Sound Waves
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Wave
a disturbance that carries energy
Medium
a substance through which a wave can travel; matter
longitudinal waves
the particles of the medium vibrate along the path that the wave takes; requires a medium to move through
compressional wave
also known as a longitudinal wave
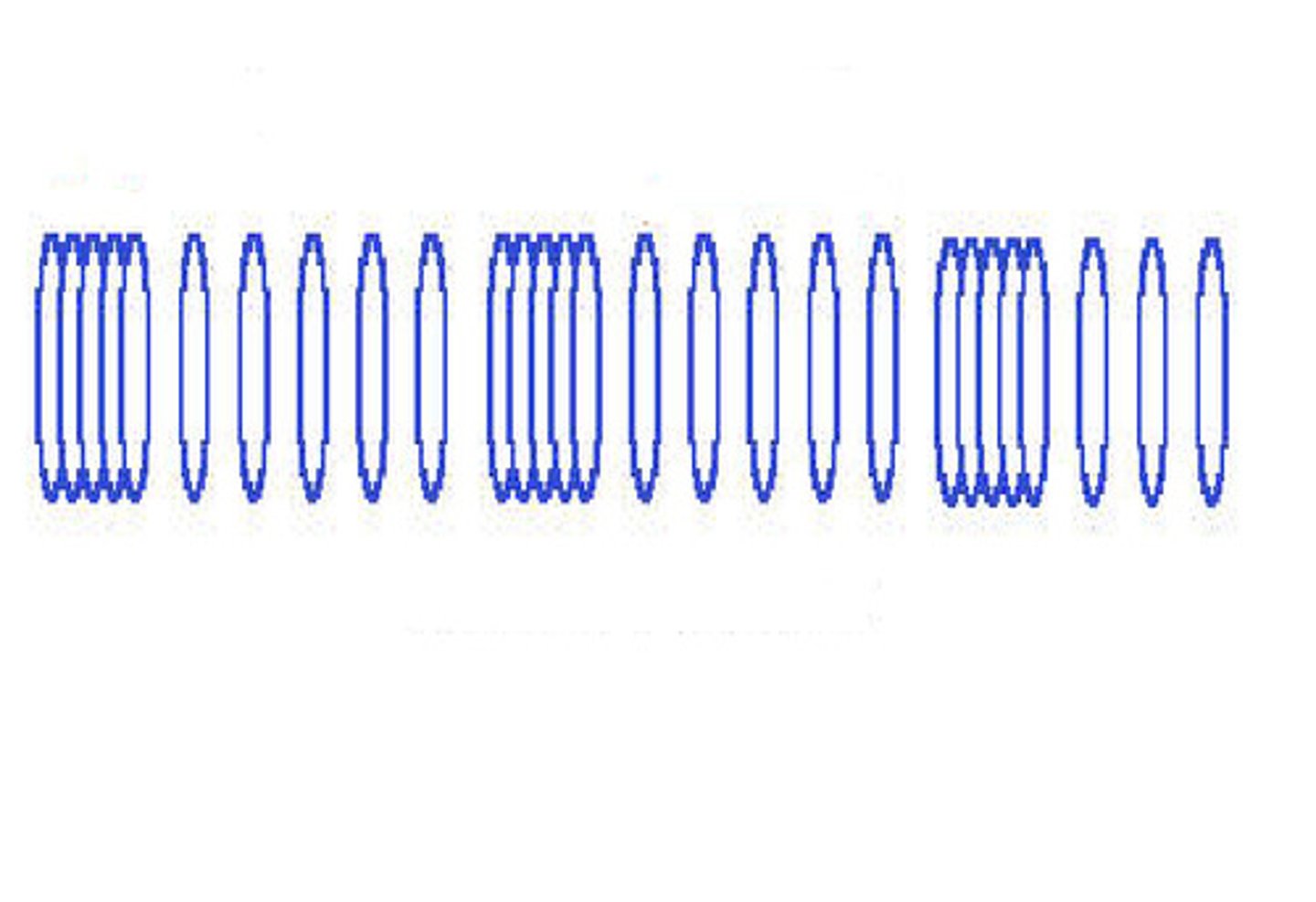
compression
the area in a longitudinal wave where the particles are pressed closely together.
Rarefaction
the area in the longitudinal wave where the particles are spread apart.
Reflection
when a wave bounces back after striking a surface
Refraction
the bending of light as it passes, at an angle, from medium to another
Diffraction
the bending of waves around a barrier or through an opening. For instance hearing a person around a corner before seeing them.
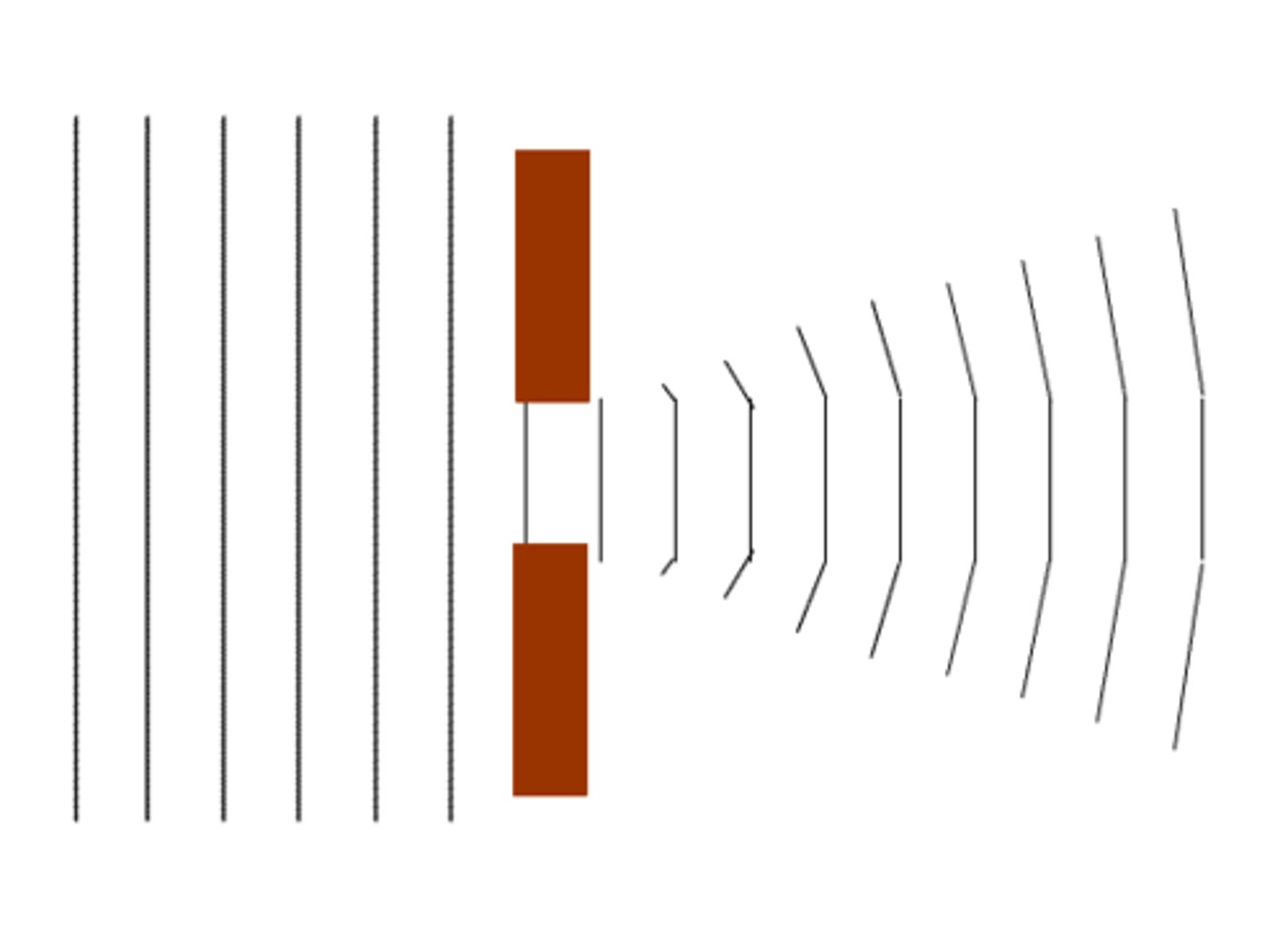
Interference
the result when two or more waves overlap.
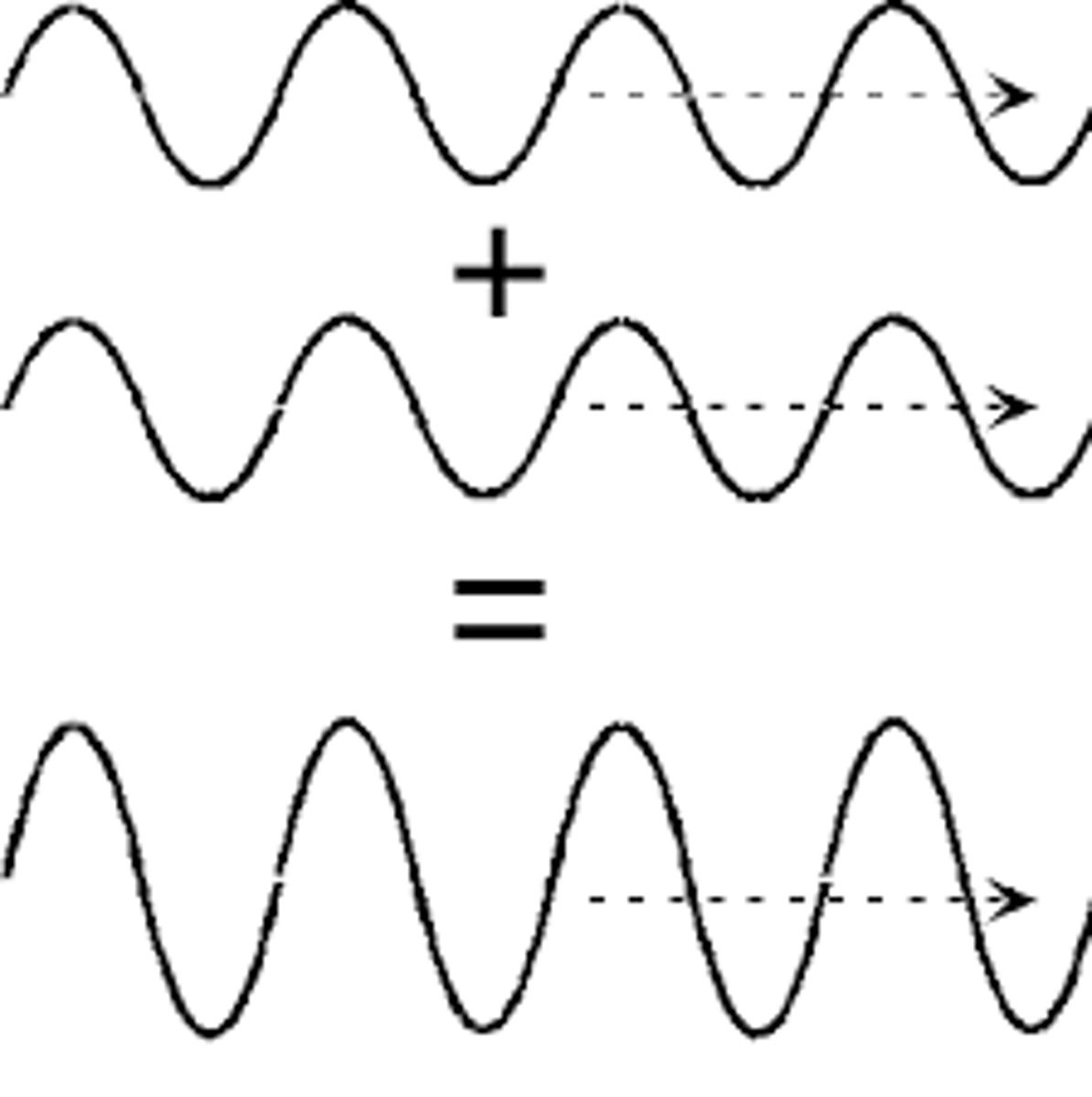
constructive interference
when a crest of one wave and the crest of another wave overlap. Creates a larger amplitude
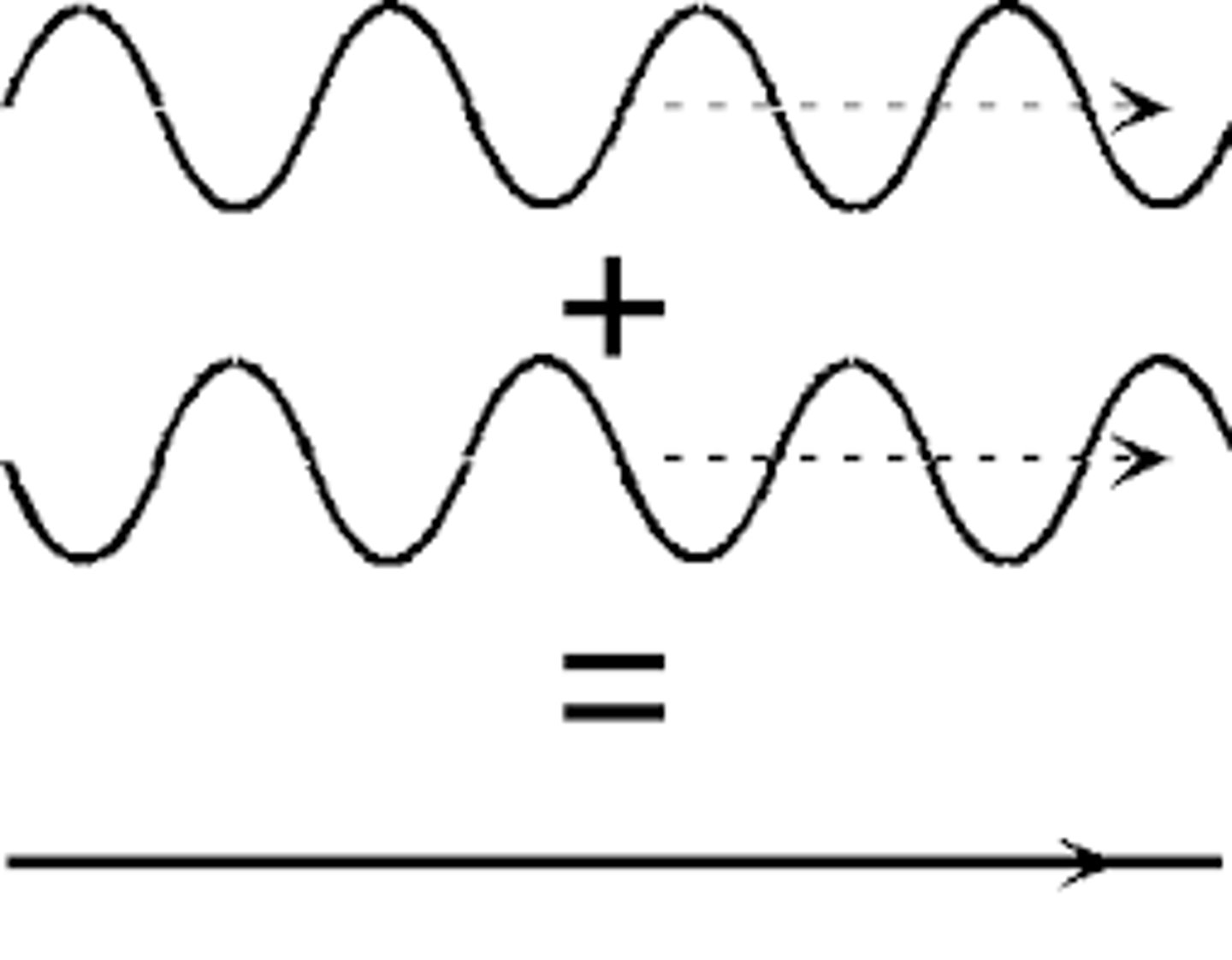
Destructive interference
when a crest of one wave and a trough of another wave overlap, results in a smaller (or no) amplitude.
Resonance
When the vibration of an object causes a second object to vibrate at the same frequency. For instance, when a piano playing causes the water in a glass nearby to vibrate at the same frequency.
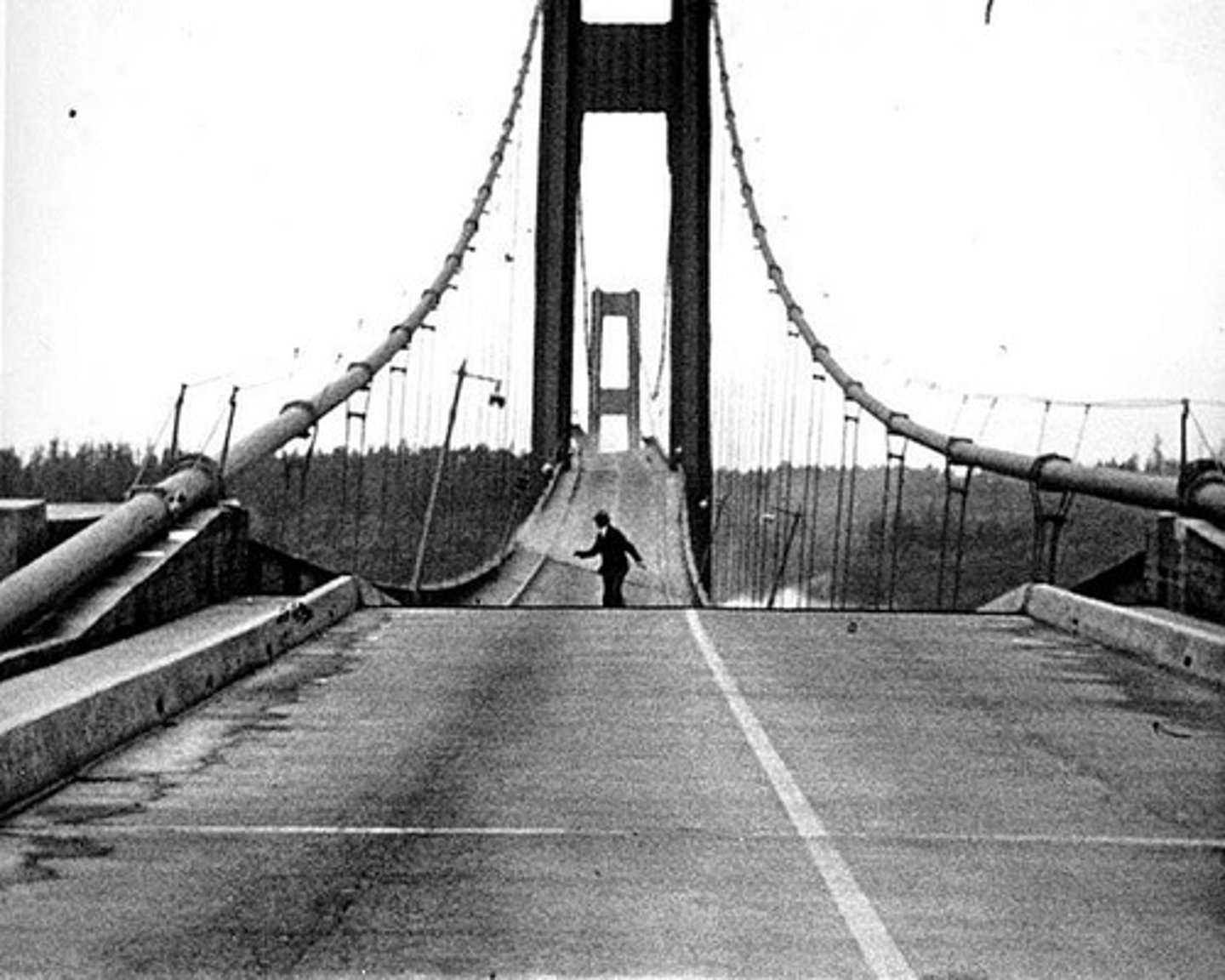
Tacoma Narrows Bridge
A bridge destroyed on 11/7/1940 caused, in part, by resonance. The wind blowing across the bridge caused vibrations to move through the bridge at its resonant frequency. These waves interfered with each other (constructively) and caused a large build up in energy until the bridge began to twist and then collapse.

Wave Speed
the rate at which the sound wave moves, depends on the density (type) of the medium and the temperature of the medium. Speed increases when density and/or temperature increases.
Ultrasonic waves
sound waves with a frequency above 20,000 Hz, outside the range of normal human hearing.
Amplitude
The wave height, also a measure of loudness of a sound. The larger the amplitude, the louder the sound.
Echolocation
The use of sound waves reflections (echo) by animals to locate objects.
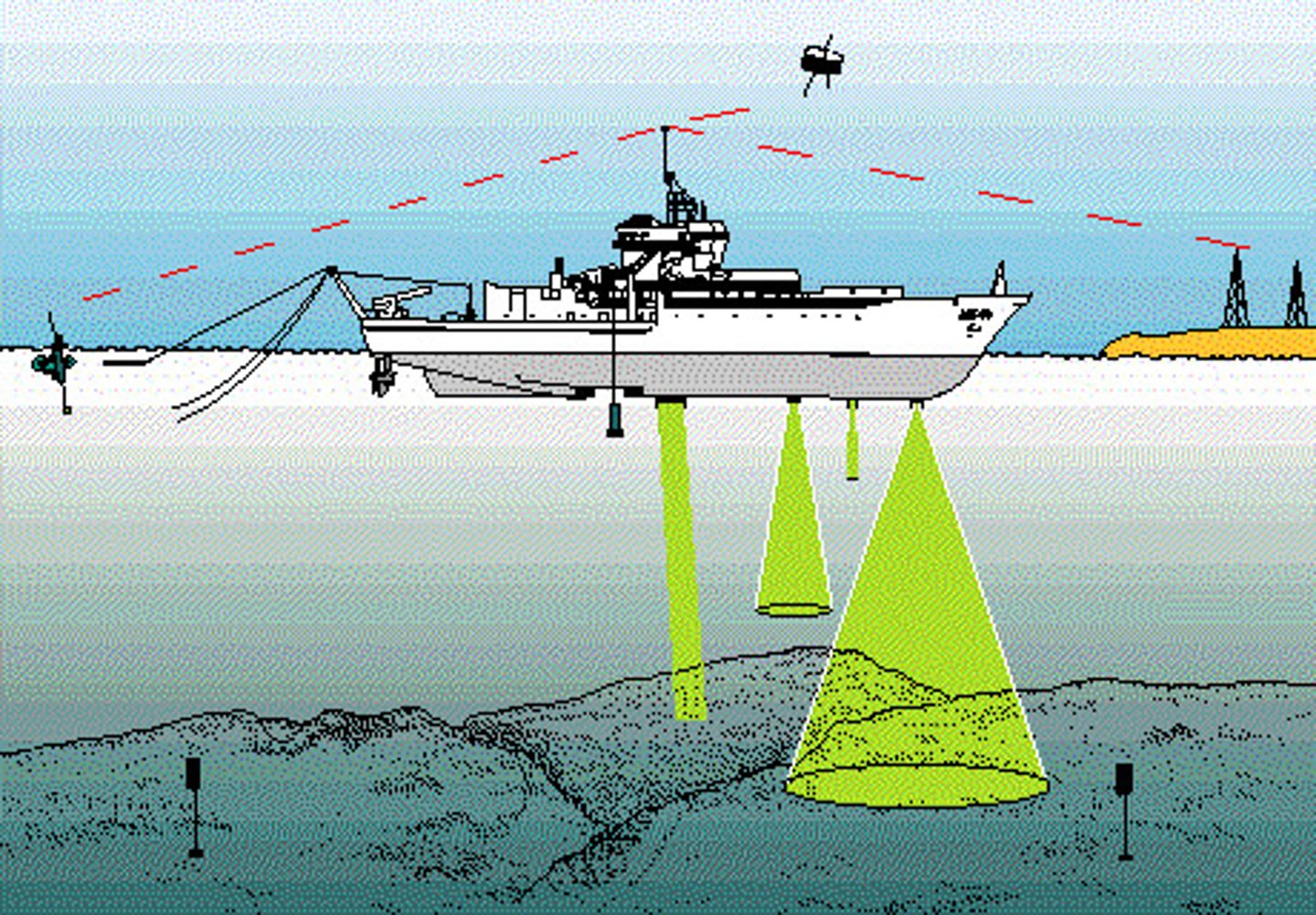
SONAR
SOund Navigation And Ranging. The human form of echolocation. Used by the navy, oceanographers, and fisherman. Ultrasonic waves are used and a machine monitors the echo to determine what objects are around and the distance those objects are from the source/boat.
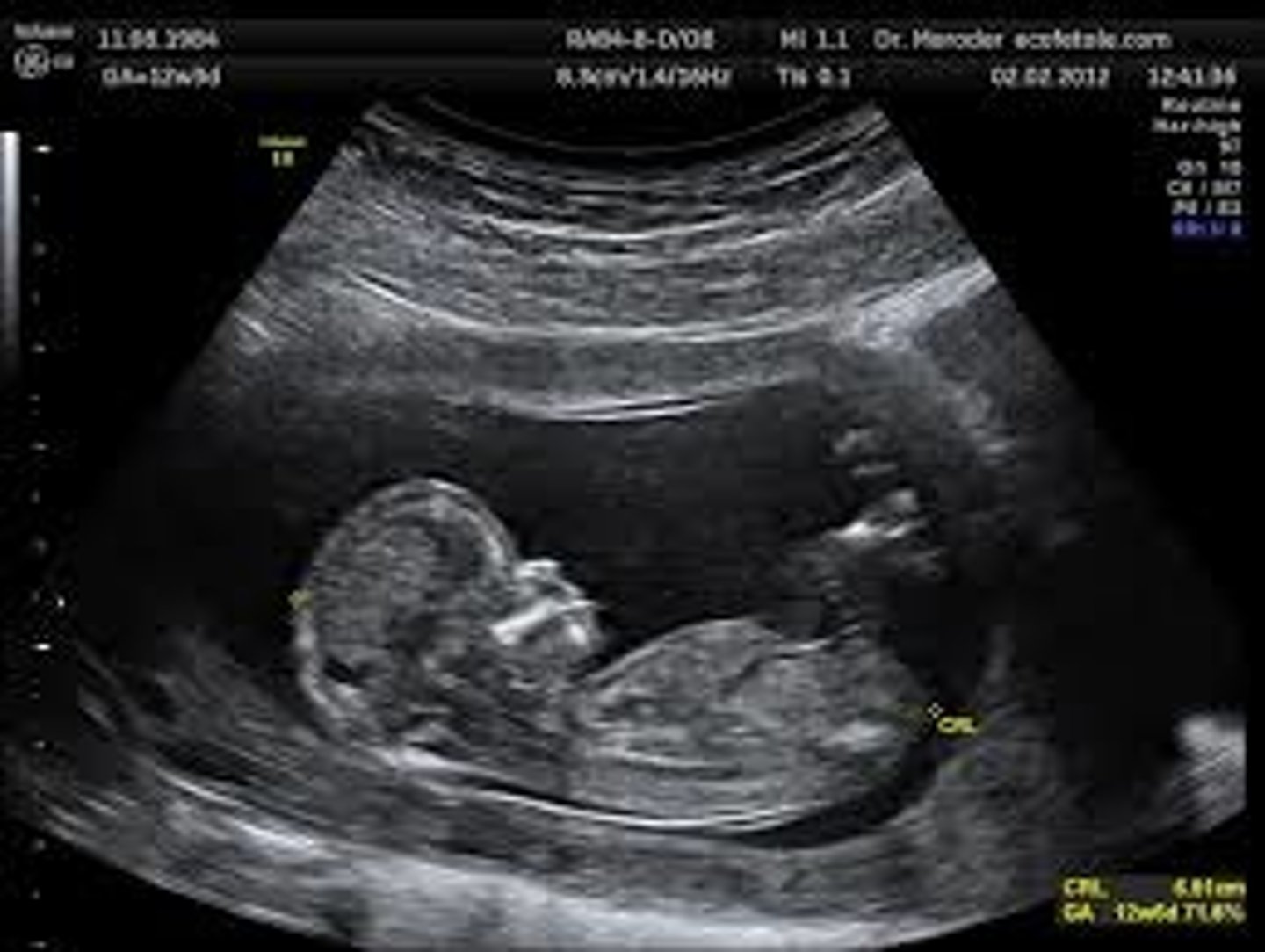
Ultrasounds
the use of ultrasonic waves to see inside the body without performing surgery. This is used to see babies inside the womb as well as internal organs.
Sound Energy
The energy from an object vibrating.