Chapter 10: Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
NADH
2.5 ATP equivalents
FADH2
1.5 ATP equivalents
GTP
1 ATP equivalent
How are NADH and FADH2 converted to ATP equivalents?
Through oxidative phosphorylation, where their electrons are passed along the electron transport chain (ETC) in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
NADH and FADH2 act as ______________ to the electron transport chain (ETC)
Electron donors
These electrons are eventually transferred to….
Molecular oxygen to reduce O2 to 2H2O
ETC involves five protein complexes - Complex I
NADH Dehydrogenase Complex
Complex II
Succinate Dehydrogenase Complex
Complex III
Cytochrome BC1 Complex
Complex IV
Cytochrome Oxidase
Complex V
ATP Synthetase Complex
The five complexes involved in ETC and ATP synthesis are located on the…
Inner membrane of the mitochondrion
The mitochondrion is a….
Double membrane organelle
NADH and FADH2 transfers ___________ to the ETC
High energy electrons
The energy is used to develop a ________________ across the inner mitochondrial membrane
Concentration gradient of hydrogen ions
___________ uses the energy stored in the concentration gradient (of hydrogen ions) to convert ____________.
ATP synthetase
ADP to ATP
Chemiosmotic Theory
________ transfers electrons to Complex I
NADH
________ transfers electrons to Complex II
FADH
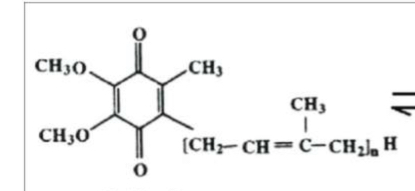
What structure is this?
Coenzyme Q10 - Oxidized Form
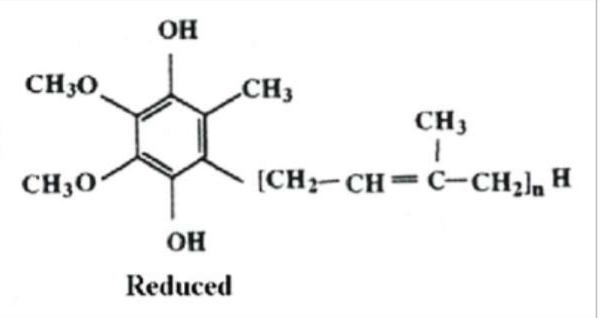
What structure is this?
Coenzyme Q10 - Reduced Form
Coenzyme Q10
A fat-soluble compound that the body produces and uses to create energy and act as an antioxidant.
Crucial component of the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC)
Transfers electrons and pumps protons to generate ATP (Cellular energy)
True or False - Coenzyme Q10 accepts electrons from Complex I and II and transfers them to Complex III
True
Key step in oxidative phosphorylation
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
Cellular process that generates the majority of the cell’s energy by using the energy from the oxidation of NADH and FADH2 to create ATP
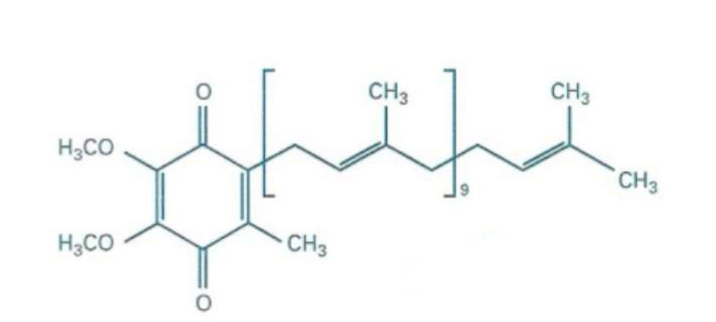
What structure is this?
Ubiquinone - Oxidized form of Coenzyme Q10
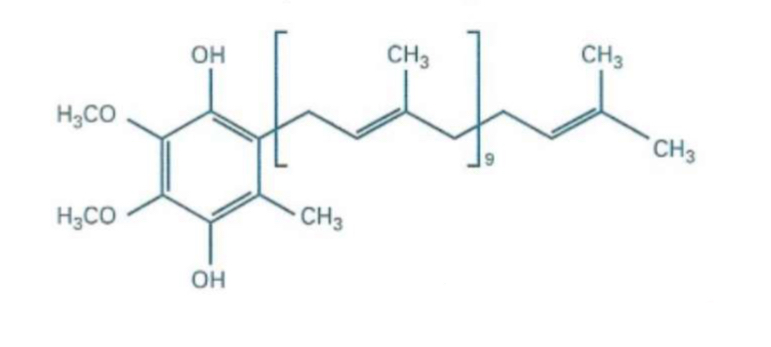
What structure is this?
Ubiquinol - Reduced form of Coenzyme Q10
_______________ is generated in Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Reaction Oxygen Species (ROS)
What are Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)?
When electrons are improperly transferred from the complexes to oxygen
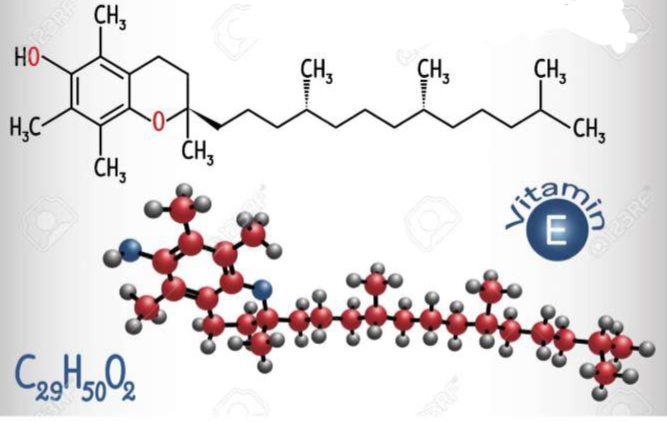
What structure is this?
Vitamin E
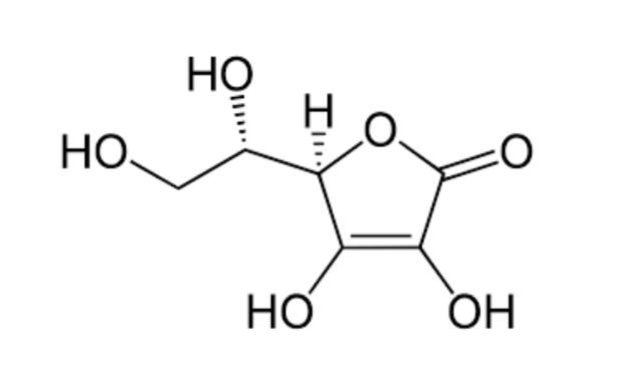
What structure is this?
Vitamin C
Vitamin E
Alpha tocopherol
Lipid Soluble Antioxidant
Vitamin C
Ascorbic Acid
Water Soluble Antioxidant
Most important