Sensory Pathways
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Sensory Pathways
Somatosensory
auditory
visual
Somatosensory pathways
carry sensory info to cerebral cortex
dorsal column pathway
spinothalamic tract
3-neuron chain pathways
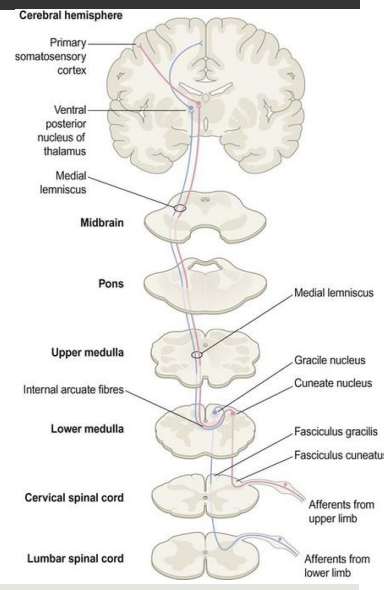
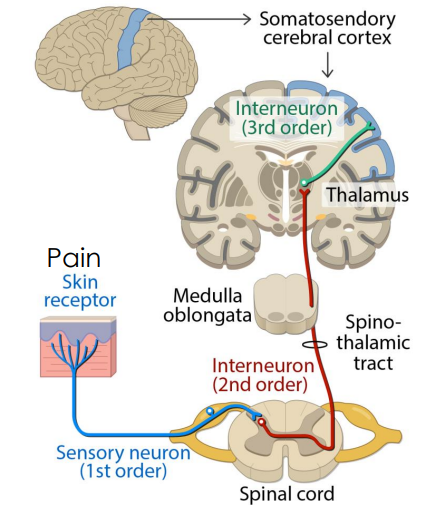
First-order neurons
Second-order neurons
Third-order neurons
First-order neurons
Start as peripheral nerve & enter spinal cord
Cell bodies in dorsal root ganglia
Second-order neurons
Axons cross midline before ascending to thalamus
Cell bodies in grey matter of brainstem/spinal cord
Third-order neurons
Start in thalamus
Via internal capsule
To primary somatosensory cortex
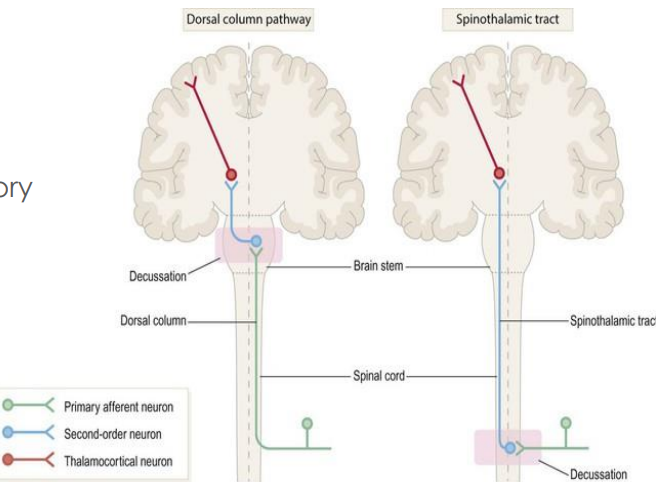
Dorsal column pathway
somatosensory pathway
Function: mechanoreception: localised touch and pressure, vibration, proprioception
2nd order neuron - cross together at medulla in sensory decussation
Spinothalamic pathway
somatosensory pathway
Function: nociception (pain) and thermorecepetion (temp)
2nd order neuron - cross immediately at different levels of the spinal cord
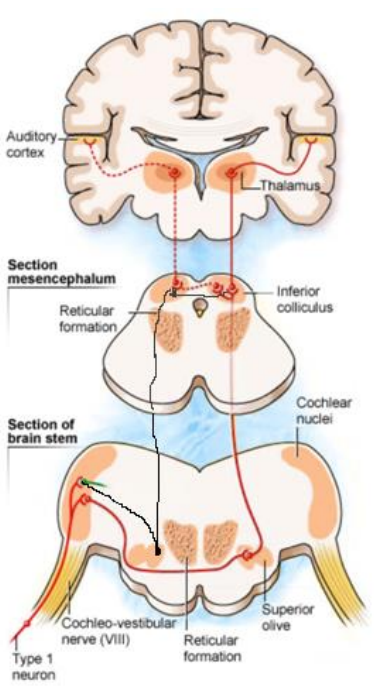
Auditory sensory pathways
Auditory information travels from inner ear to brainstem via CN VIII
In brainstem:
1 st relay
Cochlear nuclei
2 nd relay
Superior Olivary Complex
3 rd relay
Inferior colliculus
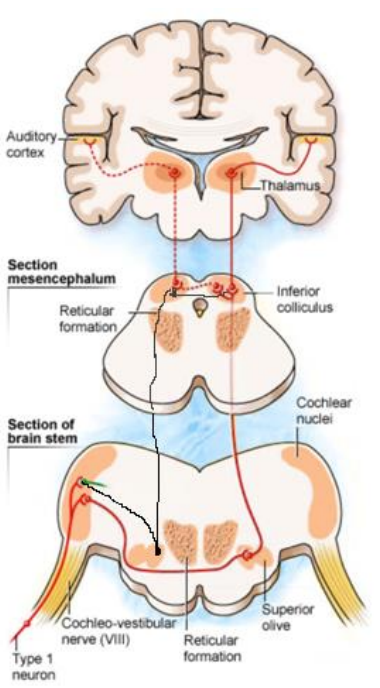
Auditory sensory pathways cont.
From brainstem to medial geniculate body in thalamus
From thalamus to primary auditory cortex (Heschl’s gyrus)
Message recognised, memorised & integrated into voluntary response
has bilateral innervation - therefore lesions in central auditory pathway in 1 hemisphere won’t result in unilateral deafness
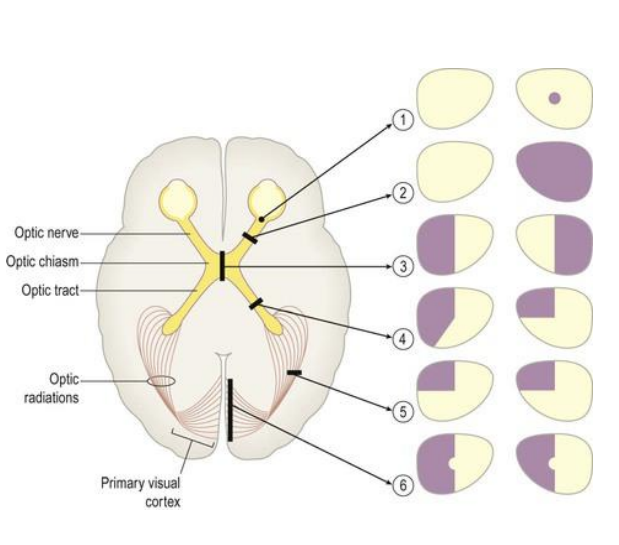
Visual Sensory Pathways
Retina has point-to-point representation of visual fields
Axons of retinal ganglion cells leave eye as optic nerve
Optic nerves unite in optic chiasm
After chiasm optic tracts go to thalamus
Project to primary visual cortex via optic radiations
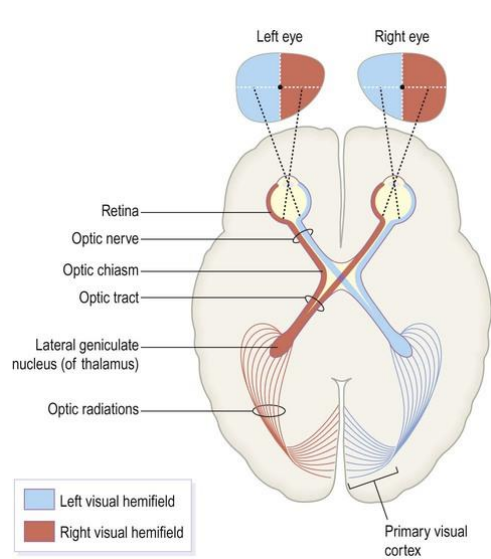
Visual pathways are crossed
R visual field processed in L occipital lobe
R half of visual field projects to L half of each retina
Axons from left half of each retina project to L hemisphere
Nerve fibres from inner half of retina cross midline to enter opposite tract at optic chiasm
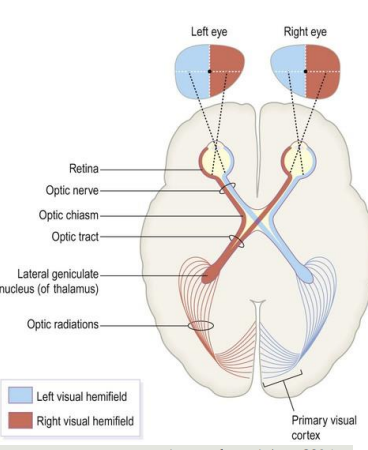
Path of R visual field info
R visual field: area R to own midline when looking ahead
light from R visual field strikes L half of each retina
L of L retina: temporal projection to ipsilateral V1
L of R retina: nasal projection crosses midline at chiasm to contralateral V1
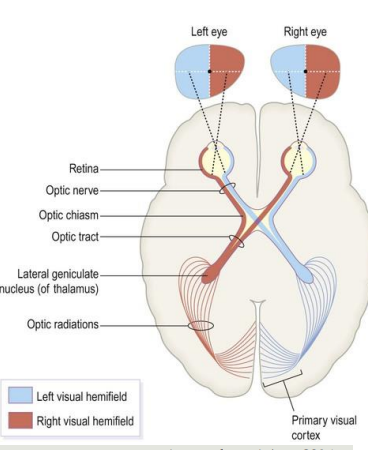
Lesions in visual sensory pathways can result in
Scotoma (small blind spot)
Monocular blindness
Bitemporal hemianopia (tunnel vision)
Heteronymous left-sided field defect
Left superior quadrantanopia (homonymous)
Left hemianopia with macular sparing