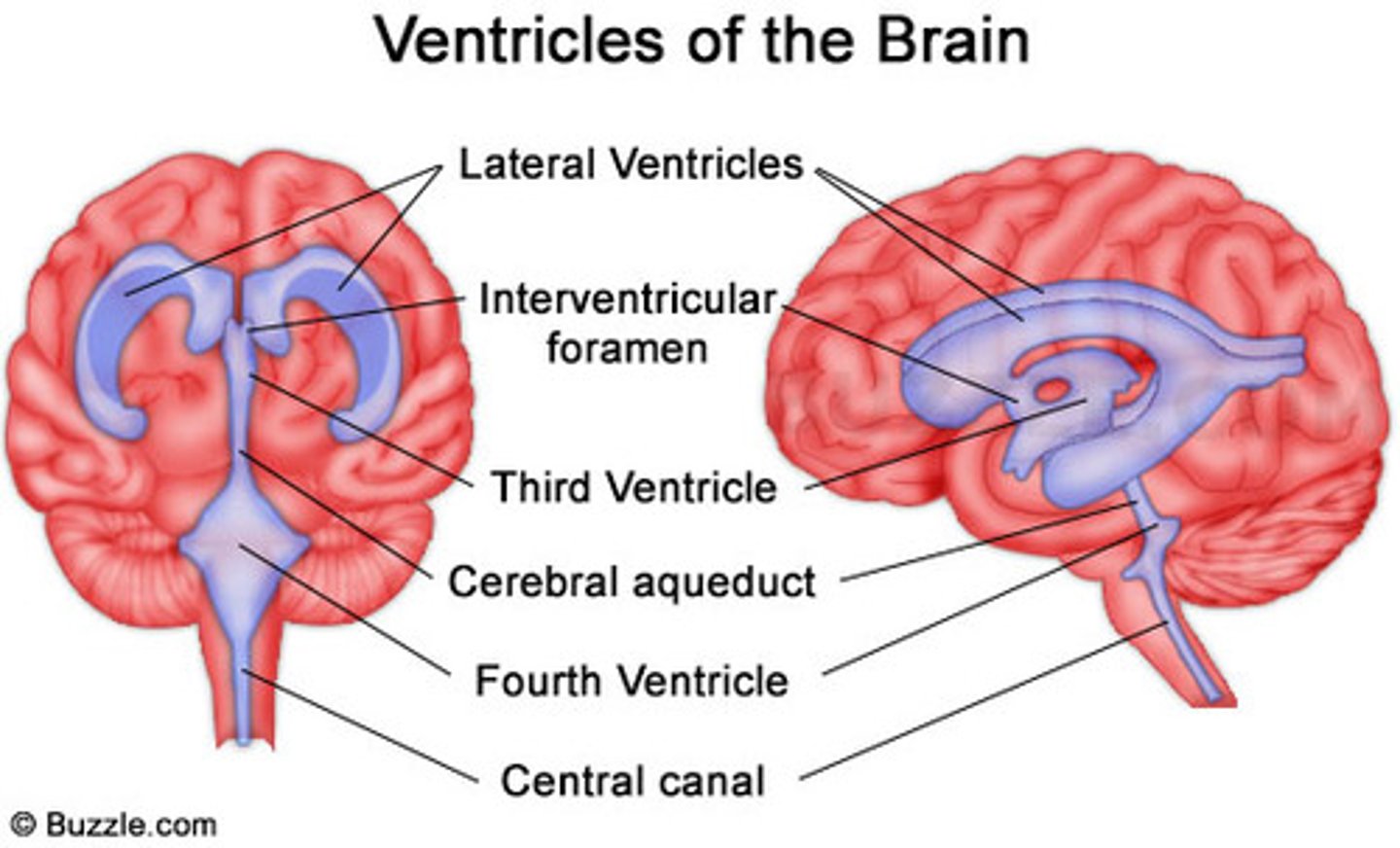
Fourth Ventricle
becomes continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord
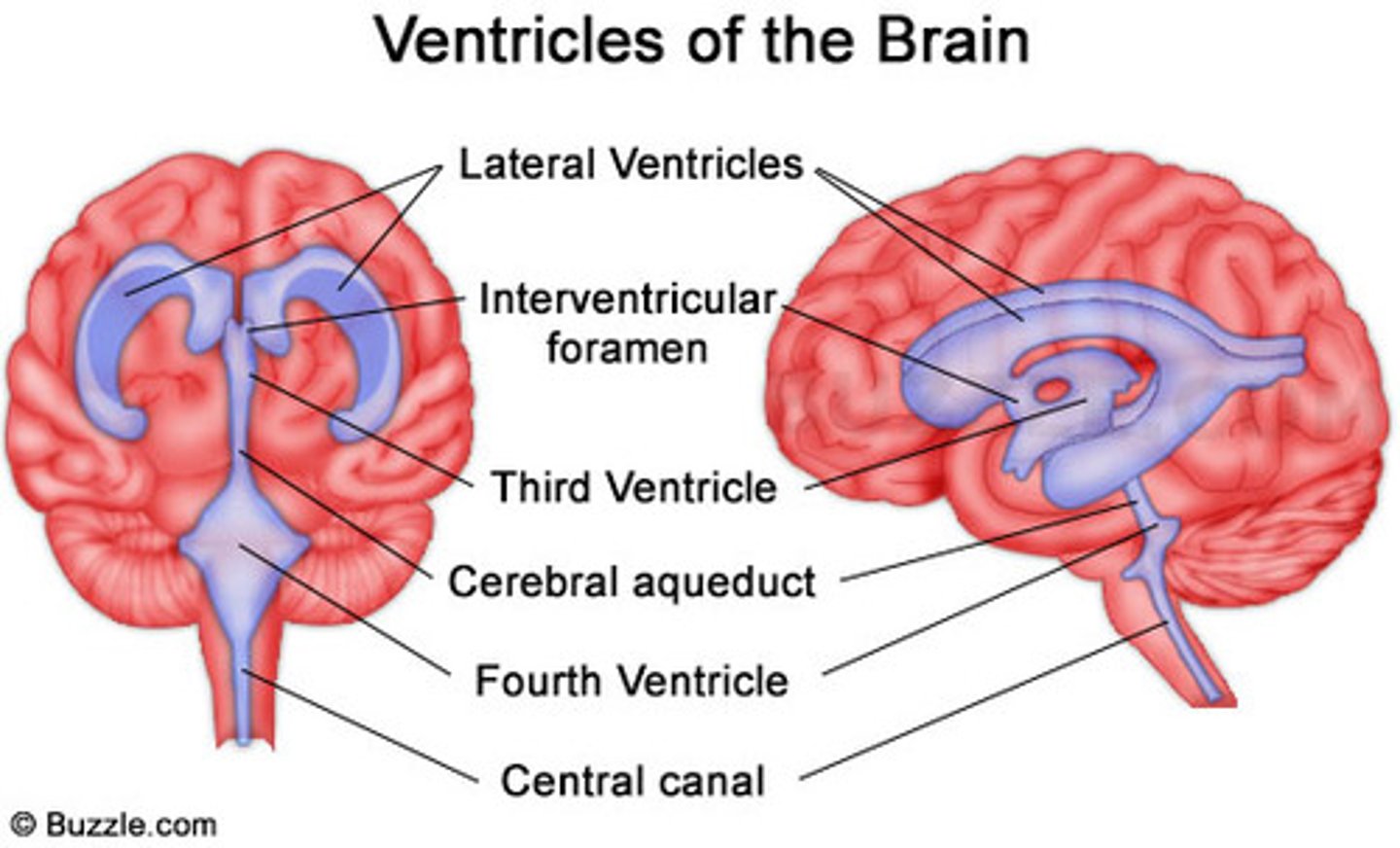
Cerebral Aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
Cerebral Hemispheres
the right and left halves of the cerebrum
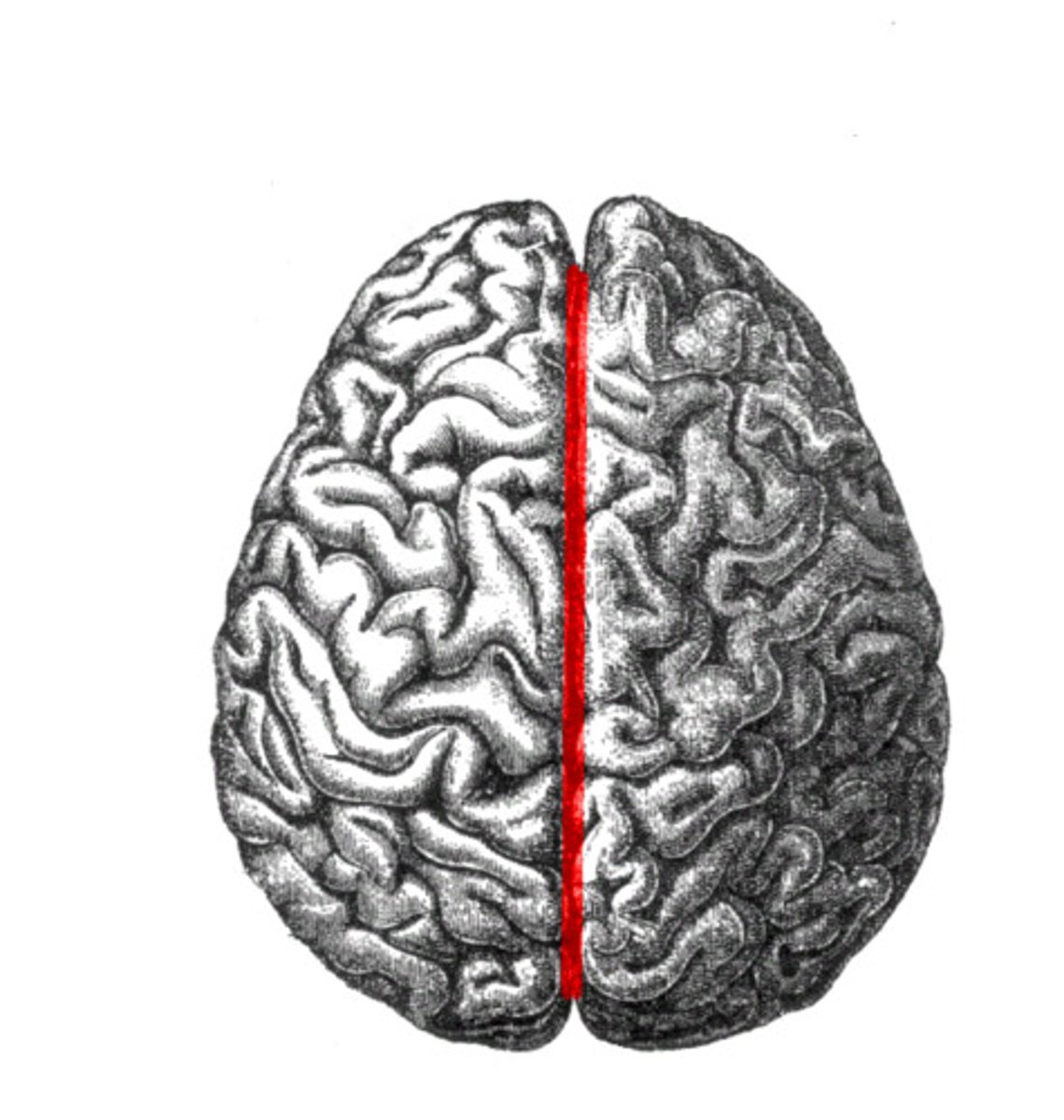
Longitudinal Fissure
separates cerebral hemispheres
Transverse Fissure
separates cerebrum from cerebellum
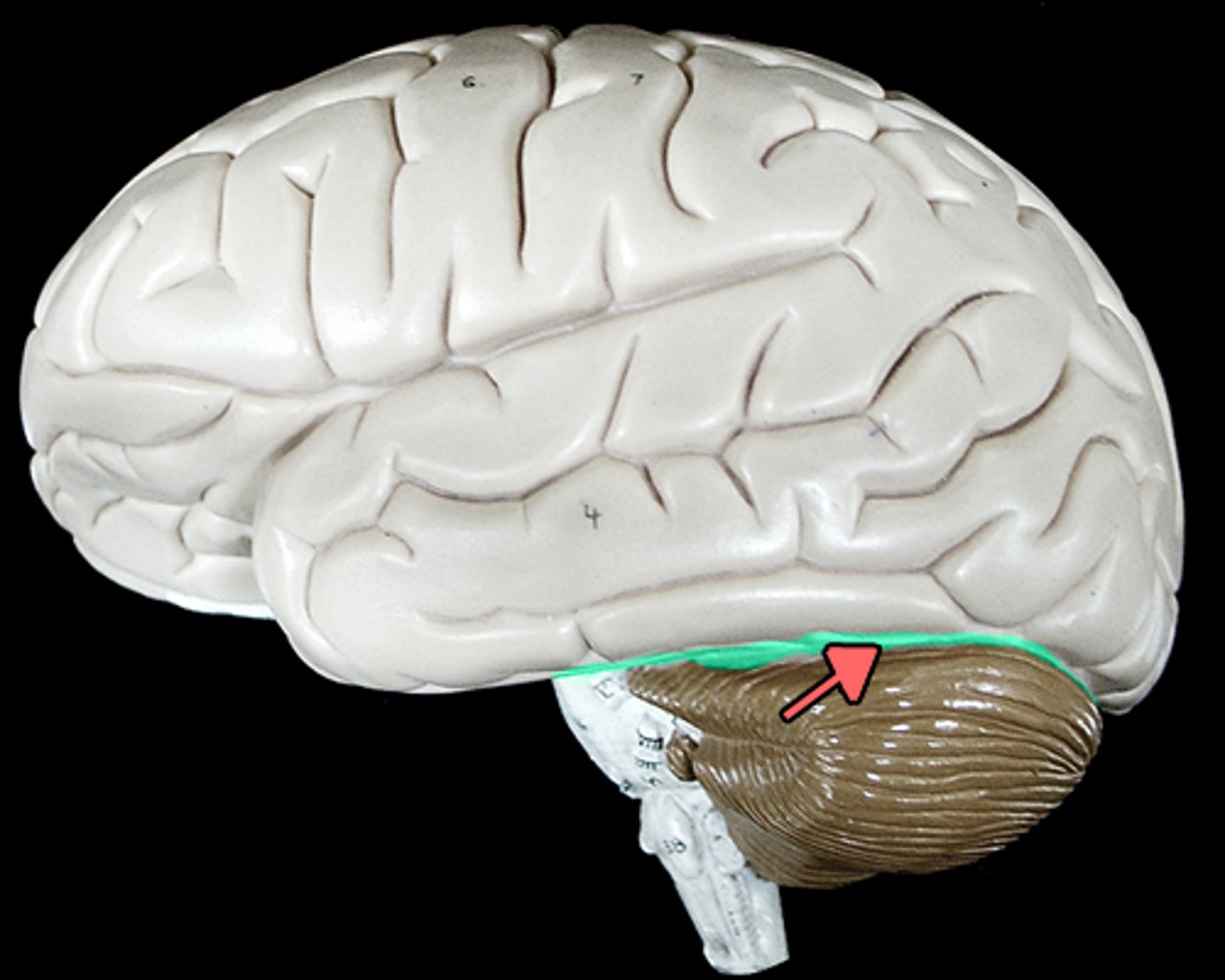
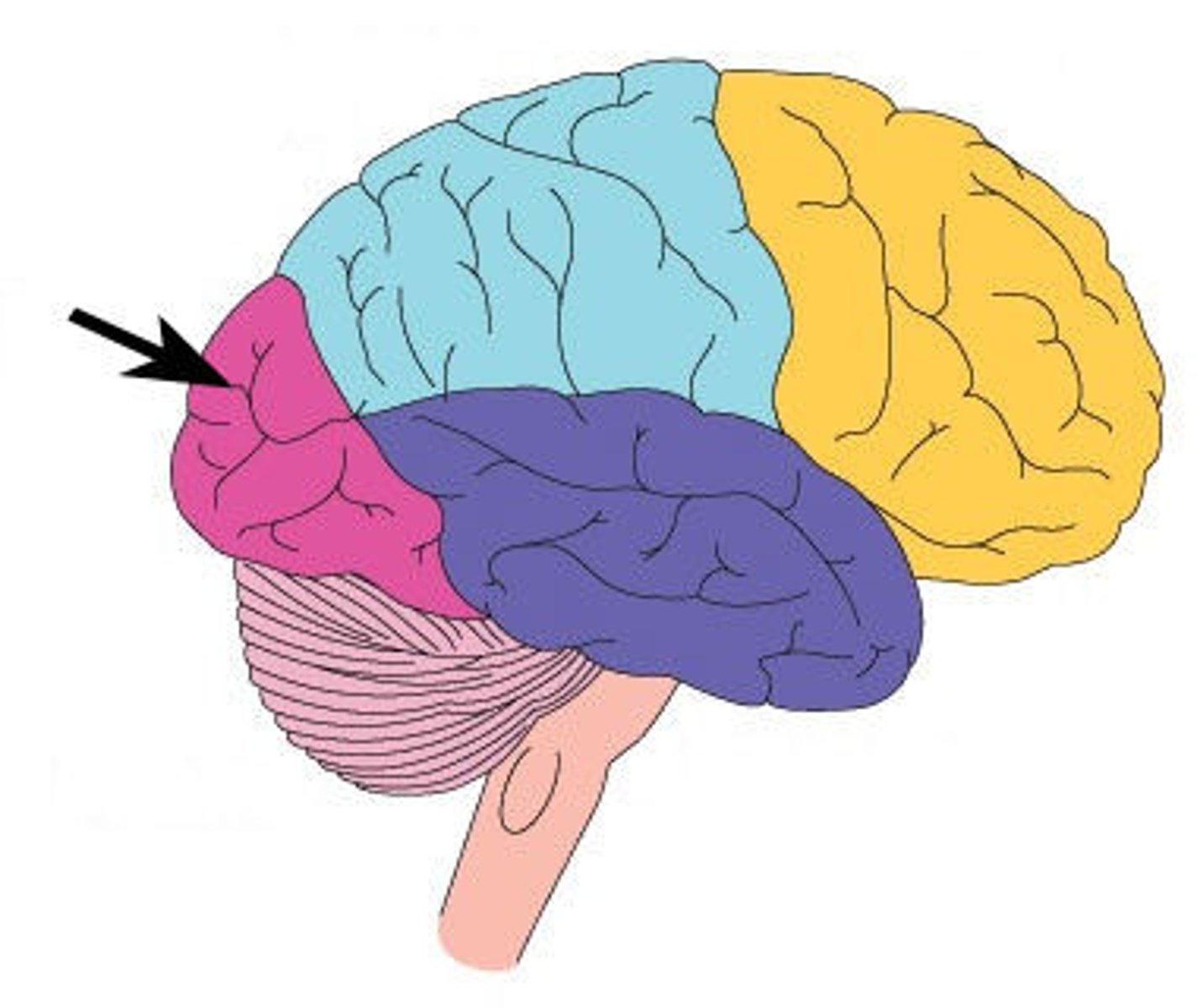
Frontal Lobe
a region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
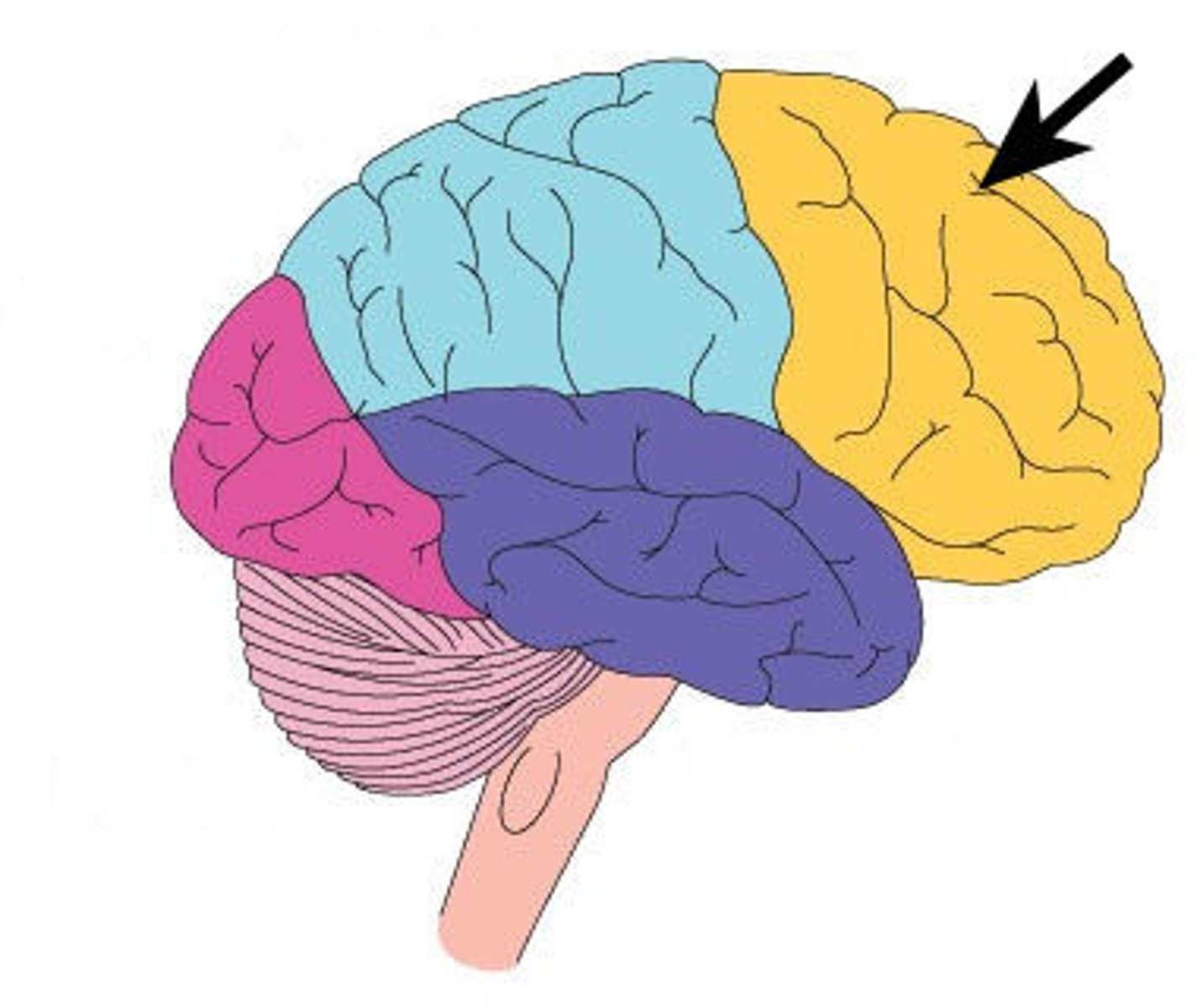
Parietal Lobe
a region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch
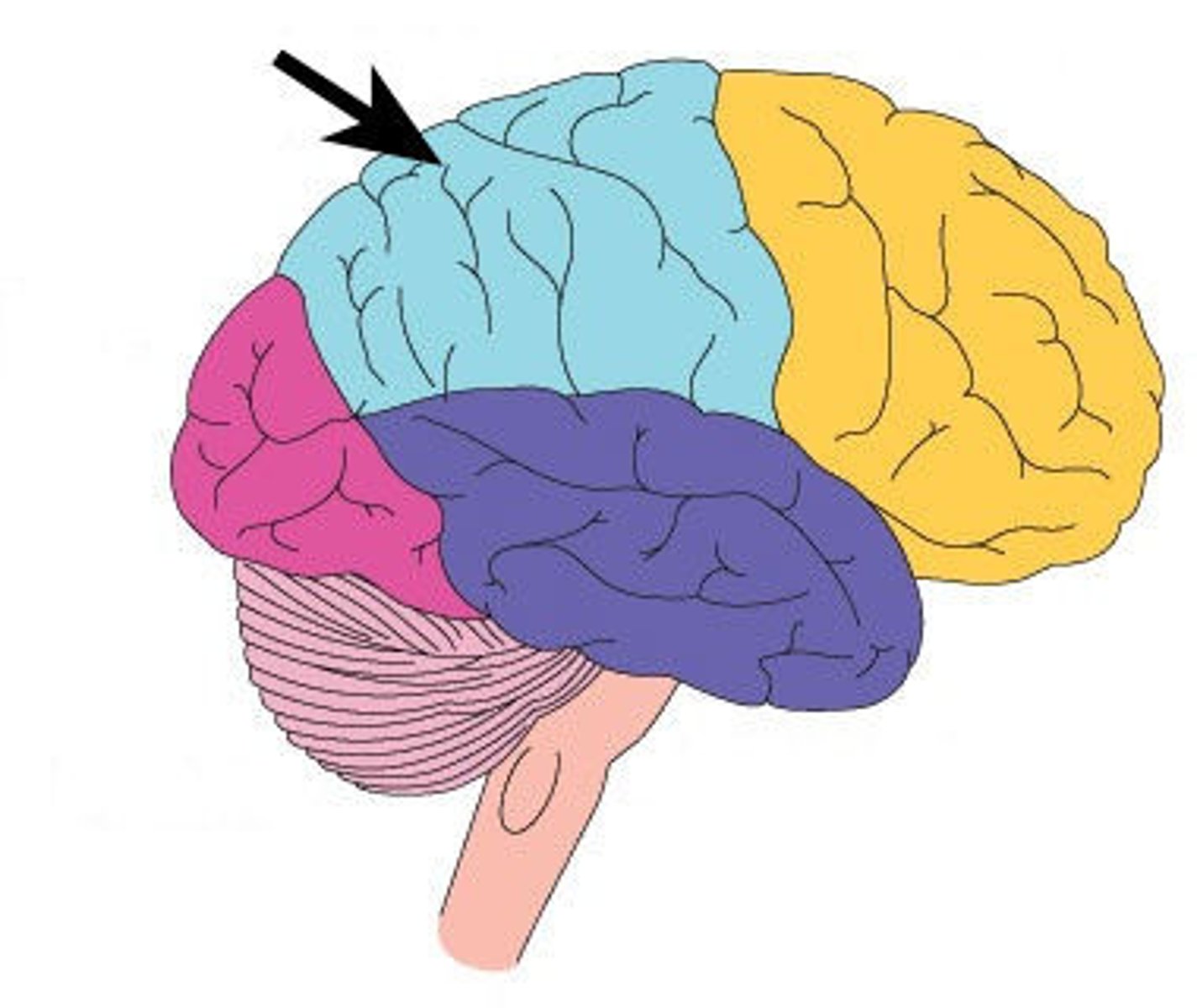
Temporal Lobe
a region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language
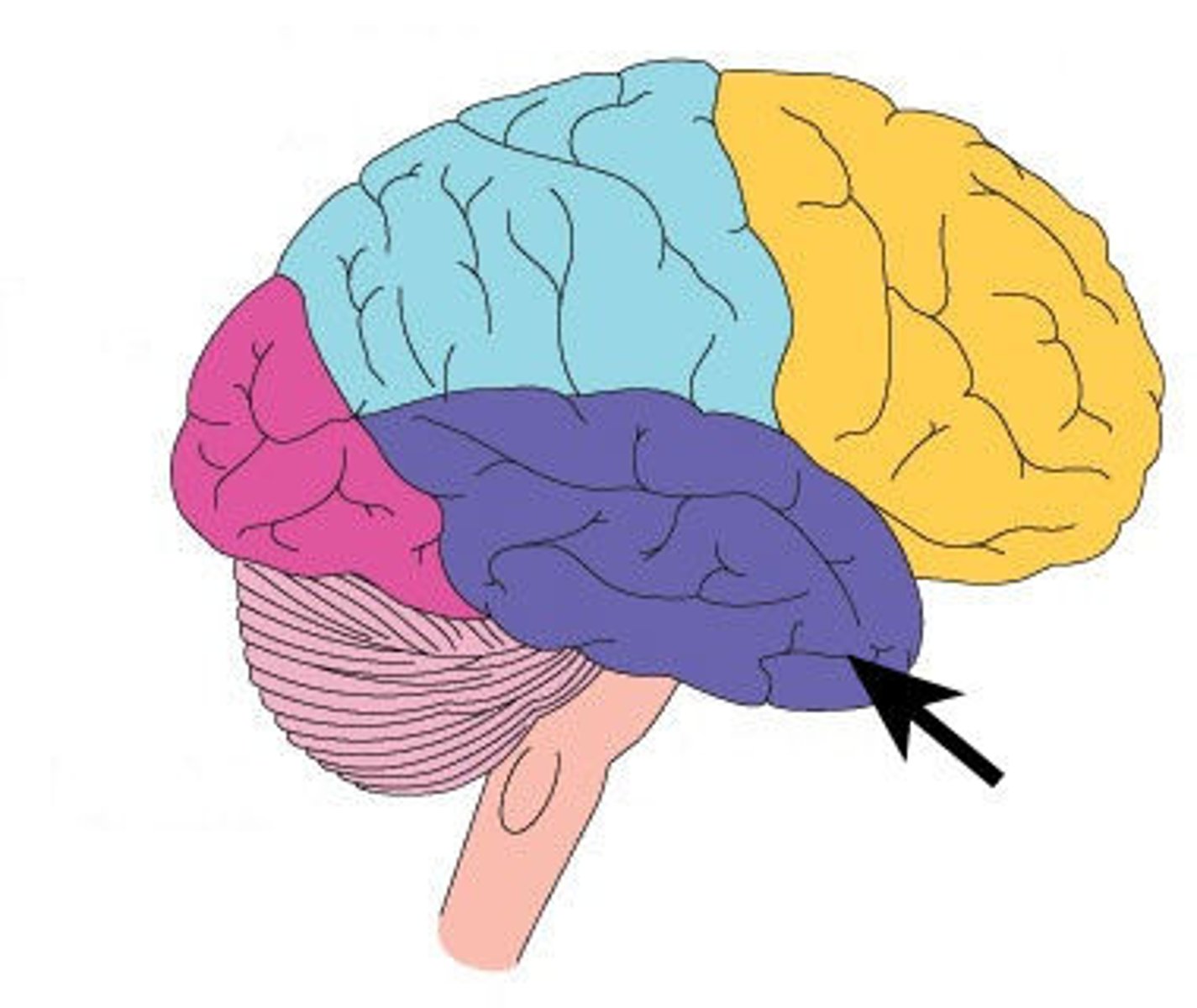
Occipital Lobe
a region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
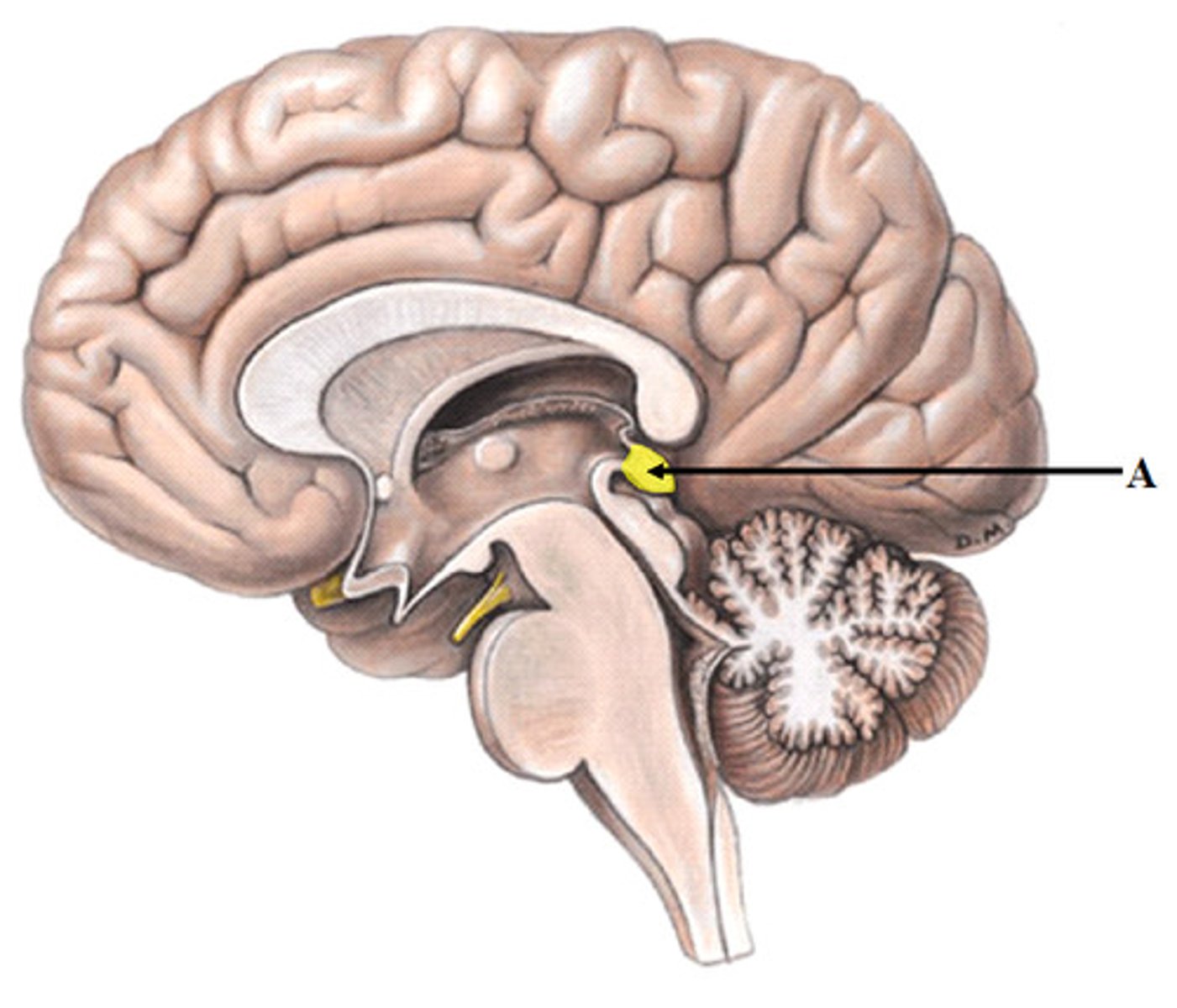
Pineal gland
produces melatonin
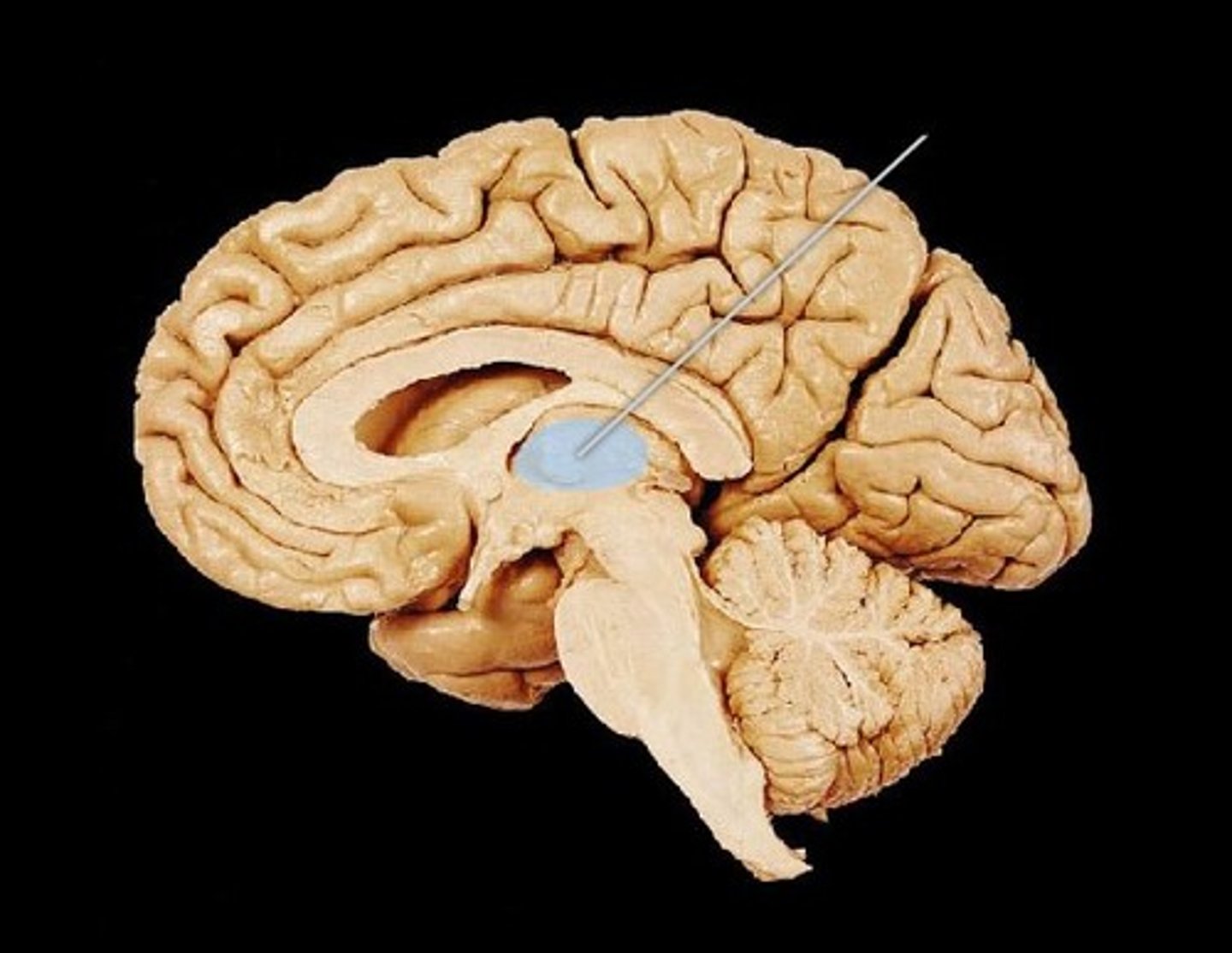
Thalamus
relays messages between lower brain centers and cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus
-a neural structure lying below the thalamus
-directs eating, drinking, body temperature
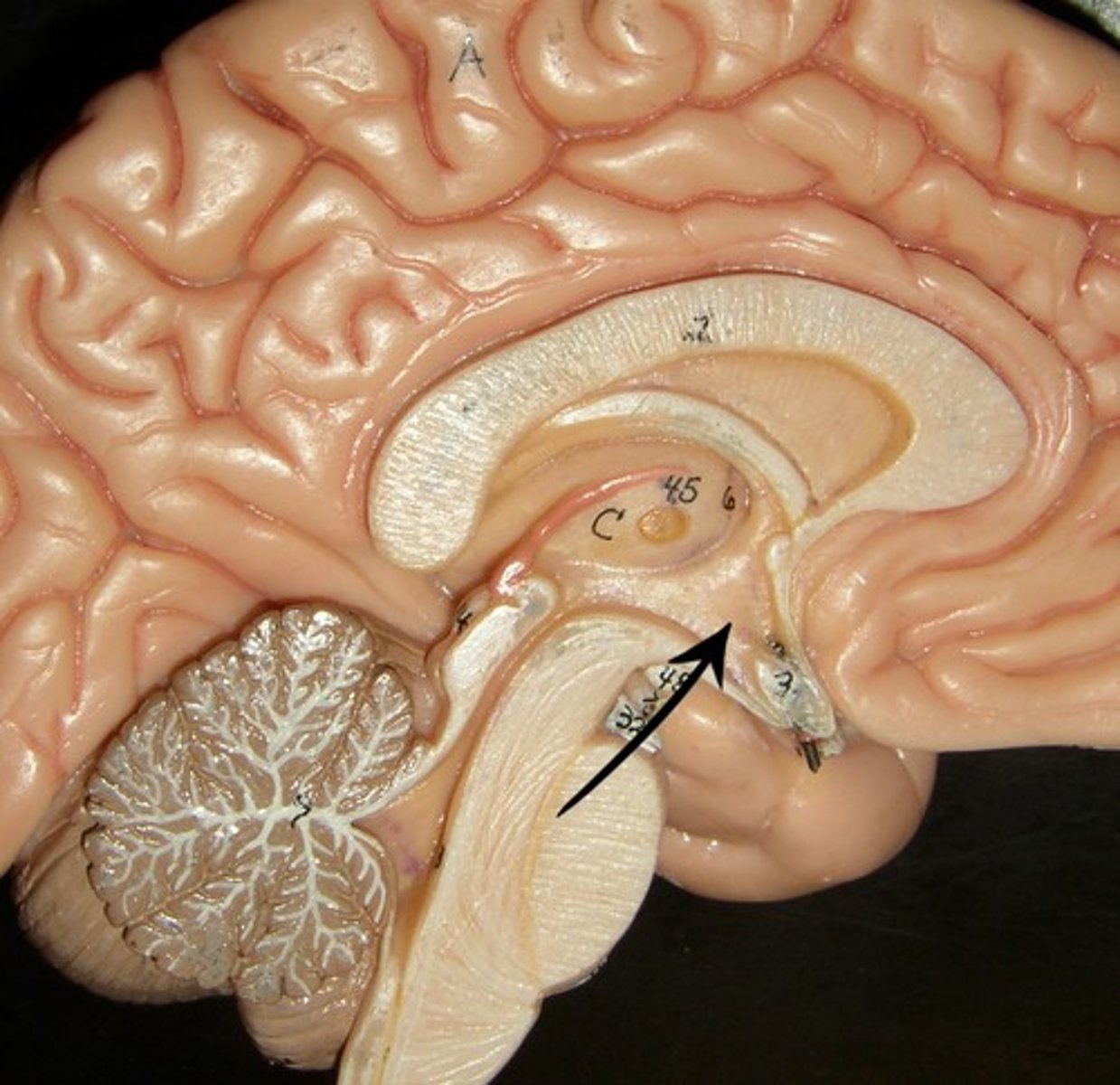
Infundibulum
a stalk that attaches the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus
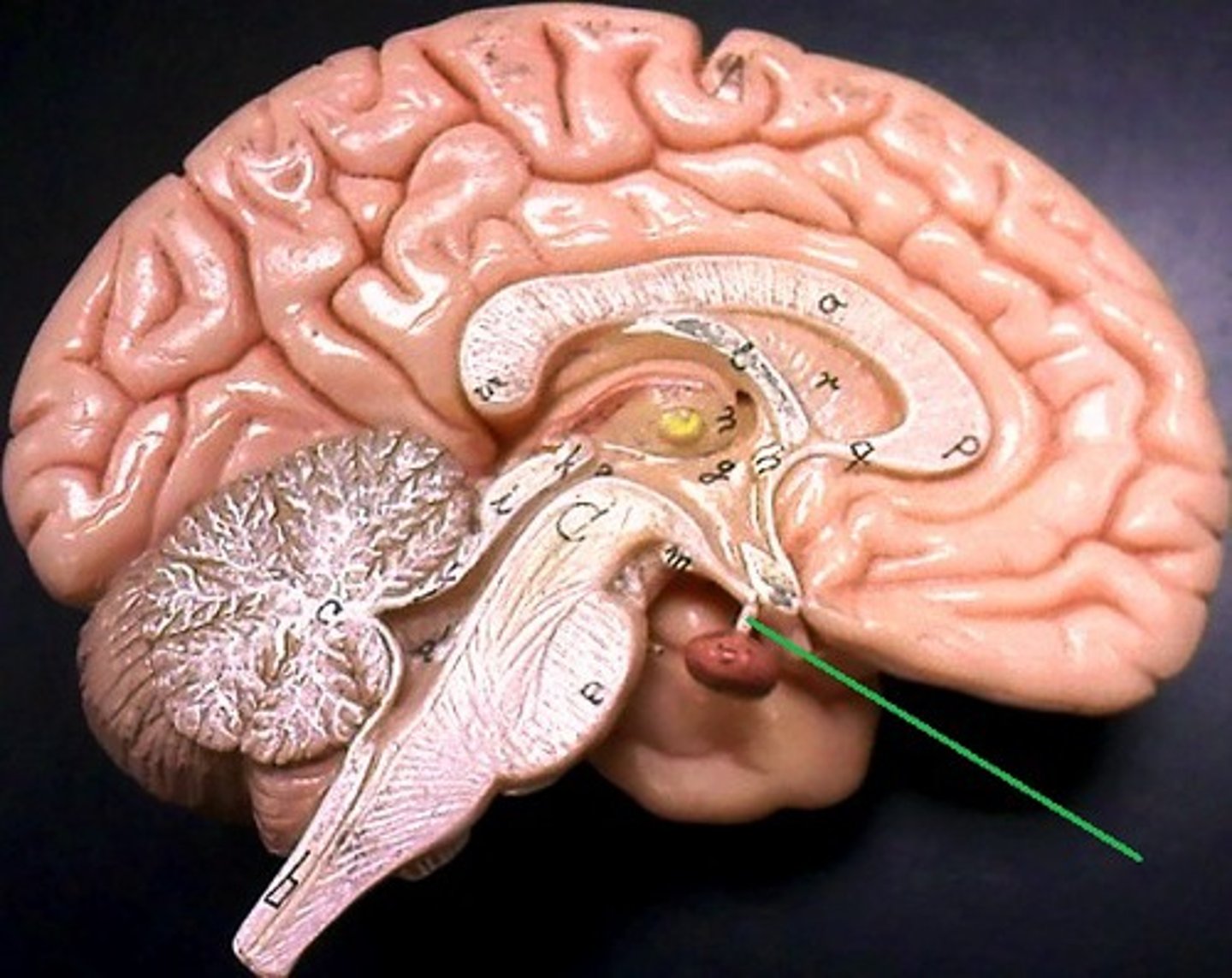
Pituitary Gland
endocrine gland at the base of the brain
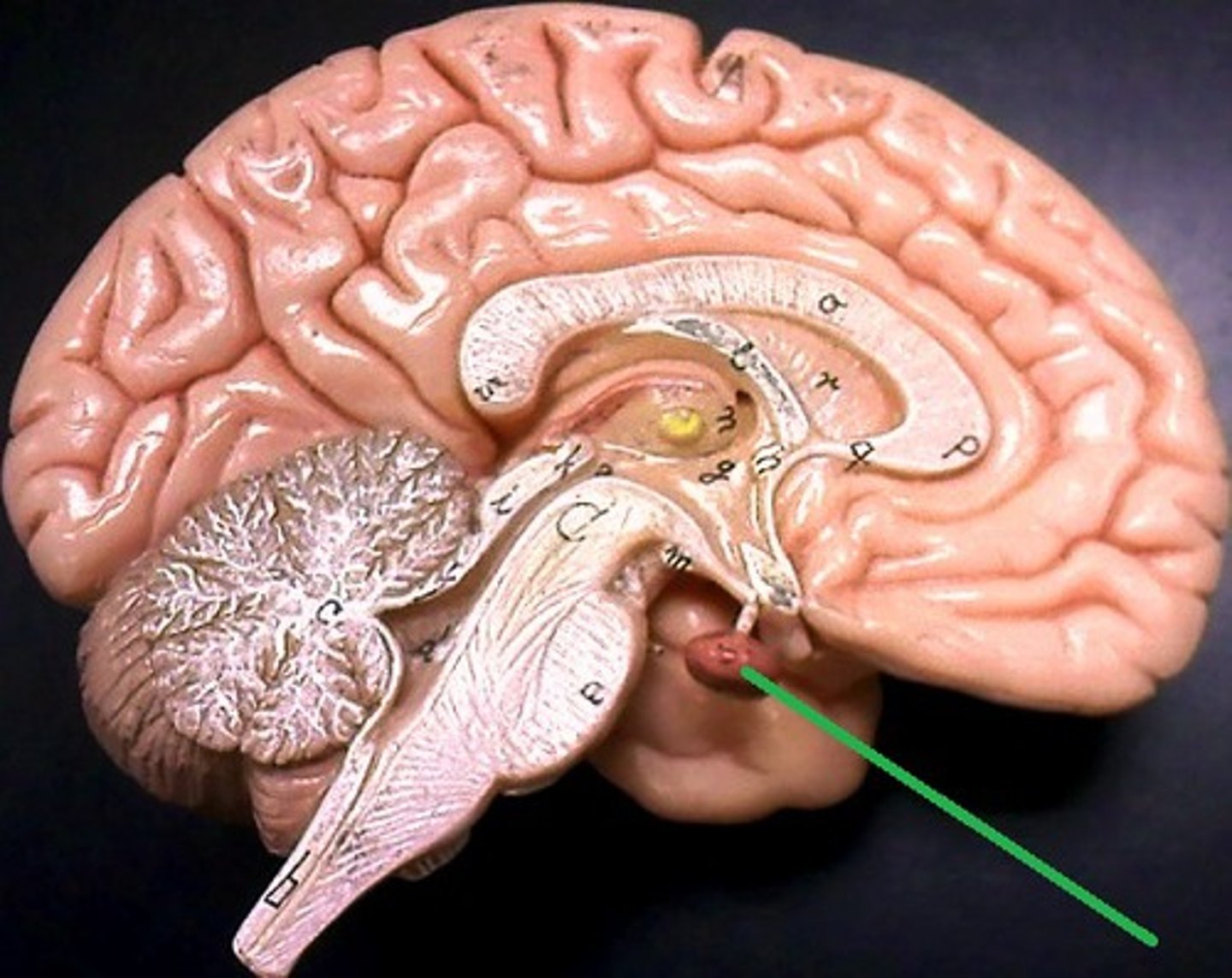
Optic Chiasma
where optic nerves cross
Optic Tract
leads from optic chiasma to the thalamus
Mammillary Body
one of a pair of limbic system structures that are connected to the hippocampus
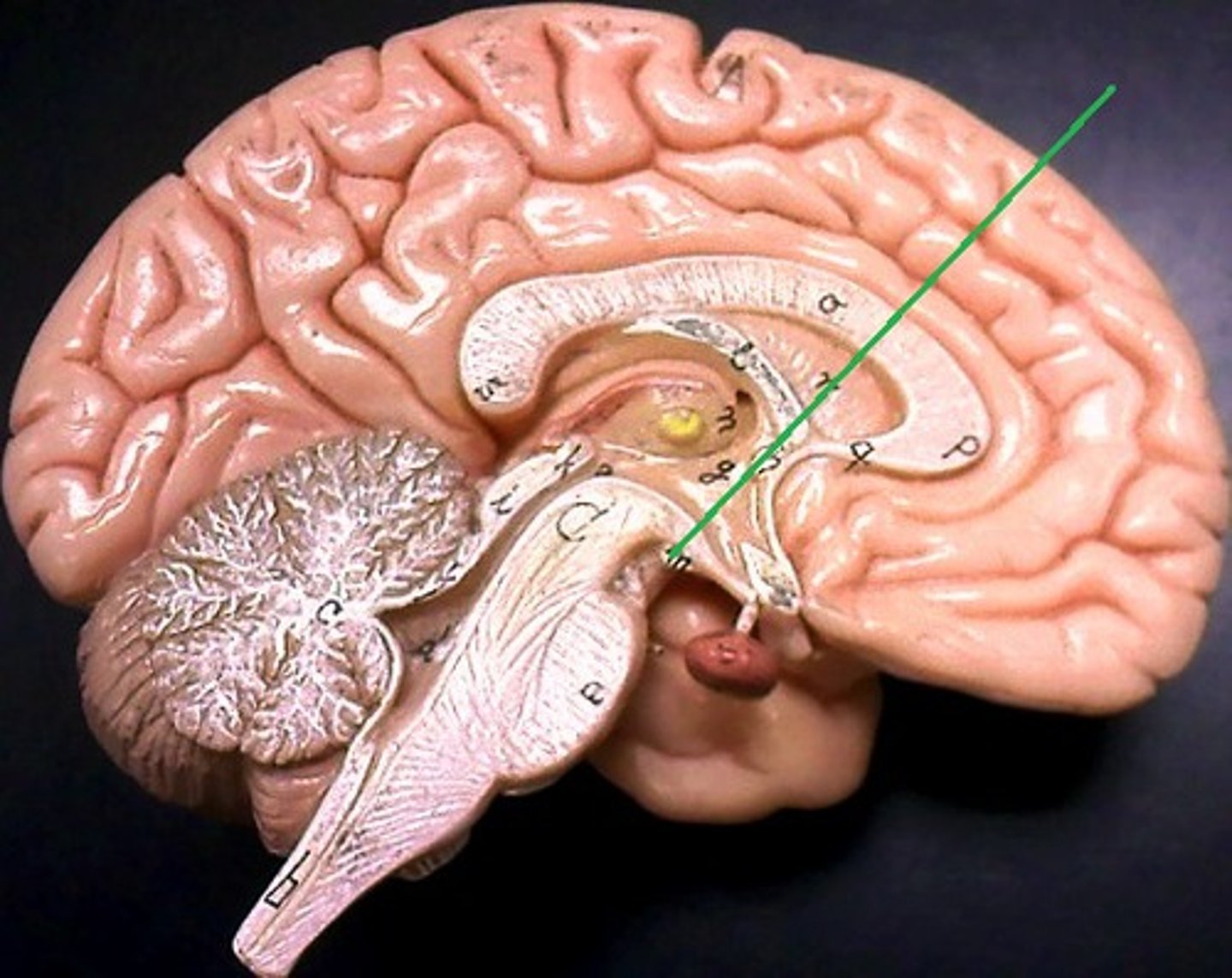
Midbrain
a small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward
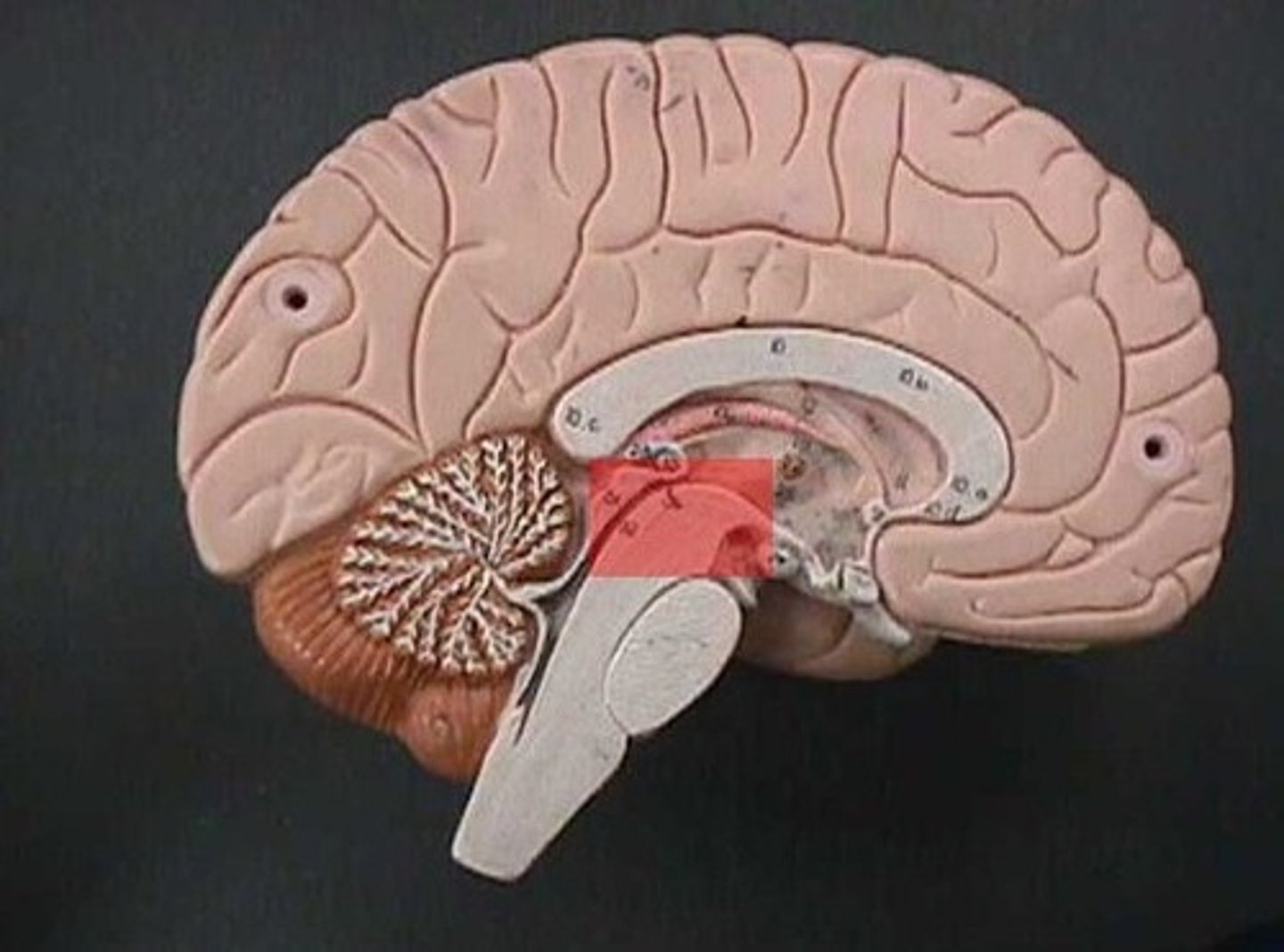
Corpora Quadrigemina
located in the midbrain; contains reflex centers for visual and auditory reflexes
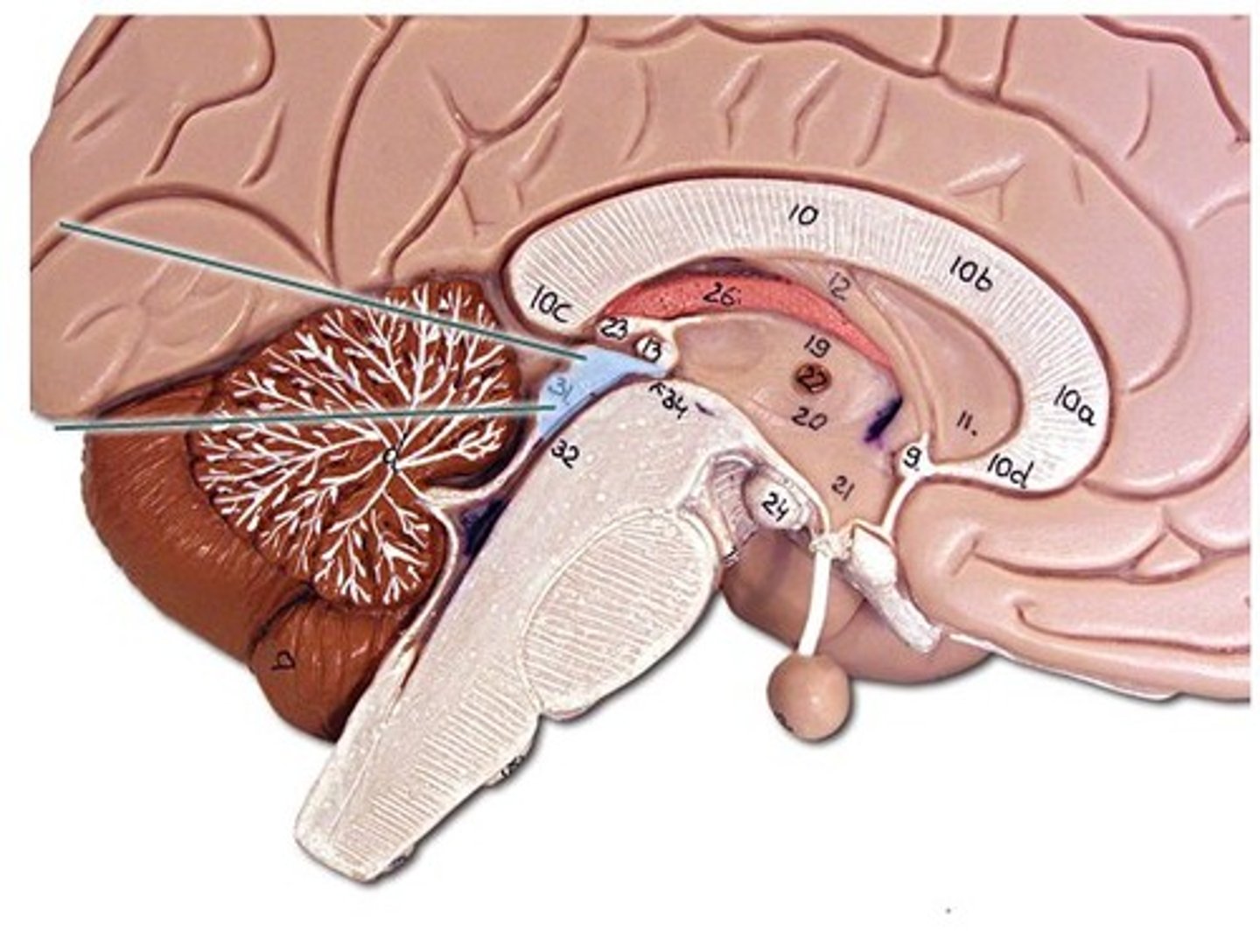
Superior Colliculi
visual reflexes
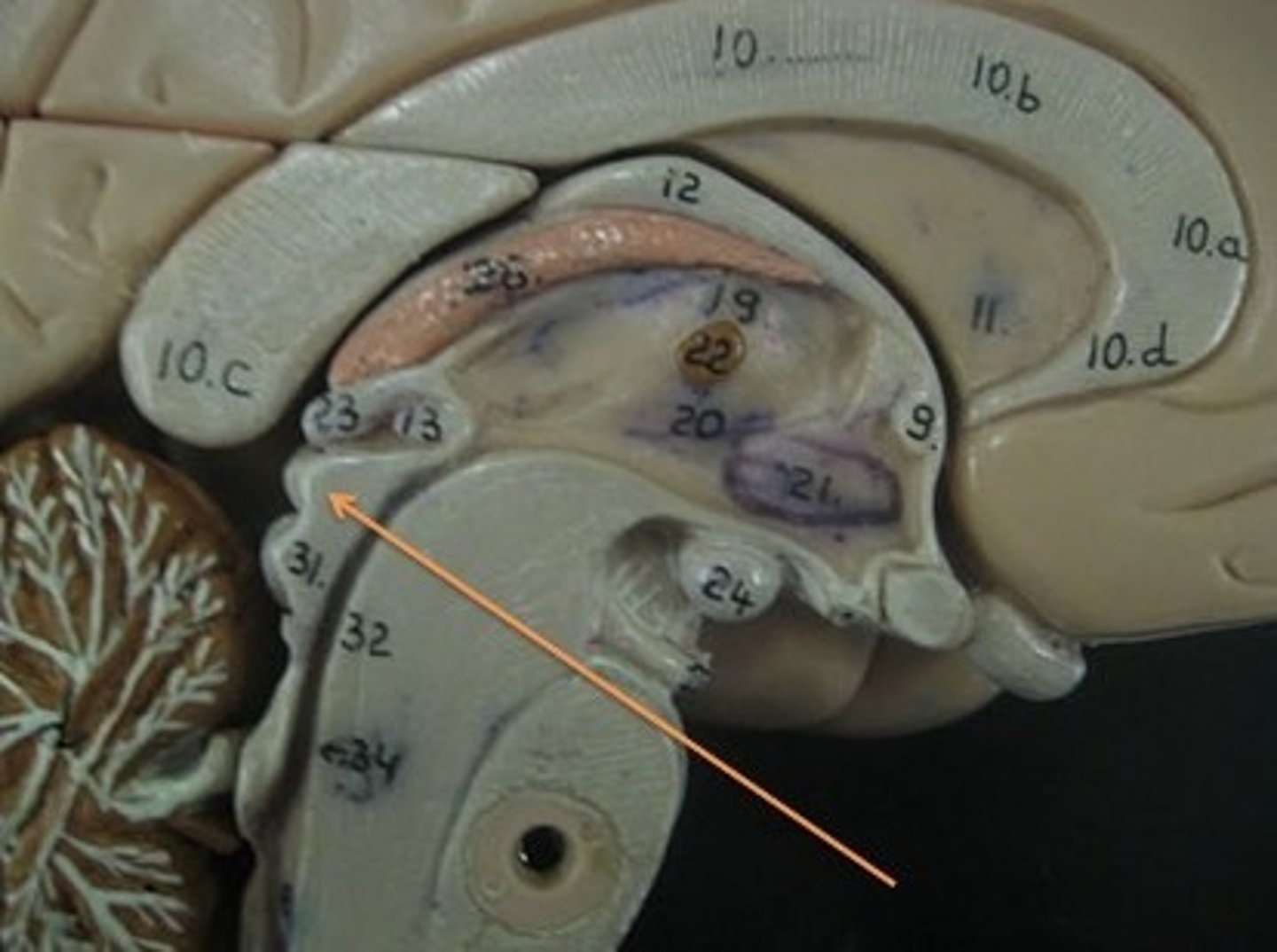
Inferior Colliculi
auditory reflexes
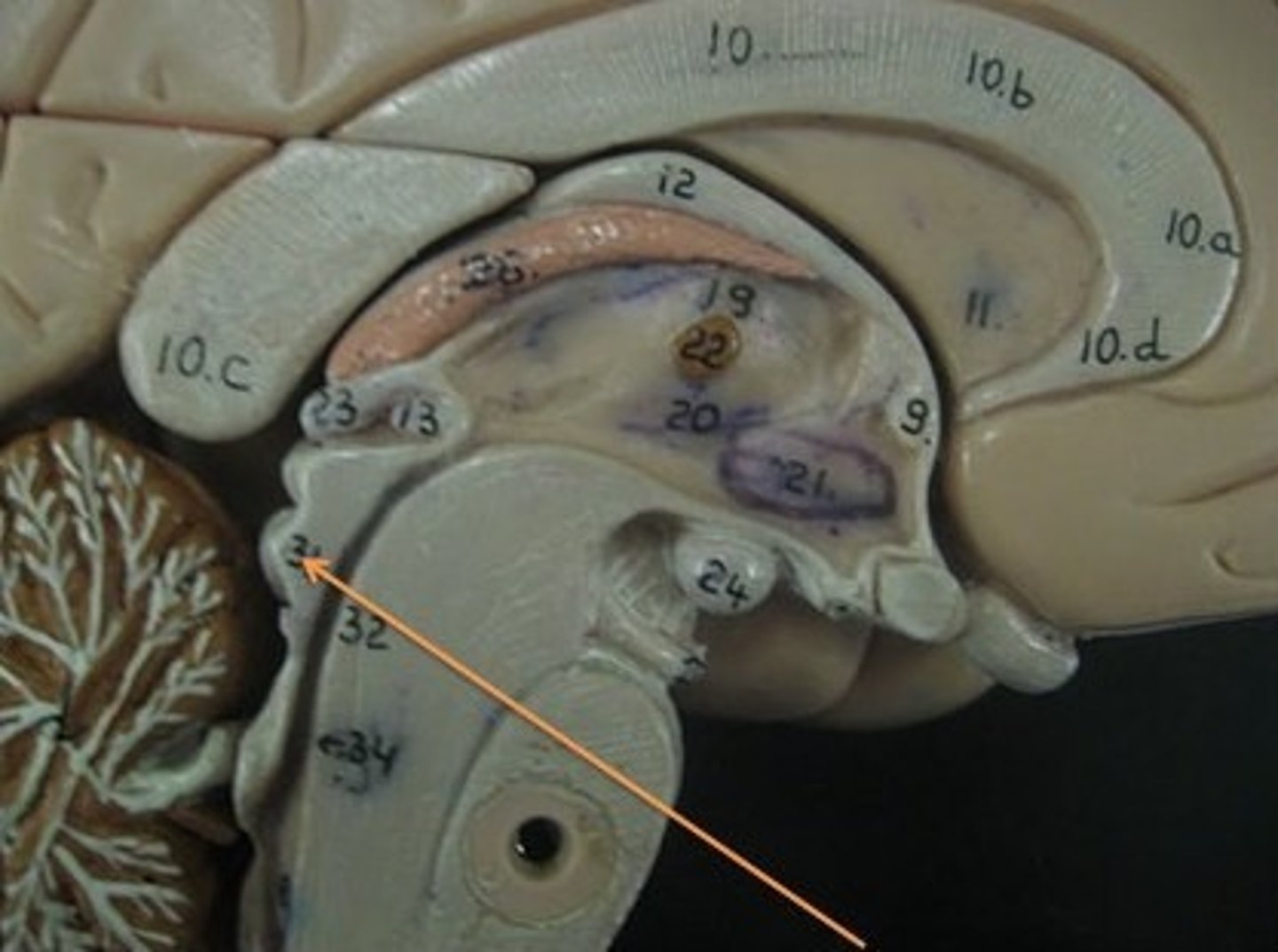
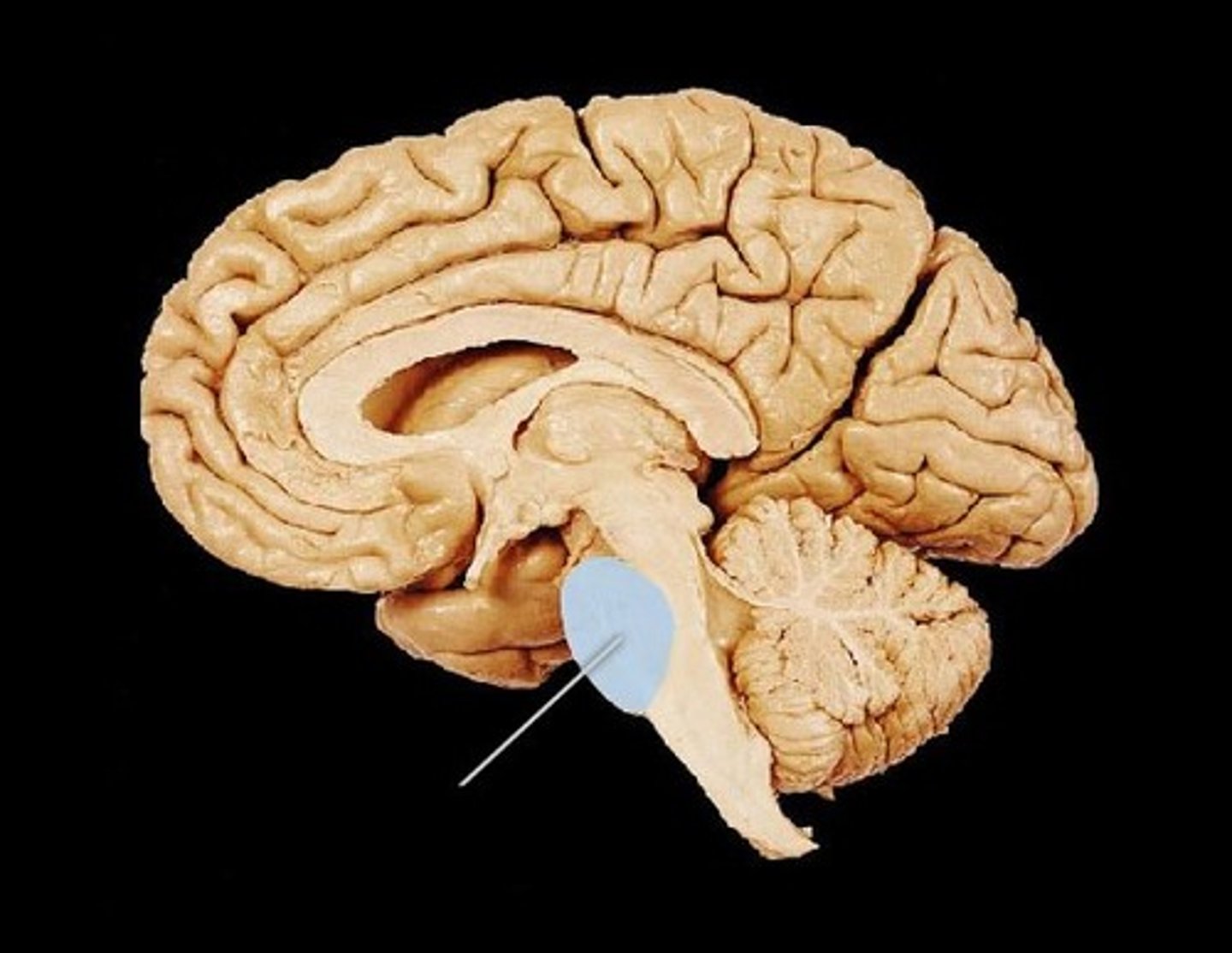
Pons
a brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
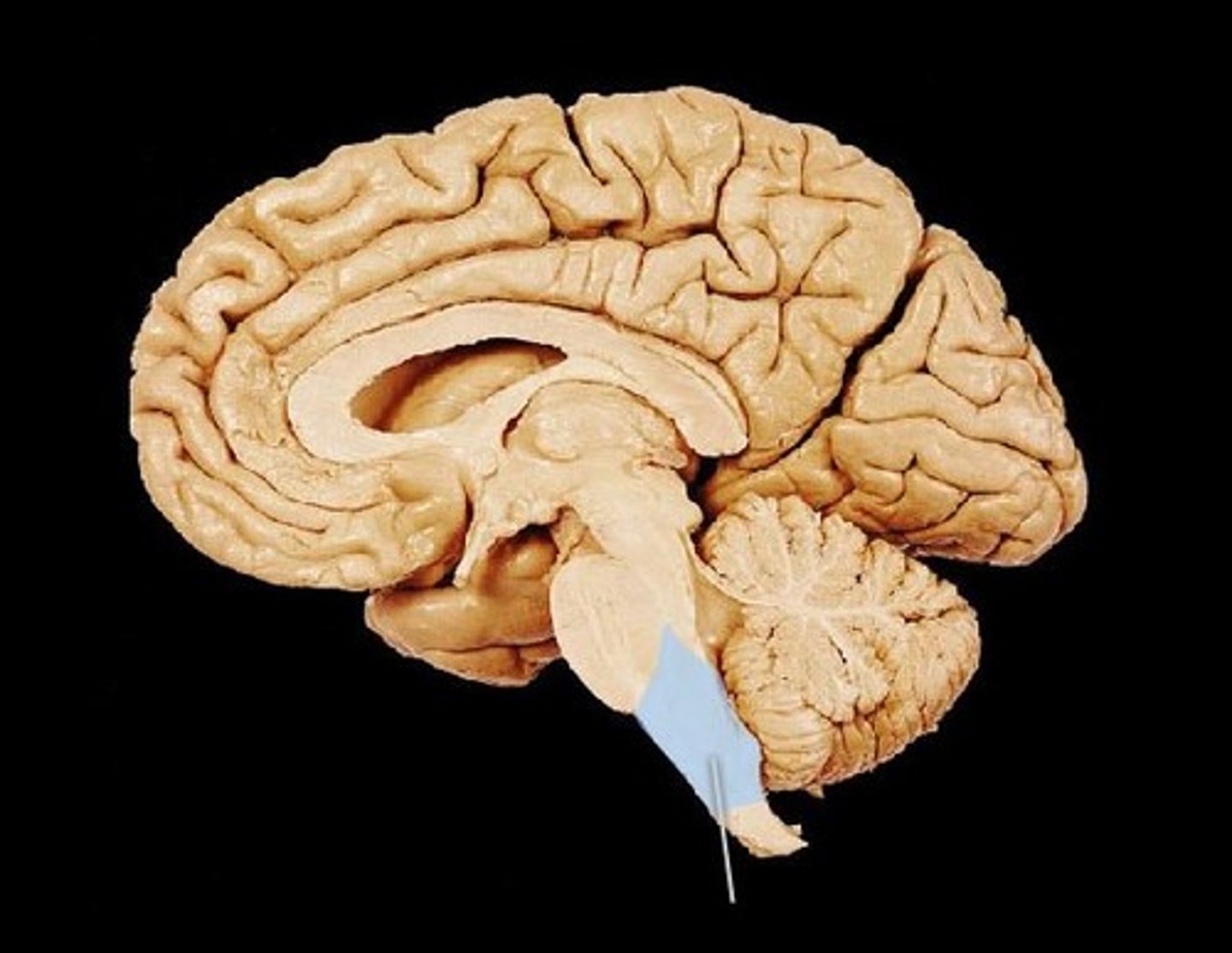
Medulla Oblongata
the posterior part of the brain that controls the rate of breathing and other autonomic functions
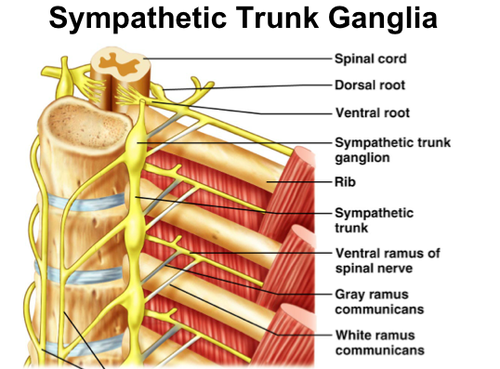
Sympathetic Ganglia
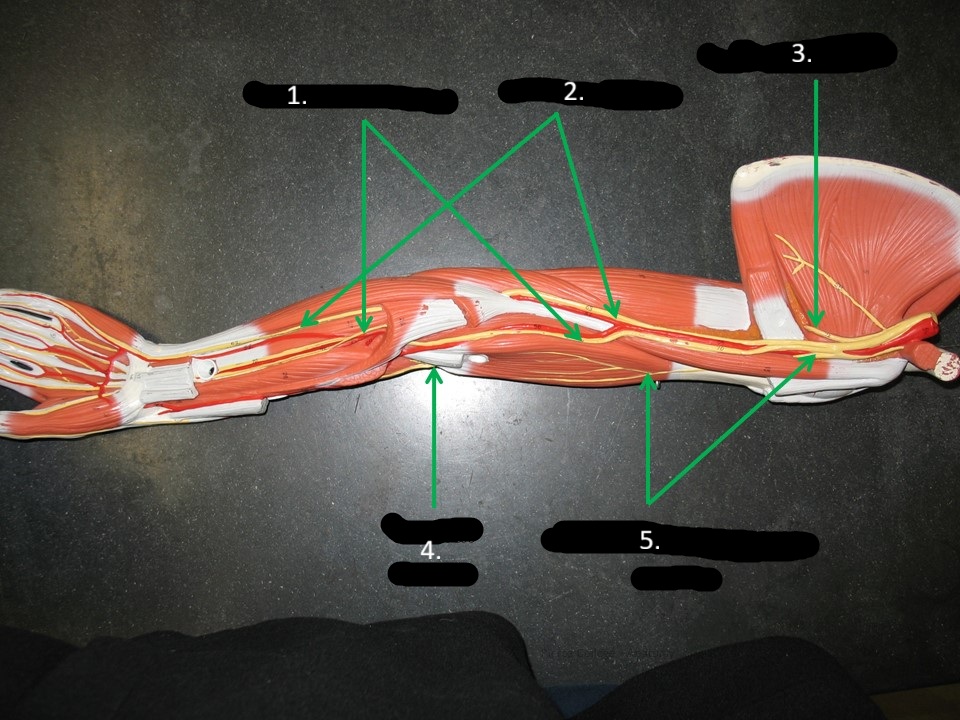
axillary nerve
TOP arrow
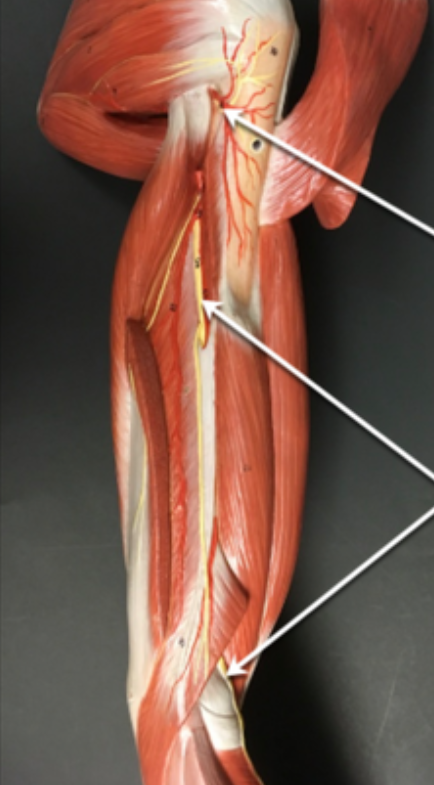
ulnar nerve
2
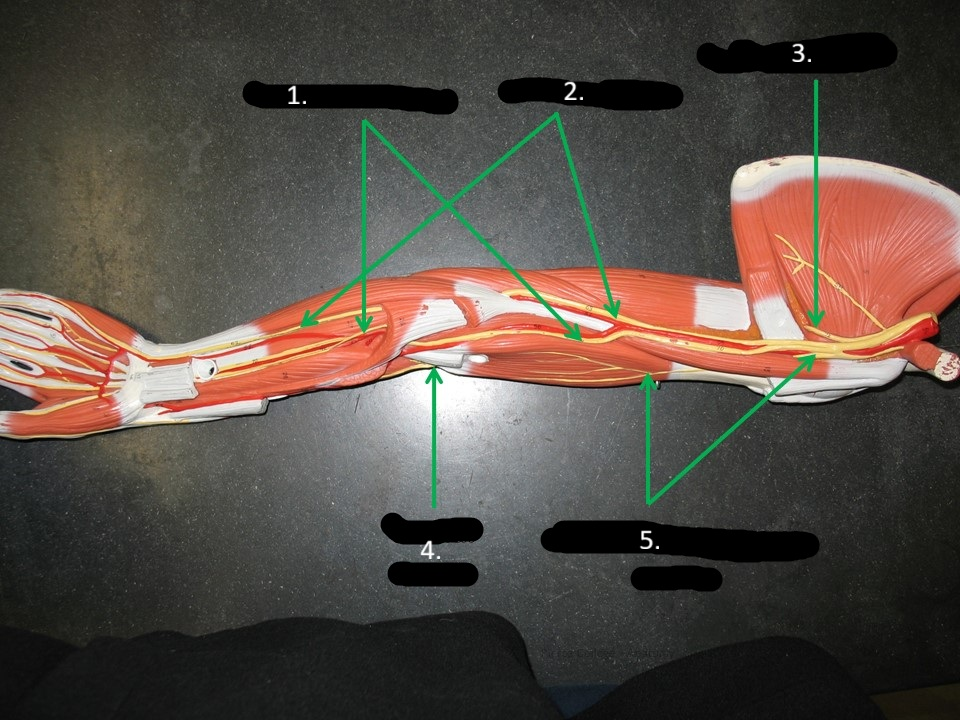
axillary nerve
3
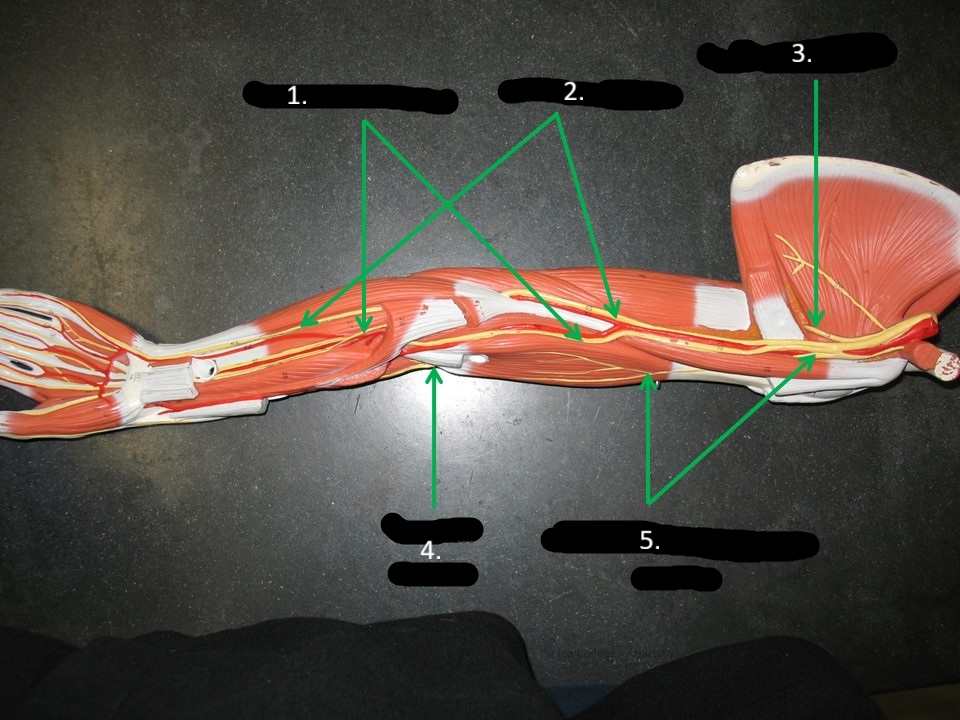
radial nerve
4
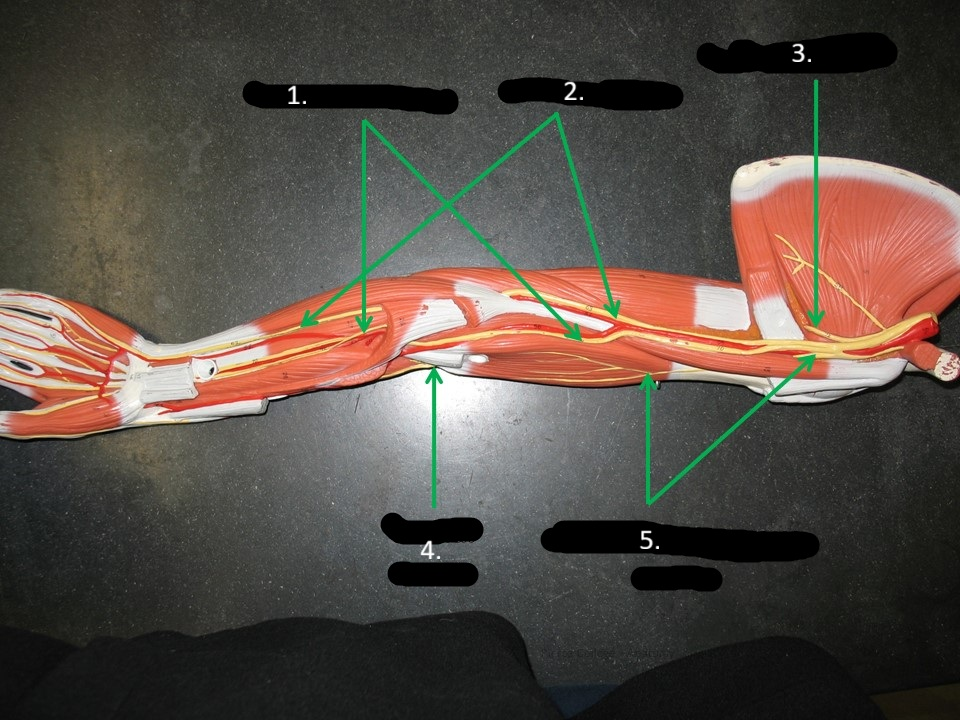
musculocutaneous nerve
5