Week 1 - From Transistors to Turing Machines
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
what is computer science?
playing computer games?
designing web pages?
using a spreadsheet?
writing software?
designing computers?
why study computer science?
one of the newest of the sciences
applications ot most human activity
understanding the world around you
the many hats of computer science
mathematician
engineer
artist
scientist
what is abstraction?
not ignoring “low level“
not saying “I dont’ have to care about…“
understanding the “right“ level of detail to focus on
ladder of abstraction
ladder of abstraction
solid-state physics
transistor circuits
logic design
system design
system software
application software
theory
core areas of computer science
algorithms and data structures
architecture
artificial intelligence and robotics
database and information retrieval
human-computer interaction
numerical and symbolic computation
operating systems
programming languages
software methodology and engineering
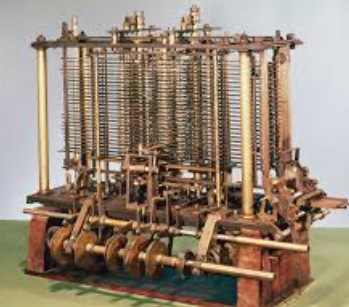
early computer history: charles babbage
Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at Cambridge
Difference Engine
Analytical Engine
difference engine
a mechincal calulator that was designed to automatically calculate and print polynomial functions and numerical tables.

analytical engine
a mechanical computer that performed mathematical calculations.
early computer history: konrad zuse
germany civil engineer
1930s and 40s
the world’s first functional program-controlled turing-commpleted computer, the Z3, in 1941
z1: first of zuse’s calculators, a mechincal binary calculator with limited programmability
z2: a follow-up to the z1, based on many of the same ideas
z3: the world’s first fully functional program-controlled electromechanical digital computer

other early computer history
vannevar bush: mechanical analog computer—differential analyzer
howard aiken: hardard mark I—electromechanical
j prepser eckert and john machly: ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC
the word computer
before 1930: a person who computes
after 1950: a machine that computes
what about software?
ada lovelace: THE notes
grace hopper:
wrote hardward mark I manual
developed early compiler technology
major influence in COBOL
the ENIAC “Six“:
jean jennings bartik, kay mcnulty machly, betty snyder holburton, fran bilas spence, marlyn wescoff meltzer, and ruth lichterman titlebaum
hired as human computers, then assigned to the ENIAC
developed techniques as we still use, like breakpoints
ENIAC
Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC)
the world’s first general-purpse electronic computer
a major breakthrough in computing technology
debugging
“I realized that a large part of my life from then on was going to be spent in finding mistakes in my own programs.” — Maurice Wilkes