Chapter 3: Biological Molecules
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
The ---- of carbon allow it to from a wide variety of chain and ring structures
bonding properties
Functional groups are linked by--- to other atoms in biological molecules.
covelant bonds
Functional groups are linked to other biological molecules through the ---- atoms
carbon
Hydroxl Group
(-OH)
Carbonyl Group
(C=O)
Carboxyl Group
(C=O=O-H)
Amino Group
(-NH2)
Phosphate Group
(-OPO32-)
Sulfhydrl Group
(-SH)
Methyl Group
(-CH3)
Two molecules that have the same chemical formulas, but have different molecular structures
Isomers
Stereoisomers
isomers that mirror images of each other
Functional groups are important to functionals of biological molecules as they determine....(4)
- molecule's overall chemical properties
- polarity
-acidity
- reactivity
Isomers are relevant to biochemical reactions because reactions...
distinguish between isomers and interact with only one form, while ignoring or reacting differently with others.
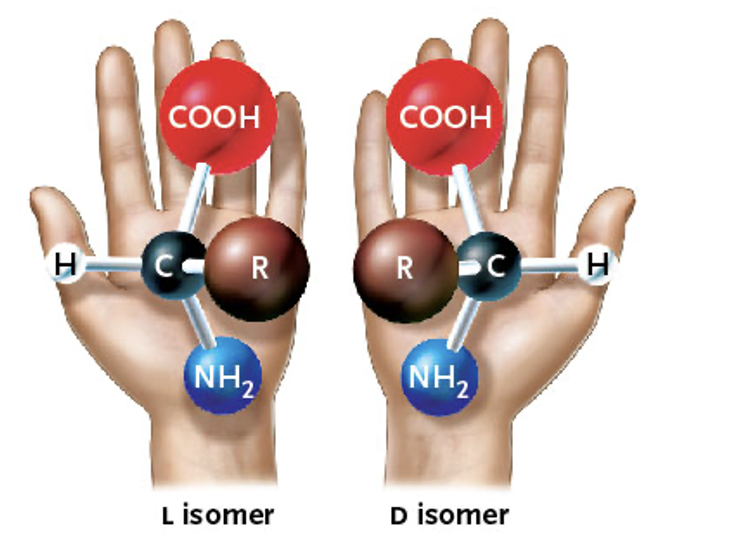
What type of isomer is this?
Stereoisomer
Two molecules that have the same molecules, but are arranged in different ways.
Structural Isomers
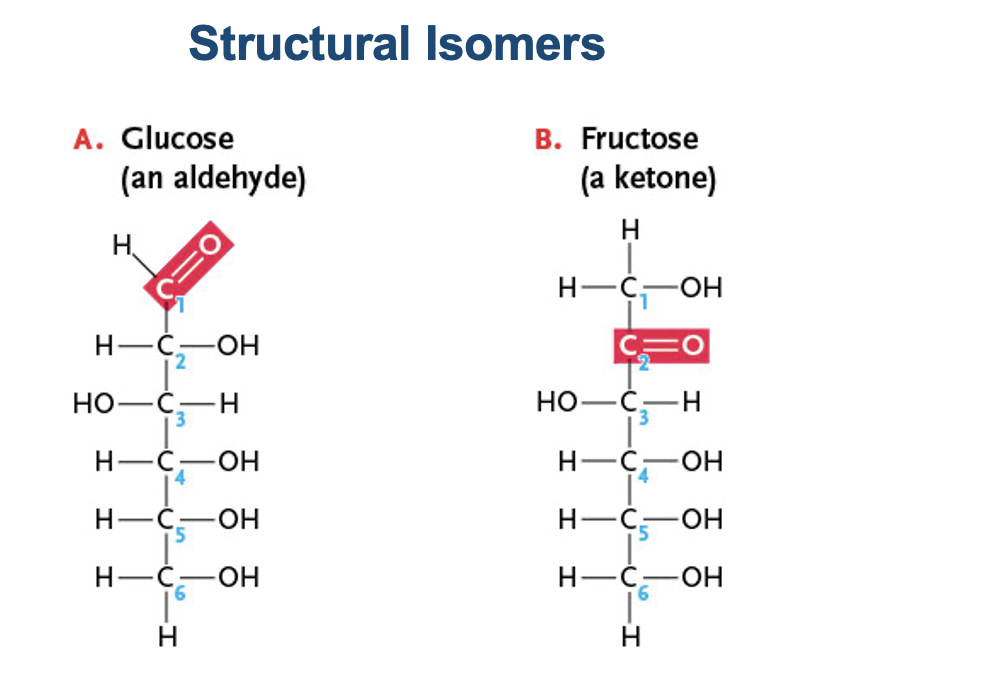
What type of isomer is this?
Structural Isomers
In many reactions involving functional groups, components of a —— molecule are removed and added as the groups interact.
water
When water components are removed, the reaction is called a——-
dehydration synthesis reaction
— is another name for a dehydration synthesis reaction
condensation reaction
When water components are added, the reaction is called a—-
hydrolysis
In a dehydration syntheis reacton, water components are removed as ——— join to form a ——-
covelant bonds; larger molecule
In a hydrolysis reaction, water components are added as covelant bonds are—— into ——-
broken; smaller subunits
Large components assembled from smaller subunits
Macromolecules
A repeating subunit is called a —
Monomer
A chain of monomers linked together though covelant bonds is called a —
polymer
The process of monomers assembling into polymers is called —-
polymerization.
Polymerization reactions are really —- reactions ( hint: water components removed to link smaller subunits to form a larger molecule)
Dehydration Synthesis
Lipids are not considered macromolecules because….
they are not large enough
basic functions of carbohydrates(3)
-energy
-adhesion
-structural support
Carbohydrate subunits are linked together through ———
glycosidic bonds
carbohydrates only contain—-,—— and—— molecules
oxygen
hydrogen
carbon
Polysaccharides are may be —— and —— molecules
linear, unbranched
Carbohydrates ring forms are formed when ——-
monosaccharides with 5 or more carbons fold back on themselves through a reaction between 2 functional groups.
All monosaccahrises can occur in — form
linear
water-insoluble, primarily nonpolar biological molecules composed of mostly hydrocarbons.
Lipids
Types of Lipids(3)& function
Neutral Lipids- energy source
Steroids- regulate cell activities
Phospholipids form cell membranes
Neutral Lipids are considered neutral becuase
at cellular pH, they have no charged groups
almost all neutral lipids are formed through a ——- reaction
dehydration synthesis reaction
What components make up a neutral lipid(2) …
three fatty acids
glycerol
The product of the dehydration synthesis involving a glycerol and 3 fatty acids is called —
triglyceride
Triglycerides serve as—- in animals
energy reserves
A covelant bond called an —- forms between the -COOH group of the fatty acid and the -OH group of the glycerol.
ester linkage
What type of bond is an ester linkage?
A covelant bond
An ester linkage is created involving what groups of which molecules.(2)
The carboxyl(-COOH) group of the fatty acids
The hydroxyl(-OH) group of the glycerol
Triglyceride is a — molecule( hint: polar/non-polar)
non-polar
How does a triglyceride become non-polar?
When triglycerides are formed, the polar groups of glycerol are eliminated making it a non-polar molecule.
What is the difference between Saturated Fatty Acids and Unsaturated Fatty Acids?
Unsaturated fatty acids bond at a double dond and are more fluid at biological temperatures.
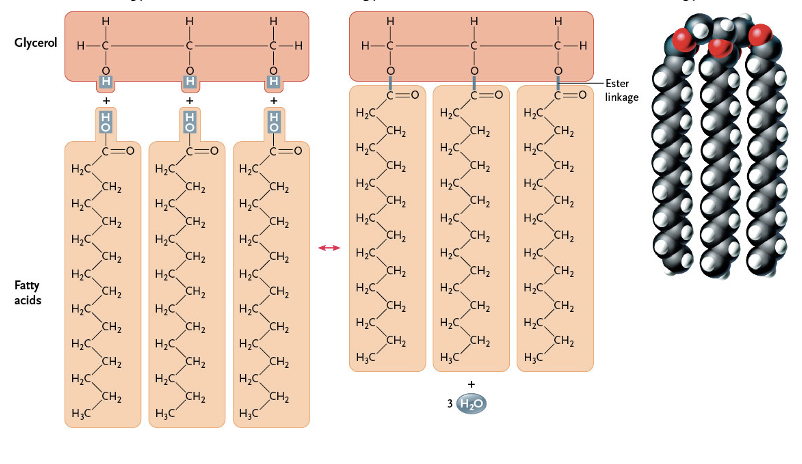
What type of lipid is this?
Neutral Lipid( Triglyceride)
A—- fatty acid binds the maximum number of hydrogen bonds
saturated
As the carbon chain of a fatty acid increses in length, the fatty acid becomes ——
less water- soluble
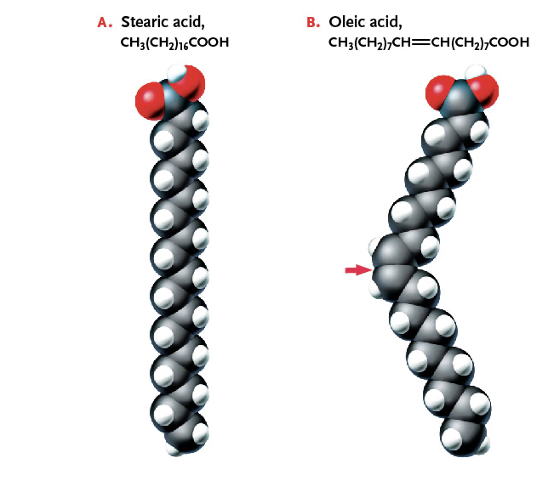
Identify the Unsaturated and Saturated Fatty Acid
A) Saturated
B) Unsaturated
How does one tell an unsaturated fatty acid from a saturated acid?
The unsaturated fatty acid has a double bond/ “kink”
The type of lipid that is phosphate- containing is called a -
phospholipid
Phospholids are the primary lipids of cell membranes. True or False
True
Phospholipids are an example of amphiphiles. What is an amphiphile?
A molecules that has both hydrophilic and lipholic properties due to its structure
In most phospholipids, —- is the backbone of the structure.
glycerol
In a phospholipid, the end of the molecule with the fatty acid is —-, while the the end of the molecule with the phosphate group is ——
nonpolar, polar
In polar environments, such as a water solution,—— assume arrangements in which only their polar ends are exposed to the water, and their nonpolar ends collect together in a region that excludes water.
phospholipids
In polar environments, such as a water solution, phospholipids assume arrangements in which only their polar ends are exposed to the water, and their nonpolar ends collect together in a region that excludes water. Why is that?
Becuase of its structure, it has both water loving and fat loving properties,
Describe a phospholipid bilayer.
the fundamental structure of all biological membranes, formed by two layers of phospholipid molecules arranged with their hydrophilic (water-attracting) phosphate heads facing outward and their hydrophobic (water-repelling) fatty acid tails facing inward.
A group of lipids with structures based on a framework of four carbon rings are —-
Steroids.
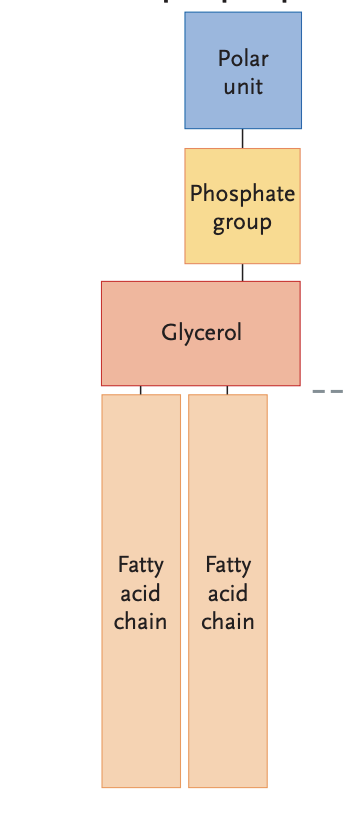
What type of lipid is this?
Phospholid
How are steroids distinguised from each other?
Through small differences in the chemical groups attached to the rings.
—, the most abundant steroids.
Sterols
How are sterols structured?
Sterols have a single polar(-OH) group linked to one end of the ring framework and a complex hydrocarbon chain at the other end.
Although sterols are almost completely hydrophobic, what makes them have a slight polar hydrophilic character
the single hydroxl group on one end of the molecule.
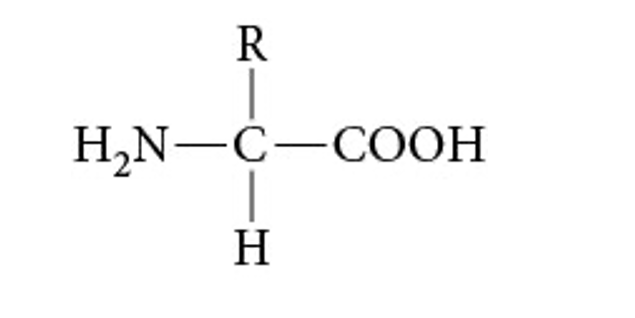
Identify this structure. Describe the components.
Amino Acid: Structure: a central carbon atom attached to an amino group (ONH2), a carboxyl group (OCOOH), and a hydrogen atom and a side chain( R group)
Cells use — different amino acids as the building blocks of proteins and out of them, —- are structurally the same
20,19
How does proline differ in structure from other amino acids?
that it has a ring structure that includes the central carbon atom – the central carbon bonds to a —COOH group on one side and to an =NH (imino) group at the other side.
All amino acids act as only acids. True or False
False. All amino acids can act as acids or bases.
List some of the main functions of proteins
structural support
enzymes
movement
transport
recognition and receptor molecules
recognition of proteins and DNA
hormones, antibodies and venoms.
What do peptide bonds do?
Peptide bonds link amino acids into polypeptide chains
Describe how peptide bonds are formed.
Peptide bonds are formed by a dehydration synthesis reaction between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of a second (
The chain of amino acids formed by sequential peptide bonds is a
polypeptide
Describe the primary structure of proteins.
The primary structure is a linear sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Tertiary structure determines the DNA. True of False
False. DNA is determined by the primary structure
The tertiary structure of proteins is the three-dimensional shape comprised of two or more polypeptides.True or False
False. the tertiary structure determines overall 3d shape as the folding of the complete amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain with its secondary structures into its 3d shape.
A hydrogen bond between the amino acid side chains (R groups) of two different polypeptide chains in a multichain protein would be considered part of the ____ structure of the protein.
secondary
What does the secondary level of proteins structure look like?
It is the coiling and/or folding of a segment of a polypeptide chain produced by hydrogen bonding between different amino acids in the segment.
Two highly regular secondary structures are particularly stable and make an amino acid chain resistant to bending. What are they called?
the alpha helix and the beta strand.
A nucleotide, the monomer of nucleic acids, consists of three parts linked together by covalent bonds. What are those parts?
a nitrogenous base
a five-carbon, ring-shaped sugar
one to three phosphate groups
How do pyrimidines and purine differ from each other?
pyrimidines has one carbon nitrogen ring, while purine has two carbon nitrogen rings.
Purines are adenine (A) and guanine (G), while pyrimidines are uracil (U), thymine (T), and cytosine (C). True or False
True. Purine are A or G, Pyrimides are U/T or C
Describe the monomer of nucleic acids( nucleotide).
a nitrogenous base, five carbon ring shaped sugar and one to three phosphate groups all linked together by covelant bonds.
DNA nucleotides=——; RNA nucleotides=——
Deoxyribose; Ribose
A structure containing only a nitrogenous base and a fivecarbon sugar is called a
nucleoside
Nucleotides perform many functions in cells in addition to serving as the building blocks of nucleic acids. What are those functions?
Two ribosecontaining nucleotides in particular, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and guanosine triphosphate (GTP), are the primary molecules that transport chemical energy from one reaction system to another. The same nucleotides regulate and adjust cellular activity.
The differences in carbon and purine bases between DNA and RNA account for important differences in the structures and functions of these nucleic acids inside cells. True or False
False. The differences in sugar and pyrimidine bases between DNA and RNA account for important differences in the structures and functions of these nucleic acids inside cells.
What does a DNA base pair consist of? describe it
It consists of one purine and pyrimidine.
•Adenine pairs only with thymine (A–T), forming two stabilizing hydrogen bonds
•Guanine pairs only with cytosine (G–C), forming three hydrogen bonds
Formation of A–T and G–C pairs allows the sequence of one polynucleotide chain to determine the sequence of its partner in the double helix. True or False.
The nucleotide sequence of one chain is said to be complementary to the nucleotide sequence of the other chain. In DNA replication, one polynucleotide chain is used as a template for the assembly of a complementary chain according to the A–T and G–C base-pairing rules.