Lecture 16 - Chromosome Structure and Dynamics
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Genetic information in DNA is passed to the next generation by
DNA replication
Cell division
2 (or 3) genomes found in cells
nuclear, mitochondrial, chloroplast
Genome is a _____ copy of all the genetic information of an organism or virus
complete
Cell nucleus diameter
5-8 um
_____ are the most abundant proteins in chromosomes
Histones
Most abundant amino acids in histones
lysine and arginine
Histones are responsible for the first and most fundamental level of chromatin packing in the ______
nucleosome
Histone October forms the ______ ______ ______ (made of eight histone particles)
nucleosome core particle
4 core particles of histones
H2A
H2B
H3
H4
Histones are ____ charged
positively
Each of the histones in the octamer have long _______ amino acid tails
N-terminal
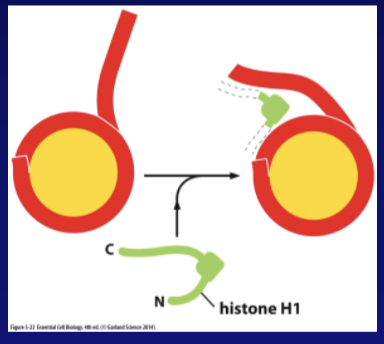
Further packing of the nucleosome relies on ______ ___ which pulls nucleosomes together
histone H1
purpose of packaging DNA in chromosomes
allows cell to accommodate huge genomes
protects DNA from nucleases
enhances the regulation of gene expression
extended chromosome material
euchromatin
condensed chromosome material
heterochromatin
Heterochromatin regions are found throughout the chromosome but are most concentrated near _____ and _____
centromeres; telomeres
Heterochromatin corresponds to _____ genes
quiescent
What happens to genes that accidentally become packaged into heterochromatin
fail to express
_____ is transcriptionally active DNA
euchromatin
(T or F) a cell can adjust its chromatin structure to expose specific regions of DNA to give access to other proteins
true
Adjusting of chromatin structure by ____ _____ ______
chromatin remodling complexes
chromatin remodeling complexes can both ____ and _____ chromatin
unwind; condense
Chromatin structure adjustment occurs via _____ ______
histone modifications
the ____ of all 4 core histones are subject to covalent modifications
tails
3 types of covalent modifications used in histone modifications
acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation
How do covalent modifications adjust histones
reduce/increase affinity of tails for DNA
create docking sites for regulatory proteins
Epigenetic modifications do not alter the ___ ______, but can alter gene expression patterns in a cell
DNA sequence
Dynamic adjustment of local chromatin packing by chromatin remolding complexes and histone modifications results in ___-_____ packing of interphase chromosomes
non-uniform
Example of useful heterochromatin
telomeres
Do telomeres code for proteins?
no
Telomeres are found on ___ ends of the chromosome
both