Human Metabolism Lecture 4: Serine Proteases and Protease Inhibitors
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Proteases are:
enzymes that catalyze the breaking of peptide bonds
Reasons why we would need to break a peptide bond
-Break down proteins ingested into our body (food)
-Break down & recycle proteins that used by our cells
-Activate or deactivate important biological molecules and pathways
The 2 types of cleavages
-Endopeptidase
-Exopeptidase
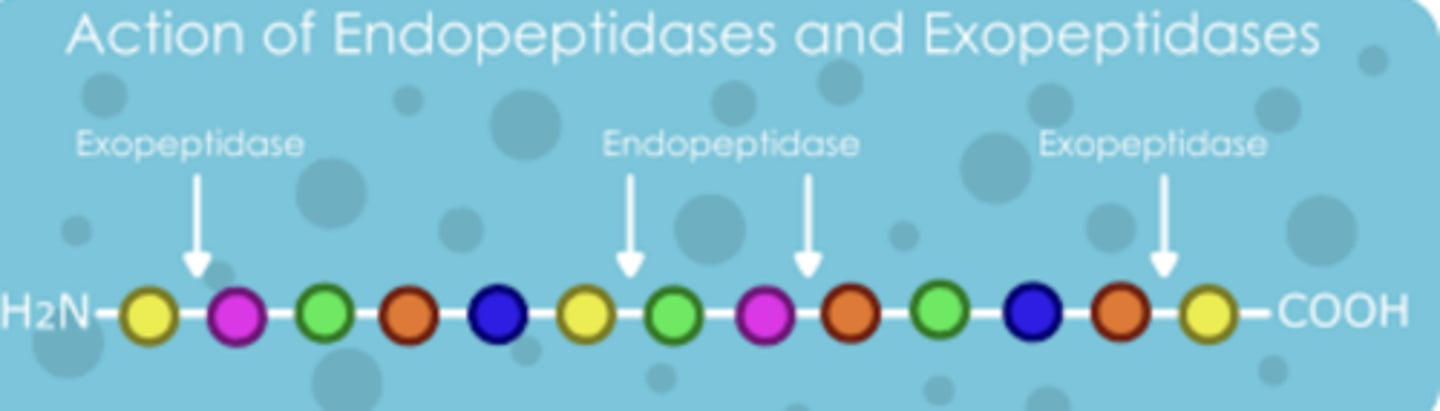
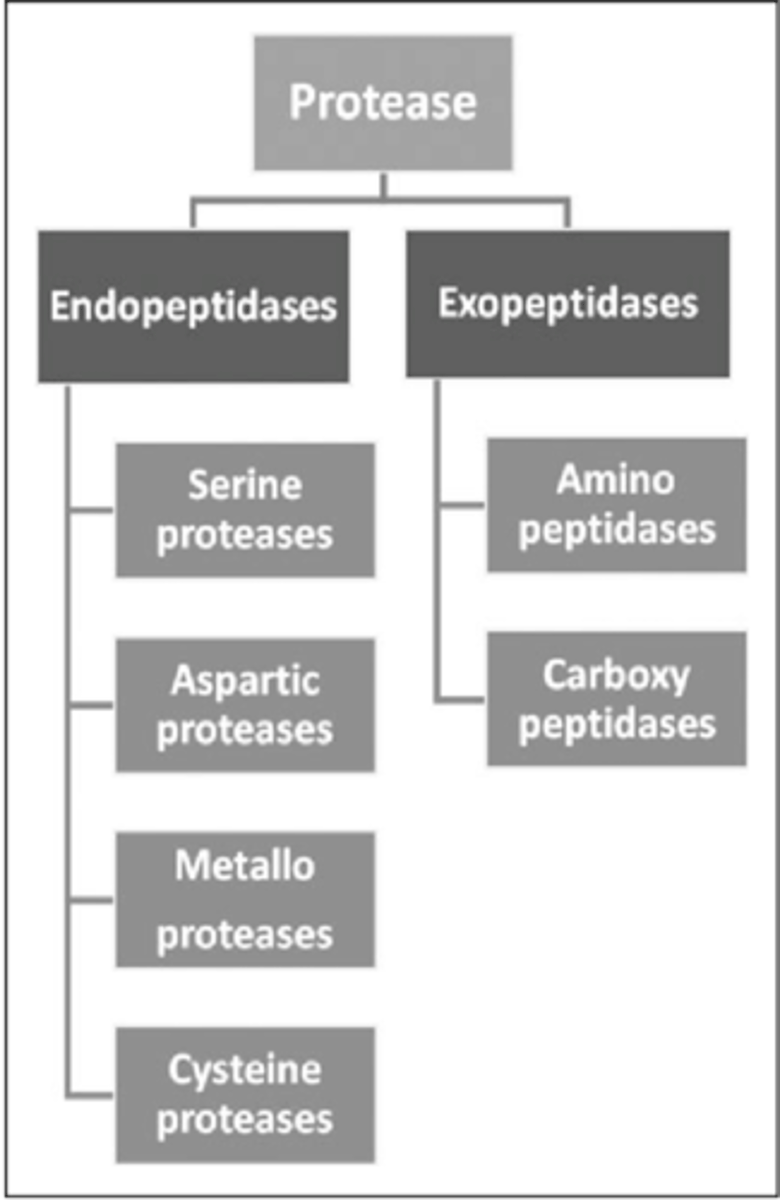
What are the 4 endopeptidases?
-Serine proteases
-Cysteine proteases
-Aspartyl/proteases
-Metallo proteases
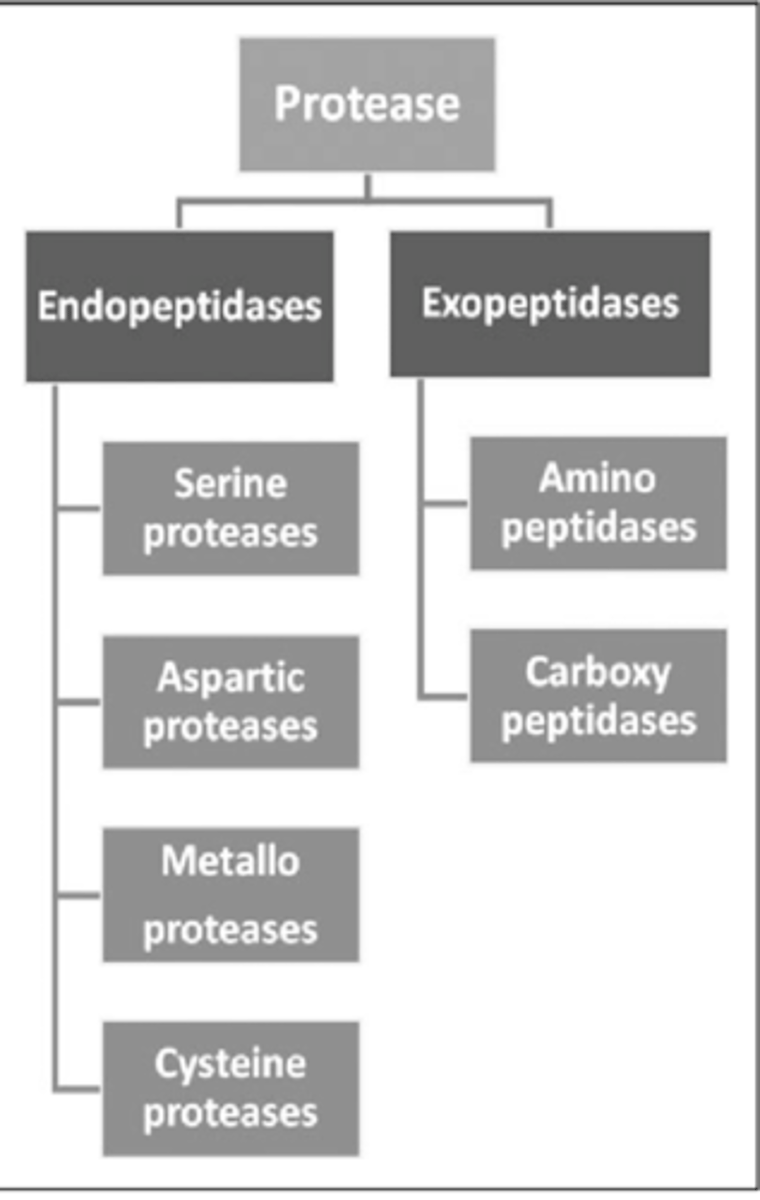
What are the 2 exopeptidases?
-Amino peptidases
-Carboxyl peptidases
4 examples of serine proteases
-Trypsin
-Elastase
-Chymotrypsin
-Thrombin (blood clotting cascade)
The active site of serine proteases
Serine -OH
Ser is part of a catalytic triad. What are the 3 parts of this triad?
-Ser (serine)
-His (histidine)
-Asp (aspartic acid)
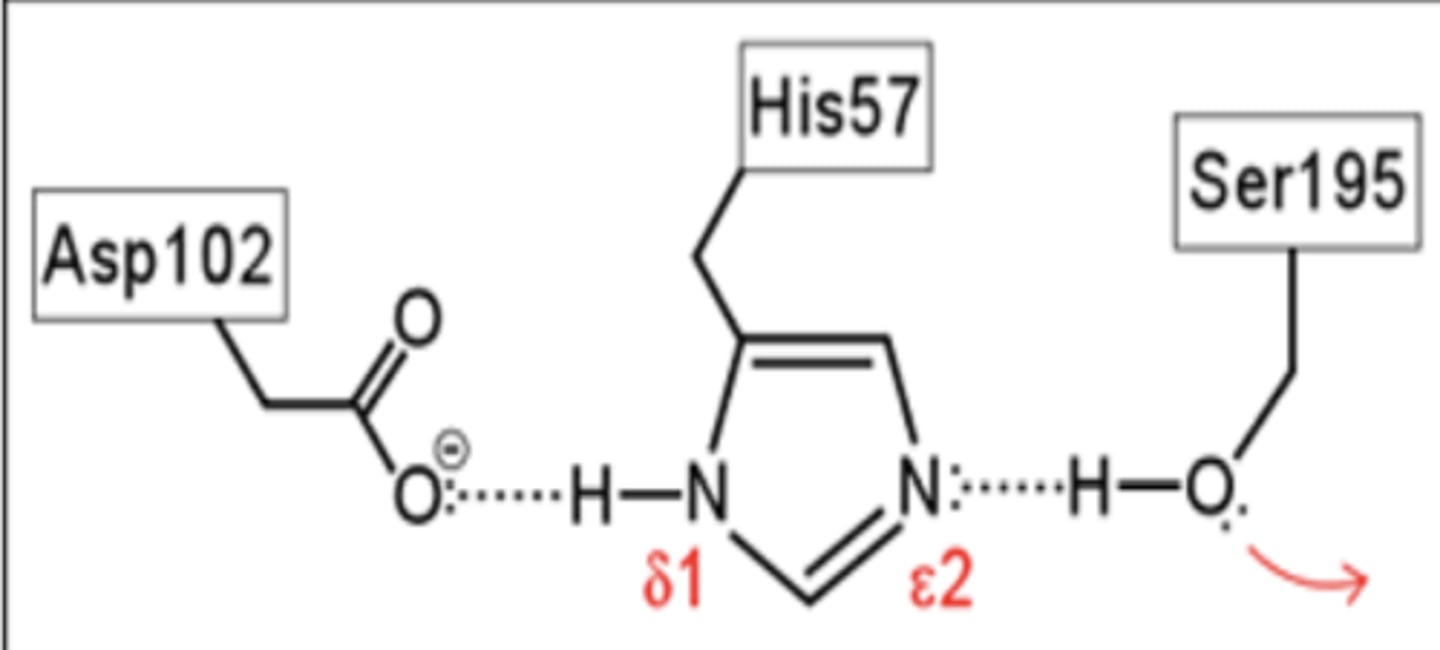
Serine proteases are _______________ but locations of the 3 crucial residues ___________ somewhat.
homologous
differ
Asp-102 functions to
orient His-57
His-57 acts as a
general acid and base
Ser-195 form a
covalent bond with peptide to be cleaved
What are the pancreatic proteases?
Trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase (aid in digestion)
The serine protease in the blood clotting cascade
thrombin
All serine proteases cleave peptide bonds by a similar mechanism of action but differ in their..............
specificity and regulation
Zymogen (proenzymes)
an inactive form of enzymes
How are zymogens (proenzymes) activated?
activated by cleavage of one or a few specific peptide bonds (Zymogen activation) (proteolysis)
Examples of specific proteolysis
Digestive enzymes
-synthesized as zymogens in the stomach and pancreas
Blood clotting enzymes
-a cascade of proteolytic activations
Protein hormones
-proinsulin to insulin by removal of a single peptide
Zymogens secreted by the pancreas area activated in the ___________________
intestinal tract (to trypsin and chymotrypsin)
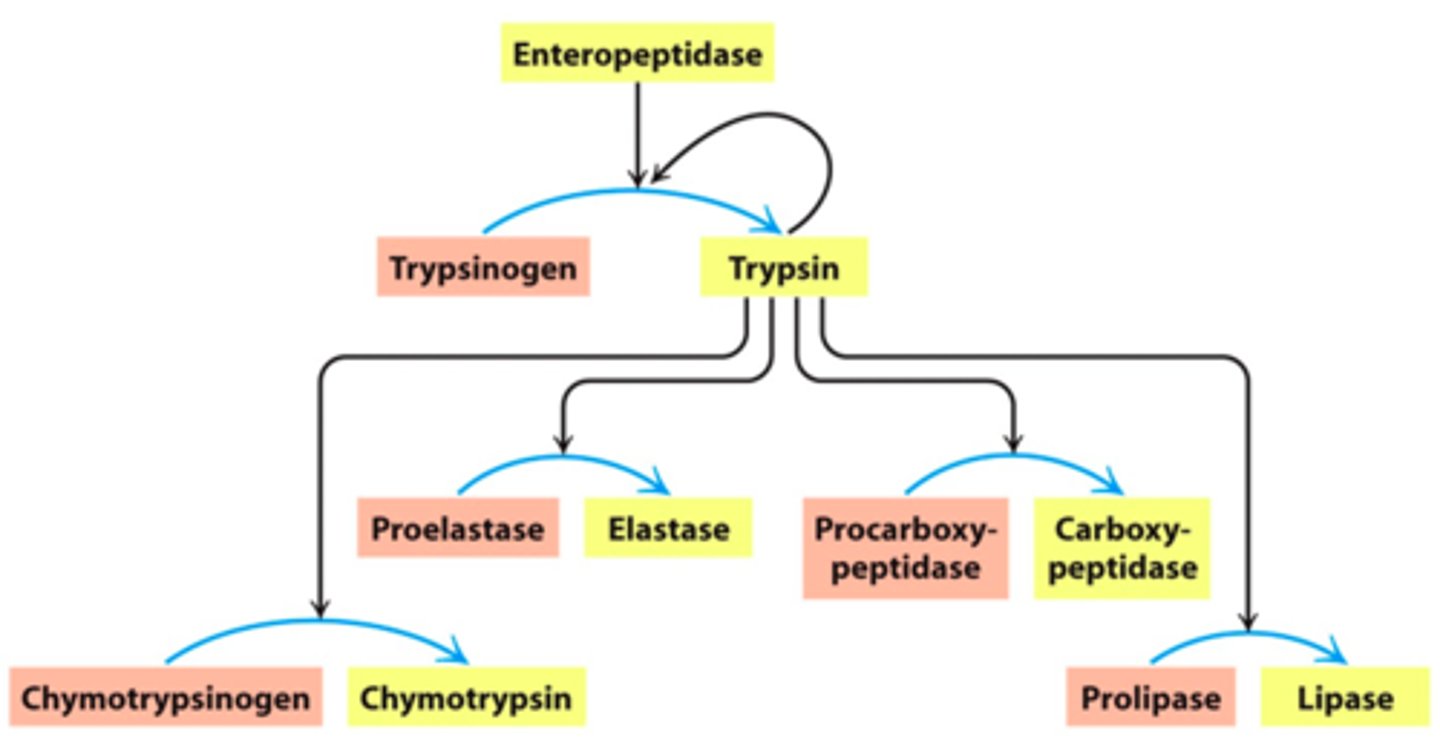
Trypsin itself is activated by ...........
enteropeptidase, secreted by cells lining the digestive tract
(Trypsin activates other enzymes)
Chymotrypsinogen is produced by
the pancreas
Chymotrypsinogen is activated by
proteolytic cleavage by trypsin into chymotrypsin (serine protease in the small intestine)
Activation of chymotrypsinogen involves proteolytic cleavage at __________ sites resulting in the formation of ______ chains held together by ______________.
-2 sites
-3 chains
-disulfide bonds
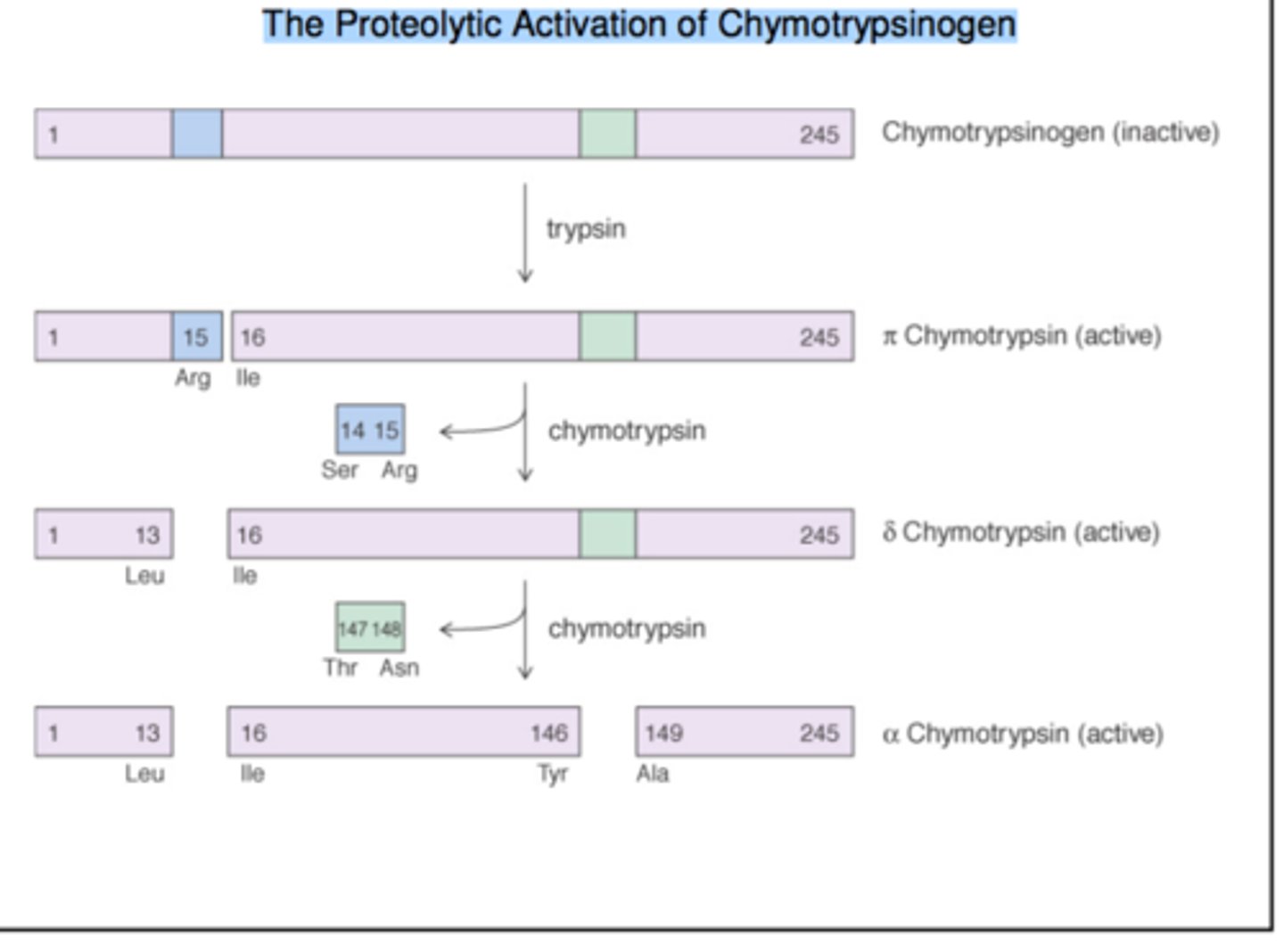
Alpha Chymotrypsin
the fully active and stable form
-responsible for most of the proteolytic activity in protein digeston
Pi Chymotrypsin and Delta Chymotrypsin
intermediate forms during the activation of chymotrypsinogen into alpha chymotrypsin.
-Have limited enzymatic activity
-Less stable than alpha chymotrypsin
The active site of chymotrypsin
catalytic triad of serine-histidine-aspartic acid
Where is the substrate binding site of chymotrypsin?
The S1 pocket
Traits of the S1 pocket in chymotrypsin
-Relatively deep/broad
-Hydrophobic (nonpolar)
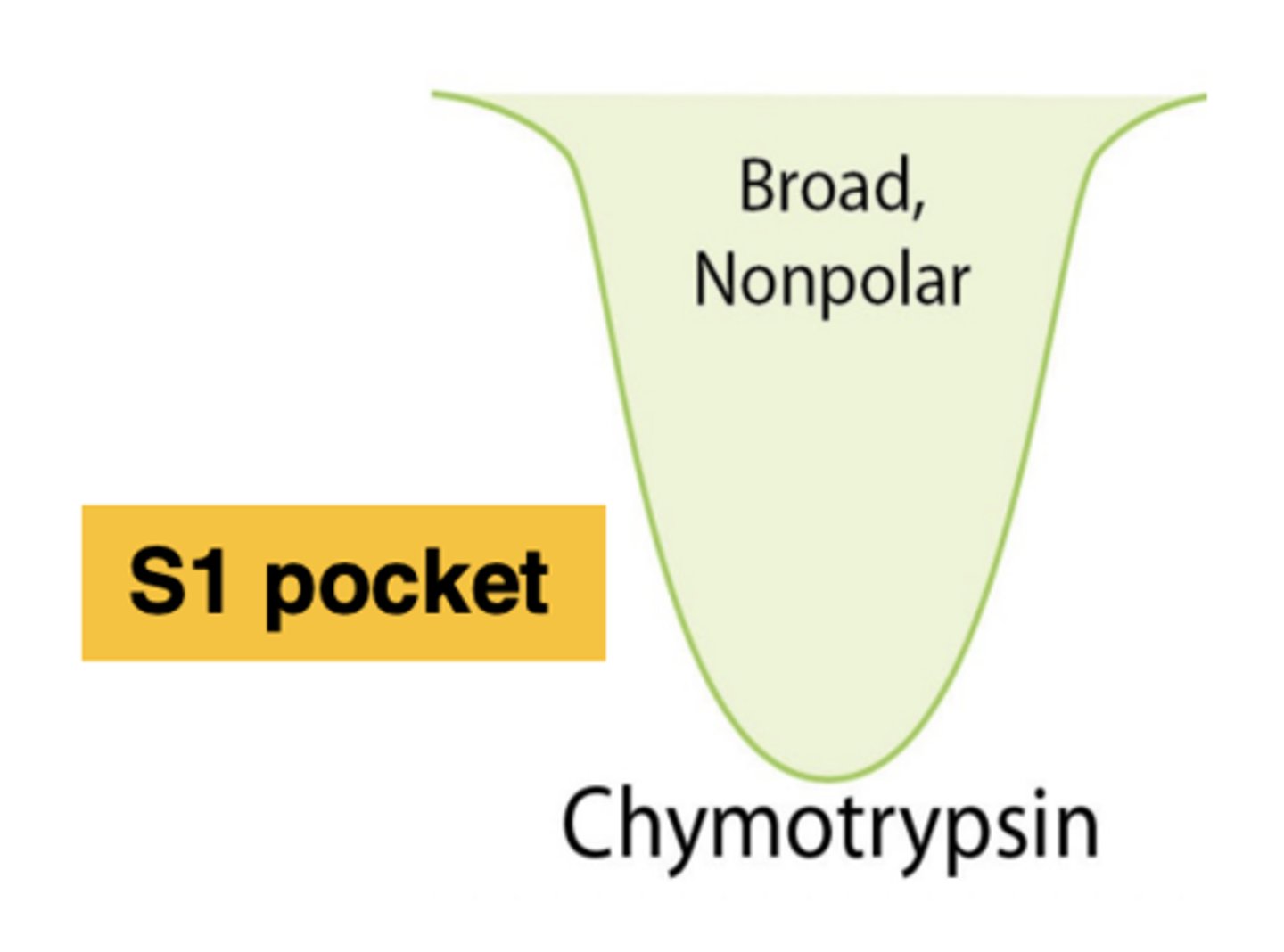
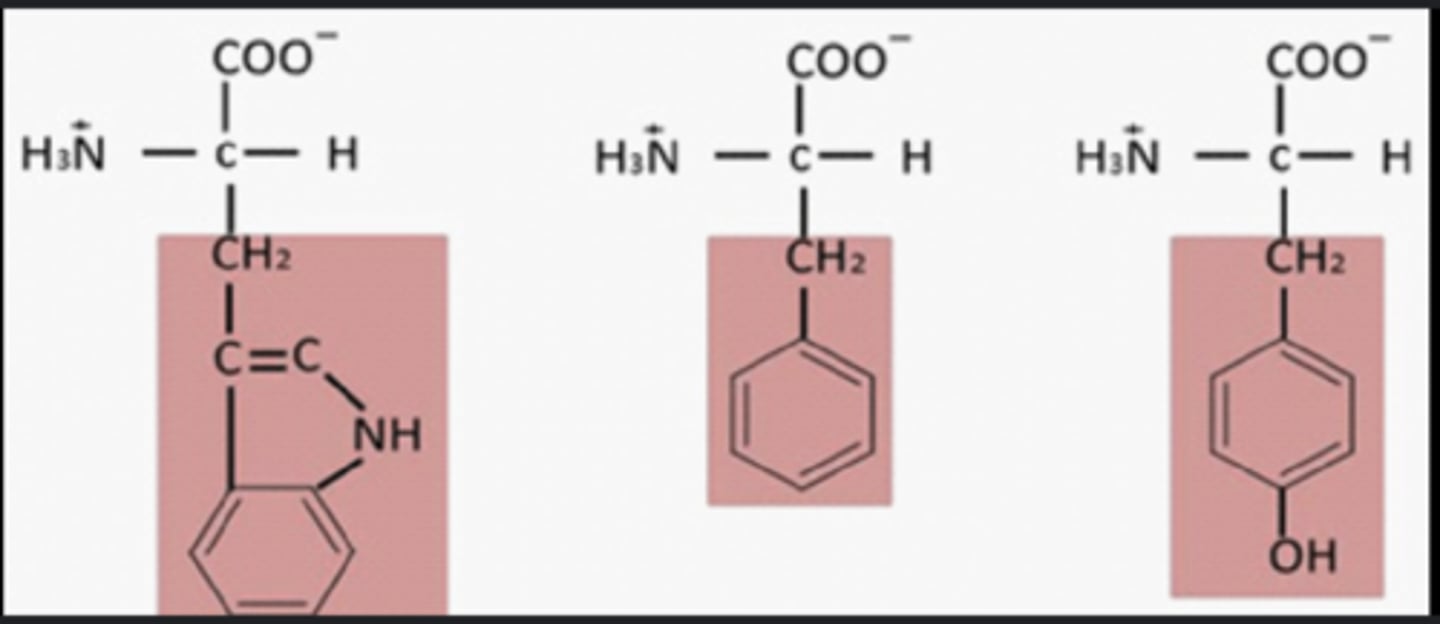
Chymotrypsin catalyzes .........
bulky, hydrophobic amino acids
The S1 pocket in chymotrypsin catalyzes the cleavage of peptide bonds on the.........(4 amino acids)
carboxyl side of bulky, hydrophobic amino acids:
tryptophan, methionine, tyrosine, and phenylalanine
What are the 4 amino acids chymotrypsin catalyzes
tryptophan, methionine (s), tyrosine, and phenylalanine
Chymotrypsinogen must remain inactive until it reaches the digestive tract to............
prevent damage to the pancreas; premature activation of zymogens can lead to acute pancreatitis
Traits of the S1 pocket in trypsin
Has an aspartate residue; a negatively charged bottom
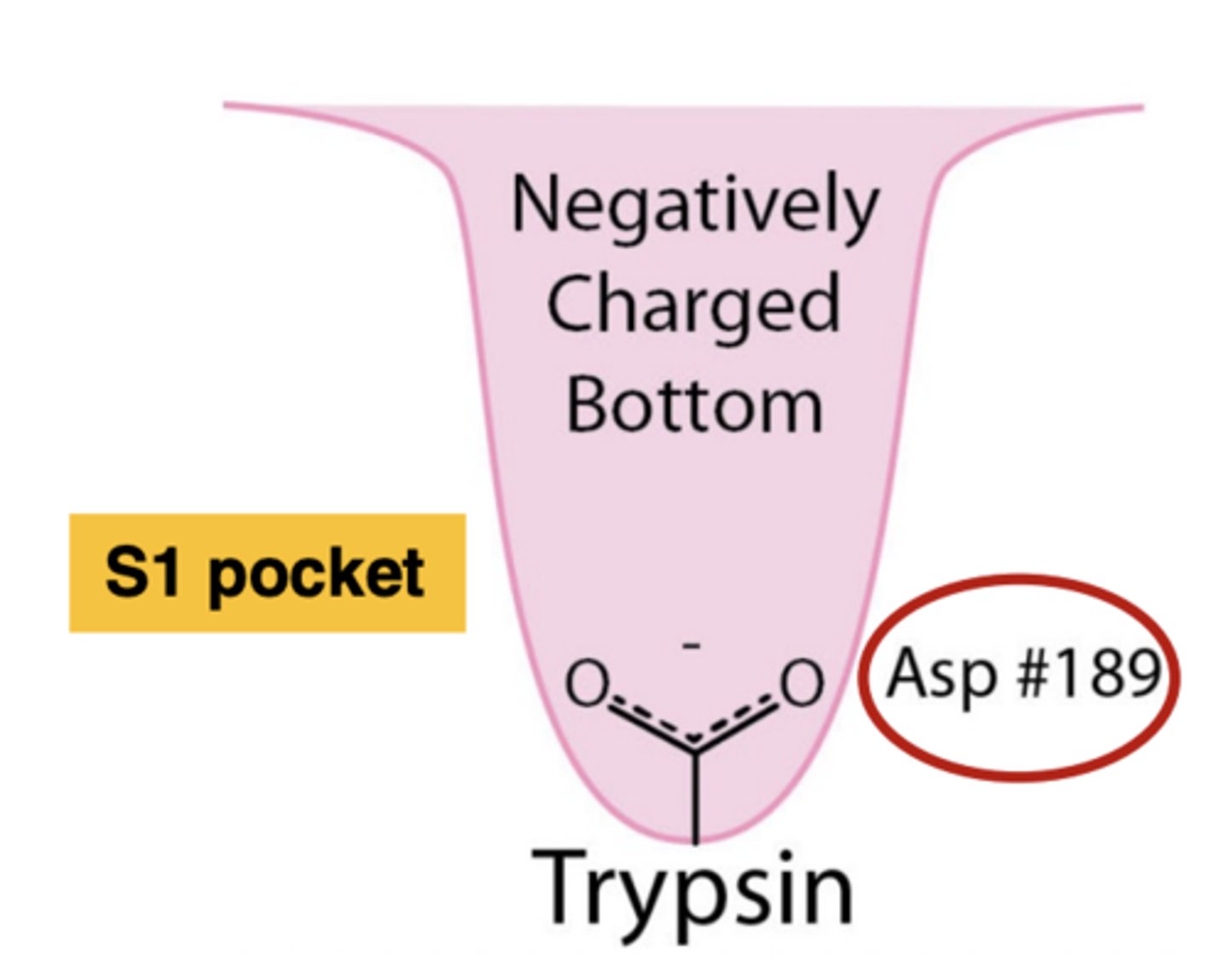
1. What is at the bottom of the active site of trypsin (S1 pocket)?
2. What charge is the S1 pocket, and how does this help?
1. aspartate residue
2. Negative charge of the aspartate (bottom of pocket) will stabilize amino acids with positively charged chains
How does the aspartate residue at the bottom of the active site of trypsin contribute to its substrate specificity?
The negative charge of the aspartate residue stabilizes the positively charged side chains of lysine and arginine, facilitating their cleavage.
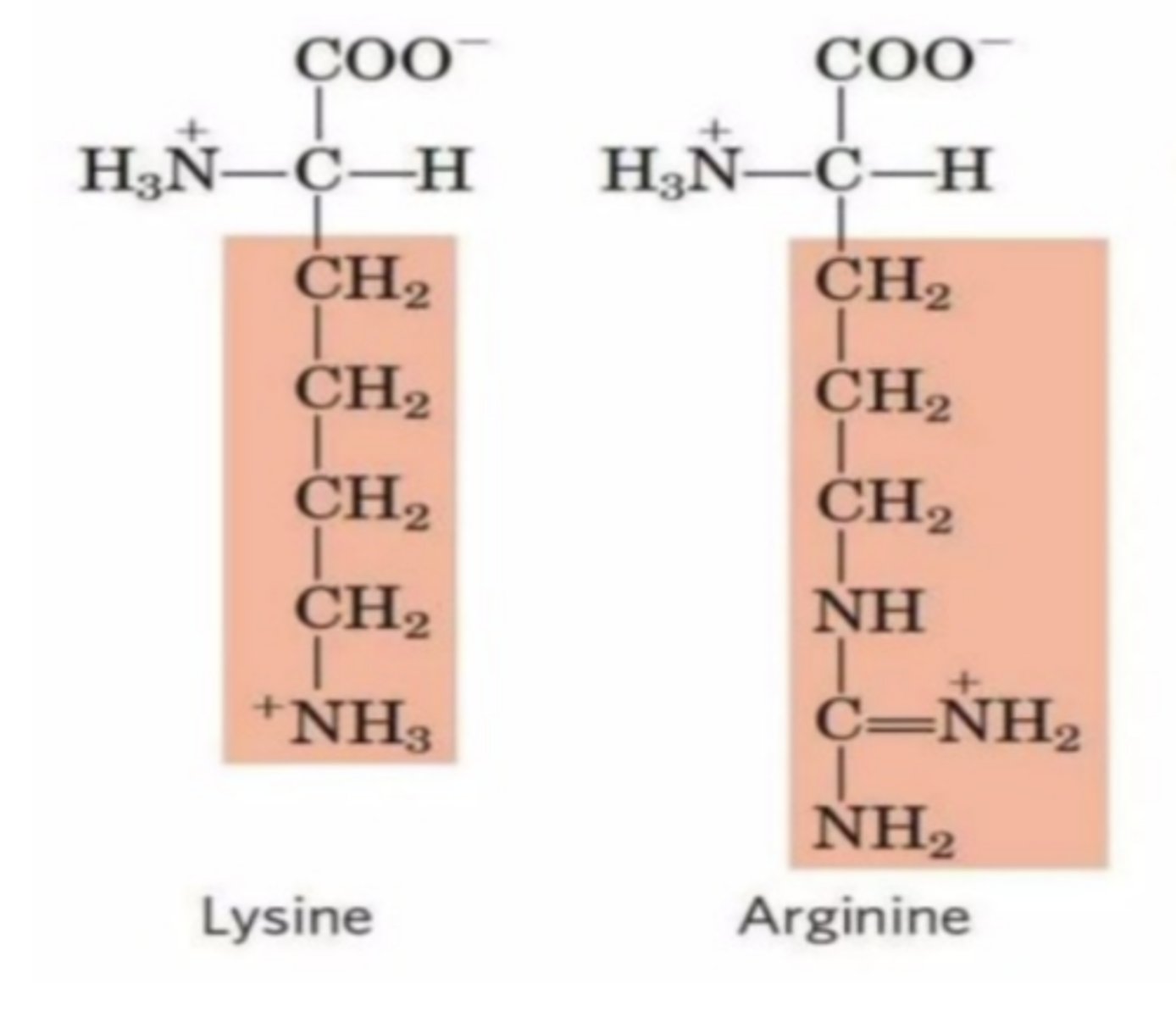
Trypsin cleaves peptide bonds on the......(2 amino acids)
carboxyl side of lysine and arginine amino acids
What are the characteristics of the S1 pocket of elastase
narrow, nonpolar, has 2 valine residues
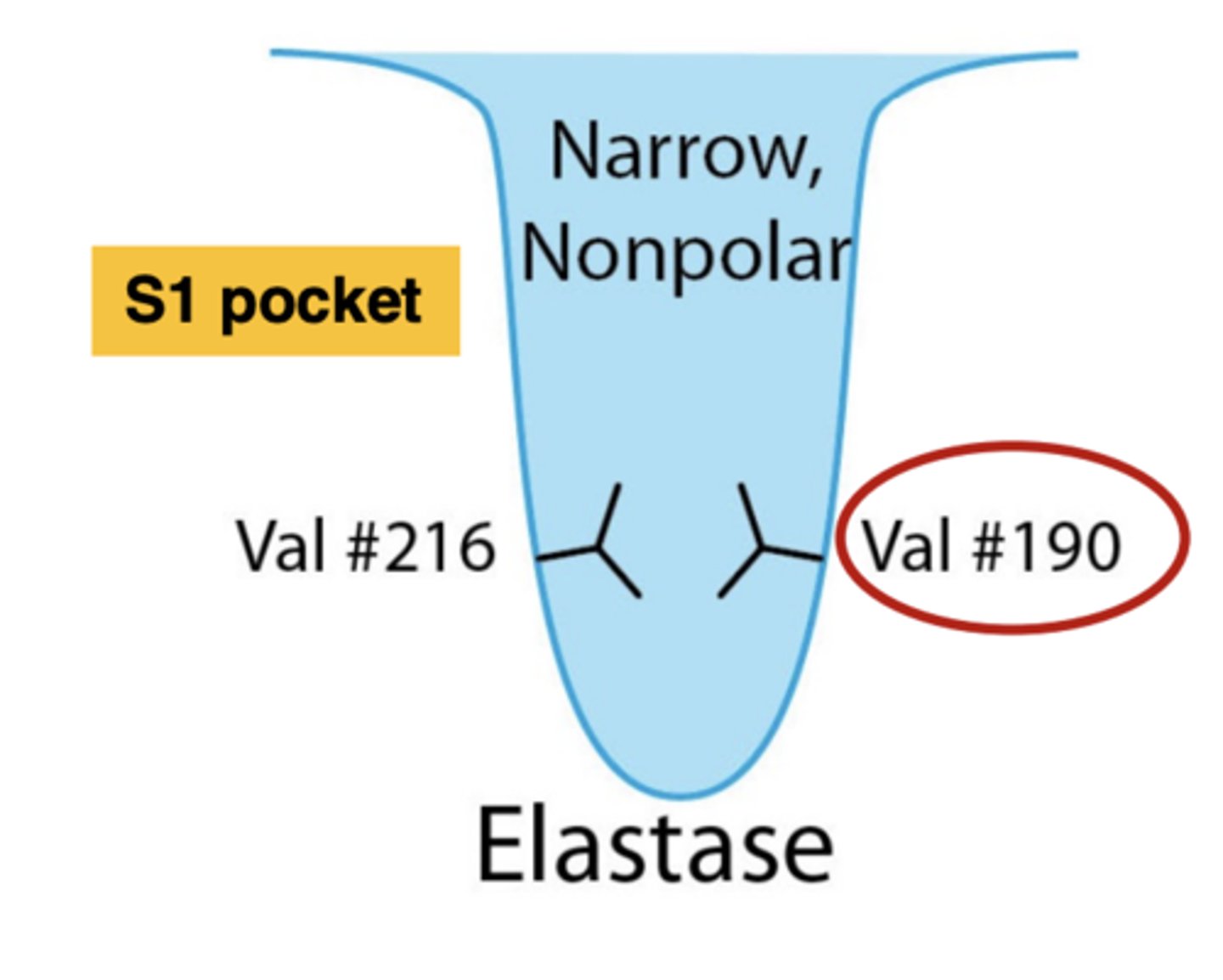
Elastase cleaves peptide bonds of......(5 amino acids)
small, hydrophobic amino acids: glycine (H), valine, alanine (CH3), leucine, and isoleucine
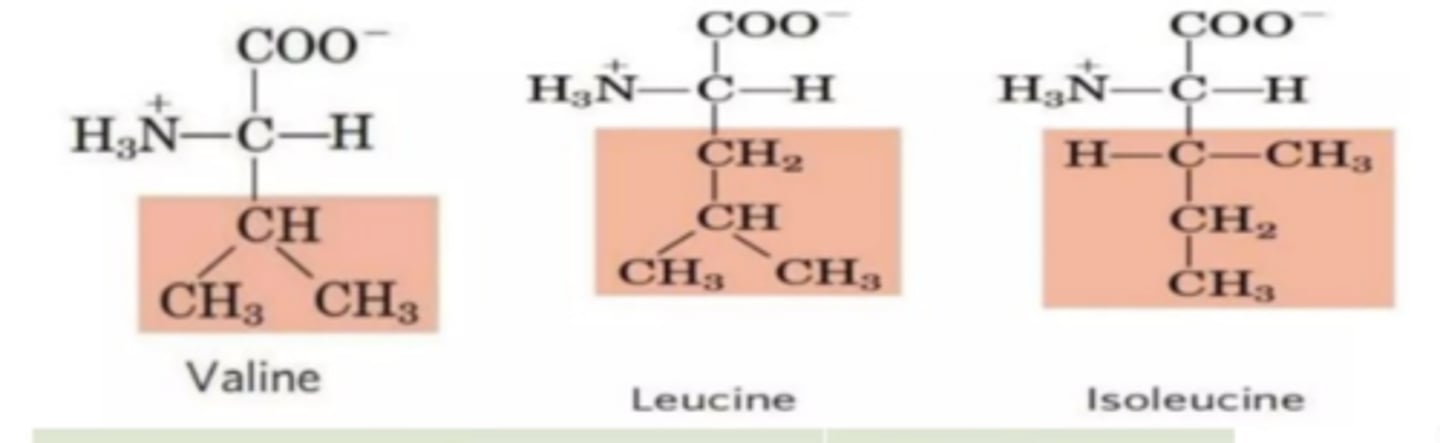
__________________ residues block off the majority of the pocket in elastase
Two valine residues
Proprotein convertases (PCs)
family of proteins that activate other proteins (e.g., proinsulin-->insulin)
Many proteins are inactive when they are first synthesized because....
Pcs activate them by....
they contain chains of amino acids that block their activity.
PCs remove those chains and activate the protein
Mutations in PC1 can lead to
severe PC1 deficiency such as elevated proinsulin and obesity
Serine protease inhibitors
-regulates/maintains balance of proteolytic activity of serine proteases
When the balance of serine protease is disturbed, this can lead to..
cancer, inflammatory diseases, diabetes, neurogenerative disorders
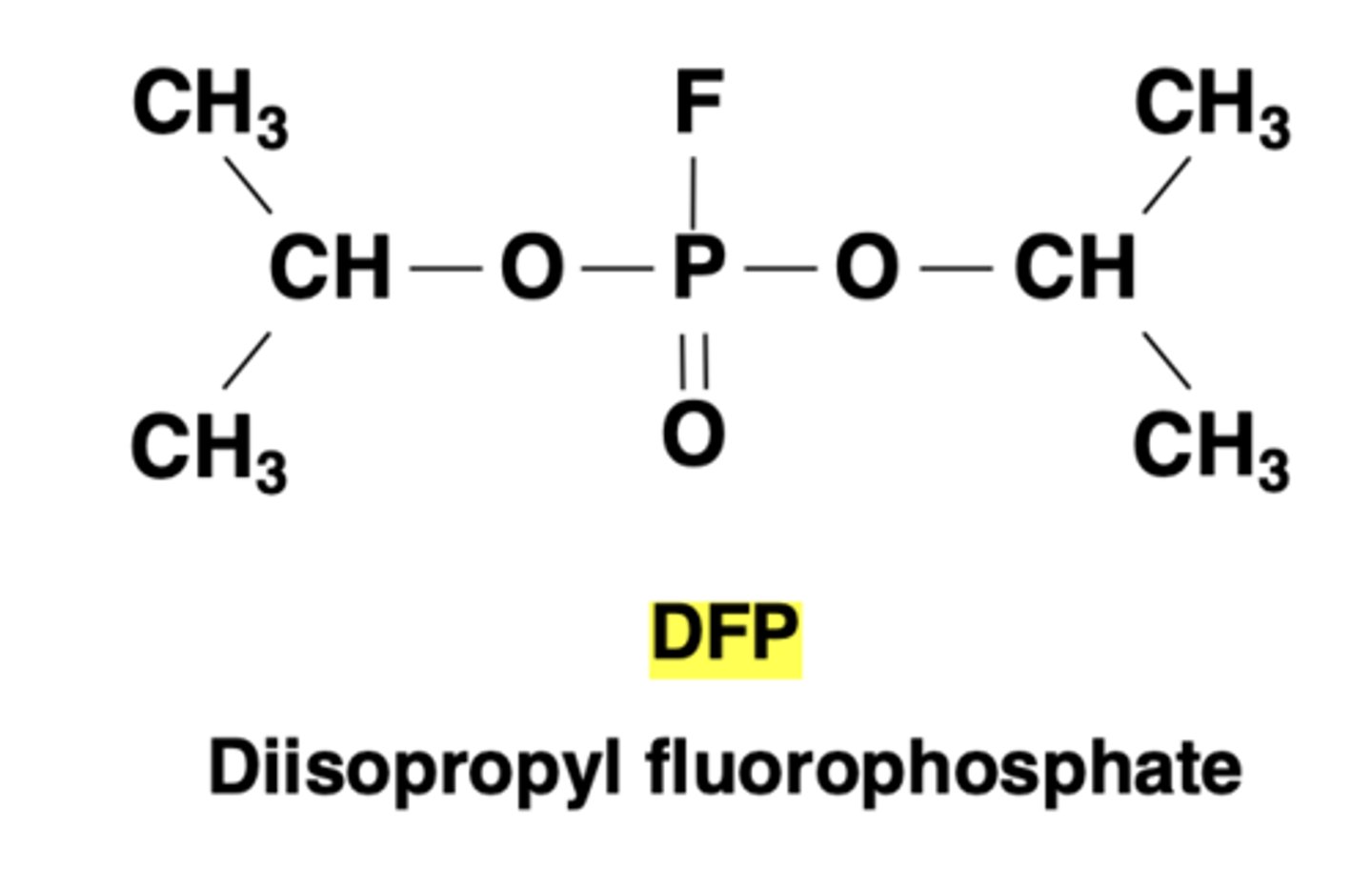
The most effective inhibitor of serine proteases (irreversibly binds with the enzymes)
Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DFP)
Aspartic proteases involve ____________ residues at the active site
2 Asp residues
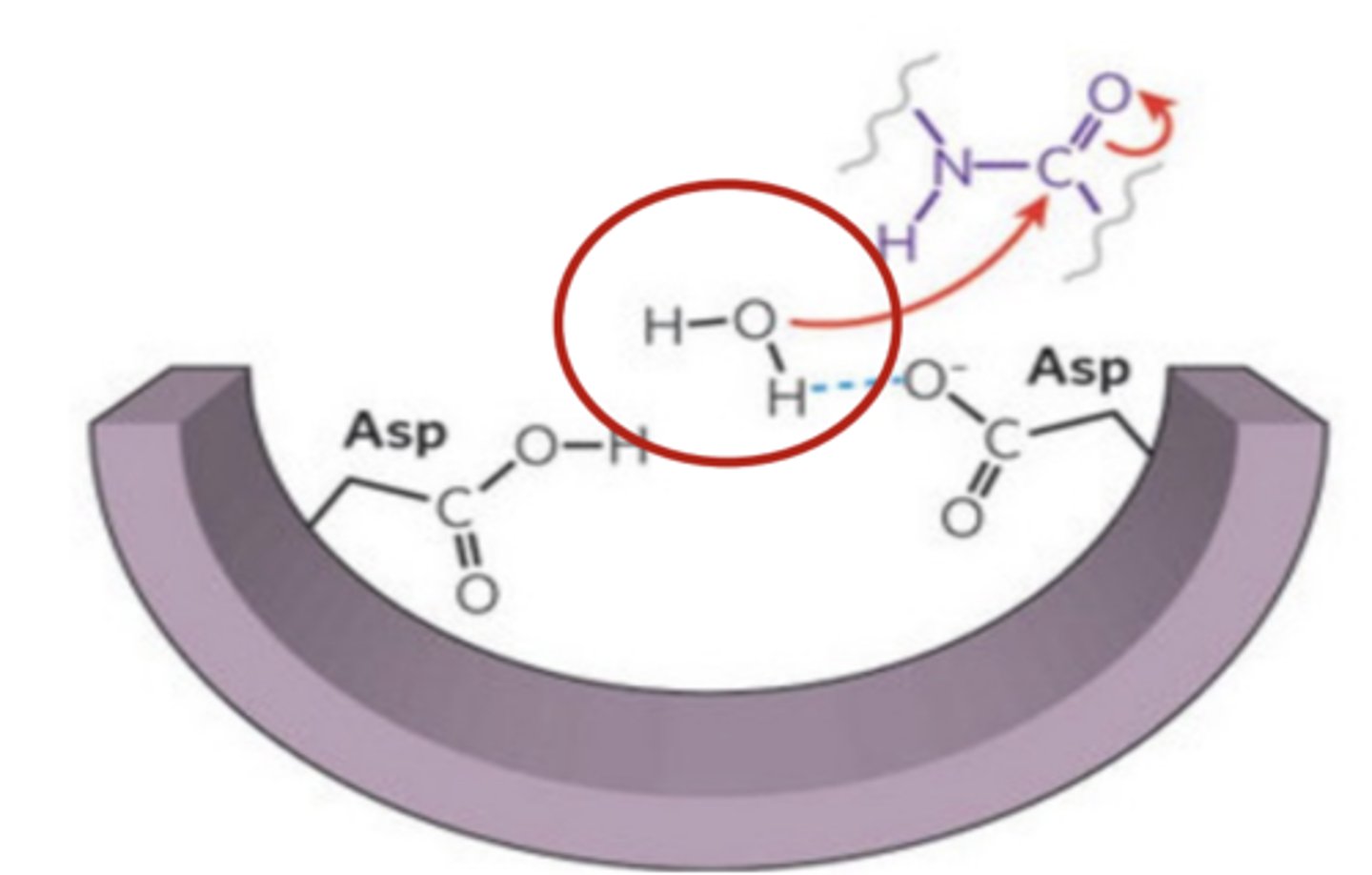
Aspartyl proteases active a __________________ to serve as the nucleophile instead of using a functional group of the enzyme itself
water molecule
A ___________________ donates an electron pair to attack and cleave the peptide bond in a substrate protein
nucelophile
Name an example of an aspartic acid protease
HIV-1 protease
HIV-1 protease
cleaves the polyprotein products of the HIV genome
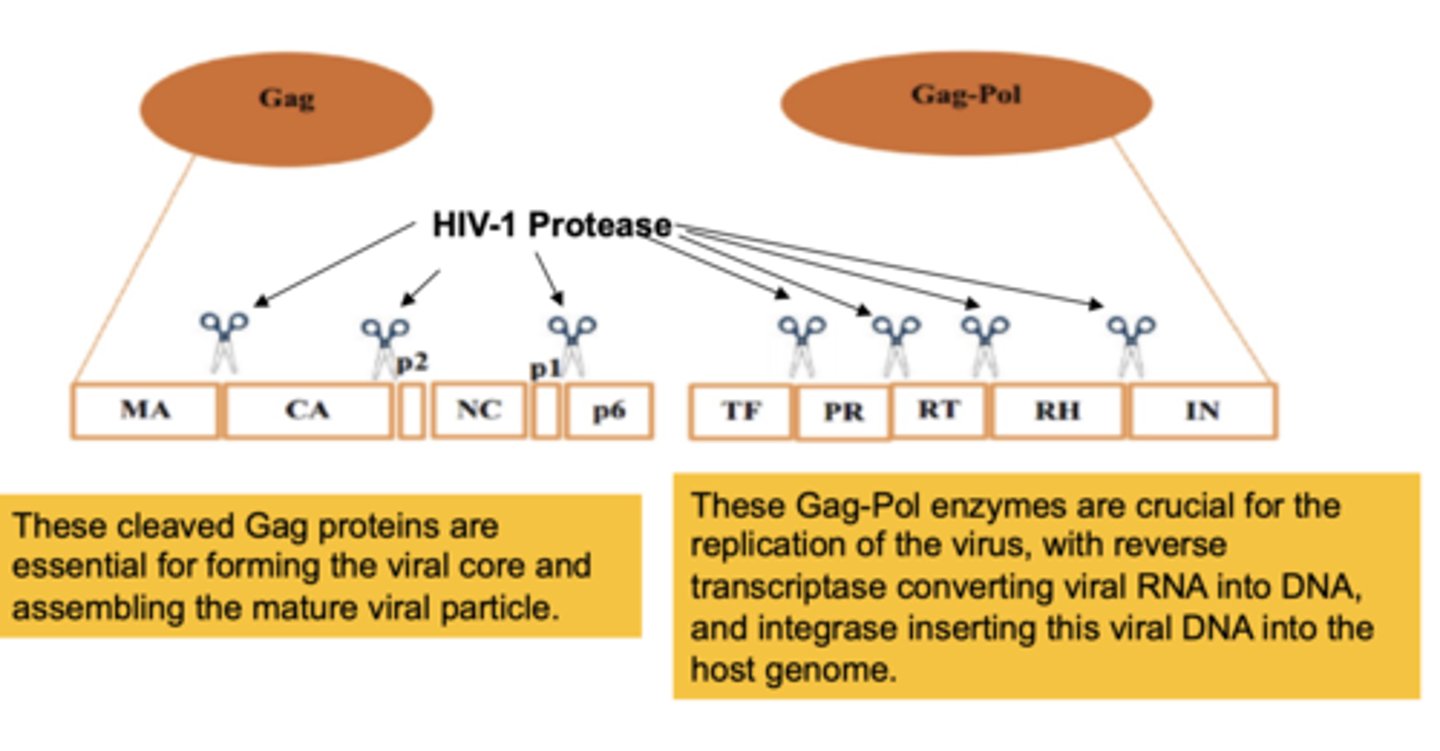
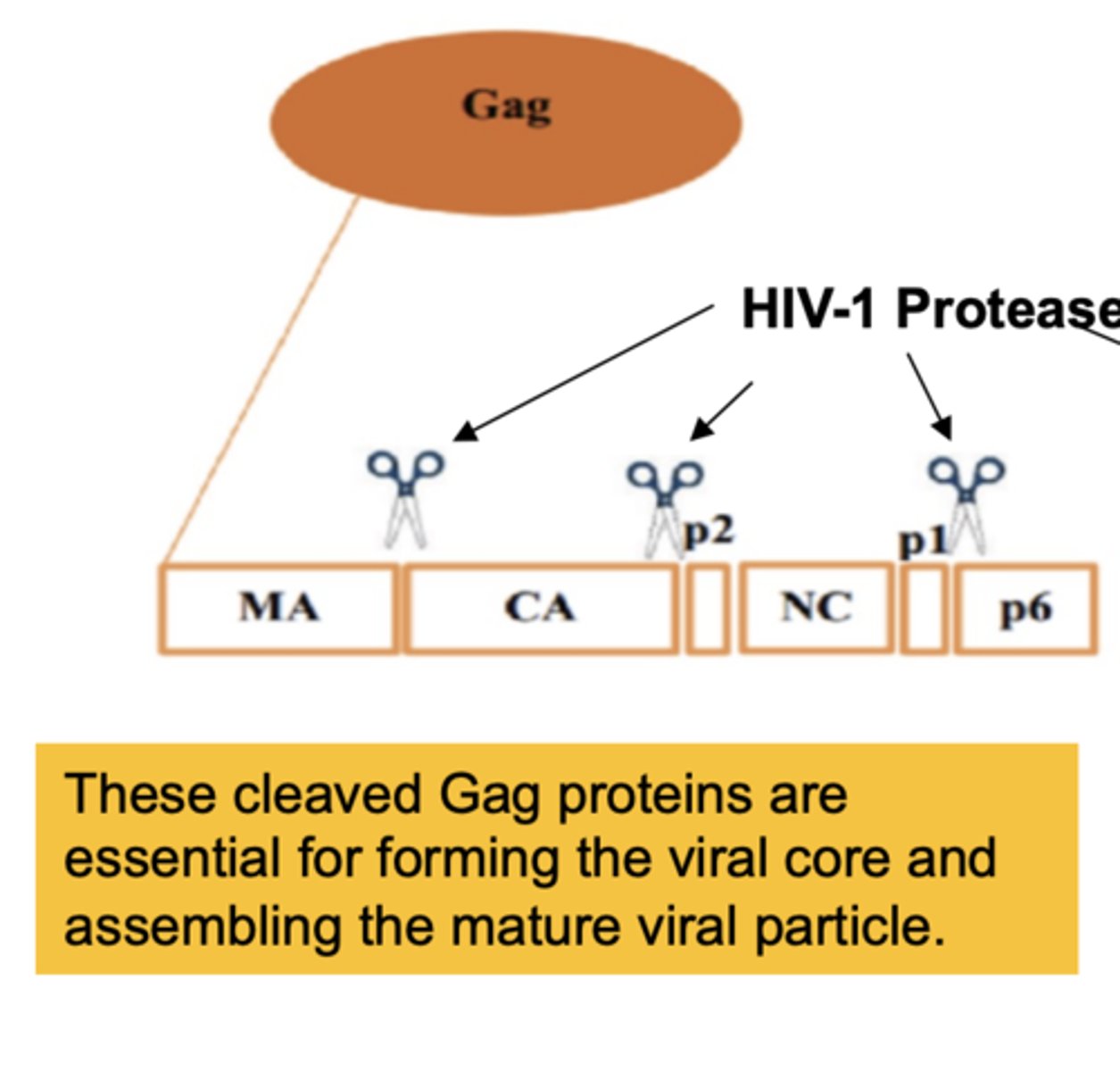
The Gag proteins are essential for
forming the viral core and assembling the mature viral particle
The Gag-Pol enzymes are essential for
the replication of the virus, reverse transcriptiptase (RNA-> DNA), & integrase inserting viral DNA into host genome
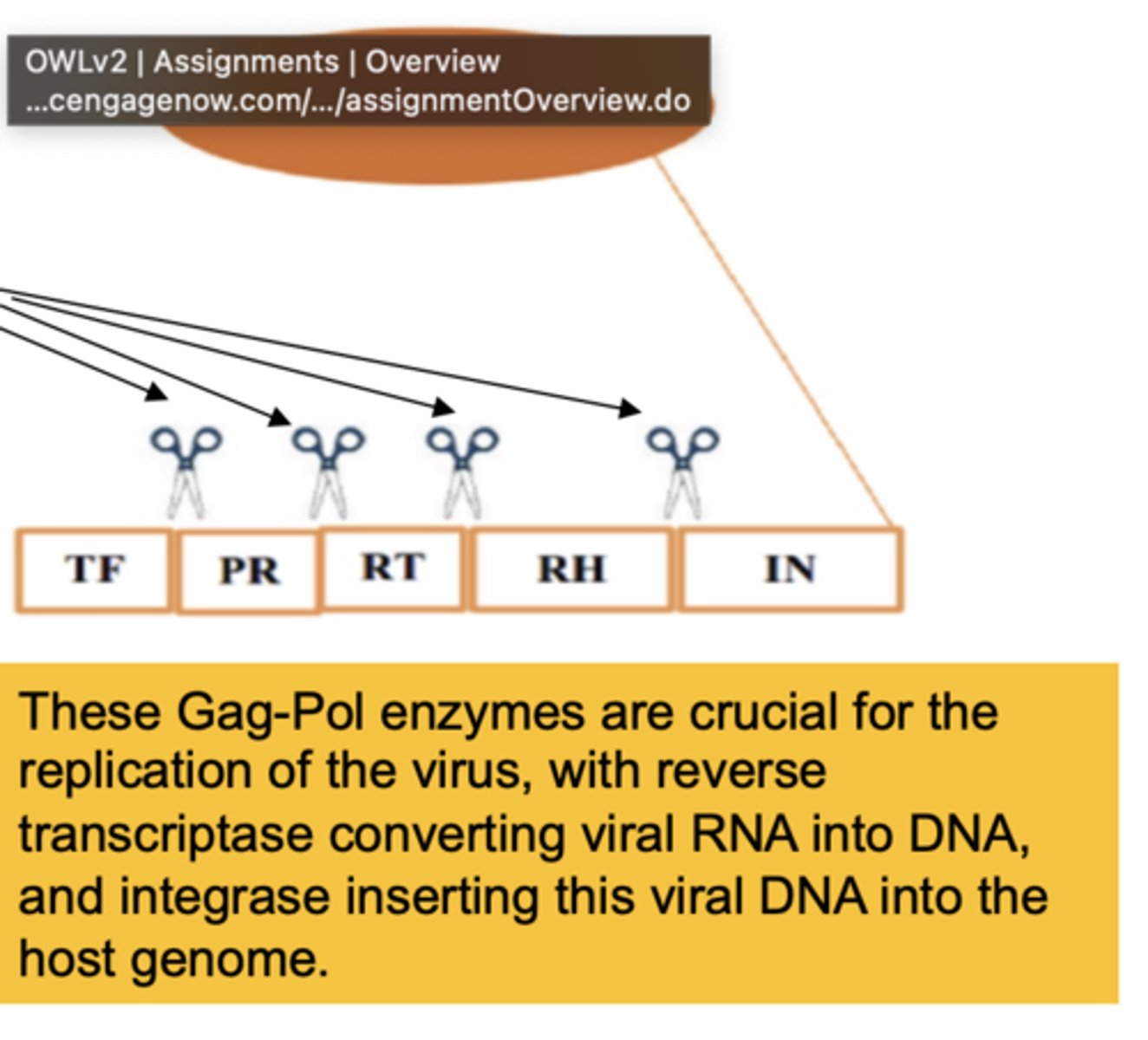
a successful HIV drug must be able to kill the virus without
blocking other essential proteases in the body
Which of the following statements accurately describes HIV protease?
HIV protease cleaves polyprotein precursors into functional viral proteins, which are essential for the assembly of new virions.
HIV protease is which of the following:
aspartic protease
Cysteine proteases (thiol proteases)
Hydrolase enzymes that degrade proteins
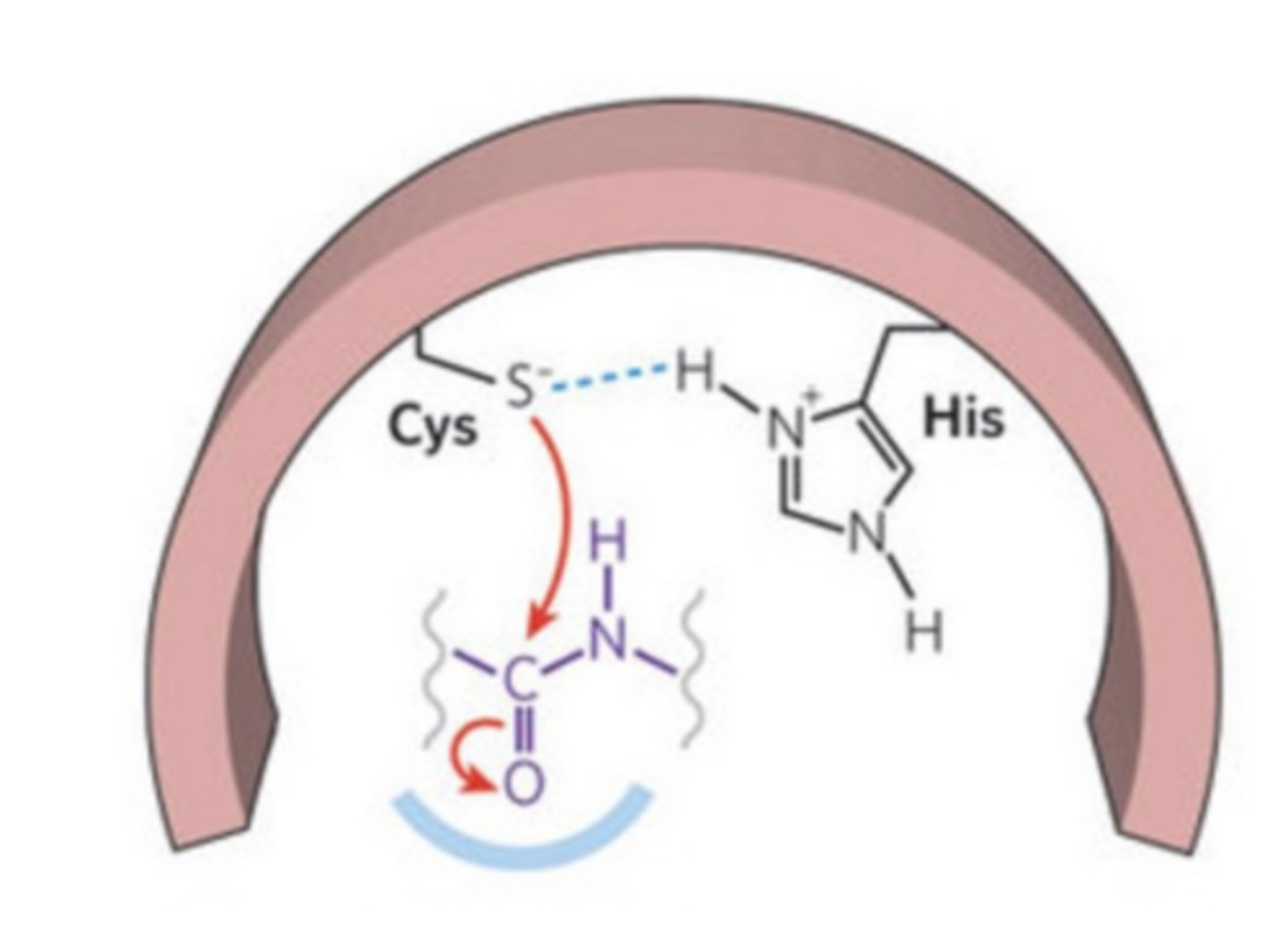
What is the active site of cysteine proteases?
consists of a His/Cys catalytic dyad
What acts as the nucleophile in cysteine proteases?
cysteine acts as the nucleophilic agent
Cysteine is activated into a good nucleophile by the action of a
histidine residue
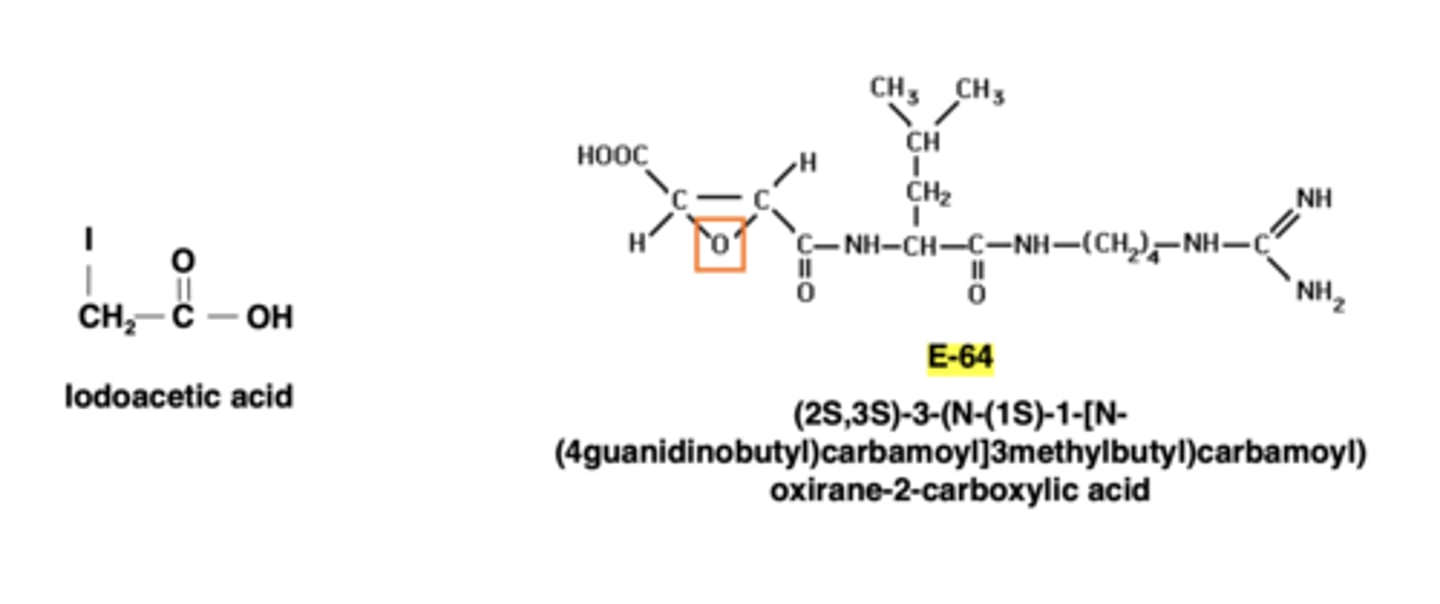
What are 2 examples of cysteine protease inhibitors?
iodoacetic acid-acts as an electrophile that can covalently modify sulfhydryl groups present in the cysteine side chain
E-64 can irreversibly inhibit a wide range of cysteine peptidases, such as papain, cathepsin B, cathepsin L, and calpain
Metalloproteinase
any protease enzyme whose catalytic mechanism involves a metal
T/F: Proteases used as diagnostic & therapeutics are not accepted. Enzymes have not been in use for many years
FALSE
they are widely accepted & several enzymes have been in use for years
-anti-cancer agents
-anti-inflammatory
-antimicrobial
-clot dissolving agents
The S1 pocket of chymotrypsin is relatively deep/broad and is hydrophobic. Thus, it catalyzes the cleavage of peptide bonds on the carboxyl side of:
a) phenylalanine
b) glycine
c) lysine
d) alanine
a) phenylalanine
The catalytic triad of serine proteases are composed on which of the following
a) Ser (serine), Val (valine), Asp (aspartic acid)
b) Ser (serine), His (histidine), Asp (aspartic acid)
c) Ser (serine), Val (valine), Val (valine)
a) Ser (serine), Asp (aspartic acid), Asp (aspartic acid)
b) Ser (serine), His (histidine), Asp (aspartic acid)
Chymotrypsin is a _______ protease
serine protease