Core Concepts: Carbohydrates
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:21 PM on 5/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
1
New cards
What are the **functions** of carbohydrates?
1. **Instant energy sources**
2. **Transportable/Storable energy sources**
3. **Structural Materials**
2
New cards
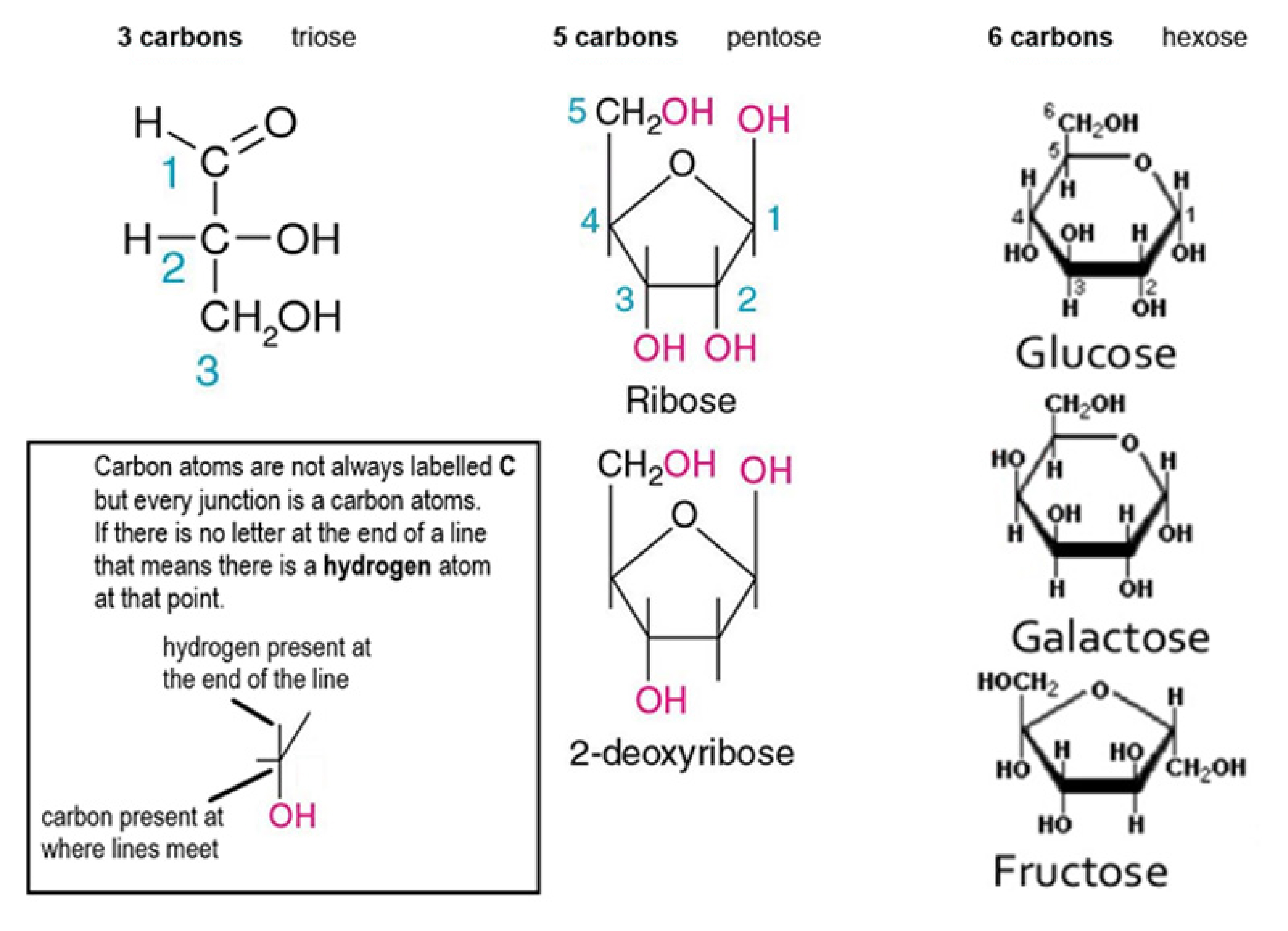
What is a **monosaccharide**?
**monomers** - single sugars named according to the number of carbon atoms in the molecule
3
New cards
What is the general formula for monosaccharides?
C(H²O)n
4
New cards
What is a triose sugar?
A **triose** is a monosaccharide containing three carbon atoms.
5
New cards
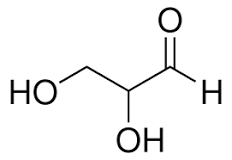
Give an example of a triose sugar
Glyceraldehyde
6
New cards
What is a pentose sugar?
A pentose is a monosaccharide with five carbon atoms.
7
New cards
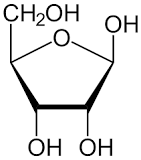
Give an example of a pentose sugar
Ribose (*found in RNA*)
8
New cards
What is a hexose sugar?
A hexose is a monosaccharide with six carbon atoms.
9
New cards
Give an example of a hexose sugar
Glucose
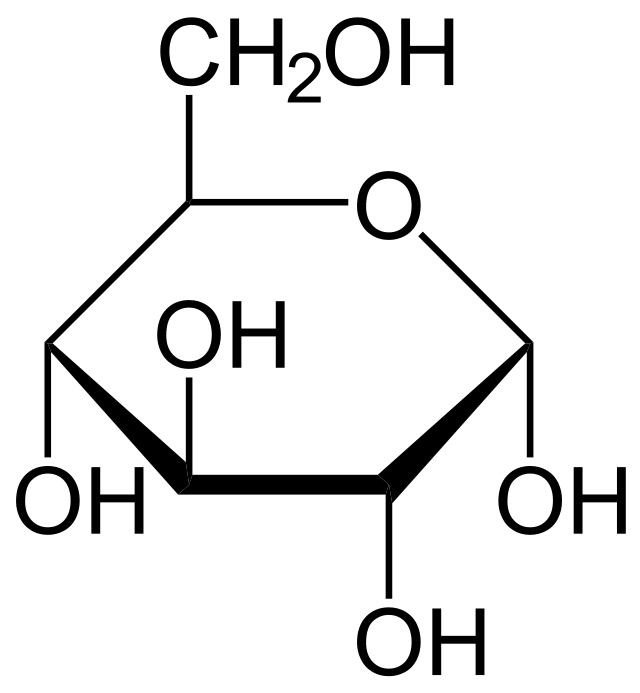
10
New cards
What are **isomers**?
Molecules with the **same molecular formula** but with **different arrangements** of their atoms are called **structural isomers**
11
New cards
Give an example of **2** types of isomer
* Alpha and Beta Isomers
* Ring and Straight Chain Isomers
* Ring and Straight Chain Isomers
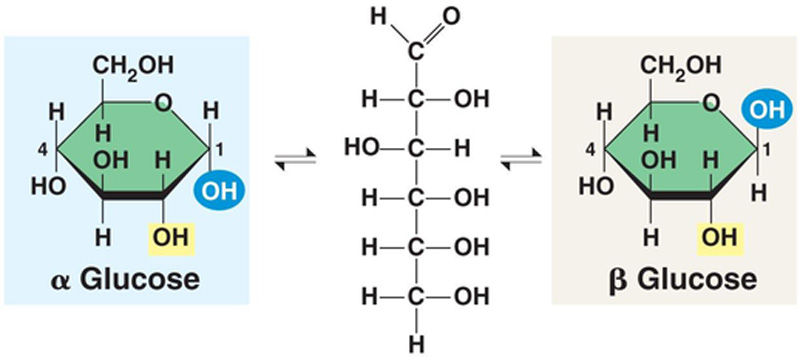
12
New cards
What does **ABBA** stand for?
*Alpha -* Below
*Beta -* Above
*Beta -* Above
13
New cards
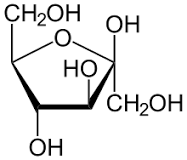
Which monosaccharide is this?
Fructose
14
New cards
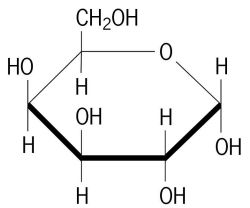
Which monosaccharide is this?
Galactose
15
New cards
Glucose is the **major**…?
**Respiratory substrate** which is broken down to make ATP
16
New cards
Where is alpha glucose found?
blood plasma
17
New cards
Where is beta glucose found?
In plants
18
New cards
Where is fructose found?
Fruits
19
New cards
Where is galactose found?
Milk
20
New cards
What happens in a **condensation** reaction?
* A water molecule is **removed**
* A new **covalent bond** is formed
* **Larger molecules** are formed
* A new **covalent bond** is formed
* **Larger molecules** are formed
21
New cards
What happens in a **hydrolysis** reaction?
* A water molecule is **added**
* A **covalent** bond is **broken**
* A **smaller** molecule is formed
* A **covalent** bond is **broken**
* A **smaller** molecule is formed
22
New cards
What is a **disaccharide?**
**2 monosaccharides** can join together through a **condensation reaction** to form a **disaccharide**
23
New cards
When a condensation reaction between 2 **alpha glucose** molecules occur, what is the product?
maltose
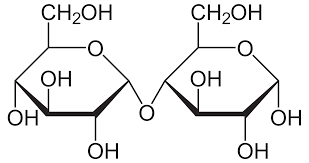
24
New cards
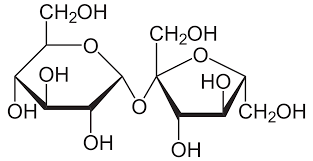
Which 2 monosaccharides join to form **sucrose**?
Glucose +Frutose
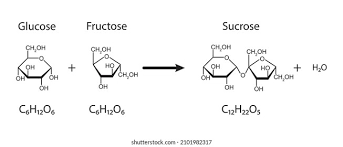
25
New cards
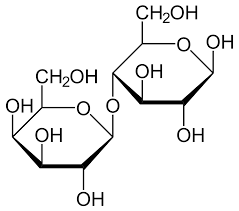
Which 2 monosaccharides join to form **lactose**?
Glucose +Galactose
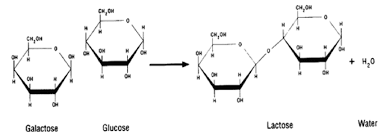
26
New cards
What is a **polysaccharide**?
A **polymer** made of **many** glucose molecules linked together.
27
New cards
What is the **storage polysaccharide** found in **animals**?
Glycogen
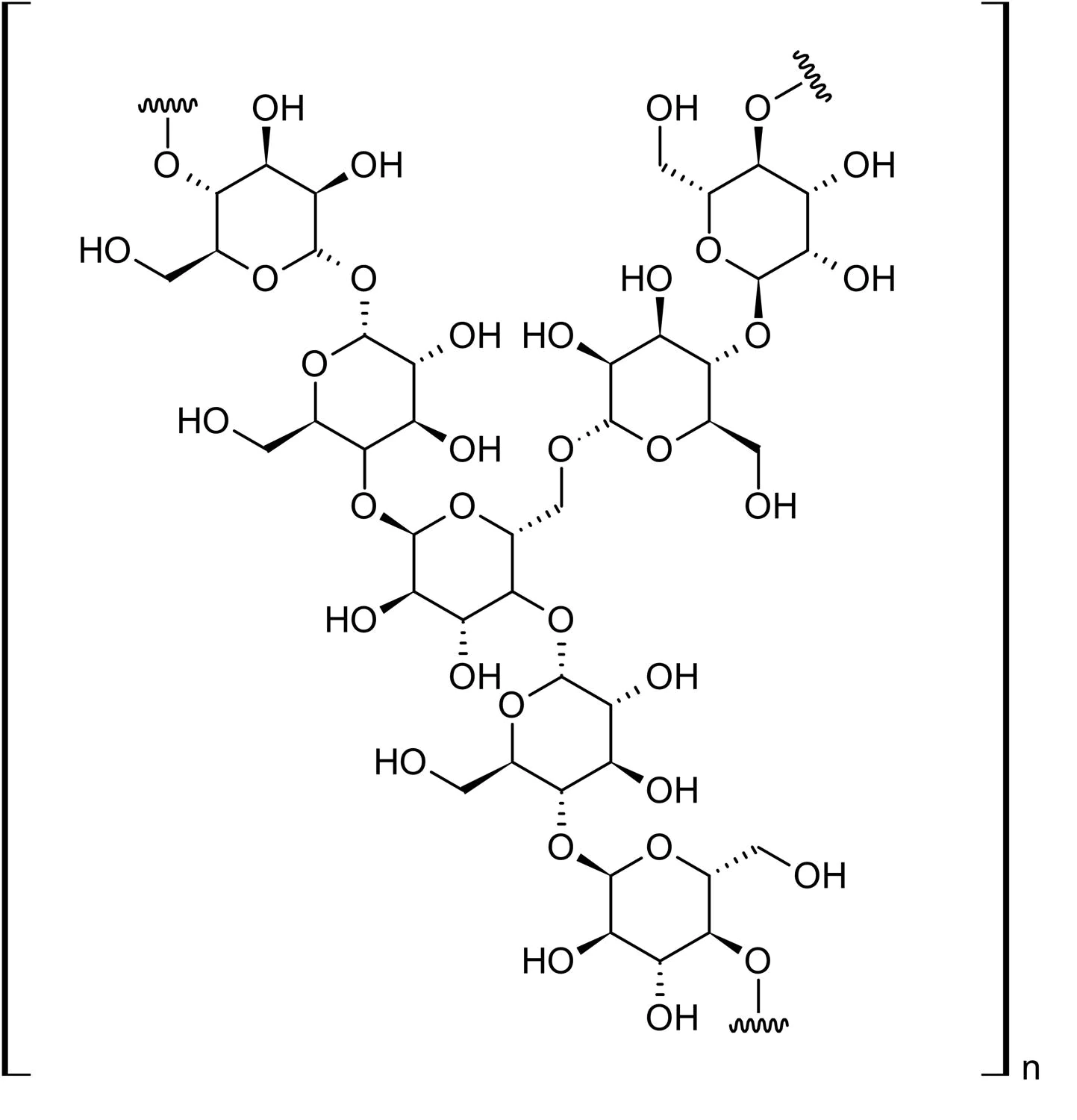
28
New cards
What is the **storage polysaccharide** found in **plants**?
Starch
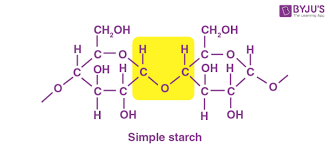
29
New cards
What is the **structural polysaccharide** found in **plant cell walls**?
Cellulose
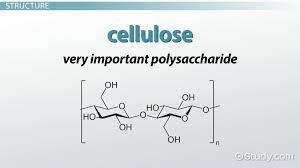
30
New cards
What **4 components** make polysaccharides ideal for storage?
* No osmotic effect
* Compact
* Glucose can easily be **added** or **removed** by hydrolysis or condensation
* Insoluble
* Compact
* Glucose can easily be **added** or **removed** by hydrolysis or condensation
* Insoluble
31
New cards
What two polymers make up **starch?**
Amylose + Amylopectin
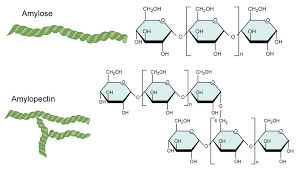
32
New cards
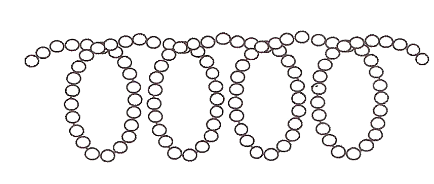
What is **amylose**?
Polymer of alpha glucose joined by 1,4 **glycosidic chains** to form **coiled chains**
33
New cards
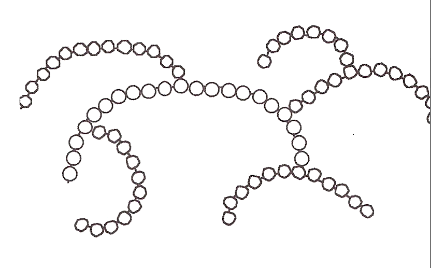
What is **amylopectin**?
**branched polymer** - links between **carbon 1 and 6**
34
New cards
What is **glycogen?**
* Polymer of alpha glucose joined by **1,4 glycosidic links** to form coiled chains
* Many side chains are linked by **1,6 glycosidic links**
* Many side chains are linked by **1,6 glycosidic links**
35
New cards
Where is **glycogen** stored?
as **glycogen granules** in the @@liver and muscle cells@@
36
New cards
Which is more compact, **glycogen** or **starch**?
Glycogen
37
New cards
What is **cellulose?**
* An **insoluble** polysaccharide made from long, straight chains of **beta glucose**
* **Joined by Beta glucose** 1,4 chains
* Each molecule is rotated 180 degrees
* **Joined by Beta glucose** 1,4 chains
* Each molecule is rotated 180 degrees
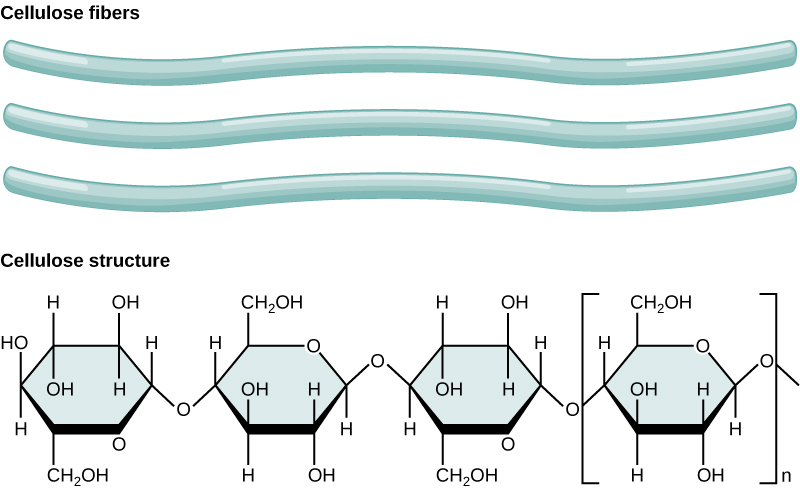
38
New cards
The **structure** of cellulose is in a ….
Microfibril - makes it very strong
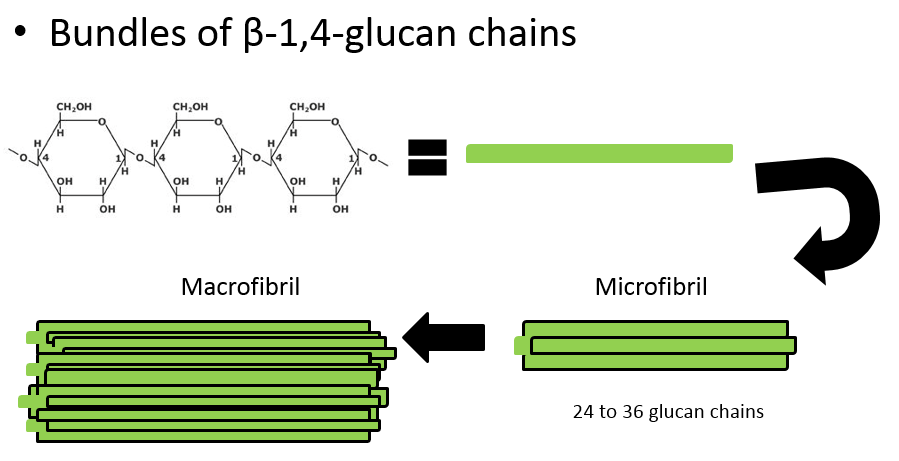
39
New cards
**True/False:** Most organisms cannot digest/hydrolyse cellulose
**True**
40
New cards
Give a function of cellulose in the cell wall
Prevents the cell wall from bursting when the cell becomes turgid
41
New cards
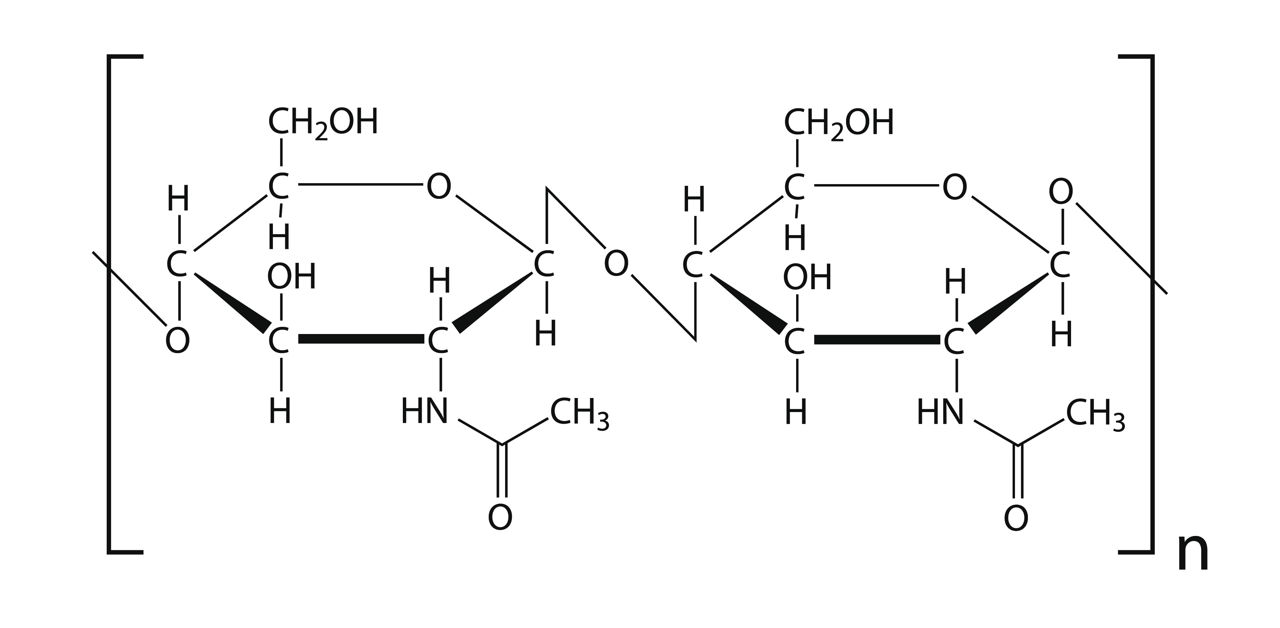
What is chitin?
A **structural** carbohydrate found in the **exoskeletons of insects** and the **cell walls of fungi**
42
New cards
What is the main difference between the structure of **chitin** compared to **cellulose**?
Chitin has an **acetyl amide** group (CH3CONH2)
43
New cards
Give three features of **chitin**
* Strong
* Waterproof
* *Light for flight*
* Waterproof
* *Light for flight*
44
New cards
**True/False:** Cellulose microfibrils have more tensile strength than chitin microfibrils
**False** - Chitin microfibrils have greater tensile strength than those of cellulose due to having more N groups which helps form more hydrogen bonds