ap microeconomics
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
scarcity
the inability of limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants
unlimited resources
land, labor, entrepreneurship, capital
what are the two main types of economies?
market economy and command economy
market economy
use prices to distribute resources, goods, and services
command economy
government controls allocation of resources, goods, and services
opportunity cost
value of the best alternative NOT chosen
production possibility curve
inside production possibilites curve
all resources are not being used
outside production possibilities curve
impossible
along the curve
closer to the top- more of good y than good x
closer to bottom- more of good x than good y
linear ppc
constant opportunity cost
curved ppc
increasing opportunity cost
determinants of ppc
changes in resources, technology, productivity, and trade
absolute advantage
a is better than b because a>b
comparative advantage
ability to produce at lower oppurtunity cost
output (goods produced) - other over
input (resources used) - it over
mutually beneficial terms of trade
between the two opportunity costs for a calculated comparative advantage
marginal analysis
analyzing how much benefit selling or buying a certain good provides compared to its cost
benefit maximizing behavior
where the marginal cost is less than or equal to the marginal benefit
calculating marginal utility
the marginal utility (in utils) divided by the cost = MU/$
diminishing marginal utility
as more units of a product are consumed, the satisfaction/utility it provides tends to decline
law of demand
consumers buy less at high prices and more at low prices
demand curve
downward
demand curve moves right
increase
demand curve moves left
decrease
demand shifters
taste and preference
market size
expectations
price of related goods
- substitutes - $ of good up, demand for sub up
- complements - $ of good up, demand for comp down
changes in income
- normal goods - $ up, demand up
- inferirior goods - $ up, demand down
law of supply
producers sell more at high prices and less at low prices
demand curve
upwards
supply shifters
resource costs
government - taxes, subsidies
# of sellers
technology
price of other goods
producer expectations
price elasticity of demand
inelastic - demand changes little with price changes (more vertical)
elastic - demand changes with price changes (more horizontal)
price elasticity of demand/ supply equation
demand - %∆Qd/%∆P
supply - %∆Qs/%∆P
elastic
goods affected by change in price, more horizontal
inelastic
goods not affected by change in price, more vertical
total revenue test
a method to determine the price elasticity of demand
total revenue increases when price falls, demand is elastic
total revenue decreases, demand is inelastic
characteristics of elastic supply
easy production, low cost, easy to switch to, low barriers to entry
characteristics of inelastic supply
difficult production, high costs, hard to change to alternative, high barriers to entry
characteristics of elastic demand
sensitive to price change, substitutes, luxury items, large portion of income, not needed immediately
characteristics of inelastic demand
few substitutes, required now, small portion of income
price elasticity of demand/ supply meaning
relatively elastic: >1
unit elastic: 1
relatively inelastic: <1
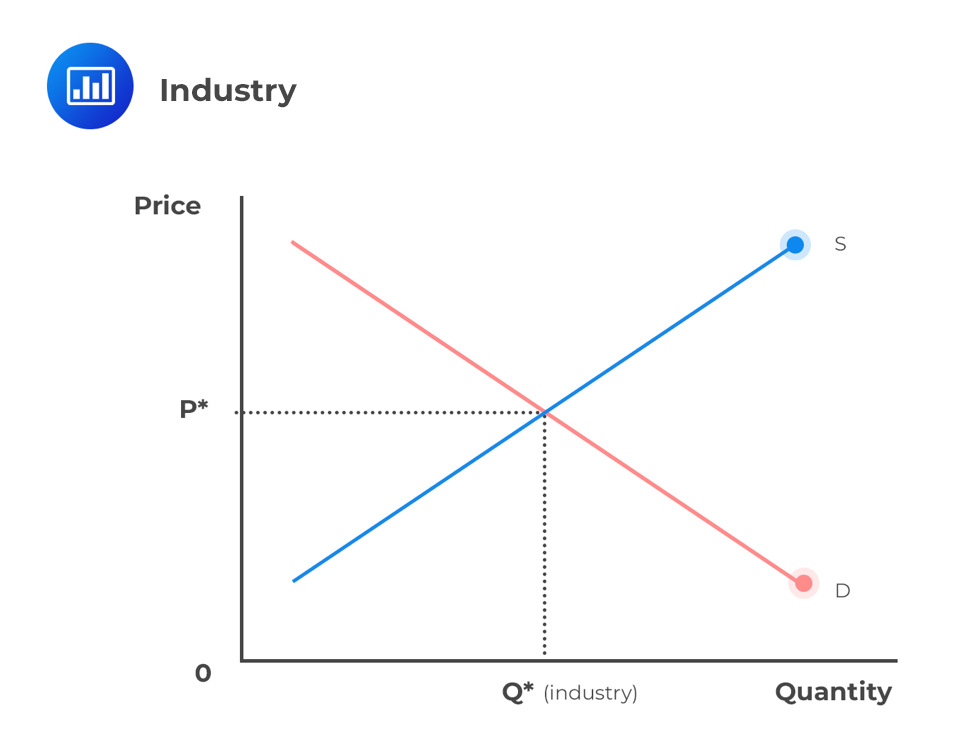
market equilibrium
Qs = Qd
price below the equilibrium is shortage
consumer surplus
price consumers are willing to pay - actual price
producer surplus
actual price -price the producer is willing to sell for
demand increase
price and quantity increase
demand decrease
price and quantity decrease
supply increase
price decreases, quantity increases
supply decrease
price increases, quantity decreases
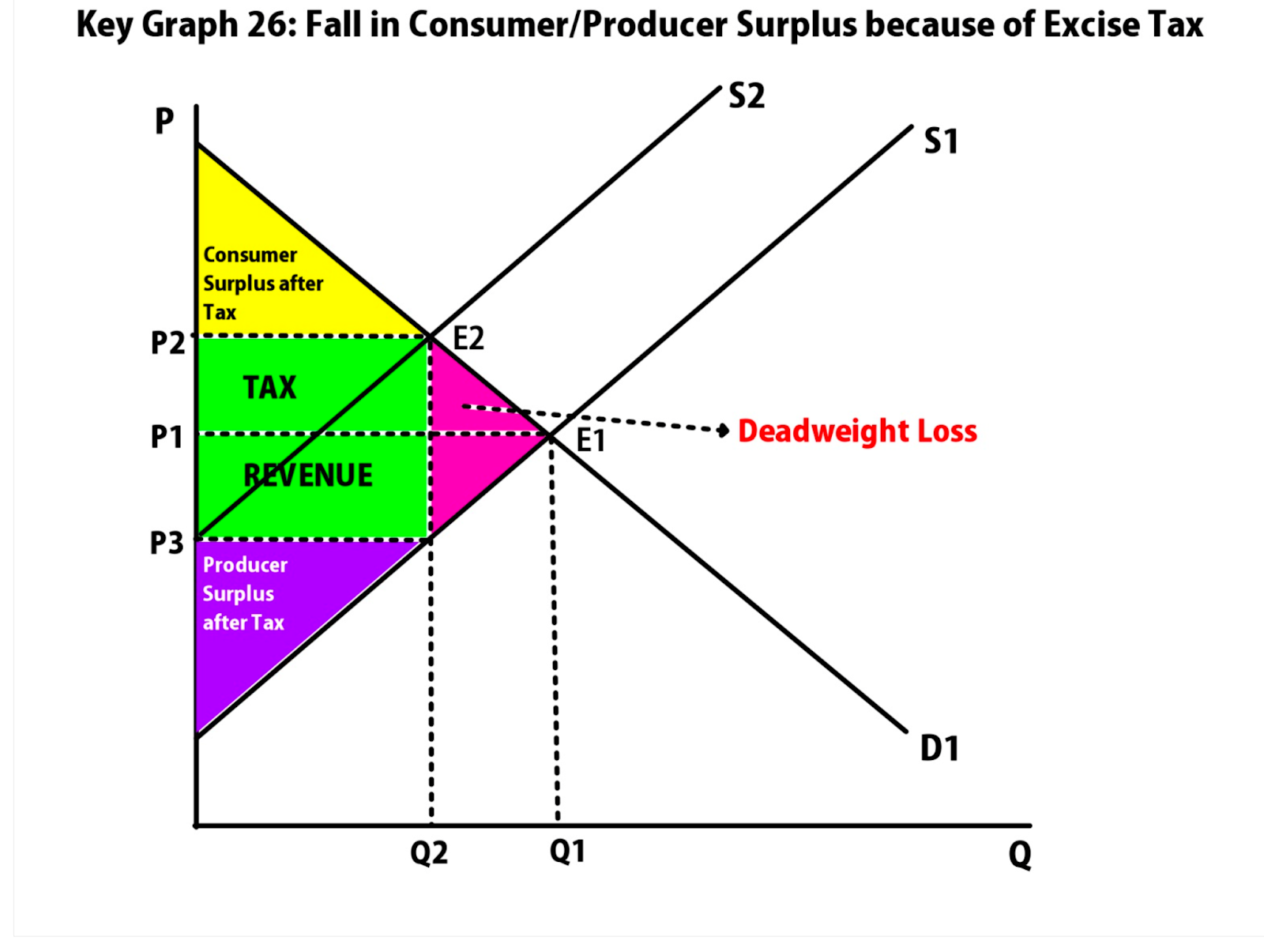
deadweight loss
transactions that should occur, but don’t because of government intervention
market disequilibrium
shortage : Qs < Qd, price is lower than equilibrium
surplus : Qs > Qd, price is above equilibrium
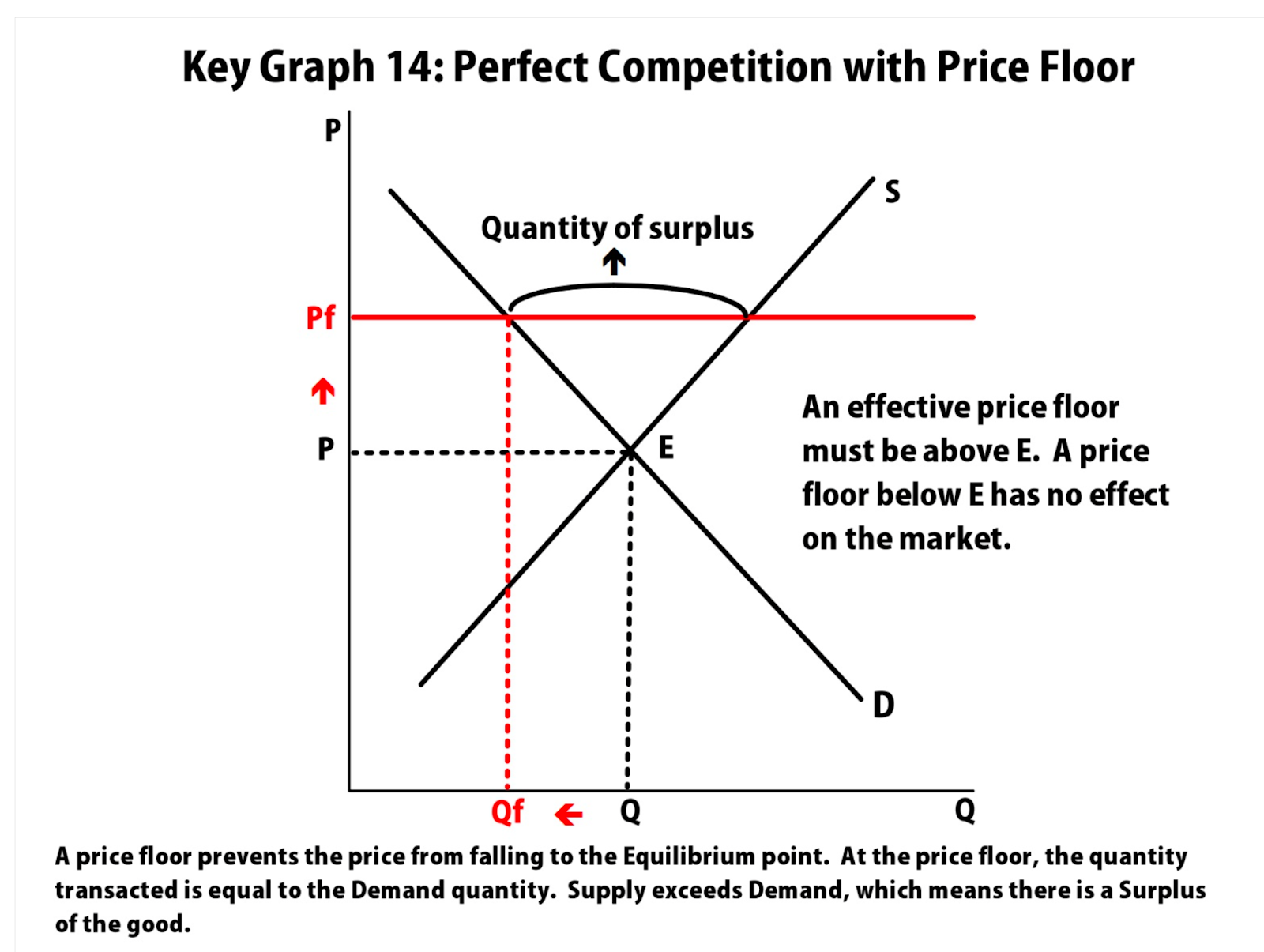
price floor
minimum price a supplier can charge
price is set above equilibrium (causes shortage)
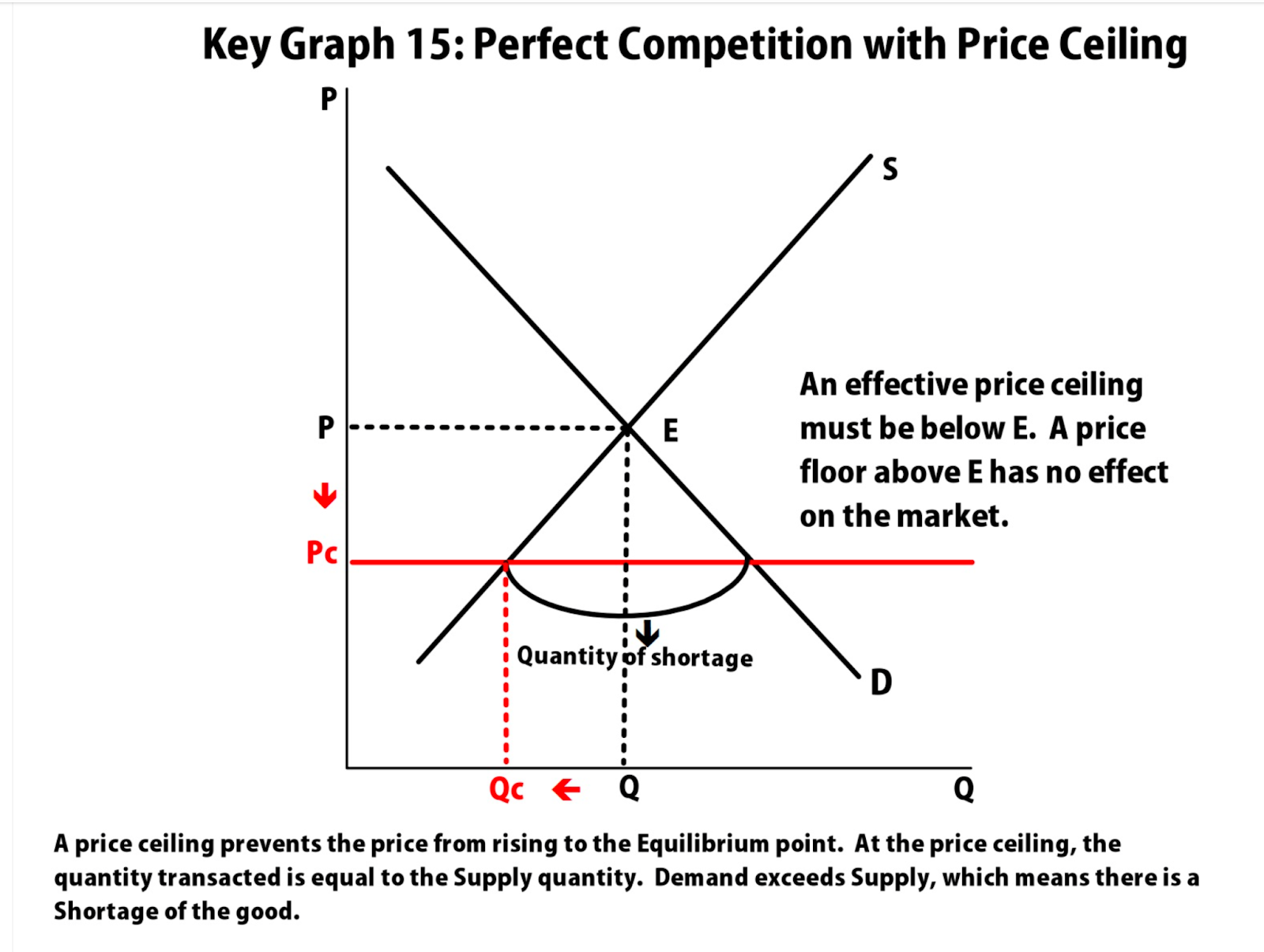
price ceiling
maximum price a supplier can charge
price is set below equilibrium (causes surplus)
demand price
the price at which consumers will demand that quantity
supply price
the price at which producers will supply that quantity
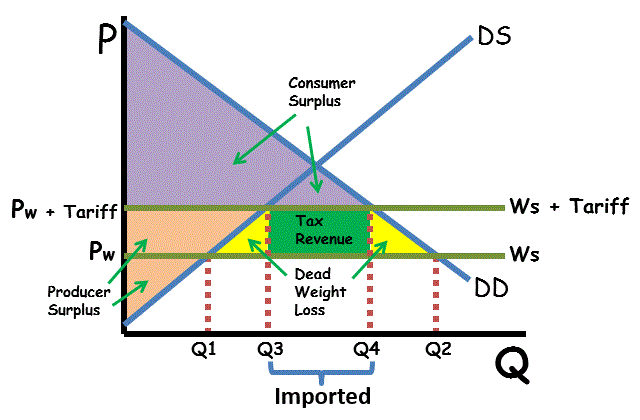
quota rent
difference between demand price and supply price
tariffs
tax placed on a good that is imported or exported
production function
relation between the quantity of inputs a firm uses and the quantity of output it produces
fixed input
an input whose quantity doesn’t change
variable input
an input whose quantity can change
long run : time period in which all inputs can be variable
short run : time period in which at least 1 input is fixed
marginal product of labor
the extra output generated by employing one additional unit of labor, while keeping all other inputs constant
change in output/ change in labor
∆Q/∆L
production function
shows the relationship between the amount of labor and amount of output
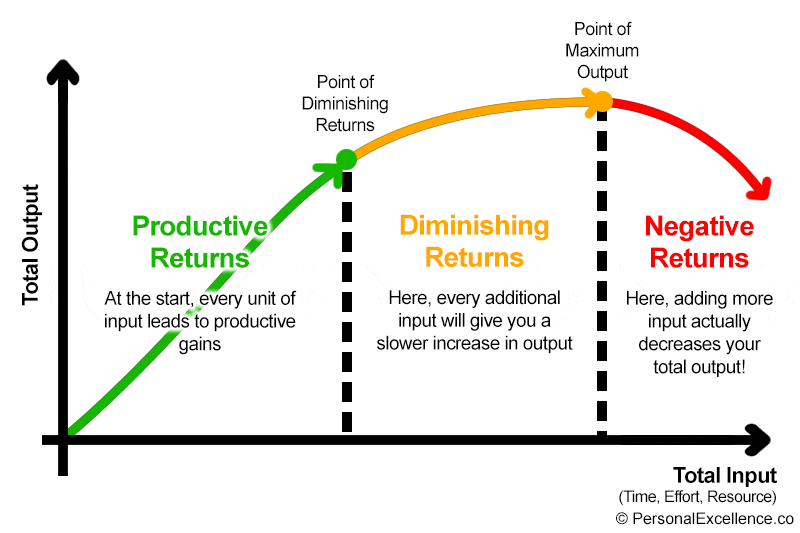
law of diminishing marginal returns
increasing, decreasing, negatives
marginal cost of labor
wage / marginal production eq
W / (Q/L)
marginal cost vs marginal production
flipped graphs and inverse relationship
fixed cost
doesn’t change with out put (ex 1 muffin in an oven vs 20 muffins)
variable cost
cost that varies with output (ex labor)
total costs
variable + fixed
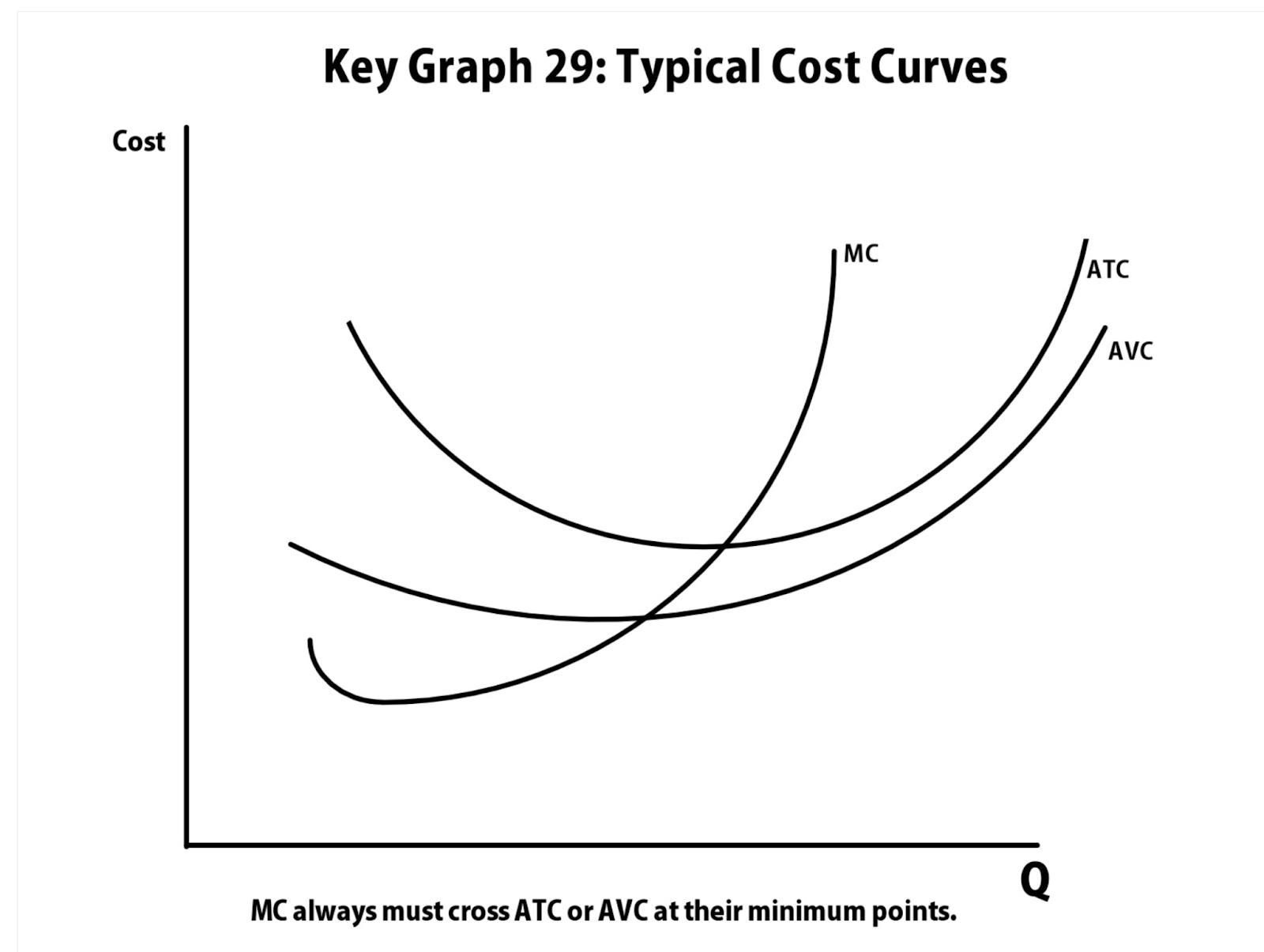
average fixed cost (AFC)
average variable cost (AVC)
average total cost (ATC)
FC / Q
VC / Q
AC / Q
change in fixed cost?
moves average variable cost curve only
change in variable cost?
moves all three curves
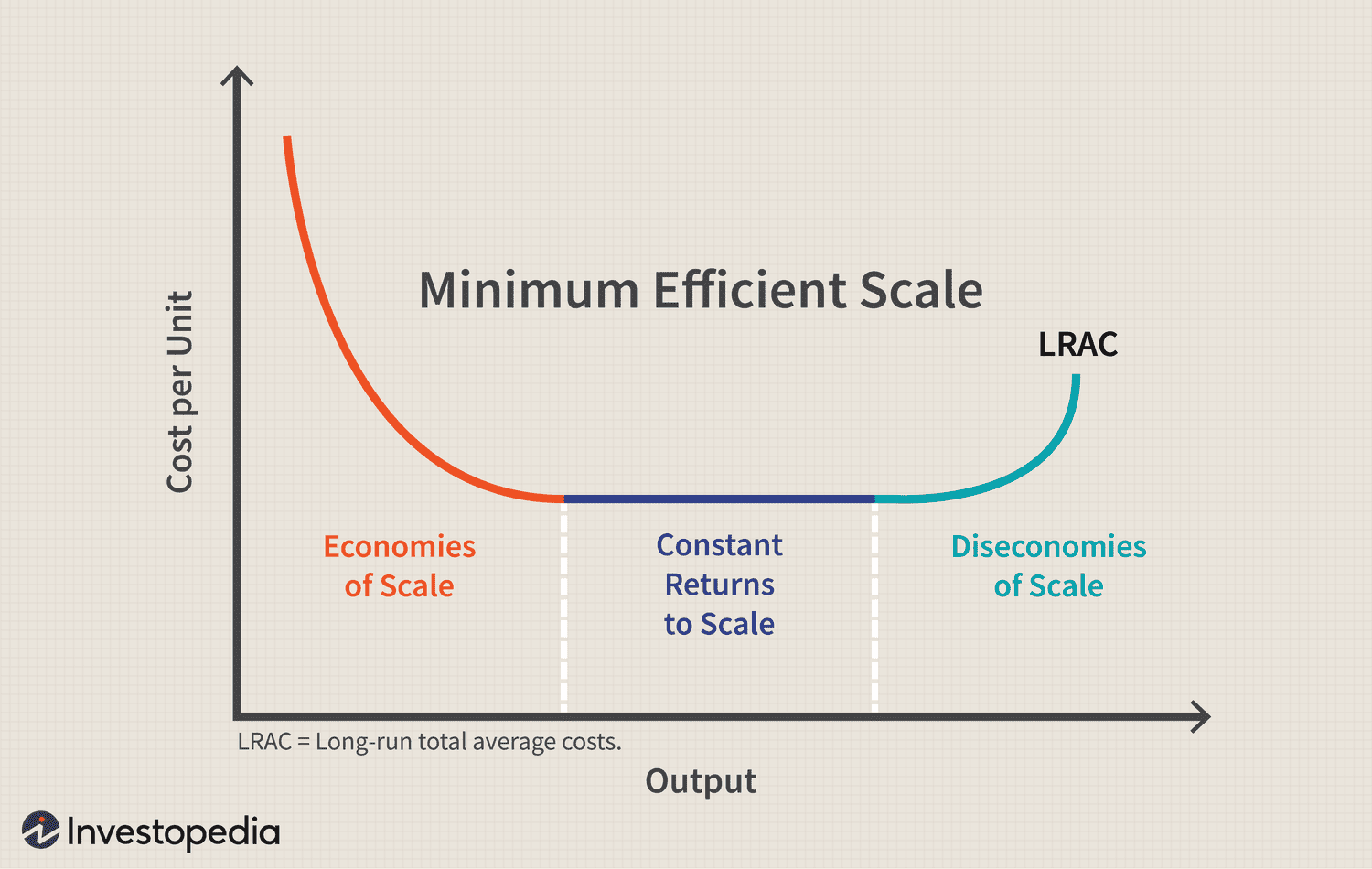
minimum effiency scale
the point at which a firm can produce its products for the lowest constant cost
accounting profit
revenue - explicit cost
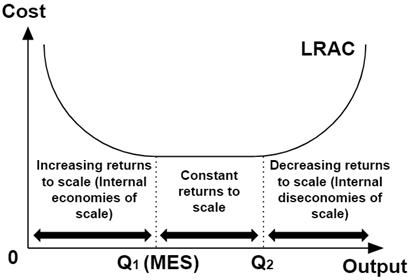
long run average total cost
the average total cost of production when all inputs can be varied, allowing firms to achieve economies of scale
accounting profit
total revenue (price times quantity) - explicit costs
economic profit
total revenue (price times quantity) - explicit costs - implicit costs
normal profit
economic profit is zero
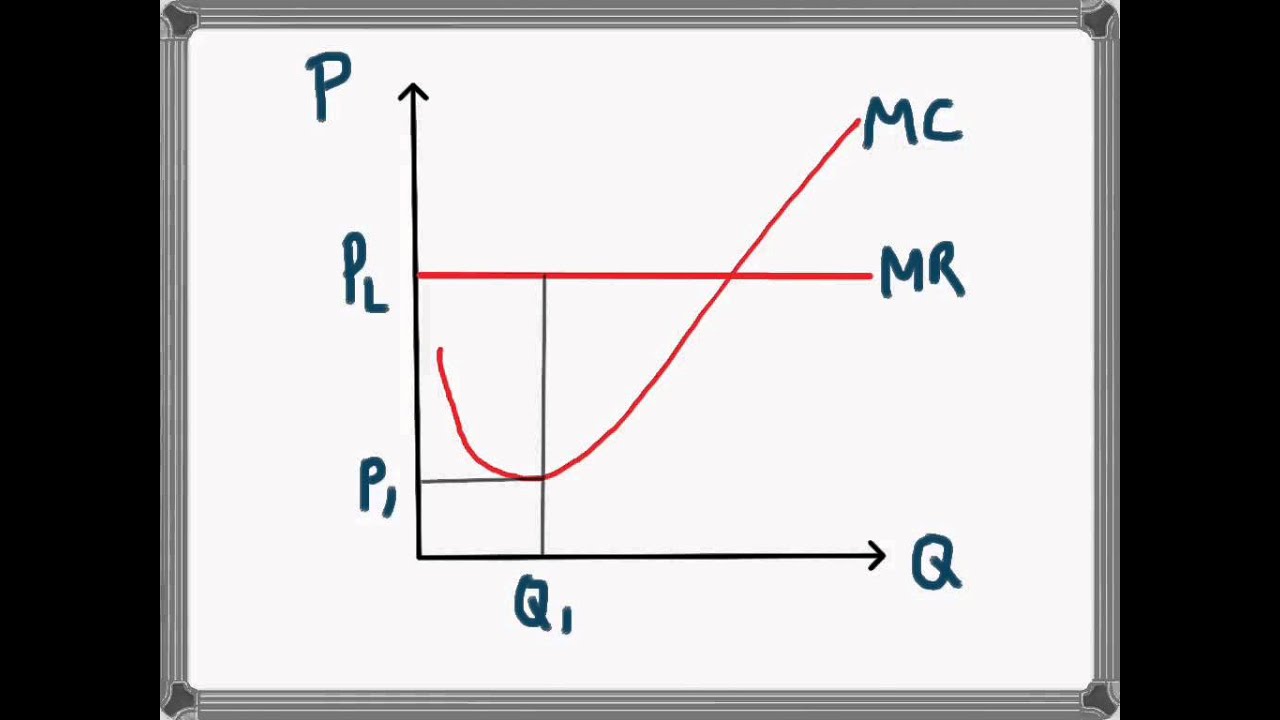
marginal revenue
TR/Q