RS and GIS
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
Electromagnetic Radiation Interactions
EM energy can be reflected, transmitted (refracted), or absorbed.These interactions occur with matter at various frequencies, affecting how electromagnetic waves propagate and interact with different materials.

Law of Reflection
The principle that states reflection follows specific angles of incidence (\thetai) and reflection (\thetar), where \thetai = \thetar.
Transmission and Refraction
Transmission involves refraction due to a change in the velocity of EM energy when passing between media of different densities.
Absorption
The process of converting energy to heat, which may be re-emitted as thermal radiation.
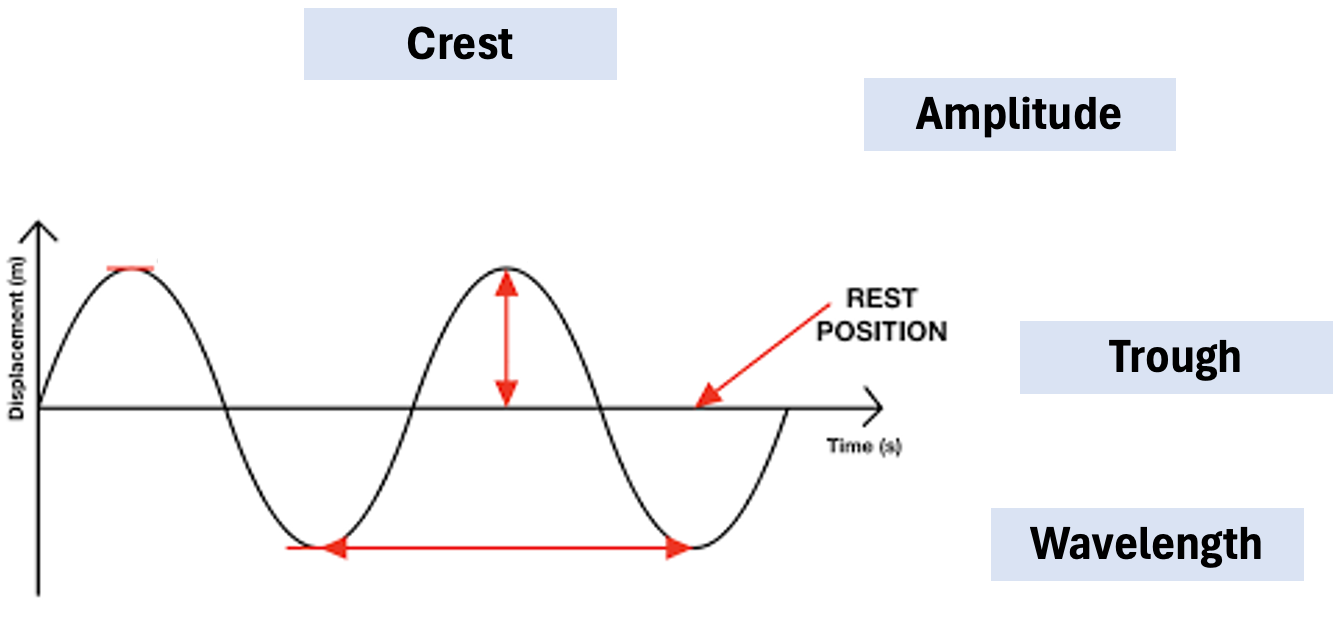
Wave Properties and Label Diagram
A wave transfers energy without transferring matter, characterized by crests and troughs. The diagram illustrating wave properties should label crests, troughs, wavelength, and amplitude.
Amplitude
Controls the energy level of the wave, measured as the vertical distance from the equilibrium to the crest.
Wavelength
Defines the position of the wave in the electromagnetic spectrum (\lambda), measured as the distance between two successive crests.
Atmospheric Windows
Regions of the atmosphere that selectively absorb EM radiation, allowing high transmission in specific bands.
Visible and Thermal IR
Major atmospheric windows that sensor systems are designed to operate within to minimize signal loss.
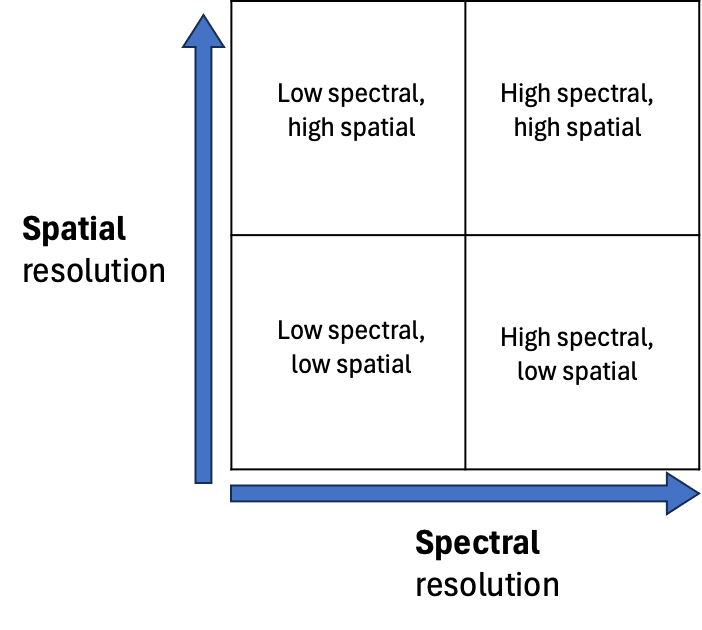
Sensor Resolution Trade-offs
Balance between spatial resolution (pixel size) and spectral resolution (number of bands) in sensor technology.
MODIS
A sensor with low spatial resolution (250m to 1km) and high spectral resolution (36 bands).
Sentinel-2
A sensor providing a balance between spatial (10m to 60m) and spectral resolution (13 bands).
Planet
A sensor known for high spatial resolution (3m) but low spectral resolution (typically 4 to 8 bands).
Vegetation Spectral Curves
Reflectance patterns indicating chlorophyll absorption and reflectivity in various wavelengths.
Green Peak
Occurs at approximately 0.55µm in the vegetation spectral curve, where light is reflected more than in the blue or red bands.
Red Edge
A sharp change in reflectance near 0.7µm, indicating the transition from chlorophyll absorption to leaf structure scattering.
NIR Reflectance
High reflectance in the near-infrared region (NIR) triggered by the internal cellular structure (spongy mesophyll) of leaves.
SWIR Absorption
Controlled by water content in vegetation; higher water content leads to deeper absorption features in the Short-Wave Infrared region.
Remote Sensing Workflow
Energy Source (Sun/Sensor)
Atmosphere (Scattering/Absorption)
Surface Interaction (Reflection)
Sensor Recording (Data capture)
Interpretation (Analysis)
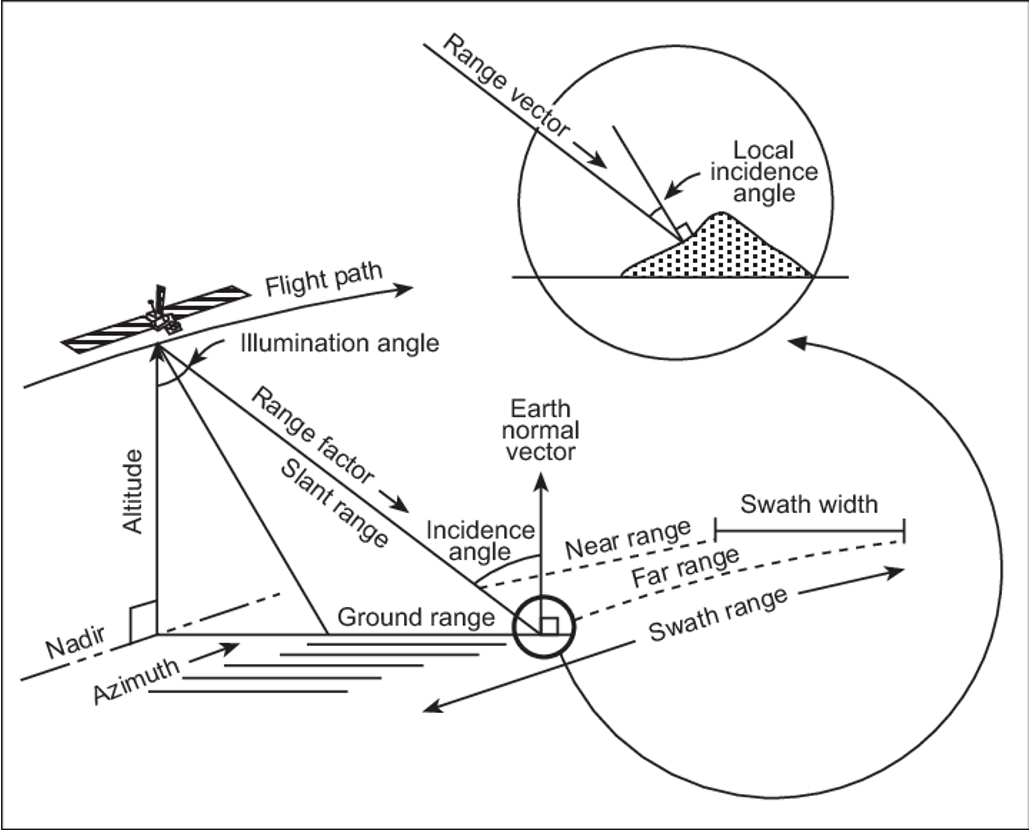
Radar Geometry
Describes the active side-looking microwave system parameters including azimuth and range.
Slant Range vs Ground Range
Slant Range is the direct line-of-sight distance from the sensor to the target; Ground Range is the horizontal distance on the terrain.
Incidence Angle
The angle between the radar beam and the surface normal, which significantly controls backscatter intensity.
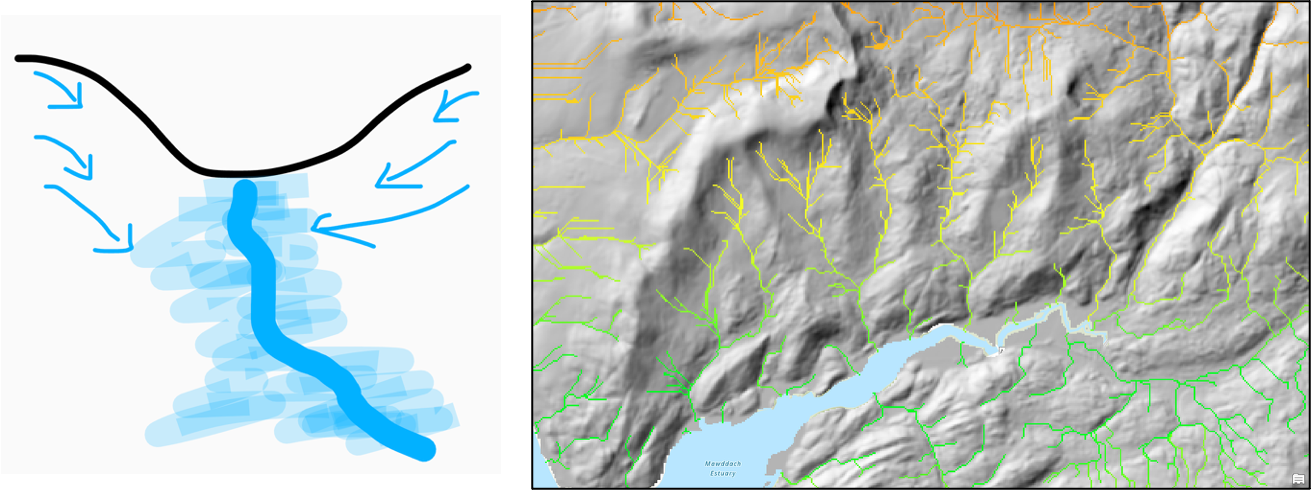
DEM Hydrology
Digital Elevation Model representing elevation and water flow dynamics across a landscape.
Flow Direction
Defines the movement of water downslope in the landscape, often using the D8 algorithm (8 cardinal directions).
Flow Accumulation
Identifies areas of converging flow by counting how many upslope cells drain into a single cell.
Threshold
Technique used to extract stream channels by selecting cells with a flow accumulation value above a specific limit.
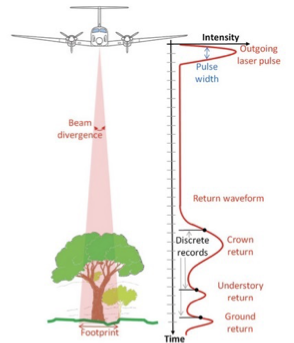
LiDAR Waveform
Represents the intensity of laser pulses over time.
Canopy Height Calculation
Derived by subtracting the ground return elevation from the first return elevation in a LiDAR point cloud or waveform.
Airborne LiDAR
Characterized by a small laser footprint and high point density (30 pts/m^2), ideal for detailed forest mapping.
Spaceborne LiDAR
Features a large footprint (70m for GEDI) and sparse coverage, but provides global sampling of forest structure.
Biomass Mapping
Utilizes height data from LiDAR to estimate the total organic matter in an area, crucial for carbon cycle studies.
Can you define the four types of resolution in EO remote sensing?
The four types of resolution in Earth Observation remote sensing are spatial resolution, spectral resolution, temporal resolution, and radiometric resolution. Spatial resolution refers to the size of the smallest object that can be detected. Spectral resolution indicates the number of wavelengths or spectral bands captured. Temporal resolution measures the frequency of data collection over time. Radiometric resolution describes the sensitivity to detect variations in energy values.
what are the 3 stages from DN to AT-surface Reflactance?
1. Stage 1 (DN to At-Sensor Radiance): Converts raw DNDN values into physical units of spectral radiance.
Stage 2 (Radiance to TOA Reflectance): Normalises radiance data for illumination variations (EarthEarth-SunSun distance, solar angle) to compare images from different dates. Result is Top of Atmosphere (TOATOA) reflectance (values between 00 and 11).
Stage 3 (Atmospheric Correction): Removes atmospheric effects (scattering, absorption by water vapour, etc.) to get the true At-Surface (Bottom of Atmosphere) reflectance.
Can you name one approach for atmospherically correcting optical satellite imagery?
One approach for atmospherically correcting optical satellite imagery is the use of the Dark Object Subtraction (DOS) method, which removes atmospheric effects by identifying and correcting for the darkest pixels in the image.
Another one is Empirical line calibration and finally Physical atmospheric modelling.
label this diagram of a radar: include Range vector, Local incidence angle, flight path, illumination angle, range factor, slant range, incidence range, earth normal vector, near range, far range, ground range, azimuth, nadir, altitude , swath range and swath width
correct labels -
How do we retrieve hydrological information from a DEM?
Hydrological information from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) is retrieved by analyzing the terrain to delineate watersheds, identifying flow directions, and calculating flow accumulation, which helps in modeling water movement and drainage patterns.
Describe how we can calculate a channel network?
A channel network can be calculated by using a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) to analyze the terrain, applying methods like flow direction and flow accumulation analyses, which identify interconnected pathways that allow water to flow.
1.Fill sinks
2.Flow direction (Dinf)
3.Flow accumulation
4.Threshold on flow accumulation to identify stream network
What are the primary differences between airborne and spaceborne LiDAR
Airborne LiDAR operates from aircraft and typically captures high-resolution data over smaller areas, while spaceborne LiDAR uses satellites to gather data over larger regions with lower resolution. This results in differences in applications, precision, and scale between the two methods.
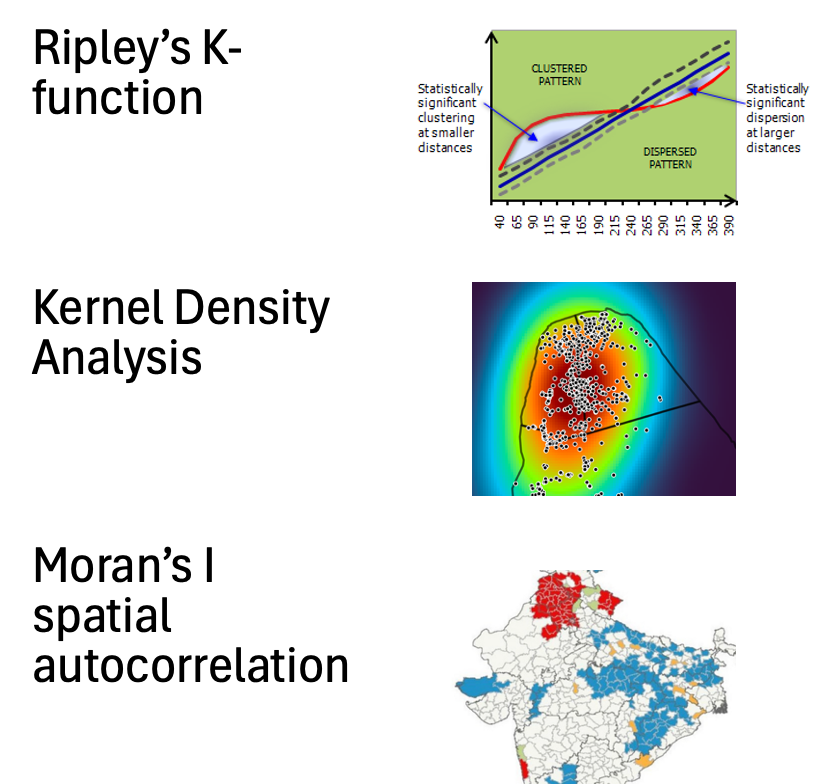
How would you analyse spatial patterns in the following datasets?
•Location of diseased trees in a forest
•Smoking rates across counties in the UK
Spatial patterns in these datasets can be analyzed using methods like spatial autocorrelation, kernel density estimation, and hot spot analysis. These techniques help identify clusters, trends, and relationships within the geographic distribution of the data. These analyses reveal spatial clustering, correlations, and variations in patterns, informing management strategies and public health initiatives.
Ellipsoid
coordinate systems describe how spatial locations are represented in terms of numerical values, defining the position of points in a given space using systems like Cartesian, polar, or geographic coordinates.
Datum
A reference point or surface from which measurements are made in geospatial data, crucial for establishing the position of locations in relation to the Earth's surface.
Projection
A method for representing the curved surface of the Earth on a flat map, involving transformations of geographic coordinates to map coordinates.
Geoid
A model of the Earth's shape that accounts for variations in gravitational field, representing the mean sea level across the globe. It serves as a reference surface for measuring elevations and depths.
Mean sea level
the reference surface used to define the geoid, representing the average height of the ocean's surface under the influence of Earth's gravity and rotation.
Float
A data type that stores real numbers with decimal values.
Integer
A data type that stores whole numbers with no decimal places.
Spectral Regions
Ranges of wavelengths associated with specific colors or types of light.
Blue Light
The spectral region from approximately 450 to 500 nm.
Red Light
The spectral region from approximately 650 to 680 nm.
Shortwave Infrared (SWIR)
The spectral region from approximately 2000 to 2500 nm.
Spatial Resolution
The amount of detail in an image, determining how small specific objects can be resolved.
Thermal Infrared
Wavelengths longer than visible light that provide thermal images of surfaces.
Red Edge
The sharp increase in vegetation reflectance between red and near-infrared wavelengths.
UTM Zones
A global system divided into 60 zones, each spanning 6 degrees of longitude.
Transverse Cylindrical Projection
A map projection that minimizes distortion in narrow north-south zones.
Equal-area Cylindrical Projection
A projection that preserves area, suitable for measuring deforestation.
LiDAR Footprint
The area on the ground illuminated by a single LiDAR laser pulse.
Digital Terrain Model (DTM)
A representation of the ground surface created from ground returns in LiDAR.
Linear Spectral Unmixing
A technique modeling pixel reflectance as a linear combination of spectral endmembers.
Problem Solving Steps
Define the problem, collect data, analyze data, interpret results.
Ripley’s K Function
A statistic to determine if point patterns are clustered, dispersed, or random.
Real Aperture Radar
Radar relying on antenna size for resolution.
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)
Radar that synthesizes a large antenna using platform motion for higher resolution.
Radar Cross-Section (σ)
The measure of strength of backscattered energy from a target.
Orthorectification
Geometric correction of imagery to remove terrain-induced distortions.
Atmospheric Scattering
The process that redistributes energy in the atmosphere.
Atmospheric Absorption
The removal of energy at specific wavelengths due to atmospheric gases.
Energy Transfer Model Components
Incoming solar radiation, atmospheric interactions, surface reflection, sensor radiance.
Spectral Curve
A graphical representation of reflectance values across different wavelengths.
Albedo
The proportion of solar radiation reflected by a surface.
Sensor Altitude
The height of the sensor which affects atmospheric path length.
Spectral Resolution
The ability to resolve different wavelengths in remotely sensed data.
Temporal Resolution
The frequency at which data is captured or observed.
Fixed-wing Drones
Drones known for long endurance and large coverage area.
Rotary Drones
Drones characterized by vertical take-off and precise maneuverability.
Field Spectroscopy Data
Ground truth data used for calibration and validation of remote sensing.
GIS Buffer Operation
An operation that creates zones around spatial features at a specified distance.
Surface Reflectance
The proportion of radiation reflected by a surface after removing atmospheric effects.
Online Map Presentation
The design of maps for improved accessibility and understanding.
Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA)
A method for combining multiple criteria to aid decision-making.
Dissolve Operation
A GIS operation that merges adjacent polygons with a common attribute.
Spatial Join
An operation to transfer attributes between layers based on spatial relationships.
Electromagnetic Energy
Energy radiated from the Sun that can be absorbed, reflected, transmitted, or scattered.
Wave
A transfer of energy characterized by wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and polarization.
Frequency
The number of wave cycles passing a point per second.
Types of Resolution in EO Remote Sensing
Spatial, spectral, temporal, and radiometric resolution.
Atmospheric Correction Approaches
Methods like Dark Object Subtraction or Empirical Line Calibration used to correct imagery.
Radar in Vegetation Studies
Radar is useful as it can penetrate cloud cover and is sensitive to vegetation structure.
Digital Elevation Models (DEMs)
Models that support hydrological analysis by providing topographic details.
LiDAR for Biomass Estimation
LiDAR provides information on tree height and structure related to biomass.
Combining Optical and Radar Data
Using both types of data for enhanced accuracy in mapping wetlands.
What happens to electromagnetic energy from the Sun?
Electromagnetic energy from the Sun can be reflected, absorbed, transmitted, or scattered by the atmosphere and Earth’s surface.
Define a wave in remote sensing.
A wave is a means of energy transfer characterised by wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and polarisation.
Define frequency.
Frequency is the number of wave cycles passing a point per second, measured in Hertz (Hz).
What are the four types of resolution in Earth Observation remote sensing?
Spatial resolution, spectral resolution, temporal resolution, and radiometric resolution.
Explain spatial resolution.
Spatial resolution refers to the ground area represented by a single pixel in an image.
Explain spectral resolution.
Spectral resolution describes a sensor’s ability to distinguish between different wavelengths of electromagnetic energy.
How do we convert DN values to at-surface reflectance?
Stage 1: Convert DN to at-sensor radiance. Stage 2: Convert radiance to top-of-atmosphere reflectance. Stage 3: Apply atmospheric correction to obtain at-surface reflectance.
What is atmospheric correction?
Atmospheric correction removes the effects of scattering and absorption by gases and aerosols to retrieve true surface reflectance.