BIO 107: Unit 1 - Ch 5 Histology
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What are cell junctions?
How do cells connect to form tissues?
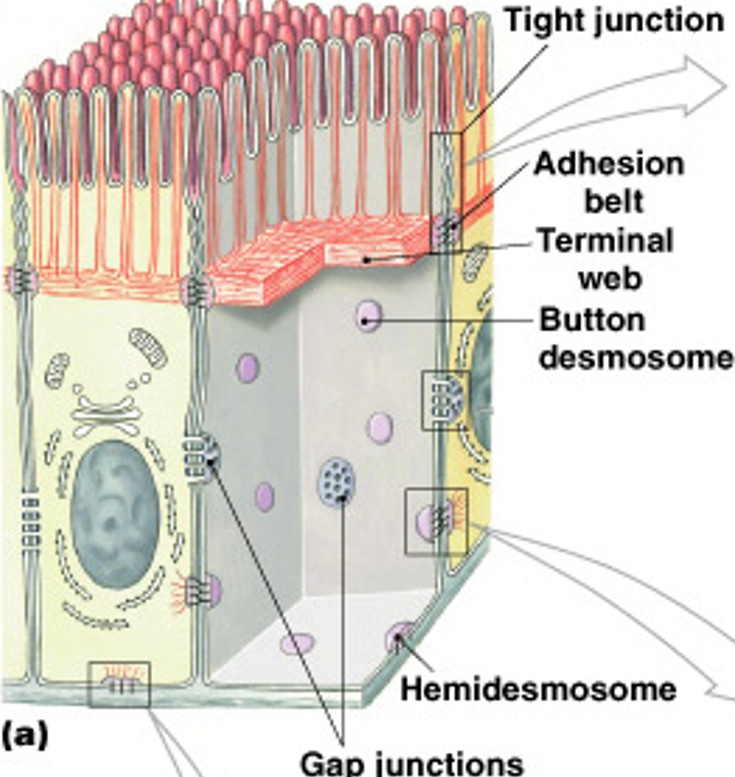
What are tight junctions?
Which type of junction is:
Very tight
Does not allow even water through
Interlocking web-like proteins
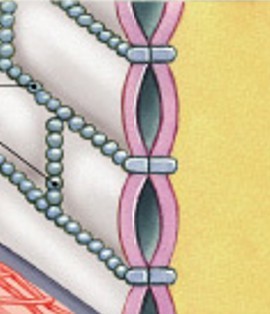
What is adhesion belt?
Which type of junction is:
Very tight
Forms a belt of interlocking membrane proteins
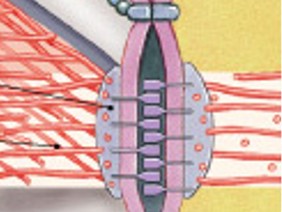
What are desmosomes?
Which type of junction is:
Like a button or spot weld
Resists stretching and twisting
Cell to cell
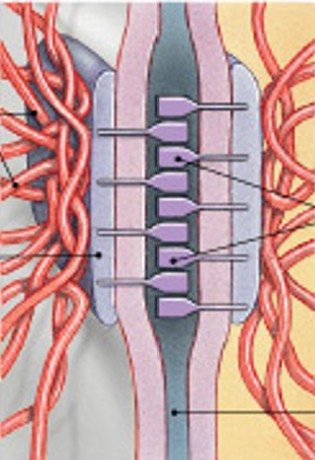
What are hemidesmosomes?
Which type of junction is:
Half button
Resists stretching and twisting
Cell to basement membrane
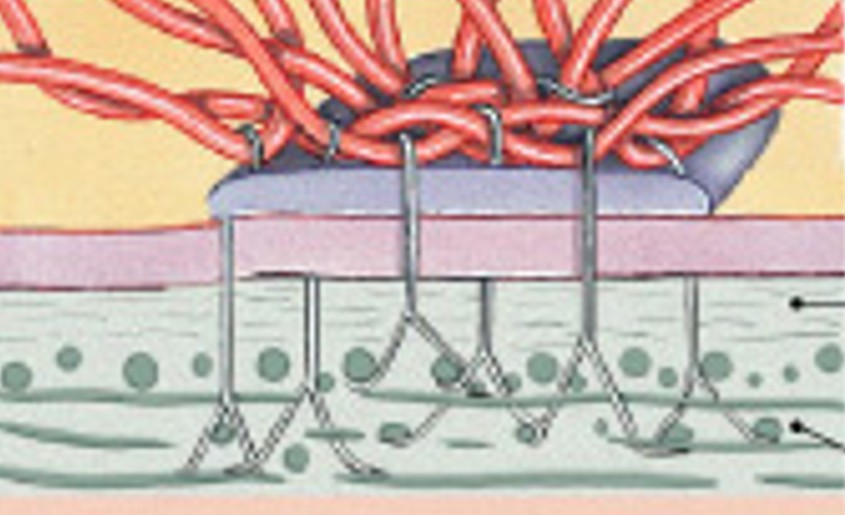
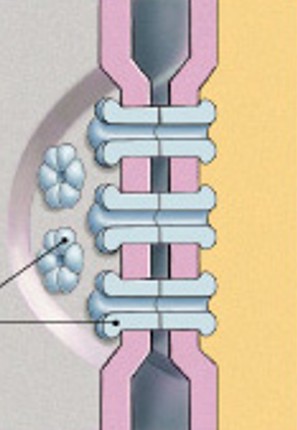
What are gap junctions?
Which type of junction is:
Tiny fluid filled tubes
Uses channel proteins
Allows some movement in & out of cell
What is epithelia?
What covers internal & external surfaces?
What are glands?
What produces fluid secretions?
What are the characteristics of epithelia?
What are these characteristics of:
Cell junctions.
Polarity - apical (top) and (bottom) surfaces.
Attachment (basal lamina).
Avascular - does not receive direct blood flow.
Regeneration - very fast (1-2 days), stem cells are very active.
What is avascular?
What does not receive direct blood flow?
What are the functions of epithelial tissue?
What are these functions of:
Provide physical protection - physical & chemical
Control permeability - controls what enters & exits the body & tissues.
Provide sensation - responds very well to stimuli.
Produce specialized secretions (glandular epithelium) - cells discharge contents.
What is simple squamous epithelium?
Which classes of epithelium is:
Single layer.
Flattened (diffusion, filtration).
Cap. walls, air sacs, linings of body cavities.
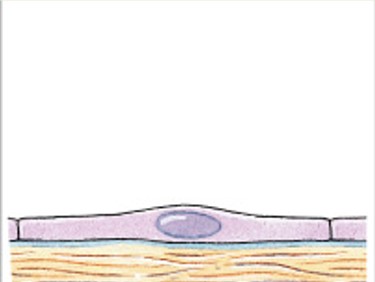
What is simple cuboidal epithelium?
Which classes of epithelium is:
Single layer.
Cube-shaped (excretion, secretion, absorption).
Ovaries, kidney tubules.
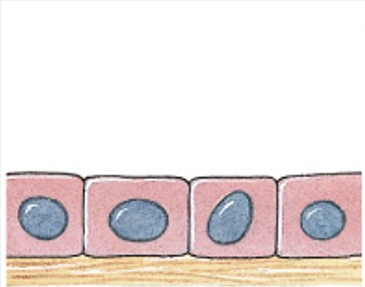
What is simple columnar epithelia?
Which classes of epithelium is:
Single layer.
Tall.
Ciliated (transportive) lining of uterine tubes.
Nonciliated (protection, secretion, absorption) lining of digestive tact.
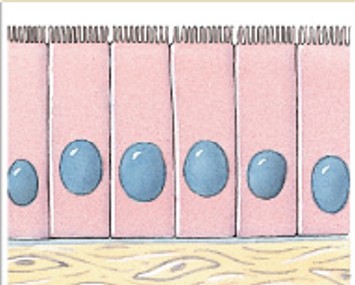
What is stratified squamous epithelium?
Which classes of epithelium is:
Numerous layers.
Outer layer flattened (protection).
Skin, linings of body openings.
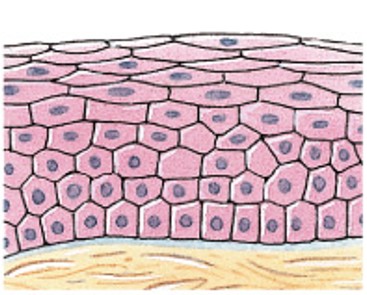
What is stratified cuboidal epithelium?
Which classes of epithelium is:
2 or more layers of cube-shaped cells (absorption, protection).
Sweat & esophageal glands, around ovum.
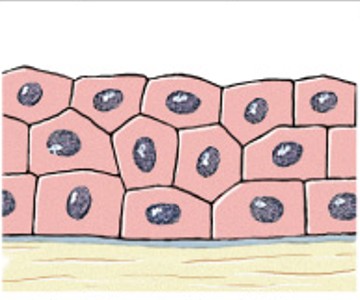
What is stratified columnar epithelium?
Which classes of epithelium is:
2 layers of tall rectangular cells (strengthen luminal walls).
Salivary gland duct, larger ducts-sweat, pancreas.
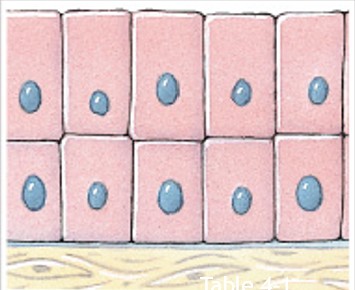
What is transitional epithelium?
Which classes of epithelium is:
Numerous layers of rounded cells (distension).
Urinary bladder.

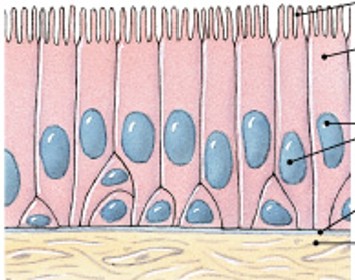
What is pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
Which classes of epithelium is:
Single layer of irregular ciliated cells, goblet cells (protection, secretion, ciliary movement)
Linings of respiratory passage.
What is exocrine glands?
Which type of glands produce secretions onto epithelial surfaces through ducts?
What is endocrine glands?
Which type of glands release hormones into interstitial fluid, no duct?
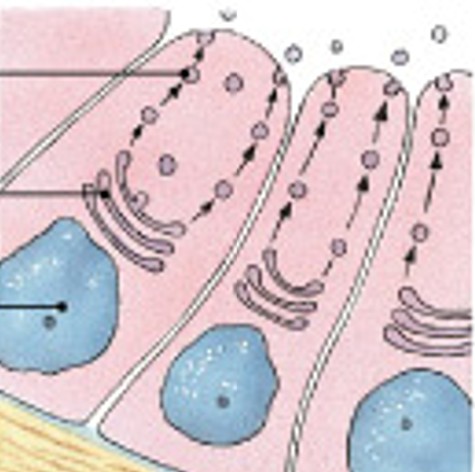
What are merocrine secretions?
Which modes of secretion are:
Are produced in Golgi apparatus.
Are released by vesicles (exocytosis).
Ex: sweat glands.
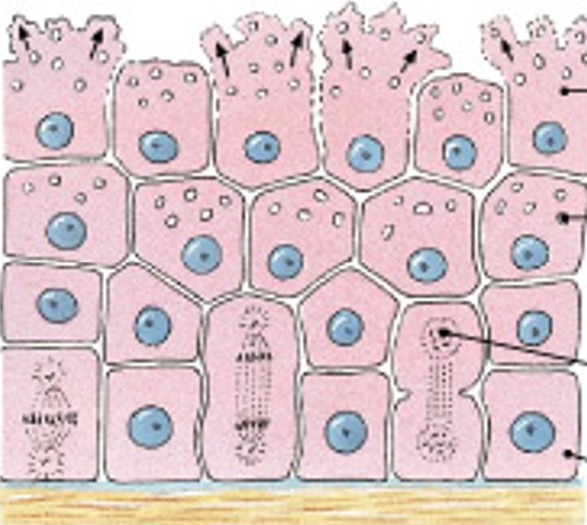
What are apocrine secretions?
Which modes of secretion are:
Are produced in Golgi apparatus.
Are released by shedding cytoplasm.
Ex: mammary gland.
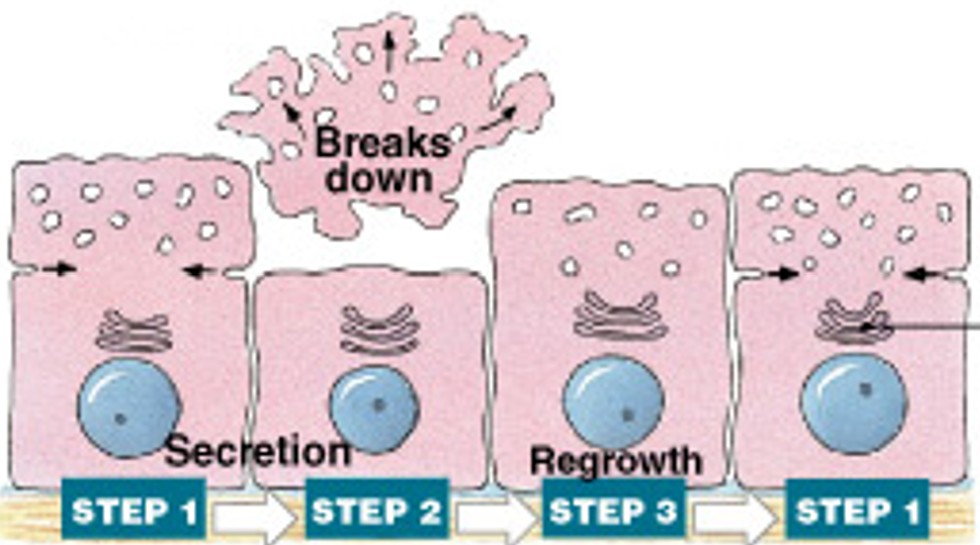
What are holocrine secretion?
Which modes of secretion are:
Are released by cells bursting, killing gland cells.
Gland cells replaced by stem cells.
Ex sebaceous gland.
What are the functions of connective tissue?
What are these functions of:
Never faces lumen
Connects epithelium to the rest of the body
Has no contact with outside environment
Provide structural framework and to protect organs
Store energy (fat)
Transport fluids (blood) & dissolved materials
Defend against microorganisms
What are fibroblasts?
Which type of connective tissue cell has:
The most abundant cell type
Found in all connective tissue proper
Secrete proteins and cellular cement
What are macrophages?
Which type of connective tissue cell has:
large cells of the immune system
Eat pathogens and damaged cells
What are adipocytes?
Which type of connective tissue cell has:
Each cell stores a single
Large fat droplet
What are mesenchymal cells?
Which type of connective tissue cell has:
Stem cells that respond to injury or inflection
What are melanocytes?
Which type of connective tissue cell has:
Synthesize and store the brown pigment melanin
What are mast cells?
Which type of connective tissue cell has:
Stimulate inflammation after injury or inflection
Mast cells are carried by blood
Release histamine and heparin
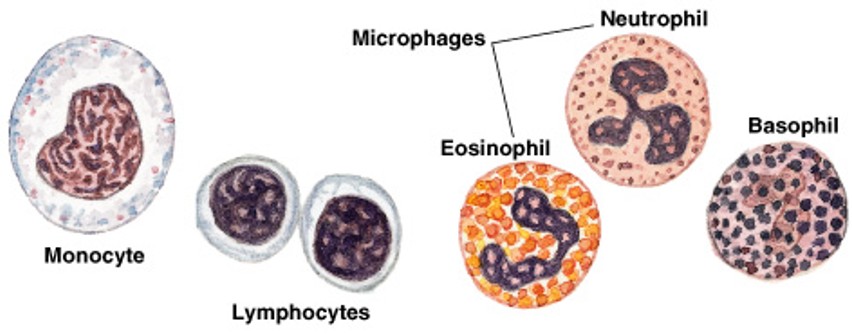
What are lymphocytes?
Which type of connective tissue cell has:
Specialized immune cells in lymphatic which produce antibodies from plasma cells
What are microphages?
Which type of connective tissue cell has:
Phagocytic blood cells which respond to signals from macrophages and mast cells
What are collagen fibers?
Which type of fiber has:
Most common fibers in CTP
Long, straight, and unbranched
Strong and flexible
Resists force in 1 direction
Tendons and ligaments
What are reticular fibers?
Which type of fiber has:
Network of interwoven fibers
Strong and flexible
Resists force in many directions
Stabilizes functional cells and structures
Sheaths around organs
What are elastic fibers?
Which type of fiber has:
Contain elastin
Branched and wavy
Return to original length after stretching
Elastic ligaments of vertebrae
What is ground substance?
What is found in connective tissue, clear, colorless, and viscous, fills spaces between cells and slows pathogens?
What is loose (areolar) tissue?
Which type of connective tissue has:
Open framework, viscous ground substance
Holds blood vessels and capillary beds
Under skin (subcutaneous layer)
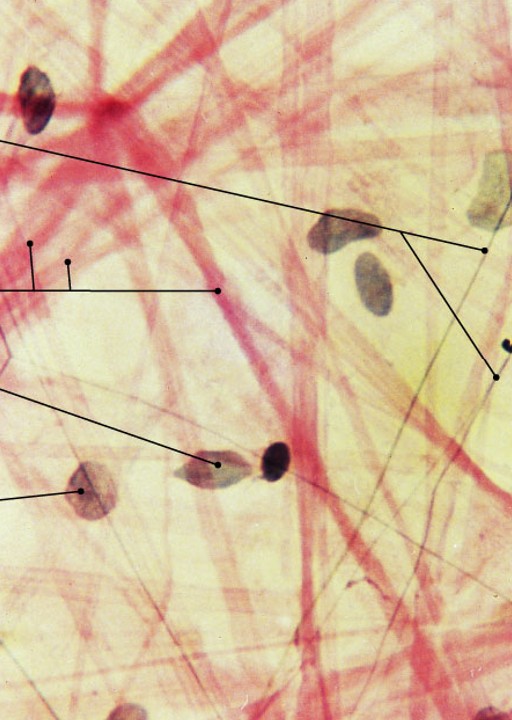
What is reticular tissue?
Which type of connective tissue has:
Complex, 3-dimensional network
Supportive fibers, support functional cells
Reticular organs:
spleen, liver, lymph nodes, and bone marrow
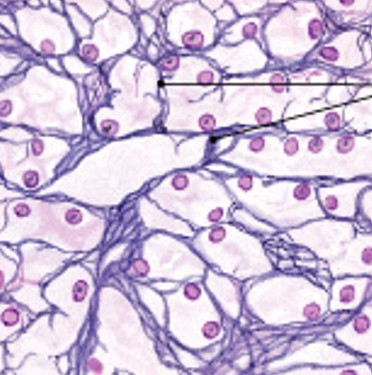
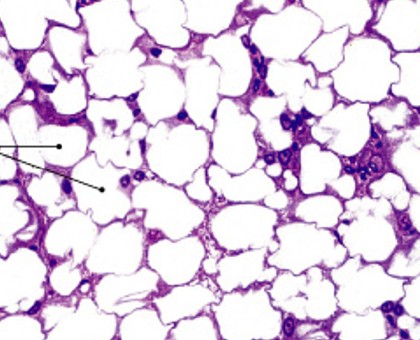
What is adipose tissue?
Which type of connective tissue has:
Contains many adipocytes (fat cells)
Stores fat
Absorbs shocks
Slows heat loss (insulation)
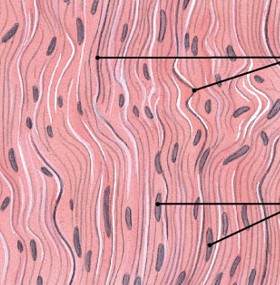
What is dense regular connective tissue?
Which type of connective tissue has:
Attachment and stabilization
Tightly packed, parallel collagen fibers
tendons attach muscles to bones
ligaments connect bone to bone and stabilize organs
What is dense irregular connective tissue?
Which type of connective tissue has:
Strength in many directions
Interwoven networks of collagen fibers
layered in skin, around cartilages, around bones
form capsules around some organs
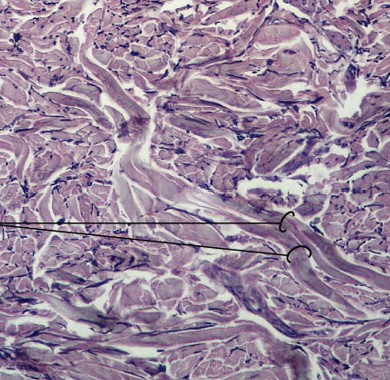
What is fluid connective tissue?
Which type of connective tissue has:
Blood and lymph
Watery matrix of dissolved proteins
Carry specific cell types
What is hemopoietic?
What is red bone marrow connective tissue?
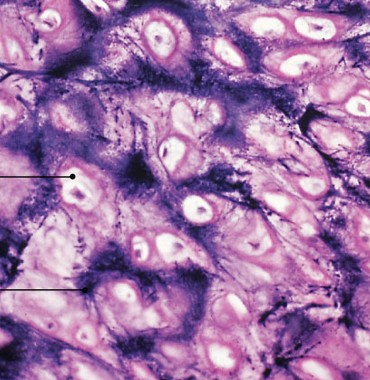
What is hyaline cartilage?
Which type of cartilage has:
Translucent matrix, extremely fine collagenous fibers, no prominent fibers
Reduces friction in joints & between bones
Found in synovial joints & on rib tips
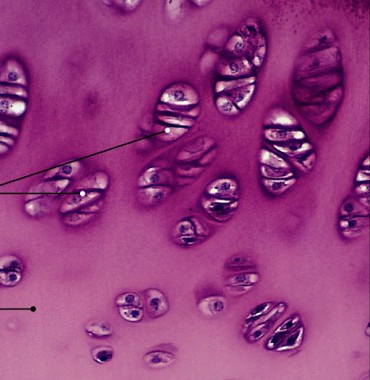
What is elastic cartilage?
Which type of cartilage has:
Elastic fibers within a matrix
Flexible support, supportive but bends easily
found in external ear and epiglottis
What is fibrocartilage?
Which type of cartilage has:
Collagenous fibers within a matrix
Resists compression, limits movement
Prevents bone-to-bone contact
Pads knee joints, between pubic bones and intervertebral discs
What is compact bone?
Which type of bone has:
Harder outer bone, also osseous tissue
strong (calcium salt deposits)
resists shattering (flexible collagen fibers)
Tree rings
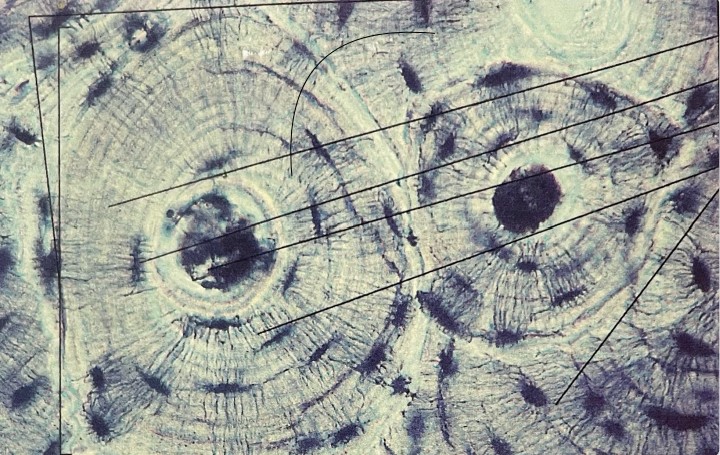

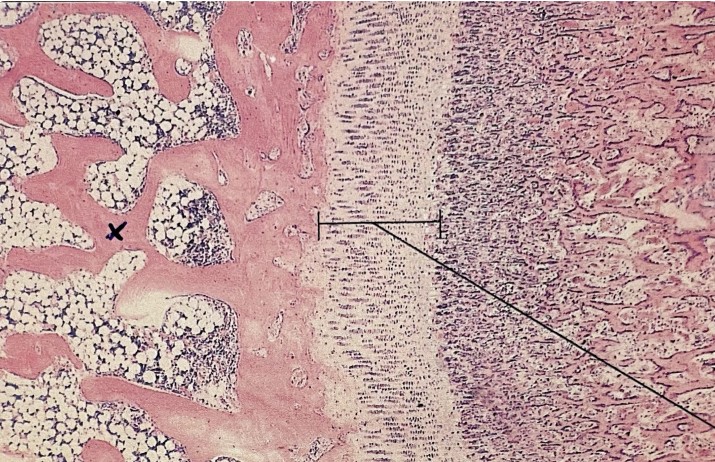
What is spongy bone?
Which type of bone has:
Inner bone, web like - trabeculae, bone marrow
What are the four types of membrane?
What are mucous, serous, cutaneous, synovial?
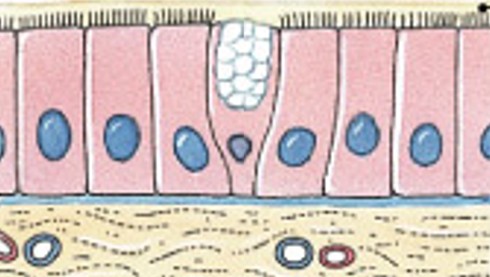
What is mucous membrane?
Which type of membrane has:
Line passageways that have external connections
Also in digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts
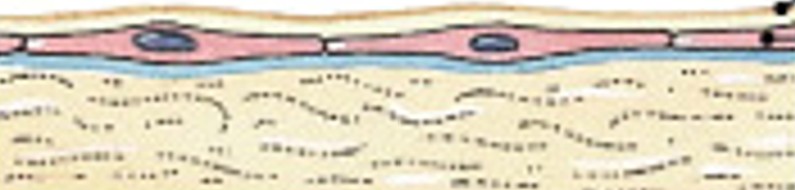
What is serous membrane?
Which type of membrane has:
Line cavities not open to the outside
Are thin but strong
Have fluid to reduce friction
What is cutaneous membrane?
Which type of membrane has:
Is skin, surface of the body
Thick, waterproof, and dry
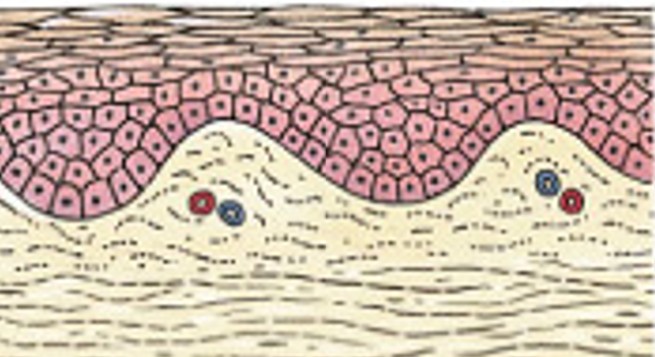
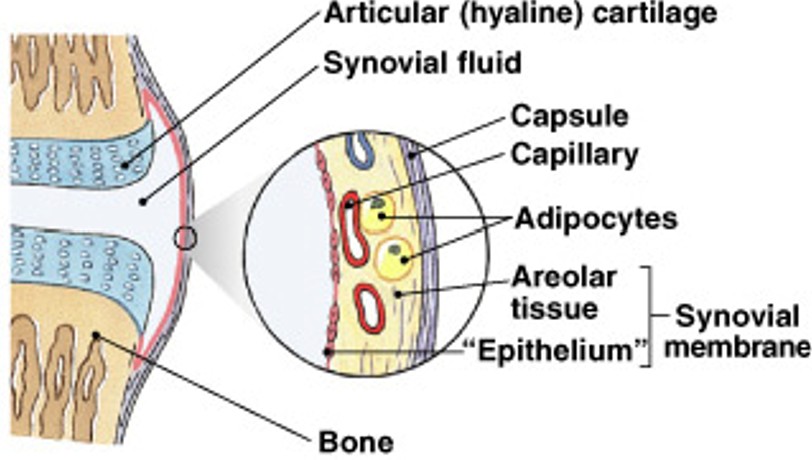
What is synovial membrane?
Which type of membrane has:
Line articulating (moving) joint cavities
Produce synovial fluid (lubricant)
Protect the ends of bones
What is fasciae?
What is the connective tissue framework?
What is superficial fascia?
Which type of fasciae is:
Between skin & organs (subcutaneous/hypodermis), {areolar & adipose tissues}
What is deep fascia?
Which type of fasciae is:
strong fibrous network, dense connective tissue
What is subserous fascia?
Which type of fasciae is:
Between serous membrane & deep fascia
What is skeletal muscle?
Which type of muscle is:
Striated, voluntary, and multinucleated
are long and thin, are usually called muscle fibers
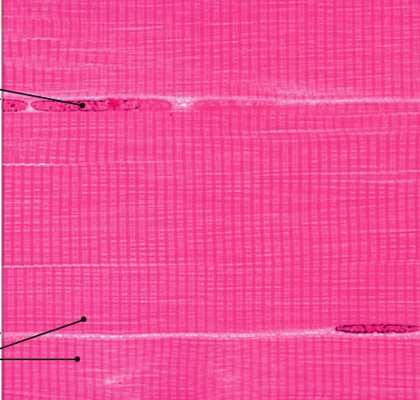

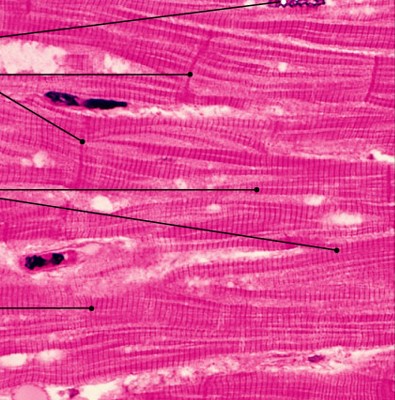
What is cardiac muscle?
Which type of muscle is:
Are striated, involuntary, heart muscle
Form branching networks - bifurcated
Connected at intercalated disks
Have large round nuclei
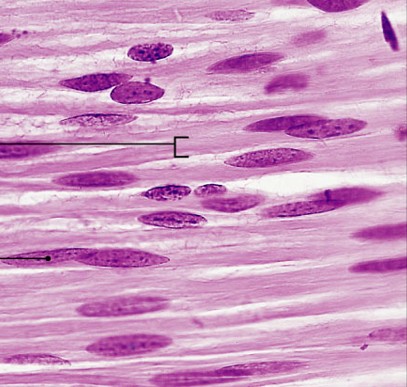
What is smooth muscle?
Which type of muscle is:
Nonstriated, involuntary
Long and spindle-shaped, single nucleus
Walls of blood vessels, digestive tact
What is neural tissue?
What is specialized for conducting electrical impulses?
What are neurons?
Which type of neural tissue are nerve cells, perform electrical communication?
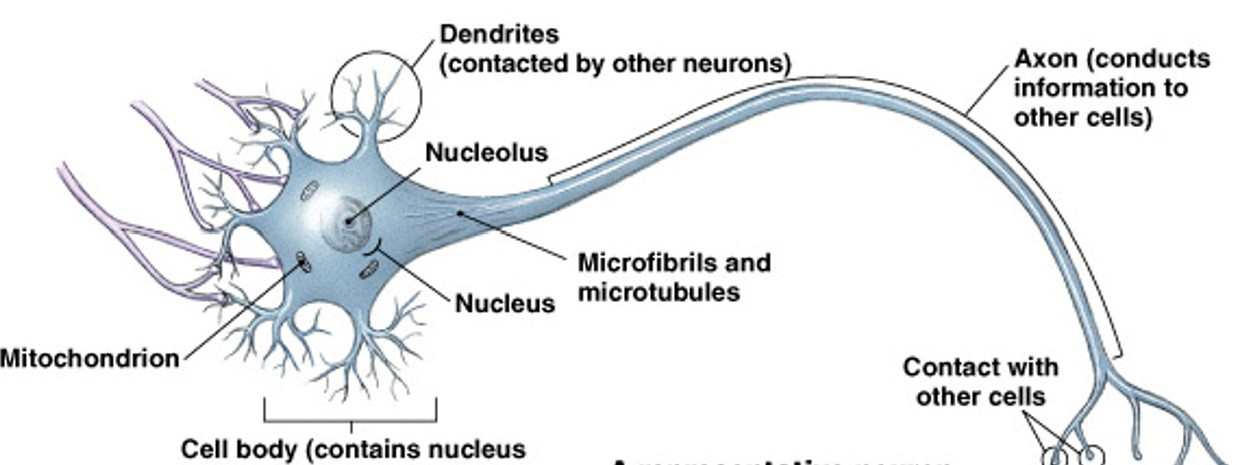
What are neuroglia?
Which type of neural tissue are support cells, repair and supply nutrients to neurons, anchor neurons?
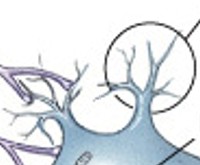
What are dendrites?
What are short branches extending from the cell body, receive incoming signals?
What is the cell body of a neuron?
What contains the nucleus and nucleolus in a neuron?
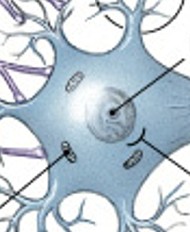
What is the nucleus of a neuron?
What is the control center of a neuron?

What is an axon?
What is the long, thin extension of the cell body, carries outgoing electrical signals to their destination?
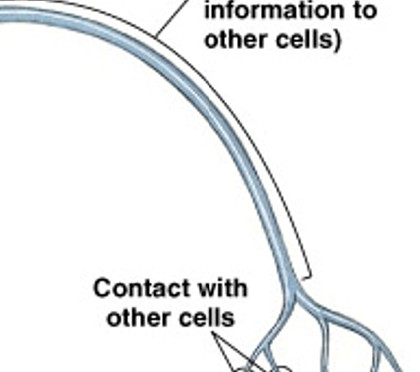
What are synaptic terminals?
What sends message to the next cell?
What is inflammation?
What is the tissue’s first response to injury?
What are signs of inflammatory response?
The following are signs of what:
Swelling
Redness
Heat
Pain
What are the steps of inflammatory response?
What are these steps for:
Can be triggered by trauma and infection.
Damaged cells release chemical signals into the surrounding interstitial fluid.
As cells break down, lysosomes release enzymes that destroy the injured cell and attack surrounding tissues.
Necrotic tissues and cellular debris (pus) accumulate in the wound.
Injury stimulates mast cells to release histamine, heparin, and prostaglandins.
Which dilate surrounding blood vessels.
Dilation of blood vessels increases blood circulation in the area.
Phagocytic white blood cells clean up the area.
What is regeneration?
What occurs when the injury or infection is cleaned up and fibroblasts move into necrotic area lay down collagen fibers to bind the area together?