National Boards Dental Hygiene Exam
1/513
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
514 Terms
Sharpey's fibers
connect periosteum to bone
What fibers of the PDL are the most prominent?
Oblique fibers
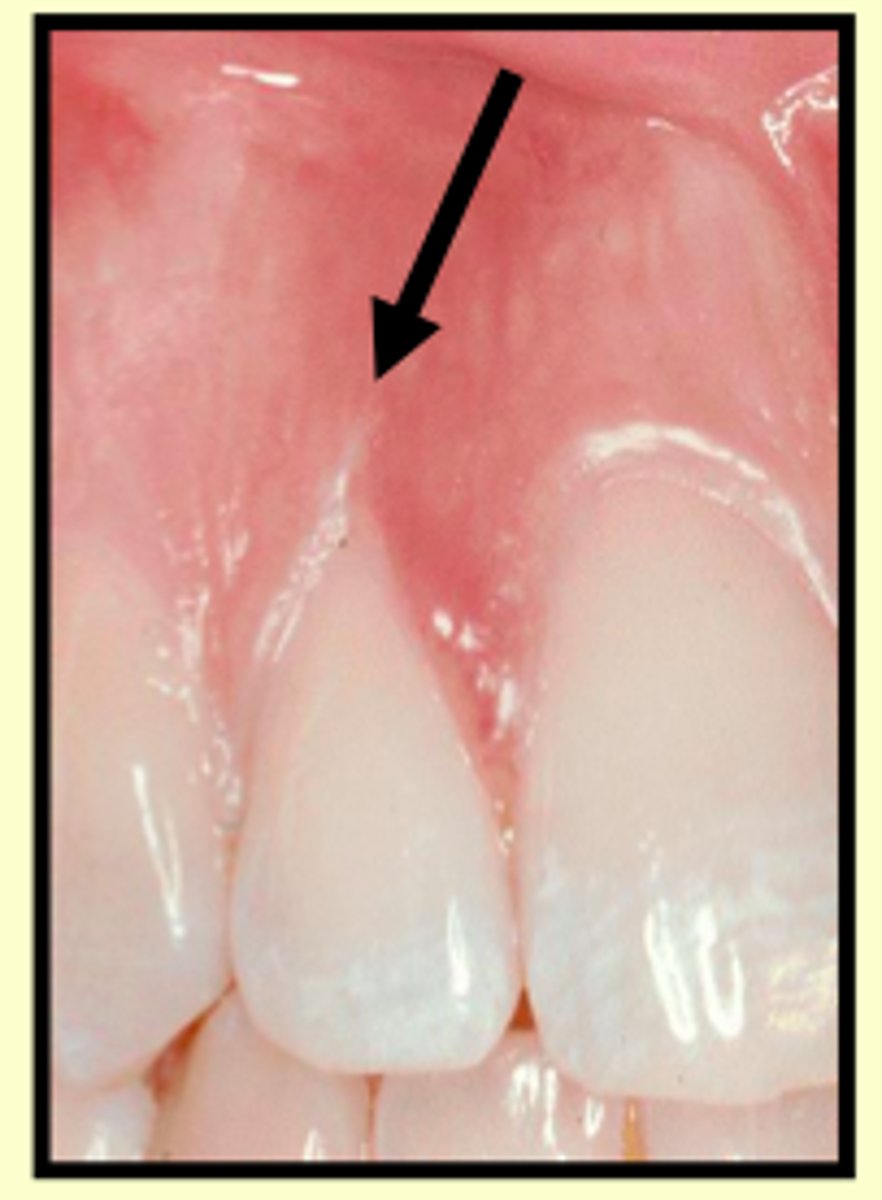
Stillman's cleft
v shaped loss of gingiva. Due to bad flossing habits
McCall's festoon
innertube shaped swelling at the marginal gingiva
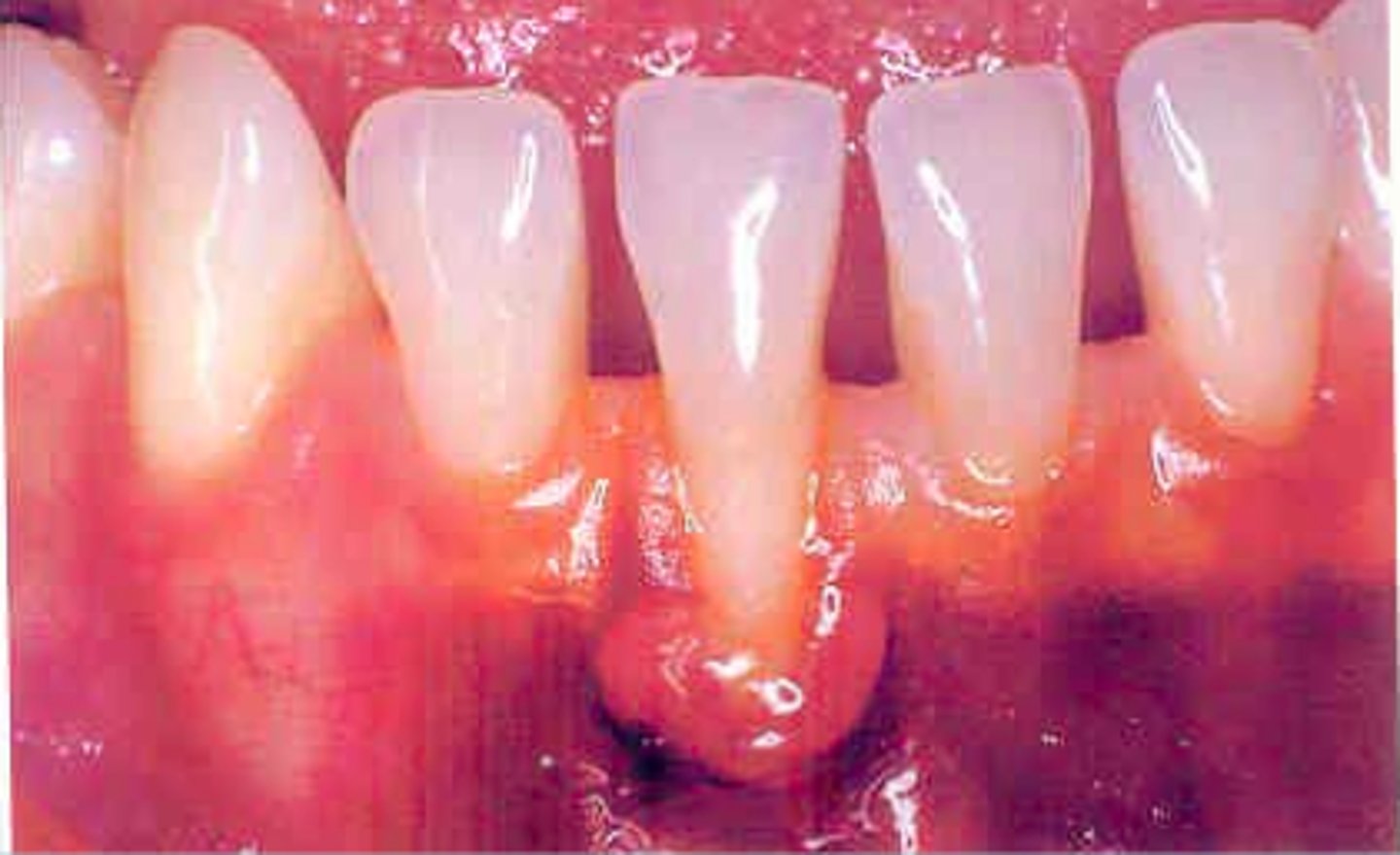
Drug induced gingival hyperplasia
Dilantin (Phenytoin)
Procardia (Nifedipine)
Cyclosporin (immunosuppressant)
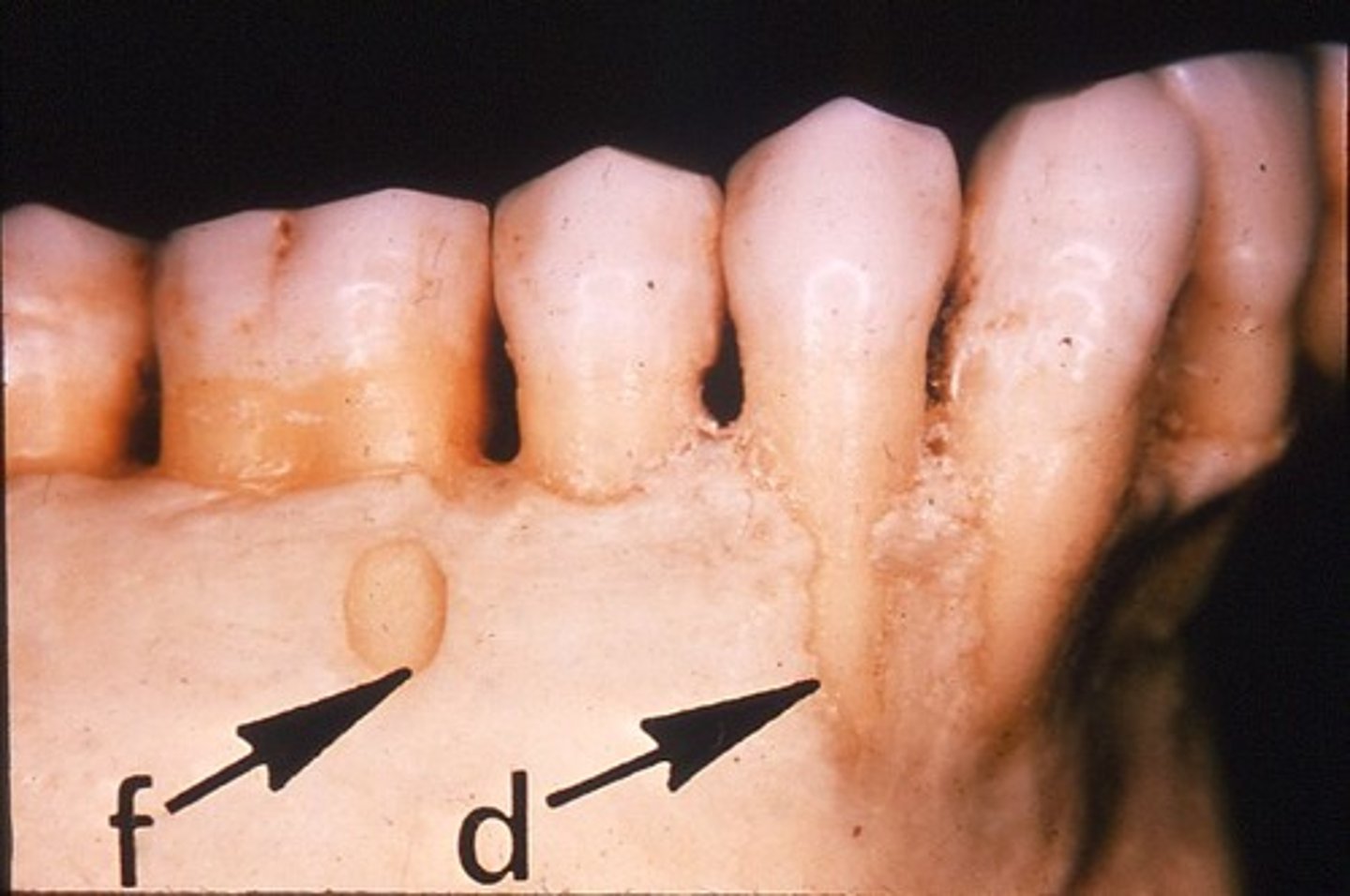
dihiscence
loss of alveolar bone
oval shaped root exposure apical to CEJ
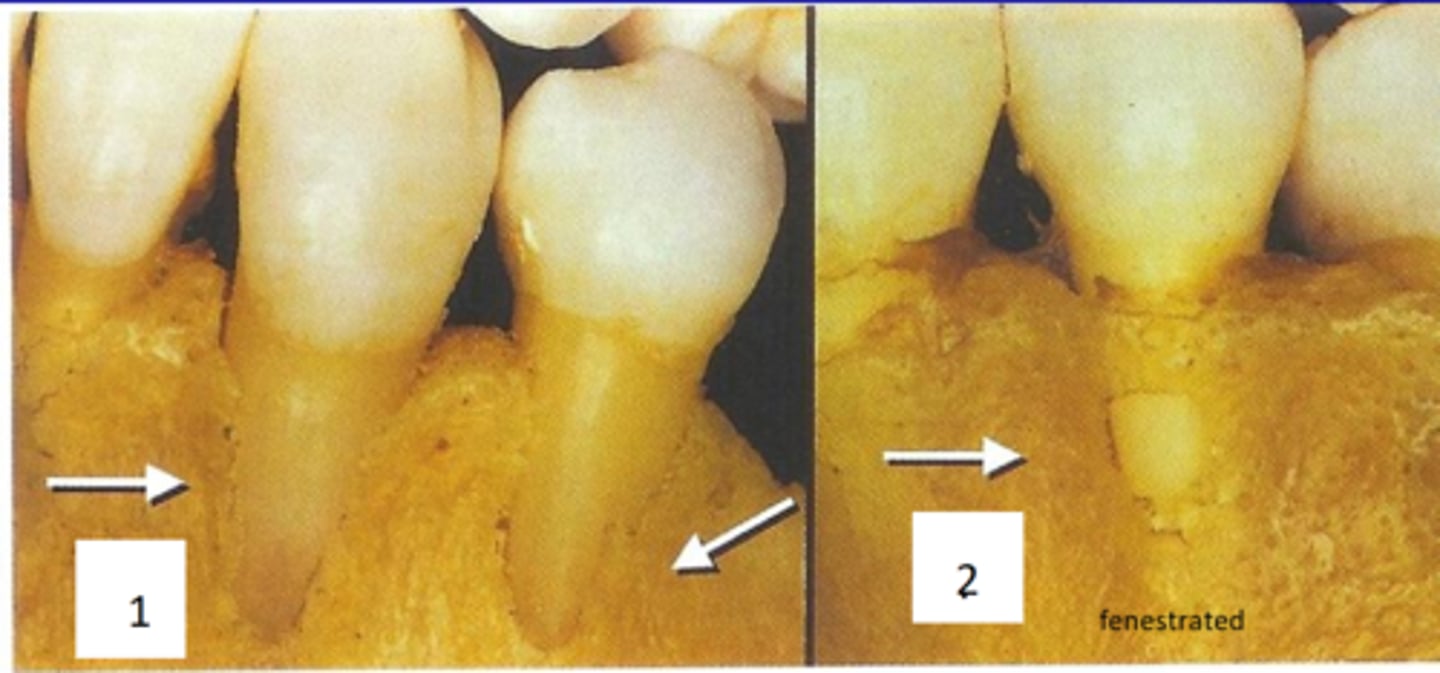
Fenestration
a window-like opening in the bone covering the root of a tooth bordered by alveolar bone on the coronal aspect of the tooth.
Bacteria shape present in early plaque formation
cocci shaped, aerobic
Bacteria shape in periodontal disease
baccilli, anaerobic
Bacteria shape present in NUG/NUP
spirochetes
periodontal bacteria in health
aerobic, cocci, gram +
Periodontal bacteria in diease
anaerobic, baccilli, gram -
Names of the bacteria that cause periodontal disease
P. Gingivalis
F. Nucletum
T. Forsythia
A. Actinomycetescomatins
Bacteria responsible for NUG
P. Gingivalis
T. Dentacolo
P. Intermedian
Fusobactrium
Bacteria responsible for caries
S. Mutans
Lactobacillus
S. Sobrinus
What bacteria is most commonly associated with aggressive periodontitis
A. Actinomycetescomatins
Is plankton plaque adherent or non adherent?
non adherent
how do endotoxins contribute to tissue destruction?
Stimulate osteoclast
periodontal disease
apical migration of the junctional epithelium
CAL
measures attachment loss
CEJ to base of pocket
What instrument is best to detect a furcation
Nabers Probe
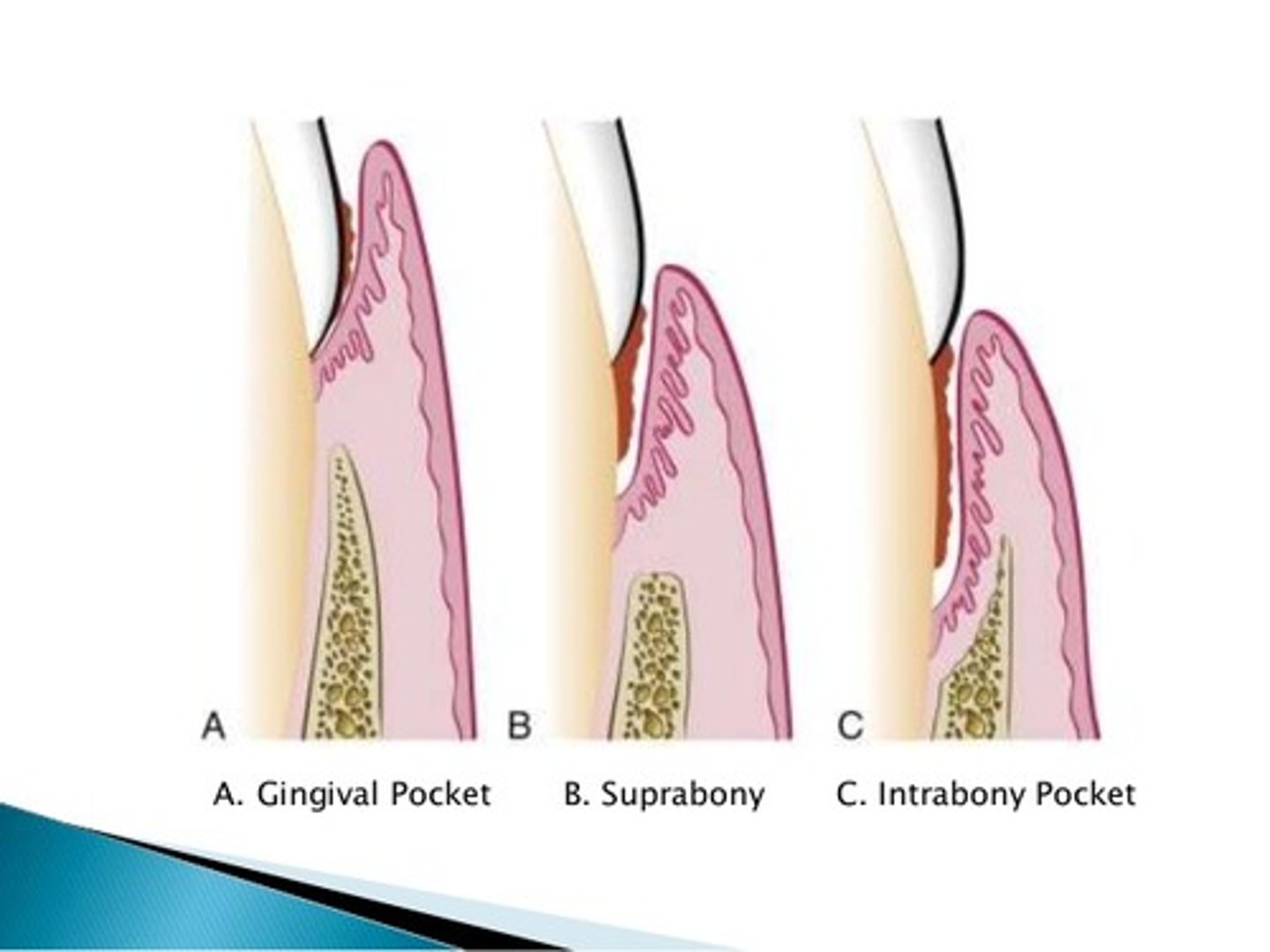
Suprabony pocket
The pocket is located above the level of the bone, NOT visible on a radiograph.
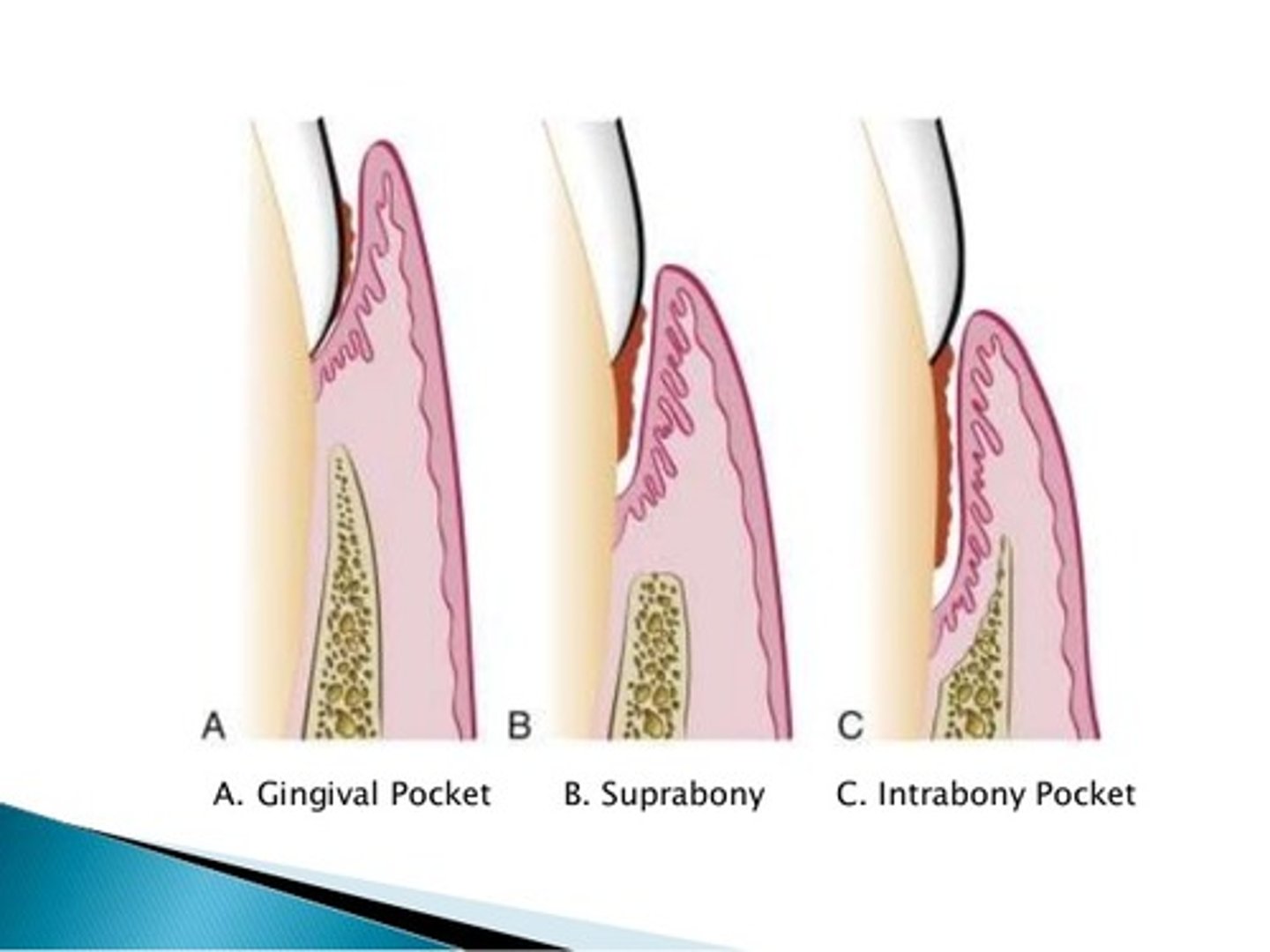
Infrabony pocket
base of pocket is apical to crest of alveolar bone
Does occlusal trauma cause periodontal disease
No
Primary Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
HSV type 1
usually affects children younger than 6
Inflamed, enlarged marginal gingiva; gingival bleeding
pin point vesicles -> ulcers throughout the mouth and lips w/ sig pain
Malise
low grade fever
sore throat, lymphadenopathy
doesnt want to drink water
Is a patient with down syndrome at a greater risk for caries
No, but they are at an increased risk for perio
How to treat NUG/NUP
Tetracycline
Can a periodontal abscess be a result of periodontal debridement
yes
First step of hemodynamic changes
1. Temporary (transient) vasoconstriction THEN vasodialation takes place
Hyperemia
excess of blood in an area of the body
Margination
Movement of WBC to periphery vessel wall
Pavementing
WBC line walls of blood vessel
Diapedesis
neutrophils squeeze through capillary walls and begin phagocytosis
Chemotaxis
cells move to the site of inflammation
Neutrophils (PMNs)
Function in phagocytosis, it is the most common cell in acute inflammation. It is a key WBC in the development and progression of disease
WBC associated with chronic inflammation
Macrophage
What biochemical mediator allows cells to leave the blood vessels?
Interleukins
What biochemical mediator is associated with pain and swelling?
Prostaglandins
P=Pain
What biochemical mediator causes bronchoconstriction?
Leukotrienes
L=Lungs
What are the stages of a periodontal lesion?
Stage I: Initial lesion (2-4 days)
Stage II: Early lesion (4-7 days)
Stage III: Established Lesion (2-3 weeks)
Stage IV: Advanced lesion (3 weeks- years)
In which stage of a periodontal lesion is there no clinical changes?
Stage I
Gingivitis begins to appear at what stage of a periodontal lesion?
Stage II, bleeding will occur
What stage of a periodontal lesion is periodontal disease considered to be?
Stage IV
Gingival edema begins to occur at what stage of a periodontal lesion?
Stage III
Diabetes mellitus
-Pts at greater risk for xerostomia, caries, and periodontal disease
-candidiasis
-delayed wound healing
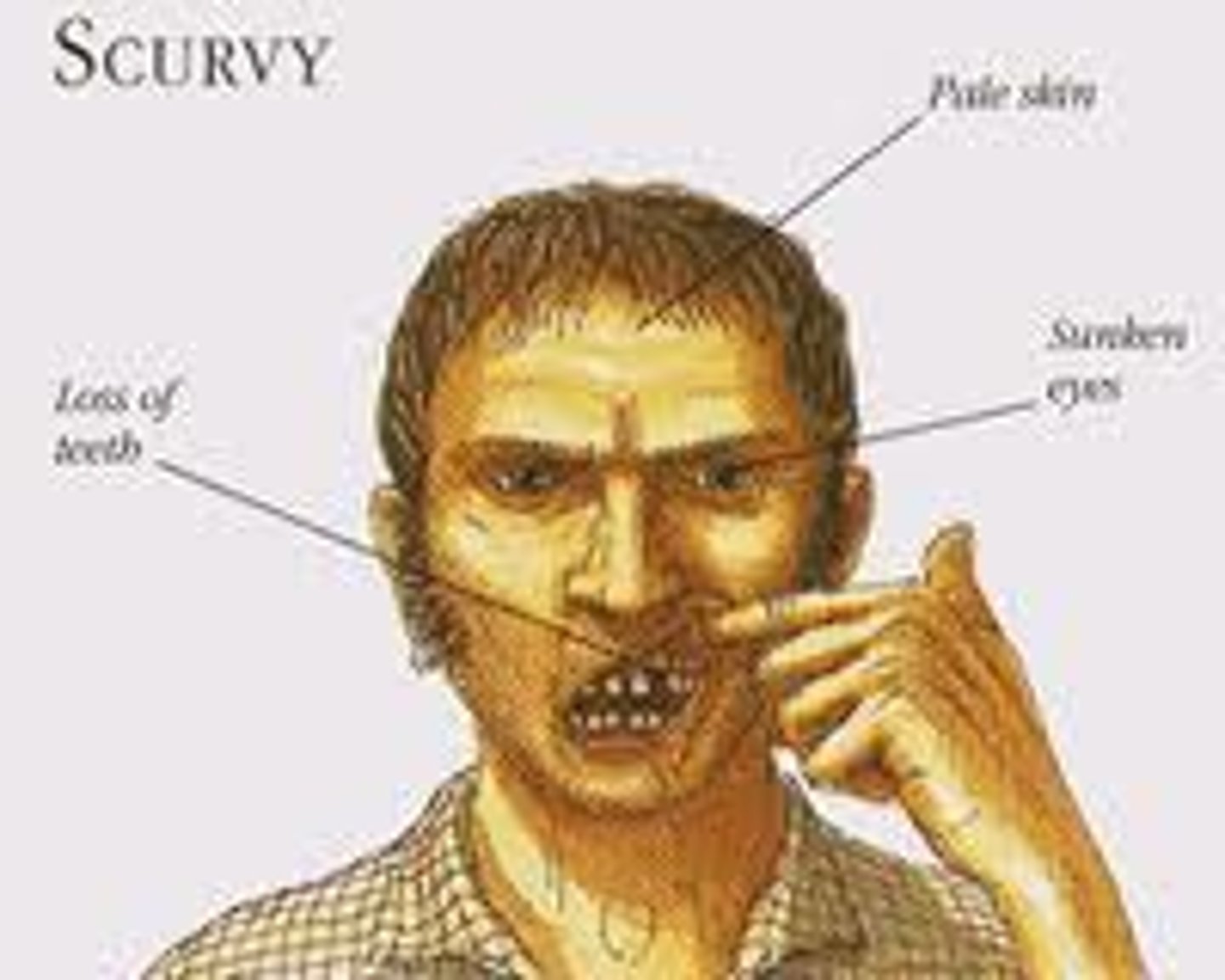
Scurvy
Vitamin C deficiency, it is needed for collagen production and wound healing
What bacteria is associated with pregnancy gingivitis?
Prevotella intermedia, campylobacter retus
How does smoking affect the periodontium?
Vasoconstriction
impaired neutrophil response to perio pathogens
oral mucositis
inflammation of oral tissues
often seen in cancer pts
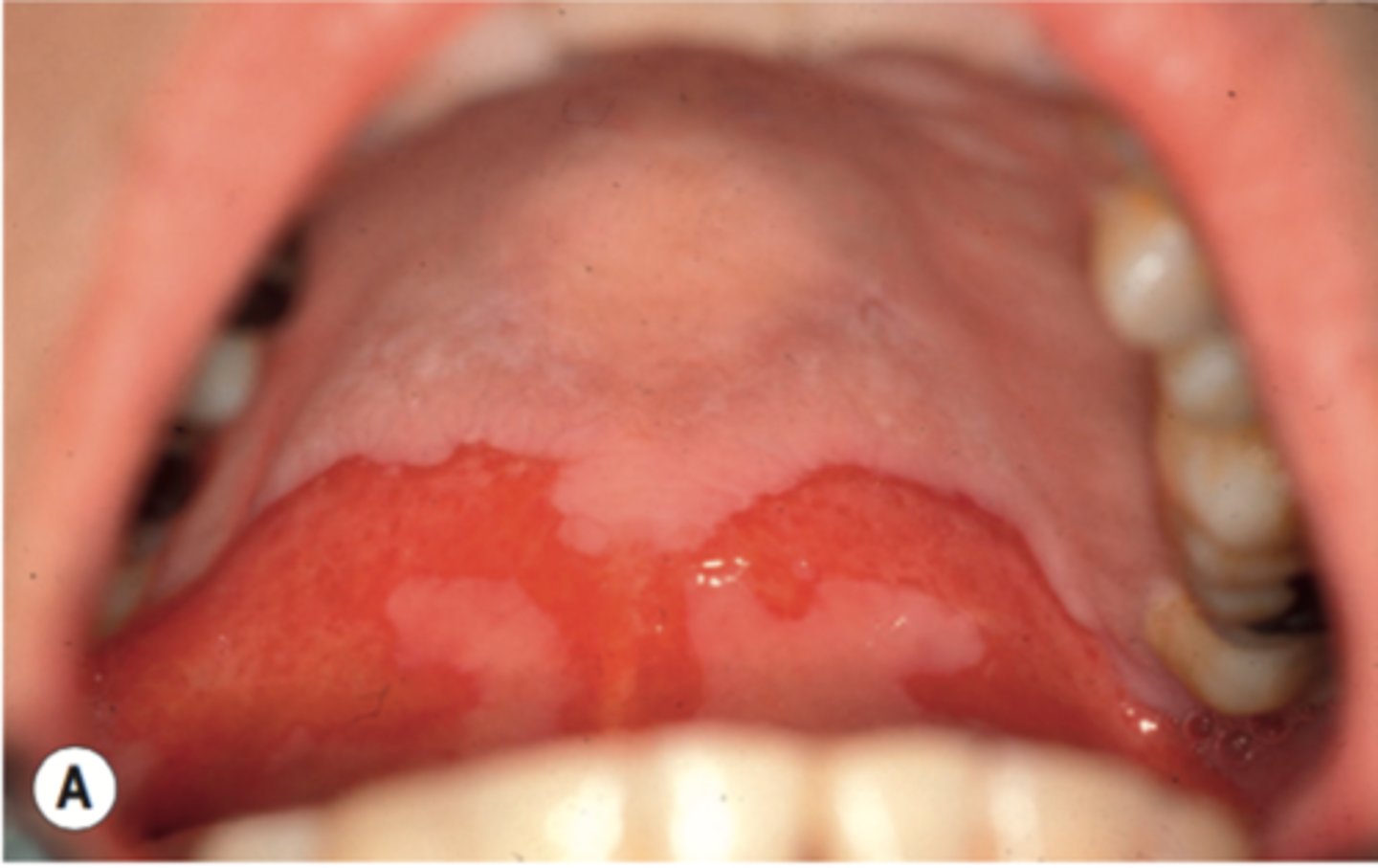
dysgeusia
altered taste
urticaria
hives
emesis
vomiting
Periodontal presentation of HIV
- Oral hairy leukoplakia
-Linear Gingival erythrma
- NUP
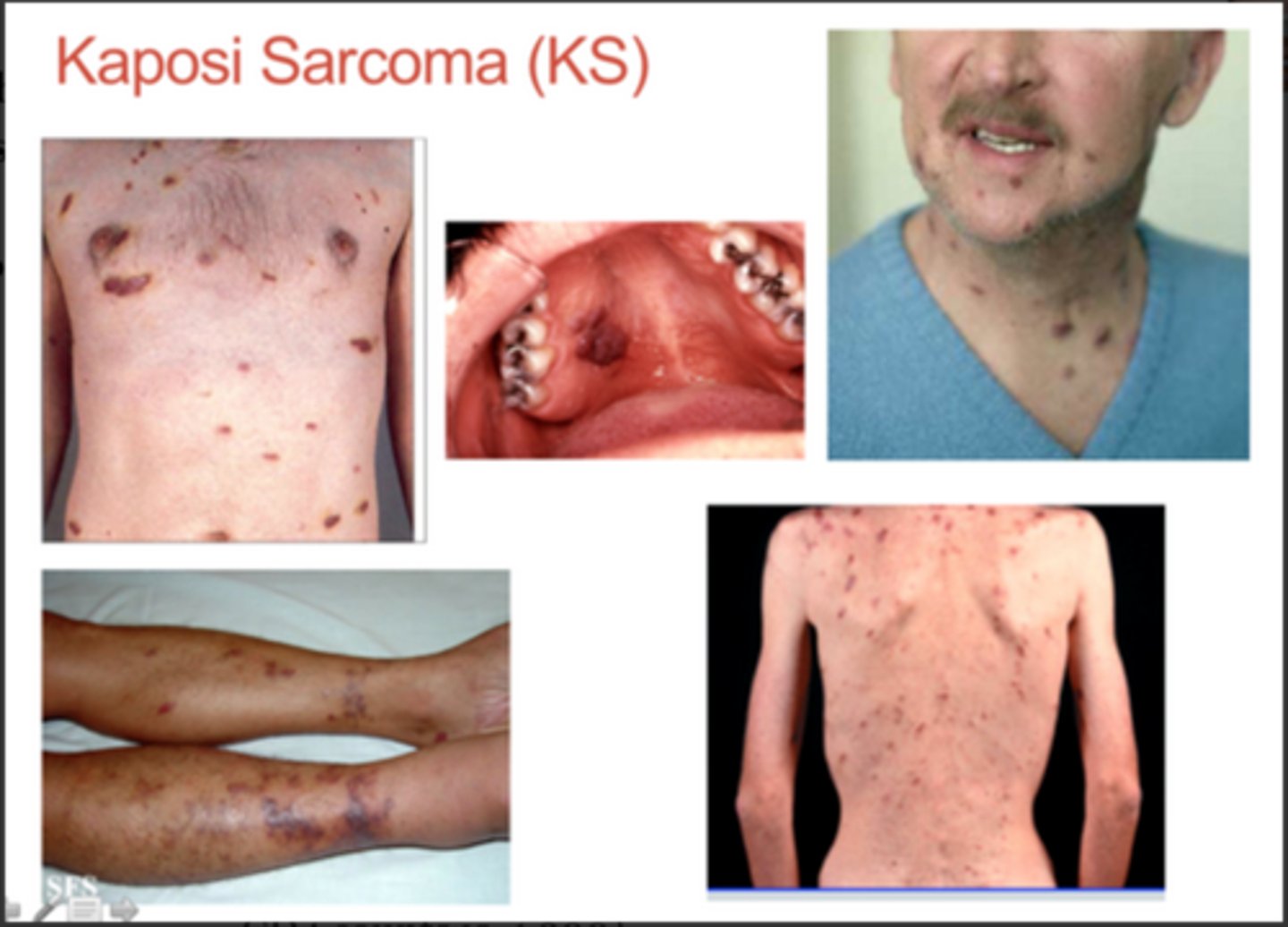
- Kaposi's sarcoma
Kaposi's Sarcoma (HHV-8)
malignancy of blood vessels
presents as a blue/ purple macule
Post SRP
Have a re-evaluation appoint 4-6 weeks later
1st step is to assess the gingiva
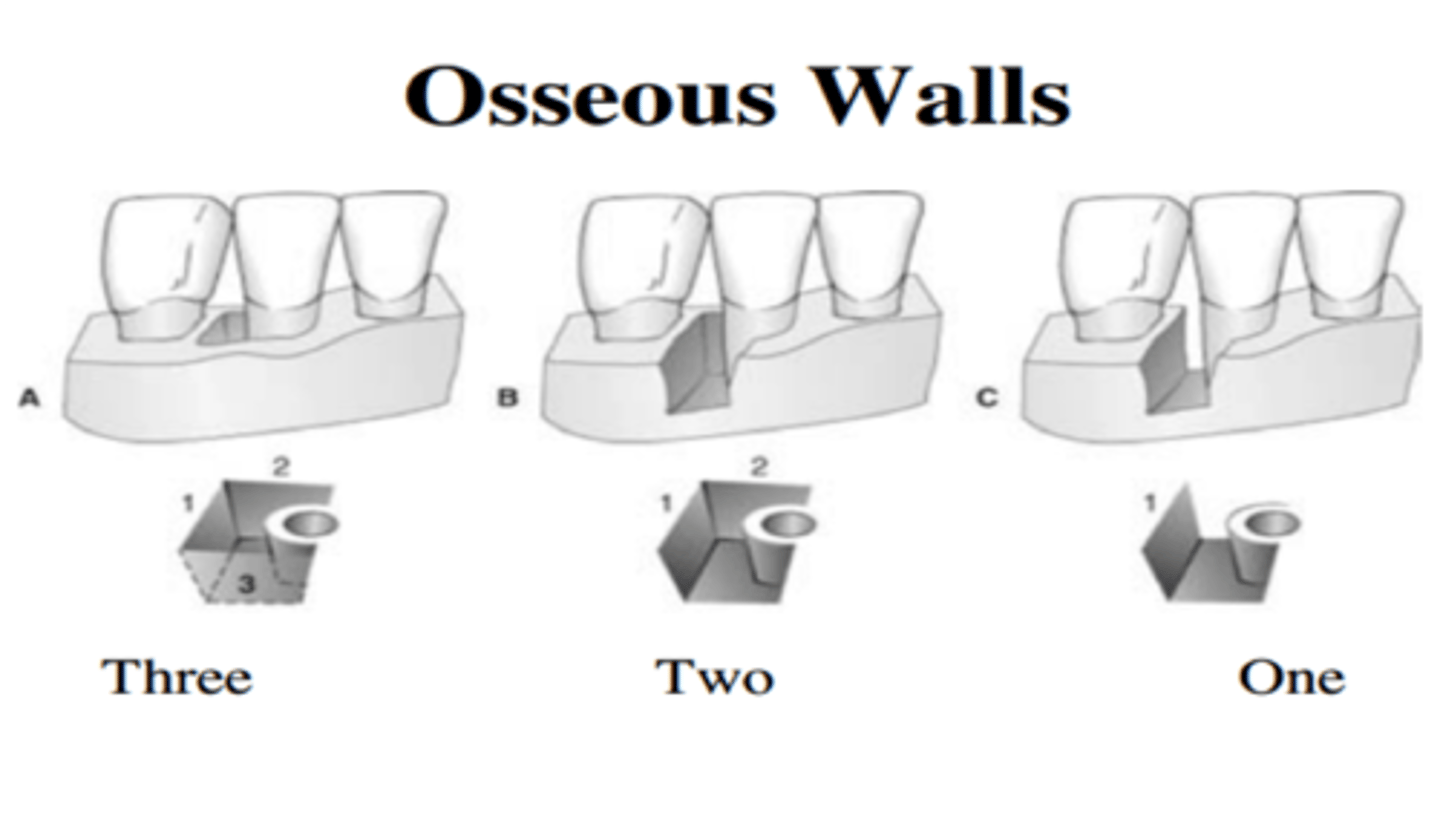
What has a better prognosis? A 3 wall defect or a 1 wall defect?
a 3 wall defect. The more walls (higher #) means there are more walls supporting the tooth
Active ingredient in Arestin?
minocycline
Active ingredient in Periochip?
Chlorahexidine
What is the most common procedure to reduce periodontal pockets?
Gingivectomy.
Removal of soft tissue only. For hyperplasia/ pseudo pockets
Gut sutures are placed after surgery. What does this mean?
The stiches are bioabsorbale
Silk sutures are
non-absorbable
Does a periodontal dressing prevent plaque build up?
no
How do you treat an infrabony defect?
Guided tissue regeneration
osseous or soft tissue graft
(the picture is of a dogs mouth, but still helpful as a visual)
What are the four stages of fibrous repair?
1. Blood clotting
2. Wound cleansing
3. Tissue rebuilding
4. Wound remodeling
At which stage of fibrous repair is granulation tissue introduced?
3. Tissue rebuilding
In which stage of fibrous repair are macrophages introduced?
wound cleansing
Tobacco use affects the periodontium by
a. vasodilation
b. loss of protective keratin
c. reduced blood supply to the tissues
d. enhanced phagocytosis
C. Reduced blood supply to the tissues
The most common type of bacteria on the dorsum of the tongue and other soft tissues in a healthy mouth?
a. Streptococci
b. Staphylococci
c. Fusobacterium
d. porphyromonas
a. streptococci
Porphyromonas gingivalis are?
Pathogenic bacillus bacteria that are prevalent in many chronic periodontal diseases
Initial gingival lesion (stage I) will exhibit
no clinical signs
What bacteria is not associated with chronic periodontitis ?
A) T. Denticola
B) P. Intermedia
C) S. Mutans
D) P. Gingivalis
S. mutans
Which of the following is a characteristic of the progression of periodontal disease?
a. Cocci
b. Motile organisms
c. Aerobic organisms
d. gram + organisms
motile organism
Endotoxins
A) Is produced by a mast cell
B) Stimulates osteoclast activity
C) Is produced by B-lymphocytes
D) Stimulates the secretion of immunoglobulins
Stimulates osteoclast activtity
Which assessment finding indicates that a pts periodontal disease progressing?
a. periodontal pockets
b. BOP
c. evidence of radiographic bone loss
d. attachment loss increasing over time
attachment loss increasing over time
Sharpeys fibers are found in
Cementum and alveolar bone
when probing a class II furcation
the probe will penetrate the furcation but not pass complete through
After perio surgery, patients who smoke
heal slower due to reduced fibroblast migration and a reduction in the positive effects of the inflammatory response
circular fibers
a. resist horizontal tooth movements
b. supply nutrient to periodontal structures
c. resist intrusive and extrusive forces on a tooth
d. assist in maintaining marginal gingival integrity with a tooth surface
What is the only bone that is not attached to another bone
hyoid bone
which foramen does the 7th cranial nerve run through
stylomasto foramen
through which bone does all three divisions of the trigeminal nerve run through
sphenoid bone
superior orbital fissure of sphenoid bone
the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve runs through here
foramen rotundum of sphenoid bone
maxillary division of trigeminal nerve division of the trigeminal nerve runs through here
foramen ovale of sphenoid bone
mandibular branch division of the trigeminal nerve run through here
what muscles of the tongue protrudes it outwards
genioglossus
how many cranial nerves are there?
12
"Oh, Oh, Oh, To, Touch, And, Feel, Very, Good, Velvet"
"Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Boobs Matter More"
What is cranial nerve V?
trigeminal nerve
What is cranial nerve VII?
facial nerve, it supplies the facial muscles, taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue, and the parasympathetic intervention of the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
What is cranial nerve IX
Glossopharyngeal; responsible for senses, taste of the posterior 1/3 of tongue and parasympathetic innervation of the parotid gland
what is cranial nerve XII?
Hypoglossal; controls most of the tongue movements, important for speech and swallowing. It does not include the palatoglossal muscle
PSA block anesthetizes:
Maxillary molars EXCEPT the MB root of the first molar and facial gingival tissue
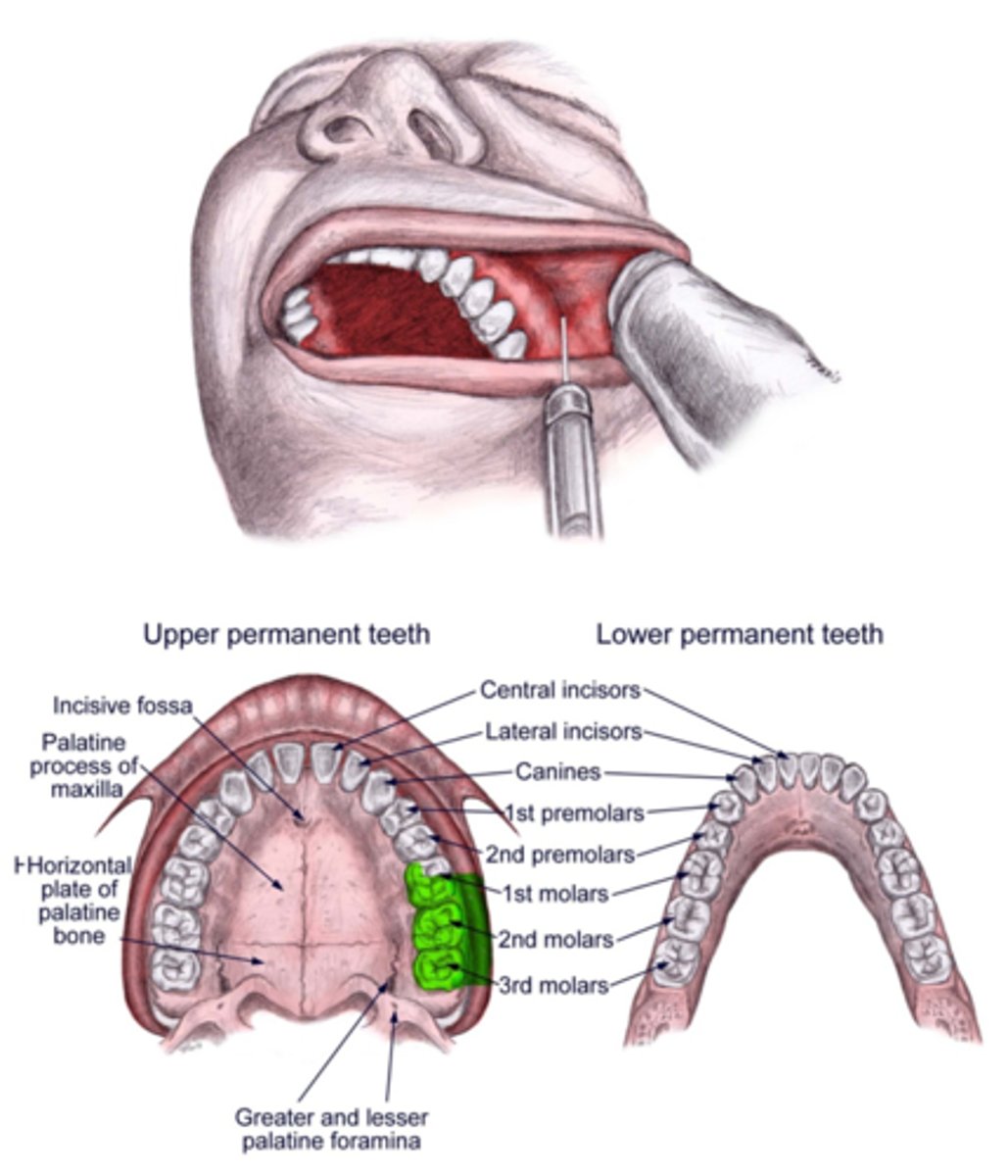
MSA block will provide anesthesia to what areas?
Max Premolars and the MB root of Mx 1st molar, AND the facial gingival tissue
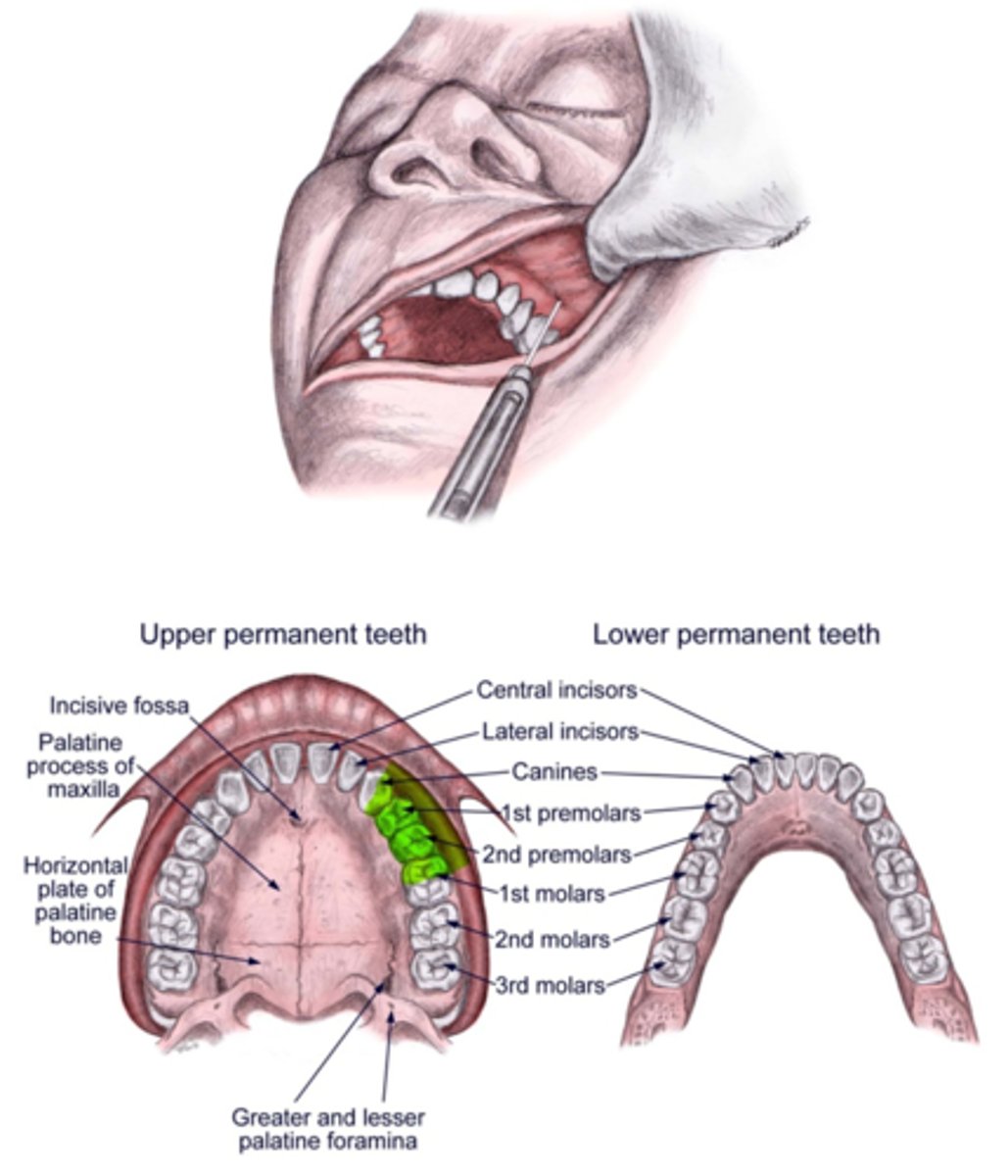
ASA block will provide anesthesia to what areas?
Max anterior teeth and facial gingival tissue
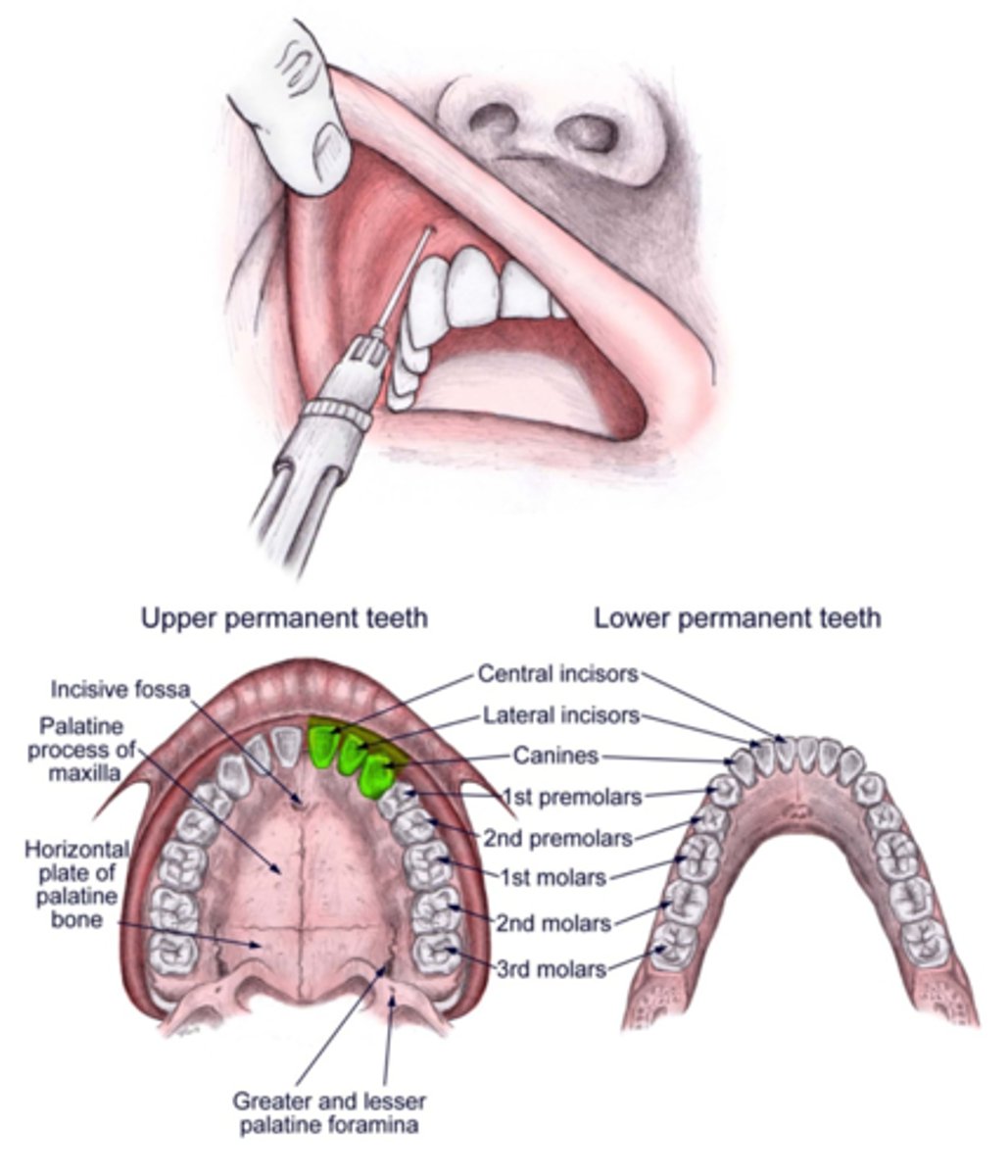
IA block will provide anesthesia to what areas?
All areas of the manible except the buccals of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd molars
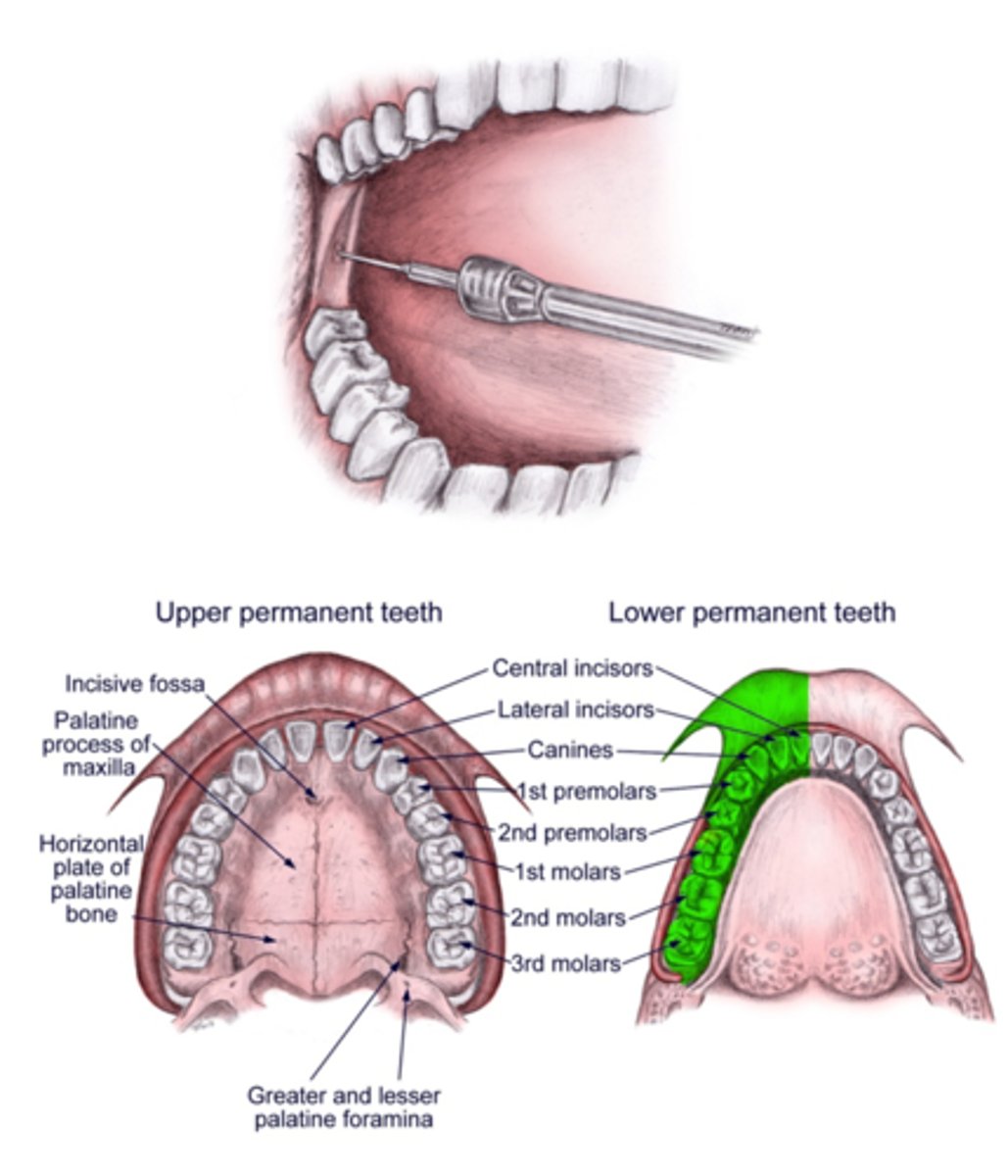
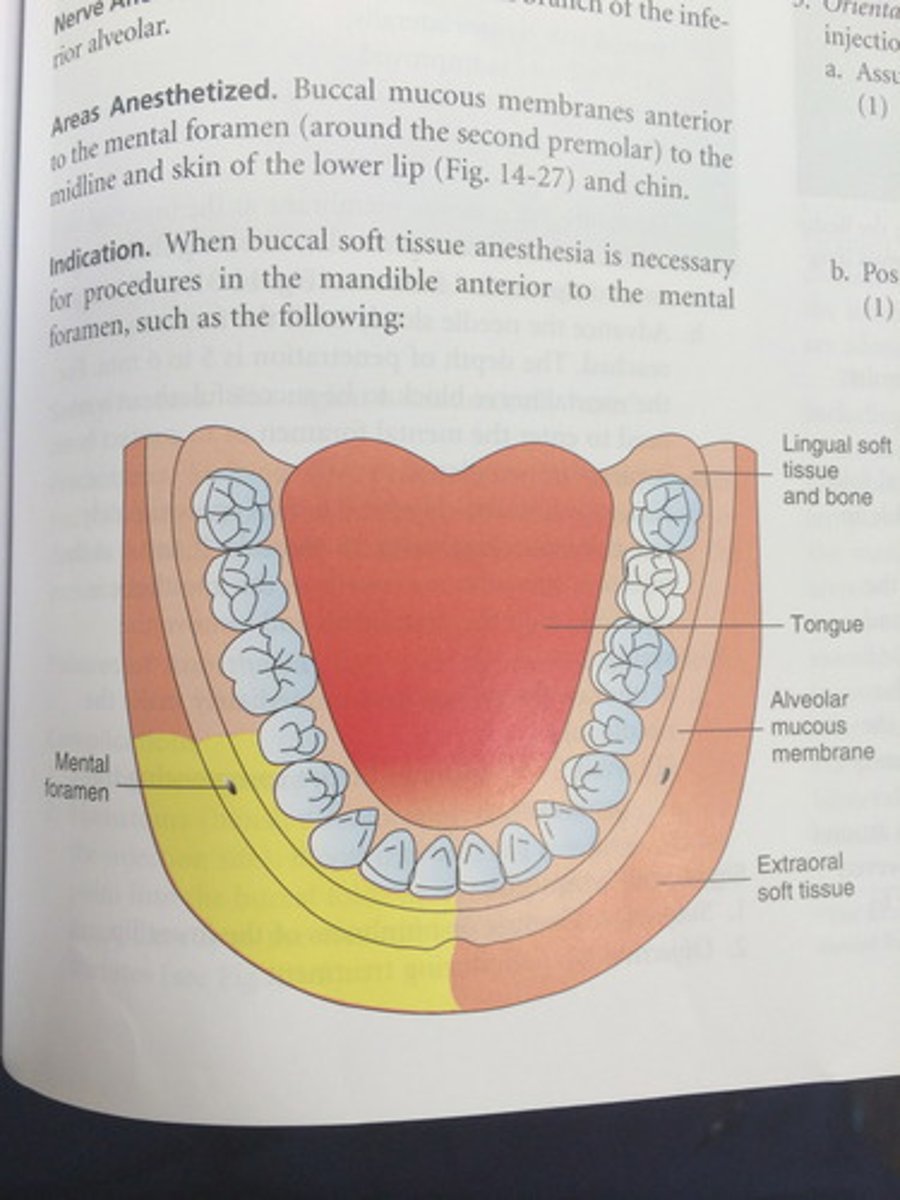
Mental block will provide anesthesia to what areas?
first mandibular premolar to midline. No teeth are anesthetized!! Soft tissue only
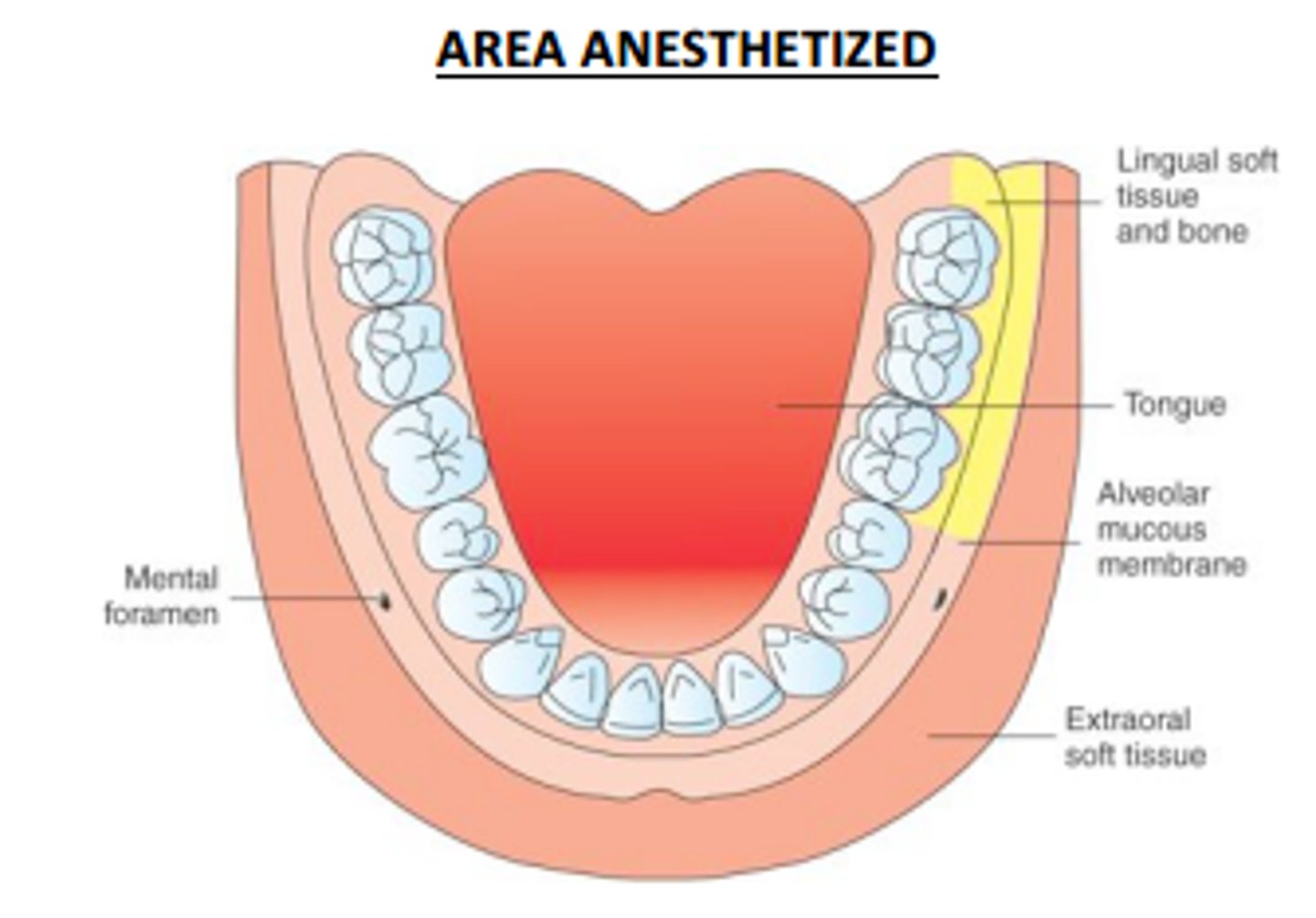
Buccal block will provide anesthesia to what areas?
Buccal gingival tissue of molars
What branch of the trigeminal nerve innervates the muscles of mastication?
V3: the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve
What muscles open the mouth?
lateral pterygoid, and hyoid muscles
What are the muscles of mastication?
temporalis, masseter, lateral pterygoid, medial pterygoid
Trismis
condition that causes reduced mobility of the jaw