Pitt Intro to Africana Studies - AFRCNA 0031 - Midterm Study Guide
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
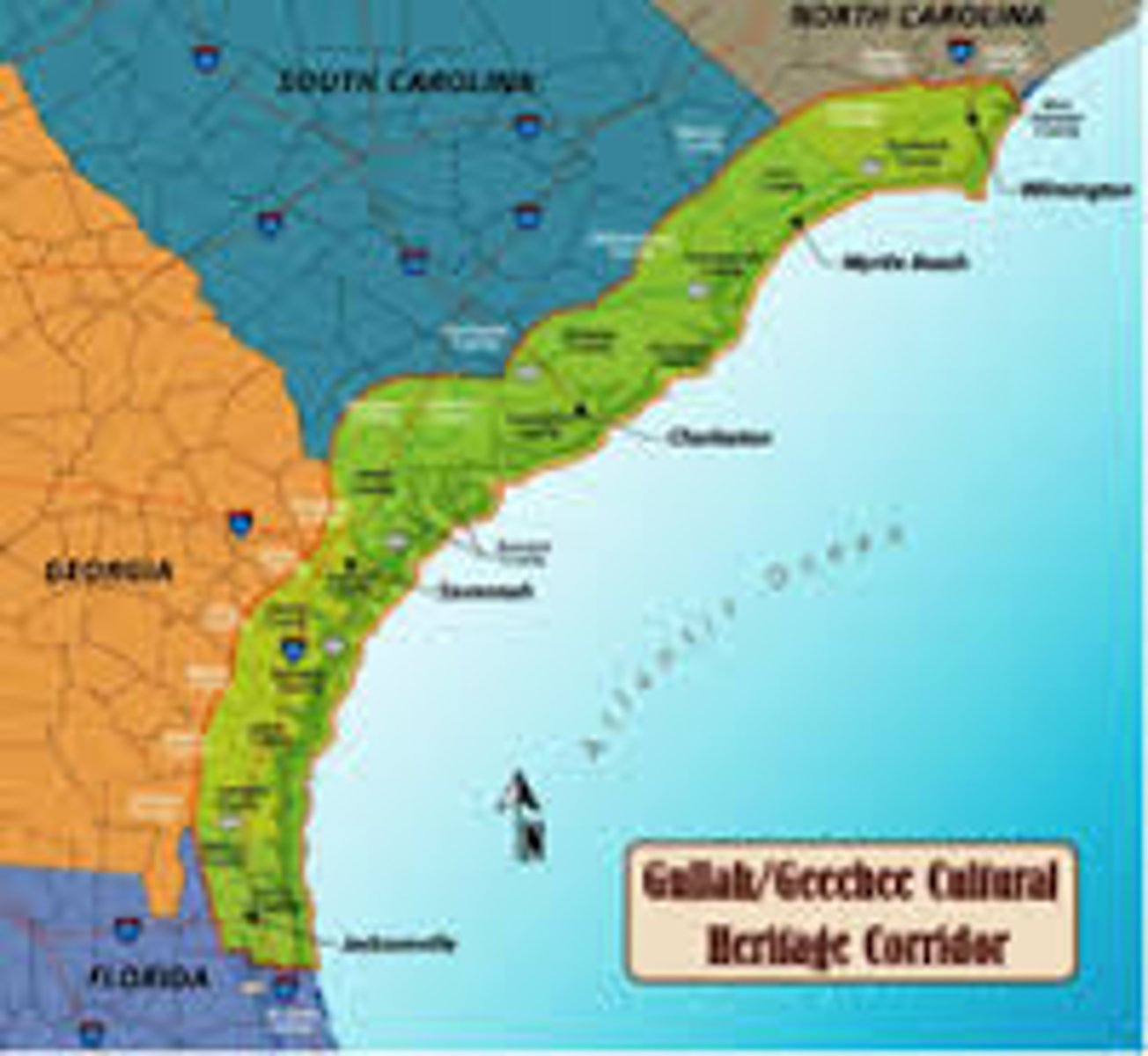
South Carolina/Georgia Sea Islands
Gullah (a African/American creole language) is spoken here.
Africanization
the African influence on cross-fertilization of cultures
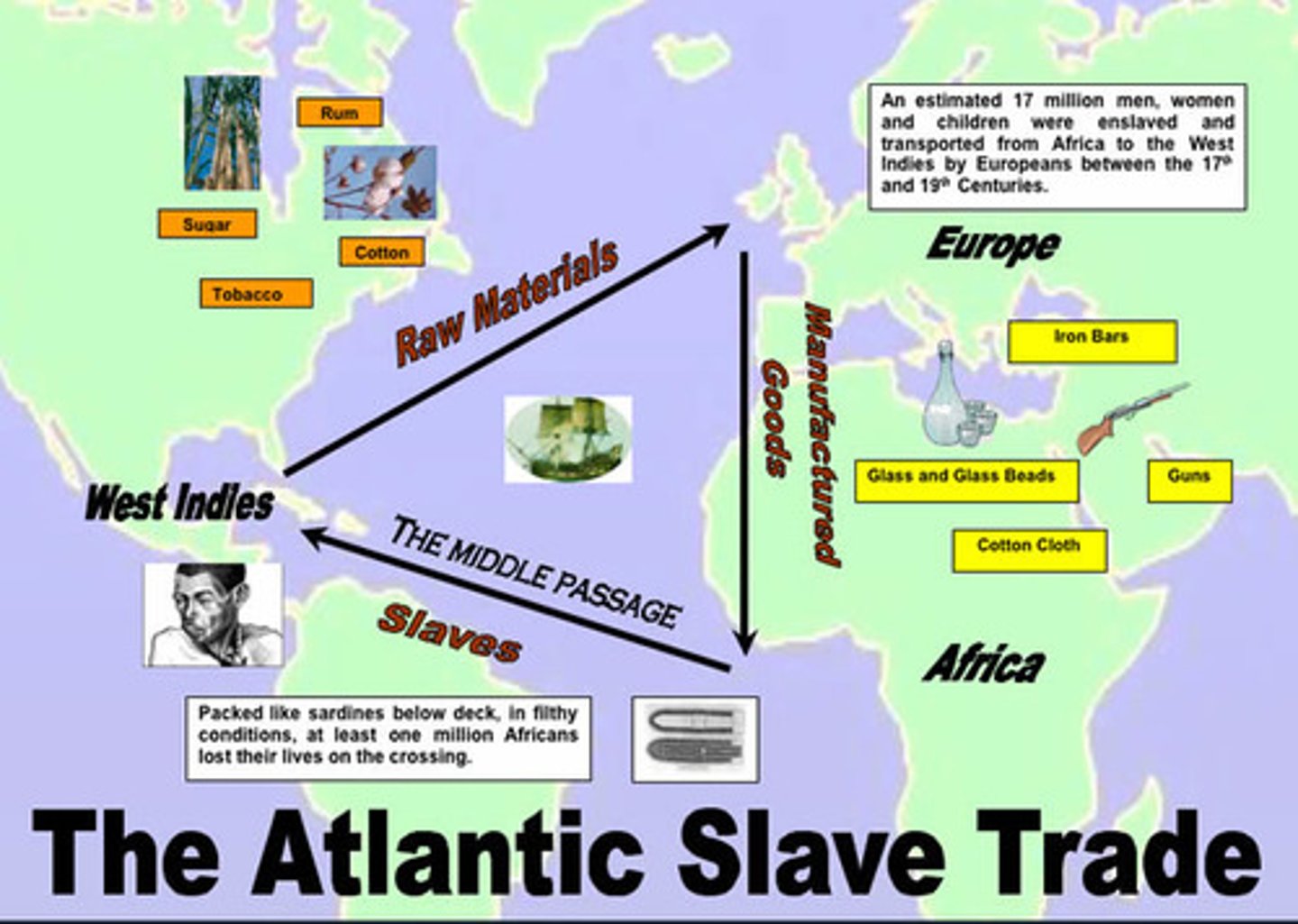
Triangular Trade
A three way system of trade during 1600-1800s Africa sent slaves to America, America sent Raw Materials to Europe, and Europe sent Guns and Rum to Africa
Maroon
A slave who ran away from his or her master. Often a member of a community of runaway slaves in the West Indies and South America.

Haitian Revolution
First successful slave revolt

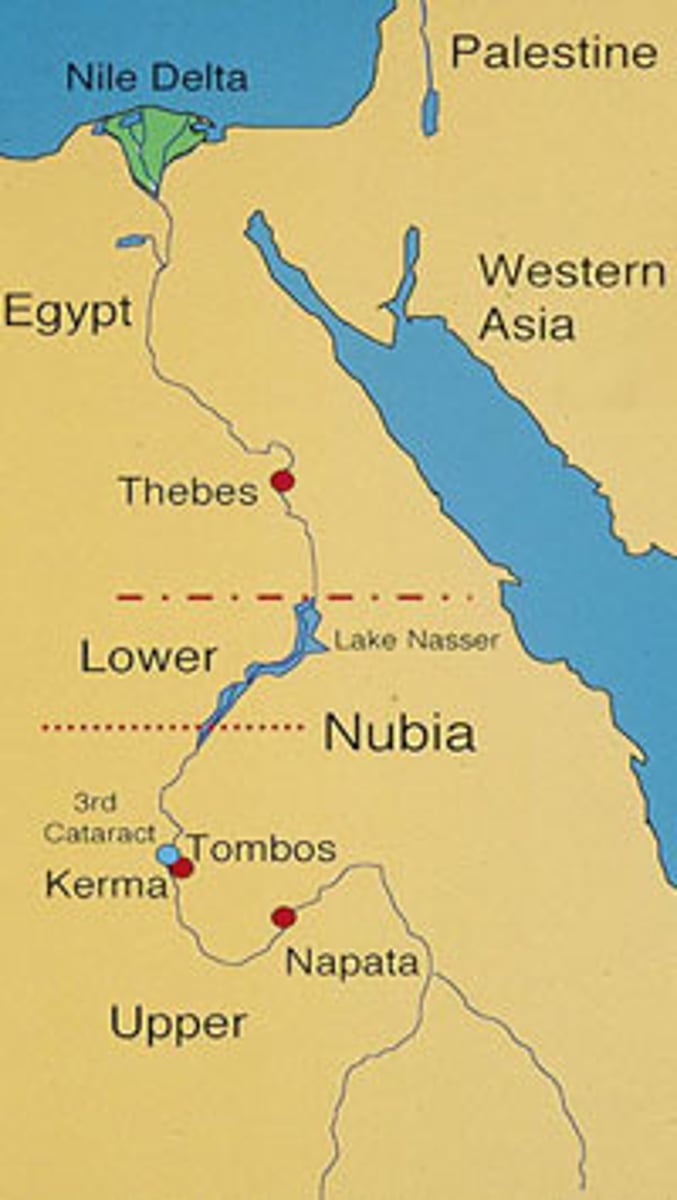
Nubia
A civilization to the south of Egypt in the Nile Valley, noted for development of an alphabetic writing system and a major iron working industry by 500 BCE
Racialization of Slavery
how slavery came to be associated with Africans.
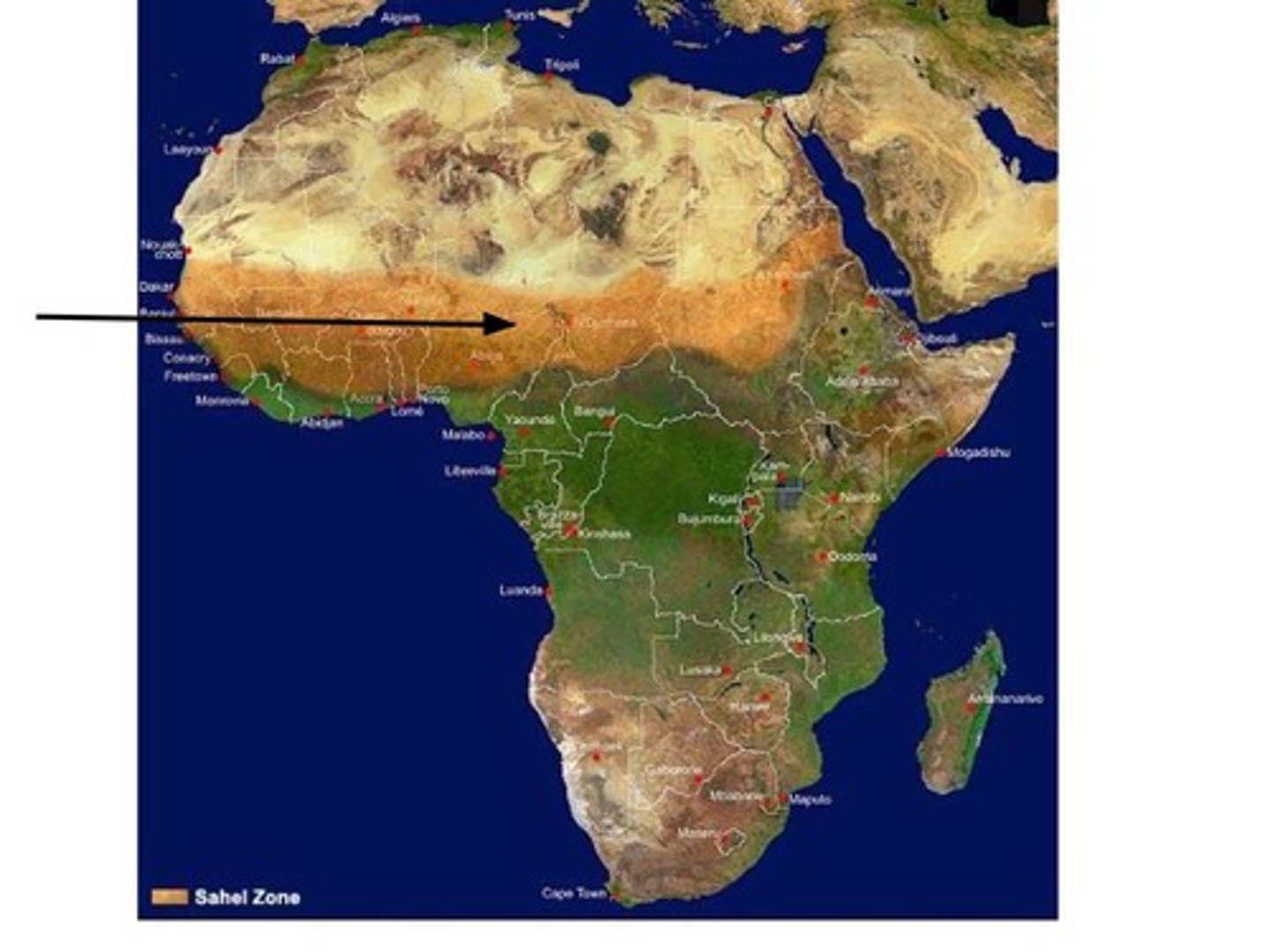
Sahel
Belt south of the Sahara where it transitions into savanna across central Africa. It means literally 'coastland' in Arabic.
griot
A West African storyteller

trans-Saharan trade
route across the sahara desert. Major trade route that traded for gold and salt, created caravan routes, economic benefit for controlling dessert, camels played a huge role in the trading. Made empires like Mali very wealthy.

Stono Rebellion
The most serious slave rebellion in the the colonial period which occurred in 1739 in South Carolina. 100 African Americans rose up, got weapons and killed several whites then tried to escape to S. Florida. The uprising was crushed and the participants executed. The main form of rebellion was running away, though there was no where to go.

Middle Passage
A voyage that brought enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to North America and the West Indies
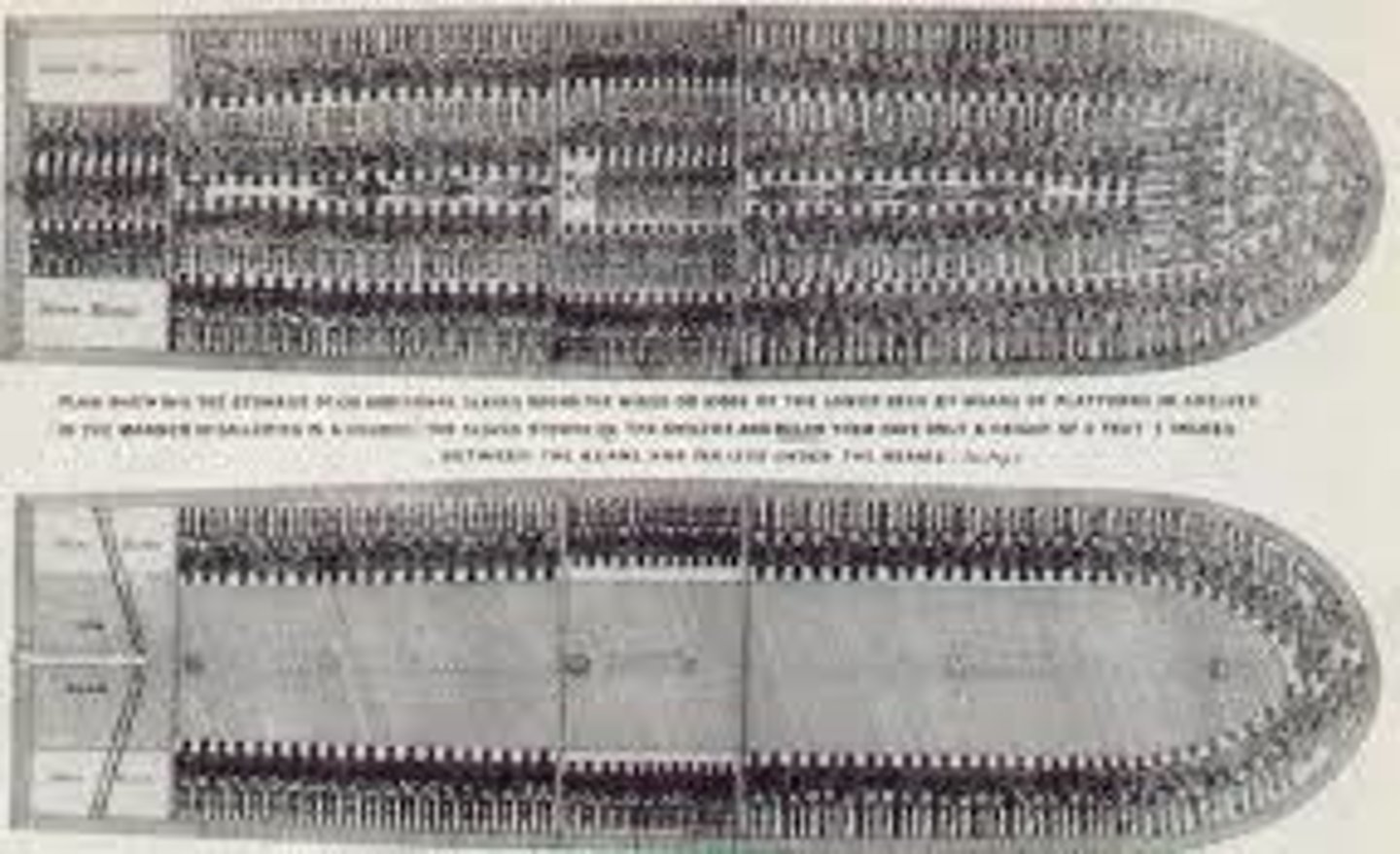
Jamestown
The first permanent English settlement in North America, found in East Virginia in 1634
Public transcript
open, public interactions between dominators and oppressed
Hidden transcript
hidden resistance to dominance, by the oppressed
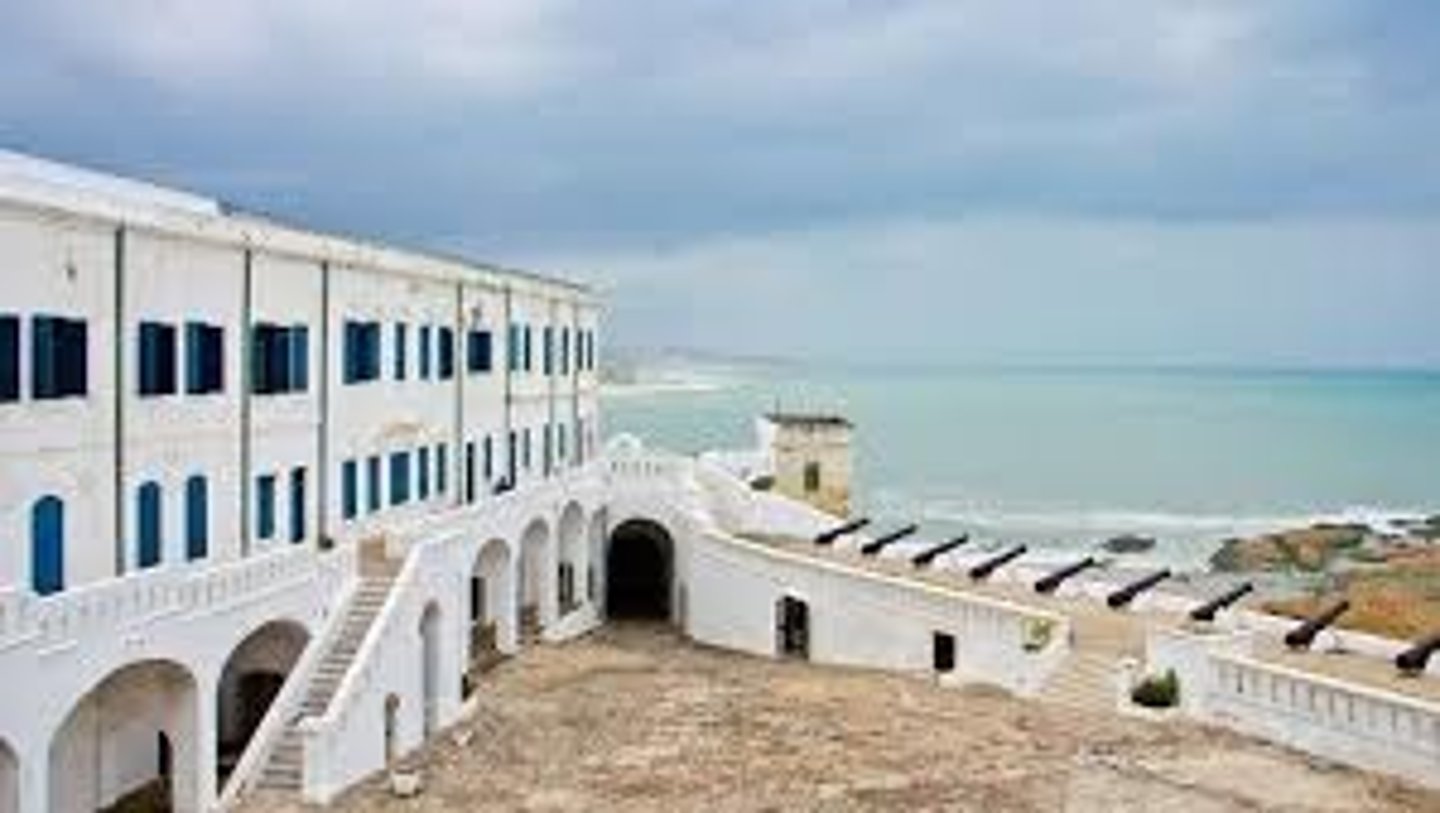
Cape Coast
Castle in Ghana was the Main British hub of the transatlantic slave trade in West Africa - had the "door of no return" - President Obama visited here.

Timbuktu
Mali trading city that became a center of wealth and learning

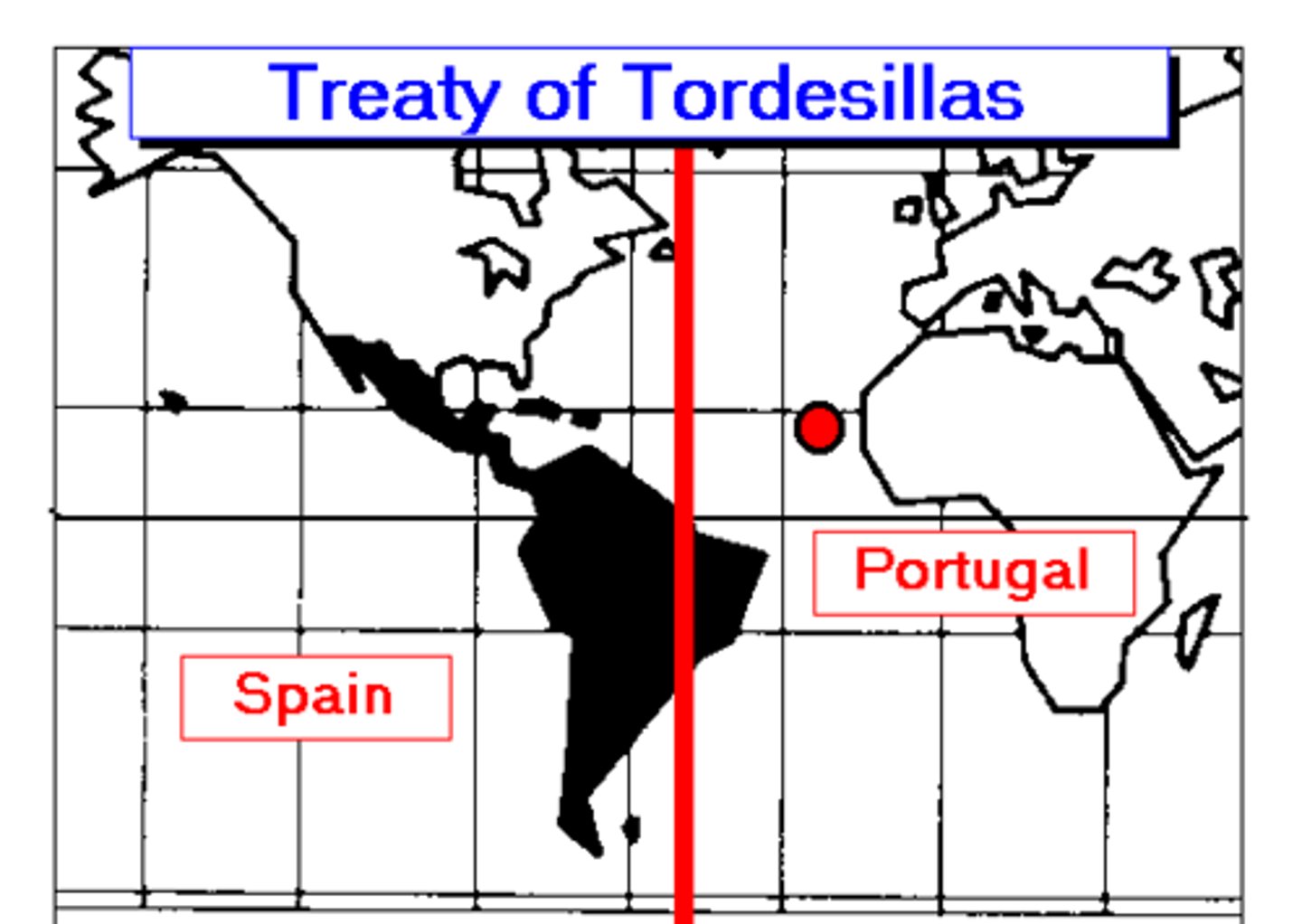
1494
When was the Treaty of Tordesillas signed?
When did the First enslaved Africans arrive in the British/English American Colonies (Virginia)
1619
When was Nat Turner's Rebellion?
1831
When was the Haitian Revolution?
1791-1804
Missouri vs. Celia
Celia, a slave girl, killed her master after he tried to rape her. Celia was convicted in this trial of murder and was condemned to death.
Siete Partidas
Spanish law that recognized slavery as legal

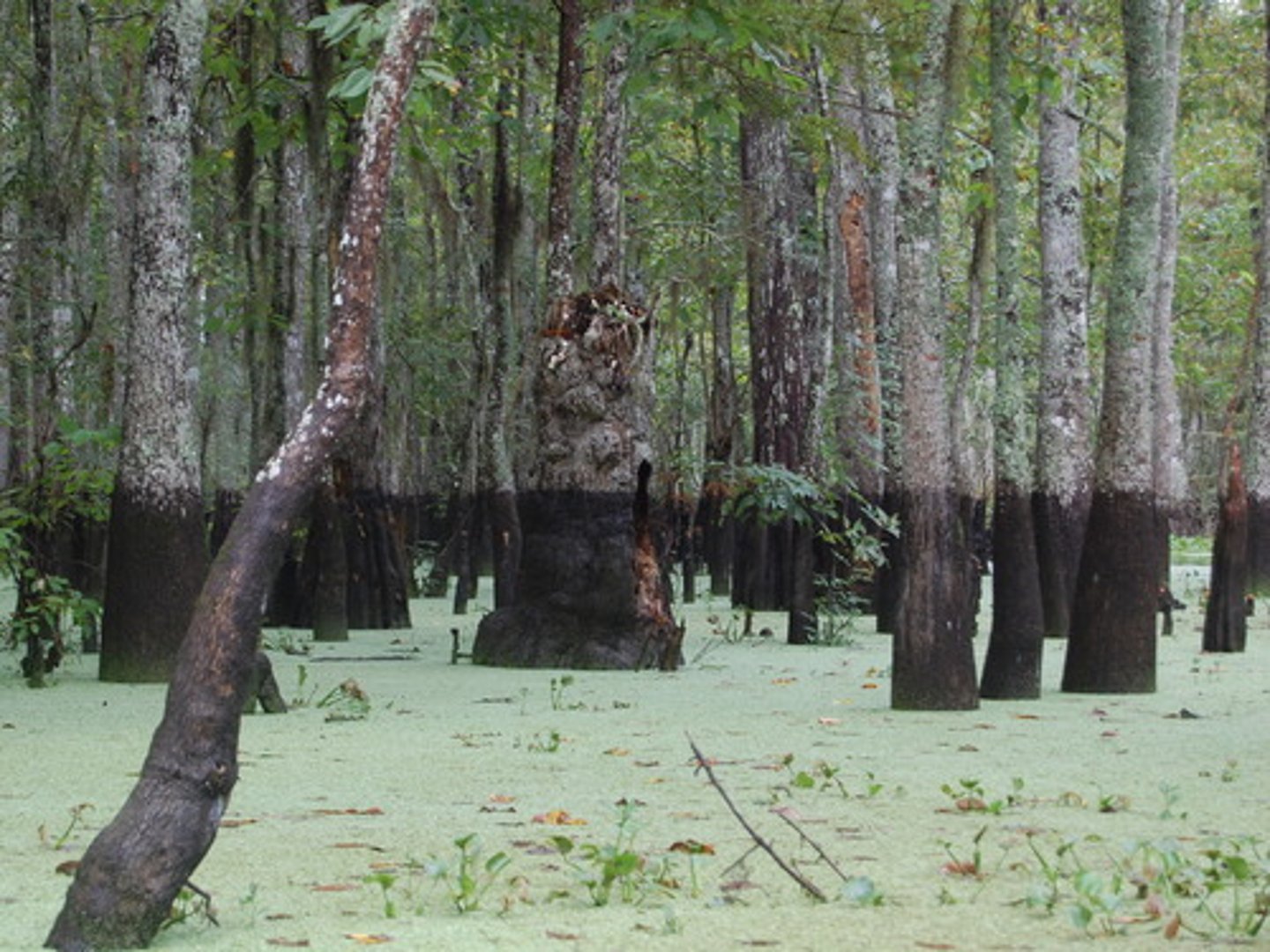
Great Dismal Swamp
A heavily forested area on the Virginia-North Carolina border that served as a refuge for fugitive slaves during the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries.

Plantation Monocrop Agriculture
A system in which one crop was harvested in a very large scale. Depletes the soil of nutrients.
Also, imported many African slaves to areas that were majority white, changed the population balance towards Africans (happened in Barbados)

Creole
Born in the Americas (a term that was used to refer to slaves, but also at times, to whites born in the Americas)

Treaty of Tordesillas
A 1494 agreement between Portugal and Spain, declaring that newly discovered lands to the west of an imaginary line in the Atlantic Ocean would belong to Spain and newly discovered lands to the east of the line would belong to Portugal.
Sex ratio
Lot more men than women in the Carribbean - Sugar cane harvesting/processing was very hard work, but the opposite in the Americas.
Mansa Musa
Emperor of the kingdom of Mali in Africa. He made a famous pilgrimage to Mecca and established trade routes to the Middle East.

sugar
Came from the juice of the sugar cane.
Led to the first monocrop plantations in the Americas. (Brazil, Caribbean)

Resistance
Slaves resisted their owners by running away, refusing to work, etc.
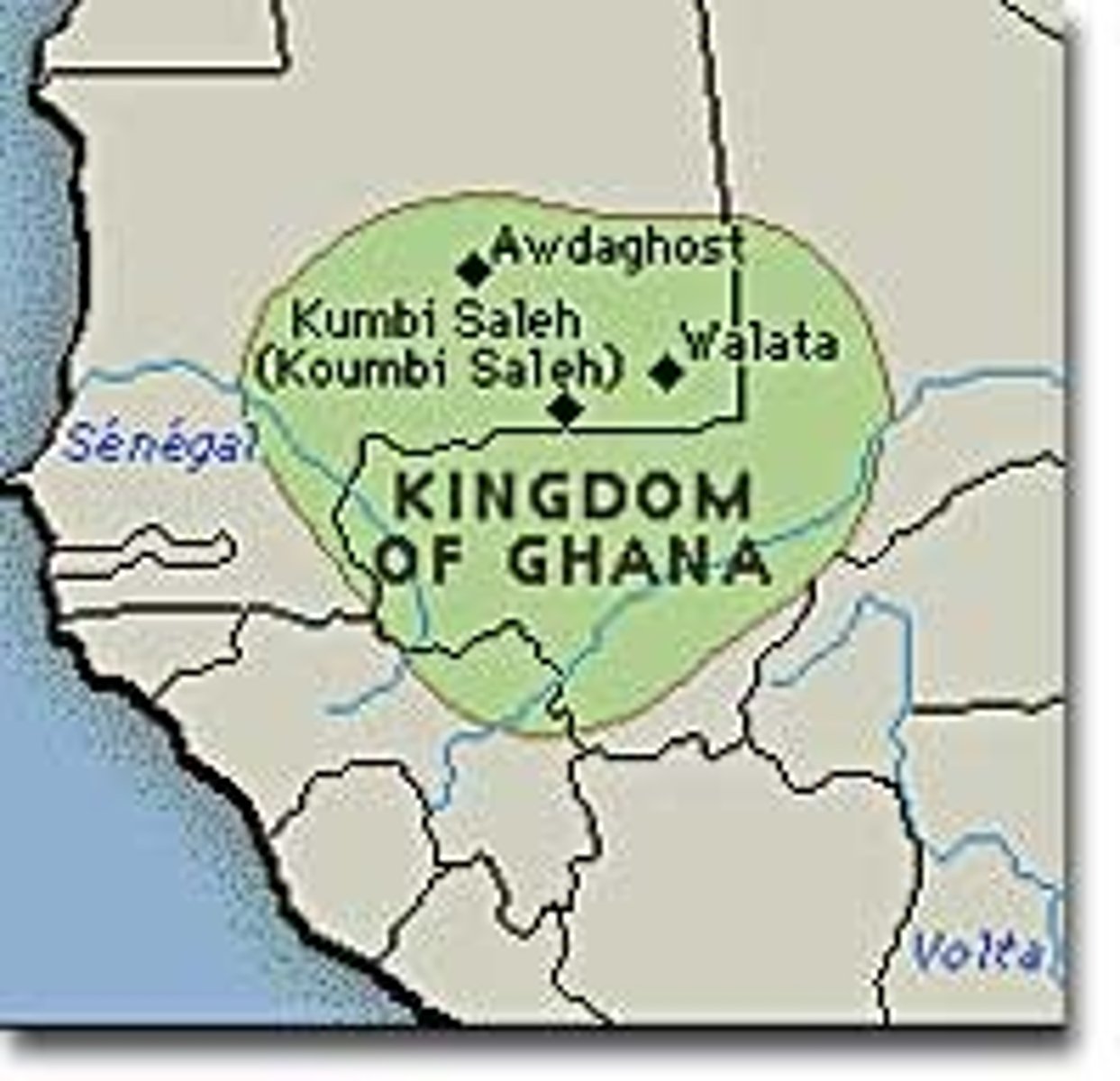
Kingdom of Ghana
First of the great medieval trading empires of western Africa (7th - 13th century). Located in what is now southeastern Mauritania and part of Mali, it acted as intermediary between Arab and Berber salt traders to the north and gold and ivory producers to the south.
Sundiata
the founder of Mali empire. He crushed his enemies and won control of the gold trade routes

Kingdom of Mali
a huge territorial empire that flourished in west Africa during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries. Its capital was Timbuktu, which became a center of Islamic learning (see Islam). The empire controlled trade routes that stretched from the edge of the Sahara in the north to forests in the south and that carried gold and other luxuries
Africanisms
cultural traits that continued into the New World.
Nat Turner
Slave in Virginia who started a slave rebellion in 1831 believing he was receiving signs from God His rebellion was the largest sign of black resistance to slavery in America and led the state legislature of Virginia to a policy that said no one could question slavery.

Asientos
large contracts for purchase of enslaved persons in Spanish America
Tobacco
Cash crop that made a profit and saved Jamestown. Also was the main cash crop in British American colonies before cotton.

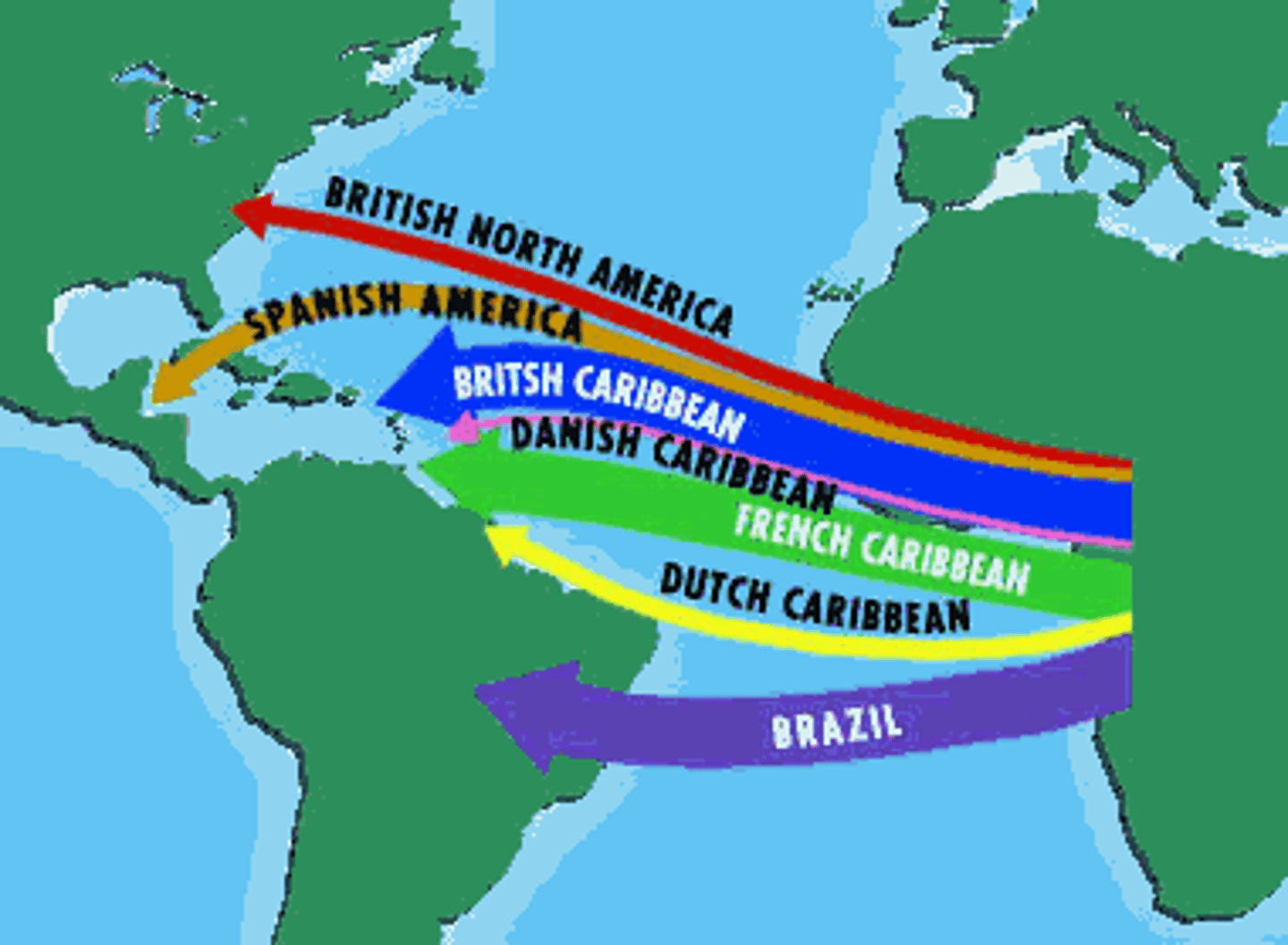
Trans-Atlantic Trade
Trade in enslaved Africans from Africa to Europe and the Americas
The largest forced migration in HUMAN HISTORY.
Harriet Jacobs
Wrote Incidents in the Life of a Slave Girl. Hid in an attic for 7 years to escape her master.

Candomble
African religious ideas and practices in Brazil, particularly among the Yoruba people. Mixed Catholicism and Yoruba religion.

Orishas
The hundreds of various Yoruba deities who are the main objects of ritual attention
Oxala - son of Olorun (High God)
Xango - thunder (war)
Oxossi (green) - the hunt (St. George/St. Michael) (warrior)
Oxum (yellow) - fresh water (goddess of love)
Yemanja (light blue) - salt water (equated to Virgin Mary)
Ogun (blue) - iron (war)
Eshu/Elegba (red/black) - messenger

David Walker
He was a black abolitionist who called for the immediate emancipation of slaves. He wrote the "Appeal to the Colored Citizens of the World." It called for a bloody end to white supremacy. He believed that the only way to end slavery was for slaves to physically revolt.

Frederick Douglass
(1817-1895) American abolitionist and writer, he escaped slavery and became a leading African American spokesman and writer. He published his biography, The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, and founded the abolitionist newspaper, the North Star.

Quilombo
escaped slave settlements (Maroon community) in Brazil.

Code Noir
a set of laws governing the conduct of the slaves during the French colonial period

Kongo cosmology
overarching conceptions of the place of human beings in the general scheme of existence and the forces engaged in the generation of that scheme
Kongo universe: two worlds
world of the living,
world of the dead
separated by a large body of water traditionally called Kalunga
ongo yowa (cross) as a cosmogram
Land of living & dead, separated by Kalunga
Belief in soul as indestructible and moving in a cycle, similar to movement of sun
Each cycle of existence more remote than the last (spiral universe)
zambi Mpungu (God)
Ancestors (bakulu)
Ghosts (min'kuyu)
Local Territorial Spirits (bisimbi)
Spiritual objects/Charms (min'kisi)
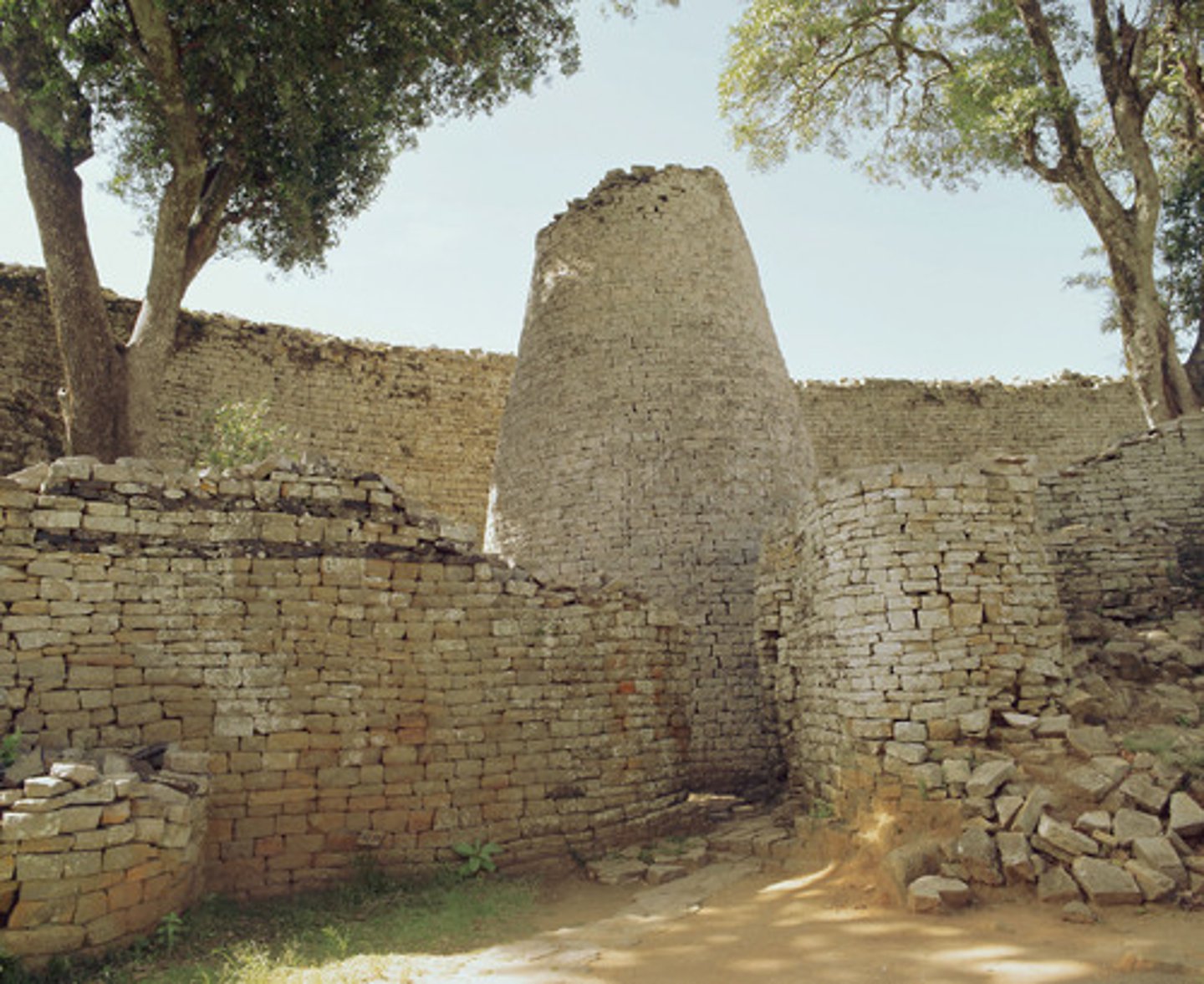
Great Zimbabwe
City, now in ruins (in the modern African country of Zimbabwe), whose many stone structures were built between about 1250 and 1450, when it was a trading center and the capital of a large state.
Also, ancestors of the Shona people
Europeans tried to discredit them by saying that Black people can't build with stone

Development of African-American Culture
The Herskovits-Frazier debate - Frazier argued that enslavement had stripped Afro-Americans of their African cultural heritage, rendering African Americans a kind of black slate in their new environment which developed into African-American culture. Herskovits, on the other hand, said that African culture continued to influence African-American culture.
Nathan Hare
Founded the first Black Studies department at San Francisco State University in 1968.

San Francisco State
First Black Studies department in the U.S.
Black students boycotted classes and picketed classroom buildings until the Black Studies Department was established.
Divination
foretelling the future by means of magic
Ifa divination (prominent in Brazil and Africa) - 16 separate nuts that are cast
For each pattern cast the baba-Iawo (father of mysteries) makes a particular mark on a tray covered in wooden dust
Each mark corresponds to an odu (saying) of which there are 256
Each odu relates to a story or myth that points to the answer to the client's problem

Diaspora
A dispersion of people from their homeland
Palmares
Kingdom of runaway slaves with a population of 8000 to 10,000 people; located in Brazil during the 17th century; leadership was Angolan.
Atlantic Islands (off African coast)
became the starting point for the plantation complex. The Portuguese first grew sugar cane here.
Cotton Gin
Changed the main cash crop in the south to cotton, Increased the ability to grow all types of cotton throughout the South.
Cotton became very profitable -> expansion of slavery in the South.

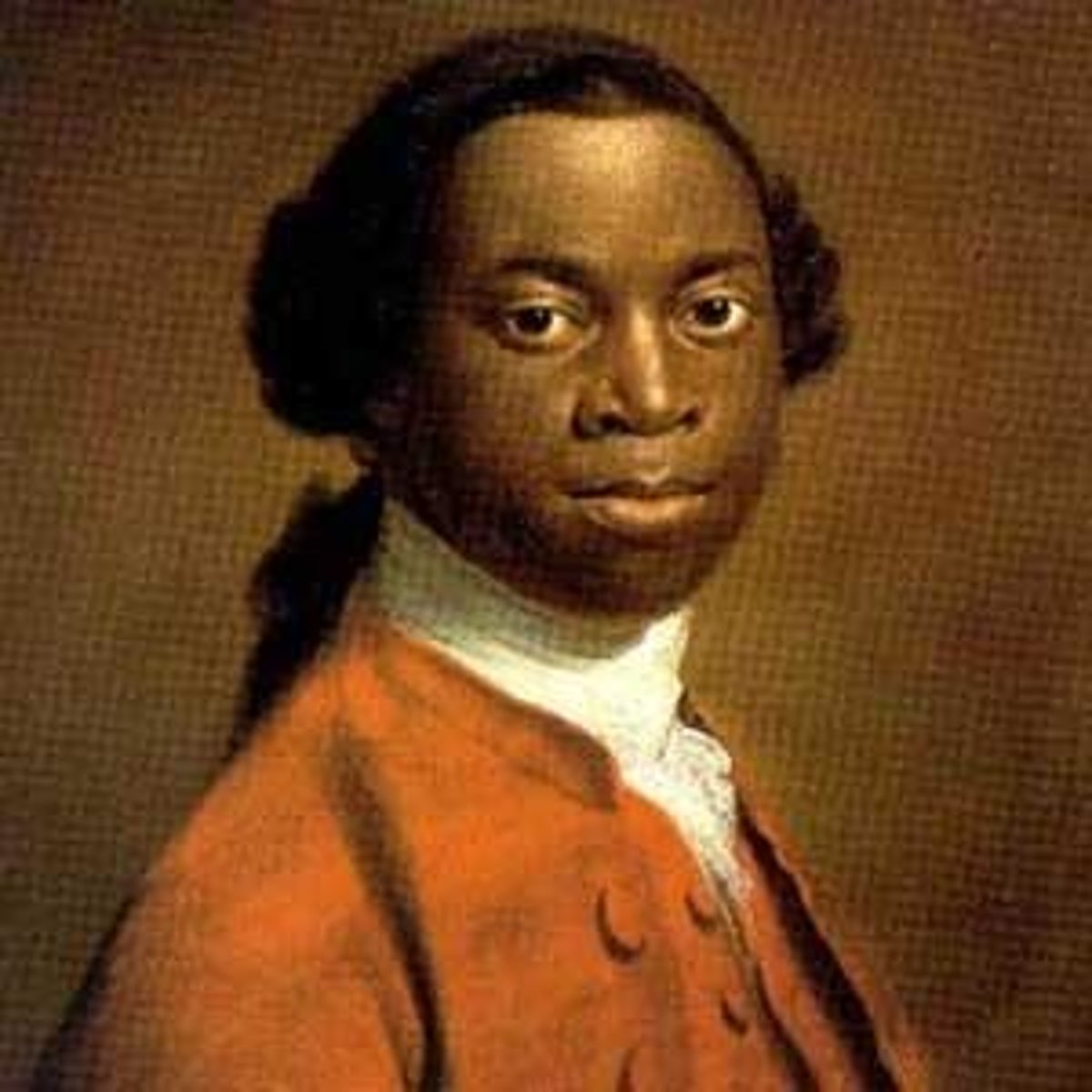
Olaudah Equiano/Gustavus Vassa
(1745-1797) African who was sold into slavery and bought his way out-kidnapped as a boy to be sold into slavery. Worked on many ships, but later sold to slave brokers who sent him to the Caribbean-from there a white colonist bought him and he eventually bought his way out of slavery-he went to England to live and published a book about slavery and his experiences-his message was widespread and helped to inspire the abolition of slavery - also wrote the first slave narrative.

Toussaint L'Ouverture
Was an important leader of the Haïtian Revolution and the first leader of a free Haiti; in a long struggle again the institution of slavery, he led the blacks to victory over the whites and free coloreds and secured native control over the colony in 1797, calling himself a dictator.

Cotton
number 1 Cash Crop in the South in the 1800's.

Rice
Africans knew how to grow rice - helped with rice planters in North and South Carolina.

Bahia
State of Brazil with largest proportion of Africans; the Candomble religion is prominent here.

Engenhos
Portuguese for sugar plantation

Mutiny on the Amistad
Slaves on the Amistad killed the captain and cook because the cook said he was going to eat them. When they arrived in Cuba, they took control of the ship, sailed to the United States where they were arrested but later given freedom in the Supreme Court Case U.S. v. The Amistad.

Yoruba
A West African people who formed several kingdoms in what is now Benin and Southern Nigeria.
This people's religion led to the development of Candomble in Brazil.

Syncretism
a blending of beliefs and practices from different religions into one faith

Melville J. Herskovits
Said that African culture continued to influence African-American culture

Kalunga
the watery line between the world of the living and the dead in Kongo cosmology. Imaged as a river or a forest, frequently represented by a mirror
E. Franklin Frazier
Frazier argued that enslavement had stripped Afro-Americans of their African cultural heritage, rendering African Americans a kind of black slate in their new environment which developed into African-American culture.

Kongo American Graves
Objects last used/most often used by deceased are placed on the grave so that they may use them in the world of the dead (ancestors).
Objects are often pierced/broken to release the spirit within to allow it to travel to world of the dead as well.
Used the color white, seashells, bath tile
Louisiana Purchase
territory in western United States purchased from France in 1803 for $15 million
Differences between enslavement/societies in Caribbean/Brazil and 13 British Colonies
Caribbean/Brazil: had sugar as main cash crop, more males than females due to harsh labor.
13 British Colonies: had tobacco/cotton/rice as main cash crop, more females than males.
How did people became enslaved in Africa?
War captives, debt slavery
as punishment for crimes (Criminals), kidnapping
Gender and Enslavement
Slave women, who were especially attractive, were targeted by their masters.
Also, slave women were often separated from their children (Frederick Douglass)
