Reproduction in humans
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Urethra
Tube which transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. In males it can also carry semen.
Ovaries
Organs which secrete oestrogen and progesterone into the bloodstream. Eggs are produced, stored and then released from here once a month.
Testis
Organs which produce testosterone. Sperm are produced here.
Ovum
The scientific term for the female gamete.
Sperm
The male gamete
Haploid
The term used to describe a cell (such as a gamete) which contains one copy of every chromosome.
Diploid
The term used to describe a cell which contains two copies of every chromosome.
Fallopian Tubes
The tubes which transport ova from the ovaries to the uterus. They are lined with ciliated epithelium. Fertilisation takes place here. Also called the oviducts.
Uterus
The organ where implantation and fetal development takes place. The lining of this organ is lost once a month in menstruation. Its muscular contractions help to force the baby through the vagina during child birth.
Cervix
The narrow gap between the vagina and the uterus. Its diameter is controlled by a ring of muscle which has to dilate up to 10cm during child birth.
Ciliated epithelium
The cells of this tissue possess many cilia which beat rhythmically to move the egg along the Fallopian tubes.
Vas deferens
The tube which transports sperm from the testis to the prostate gland.
Seminal vesicle
The gland which produces seminal fluid. This activates and nourishes the sperm in preparation for their journey to the egg.
epididymis
A set of coiled tubules which stores sperm before ejaculation.
Scrotum
The sac of skin which contains the testis. It allows the testis to sit outside of the body cavity where the temperature is lower and sperm production is faster.
prostate gland
This accessory gland in the male reproductive system produces much of the liquid component of semen. It is found under the bladder and contains the junction between the vas deferens and the urethra.
placenta
This organ is produced by the developing embryo as a site of exchange between the maternal and foetal blood. It prevents the mixing of maternal and foetal blood but allows diffusion of gases, nutrients and waste molecules. It also produces progesterone during pregnancy.
zygote
The name given to the diploid cell that is produced when a sperm fertilizes an ovum.
mitosis
The process of cell division which allows a zygote to develop into an embryo and eventually a fetus.
embryo
The name given to the developmental stage between zygote and fetus.
implantation
The process whereby an embryo implants itself into the uterus wall. It allows exchange between the embryo and the maternal blood to begin.
28 days
The length of the average menstrual cycle.
days 1 to 5
The days during which menstruation takes place.
menstruation
The breakdown and loss of the uterus lining from the vagina.
ovulation
The process whereby an egg is released from the ovary.
follicle
The structure containing the maturing egg cell in the ovary. The cells in this structure secrete the hormone estrogen into the mother's blood.
estrogen
This hormone builds up, thickens and repairs the uterus wall after menstruation. Its concentration in the blood peaks on day 14. It also stimulates the development of secondary sexual characteristics in females.
progesterone
This hormone maintains a thickened lining of the uterus. Its levels drop at the end of the month causing menstruation to occur. Levels remain high during pregnancy.
corpus luteum
The site of progesterone production in the ovary.
Amniotic sac
The protective bag that surrounds a developing embryo in the womb. It produces and contains amniotic fluid.
Amniotic fluid
The fluid which surrounds a developing embryo. It protects it from mechanical shock, provides a weightless environment in which to develop and helps to maintain a constant temperature.
Umbilical cord
The structure which joins the developing fetus to the placenta.
Umbilical artery
This blood vessel transports deoxygenated blood from the developing fetus to the placenta.
Umbilical vein
This blood vessel transports oxygenated blood from the placenta to the developing fetus.
fetus
The name given to a developing human embryo after the internal organs have developed.
Testosterone
The hormone made in the testis which controls sex drive, aggression and the development of secondary sexual characteristics in males.
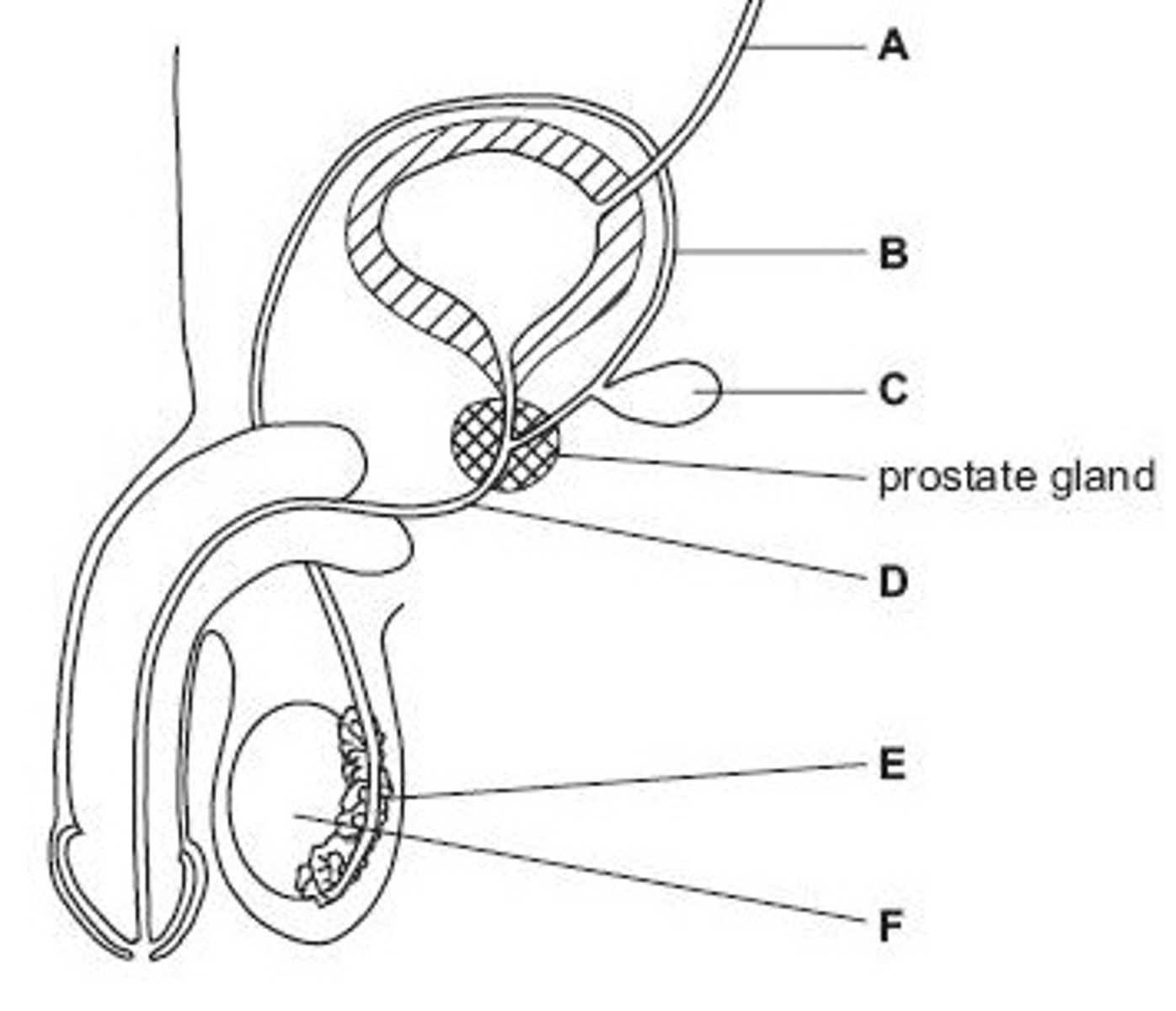
Ureter
Name structure A
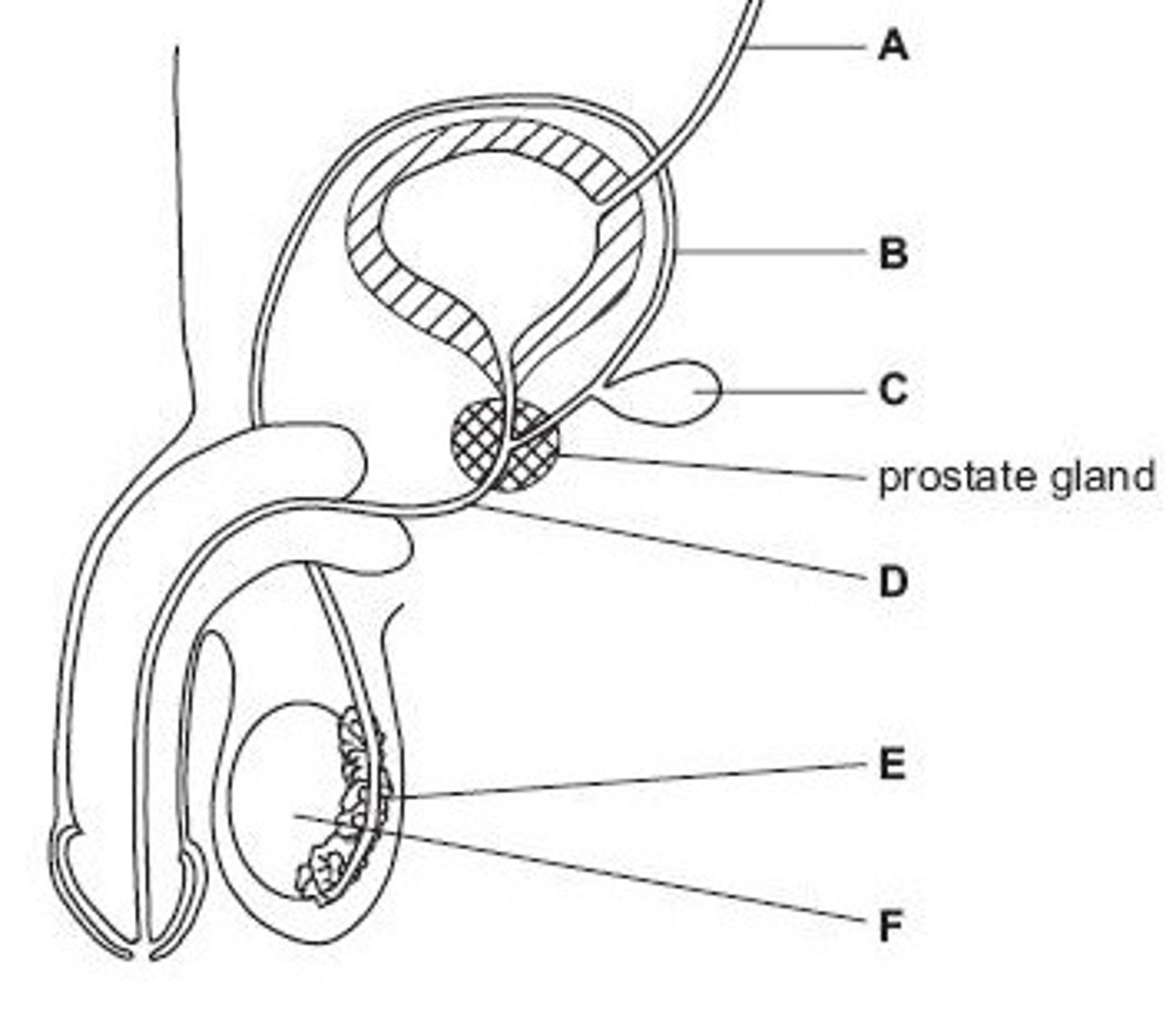
Vas deferens
Name structure B
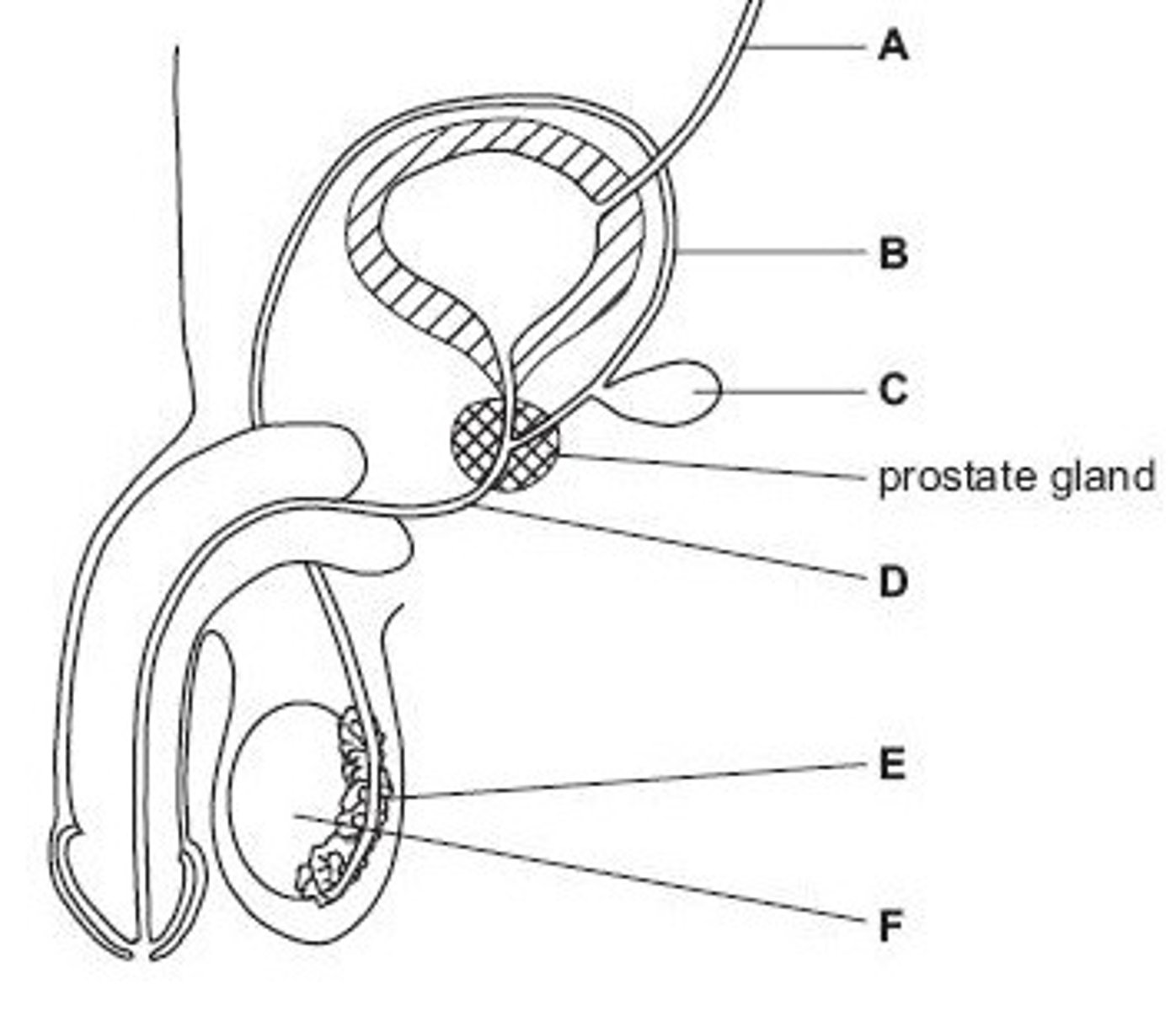
Seminal vesicle
Name structure C
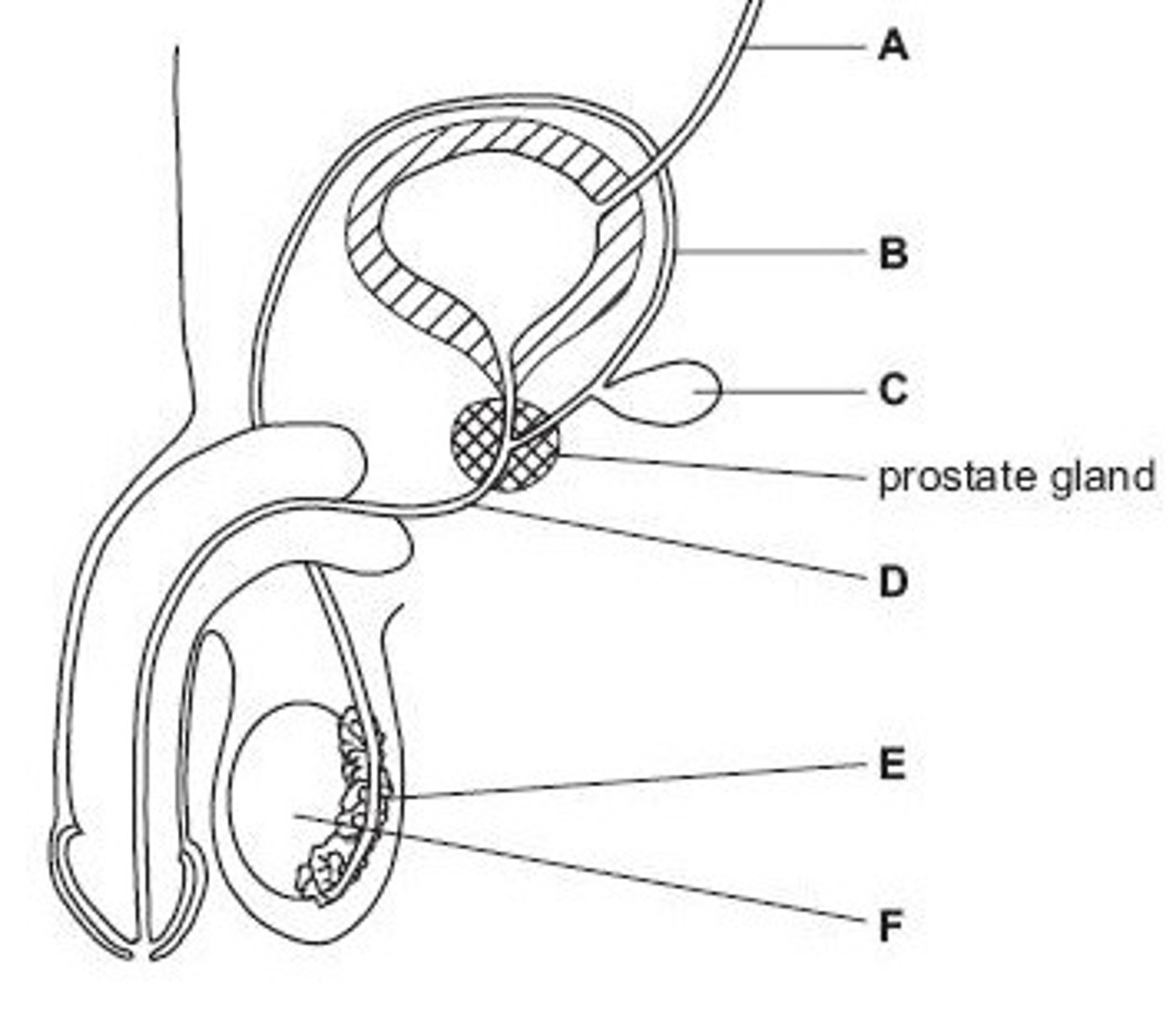
Urethra
Name structure D
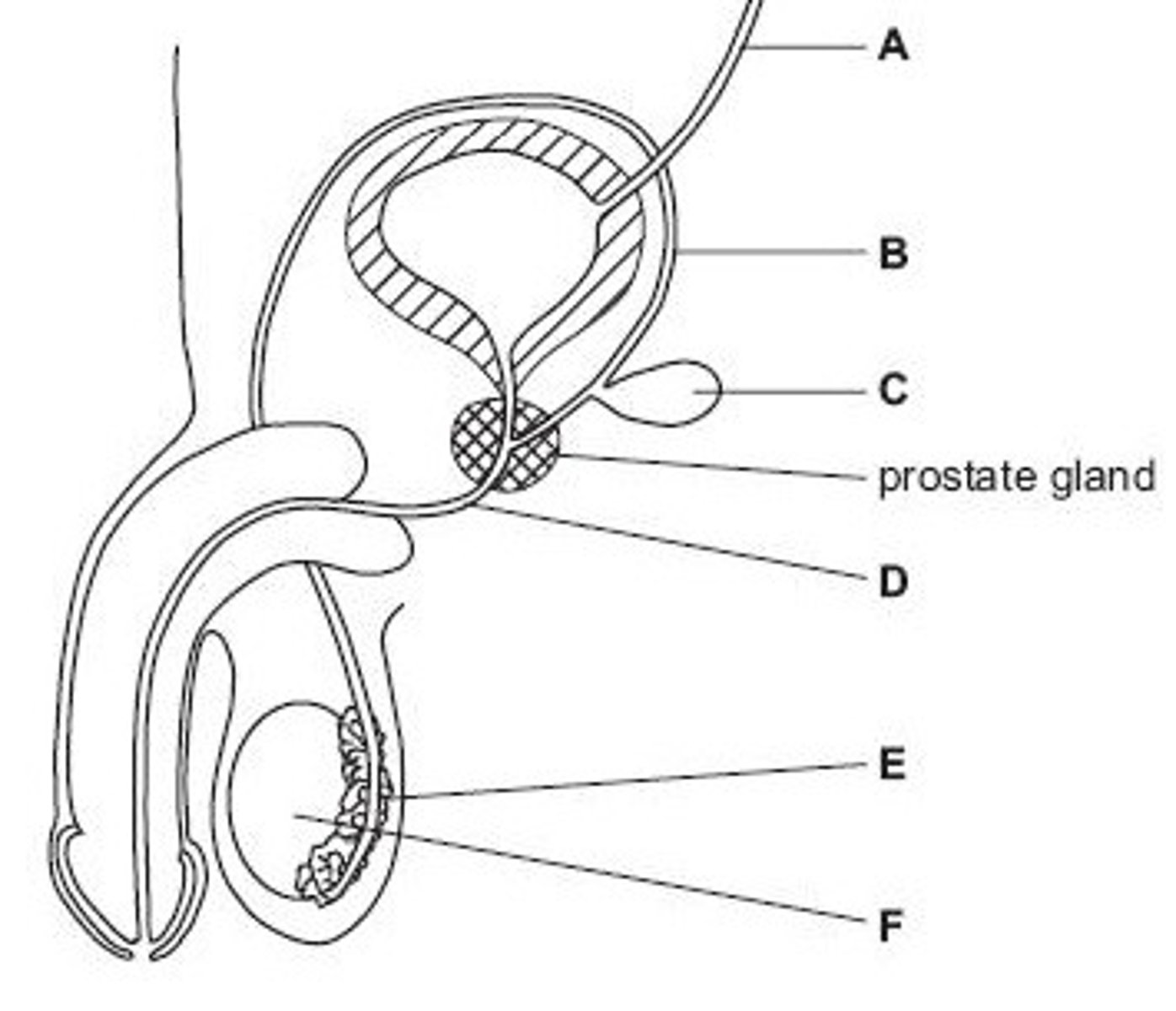
Epididymis
Name structure E
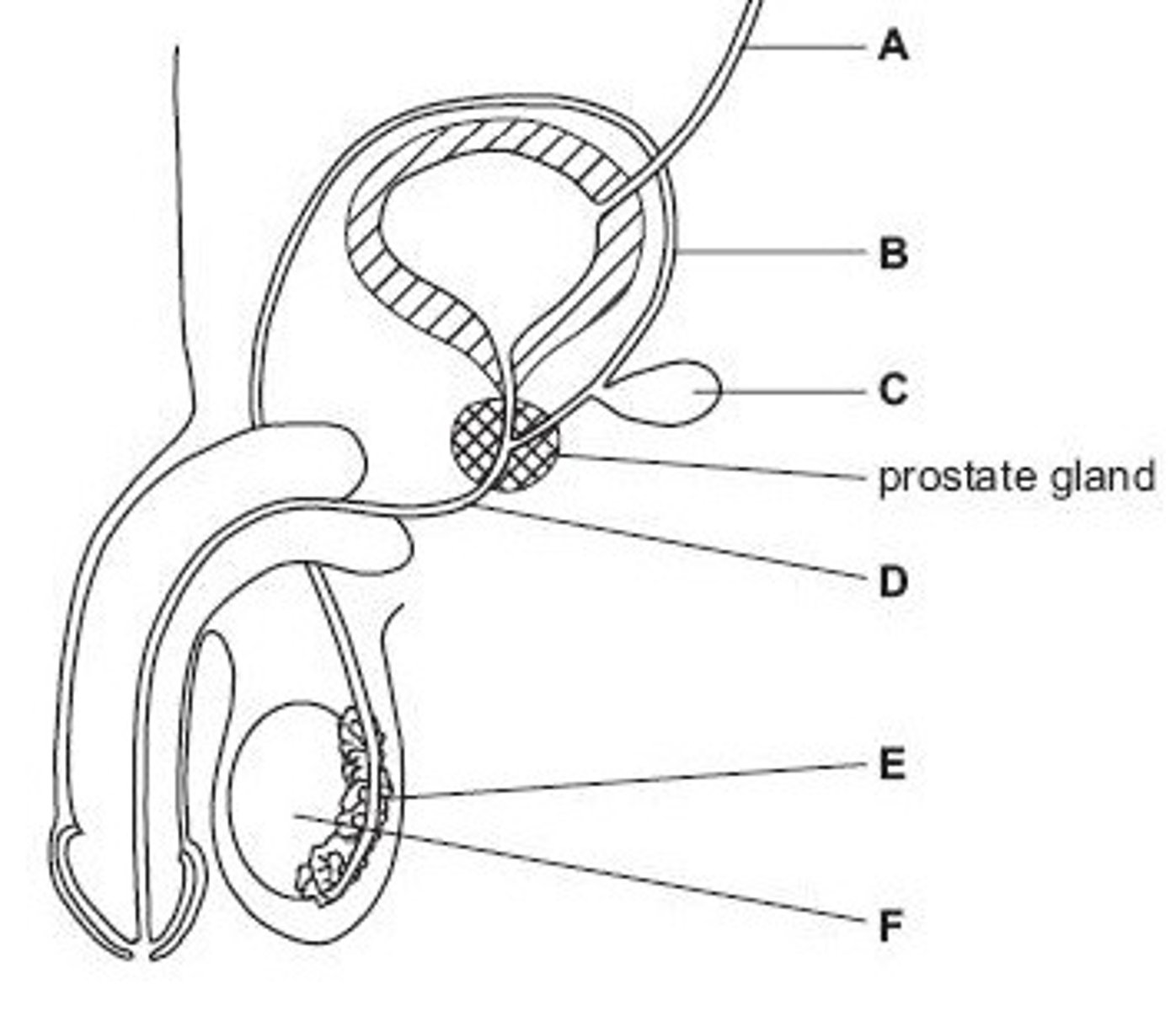
Testis
Name structure F
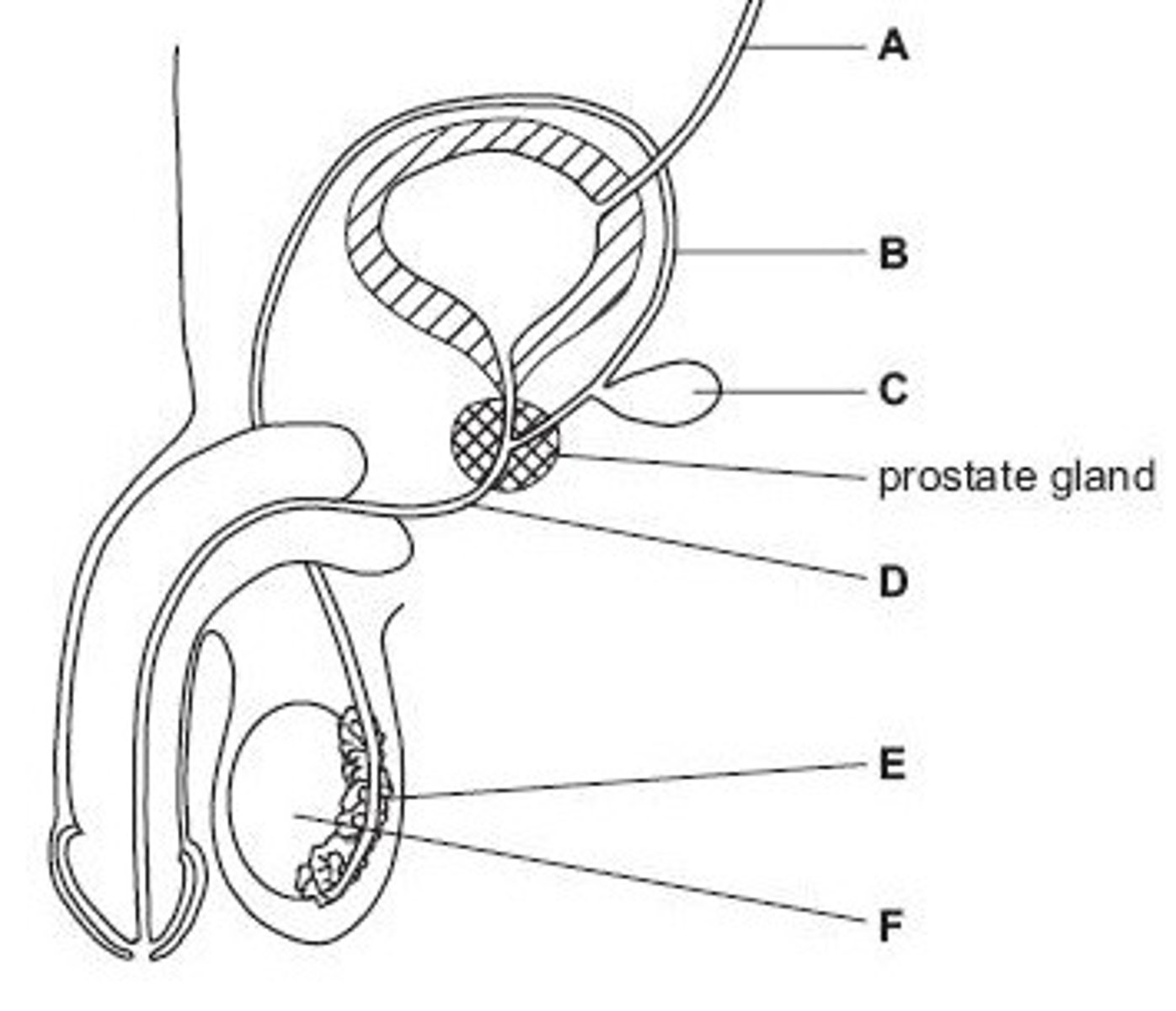
B
Give the letter of the tube which is cut during a vasectomy (sterilisation operation).
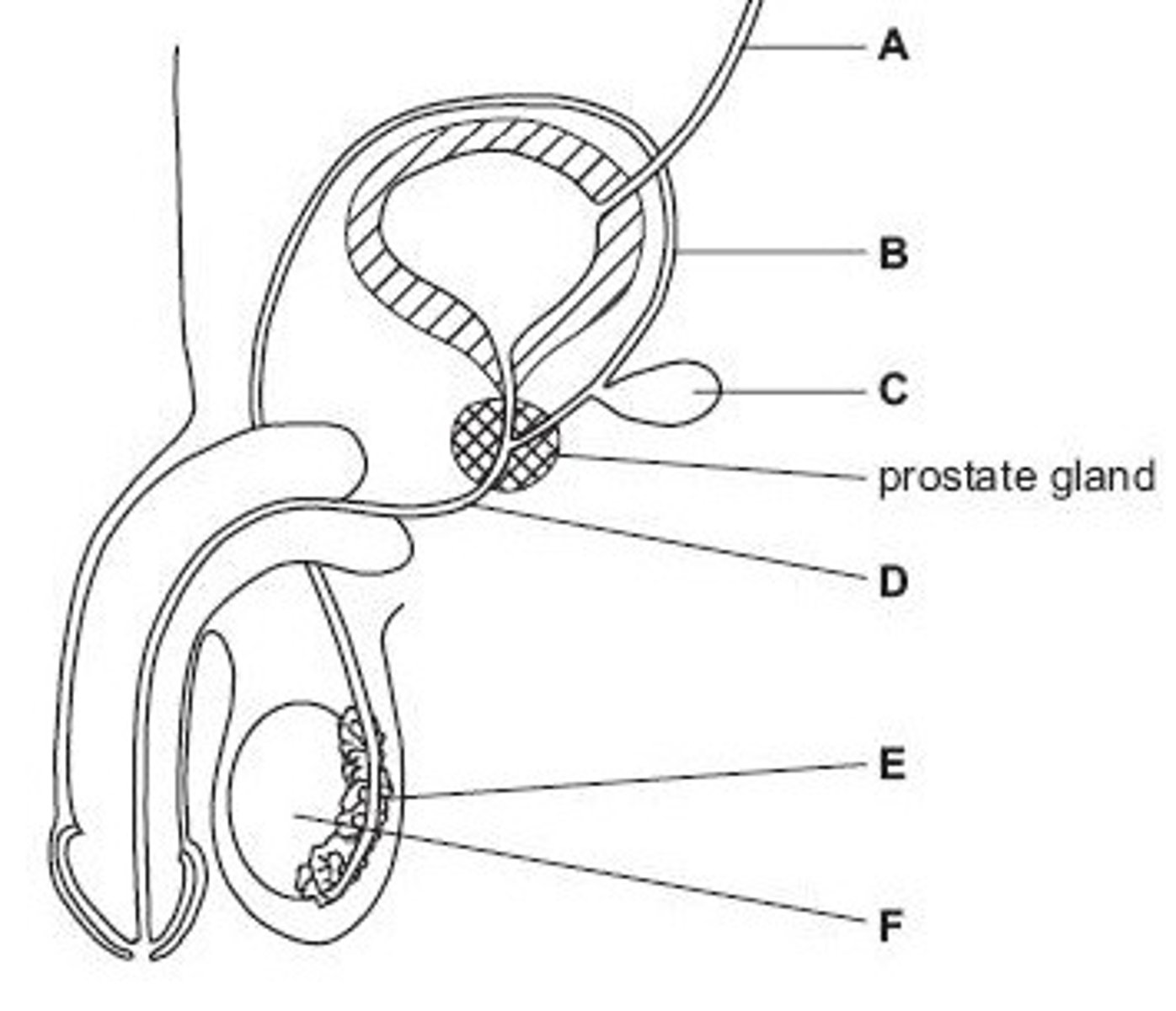
D
Give the letter of the tube which carries both urine and semen.
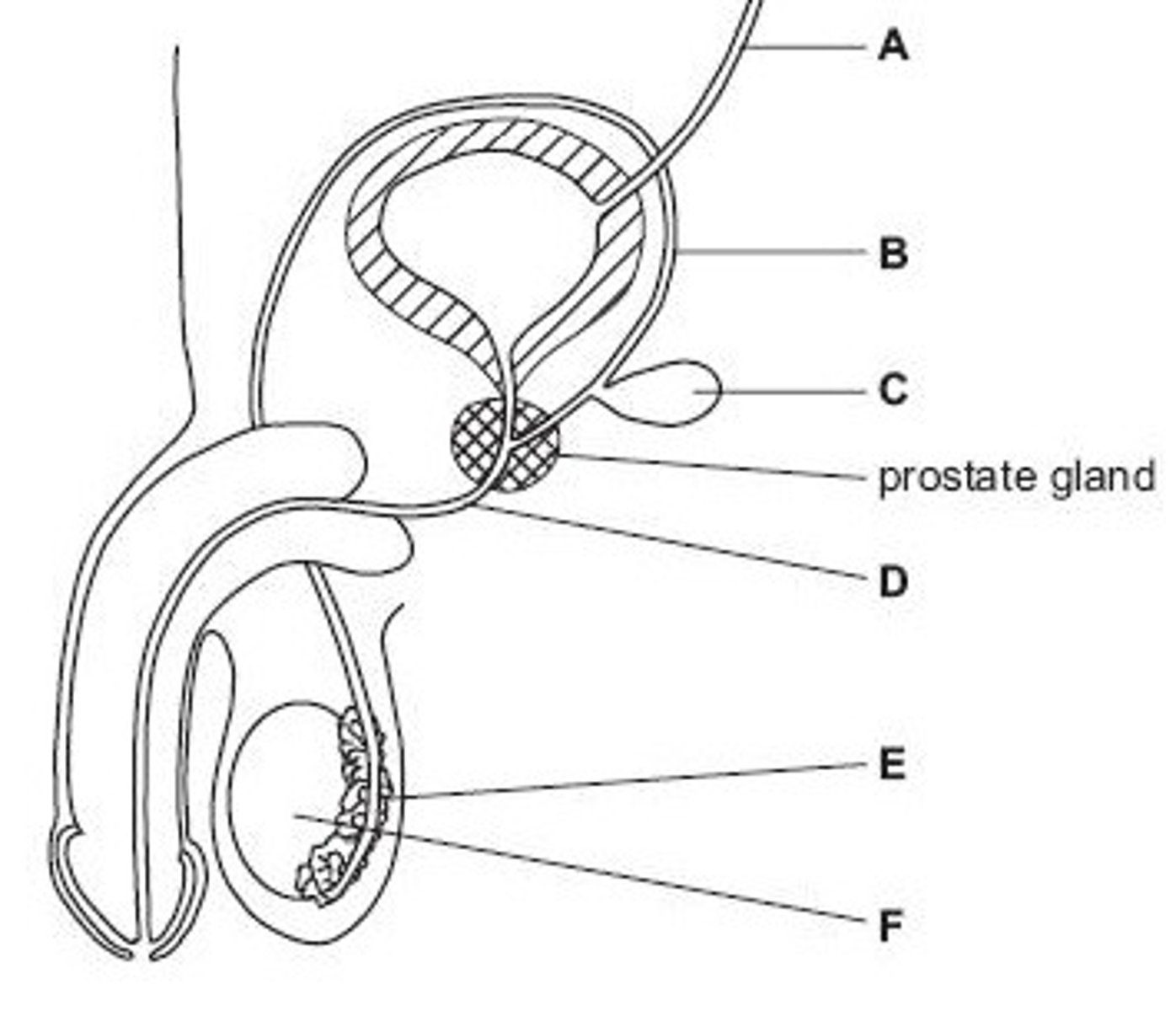
E
Give the letter of the structure where sperm are stored before ejaculation.
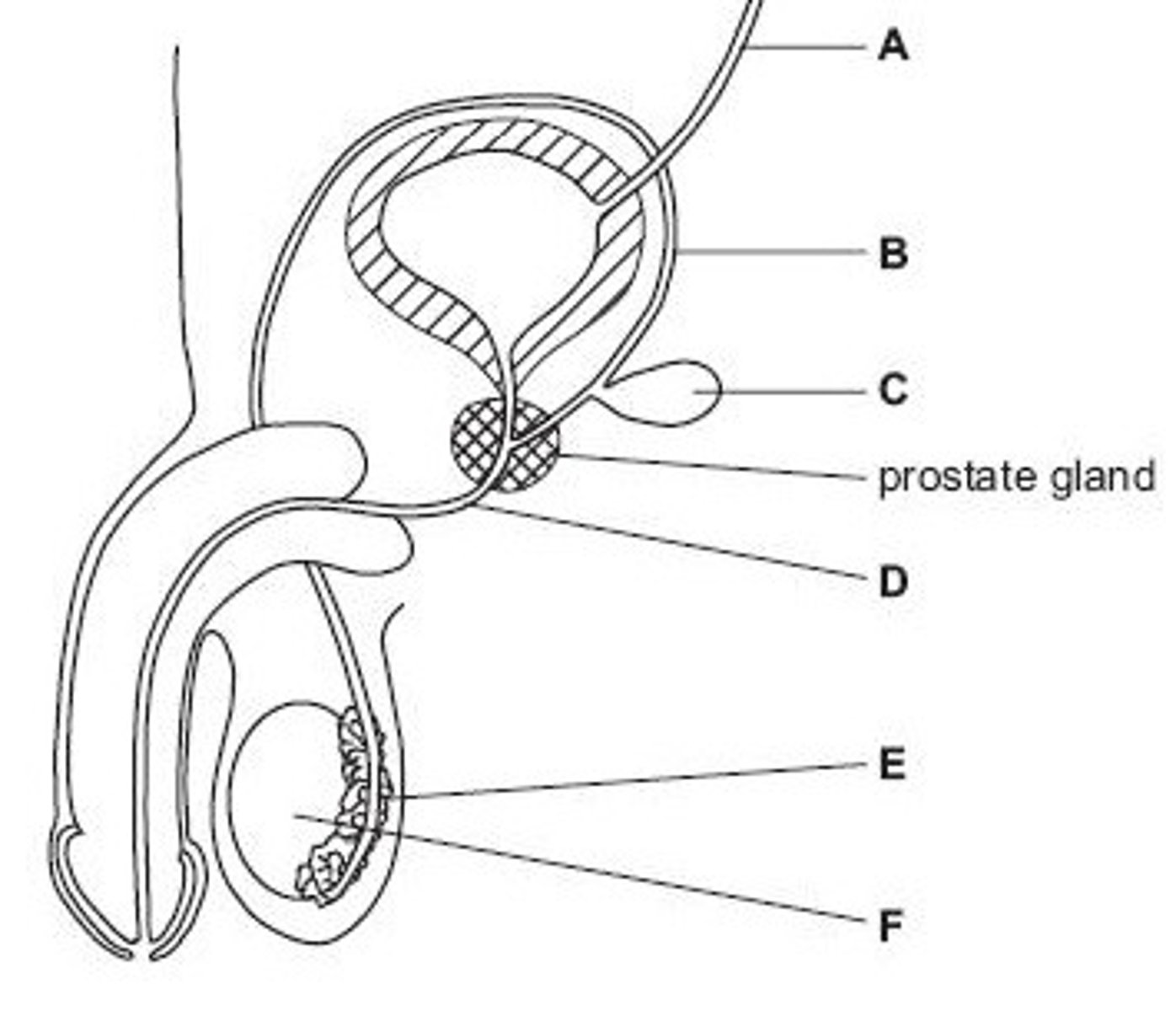
F
Give the letter of the structure where meiosis occurs
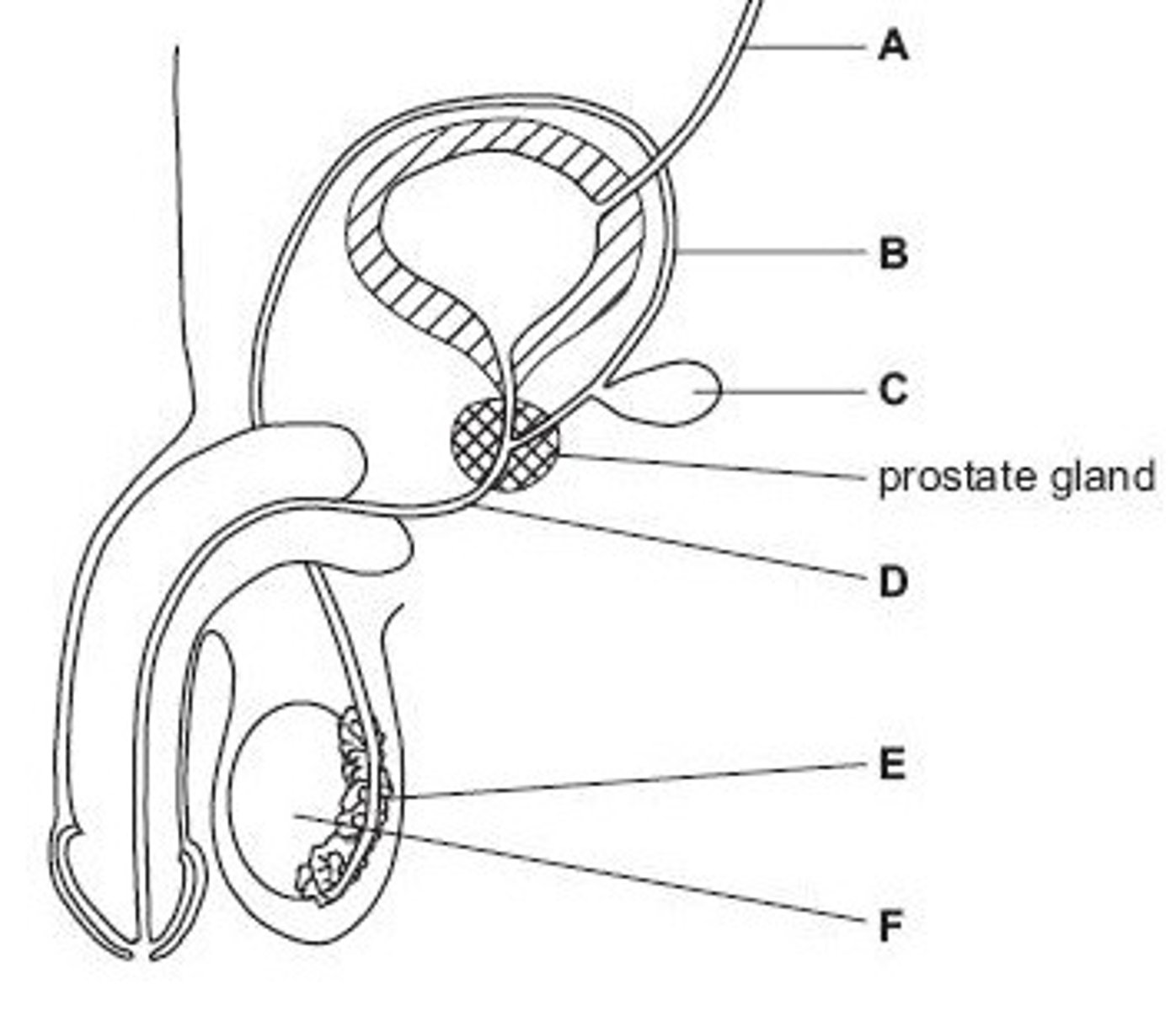
C
Give the letter of the structure which produces fluid for sperm to swim in
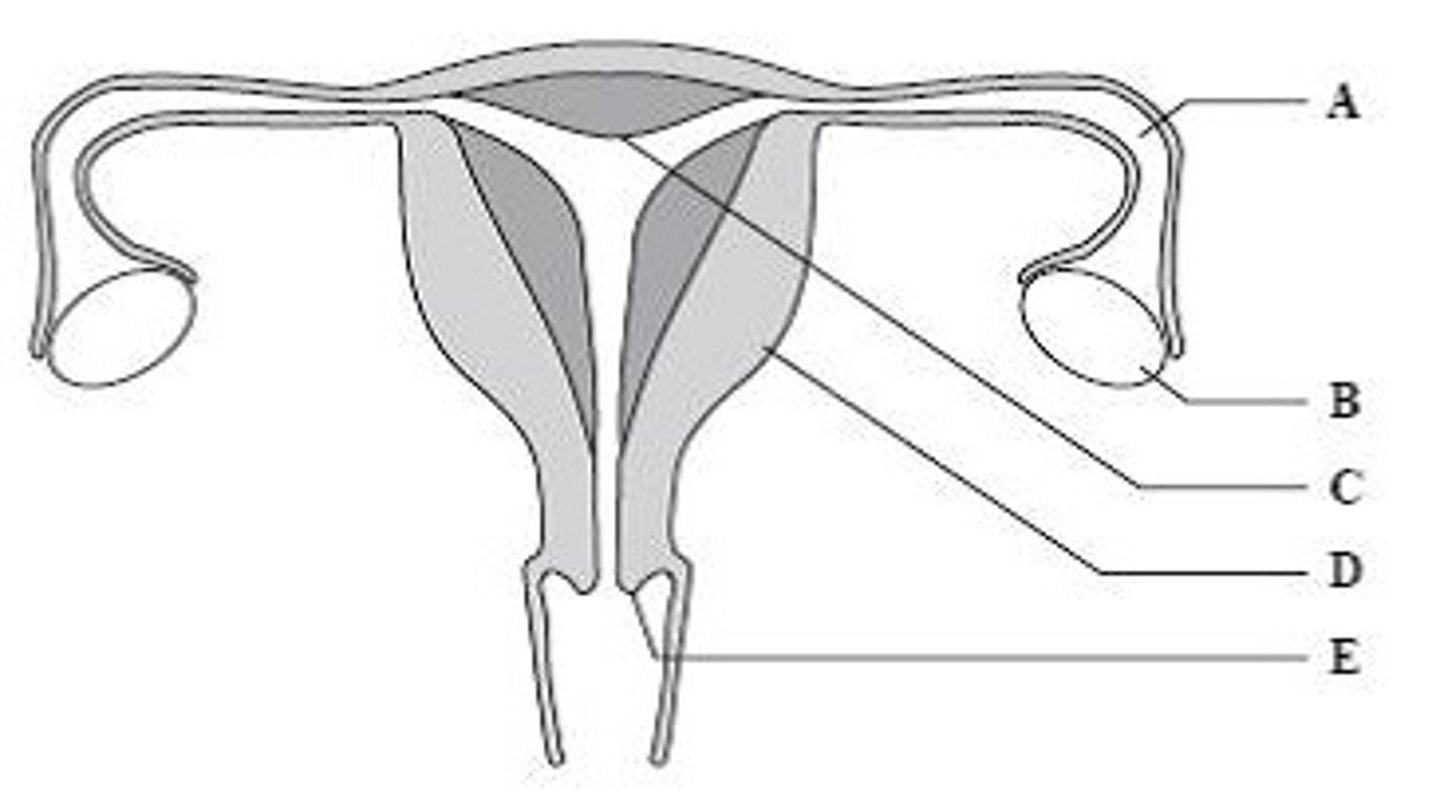
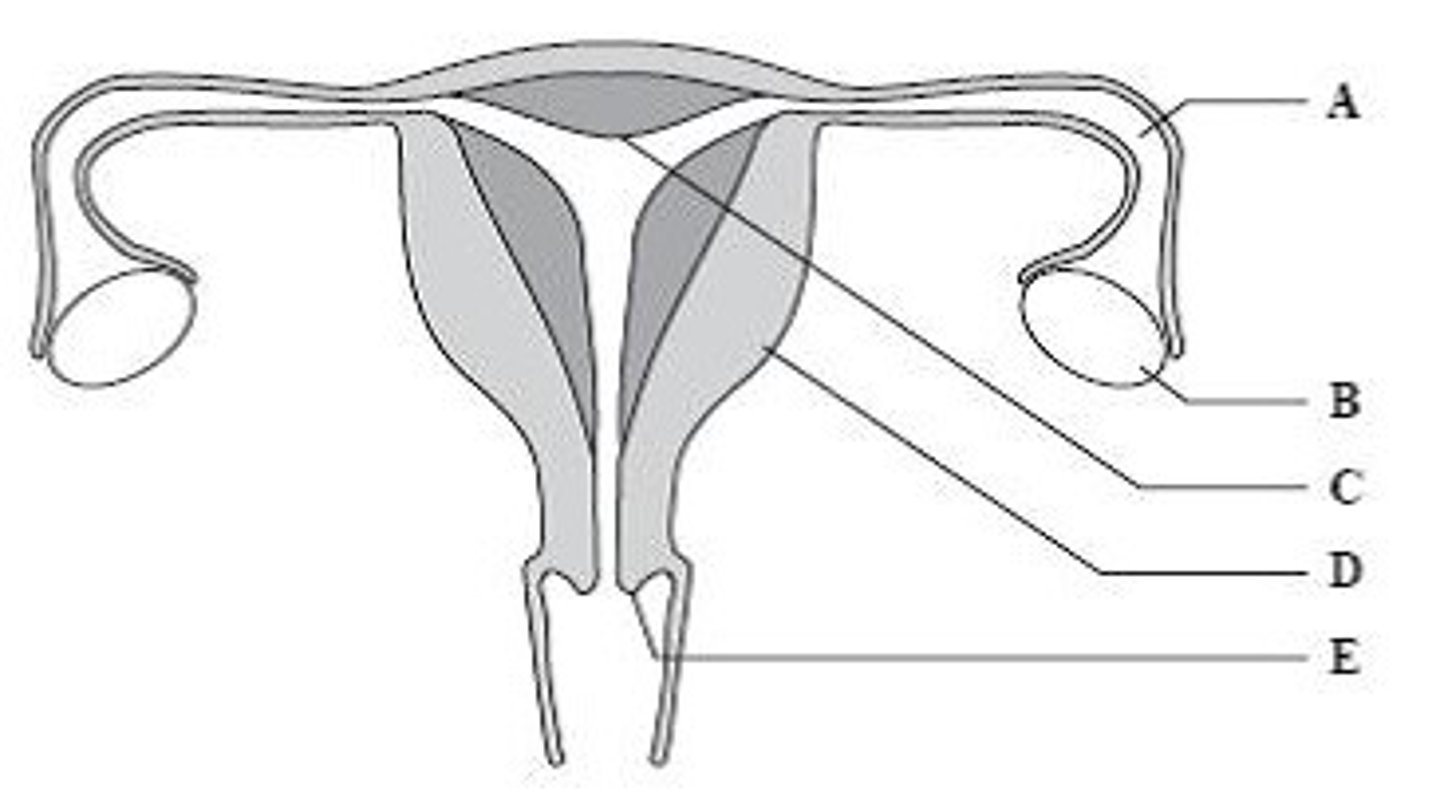
Fallopian tube
Name structure B
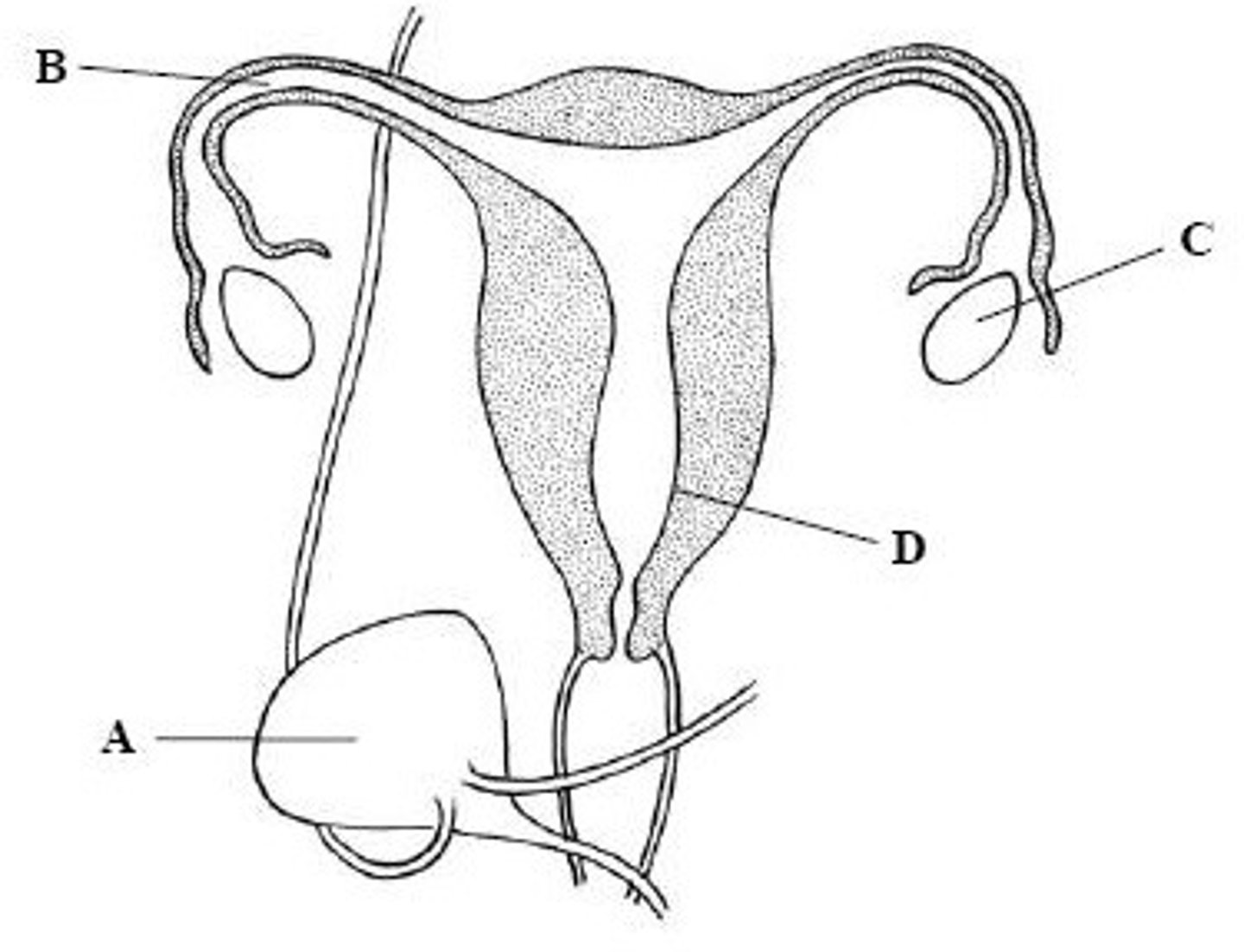
Ovary
Name structure C
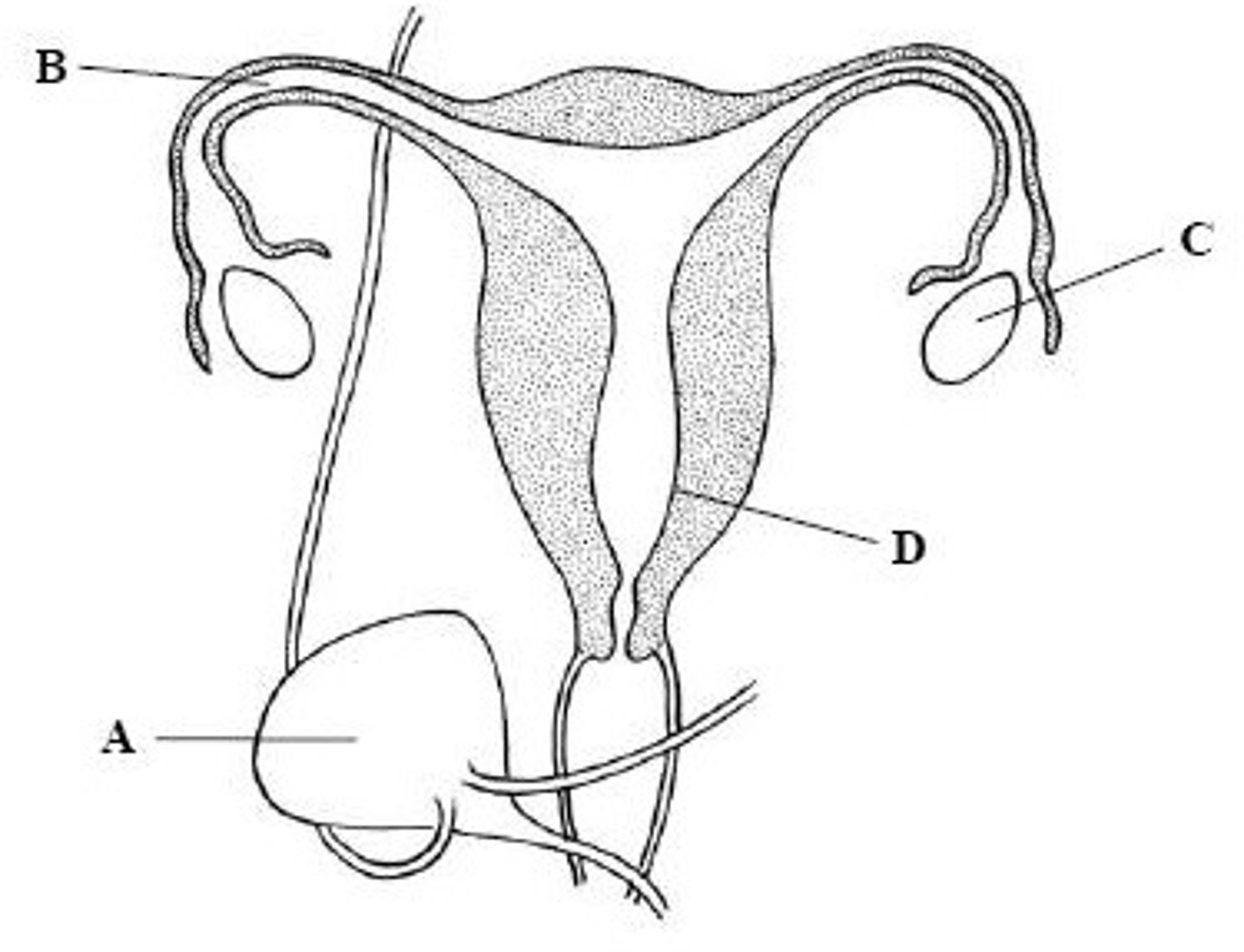
Uterus
Name structure D
Cervix
Name structure E
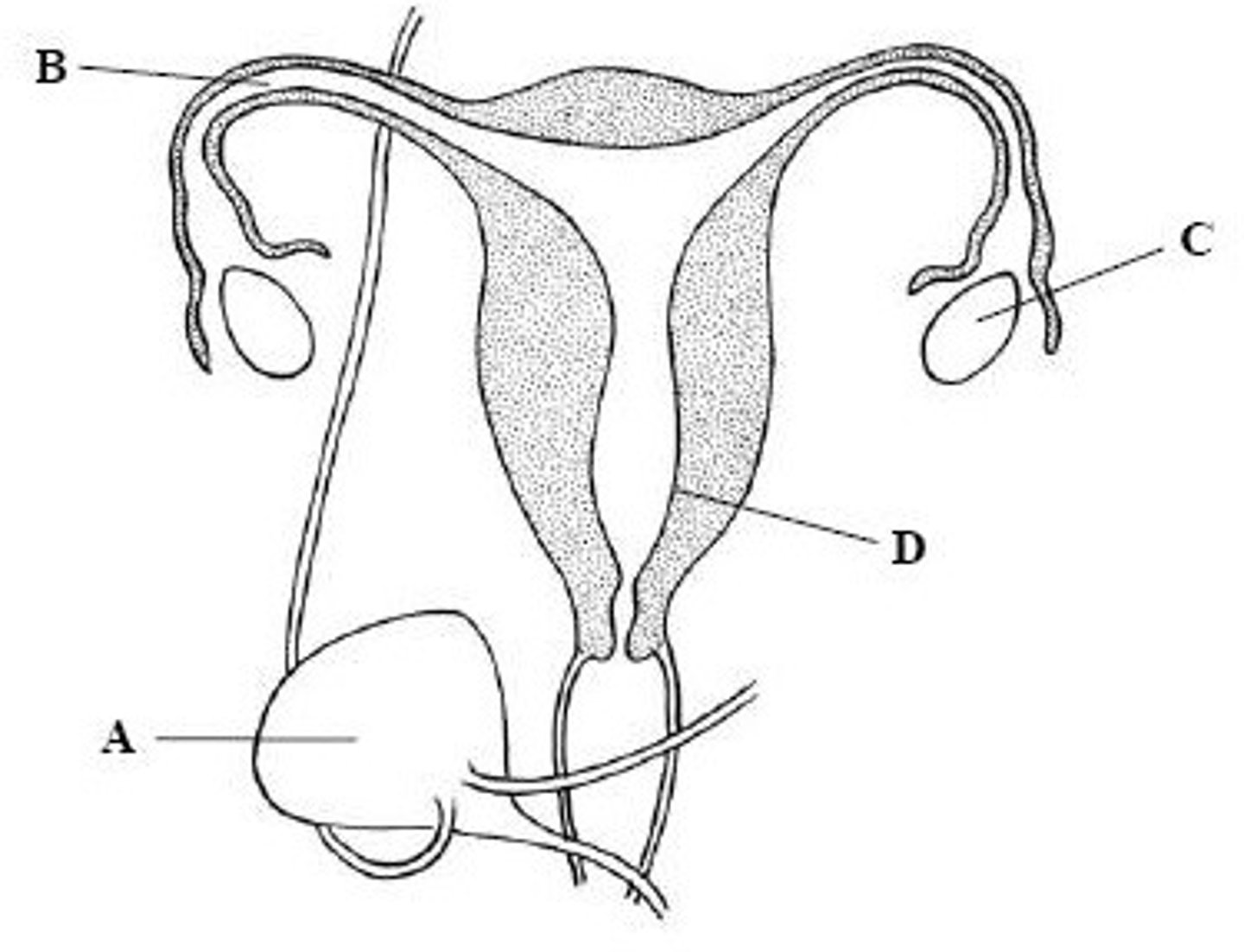
A
Give the letter which labels the structure where fertilization takes place.
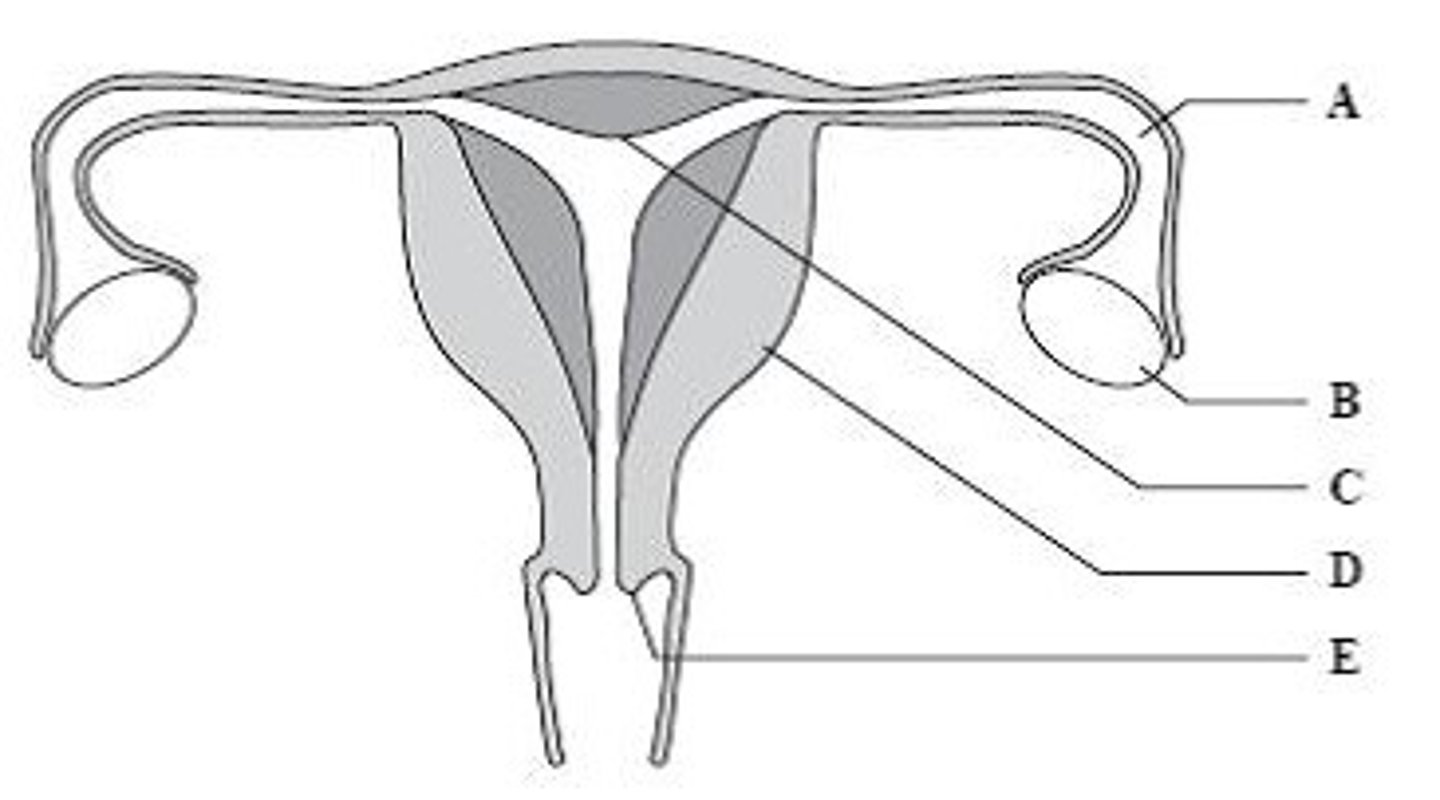
C
Give the letter which labels the structure where the placenta forms.
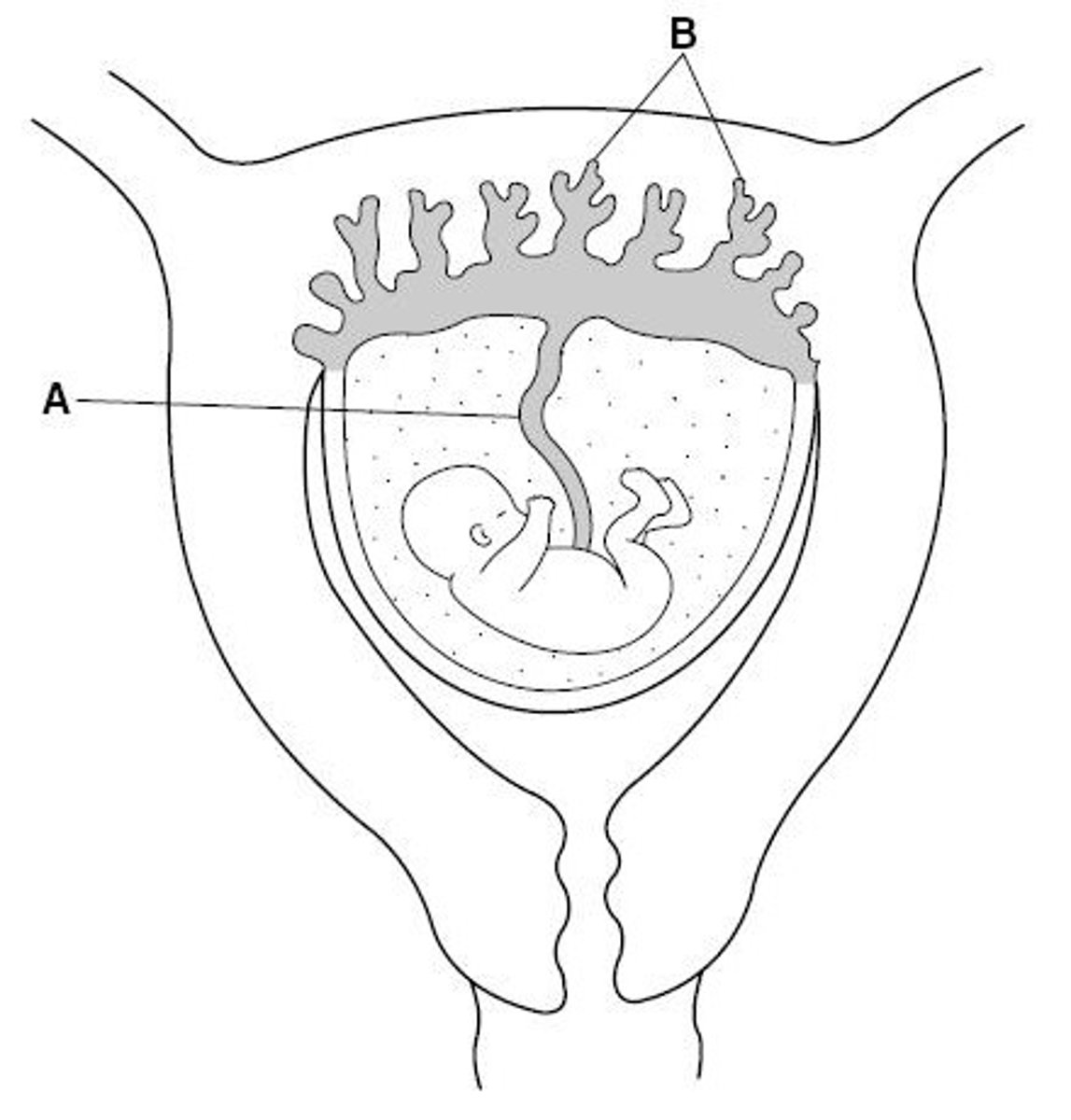
The umbilical cord
Name structure A
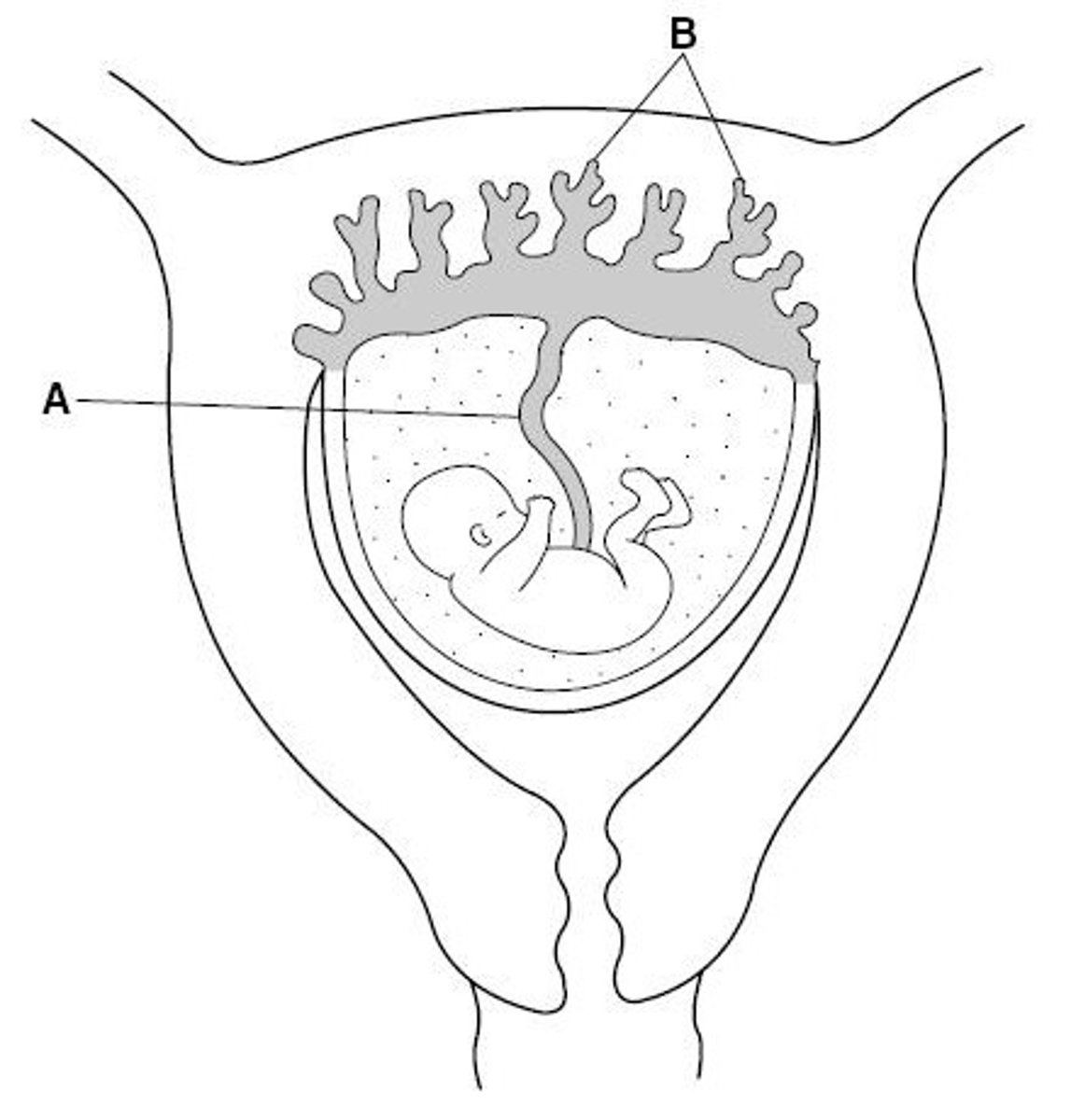
The placenta
Name structure B
Meiosis
Name the type of cell division which results in haploid games (sperm and eggs).
FSH
Pituitary gland→ Ovary
Stimulates an egg to mature inside a follicle in an ovary, triggers the ovaries to produce oestrogen.
LH
Pituitary gland→ Ovary
Triggers ovulation around day 14