Topic 9: Transport In Animals
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What is the circulatory system?
An organ system made up of a pump, blood vessels, and valves to ensure one way flow of blood.
What are the different types of circulatory systems?
Open and closed Circulatory System/Single and Double Circulatory System
What is an example of a single circulatory system?
A fish.
What is an example of a double circulatory system?
A Mammal, reptile, or bird.
What is a single circulatory system?
A circulatory system where blood passes through the heart once in a single circuit.
What is a double circulatory system?
Circulatory system where blood passes through heart twice in a single circuit.
What are the two advantages of a double circulatory system over a single circulatory system?
Blood can be easily pumped faster around the body to ensure oxygen and nutrients are delivered to the cells faster and waste products are removed quickly from the body.
Their blood can be pumped around the body at a higher pressure, making delivering materials to the body more efficient since high pressure helps to push materials out of the blood vessels into the tissue.
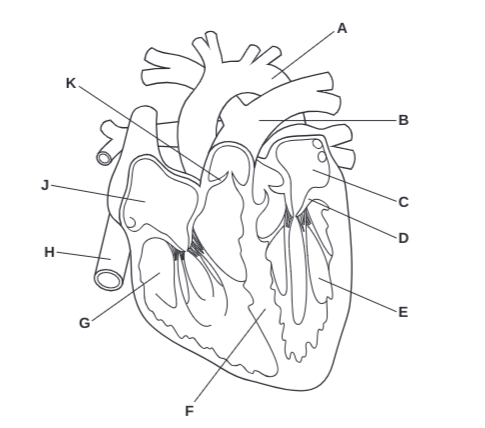
What is A?
Arota
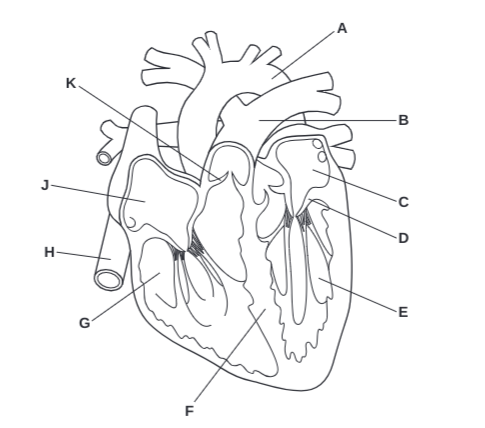
What is B?
Pulmonary Artery
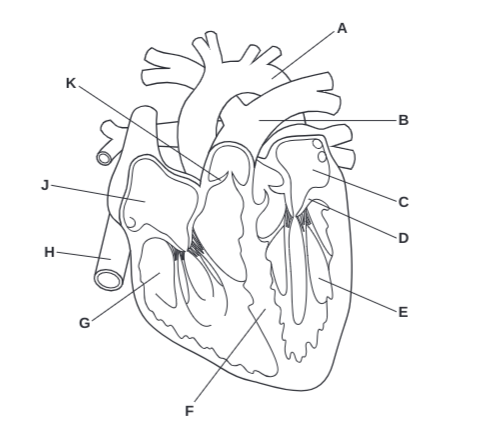
What is C?
Left Atrium
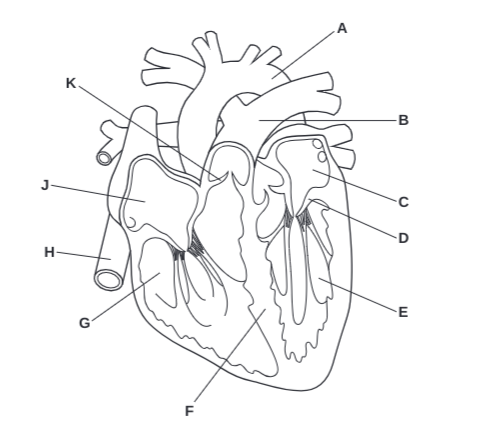
What is D?
Atrioventricular Valve
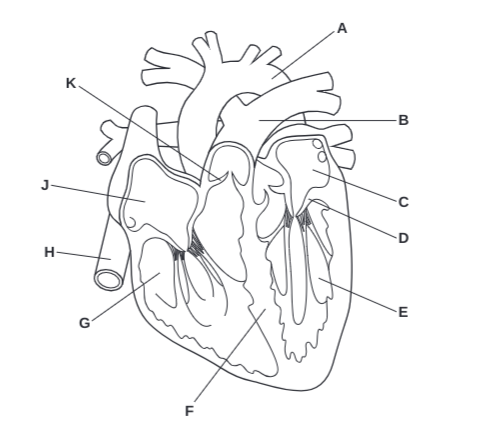
What is E?
Left Ventricle
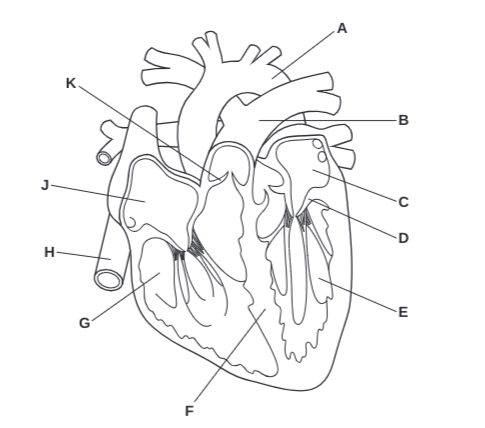
What is F?
Septum
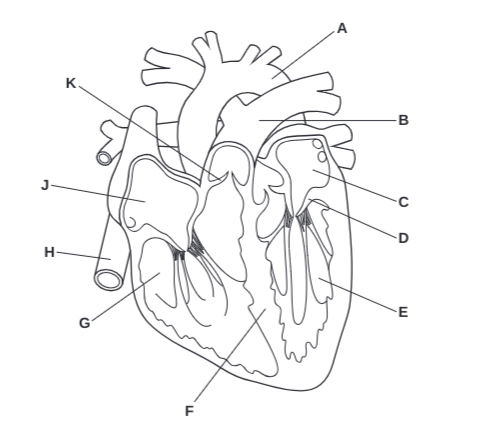
What is G?
Right Ventricle
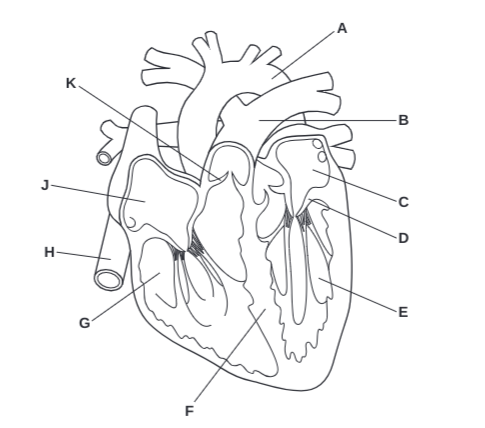
What is H?
Vena Cava
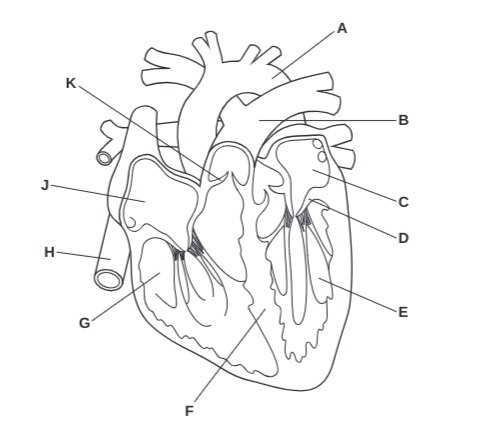
What is J?
Right Atrium
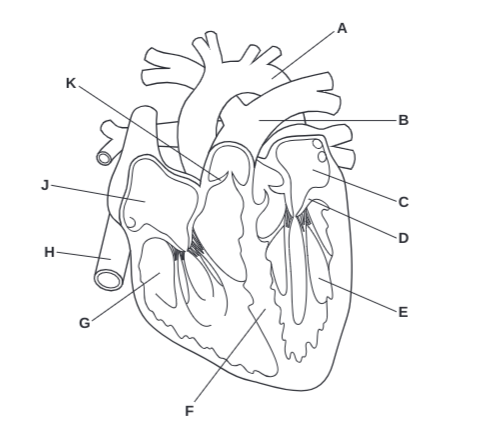
What is K?
Semilunar Valve
Define the septum.
The muscular wall between the left and the right side of the heart.
What is the septums’ function?
They separate the left and right sides of the heart, keeping oxygenated blood separate from deoxygenated blood.
What is the arteries function?
They carry blood away from the heart.
What is the function of the Arota?
They recieve oxygenated blood from the left ventricle and deliver it to the body organs.
What does the Arota have?
Semi-Lunar Valves, they prevent backflow of blood when the left ventricle relaxes.
What is the function of the Pulmonary Artery?
They transport deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
What does the Pulmonary Artery have?
Semi-Lunar Valves, they prevent blood from flowing back to the heart when the right ventricle relaxes.
What is the function of coronary arteries?
They carry oxygenated blood to the heart muscles to supply it with oxygen and other nutrients it needs to work properly
Define veins and their function.
They are thin walled vessels that take low pressure blood back towards the heart.
What is a pulmonary vein?
They carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left side of the heart. It is the only vein that carries oxygenated blood.
What is the Vena Cavas function?
They carry de-oxygenated from the rest of the body to the right atrium.
Why does the left ventricle have a thicker muscular wall than the right ventricle?
The right ventricle pumps blood to the pulmonary artery whilst the left ventricle pumps blood to the entire body, so it needs a thicker wall so it can pump blood at higher pressures.
Why are the ventricles thicker than the atria?
The ventricles pump blood out of the heart and all around the body, while the atria just recieves blood.
What is the function of valves?
They prevent the backflow of the blood when the heart contracts and relaxes.
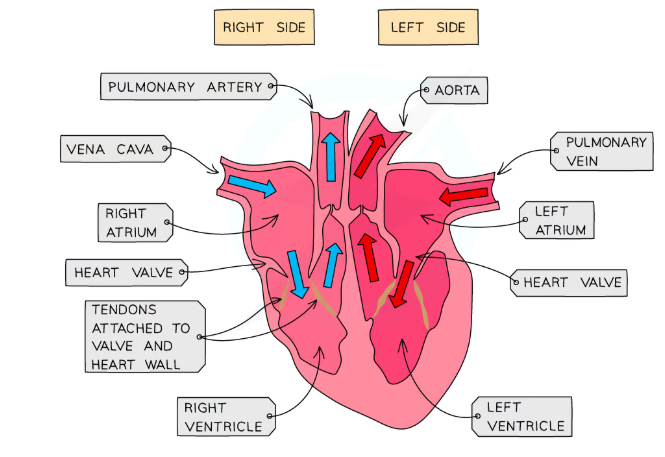
Where are the atrioventricular valves located?
Between the atrium and ventricle.
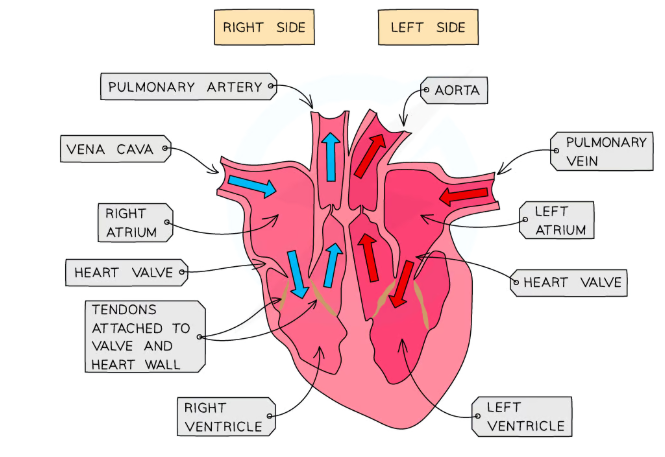
Where are the tricuspid valve located?
Located between the right atrium and the right ventricle, it has three cusps (leaflets).
Where are the bicupsid/mitral valves located?
Located between the left atrium and the left ventricle, it has two cusps.
Why do the atrioventricular valves close when the ventricles contract?
To prevent the blood from flowing back to the atria.
What is the function of right atrium?
They receive deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle.
What is the function of left atrium?
They receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it into the left ventricle.
What is the function of the right ventricle?
They receive deoxygenated blood from the atrium and pumps it to the lungs.
What is the function of left ventricle?
Receives oxygenated blood from the atrium and pumps it to the body.
What is the function of semilunar valves?
They allow blood to flow from the ventricles to the arteries, but stop it from going the other way.
What is the function of the atrioventricular valve?
It allows blood to flow from the atria to the ventricle but prevent it from going the other way.
Blood is pumped away from the heart in the...
Arteries
What is the structure of arteries?
They have a thick outer wall, narrow lumen, and a thick layer of muscles and elastic fibres.
Blood is pumped to the heart in the...
Veins
What is the structure of the veins?
They gave a thin outer wall, large lumen, and a thin layer of muscles and elastic fibres.
Define capillaries.
A tiny, one-cell thick blood vessel, that takes blood close the body cells.
What are some ways that heart activity can be monitored?
ECG, Pulse rate, Sound of valves closing
Explain the effect of physical activity on heart rate.
Heart rate increases so enough blood is pumped to your muscles for increased respiration. Muscle cells respire anaerobically and build up lactic acid/ an oxygen debt which is repaid after physical activity, causing faster and deeper breathing.
What is the Coronary Heart Disease?
A disease that results from the blockage of the coronary arteries.
What are some risks that causes CHD?
Poor diet, Stress, Lack of exercise, Smoking, Genetic predisposition, Age, Sex
What are some ways the risk of CHD can be reduced?
Stop smoking, reduce fats in diet, and exercise regularly.
What are some adaptations of capillaries?
They are one cell thick to reduce diffusion distance of materials in & out of the capillaries
A narrow lumen to increase pressure of the blood within the capillaries to ensure substances are forced out of the blood.
Contains gaps/pores on the surface to enable nutrients to leak out to supply nutrients to the cell.
They are many to increase the surface area for exchange of materials.
List the components of the blood.
Red blood cells, White blood cells, Blood Plasma, and Blood Platelets.
What are white blood cells and their function?
Large cells that have a nucleus, which help fight against pathogens.
What are red blood cells and their function?
Biconcave discs with no nucleus that contain haemoglobin. They transport oxygen around the body.
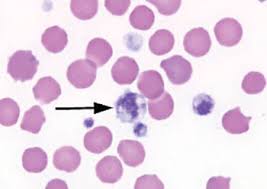
What are blood paletes and their function?
Tiny cell fragments present in blood that help with blood clotting to prevent excessive blood loss in case of a cut of a blood vessel & prevent entry of pathogens into the body.
What is blood plasma and their function?
The liquid part of blood, they help with the transportation of nutrients, mineral ions, water, and 95% of carbon dioxide, urea, hormones around the body.
Explain the process of blood clotting?
When blood cell is broken, platelets arrive to stop bleeding.
Platelets release a substance that cause fibrinogen to turn to fibrin.
Fibrin is mesh-like and traps blood cells to seal the wound.
Platelets stick together to form clumps.
Explain the role of blood clotting?
They prevent significant blood loss and entry of infection-causing microorganisms.
What is a pathogen?
A disease causing organism.
What are phagocytes?
White blood cells that destroy pathogens through phagocytosis.
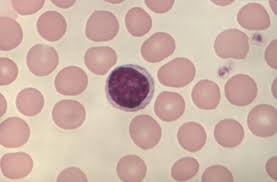
What are lymphocytes?
White blood cells that secrete antibodies.
What is phagocytosis?
Taking bacteria or other small structures into a cells cytoplasm and digesting them with enzymes.
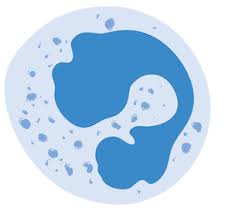
What do phagocytes look like?
They have a lobed nucleus to enable it to squeeze out of blood vessels and back.
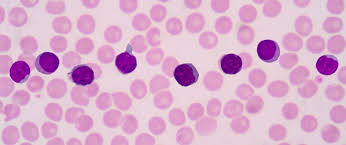
What do lymphocytes look like?
They have a very large nucleus that fills almost the whole cell to help it make antibodies.
Describe the way of the heart.
Deoxygenated blood from body --> right atrium -tricuspid valve-> right ventricle -semilunar valve --> pulmonary artery --> lungs --> pulmonary vein —>left atrium —> Bicuspid valve-> left ventricle -semilunar valve-> aorta --> oxygenated blood to body
Why do arteries have a thick outer wall and thick layer of muscle and elastic tissue?
They need strong walls to withstand the high pressure of blood flowing through them.
They need elastic tissue to help the blood flow more smoothly as the walls will stretch and recoil with the force of it.
Why do capillaries have a narrow lumen and thin, one cell thick wall?
So substances can get in and out very easily and to help blood come into close contact with body cells & tissues.
Why do veins have valves, wide lumen, thin walls, and weak muscle & elastic tissue?
The pressure of the blood has been lost, a wide lumen provides less resistance to blood flow, and valves prevent backflow.
What are the blood vessels of the kidney?
Renal Artery & Renal Vein
What are the blood vessels of the liver?
Hepatic Artery & Hepatic Vein
What is the function of the hepatic artery?
It supplies oxygenated blood to the liver.
What is the function of the hepatic vein?
They carry blood away from the liver.
What are the main blood vessels of the heart?
Vena Cava, Arota, Pulmonary Artery, Pulmonary Vein
What are the main blood vessels of the lungs?
Pulmonary Artery & Pulmonary Vein
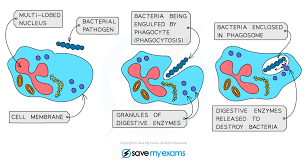
What is the process of phagocytosis?
A phagocyte moves toward a group of bacteria, and flows around them.
The phagocyte’s cell membrane fuses together, enclosing the bacteria in a vacuole.
Enzymes are secreted into the vacuole and digest the bacteria.
Soluble substances diffuse from the vacuole into phagocyte’s cytoplasm.
From where does the atria recieve blood?
The left atrium recieves blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins.
The right atrium recieves blood from the rest of the body through the Vena Cava
Define atria.
Thin-wall chambers at the top of the heart, which recieves blood.
Define ventricle.
Thick-walled chambers at the base of the heart, which pump out blood.
What are the 3 main types of blood vessels?
Arteries, Capillaries, Veins
Define artery.
A thick walled vessel that takes high pressure blood away from the heart.
What is the function of capillaries?
To take nutrients, oxygen, and other materials to all cells in the body, and to take away waste materials.
What role does haemoglobin play?
It is a protein, containing iron, that readily combines with oxygen when the oxygen concentration is high.
What is the function of the hepatic portal vein?
They bring blood from the digestive system, so that the liver can process the food which has been absorbed, before it travels to other parts of the body.