Microbiology End of Rotation
1/1407
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1408 Terms
Proper media for culture of a urethral discharge from a man include:
A. sheep blood and phenylethyl alcohol agars
B. eosin-methylene blue and sheep blood agars
C. thioglycollate broth and chocolate agar
D. chocolate and modified Thayer-Martin agars
D. chocolate and modified thayer-martin agars
A sheep blood agar plate inoculate with 0.001 mL, of urine grows 70 colonies of Staphylococcus aureus. How many colony forming units per mL of urine should be reported?
A. 70
B. 700
C. 7,000
D. 70,000
D. 70,000
The lowest concentration of antibiotic that inhibit growth of a test organism is the:
A. minimum inhibitory concentration
B. serum inhibitory concentration
C. minimum bactericidal titer
D. maximum inhibitory titer
A. minimum inhibitory concentration
Which of the following clean catch urine culture colony counts indicates the patient likely has a urinary tract infection?
A. 10^1 CFU/mL
B. 10^3 CFU/mL
C. 10^5 CFU/mL
D. no growth
B. 10^3 CFU/mL
The steam autoclave method of sterilization:
A. uses 15 lbs of pressure for 15 minutes
B. utilizes dry heat for 20 minutes
C. produces a maximum temperature of 100C
D. requires a source of ethylene oxide
A. uses 15 lbs of pressure for 15 minutes
The expected colony count in a suprapubic urine from a healthy individual is:
A. 0 CFU/mL
B. 100 CFU/mL
C. 1,000 CFU/mL
D. 100,000 CFU/mL
A. 0 CFU/mL
An aspirate of a deep wound was plated on blood agar plates and incubated aerobically and anaerobically. At 24 hours there was growth on both plates. This indicates that the organism is a(n):
A. nonfermenter
B. obligate anaerobe
C. aerobe
D. facultative anaerobe
D. facultative anaerobe
The proper blood-to-broth ratio for blood cultures to reduce the antibacterial effect of serum in adults is:
A. 1:2
B. 1:3
C. 1:10
D. 1:30
C. 1:10
A penicillin-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae produces:
A. alpha-hemolysin
B. beta-lactamase
C. enterotoxin
D. coagulase
B. beta-lactamase
Which selective medium is used for the isolation of gram-positive microorganism?
A. Columbia CNA with 5% sheep blood
B. trypticase soy agar with 5% sheep blood
C. eosin methylene blue
D. modified Thayer-Martin
A. Columbia CNA with 5% sheep blood
The most sensitive substrate for the detection of beta-lactamases is:
A. penicillin
B. ampicillin
C. cefoxitin
D. nitrocefin
D. nitrocefin
A Staphylococcus aureus isolate has an MIC of 4 ug/mL to oxacillin. There is uncertainty as to whether this represents an oxacillin (heteroresistant) resistant strain or hyperproducer of beta-lactamase.
Strain; Oxacillin; Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid
-Strain A: sus;sus
-Strain B: sus; res
-Stain C: res; sus
-Strain D: res; res
Based on the above results for oxacillin and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, which strain is heteroresistant?
A. stain A
B. strain B
C. strain C
D. strain D
D. strain D
An Enterococcus isolated from multiple blood cultures in a patient endocarditis should be:
A. screened for high level aminoglycoside resistance
B. checked fo tolerance
C. assayed for serum antimicrobial activity
D. tested for beta-lactamase production
A. screened for high level aminoglycoside resistance
In the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion susceptibility test, which variable is critical when testing Pseudomonas species for antibiotic susceptibility to aminoglycosides?
A. incubation temperature
B. duration of incubation
C. cation content of media
D. depth of agar
C. cation content of media
The procedure that assures the most accurate detection of mecA-mediated oxacillin resistance in routine broth microdilution susceptibility testing against S. aureus is:
A. addition of 4% NaCl
B. incubation at 30 C
C. incubation for 48 hours
D. use of cefoxitin for testing
D. use of cefoxitin for testing
When performing a stool culture, a colony type typical of an enteric pathogen is subcultured on a blood agar plate. The resulting pure culture is screened with several tests to obtain the following results:
-TSI: acid butt, alkaline slant, no gas, no H2S
-phenylalanine deaminase: negative
-motility: positive
-serological typing: Shigella flexneri (shigella subgroup B)
The serological typing is verified with new kit and controls. The best course of action would be to:
A. report the organism as Shigella flexneri without further testing
B. verify reactivity of motility medium with positive and negative controls
C. verify reactivity of the TSI slants with positive and negative controls for H2S production
D. verify reactivity of phenylalanine deaminase with positive and negative controls
B. verify reactivity of motility medium with positive and negative controls
Susceptibility testing performed on quality control organism using a new media lot number yielded zone sizes that were too large for all antibiotics tested. The testing was repeated using media from a previously used lot number, and all zone sizes were acceptable. Which of the following best explains the unacceptable zone sizes?
A. the antibiotic disks were not stored with the proper desiccant
B. the depth of the media was too thick
C. the depth of the media was too thin
D. the antibiotic disks were not properly applied to the media
C. the depth of the media was too thin
Three sets of blood cultures were obtained form an adult patient with fever and suspected endocariditis. The aerobic bottle of one set had growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis at 5 days of incubation. this indicates that:
A. there was low-grade bacteremia
B. the organism is most likely a contaminant
C. the patient has a line infection
D. the blood culture bottles are defective
B. the organism is most likely a contaminant
In order to isolate Camplobacter coli/jejuni, the fecal specimen should be:
A. inoculated onto selective plating media and incubated in reduced oxygen with added CO2 at 42C
B. stored in tryptic soy broth before plating to ensure growth of the organism
C. inoculated onto selective plating media incubated at both 35C and at room temperature
D. incubated at 35C for 2 hours in Cary-Blair media before inoculating onto selective plating media
A. inoculated onto selective plating media and incubated in reduced oxygen with added CO2 at 42C
An expectorated sputum is sent to the laboratory for culture from a patient with respiratory distress. The Gram stain of the specimen shows many squamous epithelial cells (>25/lpf) and rare neutrophils. The microscopic appearance of the organisms present include:
-moderate gram-positive cocci in chains and diplococci
-moderate gram-negative diplococci
-moderate palisading gram-positive bacilli all in moderate amounts
This Gram stain is most indicative of:
A. a pneumococcal pneumonia
B. an anaerobic infection
C. an Haemophilus pneumonia
D. oropharyngeal flora
D. oropharyngeal flora
Which type of microscope would be most useful in examining viruses and the structure of microbial cells?
A. electron
B. phase-contrast
C. dark-field
D. bright-field
A. electron
After satisfactory performance of daily disk diffusion susceptibility quality control is documented, the frequency of quality control can be reduced to:
A. twice a week
B. every week
C. every other week
D. every month
B. every week
In disk diffusion susceptibility testing, as an antimicrocial agent diffuses away from the disk, the concentration of antibiotic is:
A. increased
B. decreased
C. unchanged
D. inoculum dependent
B. decreased
The most common cause for failure of GasPak anaerobic jar to establish an adequate environment for anaerobic incubation is:
A. the failure of the oxidation-reduction potential indicator system due to deterioration of methylene blue
B. the failure of the packet to generate adequate H2 and/or CO2
C. condensation of water on the inner surface of the jar
D. catalysts that have become inactivated after repeated use
D. catalysts that have become inactivated after repeated use
Which of the following is the most appropriate method for collecting a urine specimen from a patient with an indwelling catheter?
A. remove the catheter, cut the tip, and submit it for culture
B. disconnect the catheter from the bag, and collect urine form the terminal end of the catheter
C. collect urine directly from the bag
D. aspirate urine aseptically from the catheter tubing
D. aspirate urine aseptically from the catheter tubing
Which one of the following specimen requests is acceptable?
A. feces submitted for anaerobic culture
B. Foley catheter tip submitted for aerobic culture
C. rectal swab submitted for direct smear for gonococci
D. urine for culture of acid-fast bacilli
D. urine for culture of acid-fast bacilli
Which of the following groups of specimens would be acceptable for anaerobic culture?
A. vaginal, eye
B. ear, leg tissue
C. pleural fluid, brain abscess
D. urine, sputum
C. pleural fluid, brain abscess
A liquid fecal specimen form a 3-month-old infant is submitted for microbiological examination. In addition to culture on routine media for Salmonella and Shigella, this specimen should routinely,
A. examined for the presence of Entamoeba hartmanni
B. examined for the presence of Camplybacter sp
C. screened for the detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
D. placed in thioglycollate broth to detect Clostridium botulinum
B. examined for the presence of Camplybacter sp
Cerebrospinal fluid from a febrile 25-year-old man with possible meningitis is rushed to the laboratory for a stat Gram stain and culture. While performing the Gram stain, the technologist accidentally spills most of the specimen. The smear shows many neutrophils and no microorganism. Since there is only enough CSF to inoculate one plate, the technologist should use a:
A. blood agar plate
B. chopped meat glucose
C. chocolate agar plate
D. Thayer-Martin plate
C. chocolate agar plate
A diabetic foot swab from a 82-year-old woman with recurrent infections is submitted for culture. The Gram stain reveals:
-many neutrophils, no squamous epithelial cells
-many gram-negative bacilli
-many gram-positive cocci in chains
The physician requests that all pathogens be worked up. In addition to the sheep blood and MacConkey agar plates routinely used for wound cultures, the technologist might also process a(n):
A. CNA agar plate
B. chocolate agar plate
C. XLD agar plate
D. chopped meat glucose
A. CNA agar plate
Which of the following is the most appropriate specimen source and primary media battery?
A. endocervical-chocolate, Martin Lewis
B. sputum-sheep blod, Thayer-Martin, KV-laked blood
C. CSF-Columbia CNA, MacConkey
D. urine-sheep blood, chocolate, Columbia CNA
A. endocervical-chocolate, Martin Lewis
Which of the following is the most appropriate organism and media combination?
A. Legionella species-Regan Lowe
B. Clostridium difficile-phenylethyl alcohol (PEA)
C. Campylobacter species-charcoal yeast extract
D. Yersinia entorocolitica-cefsulodin-irgasan-novobiocin (CIN)
D. Yersinia entorocolitica-cefsulodin-irgasan-novobiocin (CIN)
A Gram stain from a swab of a hand wound reveals:
-moderate neutrophils
-no squamous epithelial cells
-moderate gram-positive cocci in chains
-moderate large gram-negative bacilli
Select the appropriate media that will selectively isolate each organism.
A. KV-laked agar, Thayer-Martin
B. sheep blood, MacConkey
C. Columbia CNA, chocolate
D. Columbia CNA, MacConkey
D. Columbia CNA, MacConkey
Upon review of a sputum Gram stain, the technician notes that the nuclei of all of the neutrophils present in the smear are staining dark blue. The best explanation for this finding is:
A. the slide was inadequately decolorized with acetone/alcohol
B. the sputum smear was prepared too thin
C. the cellular components have stained as expected
D. the iodine was omitted from the staining procedure
A. the slide was inadequately decolorized with acetone/alcohol
When performing a Kovac indole test, the substrate must contain:
A. indole
B. tryptophan
C. ornithine
D. paradimethylaminobenzaldehyde
B. tryptophan
The ONPG test allows organisms to be classified as a lactose fermenter by testing for which of the following?
A. permease
B. beta-galactosidase
C. beta-lactamase
D. phosphatase
B. beta-galactosidase
Sodium bicarbonate and sodium citrate are components of which of the following?
A. JEMBEC system
B. MTM agar
C. NYC medium
D. ML agar
A. JEMBEC system
Chocolate agar base containing vancomycin, colistin, anisomycin, and trimethoprim is also known as:
A. EMB agar
B. modified Thayer-Martin agar
C. Columbia CNA agar
D. Martin Lewis agar
D. Martin Lewis agar
A medium that aids in the presumptive identification of organism based on their appearance on the medium is called:
A. enriched
B. selective
C. differential
D. specialized
C. differential
SPS is used as an anticoagulant for blood cultures because it:
A. inactivates penicillin and cephalosporins
B. prevents clumping of red cells
C. inactivates neutrophils and components of serum complement
D. facilitates growth of anaerobes
C. inactivates neutrophils and components of serum complement
When evaluating a new susceptibility testing system, if the new system characterizes a susceptible isolate as resistant, this is termed a:
A. very major error
B. major error
C. minor error
D. acceptable error
B. major error
Which of the following methods is inadequate for the detection of vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus?
A. broth macrodilution
B. agar dilution
C. gradient diffusion
D. disk diffusion
D. disk diffusion
In a disk diffusion susceptibility test, which of the following can result if disks are placed on the inoculated media and left at room temperature for an hour before incubation?
A. the antibiotic would not diffuse into the medium, resulting in no zones
B. zones of smaller diameter would result
C. zones of larger diameter would result
D. there would be no effect on the final zone diameter
C. zones of larger diameter would result
Which of the following factors would make an organism appear to be more resistant on a disk diffusion susceptibility test?
A. too little agar in the plate
B. too many organism in the inoculum
C. the presence of 0.5% NaCl in the medium
D. a medium with a pH of 7.4
B. too many organism in the inoculum
First-generation cephalosporins can be adequately represented by:
A. cefotetan
B. ceftriaxone
C. cephalothin
D. cefoxitin
C. cephalothin
An antibiotic that inhibits cell wall synthesis is:
A. chloramphenicol
B. penicillin
C. sulfamethoxazole
D. colistin
B. penicillin
Which one of the following organisms does not require susceptibility testing to the antimicrobial indicated when isolated form a clinically significant source?
A. Staphylocoous aureus-clindamycin
B. Proteus mirabilis-gentamicin
C. Streptococcus pyogenes-penicillin
D. Escherichia coli-levofloxacin
C. streptococcous pyogenes-penicillin
Which of the following antibiotics would routinely be tested and reported for isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
A. penicillin
B. erythromycin
C. clindamycin
D. gentamicin
D. gentamicin
Which of the following must be incubated in a microaerophilic environment for optimal recovery of the organism?
A. Campylobacter jejuni
B. Escherichia coli
C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D. Proteus mirabilis
A. Campylobacter jejuni
Diagnosis of typhoid fever can be confirmed best by culture of:
A. stool
B. urine
C. blood
D. bone marrow
D. bone marrow
Vibrio parahaemolyticus can be isolated best from feces on:
A. eosin methylene blue (EMB) agar
B. Hektoen enteric (HE) agar
C. Salmonella Shigella (SS) agar
D. thiosulfate citrate bile salts (TCBS) agar
D. thiosulfate citrate bile salts (TCBS) agar
Which of the following media can be used to culture Campylobacter jejuni?
A. Skirrow medium
B. CIN agar
C. anaerobic CNA agar
D. bismuth sulfite
A. Skirrow medium
Test for beta-lactamase production in Haemophilus influenzae:
A. are not commercially available
B. include test that measure a change to an alkaline pH
C. should be performed on all blood and CSF isolates
D. are not valid for any other bacterial species
C. should not be perfomred on all blood and CSF isolates
Media used to support growth of Legionella pneumophila should contain which of the following additives?
A. X and V factors
B. hemin and Vitamin K
C. charcoal and yeast extract
D. dextrose and laked blood
C. charcoal and yeast extract
The best medium for culture of Bordetella pertussis is:
A. Regan-Lowe agar
B. cystine blood agar
C. Martin Lewis agar
D. Ashdown agar
A. Regan-Lowe agar
The best medium for culture of Francisella tularensis is:
A. Bordet-Gengou medium
B. cystine glucose blood agar
C. Loeffler medium
D. charcoal selective medium
B. cystine glucose blood agar
The most rapid method for detection of Francisella tularensis is:
A. serological slide agglutination utilizing specific antiserum
B. dye stained clinical specimens
C. fluorescent antibody stain techniques on clinical specimens
D. polymerase chain reaction
D. polymerase chain reaction
When processing throat swabs for a group A Streptococcus culture, the medium of choice is:
A. sheep blood agar
B. rabbit blood agar
C. human blood agar
D. horse blood agar
A. sheep blood agar
The ability to detect oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus may be enhanced by:
A. shortening incubation of standard susceptibility plates
B. incubating susceptibility plates at 39-41 C
C. using Mueller-Hinton broth with 2% NaCl
D. adjusting inoculum to 0.1 McFarland before inoculating susceptibility plates
C. using Mueller-Hinton broth with 2% NaCl
The optimal wound specimen for culture of anaerobic organisms should be:
A. a swab of lesion obtained before administration of antibiotics
B. a swab of lesion obtained after administration of antibiotics
C. a syringe filled with pus, obtained before administration of antibiotics
D. a syringe filled with pus, obtained after administration of antibiotics
C. a syringe filled with pus, obtained before administration of antibiotics
A 21-year-old patient presents with pharyngitis. A throat swab is collected and submitted for anaerobic culture. This specimen should be:
A. set up immediately
B. rejected as unacceptable
C. inoculated into thioglycollate broth
D. sent to a reference laboratory
B. rejected as unacceptable
Anaerobic susceptibility testing is helpful in the management of patients with:
A. synovial infections
B. rectal abscesses
C. streptococcal pharyngitis
D. pilonidal sinuses
A. synovial infections
An antibiotic used to suppress or kill contaiminating fungi in media is:
A. penicillin
B. cycloheximide
C. streptomycin
D. amphotericin B
B. cycloheximide
Production of beta-lactamase is inducible in which of the following:
A. Haemophilus influenzae
B. Staphylococcus aureus
C. Corynebacterium diphtheriae
D. Streptococcus pyogenes
B. Staphylococcus aureus
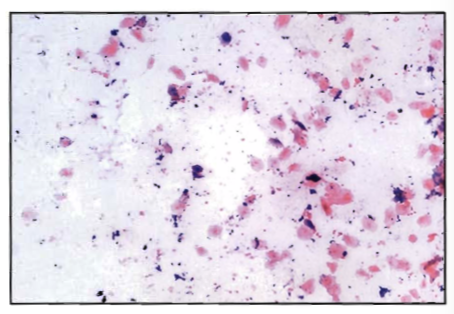
A sputum specimen is recieved for culture and Gram stain. The Gram stained smear from this specimen is seen in the image (total magnification 100X):
See BOC pg 288
The technologist's best course of action would be to:
A. inoculate appropriate media and incubate anaerobically
B. inoculate appropriate media and incubate aerobically
C. call the physician and notify him of this "life-threatening" situation
D. call the patient care area and request a new specimen
D. call the patient care area and request a new specimen
A technologist is reading a Gram stain from a CSF and observes many neutrophils and lancet-shaped gram-positive diplococci. Which set of chemistry and hematology CSF results would most likely be seen in someone with this type of infection?
CSF results: WBC; Glucose; Protein
-A: inc, inc, inc
-B: dec, dec, dec
-C: inc, dec, inc
-D: dec, inc, dec
A. result A
B. result B
C. result C
D. result D
C. result C: inc, dec, inc
Refer to the following illustration:
See BOC pg 289
Examine the broth microdilution susceptibility test shown above and determine the MIC for gentamicin.
A. >64 ug/mL
B. 32 ug/mL
C. 16 ug/mL
D. < 2 ug/mL
D. < 2 ug/mL
Which of the following test is used to monitor bactericidal activity during antimicrobic therapy in cases of endocarditis?
A. Elek
B. tolerance
C. Sherris synergis
D. Schlichter
D. Schlichter
Quality control results for disk diffusion susceptibility tests yield the following results: aminoglycoside zones too small and penicillin zones too large. This is most likely due to the:
A. inoculum being too heavy
B. inoculum being too light
C. pH of Mueller-Hinton agar being too low
D. calcium and magnesium concentration in the agar being too high
C. pH of Mueller-Hinton agar being too low
When using a control stain of Staphylococcus aureus, the technologist notices that the zone around the oxacillin disk is too small. Which of the following is the most likely explanation?
A. inoculation of the plates 10 minutes after preparing th inoculum
B. incubation of the Mueller-Hinton plates at 35C
C. use of a 0.25 McFarland standard to prepare inoculum
D. use of outdate oxacillin disks
D. use of outdate oxacillin disks
In the disk diffusion method of determining antibiotic susceptibility, the size of the inhibition zone used to indicate susceptibility has been determined by:
A. testing 30 stains of 1 genus of bacteria
B. correlating the zone size with minimum inhibitory concentrations
C. correlating the zone with minimum bactericidal concentrations
D. correlating the zone with the antibiotic content of the disk
B. correlating the zone size with minimum inhibitory concentrations
Which of the following organisms may be mistaken for Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Gram stained smears of uterine cervix exudates?
A. Lactobacillus species
B. Streptococcus agalactiae
C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D. Moraxella osloensis
D. Moraxella osloensis
A 73-year-old man diagnosed as having pneumococcal meningitis is not responding to his penicillin therapy. Which of the following tests should be performed on the isolate to best determine this organism's susceptibility to penicillin?
A. beta-lactamse
B. oxacillin disk diffusion
C. penicillin disk diffusion
D. Schlichter test
B. oxacillin disk diffusion
Salmonella enteritidis is isolated form multiple blood cultures in a patient with fever. Susceptibility results are as follows:
-ampicllin-susceptible
-ceftriaxone-susceptible
-ciprofloxacin-susceptible
-trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole-resistant
What is the next best step?
A. report all of the susceptibility testing results with no changes
B. perform a beta-lactamase test on the isolate before reporting the ampicillin as susceptible
C. test the isolate against nalidixic acid and if resistant report the ciprofloxacin as resistant
D. report gentamicin since the trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is resistant
C. test the isolate against nalidixic acid and if resistant report the ciprofloxacin as resistant
Which of the following antimicrobial would be inappropriate to report on an E. coli isolated form a would culture?
A. gentamicin
B. ampicillin
C. cefazolin
D. nitrofurantoin
D. nitrofurantoin
The susceptibility results below are reported on an Enterococcus faecalis isolated form peritoneal fluid.
-ampicillin: susceptible
-vancomycin: resistant
-clindamycin: susceptible
-levofloxacin: resistant
-linezolid: susceptible
The physician calls questioning the results. Which of the following should have been done before the report was released?
A. the clindamycin result should have been removed form the report since it is inactive against Enterococcus
B. the ampicillin result should have been changed to resistant since the isolate is vamcomycin resistant
C. the linezolid result should have been removed form the report since it is inactive against Enterococcus
D. ciprofloxacin should have been added to the report since levofloxacin was resistant
A. the clindamycin result should have been removed form the report since it is inactive against Enterococcus
A D test is performed on an isolate of Staphylococcus aureus to determine inducible clindamycin resistance:
See BOC pg 291
Based on the result seen in the image how should the erythromycin and clindamycin be reported?
A. erythromycin: resistant; clindamycin resistant
B. erythromycin: resistant; clindamycin susceptible
C. erythromycin: susceptible; clindamycin: resistant
D. erythromycin: susceptible; clindamycin; susceptible
B. erythromycin: resistant; clindamycin susceptible
Which of the following combinations is useful for confirming the presence of extended spectrum beta-lactamases in E. coli?
A. ampicillin + cefepime
B. cefoxitin + penicillin
C. ceftazidime + clavulanic acid
D. cefpodoxime + cefotaxime
C. ceftazidime + clavulanic acid
Enzymatic drug modification is a mechanism of resistance for which antimicrobial?
A. levofloxacin
B. sulfamethoxazole
C. vancomycin
D. gentamicin
D. gentamicin
Which of the following is the most important variable in the recovery of organisms in patients with bacteremia?
A. subculture of all bottles at day 5 incubation
B. the volume of blood cultured
C. use of chlorhexadine for skin antisepsis
D. collection of multiple blood culture sets from a single venipuncture
B. the volume of blood cultured
A 24-year-old man presents with pain on urination and urethral discharge. A Gram stain of the discharge is seen in the image:
See BOC pg 292 Pic 1
What is the most likely identification of this organism?
A. Acinetobacter baumanni
B. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
C. Haemophilus ducreyi
D. Escherichia coli
B. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
A 10-year-old child with systic fibrosis presents with cough and shortness of breath. Her sputum Gram stain is seen in the image:
See BOC pg 292 Pic 2
Based on the Gram stain what would be the best medium and incubation condition to optimize recovery of the organism seen?
A. MacConkey agar incubated in CO2
B. Tinsdale agar incubated in ambient air
C. chocolate agar incubated in CO2
D. CNA agar incubated in ambient air
C. chocolate agar incubated in CO2
The image depicts a Gram stain (final magnification 1,000X) of a knee fluid from a patient who has recently undergone knee replacement surgery:
See BOC pg 293
The best interpretation of this Gram stain is:
A. gram-positive cocci suggestive of Staphylococcus
B. gram-positive bacilli suggestive of Corynebacterium
C. gram-positive bacilli suggestive of Listeria
D. gram-positive cocci suggestive of Streptococcus
D. gram-positive cocci suggestive of Streptococcus
A vaginal/rectal swab is collected form a pregnant patient to screen for group B Streptococcus colonization. What is the best medium to use for specimen inoculation?
A. blood agar
B. LIM broth
C. CNA agar
D. thioglycollate broth
B. LIM broth
A pregnant patient is creened at 36 weeks gestation for group B streptococcus (GBS). A vaginal swab is collected and cultured in Todd-Hewitt broth with 8 ug gentamicin/mL and 15 ug nalidixic acid/mL. The broth is subcultured onto sheep blood agar after 24 hours of incubation. No GBS are seen on the subculture and the results are reported as negative. The patient later goes on to deliver an infant with early onset GBS disease. What is the most likely reason for the negative GBS culture?
A. the patient was screened to early since screening after 38 weeks is recommended
B. a vaginal swab was collect instead of a vaginal/rectal swab
C. the Todd-Hewitt broth used was inhibitory to the organism
D. the selective broth was incubated only 24 hours before subculture
B. a vaginal swab was collect instead of a vaginal/rectal swab
Susceptibility testing is performed on a Staphylococcus aureus isolate form a blood culture with the following results:
-oxacillin: resistant
-cefazolin: susceptible
-clindamycin: susceptible
-erythromycin: susceptible
-trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole: susceptible
-vancomycin: susceptible
What should the technologist do next?
A. ceftriaxone should be reported instead of cefazolin
B. clindamycin should be tested for inducible resistance prior to reporting
C. the trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole result should be removed since all S aureus are resistant
D. the cefazolin result should be changed to resistant since the oxacillin result is resistant
D. the cefazolin result should be changed to resistant since the oxacillin result is resistant
To quality control the autoclave, a vial of Bacillus stearothermophilus is autoclaved and should then be:
A. inoculated to blood agar
B. incubated at 37C
C. inoculated to chocolate agar
D. incubated at 56C
D. incubated at 56C
In a quality control procedure on a new batch of Mueller-Hinton plates using a stock culture of Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923), all the disk zones sizes are too small. The most likely reason for this is that the:
A. Mueller-Hinton plates were poured too thin
B. potency of the antibiotic disks is too high
C. bacterial suspension was not diluted to the proper concentration
D. disks should have been set up on mannitol salt
C. bacterial suspension was not diluted to the proper concentration
Which one of the following combinations of organisms would be appropriate as controls to test the functions listed?
A. beta-hemolysis-negative Escherichia coli and Streptococcus pyogenes
B. catalase negative Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis
C. H2S production-negative Proteus mirabilis and Staphylococcus epidermidis
D. indole-negative Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis
D. indole-negative Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis
A urine Gram stain shows gram-positive cocci in clusters. The organism tested catalase positive. To speciate this organism from culture, the technician should perform a coagulase test and a/an:
A. polymyxin B susceptibility
B. novobiocin susceptibility
C. oxidase
D. beta-lactamase
B. novobiocin susceptibility
The Gram stain from a blood culture shows gram-positive cocci in chains. No growth occurs on blood agar plates incubated both aerobically an anaerobically. Additional testing should be done to detect the presence of:
A. Staphylococcus saprophyticus
B. Aerococcus urinae
C. Abiotrophia defectiva
D. Streptococcus pneumoniae
C. Abiotrophia defectiva
Viridans streptococci can be differentiated from Streptococcus pneumoniae by:
A. alpha hemolysis
B. morphology
C. catalase reaction
D. bile solubility
D. bile solubility
A reliable test for distinguishing Staphylococcus aureus form other staphylococci is:
A. oxidase
B. coagulase
C. catalase
D. optochin susceptibility
B. coagulase
The optochin (ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) disk is used for the identification of:
A. Haemophilus influenzae
B. group A beta-hemolytic streptococcci
C. Streptococcus pneumoniae
D. alpha-hemolytic streptococci
C. Streptococcus pneumoniae
In the optochin (ethylhydorocupreine hydrochloride) susceptibility test, if there is a zone of inhibition of 19-30 mm surrounding the disk following overnight incubation at 37C, the colony most likely consists of:
A. staphylococci
B. streptococci
C. pneumococci
D. intestinal bacilli
C. pneumococci
Which 2 diseases are usually preceded by infection with beta-hemolytic streptococci?
A. rheumatic fever, undulant fever
B. glomerulonephritis, rheumatic fever
C. rheumatic fever, tularemia
D. glomerulonephritis, undulant fever
B. glomerulonephritis, rheumatic fever
The enterotoxin produced by certain stains of hemolytic, coagulase positive Staphylococcus aureus:
A. is destroyed by boiling for 15-30 minutes
B. is identical to the dermonecrotic toxin
C. causes one type of bacterial food poisoning
D. is highly antigenic
C. causes one type of bacterial food poisoning
A gamma-hemolytic Streptococcus that blackens bile esculin agar but does not grow in 6.5% NaCl broth is most likely:
A. group B Streptococcus
B. Enterococcus
C. group D streptococcus
D. Streptococcus pneumoniae
C. group D streptococcus
Gram Stain examination form a blood culture bottle shows dark blue, spherical organism in cluster. Growth on sheep blood agar shows small, round, pale yellow colonies. Further tests should include:
A. catalase production and coagulase test
B. bacitracin susceptibility and serological typing
C. oxidase and deoxyribonuclease reactions
D. Voges-Proskauer and methyl red reactions
A. catalase production and coagulase test
Gram-positive cocci in chains are seen on a Gram stain from a blood culture. The organism grows as a beta-hemolytic colony. Further tests that could be performed include:
A. bile esculin, PYR, bacitracin, and hippurate
B. catalase and coagulase
C. oxidase and deoxyribonuclease
D. Voges-Proskauer and methyl red
A. bile esculin, PYR, bacitracin, and hippurate