Aice Psychology - Research Methods
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Lab Experiment
Investigation looking for a relationship in which the IV is manipulated and is expected to be reasonable for changes in the DV
Strength:
- High standardization
-Easy to repeat for reliability
- High levels of control researchers are confident IV affects the DV
Weakness:
- Lack Ecological Validity
- Lack Mundane Realism
- Participants may respond to Demand Characteristics

Independent Variable
The variable the psychologists choose to manipulate or change
(CAUSES - WHAT SCIENTISTS MANIPULATE)
Variable which should change the dependent variable.
It is the experimental variable which causes something to happen.

Dependent Variable
The variable that the psychologist chooses to measure
(THE OUTCOME - WHAT SCIENTISTS DON'T TOUCH)
The experimental variable which is affected BY the independent variable.
Field Experiment
Takes place in a natural environment that might affect the DV (Weather, Time of day, etc.)
Strengths
- Has high ecological validity, participants do NOT know that they are part of
the study
- little to no demand characteristics
- behavior more natural and valid.
Weakness
- Situational variables hard to control so difficult to know if the IV affecting the
DV
- ethical guidelines (informed consent and deception)

Experiment types
Laboratory
- High internal validity
- High reliability
- Good ethics (consent, debriefed, Right To Withdraw)
Field
- Low internal validity
- Medium levels of reliability
- Some consent, debriefing more difficult no RTW
Natural
- Low internal validity
- Low levels of reliability
- Hard to repeat
- Hard to get consent and debrief also no RTW
Questionnaires
Strength - More likely to be truthful, large sample and short time increases the
representativeness and generalisability.
Weakness - May give socially desirable answers which lowers validity

Likert Scale (Questionnaire)
Statements (Ex. Owning a pet is good for your health, Strongly agree,
Agree, Disagree

Rating Scale (Questionnaire)
Questions or statements in a form of a number
Scale of 1-10 how happy are you in this class

Open ended (Questionnaire)
Participant develops an answer. (Ex. Tell me about a happy childhood
memory)

Closed-Question (Questionnaire)
A Yes or No, or set of options (Ex. Pick the emotion you are feeling
right now Happy, Sad, Moody, Tired)

Interviews
Answers are in spoken form
Strength
- Can give more reason why one behaves a certain way
Weakness
- Can be less likely to tell truth for social reasons
- Face-to-face
- Don't want to be judged

Structured (Interviews)
Uses a set of questions and every participant answers the same questions in the
same order
Unstructured (Interview)
Have an initial question to begin then each subsequent question will depend on the response

Semi-structured (Interview)
Involves certain questions that must be asked but can be in a different order or other questions can be asked
Case Study
In depth detailed analysis of the individual or close-knit group
Strength
- Collect a lot of rich data for more validity
Weakness
- Generalization is hard to make (only looked at one person also a relationship can form between participant/researcher which can lower validity)
Overt observation
Participant knows they are being observed

Covert observation
Participant does not know they are being watched

Participant observation
Researcher becomes part of the group they are observing and possibly interact with them
Strength
- Researcher understands motive for behaviors; increasing validity
Weakness
- Possibly informed consent or researcher just joined in
- Presence of an outsider can change the behavior of the group members

Non-Participant observation
Researcher is out of sight
Strength
- Behavior of group will not be affected
Weakness
- Don't exactly know why the behaviors are occurring so hard for qualitative data

Structured observation
Researcher has a coded behavior checklist
Strength
- The coding/checklist leads to quantitative data
Weakness
- Is very restrictive (time sampling)
- Does not give a reason why he behavior is occurring

Unstructured observation
Researcher notes all behavior they can see in qualitative form over a period of time. No checklist. Simply record what is happening in real time
Strength
- In depth Qual. data
Weakness
- may not understand why behavior is happening
Naturalistic Observation
Takes place in an animal's or person's personal environment
Strength
- Participants are unaware they are being watched
- Little demand characteristics
-General high ecological validity
Weakness
- Can't control extraneous variables
- Hard to determine cause and effect
- Replication can be difficult

Controlled Observation
Watched behind a one-way mirror so researcher can not be seen observing
Strength
- There is less chance for extraneous variables affecting the participant's behavior
Weakness
- Since settings are artificial the findings may lack ecological validity
Event Sampling in observations
Tally every time that a behavior is observed, within a set time period.

Time Sampling in observations
Behaviors are recorded in specific time intervals.(3 Types):
Instantaneous scan: record behavior at the start of each set time interval. (ie. every 10 seconds record the behavior)
Predominant activity scan: record the most frequent behavior shown in a set time period. (10 second period)
One-Zero scan: record whether the behavior happened (a 1) or didn't happen (a 0) within a set time period. frequency isn't recorded, just whether it happened or not.

Correlation
Relationship between two measured variables

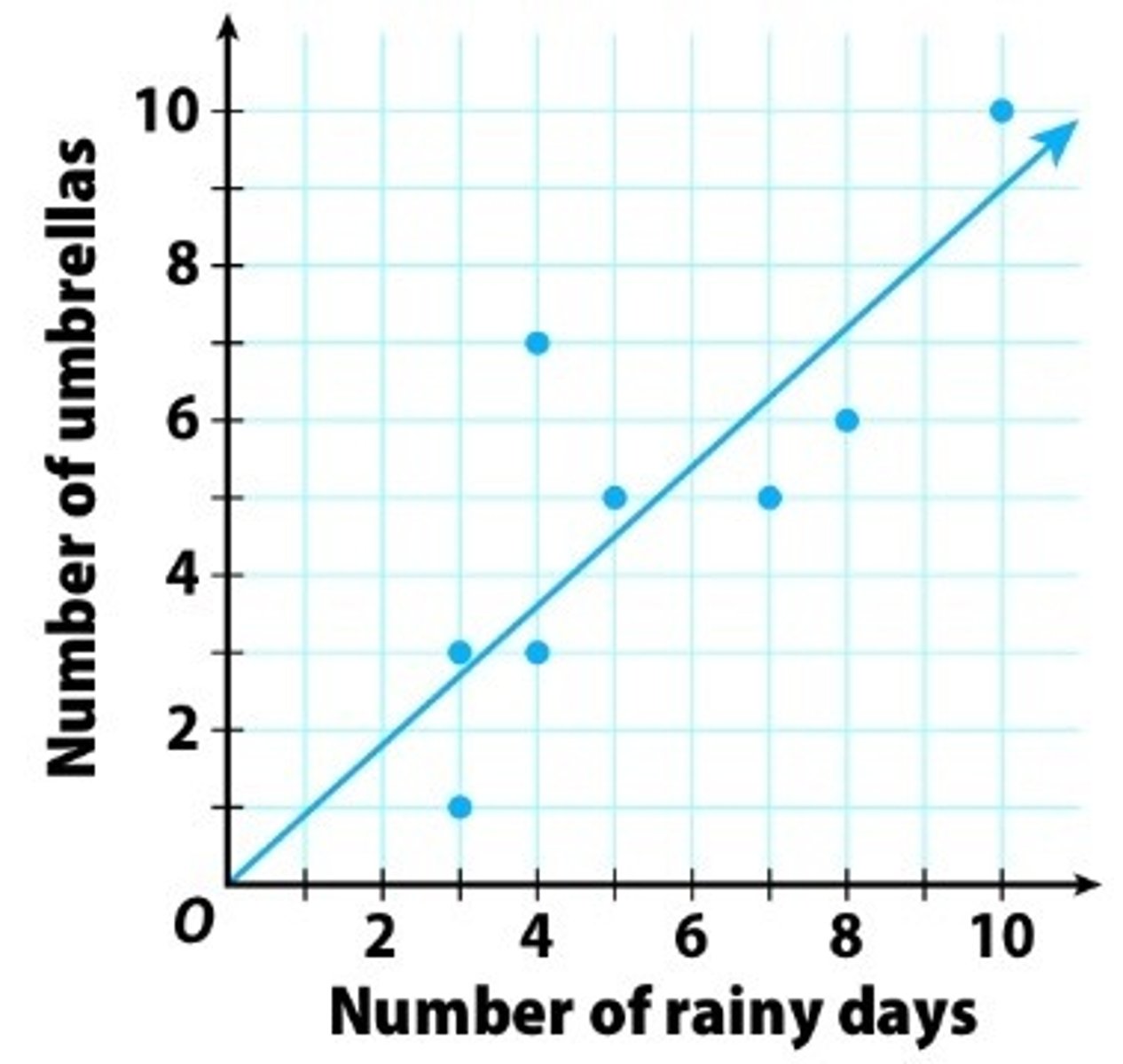
Positive Correlation
If one variable increases so does the other variable
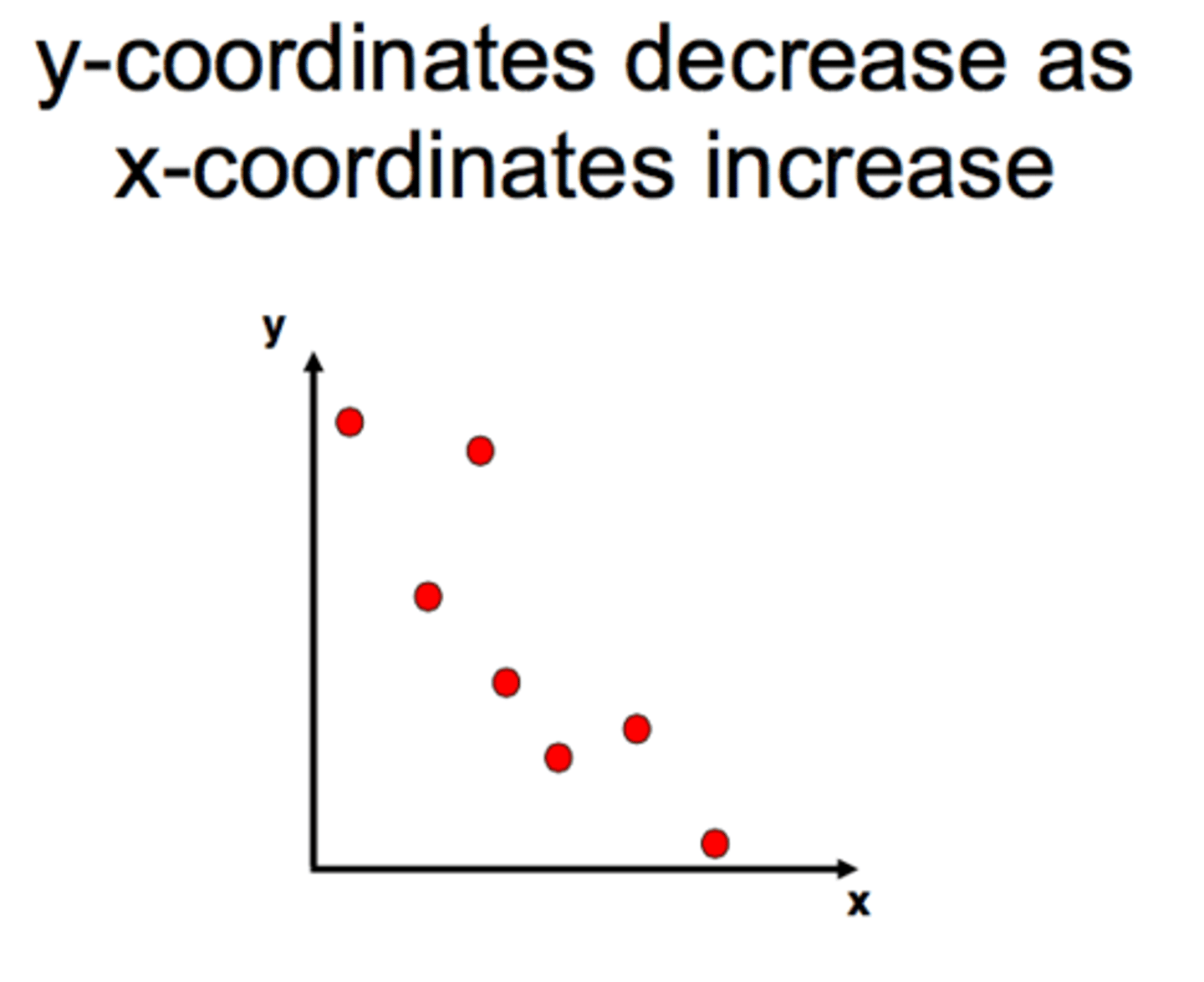
Negative Correlation
As one variable increases the other decreases
No Correlation
The two variables do NOT appear to be related
AIM
Written before study stating the study's purpose

Hypothesis
Predicts the finding of the study

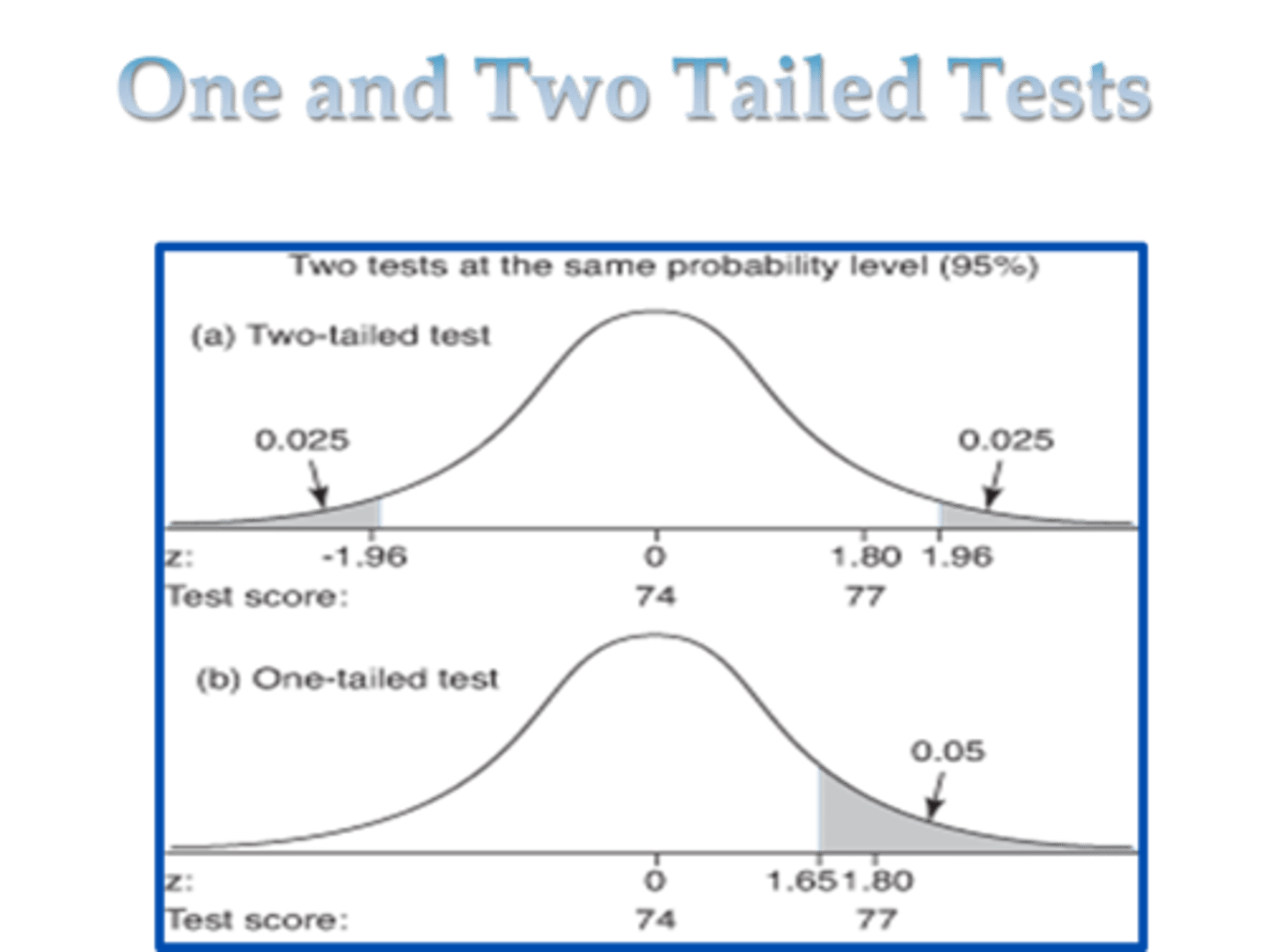
Directional (One-tailed) hypothesis
Predicts the significant difference and direction of results (EX. Females will be able to spell more words correctly out of 25 compared to males)
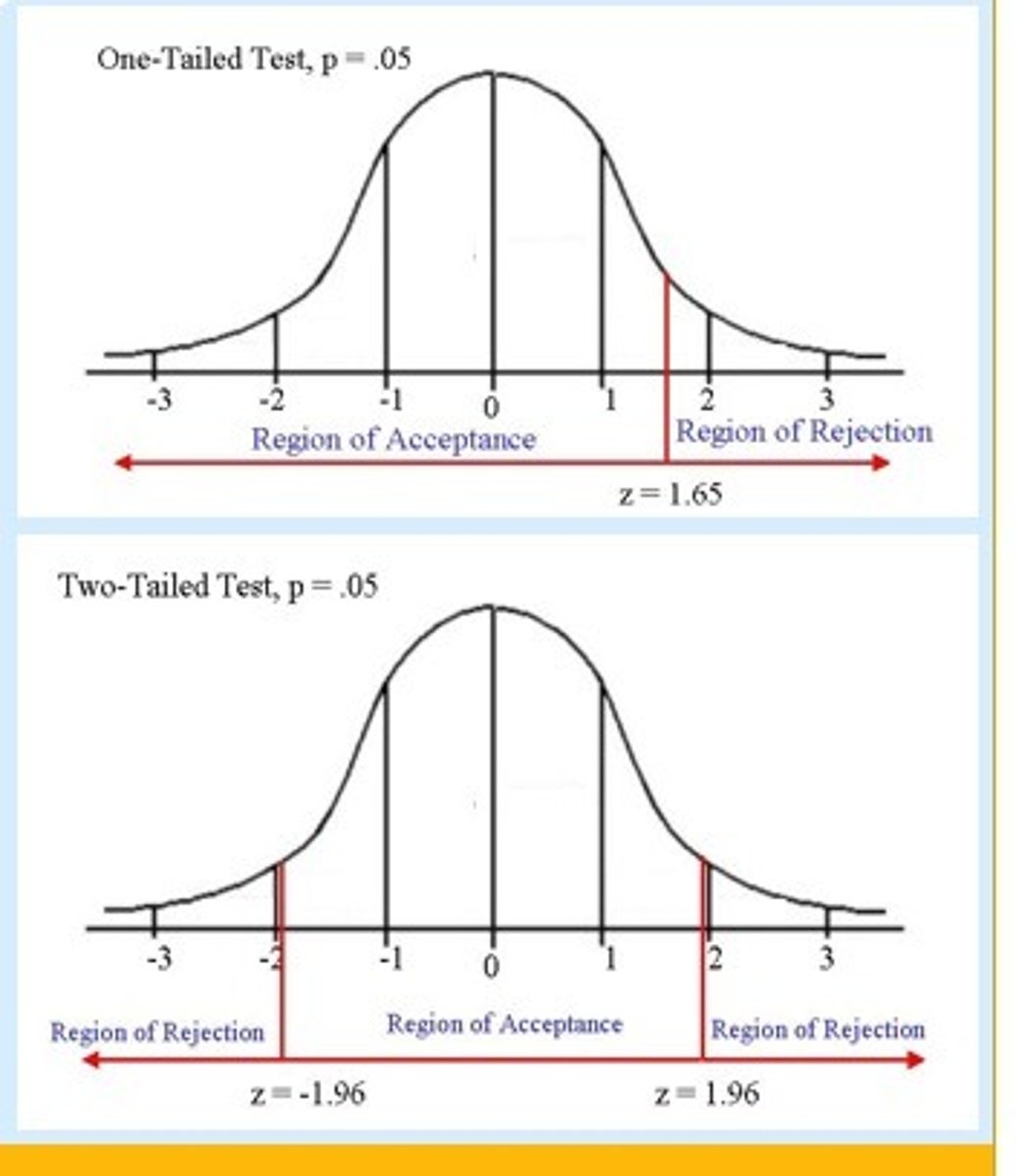
Non-Directional (Two-tailed) hypothesis
Null Hypothesis
A testable statement saying that any difference or correlation in the results is due to chance. no pattern in the the results is because of the variables being studied.

Repeated Measures
When the participant takes parts in all levels of the IV
Strength
- Controlled
- Fewer participants needed
Weakness
- Chance for demand characteristics
- Participants get better practice
- Fatigue and boredom
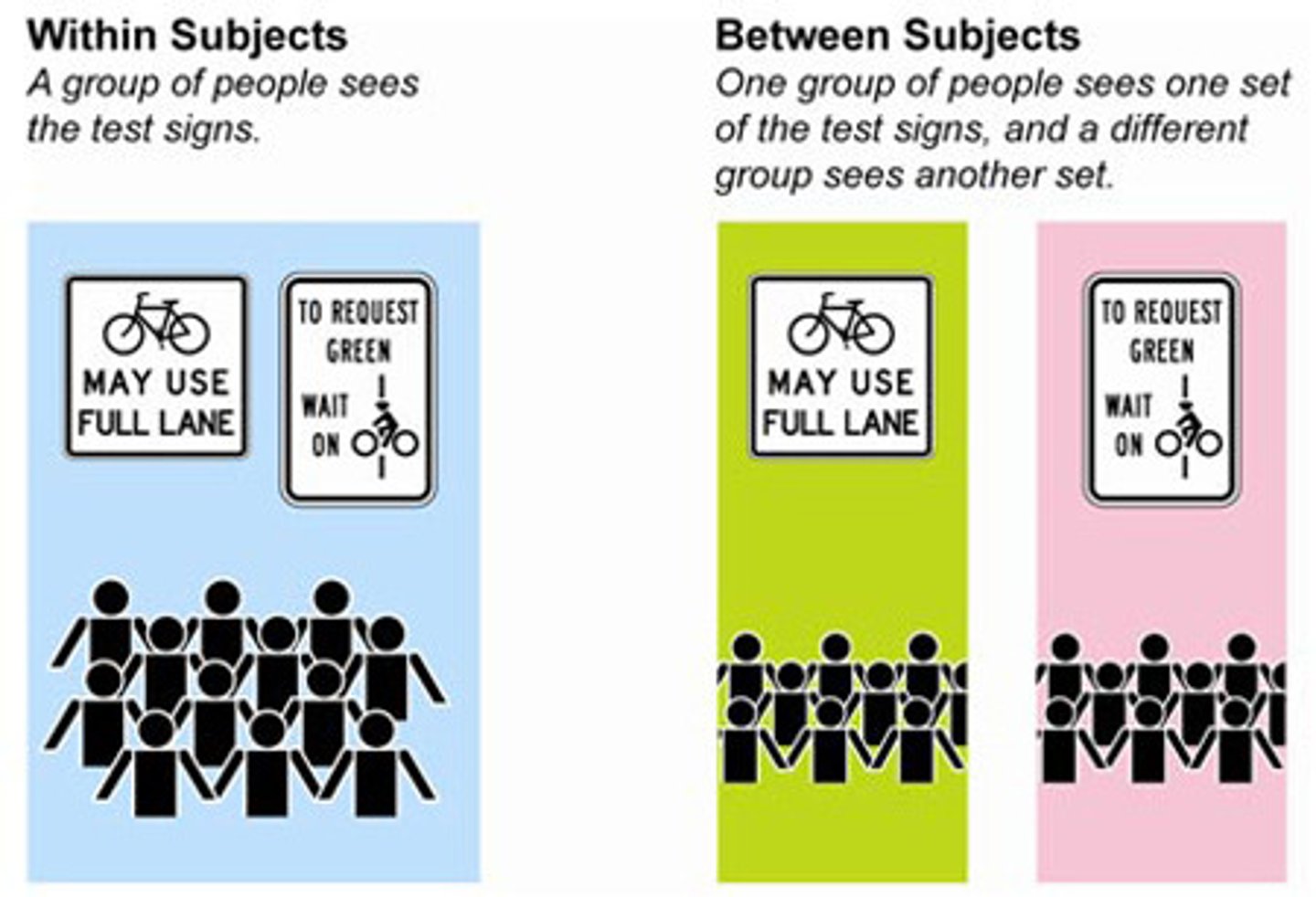
Independent Measures
When the participant takes part in only one level of the IV
Strength
- Less likely to guess AIM (demand characteristics)
Weakness
- More people are required personally could affect DV since it is just one person

Extraneous Variable
Variables that can influence the relationship between the IV & DV
- They can effect the outcome or add error to the experiment
- EX. Listening to music

Uncontrolled Variables
- Variables that cannot be controlled by the researcher
- Can lower the validity of an experiment (affects the DV)
Participant Variables
Variables that the participant brings to the study that can affect the DV ( Prejudice, previous experience with similar study, personality)
Situational Variables
Variables that the situation brings to the study that can affect the DV
EX. Noise, weather, temperature

Quantitative Data
Numerical form to get statistical analysis
Strength
- Easy to compare data and get good conclusions
Weakness
- Miss out on valuable information. If analysis is simply yes or now we don't know the WHY?
Qualitative Data
Data comes in the from of a description
Strength
- Rich and detailed responses. You get to see the WHY response
Weakness
- Interpreting Data can be very subjective
- Researchers may only only select Data to fit their AIM creating bias
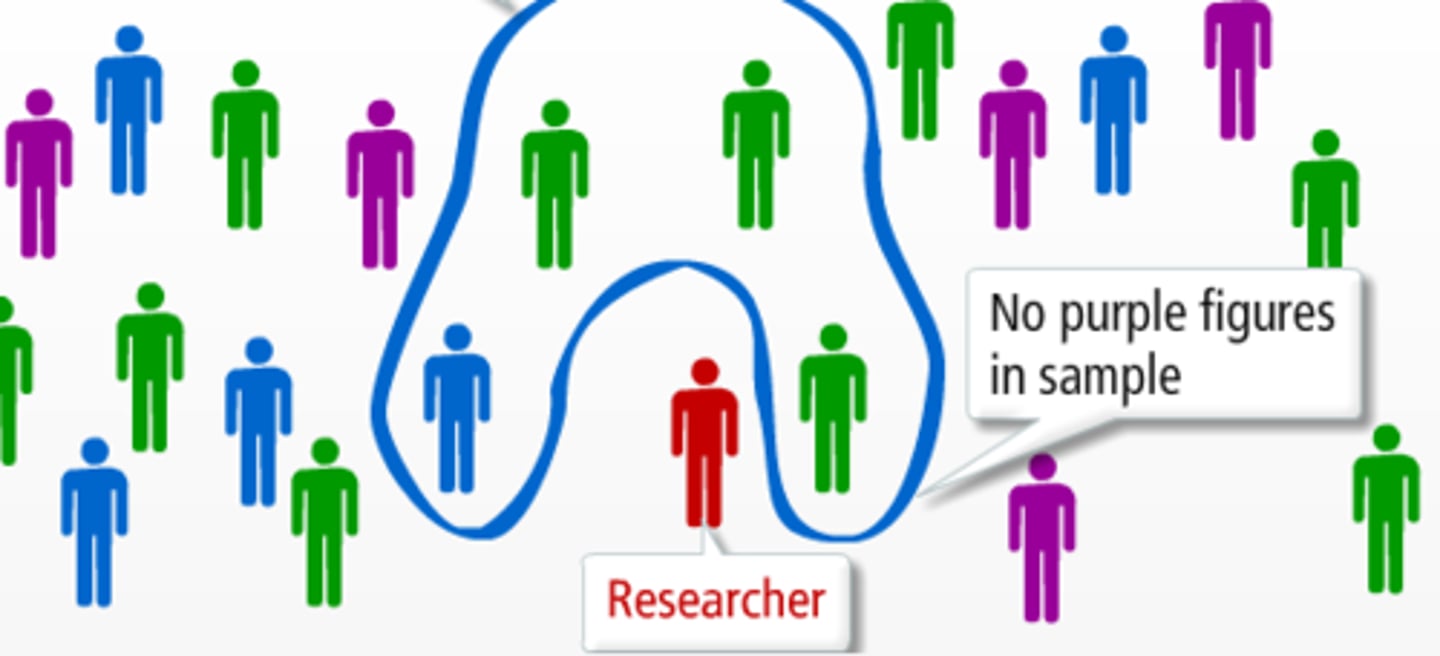
Sample
The participants with whom the study will be conducted. Should represent a wider TP allowing generalization

Opportunity Sample
Researcher recruits participants who happened to be around the time the researcher needs participants
Strength
- Large # of participants can be obtained easily
Weakness
- Unlikely to gain a wide variety of participants to allow for generalization because this draws in one type of person
Random Sample
Every Participant in the TP has an equal chance of being chosen
Strength
- Should be more representative to the population
Weakness
- obtaining details from participants
Volunteer/Self select
Researcher advertise for participants (used a lot in universities)
Strength
- Drop out rate is low, they want to participate
Weakness
- Unlikely to gain a wide variety of participants to allow for generalization

Ethics/Human
These are guidelines that should be followed when designing and running any study

Informed Consent
Giving potential participants sufficient information about research

Protection
Participants should leave the experiment in the same same manner in which they came in

Deception
Not allowing the participants to know what the true nature of the study is about

Confidentiality
Participants in research have the right to expect that information they provide will remain confidential

Privacy
Participant has the right to ignore any questions or aspect of the study. Participants should not reveal personal information

Debriefing
Appropriate information to the participants once the experiment is over
One Tailed Hypothesis (Directional Hypothesis)
these state the specific direction the researcher expects the results to move in (higher, lower, more, less)
Two Tailed Hypothesis (Non-Directional Hypothesis)
these state that a difference will be found between the conditions of the independent variable, but does not state the direction of the results. (typically these are always written "there will be a difference)
Operational Definition (i.e. operationalization)
A statement that defines the exact operations occurring in the research.
Self Report
obtaining data by asking people questions and recording their answers
Experimental Group
Subjects in an experiment who are exposed to the treatment
(INDEPENDENT VARIABLE)
Group being studied and compared to the control group
Control Group
Are not exposed to the independent variable
(DEPENDENT VARIABLE)
Results are compared to those of the experimental group
A.K.A - Control condition
Random Assignment
Assigning participants to the control and experimental groups by chance
Each participant should have an equal chance of being assigned into either group
Placebo
Researchers use a special kind of control, a placebo, to deal with expectation in some experiments
A non-active substance or condition administered instead of a drug or active agent
Given to CONTROL GROUP
Independent Groups
1. Recruit a group of participants
2. Divide into two groups
3. One group will be doing IV 1, the other group will be doing the IV 2
4. Measure the DV for each group
5. Compare results
(PROBLEMS)
-participant variable may affect DV measurement
-may seem that the IV has taken effect when it hasn't
(CONTROL)
-Randomly assigned ensure groups are similar on average.
Repeated Measures
1. Recruit a group of participants.
2. The group does the experimental task with the IV in condition 1
3. The group repeats the experimental task with the IV set in condition 2.
4. Compare
(PROBLEMS)
- Gives PP's practice
-Bore, tire
- Demand characteristics
(CONTROL)
- counterbalancing
Counterbalance
1. Identify all variables and possible conditions
2. Combine all variables in all possible order and combinations
3. Create groups
4. Expose groups to different variables in different orders
Extraneous Variables
Affect performance of participants needs to be controlled prior to experiment.