Magnetic field Qs
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms

What is the direction of the force?
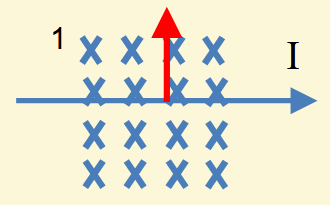
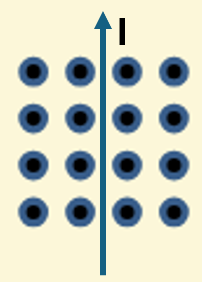
What is the direction of the force?
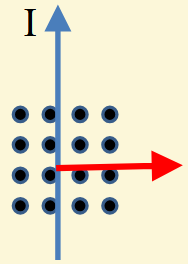
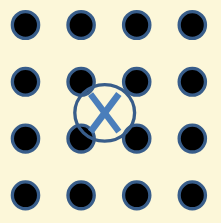
What is the direction of the force?

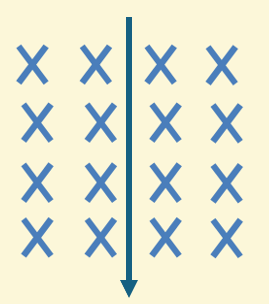
What is the direction of the force?
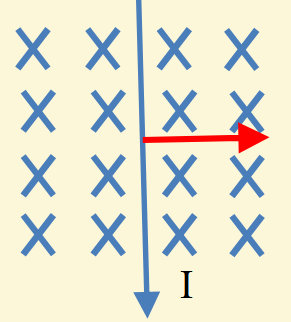
What is the direction of the force?
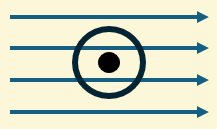
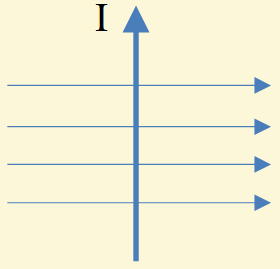
What is the direction of the force?
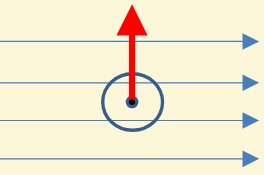

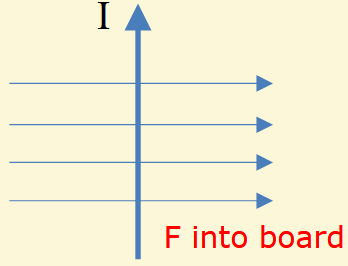
What is the direction of the force on each of the wires?
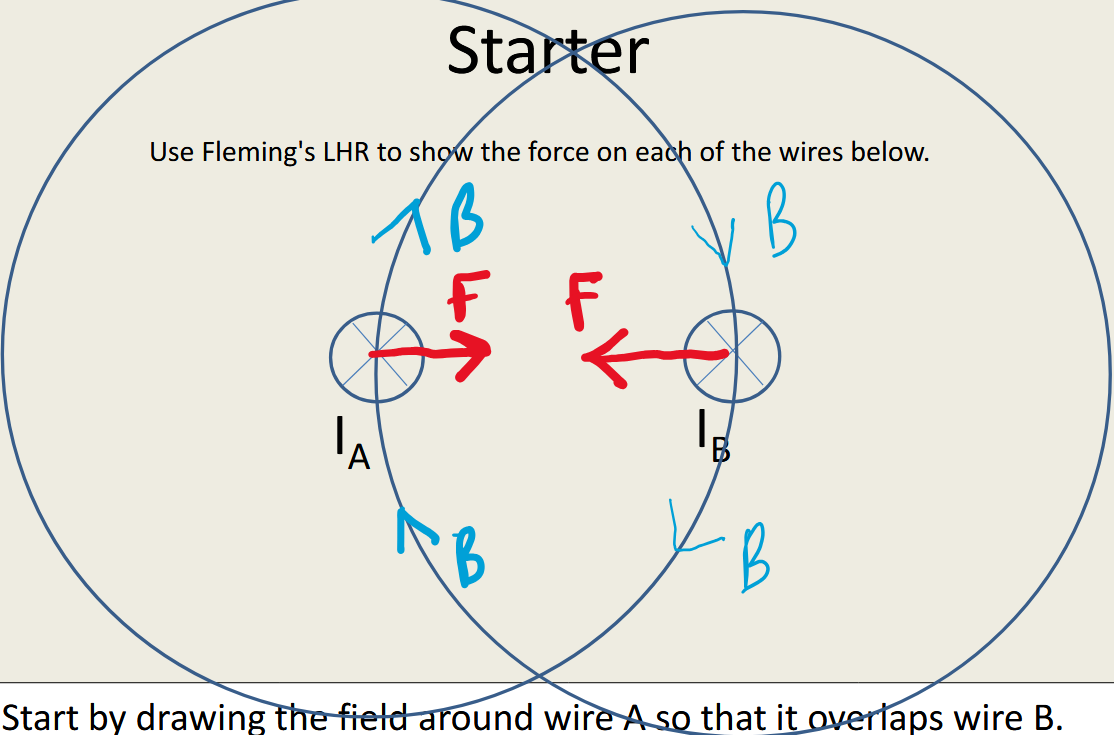

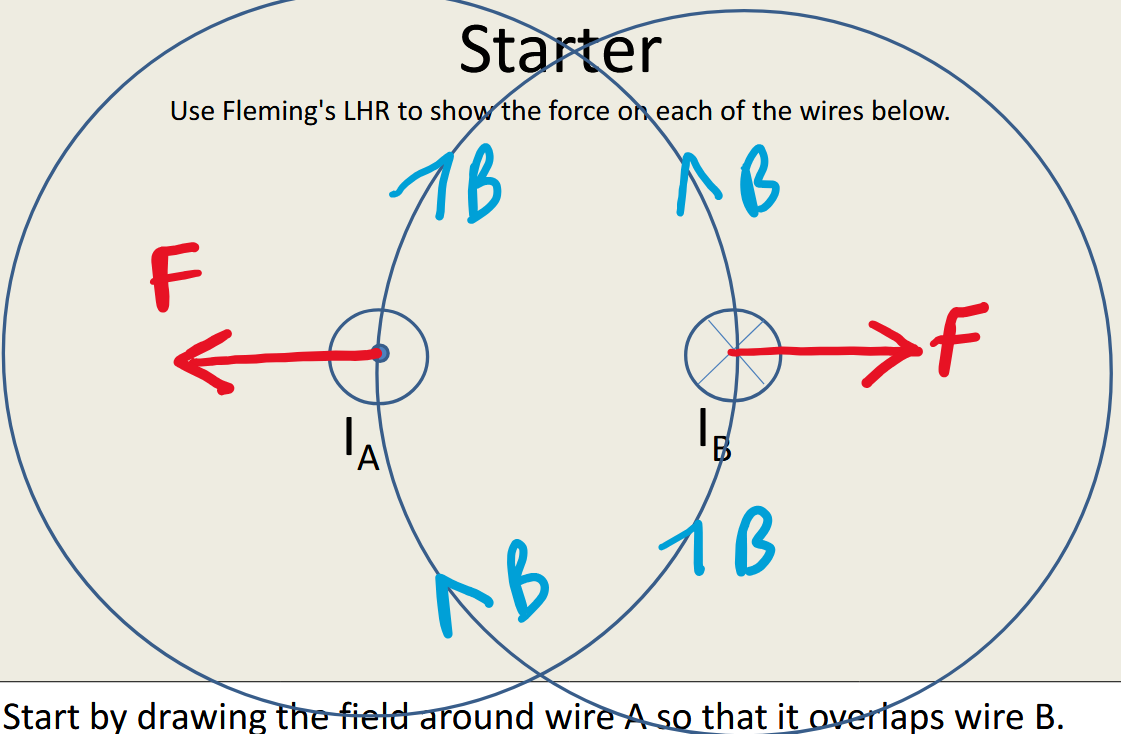
What is the direction of the force on each of the wires?
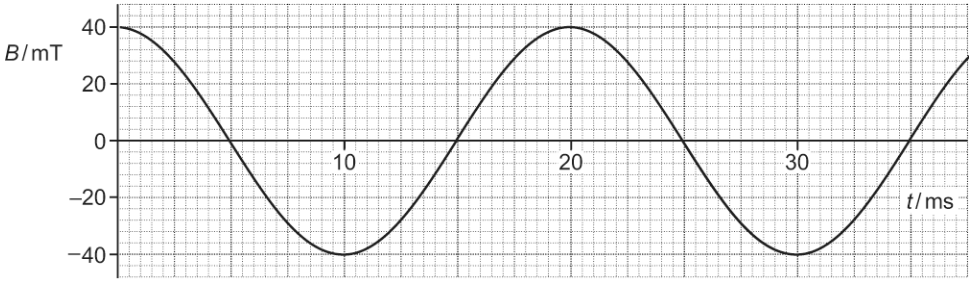
A coil is part of a simple generator and rotates in a uniform electric field. The image shows the variation of magnetic flux density B through the plane of the coil with time t as it rotates. Explain why the electromotive force (e.m.f.) induced across the ends of the coil is a maximum at the times when B = 0
The gradient is maximum meaning rate of change of flux (linkage) is maximum
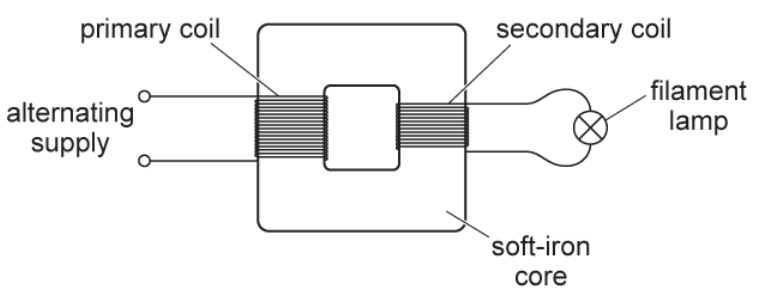
The primary coil is connected to an alternating voltage supply. A filament lamp is connected to the output of the secondary coil. Use Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction to explain why the filament lamp is lit.
There is a changing flux linkage in core and secondary coil
Faraday’s law states e.m.f. induced ∝ rate of change of magnetic flux linkage, so a e.m.f is induced in the secondary coil, producing a current and lighting the filament lamp
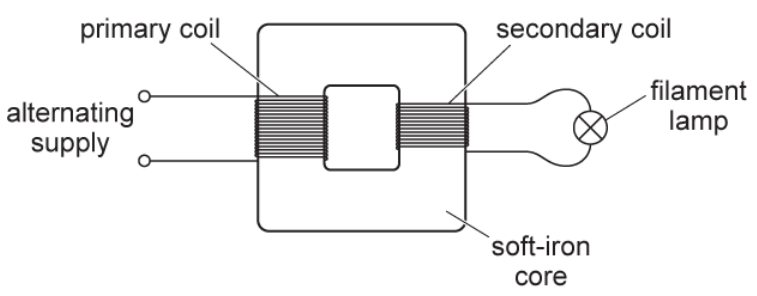
The alternating voltage supply is replaced by a battery and an open switch in series. The switch is closed. The lamp is lit for a short period of time and then remains off. Explain this observation.
There is an increasing flux and current in the primary coil at the start, so an e.m.f is induced in the secondary coil and the lamp lights up
Eventually current and flux are constant, therefore no e.m.f. is induced, so the lamp turns off