structure and functions (transport in humans)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
why unicellulars don’t need exchange surfaces/transport systems
have a very large ___:__
have very large Sa:V ratio - distance from surface to centre is very smalll. diffusion/osmosis/active transport through cell membrane occur at a sufficient rate to meet the cell’s needs.
label amoeba with entry/exit of O2, CO2, H2O, nutrients and method to get them (UNOFFICIAL)
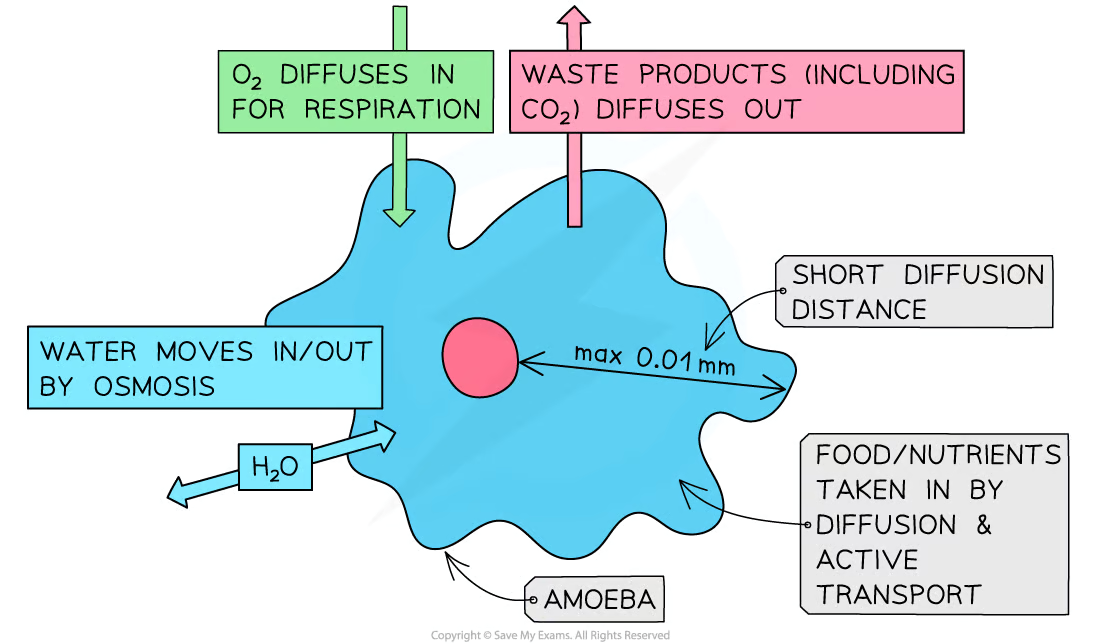
why multicellulars can’t rely on diffusion
distance between surface to centre is too large - diffusion to all cells would take too lon
so has to have transport systems to carry necessary substances
blood components + rough percentages
plasma - 55%
red blood cells - 44%
white blood cells + platelets - 1%
describe (structure) of red blood cell
biconcave disk, no nucleus (to make more space for haemoglobin)
describe (structure) of phagocyte (3)
multi-lobed nucleus, large, can change shape
describe (structure) of lymphocyte
large round nucleus, clear
describe (structure) of platelets
fragments of cells
describe (structure) of plasma
straw-coloured liquid
5 things in plasma - what they are, where they are going
CO2 - waste product of respiration, transported to lungs
Digested food/mineral ions - absorbed from small intestine, delivered to cells where necessary
Urea - waste substance produced from breakdown of proteins by LIVER, transported to kidneys
Hormones - chemical messengers from glands delivered to target tissues
Heat energy - from exothermic respiration reactions, transferred to cooler parts of body/where heat is lost
2 adaptations of red blood cells + whats inside
no nucleus → more space for haemoglobin
biconcave disc → large Sa:V ratio, max diffusion of oxygen in/out
haemoglobin → protein that binds to oxygen (to carry it around)
define pathogen
a microoorganism that can cause disease
phagocytosis process (3) sensitive _____ _______ detects ____…..
sensitive cell membrane detects chemicals produced by pathogen
when they encounter the pathogen they engulf it
and release digestive enzymes on it
phagocytosis is a ____ immune response
non-specific
antibodies are -shaped _____ that are ______ to _______ on ________ of pathogen
antibodies are Y-shaped PROTEINS that are COMPLEMENTARY to ANTIGENS on SURFACE of pathogen
define antigen UNOFFICIAL
protein on surface of cell (so that immune system can detect them)
define antitoxin
complementary/specific substance released to neutralise the toxins released (by bacteria)
lymphocytosis process (2)
antibodies attach to antigens and cause agglutination (clumping together) of pathogens
pathogens are slowed down, phagocytes are signalled to come and engulf pathogens
what is the general role of the immune system
to prevent pathogen from reproducing/to kill it
how does vaccination happen
Lymphocytes recognise the antigens in the bloodstream
The activated lymphocytes produce antibodies specific to the antigen encountered
Memory cells are produced from the lymphocytes
Memory cells and antibodies subsequently remain circulating in the blood stream
what effect does having memory cells have on the immune system response
faster, more effective, response made quicker
how do platelets make a clot/scab (2)
platelets release chemicals that form an insoluble mesh of fibrin across a wound
traps red blood cells, forms clot
importance of blood clots and scabs
blood clots - prevent significant blood loss
scab formation - prevents entry of microorganisms
what are coronary arteries
and removes what
supply cardiac muscle tissue with oxygenated blood, nutrients and remove waste products
what are valves for
to prevent backflow of blood
why does the left ventricle have a thicker wall than the right
also left - blood is ____ _____ pressure
left ventricle needs more muscle to pump blood to the whole body vs just the lungs
left - blood is under higher pressure
ventricle vs atrium
Atrium on top
Ventricle below
(think alphabet)
bicuspid vs tricuspid valve
Bicuspid - left ventricle (red oxygenated blood)
Tricuspid - right ventricle (blue deoxygenated blood)
flow of blood through heart (start with deoxy coming in)
deoxygenated blood flows through vena cava into right atrium.
goes through tricuspid valve into right ventricle.
pumped up through semilunar valve, through pulmonary artery, to the lungs.
.
oxygenated blood enters left atrium through pulmonary vein.
goes through bicuspid valve into left ventricle.
pumped up through semilunar valve, through aorta to rest of body
in which ventricle is blood under higher pressure
left ventricle higher pressure - blood up to aorta to whole body
why does heartbeat increase with exercise
vigorous exercise = muscles respire more, need more O2 supplied and more CO2 waste removed, so heart beats faster
how it happens in body that heart rate increases
exercise increases CO2 waste output
receptors in aorta/carotid notice high CO2 levels
send signal to the brain for heart to pump more frequently + with more force, esp. to get rid of waste
brief description of CHD
coronary heart disease
blockage of coronary arteries by fatty deposits (plaque) leads to increased risk of heart failure
what are the fatty deposits made of
plaque - cholesterol and fatty substances
coronary arteries blocked by _____ mean arteries _____ their _______. This means…
coronary arteries blocked by PLAQUE mean arteries LOSE their ELASTICITY. This means they can’t stretch to accommodate blood flow
reduced flow of blood to heart muscle = lack of oxygen = cell death/heart failure.
risk factors of CHD and explain (4)
obesity - extra weight puts strain on heart, can lead to type 2 diabetes which damages blood vessels
high blood pressure - increased force against artery walls, causes damage
smoking - chemicals cause plaque build up, high blood pressure
high cholesterol/lots of saturated fats in diet - increased/sped up build up of fatty deposits/plaque in arteries leads to blockages
what is the hepatic portal vein for UNOFFICIAL
vein that’s not really a vein because it doesn’t directly bring blood to heart
carries deoxygenated blood from gastrointestinal tract (intestines, gallbladder, pancreas etc.) to liver to be filtered and stuff
Artery | Vein | Capillary | |
|---|---|---|---|
pressure | |||
de/oxy blood | |||
lumen size | |||
wall features | |||
blood speed | |||
valves |
Artery | Vein | Capillary | |
|---|---|---|---|
pressure | high | low | low |
de/oxy blood | oxygenated (-pulmonary artery) | deoxygenated (- pulmonary vein) | both |
lumen size | narrow | large | very small |
wall features | thick, muscular, elastic fibres | thin walls | one-cell thick, ‘leaky' |
blood speed | fast | slow | slow |
valves | no | yes | no |
Artery | Vein | Capillary | |
|---|---|---|---|
function | |||
adaptations | 1 | 2 |
Artery | Vein | Capillary | |
|---|---|---|---|
function | carry oxygenated blood away form heart to body | carry deoxygenated blood to heart from body | allow diffusion of gas/nutrients from blood to body cells |
adaptations | thick walls with elastic fibres to withstand/acco- mmodate high pressure | valves prevent backflow of low pressure blood large lumen reduces resistance for low pressure blood | one-cell thick = short diffusion distance, easy/fast diffusion |